Abstract
It is widely accepted that tourism, given the right conditions, can be an important instrument of economic growth and a means of improving the quality of life for the societies in which it is implemented, particularly in developing territories. International financial institutions are aware of the role that tourism can play in this regard and, accordingly, have included it within their strategies to further sustainable development and financial inclusion. The World Bank is one of the institutions working to foster tourism, although, interestingly, it only began working in this area very recently (2016). This paper analyses the role of the World Bank in the inclusive financing of tourism as an instrument of sustainable development and compares it with the finance allocated to another four sectors in the branch of trade and industry. To this end, using a system of indicators previously tested in the literature, it analyses a total of ninety-two projects directly related with tourism, trade, manufacture, services, and housing construction activity. The results obtained, when compared to the finance allocated to other sectors of trade and industry (to which tourism also belongs), indicate that the World Bank’s financing of tourism could sharpen its focus on financial inclusion, which would ensure greater efficiency and efficacy in the attainment of its poverty reduction and development goals.
1. Introduction
Tourism is an activity that can contribute to development and poverty reduction in certain developing economies, especially in countries with the right potential and an appropriate strategic approach geared towards sustainability [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8].
López and Esteban [9] argue that sustainable tourism offers destinations a hugely important strategic opportunity. These authors signal that sustainable tourism development, in its three dimensions (economic, social, and environmental), dynamically integrates endogenous and exogenous resources, which, if managed correctly, can be a focus for social, economic, environmental and cultural benefits. The important thing is to ensure that sustainable development derived from tourism is possible in the medium to long term, avoiding short-term models of tourism development that do not respect the environment or local culture, break the harmony of socioeconomic development, or accelerate the depletion of resources.
Bearing in mind other factors that affect economic growth and sustainable development, the finance sector forms the foundation for the development in production sectors [10], and financial inclusiveness has emerged as an important driving force for economic growth [11], since it enables excluded sectors of society to access the formal financial system.
In general, over the past decade, inclusion has caught the attention of a great many institutions and governments [12], which have been making greater efforts than ever before to foster financial inclusion. As a consequence, the percentage of unbanked adults declined between 2011 and 2014, from 49% to 38% [13], and between 2014 and 2017, from 2000 million to 1700 million people [14].
The World Bank (hereinafter WB) states that financial inclusion is one of the objectives that must be achieved in order to attain its development goals, by investing in different strategic sectors, including tourism.
In order to achieve its development and poverty reduction goals, the WB, through the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development and the International Development Association, finances and provides technical assistance to the governments of developing countries, working with them to design the most suitable form of collaboration, first identifying the country’s main priorities to reduce poverty and improve the standard of living. Hence, the WB and the government of each country establish the core aspects of the project to be financed and its beneficiaries, and then a WB working group sets out all the other components in detail. The government of the respective country and the WB then work together to review all the analytical preparation and groundwork carried out on the project, confirming the viability of the expected outcomes and evaluation tools. Once the WB gives the project the green light, finance is approved, and implementation gets underway [15].
Since the 1970s, the WB has financed projects in sectors that have a direct influence and impact on tourism. However, the WB did not formally consider tourism as a specific sector in which it needed to act until 2016. Hence, the financing of projects that pursue the sustainable development of tourism drives governments and development partners towards a more systematic and inclusive approach when designing, implementing, and evaluating the economic, social, and environmental impacts of these investments [16].
The importance bestowed on financial inclusion by the WB is reflected in two of its active initiatives: Universal Financial Access by 2020, launched in 2013, which pledges that 1000 million adults will have access to financial services within this timeframe, and the Financial Sector Assessment Program, to help strengthen the financial systems of countries and tackle a variety of issues affecting the financial sector [15].
Bearing in mind the interest the WB has expressed in financial inclusion and the potential offered by tourism to developing economies, by promoting both aspects from the perspective of sustainability, the positive effects on the economy are multiplied, if access to the formal financial system is fostered among the most excluded population sector with the greatest influence on the development of tourism within a given destination: local SMEs [17].
Therefore, it is interesting to analyse the extent to which the WB transfers the value it bestows on the goal of financial inclusion to the financing of tourism, in comparison with other sectors of the ‘trade and industry’ branch, according to the WB classification of sectors, such as: manufacture, trade, services and housing construction, insofar as tourism is considered a fundamental sector for the achievement of its goals.
The starting hypotheses for this research, applied to the WB’s financing of tourism, since tourism has been classed as an independent sector for finance purposes, are as follows:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
The financing of tourism does not hold a prominent position with regard to the efforts made towards financial inclusion, when compared to other production sectors of trade and industry.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
The WB should improve its behavior towards financial inclusion when financing tourism, by advocating greater consideration of this target among the development goals of projects and allocating finance in accordance with criteria and conditions that are more oriented towards financial inclusion.
To test these hypotheses, the following objectives were proposed:
- To obtain the necessary information to have the database of WB development projects in productive sectors of the industry and trade branch.
- To apply the tool (system of indicators) developed by Carrillo-Hidalgo and Pulido-Fernández [18], capable of measuring the efforts made by international financial institutions in their financing of tourism to achieve financial inclusion, which is the starting point for this research.
- To type the results of the tool.
- To draw up a ranking based on the efforts made by the WB to promote financial inclusion when financing development projects in the tourism, manufacture, trade, services, and housing construction sectors.
2. Theoretical Framework
One of the most recent definitions given for the concept of financial inclusion is proposed by Nuzzo and Piermattei: “the ease of access by individuals and enterprises to appropriate and reasonably priced financial services” ([19] p. 7).
The lack of access or limited access to financial services is a reality that affects millions of people and SMEs. The data confirm this. In developed economies, 94% of adults have a current account. However, in developing economies this percentage drops to 63%. When it comes to obtaining finance, in high-income economies, more than 50% of borrowers turn to the formal financial system, a percentage that drops to less than 20% in developing economies, where people tend to turn to relatives or friends. In general, globally, around 1700 million adults do not have access to formal financial services [14].
Furthermore, those who are excluded from the formal financial system have a perfectly defined profile. The majority come from homes without financial resources, have a low level of education, are outside of the labour market or are self-employed, and a higher percentage are women [20,21]. As for companies, SMEs face the greatest difficulty accessing the financial system, since banking and non-banking financial institutions are usually reluctant to provide financing to SMEs, especially in developing countries [22].
Hence, it is fundamental to facilitate access to financial services for people who fit in with this profile, although it is also true that, in order to ensure the development of an economy, it is essential to achieve financial inclusion for the majority of the population, regardless of their condition.
Within the sphere of tourism, businesses that wish to make sustainable investments in the sector need access to long-term finance for high amounts, principally in the case of investments made in infrastructures and equipment, which require greater guarantees [23]. These conditions make it difficult for local tourism businesses, chiefly SMEs, to access finance, which limits the growth and sustainable development of this activity. Tourism multinationals achieve the highest level of integration in the financial system, since they can secure finance more easily [18].
There are studies [9,23] that demonstrate the presence of two-way causality between tourism and GDP per capita, financial development and the growth of tourist demand, showing that tourism is essential to improving growth and sustainable economic development [24].
In fact, in a study carried out in Cambodia, Ngoasong and Kimbu [25] analysed the role of micro-financial institutions in tourism enterprise, discovering that micro-financial institutions favoured business creation, especially SMEs, which are fundamental in tourism development, in which qualitative aspects are more important than quantitative ones, giving rise to a lower concentration of tourist activity within a territory [26].
International financial institutions, in order to achieve their development and poverty reduction goals, should allocate resources to the financing of development projects that play a decisive role in their outcomes, since an effective project is the reflection of an effective investment with high social and also commercial returns [27]. The WB, in particular, has carried out projects to improve financial inclusion in developing countries, adopting modern finance systems to achieve its poverty reduction goals [22].
The actions of these institutions to favour financial inclusion focus on providing liquidity in advantageous conditions, by means of a wholesale banking scheme, and through initiatives that directly or indirectly promote access to finance, such as non-financial support, financial education, technical assistance, support for system regulation, or through the creation of guarantee funds [28].
However, some development banks have tended to finance non-profitable projects from a commercial and social perspective, allocating finance to more solvent sectors with plenty of liquidity and/or the powerful elite [29].
In a study about the WB, Markandya [30] established that, until 2003, this body had not assigned a fundamental role to tourism in terms of its development strategy, although it gradually considered tourism to be more important, especially with regard to the sustainable use of natural resources and this sector’s growing weight in the economy of many developing countries.
Hawkins and Mann [16] analysed the work carried out by the WB with regard to tourism, stating that, in the view of the WB itself, as well as the destination country and the project managers, tourism is affected by a series of external factors, such as seasonal fluctuations, dependency on trends, the political and economic situation of the destination and internationally, natural disasters, etc., which are seen as a challenge when allocating finance to development.
These authors concluded that the WB made its greatest financial effort with regard to sustainability over the course of the 1990s, when the concept of sustainable tourism appeared on the back of sustainable development. This was when the WB, together with the United Nations Development Programme, created the Global Environment Facility, through which it financed tourism development projects, justifying the sustainability of the investments for the environment and cultural preservation with economic benefits.
The projects financed focused principally on environmental, cultural and social issues. However, in just 14% of the projects financed during this time was there an attempt to quantify their impacts [29,30], denoting a lack of commitment on the part of the institution [16].
When financing tourism, international financial institutions should focus on improving the sector’s competitiveness and SME access to finance, since small businesses have a positive influence on the supply of jobs, and ensuring the benefits of the sector, as well as reinforcing certification systems, since they incentivize the tourism sector and facilitate access to finance [27].
To launch sustainable tourism projects and secure funds, these institutions understand that the Departments of Tourism of the governments in which they are carried out are essential, according to Tapia [27] for the case of the Inter-American Development Bank. This view was subsequently confirmed by Carrillo-Hidalgo and Pulido-Fernández [17] in their analysis about the efforts made in terms of financial inclusion by international financial institutions in financing tourism in Latin America and the Caribbean.
Using the same tool applied in this present paper, Carrillo-Hidalgo and Pulido-Fernández [17] concluded that, in the international financing of tourism in Latin America and the Caribbean, the characteristics, volume of finance, recipients, objectives, and even the non-financial efforts made do not favour financial inclusion in destinations where the projects are carried out. In other words, “this financing is not inclusive from a financial perspective, and therefore the efforts made in this regard are not enough” [17,31].
3. Methodology
Using the tool developed by Carrillo-Hidalgo and Pulido-Fernández [18] to measure the financial inclusion orientation of projects that could influence tourism, financed by international financial institutions (Table 1), we obtained from the WB webpage all the required data about the projects financed in the housing construction, manufacture, services, tourism and trade sectors, since 2016, when tourism was formally established as a fundamental sector in which action needed to be taken in order to achieve its development and poverty reduction goals.

Table 1.
Indicators that make up the tool to measure effort in financial inclusion in the financing of tourism by international financial institutions.
This tool is made up of 39 indicators capable of evaluating management quality, which are divided into five different categories, depending on the aspects to be measured:
- Integration of financial inclusion in the development goals of the projects.
- Scope and growth of the portfolio of finance recipients and beneficiaries.
- Characteristics related with the volume of finance, its distribution and evolution.
- Characteristics of the finance itself.
- Non-financial efforts made with regard to financial inclusion through the development projects.
The indicators are also classified into two categories, positive (+) or negative (−), so that the bigger the result, better or worse behaviour, respectively, oriented towards fostering financial inclusion, reflects the attitude of institutions in tourism financing.
This research focuses on analysing projects financed by the WB that have a direct influence on the tourist sector and comparing them with finance allocated to the housing construction, manufacture, services, tourism, and trade sectors. Hence, the database used is made up of a total of 98 projects financed since 2016, up to the present day (2019), including 32 in the tourism sector, 34 in trade, 17 in housing construction, eight in manufacture, and seven in the services sector (Supplementary Table S1).
Firstly, a descriptive analysis was performed of the main characteristics of this tourism finance provided by the WB, determining and defining its main traits in general, in order subsequently to apply the tool to the database and obtain results that could preferably be interpreted in terms of the effort made by the WB with regard to financial inclusion when financing tourism and compare it with the finance allocated to the aforementioned sectors encompassed by the WB’s ‘trade and industry’ branch.
The only indicator for which we did not obtain a result was B10, about the volume of finance that has been fully repaid, since no project in the database has reached its maturity date yet.
The results yielded by the indicators are heterogeneous and expressed in different units, and consequently the data have been normalised and standardised in order to reach more global and consistent conclusions. Hence, a value has been obtained, Zij, which follows a normal distribution with a mean value of 0 and standard deviation of 1 (N(0,1)), providing relative values which reflect the number of times a value moves away from the average, either above (values above zero) or below (values below zero), applying the following formula:
where Xij indicates the value of each indicator for each sector, µj is average of the indicators values thrown by the financing of each sector, and σj is standard deviation of the indicators values thrown by the financing of each sector.
Once the results of each indicator were standardised, the mean values corresponding to each group of indicators were calculated, adding the ‘positive’ standardised results, and subtracting the ‘negative’ results for each block and institution.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
Since 2016, the year in which the WB formally established tourism as a specific sector that required finance in order to achieve its development and poverty reduction goals, this institution has allocated 1952.32 million dollars to tourism through 32 projects, 31 of which are still active, and only one, allocated five million dollars, in Samoa, has been closed since 2017, although the finance allocated will not be fully repaid until 2036. Hence, the WB corroborates the arguments put forward by Tapia [27], by financing projects that have a direct impact on tourism, a sector that can play a decisive role in its results.
The finance allocated to tourism by the WB is divided into the different regions of the world (Figure 1). The region that has received the most finance is East Asia and the Pacific (34.77%), with 678.8 million dollars, disbursed among 8 projects, followed by Africa, which has received 469.2 million dollars (24.03%), through 11 projects. South Asia occupies last place in terms of the volume of finance (10.19%); last place in terms of the number of projects awarded finance is held by Latin America and the Caribbean, with just three over the course of the last three and a half years.
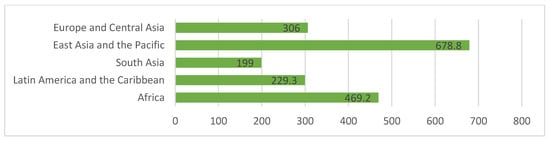
Figure 1.
Regional distribution of tourism finance allocated by the World Bank (2016–2019) (Figures expressed in millions of dollars). Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
This geographical distribution is broken down by country in Figure 2.
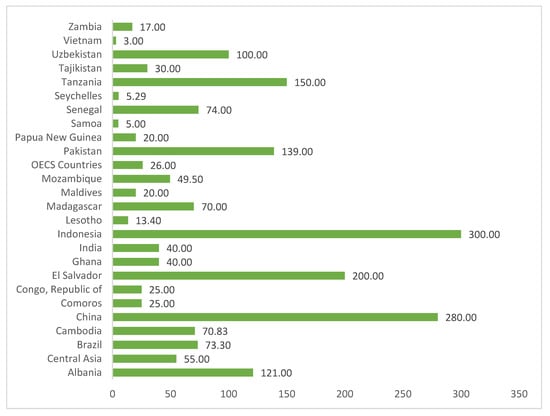
Figure 2.
Distribution by country of tourism finance allocated by the World Bank (2016–2019) (Figures expressed in millions of dollars) Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
Indonesia (15.37%), China (14.32%), and El Salvador (10.24%) have received the highest level of tourism finance from the WB. At the other end, Vietnam (0.15%), Samoa (0.26%), and the Seychelles (0.27%) have only been allocated finance for one project each, for amounts far below the average, putting them in the last place in the geographical ranking of tourism finance allocated by the WB.
Taking into account that almost half of those classed as financially excluded are concentrated in Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Nigeria, and Pakistan [12], the WB shows that it is working–partly and not 100%–with countries with the highest rate of unbanked people.
The way in which this finance is channelled is through repayable loans (82%) and non-repayable credits (18%). Guarantees are not used by the WB when financing tourism (Figure 3).
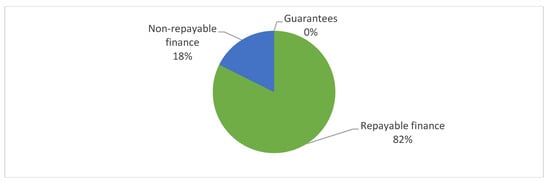
Figure 3.
Types of finance used by the World Bank in its financing of tourism (2016–2019) Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
All the projects analyzed include tourism among the main sectors affected. However, each project also influences other fundamental sectors to achieve the WB’s goals. In fact, each project has a percentage of that project linked to each sector. Figure 4 is based on this information.
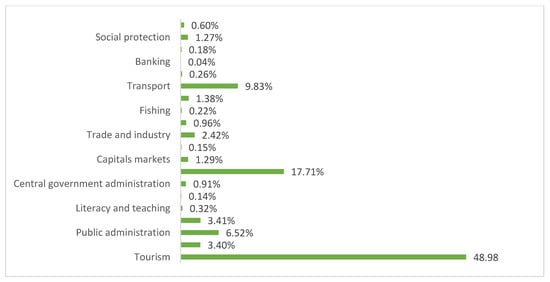
Figure 4.
Sector distribution of finance allocated to projects that influence the tourism sector (2016–2019) Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
Hence, of this finance, almost 50% affects tourism directly, and the other half is distributed among different sectors that indirectly affect tourism.
The financing of tourism carried out by the WB is channelled fundamentally to the sectors of subnational government administration (17.71%), transport (9.83%) and public administration (6.52%).
In fact, the public sector in general (public administration, central and subnational government) receives 25.14% of the total finance, distributed among 30 projects. This aspect is justified, as detailed in the next section, when analysing the results of the tool, since 31 of the 32 projects are allocated to the public sector.
Furthermore, the issues that guide the execution of projects that influence tourism, financed by the WB, are represented in Figure 5.
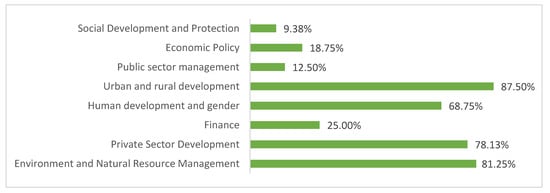
Figure 5.
Distribution by issues of the projects that influence tourism financed by the World Bank (2016–2019) Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
This thematic was introduced by the WB in 2016 for finance and assistance operations, referring to the goals and institutional priorities of this institution [15].
The majority of the projects encompass the issues of urban and rural development (87.50%), environmental and natural resource management (81.25%) and the development of the private sector (78.13%). Hence, they bear out the arguments put forward by Hawkins and Man [16] that the main goals of the tourism development projects financed by the WB focus on environmental aspects, but not on cultural and social questions.
Through the issues corresponding to each of the tourism projects financed by the WB, we can see the value attached to each of the three dimensions of sustainability. The social dimension has the lowest weighting, since development and social protection are relegated to last place (9.38%).
4.2. Results of Applying the Tool
4.2.1. Level of Immersion of Financial Inclusion in the Project Development Goals
Each of the projects financed by the WB incorporates a series of goals, and the presence of financial inclusion is represented in the block of indicators A (Table 2).

Table 2.
Indicators of the incorporation of financial inclusion in the project development goals, by sector.
Of the total number of projects and finance provided by the WB with regard to tourism, in light of indicators A1.a and A1.b (Figure 6), 25% of the projects seek to foster financial inclusion, representing 18.82% of the finance allocated.
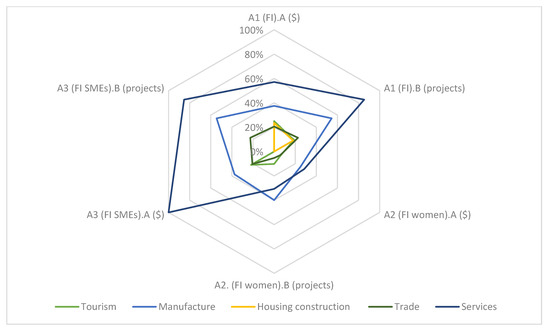
Figure 6.
Indicators A: Goal: Financial inclusion, of women and SMEs. Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
These percentages are reduced when we focus on goals aimed at fostering access for women and/or SMEs to credit, especially in the first case.
These values, related with the presence of financial inclusion among the goals of the tourism projects financed by the WB, indicate an intermediate performance, when compared with other sectors (Figure 6). Hence, above the tourism sector are the services and manufacture sectors, where financial inclusion is strongly present among the stated project goals. The performance achieved by tourism finance, in this regard, is closer to that of the trade and housing construction sectors, with the latter obtaining the lowest values.
4.2.2. Scope and Growth of the Portfolio of Finance Recipients and Beneficiaries
This next block of indicators analyses the scope and characteristics of the recipients and beneficiaries of the finance awarded, studying the composition and evolution of the portfolio of these beneficiaries. These results can be seen in Table 3.

Table 3.
Indicators of the scope and growth of the portfolio of finance recipients and beneficiaries, by sector.
Since 2016, the WB has financed projects that have an influence on tourism with a total of 28 different recipients (indicator B1), a fairly low number given the size and reach of the WB and the volume of capital it manages. However, it yields the best value when compared with the other sectors.
In all sectors, indicators B2 and B3 show that, in the portfolio of WB tourism finance recipients, women and SMEs are not present. Of the total number of recipients, 100% are public bodies or entities (indicator B6). In this regard, the results do not bear out the arguments put forward by Chandrasekhar [29], since financing the public sector is the WB’s raison d’être, working together with the governments of the recipient countries to prepare and implement the development projects, thus valuing the importance of the latter, as indicated by Carrillo-Hidalgo and Pulido-Fernández [17] and Tapia [27]. Indicator B4 (Table 3) shows that half of the tourism development projects benefit other private sector enterprises and entrepreneurs, either directly or indirectly. Indicator B5 goes into greater detail, signalling that this 50% are SMEs. The rest affect only the recipients themselves, implying a more limited scope and reach of the finance awarded. Hereof, the performance of tourism finance puts it below the finance allocated to the services sector, in which 71.43% of projects benefit other companies and SMEs, and the manufacturing sector, whose indicators show that 100% of the finance allocated benefits other companies, and 62.50% benefits SMEs. The finance allocated to the trade sector reflects the best value for indicator B4 (61.76%) and the worst value for B5 (29.41%), in comparison with tourism. Definitively, finance allocated to the construction sector has the lowest scope and reach with regard to companies and SMEs (0%).
With regard to the indicator B9, it yields a very high value in all sectors (Table 3). This shows that, the WB does not allocate finance in adequate volumes to foster financial inclusion in general, because when the indicator shows a value not greater than 250%, the volume of the funding provided is close to that of micro-financial institutions (whose method of work is better adapted to the fight against financial exclusion) [32]. However, when comparing the value of indicator B9 in tourism finance, it yields a better value, meaning that the volume of its projects is more oriented towards financial inclusion than in the other sectors.
Finally, the evolution of the portfolio of WB finance recipients is analysed.
The average year-on-year variation rate of the WB portfolio of finance recipients with regard to tourism the largest when compared to the other sectors, showing a value of 173.81% (Table 3). If we look at the evolution of this indicator (Figure 7), we see a general decreasing trend, highlighting the strong growth achieved in the tourism finance portfolio in 2017 over the others.
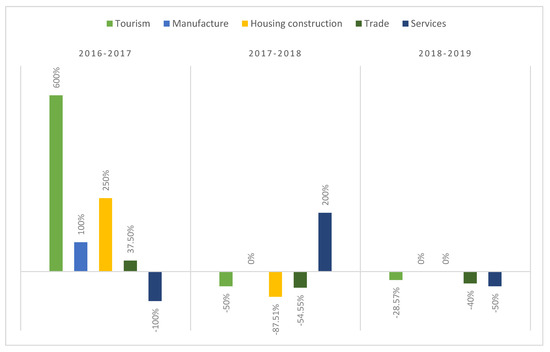
Figure 7.
Evolution of the average year-on-year variation rate in the WB portfolio of finance recipients, indicator B7, by sector (2016–2019) Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
The total growth rate in the number of recipients, since the WB began financing tourism, is on average 7.64% (indicator B8, Table 3), a higher value than the rest of the sectors, which yield negative or null mean values.
4.2.3. Volume of Finance
The third block of indicators (Table 4) analyses data related with the volume of finance and number of projects allocated.

Table 4.
Indicators of aspects related with the volume of finance, by sector.
Indicator C1 shows the average amount of finance received by each recipient through tourist activity. This indicator signals that, since the WB incorporated tourism as a specific sector in the allocation of finance, 28 recipients (indicator B1) has received finance with regard to tourism, for an average of 69.73 million (Table 4). As for new recipients (those who have not received tourism finance previously), the average allocated is 61.01 million euros (indicator C3).
Indicator C2 shows the amount financed per tourism development project, which on average is 55.63 million euros (Table 4).
When comparing these values with those yielded by the other sectors, the average finance per recipient, per new recipient and project, is less than the other sectors, except the services sector (Table 4).
Indicators C4, C5, C7, C10 and C11 corroborate the results established by B2 and B3, combining the way in which the WB operates, focusing on financing the public sector.
However, the funds allocated to these kinds of bodies whose objective is financial inclusion account for 18.82%, a similar proportion to that of the housing construction sector and lower than the rest, especially when compared with the services sector (85.30%).
The attention given to rural and excluded areas, as highlighted by indicator C6, yields a positive result, since 61.45% of the total tourism finance allocated is concentrated in these types of territories. Only the services sector yields a better value in this indicator, with 81.30% of finance aimed at these areas.
On average, according to indicator C9, each recipient has received finance through just over a tourism development projects, as it happens with the other sectors (Table 4). This means that finance is one-off, and a long-lasting relationship that might contribute to the development of the sectors financed is not established. This aspect is justified by the size of each project, reflected by indicator C2.
Year-on-year variation in the tourism finance allocated by the WB is, on average, 235% (indicator C12, Table 4) owing, chiefly, to the rate in 2017, following the launch of financing for tourism projects in 2016 with incipient values. When comparing this indicator with other sectors, tourism is ranked second, after the construction sector, which holds a substantial lead, with an average year-on-year growth rate of 1064.88%, owing fundamentally to the fact that, from 2016 to 2017, the finance allocated to this sector grew by almost 3000% (Figure 8).
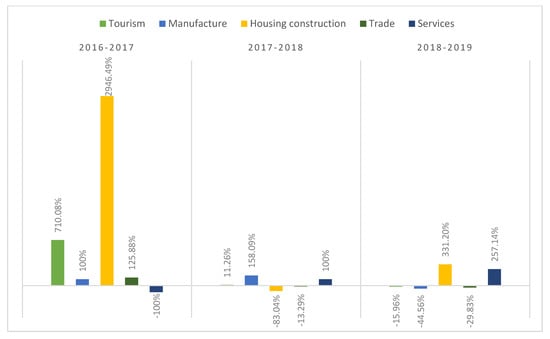
Figure 8.
Average year-on-year variation for the total tourism finance allocated, indicator C12, by sector (2016–2019). Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
The total growth rate for the volume of finance assigned to tourism is, on average, 16.87%. As with indicator C12, this value positions tourism in second place, behind the housing construction sector (25.86%) (indicator C13, Table 4).
4.2.4. Volume of Finance
Knowing the instruments, characteristics, and ways of channelling development cooperation are fundamental if we wish to ascertain whether tourism finance fosters financial inclusion. The indicators included under block D deal precisely with this aspect (Table 5).

Table 5.
Indicators of finance characteristics, by sector.
Indicator D1, also known as the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index [33], has been adapted to verify the extent to which the WB concentrates its tourism finance in specific territories, instead of disbursing funds equitably, without neglecting certain geographical areas. This indicator yields an average value below 1 in the five sectors, implying a certain degree of dispersion in finance at a country level. On this basis, tourism finance displays the highest dispersion of finance, with the lowest value obtained for indicator D1, with regard to the other sectors (Table 5).
The conditions in which finance is allocated should favour a more open financial system and greater development for those who receive finance, with quick and straightforward procedures, and instruments tailored to the circumstances of each project and recipient. In the case of repayable finance, it should be granted with low interest rates, long repayment terms, and grace periods to facilitate repayment [18,31,34].
The average period taken to approve finance (indicator D2) for the tourism development projects financed by the WB is nearly fourteen months (Table 5), ranking it second in terms of the longest approval term of the five sectors analysed, after manufacture.
With regard to repayable finance which, as indicated, is the most widely used instrument by the WB to finance tourism development projects, as well as in the rest of sectors, finance is offered at very low interest rates, with very long repayment terms and long grace periods, which favours the development of the tourist sector, in which investments are usually large.
The average interest rate agreed is 1.04% per annum (indicator D3), with an average repayment term of 22.5 years (indicator D4) and average grace periods of just over 6.5 years (indicator D5). These values place tourism finance in an intermediate position, compared with the other sectors, of which manufacture receives finance at the lowest rate of interest, construction has the longest repayment terms, and the services sector enjoys the longest grace periods (Table 5).
Hence, the way in which the finance reaches the development projects is also very important. Indicators D6, D7, D8, D9, D10, and D11 analyse the types and forms of financial instruments used (Table 5).
The WB has not allocated any emergency finance (indicator D6), destined for events described as ‘difficult and unpredictable’, or any small loans (indicator D7), less than 30% of per capita GDP [31], in tourism finance.
As indicated above, 82.37% of tourism finance has been channelled through repayable loans, and the remainder (17.63%) has been carried out by means of donations (indicator D8). Guarantees, however, have not been used by the WB in financing tourism (indicator D9). The WB has not allocated any emergency finance (indicator D6), destined for events described as ‘difficult and unpredictable’, except one financed to the construction sector and carried out in Sint Maarten, nor has it carried out financing through small loans (indicator D7), less than 30% of per capita GDP [31], in the financing of any sector analysed.
As indicated above, 82.37% of tourism finance has been channelled through repayable loans, and the remainder (17.63%) has been carried out by means of donations (indicator D8) (Figure 9). Therefore, it receives more finance than any other sector through donations, followed by the construction sector. Guarantees, however, have not been used by the WB in financing these sectors in the period studied (indicator D9).
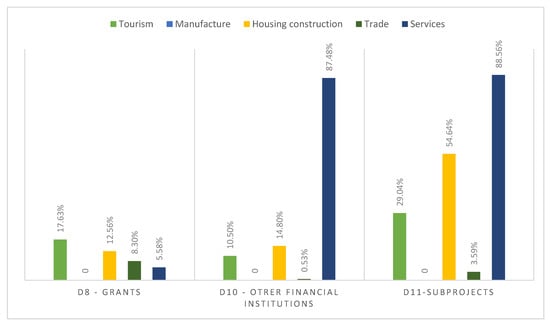
Figure 9.
Indicators D8, D10, and D11. Financial instruments used by the WB, by sector (2016–2019). Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
These proportions are a reflection of the traditional forms of finance favoured by the WB when financing development projects, during the period of study, in contrast to the arguments put forward by Rasheed et al. [22].
Channelling tourism finance through other financial institutions, or through sub-projects, allows a greater number of recipients to be reached, and also helps to open up the formal financial system [17].
The WB has channelled 10.50% of tourism finance through financial institutions, and 29.04% through sub-projects (indicators D10 and D11). These values do not place this sector in a particularly prominent position; the largest proportion of finance channelled in this way is allocated to the services sector (indicator D10, 87.48% and indicator D11, 88.76%) and, especially, to the construction sector (indicator D10, 14.80% and indicator D11, 54.64%) (Figure 9).
4.2.5. Non-Financial Effort in Financial Inclusion
Technical support and training in project execution are fundamental to achieve the goals of international institutions, as Kulfas [28] points out. Hence, the indicators grouped under block E seek to measure this non-financial effort (Table 6).

Table 6.
Indicators of non-financial characteristics, by sector.
The WB strongly advocates this type of support, since 90.63% of the tourism finance allocated has been granted along with technical assistance, and 53.13% incorporates training activities, either for members of the team responsible for the project or third parties who benefit from the project. When comparing these values with those obtained for the other sectors, 100% of the finance allocated to the manufacture, housing construction, and services sectors is awarded alongside technical assistance. However, in terms of the training provided, only finance received by manufacture exceeds the level received by tourism.
This pattern demonstrates the WB’s commitment in the execution of projects, in contrast to the arguments put forward by Hawkins and Mann [16].
4.3. Standardised Results
Once the results provided by the tool were analysed, a behaviour diagnosis was conducted for each of the indicators once the data obtained had been standardised, in accordance with the methodology section.
The standardised results for each of the indicators are shown in Table 7, and for each block, and the tool as a whole can be found in Table 8.

Table 7.
Standardized results provided by the tool.

Table 8.
Standardised results of the tool, by block and overall.
Almost all sectors, except the services sector, in all blocks of indicators reflect below average behaviour, with a relative mean value of less than zero in terms of the indicators’ orientation towards financial inclusion. The only exceptions are the indicators in block E, which measure non-financial effort.
In tourism financing by the WB, since four of the five blocks have mean relative values below zero for the indicators, the total value of the tool is −0.26. Therefore, it could be said that, in financing projects that have a direct influence on tourism, since this activity has been considered an independent sector in which to act, the behaviour and performance of the WB has been below average.
The standardised results by blocks are represented, for each of the sectors, in Figure 10. This Figure shows that the finance allocated by the WB to tourism stands out with regard to the other sectors in terms of the size and growth of the portfolio of recipients (indicators B), putting it in second place when evaluating aspects related with the volume of finance (indicators D), and the non-financial effort made (indicators E). The poorest performance is found when evaluating the involvement of financial inclusion in the development goals of projects (indicators A) and in the characteristics of the finance (indicators D), where it is ranked in the penultimate position, below the construction sector, in both cases.
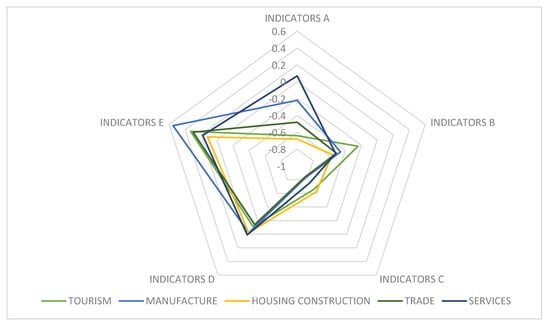
Figure 10.
Standardised results of the tool, by block. Source: Authors’ own based on World Bank data [15].
On account of the volume and projects considered, in addition to the medium-term period analysed, we are unable to corroborate the arguments put forward by Carrillo-Hidalgo and Pulido-Fernández [17] about the relevance or otherwise of the efforts made by the WB with regard to financial inclusion in its financing of tourism. However, a ranking can be established based on the total value obtained with the tool used, presenting in descending order the efforts made by the WB to foster financial inclusion when allocating finance to each of the sectors. The classification is as follows:
- Manufacture (−0.196).
- Services (−0.202).
- Tourism (−0.264).
- Trade (−0.321).
- Construction (−0.344).
When awarding finance to these five sectors, the WB is underperforming with regard to the average, making the greatest effort to promote financial inclusion in relation to the manufacturing sector, with tourism occupying an intermediate position.
5. Conclusions
In this research paper, a descriptive analysis has been conducted of the efforts made by the WB in financing tourism, and the tool developed by Carrillo-Hidalgo and Pulido-Fernández [18] has been applied to development projects financed by the WB since 2016, in the sectors of tourism, manufacture, housing construction, trade and services, drawing comparisons between them, after typing the results, and establishing a ranking in accordance with the efforts made to promote financial inclusion as determined by the results. Therefore, the research objectives have been met.
The management of natural resources and the environment and the development of the private sector, the human factor and gender issues, as well as the urban and rural nature of the destinations financed are the factors that define this tourism finance agenda, leaving economic policy and development and social protection in the background.
When applying the tool utilised we see that, of all the sectors analysed, tourism does not lead the rankings in terms of promoting financial inclusion among the development goals of the projects financed, and in fact it is ranked below all the sectors analysed in this article with the exception of housing construction.
These tourism development projects receive a high volume of finance, allocated to national governments, as one-off financing facilities, by means of repayable loans under more favourable terms than the prevailing market conditions. The conditions and characteristics of the finance allocated to tourism are not the best, compared to other sectors, such as those enjoyed by development projects in the services sector, which are ahead of the other sectors.
Population sectors that are generally more excluded from the formal system, such as SMEs and women entrepreneurs, are not always the ultimate beneficiaries of these projects, which would give rise to greater empowerment of excluded groups [21] and have a major impact on development and financial inclusion in developing countries. Indeed, tourism SMEs are one of the fundamental pillars in sustainable tourism development. However, when comparing performance with regard to the portfolio of beneficiaries, tourism outperforms the other sectors analysed.
The WB has a whole host of resources and instruments to disburse finance. Yet, when it comes to tourism, it focuses on repayable finance, with grants relegated to the background. Even so, tourism receives the highest level of finance of any sector through donations.
Financial support provided by means of guarantees, a low-cost instrument that offers development and self-sufficiency to those under guarantee, has not been used for any of the sectors during the period analysed.
The location of tourism development projects, however, does show a certain criterion oriented towards financial inclusion, since rural and excluded areas receive close to 61.45% of the finance allocated, a value exceeded only by the services sector, and half of the countries considered to be among the most financially excluded in the world receive the highest levels of finance.
With regard to non-financial effort, the WB focuses not only on supporting these projects financially, but also provides technical assistance and training in the majority of projects financed, which makes them more effective and efficient. In this aspect, finance allocated to tourism occupies secondary positions, in comparison with the non-financial effort made for the rest of the sectors analysed.
Finally, a ranking has been established according to the value yielded by the tool used to measure efforts made by the WB with regard to financial inclusion when financing development projects between 2016 and 2019, with tourism occupying an intermediate position (ranked three out of five). Therefore, tourism financing, with a total value obtained with the tool of −0.264, the Hypothesis 1 is validated. This score is an intermediate value between the one obtained by manufacture financing (−0.196), with the greatest orientation towards financial inclusion, and construction financing (−0.344), which shows the least behavior in this regard.
Taking into account the results of the tool achieved by indicator blocks, the worst values obtained by tourism financing are attained in indicators A and D. Thereupon, the WB should improve its behavior, when financing tourism, giving greater consideration to financial inclusion among the development goals of projects and awarding finance in accordance with criteria and conditions that are more geared towards financial inclusion. Therefore, this statement validates the Hypothesis 2, thus confirming the two starting hypotheses.
The findings of this research are important for managers of development projects and international development bodies, since they provide important research about aspects that need to be emphasised in order to improve performance aimed at promoting financial inclusion when financing development projects, particularly in tourism, which would afford such bodies greater efficiency and efficacy in the achievement of their poverty reduction and development goals.
In the future, this analysis could be combined with the WB’s performance in tourism financing, studying the project evaluation reports, and broadening the comparison to other sectors over a longer period of time.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/1/285/s1, Table S1: Projects funded by the WB in tourism, trade, services, housing construction and manufacture (2016–2019).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.I.P.-F.; methodology, I.C.-H.; formal analysis, I.C.-H.; investigation, I.C.-H.; resources, I.C.-H.; data curation, I.C.-H.; writing—original draft preparation, I.C.-H.; writing—review and editing, J.I.P.-F; visualization, J.I.P.-F; supervision, J.I.P.-F; project administration, I.C.-H. and J.I.P.-F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ashley, C.; De Brine, P.; Lehr, A.; Wilde, H. The Role of the Tourism Sector in Expanding Economic Opportunity. In Corporate Social Responsibility Initiative; John F. Kennedy School of Government; Harvard University: Cambridge, UK, 2007; Report 23. [Google Scholar]
- Conrady, R.; Buck, M. Trends and Issues in Global Tourism; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas-García, P.J.; Sánchez-Rivero, M.; Pulido-Fernández, J.I. Does tourism growth influence economic development? J. Travel Res. 2015, 54, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, D.; Barroso, M.O. La demanda turística internacional. Medio Siglo de evolución. Revista de Economía Mundial 2012, 32, 127–149. [Google Scholar]
- Goded, M. La promoción de la actividad turística: ¿una política de desarrollo acertada? Revista de Economía Mundial 2002, 7, 111–133. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, J. Research and Scholarship: The Basis of Tourism Education. J. Tour. Stud. 2001, 1, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido-Fernández, J.I.; Flores, D.; Vargas-Machuca, M.J. Gestión activa de la deuda externa y desarrollo turístico. Los swaps deuda-turismo sostenible. Revista de Economía Mundial 2008, 20, 197–227. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, R.; Telfer, D. Tourism and Development: Concepts and Issues; Channel View Publications: Clevedon, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- López, A.; Esteban, J. El turismo sostenible como dinamizador local. Obs. Medioambient. 2010, 13, 109–129. [Google Scholar]
- Papa, E.; Arcos Alonso, A.; Arcos Alonso, A.; Olea, A.; José, M. Microfinanzas e inclusión financiera en el Sahel senegalés: Análisis desde los valores de la ESS. Revista Iberoamericana de Economía Solidaria e Innovación Socioecológica 2018, 1, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Kumar, R.R.; Ivanov, S.; Loganathan, N. The nexus between tourism demand and output per capita with the relative importance of trade openness and financial development: A study of Malaysia. Tour. Econ. 2017, 23, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, M.; Weingärtner, L.; Kroessin, M.R. Investing in financial inclusion for climate resilience and adaptation. In The Role of Islamic Financial Services; ODI: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Demirguc-Kunt, A.; Klapper, L.; Singer, D.; Van Oudheusden, P. The Global Findex Database 2014: Measuring Financial Inclusion around the World; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA; UUEE: Khimki, Russia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Demirguc-Kunt, A.; Klapper, L.; Singer, D.; Ansar, S.; Hess, J. The Global Findex Database 2017: Measuring Financial Inclusion and the Fintech Revolution; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA; UUEE: Khimki, Russia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Available online: www.theworldbank.org (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Hawkins, D.; Mann, S. The World Bank’s role in tourism development. Ann. Tour. Res. 2007, 34, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Hidalgo, I.; Pulido-Fernández, J.I. Measuring the inclusiveness of international financing to tourism in Latin America and the Caribbean. Invest. Manag. Financ. Innov. 2018, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Hidalgo, I.; Pulido-Fernández, J.I. Is the financing of tourism by international financial institutions inclusive? A proposal for measurement. Curr. Issues Tour. 2019, 22, 330–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, G.; Piermattei, S. Measuring Financial Inclusion in the Main Euro Area Countries: The Role of Electronic Cards; Bank of Italy: Rome, Italy, 2019; p. 504. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Global Financial Inclusion and Consumer Protection Survey; 2017 Report; The World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- García, A.F.H. Inclusión financiera femenina en México: Una herramienta para su empoderamiento = Financial Inclusion for Women in Mexico: A Tool for their Empowerement. FEMERIS Revista Multidisciplinar de Estudios de Género 2019, 4, 158–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, R.; Siddiqui, S.H.; Mahmood, I.; Khan, S.N. Financial Inclusion for SMEs: Role of Digital Micro-Financial Services. Rev. Econ. Dev. Stud. 2019, 5, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlan, R. The relationship between tourism, financial development and economic growth in India. Future Bus. J. 2017, 3, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Fernández, J.I.; Andrades-Caldito, L.; Sánchez-Rivero, M. Is sustainable tourism an obstacle to the economic performance of the tourism industry? Evidence from an international empirical study. J. Sustain. Tour. 2015, 23, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoasong, M.Z.; Kimbu, A.N. Informal microfinance institutions and development-led tourism entrepreneurship. Tour. Manag. 2016, 52, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altés, C. El turismo en América Latina y el Caribe y la Experiencia del BID; Inter-American Development Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia, G. Turismo sostenible. Introducción y marco financiero. Revista de Investigación en Modelos Financieros 2014, 4, 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Kulfas, M. Banca de Desarrollo e Inclusión Financiera de las Pequeñas y Medianas Empresas: Un Estudio a Partir de Los Casos de la Argentina, Colombia, Costa Rica y el Perú; Naciones Unidas: Santiago, Chile, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar, C.P. Estrategias Nacionales de Desarrollo. Guías de Orientación de Políticas Públicas. Políticas Financieras; Naciones Unidas DAES: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Markandya, A.; Taylor, T.; Pedroso, S. Tourism and sustainable development: Lessons from recent World Bank experience. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Tourism and Sustainable Economic Development: Macro and Micro Economic Issues, CRENoS (Università di Cagliari e Sassari, Italy) and Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei, Chia Laguna Hotel, Sardinia, Italy, 15–16 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- CERISE. SPI Gide v3.3; CERISE: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, R. Measuring Results of Microfinance Institutions: Minimum Indicators that Donors and Investors Should Track—A Technical Guide; CGAP: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman, A.O. The paternity of an Index. Am. Econ. Rev. 1964, 54, 761. [Google Scholar]
- Demirgüç-Kunt, A.; Maksimovic, V. Institutions, Financial Markets, and Firms’ Choice of Debt Maturity; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).