Sustainable Conservation Tillage Improves Soil Nutrients and Reduces Nitrogen and Phosphorous Losses in Maize Farmland in Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
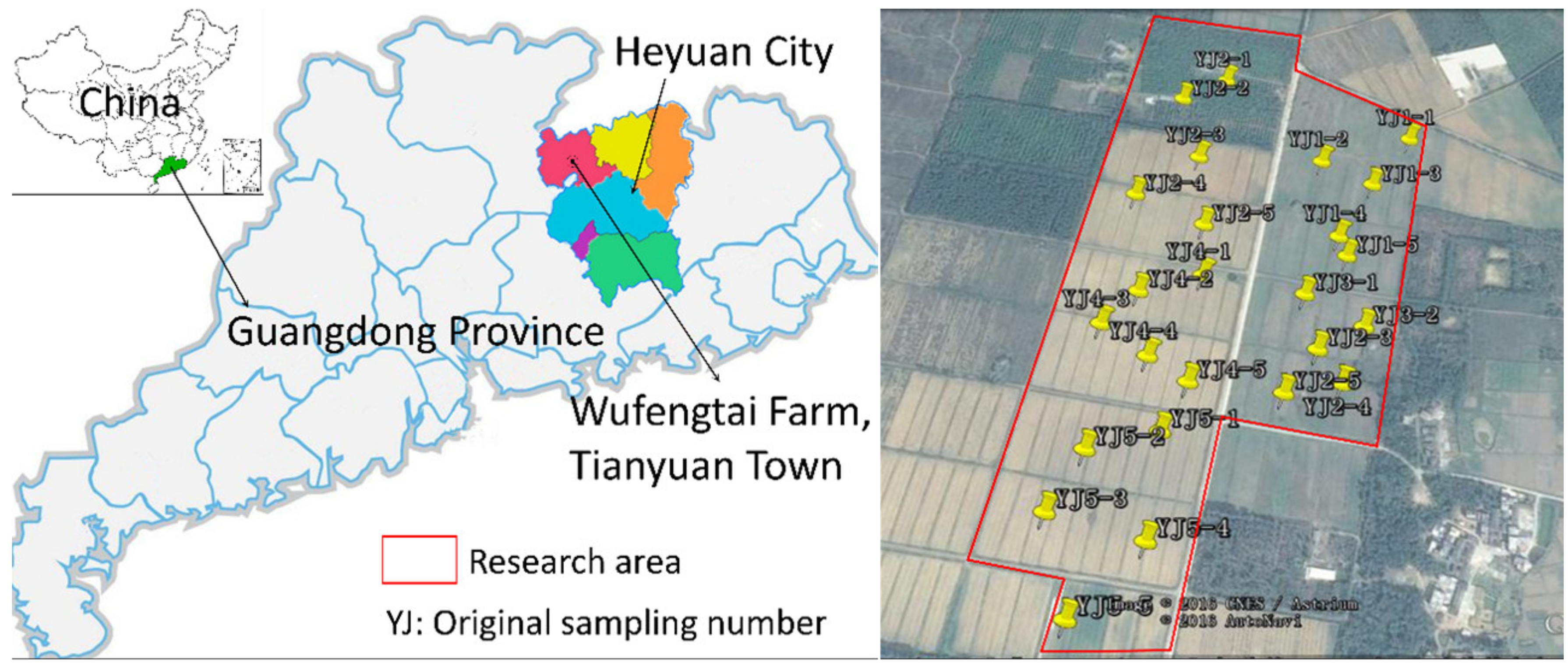
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Nitrogen and Phosphorous Losses in Runoff
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Bulk Densityat the Depth of 0–20 cm
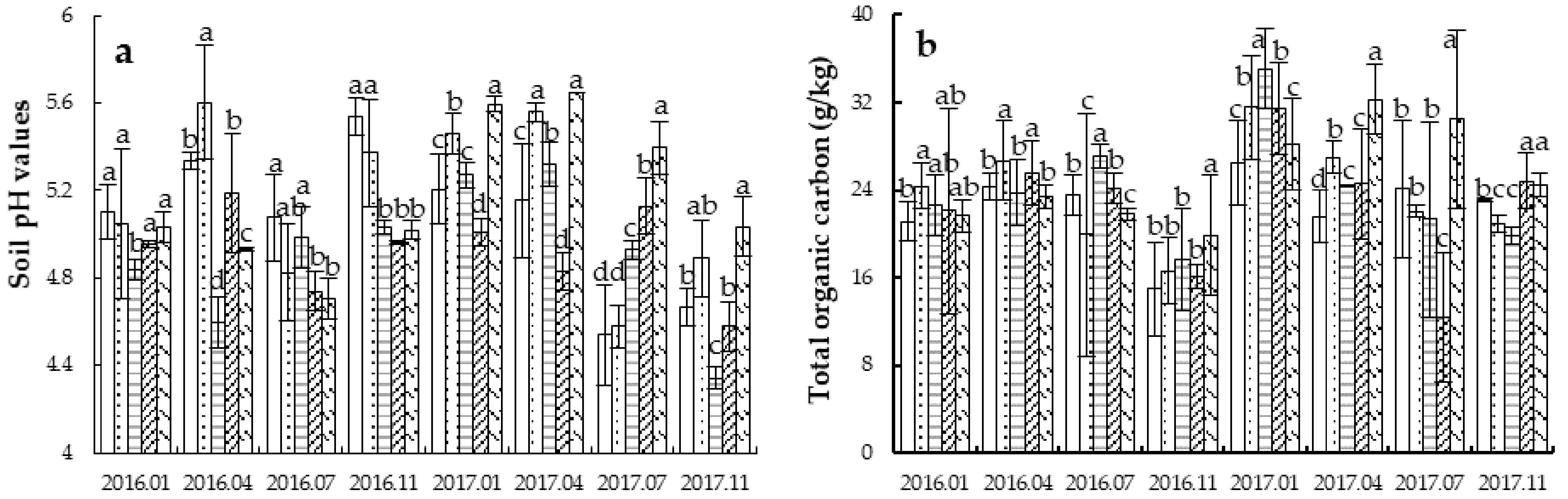
3.2. Soil Chemical Properties at the Depth of 0–20 cm
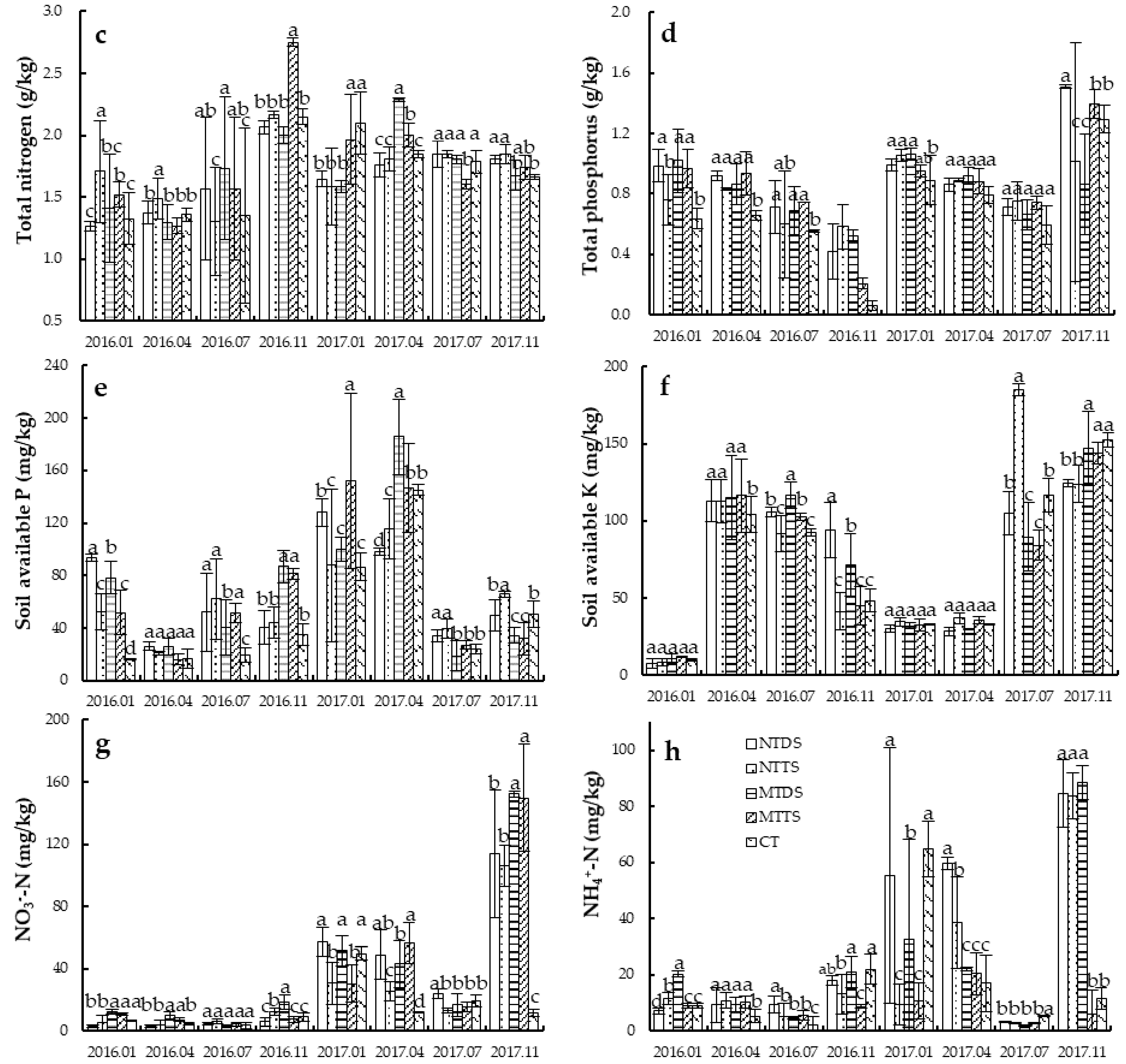
3.3. N and P Movement Along the Soil Profile (0–100 cm) in 2016 and 2017
3.4. Runoff N and P Loss
4. Discussion
4.1. Tillage Effects on Bulk Density
4.2. Effect of Tillage Methods on Soil Chemical Properties
4.3. N and P Movement along the Soil Profile (0–100 cm)
4.4. Runoff N and P Loss
4.5. Implication of Conservation Tillage for NPS N and P Control on the Environment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, F.; Norse, D.; Zhu, Z. Agricultural non-point source pollution in China: Causes and mitigation measures. Ambio 2012, 41, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.G.; Qin, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. Environmentally-friendly agricultural practices and their acceptance by smallholder farmers in China—A case study in Xinxiang County, Henan Province. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norse, D. Non-point pollution from crop production: Global, regional and national issues. Pedosphere 2005, 15, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEP); National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China (NBS); Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (MOA). The First National Survey of Pollution Sources Bulletin. 2010. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/jrzg/2010-02/10/content_1532174.htm (accessed on 6 October 2011). (In Chinese)
- Zhu, Z.L.; Chen, D.L. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China—Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.H.; Huang, J.F.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, A.F. Soil quality evolution after land use change from paddy soil to vegetable land. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Liao, Q.; Hong, Q.; Gong, Y.W. An overview of research on agricultural non-point source pollution modelling in China. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 84, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Mahmood, T.; Islam, K.R. Effect of long term no-till and conventional tillage practices on soil quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 131, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.M.F.; Reicosky, D.; Allmaras, R.; Archer, D.; Wilhelm, W. A matter of balance: Conservation and renewable energy. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 61, 120a–125a. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Kuhn, N.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, X.R.; Li, H.W. Effects of 10 years of conservation tillage on soil properties and productivity in the farming-pastoral ecotone of Inner Mongolia, China. Soil Use Manag. 2009, 25, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Okubo, A.; Sugiyama, S.; Mayland, H.F. Physical, chemical and microbiological properties of an Andisol as related to land use and tillage practice. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 101, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Shi, X. Comparison of multivariate methods for estimating selected soil properties from intact soil cores of paddy fields by Vis–NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 2018, 310 (Suppl. C), 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Shi, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, S. In Situ Measurement of Some Soil Properties in Paddy Soil Using Visible and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Fernández, J.; Taboada, Á.; Fichtner, A.; Härdtle, W.; Calvo, L.; Marcos, E. Time- and age-related effects of experimentally simulated nitrogen deposition on the functioning of montane heathland ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614 (Suppl. C), 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Zeng, X.B.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Su, S.; Bai, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T. Effect of exogenous phosphate on the lability and phytoavailability of arsenic in soils. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.R.; Lu, Q.; Li, W.Y.; Ren, Z.L.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, Y.T. Factors controlling cadmium and lead activities in different parent material-derived soils from the Pearl River Basin. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, G.; Crawley, M.J.; Fornara, D.A. Effects of long-term grassland management on the carbon and nitrogen pools of different soil aggregate fractions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614 (Suppl. C), 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yan, C.R.; Liu, E.K.; Chen, B.Q. Soil nitrogen and its fractions between long-term conventional and no-tillage systems with straw retention in dryland farming in northern China. Geoderma 2016, 269, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, T.; Yunghui, M.; Komatsuzaki, M.; Miura, S.; Hirata, T.; Araki, H.; Kaneko, N.; Ohta, H. Tillage and cover crop species affect soil organic carbon in Andosol, Kanto, Japan. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 138, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, V.; Raiesi, F.; Ghazavi, M.A. Six years of different tillage systems affected aggregate-associated SOM in a semi-arid loam soil from Central Iran. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 154, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Lal, R. Tillage effects on soil properties at different levels of fertilizer application in Punjab, Pakistan. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 68, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, M.V. Long-term tillage and crop rotation effects on soil chemical and mineral properties. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houx, J.H.; Wiebold, W.J.; Fritschi, F.B. Long-term tillage and crop rotation determines the mineral nutrient distributions of some elements in a Vertic Epiaqualf. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Is crop residue a waste? J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 59, 136a–139a. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.F.; Pu, C.; Liu, S.L.; Chen, Z.D.; Chen, F.; Xiao, X.P.; Lal, R.; Zhang, H.L. Effects of tillage systems on soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in a double paddy cropping system in Southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 153, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.M.; Ochsner, T.E.; Venterea, R.T.; Griffis, T.J. Tillage and soil carbon sequestration—What do we really know? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puget, P.; Lal, R. Soil organic carbon and nitrogen in a Mollisol in central Ohio as affected by tillage and land use. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 80, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.L.; Xu, M.G.; Chen, X.N.; He, X.H.; Zhao, K. Stratification of soil organic C, N and C:N ratio as affected by conservation tillage in two maize fields of China. Catena 2012, 95, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.J. Soil organic matter stratification ratio as an indicator of soil quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 66, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.O.; Post, W.M. Soil organic carbon sequestration rates by tillage and crop rotation: A global data analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1930–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oorts, K.; Nicolardot, B.; Merckx, R.; Richard, G.; Boizard, H. C and N mineralization of undisrupted and disrupted soil from different structural zones of conventional tillage and no-tillage systems in northern France. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupwayi, N.Z.; Clayton, G.W.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Harker, K.N.; Turkington, T.K.; Soon, Y.K. Nitrogen release during decomposition of crop residues under conventional and zero tillage. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 86, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Q.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhu, C.Y.; Lin, L.M.; Xu, L.X. No-tillage effects on N and P exports across a rice-planted watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8598–8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainju, U.M.; Caesar-Tonthat, T.; Lenssen, A.W.; Evans, R.G.; Kolberg, R. Tillage and cropping sequence impacts on nitrogen cycling in dryland farming in eastern Montana, USA. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 103, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.; Sullivan, D.; Wolf, A.; Brandt, R.; Dou, Z.X.; Elliott, H.; Kovar, J.; Leytem, A.; Maguire, R.; Moore, P.; et al. Selection of a water-extractable phosphorus test for manures and biosolids as an indicator of runoff loss potential. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djodjic, F.; Borling, K.; Bergstrom, L. Phosphorus leaching in relation to soil type and soil phosphorus content. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Church, C.; Saporito, L.S.; McGrath, J.M.; Reiter, M.S.; Allen, A.L.; Tingle, S.; Binford, G.D.; Han, K.; Joern, B.C. Phosphorus Leaching from Agricultural Soils of the Delmarva Peninsula, USA. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kladivko, E.J.; Frankenberger, J.R.; Jaynes, D.B.; Meek, D.W.; Jenkinson, B.J.; Fausey, N.R. Nitrate leaching to subsurface drains as affected by drain spacing and changes in crop production system. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | pH | TOC (g·kg−1) | Total N (g·kg−1) | Total P (g·kg−1) | Alkaline-N (mg·kg−1) | NO3−–N (mg·kg−1) | NH4+–N (mg·kg−1) | Availa le P (mg·kg−1) | Available K (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.67 ± 0.07 | 5.05 ± 0.34 | 24.40 ± 2.03 | 1.71 ± 0.42 | 0.76 ± 0.17 | 8.87 ± 2.38 | 4.49 ± 1.91 | 7.86 ± 2.92 | 26.27 ± 10.12 | 173.33 ± 30.55 |
| Tillage Technique | 2016 Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | 2017 Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | April | July | November | Jan | April | July | November | |
| NTTS | 1.54 ± 0.07a | 1.51 ± 0.06a | 1.40 ± 0.06ab | 1.44 ± 0.06a | 1.45 ± 0.03a | 1.43 ± 0.02a | 1.38 ± 0.02a | 1.41 ± 0.02a |
| NTDS | 1.47 ± 0.05ab | 1.48 ± 0.04a | 1.42 ± 0.02a | 1.45 ± 0.02a | 1.44 ± 0.01a | 1.40 ± 0.01a | 1.35 ± 0.01a | 1.41 ± 0.01ab |
| MTTS | 1.37 ± 0.02bc | 1.35 ± 0.02b | 1.29 ± 0.02cd | 1.35 ± 0.01ab | 1.37 ± 0.01b | 1.17 ± 0.05b | 1.15 ± 0.09b | 1.35 ± 0.01bc |
| MTDS | 1.34 ± 0.02bc | 1.33 ± 0.02b | 1.29 ± 0.01bc | 1.32 ± 0.01bc | 1.34 ± 0.01b | 1.21 ± 0.02b | 1.19 ± 0.01b | 1.31 ± 0.01cd |
| CT | 1.28 ± 0.01c | 1.25 ± 0.01b | 1.18 ± 0.01d | 1.23 ± 0.01c | 1.31 ± 0.03b | 1.16 ± 0.01b | 1.07 ± 0.04b | 1.28 ± 0.03d |
| Tillage Technique | Runoff (mm) | Sediment (g·m−2) | Runoff Sediment Bound TP (g·m−2) | Concentration of TP in Runoff Water (mg·L−1) | Runoff Sediment Bound TN (g·m−2) | Concentration of TN in Runoff Water (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTTS | 188 ± 17c | 600 ± 28b | 113 ± 19c | 1.98 ± 0.06b | 183 ± 16c | 1.08 ± 0.14b |
| NTDS | 188 ± 14c | 600 ± 46b | 112 ± 14c | 2.08 ± 0.07b | 185 ± 17c | 1.14 ± 0.06b |
| MTTS | 263 ± 18b | 664 ± 25ab | 222 ± 20b | 2.34 ± 0.06ab | 236 ± 24b | 1.34 ± 0.02ab |
| MTDS | 273 ± 18ab | 655 ± 21ab | 219 ± 26b | 2.37 ± 0.18ab | 237 ± 10b | 1.36 ± 0.13ab |
| CT | 312 ± 4a | 688 ± 15a | 242 ± 18a | 2.91 ± 0.44a | 280 ± 29a | 1.71 ± 0.19a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Issaka, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Asenso, E.; Li, J.-H.; Li, Y.-T.; Wang, J.-J. Sustainable Conservation Tillage Improves Soil Nutrients and Reduces Nitrogen and Phosphorous Losses in Maize Farmland in Southern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082397
Issaka F, Zhang Z, Zhao Z-Q, Asenso E, Li J-H, Li Y-T, Wang J-J. Sustainable Conservation Tillage Improves Soil Nutrients and Reduces Nitrogen and Phosphorous Losses in Maize Farmland in Southern China. Sustainability. 2019; 11(8):2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082397
Chicago/Turabian StyleIssaka, Fuseini, Zhen Zhang, Zhong-Qiu Zhao, Evans Asenso, Jiu-Hao Li, Yong-Tao Li, and Jin-Jin Wang. 2019. "Sustainable Conservation Tillage Improves Soil Nutrients and Reduces Nitrogen and Phosphorous Losses in Maize Farmland in Southern China" Sustainability 11, no. 8: 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082397
APA StyleIssaka, F., Zhang, Z., Zhao, Z.-Q., Asenso, E., Li, J.-H., Li, Y.-T., & Wang, J.-J. (2019). Sustainable Conservation Tillage Improves Soil Nutrients and Reduces Nitrogen and Phosphorous Losses in Maize Farmland in Southern China. Sustainability, 11(8), 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082397







