Defining Sustainability Core Competencies in Business and Management Studies Based on Multinational Stakeholders’ Perceptions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. What Is Sustainable Development
2.2. The Role of Higher Education in Sustainable Development and Its Inclusion in the Curricula
2.3. Sustainability Competencies in Higher Education Curricula
2.4. Educational Harmonization Projects for the Development of Competencies: Tuning Projects
3. Research Objectives and Methodology
3.1. Objectives and Research Questions
3.2. Selection of the Projects
3.3. Sample and Methodology
4. Discussion of Results
5. Conclusions, Implications, Limitations and Future Lines of Research
5.1. Conclusions and Implications
5.2. Limitations and Future Lines of Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergman, M.M.; Bergman, Z.; Berger, L. An Empirical Exploration, Typology, and Definition of Corporate Sustainability. Sustainability 2017, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R. Envisioning sustainability three-dimensionally. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setó-Pamies, D.; Papaoikonomou, E. A Multi-level Perspective for the Integration of Ethics, Corporate Social Responsibility and Sustainability (ECSRS) in Management Education. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 136, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piza, V.; Aparicio, J.; Rodríguez, C.; Marín, R.; Beltrán, J.; Bedolla, R. Sustainability in Higher Education: A Didactic Strategy for Environmental Mainstreaming. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. UNESCO World Conference on Education for Sustainable Development: Bonn Declaration. UNESCO: Paris, France, 2009. Available online: http://www.esd-world-conference-2009.org/fileadmin/download/ESD2009_BonnDeclaration080409.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Cebrián, G.; Junyent, M. Competencies in Education for Sustainable Development: Exploring the Student Teachers’ Views. Sustainability 2015, 7, 2768–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, W.; Mulà, I.; Ceulemans, K.; Molderez, I.; Gaeremynck, V. The integration of competences for sustainable development in higher education: An analysis of bachelor programs in management. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 48, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, O.; Holdsworth, S.; Thomas, I. Vignette question design for the assessment of graduate sustainability learning outcomes. Environ. Educ. Res. 2018, 24, 406–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Ceulemans, K.; Alonso-Almeida, M.; Huisingh, D.; Lozano, F.J.; Waas, T.; Hugé, J. A review of commitment and implementation of sustainable development in higher education: Results from a worldwide survey. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, C.B.; Whelan, R.; Stoffer, H.; Todd, E.; Kern, C.L. Developing a university-wide course on sustainability: A critical evaluation of planning and implementation. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 106, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, F. Dissonance in students’ perceptions of sustainable development and sustainability: Implications for curriculum change. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2007, 8, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Godemann, J.; Rieckmann, M.; Stoltenberg, U. Developing key competencies for sustainable development in higher education. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2007, 8, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiek, A.; Withycombe, L.; Redman, C.L. Key Competencies in Sustainability: A Reference Framework for Academic Program Development. Sustain. Sci. 2011, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haan, G. The BLK ‘21’ programme in Germany: A ‘Gestaltungskompetenz’-based model for education for sustainable development. Environ. Educ. Res. 2006, 1, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Merrill, M.Y.; Sammalisto, K.; Ceulemans, K.; Lozano, F.J. Connecting Competences and Pedagogical Approaches for Sustainable Development in Higher Education: A Literature Review and Framework Proposal. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Education for Sustainable Development Goals: Learning Objectives; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017; Available online: http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0024/002474/247444e.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Mochizuki, Y.; Fadeeva, Z. Competences for Sustainable Development and Sustainability. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2010, 11, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C. The evolution of sustainability. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 1992, 5, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruta, G.; Hamilton, K. The capital approach to sustainability. In Handbook of Sustainable Development; Atkinson, G., Dietz, S., Neumayer, E., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, P.C.; Hatch, N.W. Researching Corporate Social Responsibility: An Agenda for the 21st Century. J. Bus. Ethics 2007, 70, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martell, J. University Social Responsibility: Origins, Scope, and Potential Future. J. Int. Bus. Educ. 2012, 7, 77–102. [Google Scholar]
- Miotto, G.; Blanco González, A.; Del Castillo Feito, C. Social Responsibility: A Tool for Legitimation in Spanish Universities’ Strategic Plans. Trípodos 2018, 42, 59–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore-Álvarez, A.; Ruiz-Lozano, M. University Social Responsibility (USR) in the Global Context: An Overview of Literature. Bus. Prof. Ethics J. 2012, 31, 475–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, J. Cannibals with Forks; New Society: Gabriela Island, BC, Canada, 1999; Available online: www.newsociety.com (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- World Commission on Environment and Development. Our Common Future; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Boström, M. A missing pillar? Challenges in theorizing and practicing social sustainability: Introduction to the special issue. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2012, 8, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, R.; Martens, P. Sustainable Development: How to manage something that is subjective and never can be achieved? Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2007, 3, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormo-Carbó, G.; Seguí-Mas, E.; Oltra, V. Business Ethics as a Sustainability Challenge: Higher Education Implications. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, M.A. Wrapping our brains around sustainability. Sustainability 2009, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, R.H.; Peterson, N.D.; Arora, P.; Caldwell, K. Five approaches to social sustainability and an integrated way forward. Sustainability 2016, 8, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeve-de Pauw, J.; Gericke, N.; Olsson, D.; Berglund, T. The effectiveness of education for sustainable development. Sustainability 2015, 7, 15693–15717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. United Nations Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (2005–2014): Draft International Implementation Scheme; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2005; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000148654 (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Peterson, N.D. Introduction to the special issue on social sustainability: Integration, context, and governance. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2016, 12, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghezzo, L. The five dimensions of sustainability. Environ. Politics 2009, 18, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, J.; Bullard, R.D.; Evans, B. 2002 Exploring the Nexus: Bringing Together Sustainability, Environmental Justice and Equity. Space Pol. 2002, 6, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, M.; Andersson, E.; Berg, M.; Gustafsson, K.; Gustavsson, E.; Hysing, E.; Lidskog, R.; Löfmarck, E.; Ojala, M.; Olsson, J.; et al. Conditions for Transformative Learning for Sustainable Development: A Theoretical Review and Approach. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.K.; Lozano, R.; Noyes, C.; Rodgers, M. Assessing curricula contribution to sustainability more holistically: Experiences from the integration of curricula assessment and students’ perceptions at the Georgia Institute of Technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 61, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbel, A. Pathways towards sustainability through higher education. Int. J. Sust. High. Educ. 2009, 10, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, S.L.T. Alternative communications about sustainability education. Sustainability 2013, 5, 3562–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Education for Sustainable Development-Building a Better, Fairer World for the 21st Century. 2012. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000216673 (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- United Nations Global Impact. The Principles for Responsible Management Education; United Nations Global Compact: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Segalàs, J.; Ferrer-Balas, D.; Svanström, M.; Lundqvist, U.; Mulder, K.F. What has to be learnt for sustainability? A comparison of bachelor engineering education competences at three European universities. Sustain. Sci. 2009, 4, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigmore-Álvarez, A.; Ruiz-Lozano, M. The United Nations Global Compact Progress Reports as Management Control Instruments for Social Responsibility at Spanish Universities. SAGE Open 2014, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallaeys, F.; Álvarez Rodríguez, J. Hacia una definición latinoamericana de Responsabilidad Social Universitaria. Aproximación a las preferencias conceptuales de los universitarios. Educ. XX1 2019, 22, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Nasongkhla, J.; Donaldson, J.A. University Social Responsibility (USR): Identifying an Ethical Foundation within Higher Education Institutions. Turk. Online J. Educ. Technol. 2015, 14, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, R.; Lukman, R.; Lozano, F.J.; Huisingh, D.; Lambrechts, W. Declarations for sustainability in higher education: Becoming better leaders, through addressing the university system. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 48, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Adombent, M.; Fischer, D.; Richter, S.; Rieckmann, M. Learning to change universities from within: A service-learning perspective on promoting sustainable consumption in higher education. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 62, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, A.D. The critical role of higher education in creating a sustainable future. Plan. High. Educ. 2003, 31, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, R.; Ceulemans, K.; Seatter, C.S. Teaching organisational change management for sustainability: Designing and delivering a course at the University of Leeds to better prepare future sustainability change agents. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 106, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz-Sisitka, H.; Raven, G. South Africa: Applied competence as the guiding framework for environmental and sustainability education. In Work, Learning and Sustainable Development; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sleurs, W. Competencies for ESD (Education for Sustainable Development) Teachers: A Framework to Integrate ESD in the Curriculum of Teacher Training Institutes-Comenius 2.1 Project 118277- CP-1-2004-BE-Comenius-C2.1. 2008. Available online: http://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/env/esd/inf.meeting.docs/EGonInd/8mtg/CSCT%20Handbook_Extract.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Cebrián, G.; Junyent, M. Competencias profesionales en Educación para la Sostenibilidad: Un estudio exploratorio de la visión de futuros maestros. Enseñanza de las Ciencias 2014, 32, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.; Wagenaar, R. Tuning Educational Structures in Europe; Final Report; University of Deusto: Bilbao, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- González, J.; Wagenaar, R.; Beneitone, P. Tuning-América Latina: Un proyecto de las universidades. Revista iberoamericana de educación 2004, 35, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Tuning Academy. Available online: http://tuningacademy.org (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Chyung, S.Y.; Stepich, D.; Cox, D. Building a competency-based curriculum architecture to educate 21st-century business practitioners. J. Educ. Bus. 2006, 81, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedenweg, K.; Monroe, M.C.; Oxarart, A. The importance of teaching ethics of sustainability. Int. J. Sustain. Higher Educ. 2013, 14, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amekudzi, A.A.; Khayesi, M.; Khisty, J.C. Sustainable development footprint: A framework for assessing sustainable development risks and opportunities in time and space. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 18, 9–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuning Academy. Tuning Europe. Available online: http://tuningacademy.org/tuning-europe-i-iv/?lang=en (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Tuning Academy. Tuning Latin America. Available online: http://tuningacademy.org/tuning-latin-america-i/?lang=en (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Tuning Central Asia. Available online: http://www.tucahea.org/ (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Lorenzo-Seva, U.; Ferrando, P.J. FACTOR: A computer program to fit the exploratory factor analysis model. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglin, J. Improving Your Exploratory Factor Analysis for Ordinal Data: A Demonstration Using FACTOR. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2014, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
| List of generic competencies used in the Tuning Europe project (2006–2009) |
| Ability for abstract thinking, analysis and synthesis; Ability to apply knowledge in practical situations; Ability to plan and manage time; Knowledge and understanding of the subject area and understanding of the profession; Ability to communicate both orally and through the written word in native language; Ability to communicate in a second language; Skills in the use of information and communication technologies; Ability to undertake research at an appropriate level; Capacity to learn and stay up-to-date with learning; Ability to search for, process and analyze information from a variety of sources; Ability to be critical and self-critical; Ability to adapt to and act in new situations; Capacity to generate new ideas (creativity); Ability to identify, pose and resolve problems; Ability to make reasoned decisions; Ability to work in a team; Interpersonal and interaction skills; Ability to motivate people and move toward common goals; Ability to communicate with non-experts of one’s field; Appreciation and respect for diversity and multiculturality; Ability to work in an international context; Ability to work autonomously; Ability to design and manage projects; Commitment to safety; Spirit of enterprise, ability to take initiative; Ability to act on the basis of ethical reasoning; Ability to evaluate and maintain quality of work produced; Determination and perseverance in the tasks given and responsibilities taken; Commitment to the conservation of the environment; Ability to act with social responsibility and civic awareness; Ability to show awareness of equal opportunities and gender issues. |
| List of generic competencies used in the Tuning Latin America project (2004–2007) |
| Capacity for abstraction, analysis, and synthesis; Ability to apply knowledge in practice; Ability to organize and plan time; Knowledge regarding the area of study and related professions; Social responsibility and commitment to citizenship; Capacity for oral and written communication; Ability to communicate in a second language; Ability to use information and communication technology; Capacity for investigation; Ability to learn and update learning; Ability to search for, process, and analyze information from a variety of sources; Critical and self-critical abilities; Ability to react to new situations; Creative skills; Ability to identify, pose, and solve problems; Ability to make decisions; Ability to work as part of a team; Interpersonal skills; Ability to motivate and work towards common goals; Commitment to look after the environment; Commitment to socio-cultural environment; Value and respect for diversity and multiculturality; Ability to work in international contexts; Ability to work autonomously; Ability to formulate and manage projects; Ethical commitment; Commitment to quality. |
| List of generic competencies used in the Tuning Central Asia project (2012–2016) |
| Ability to analyze and synthesize; Ability to use logical and critical. thinking for solving problems; Ability to model, design and forecast; Ability to carry out research applying appropriate methods; Ability to take initiatives and entrepreneurship; Ability to innovate; Ability to develop general knowledge; Ability to learn including autonomous learning; Ability to communicate interactively and receive feedback; Knowledge of the professional field; Ability to communicate in multicultural context; Ability to communicate in official state, Russian and foreign languages; Ability to lead people and work in a team; Ability to manage information; Ability to use information and communication technologies; Social responsibility; Ability to follow a healthy lifestyle; Ecological and environmental responsibility; Knowledge of the laws; Ability to prevent and resolve conflicts; Patriotism and preservation of own cultural values; Tolerance and respect for others; Commitment to quality result; Flexibility; Ability to apply knowledge in practice; Orientation toward the needs of the user; Ability to work autonomously; Ability to adapt to change; Ability to make decisions; Time-management. |
| Tuning Europe (2006–2009) | Tuning Latin America (2004–2007) | Tuning Central Asia (2012–2016) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Responses Obtained with Respect to Generic Competencies | 1081 | 100.0% | 7797 | 100.0% | 1411 | 100.0% |
| • Academics | 232 | 21.5% | 815 | 9.7% | 434 | 30.8% |
| • Employers | 158 | 14.6% | 714 | 8.5% | 123 | 8.7% |
| • Students | 452 | 41.8% | 2922 | 34.8% | 682 | 48.3% |
| • Graduates | 239 | 22.1% | 3944 | 47.0% | 172 | 12.2% |
| Multivariate Test for Skewness | Multivariate Test for Kurtosis | Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) Test | Bartlett’s Test | Factors Retained | % Explained Variance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | 13,659.6 d.f. = 54565 p = 1.00 | 59.19 p < 0.001 | 0.91 | 8850.81 d.f. = 465 p < 0.001 | 7 | 76.47 |
| Latin America | 84,982.8 d.f. = 3654 p = 1.00 | 427.79 p < 0.001 | 0.96 | 8876.80 d.f. = 351 p < 0.001 | 4 | 82.09 |
| Central Asia | 61,152.9 d.f. = 4960 p = 1.00 | 488.1 p < 0.001 | 0.96 | 25,192.3 d.f. = 435 p < 0.001 | 4 | 73.21 |
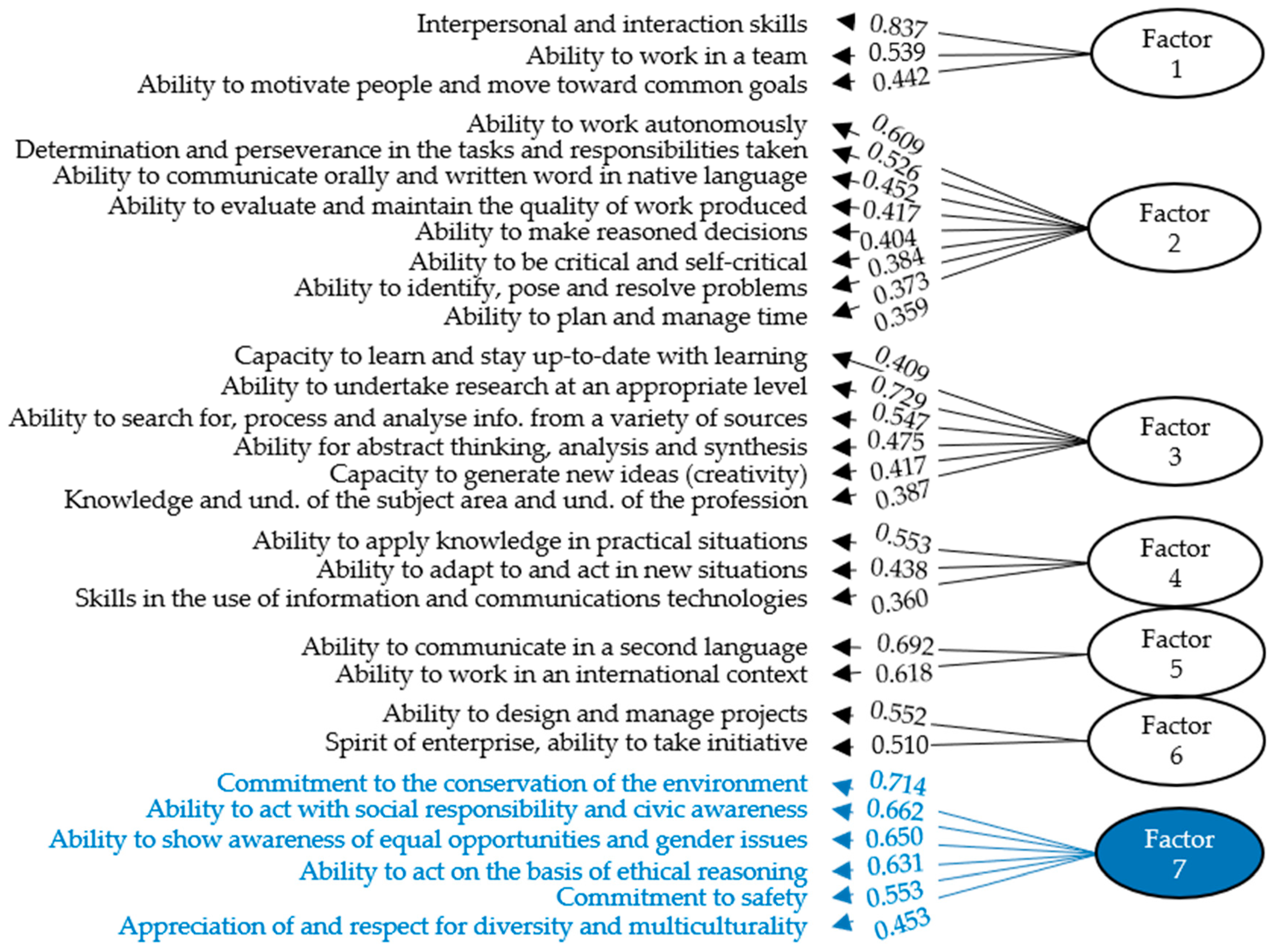
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interpersonal and interaction skills | 0.837 | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to work in a team | 0.539 | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to motivate people and move to common goals | 0.442 | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.406 | __ |
| Ability to work autonomously | __ | 0.609 | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Determination and perseverance tasks given and response. | __ | 0.526 | __ | __ | __ | 0.356 | __ |
| Ability to communicate orally and written native language | __ | 0.452 | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to evaluate and maintain quality work produced | __ | 0.417 | 0.313 | __ | __ | __ | 0.300 |
| Ability to make reasoned decisions | __ | 0.404 | __ | __ | __ | 0.333 | __ |
| Ability to be critical and self-critical | __ | 0.384 | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to identify, pose and resolve problems | __ | 0.373 | __ | 0.364 | __ | 0.359 | __ |
| Ability to plan and manage time | __ | 0.359 | __ | 0.303 | __ | __ | __ |
| Capacity to learn and stay up-to-date with learning | __ | 0.316 | 0.409 | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to undertake research at an appropriate level | __ | __ | 0.729 | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to search for, process and analyze information... | __ | __ | 0.547 | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability for abstract thinking, analysis and synthesis | __ | __ | 0.475 | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Capacity to generate new ideas (creativity) | __ | __ | 0.417 | __ | __ | 0.468 | __ |
| Knowledge and und. of the subject area and profession | __ | __ | 0.387 | __ | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to apply knowledge in practical situations | __ | __ | __ | 0.553 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to adapt to and act in new situations | __ | __ | __ | 0.438 | __ | 0.373 | __ |
| Skills in the use of information and comm. technologies | __ | __ | __ | 0.360 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to communicate in a second language | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.692 | __ | __ |
| Ability to work in an international context | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.618 | __ | __ |
| Ability to design and manage projects | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.552 | __ |
| Spirit of enterprise, ability to take initiative | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.510 | 0.342 |
| Commitment to the conservation of the environment | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.714 |
| Ability to act with social responsibility and civic awareness | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.662 |
| Ability to show awareness equal oppo. and gender issues | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.650 |
| Ability to act on the basis of ethical reasoning | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.631 |
| Commitment to safety | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.553 |
| Appreciation of and respect for diversity and multicult. | __ | __ | __ | __ | 0.404 | __ | 0.453 |
| Ability to communicate with non-experts of one’s field | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ | __ |
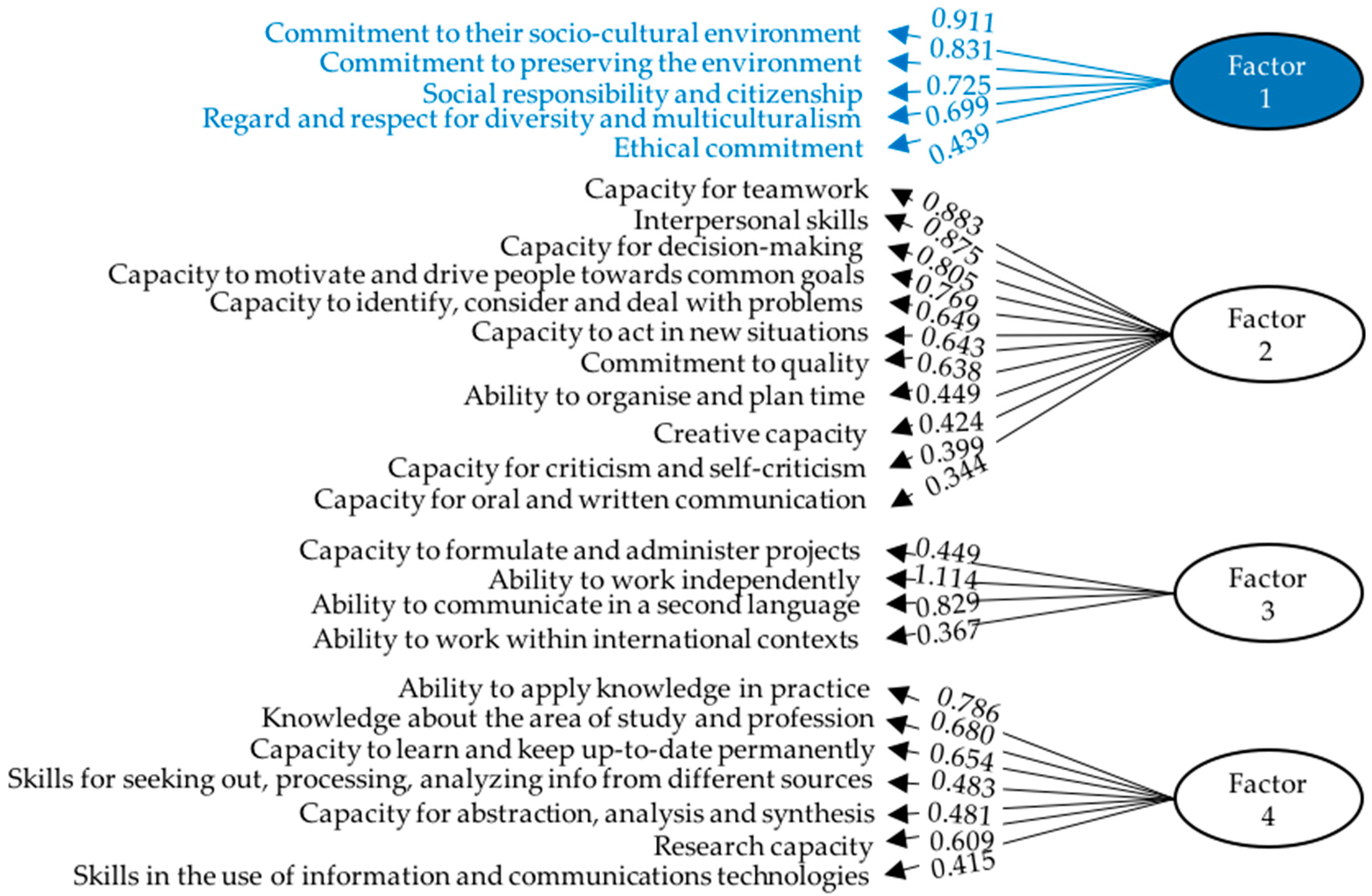
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commitment to their socio-cultural environment | 0.911 | __ | __ | __ |
| Commitment to preserving the environment | 0.831 | __ | __ | __ |
| Social responsibility and citizenship | 0.725 | __ | −0.305 | 0.402 |
| Regard and respect for diversity and multiculturalism | 0.699 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ethical commitment | 0.439 | 0.551 | __ | __ |
| Capacity for teamwork | __ | 0.883 | __ | __ |
| Interpersonal skills | __ | 0.875 | __ | __ |
| Capacity for decision-making | __ | 0.805 | __ | __ |
| Capacity to motivate and drive people towards common goals | __ | 0.769 | __ | __ |
| Capacity to identify, consider and deal with problems | __ | 0.649 | __ | __ |
| Capacity to act in new situations | __ | 0.643 | __ | __ |
| Commitment to quality | __ | 0.638 | __ | __ |
| Ability to organize and plan time | __ | 0.449 | __ | 0.311 |
| Creative capacity | __ | 0.424 | __ | __ |
| Capacity for criticism and self-criticism | __ | 0.399 | __ | __ |
| Capacity for oral and written communication | __ | 0.344 | __ | 0.371 |
| Capacity to formulate and administer projects | __ | 0.302 | 0.499 | __ |
| Ability to work independently | __ | __ | 1.114 | −0.303 |
| Ability to communicate in a second language | __ | __ | 0.829 | __ |
| Ability to work within international contexts | __ | __ | 0.367 | __ |
| Ability to apply knowledge in practice | __ | __ | __ | 0.786 |
| Knowledge about the area of study and profession | __ | __ | __ | 0.680 |
| Capacity to learn and keep up-to-date permanently | __ | __ | __ | 0.654 |
| Skills for seeking out, processing and analyzing info from different sources | __ | __ | __ | 0.483 |
| Capacity for abstraction, analysis and synthesis | __ | __ | __ | 0.481 |
| Research capacity | __ | −0.316 | __ | 0.609 |
| Skills in the use of information and communications technologies | __ | __ | 0.369 | 0.415 |
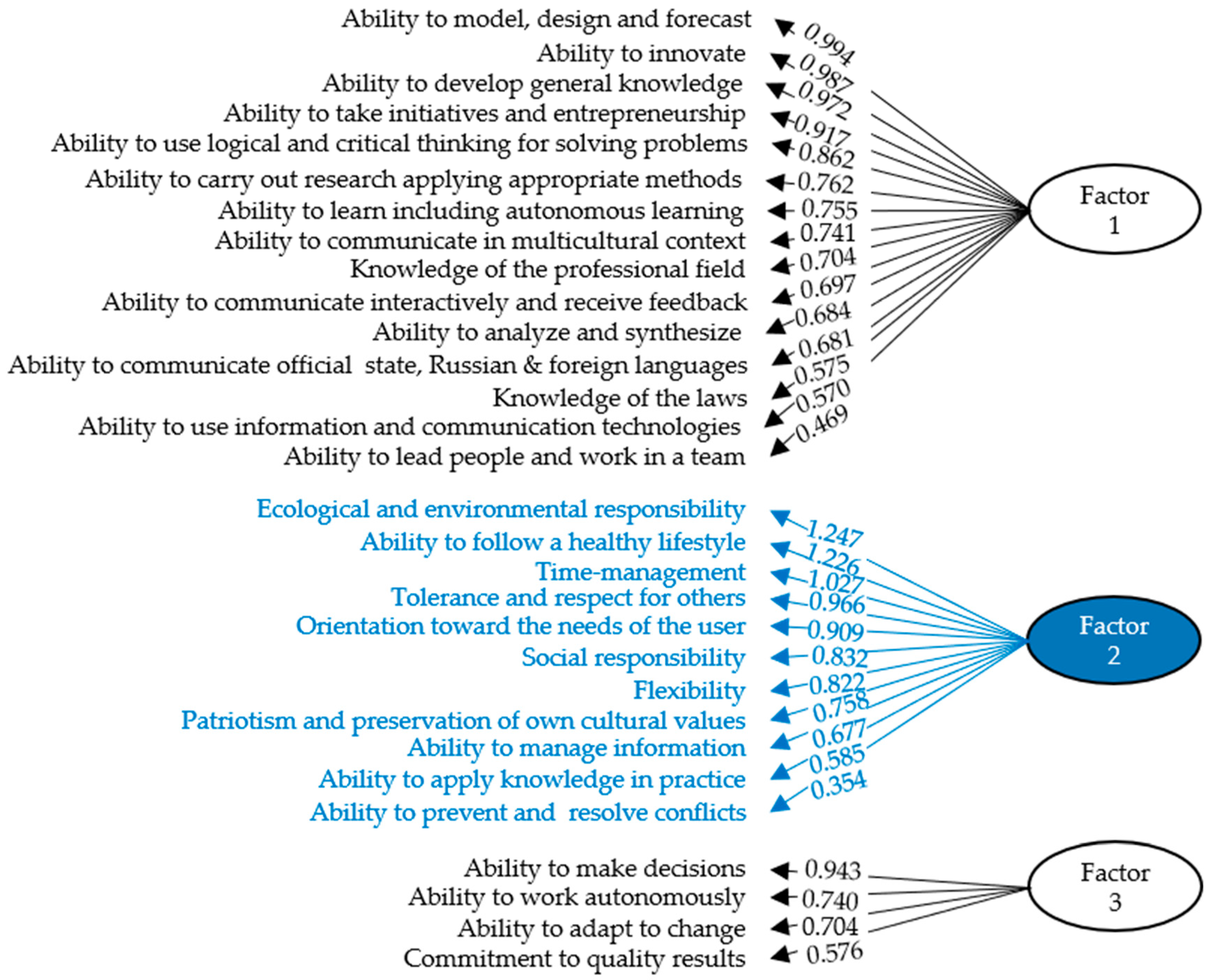
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ability to model, design and forecast | 0.994 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to innovate | 0.987 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to develop general knowledge | 0.972 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to take initiatives and entrepreneurship | 0.917 | −0.329 | __ | __ |
| Ability to use logical and critical thinking for solving problems | 0.862 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to carry out research applying appropriate methods | 0.762 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to learn including autonomous learning | 0.755 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to communicate in multicultural context | 0.741 | __ | __ | __ |
| Knowledge of the professional field | 0.704 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to communicate interactively and receive feedback | 0.697 | __ | __ | 0.322 |
| Ability to analyze and synthesize | 0.684 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to communicate in office, state, Russian and foreign languages | 0.681 | __ | __ | __ |
| Knowledge of the laws | 0.575 | __ | __ | __ |
| Ability to use information and communication technologies | 0.570 | 0.351 | __ | __ |
| Ability to lead people and work in a team | 0.469 | __ | 0.320 | __ |
| Ecological and environmental responsibility. Ability to prevent and resolve conflicts | __ | 1.247 | −0.592 | __ |
| Ability to follow a healthy lifestyle | __ | 1.226 | −0.609 | __ |
| Time-management | −0.412 | 1.027 | __ | __ |
| Tolerance and respect for others | __ | 0.966 | __ | __ |
| Orientation toward the needs of the user | −0.331 | 0.909 | __ | __ |
| Social responsibility | 0.410 | 0.832 | −0.476 | __ |
| Flexibility | __ | 0.822 | __ | __ |
| Patriotism and preservation of own cultural values | __ | 0.758 | __ | __ |
| Ability to manage information | __ | 0.677 | __ | __ |
| Ability to apply knowledge in practice | __ | 0.585 | __ | −0.526 |
| Ability to prevent and resolve conflicts | __ | 0.354 | 0.313 | __ |
| Ability to make decisions | __ | __ | 0.943 | __ |
| Ability to work autonomously | __ | __ | 0.740 | __ |
| Ability to adapt to change | __ | __ | 0.704 | __ |
| Commitment to quality results | __ | __ | 0.576 | __ |
| Europe | Latin America | Central Asia |
|---|---|---|
| Factor 7 | Factor 1 | Factor 2 |
|
|
|
| Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.823 | Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.818 | Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.861 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eizaguirre, A.; García-Feijoo, M.; Laka, J.P. Defining Sustainability Core Competencies in Business and Management Studies Based on Multinational Stakeholders’ Perceptions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082303
Eizaguirre A, García-Feijoo M, Laka JP. Defining Sustainability Core Competencies in Business and Management Studies Based on Multinational Stakeholders’ Perceptions. Sustainability. 2019; 11(8):2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082303
Chicago/Turabian StyleEizaguirre, Almudena, María García-Feijoo, and Jon Paul Laka. 2019. "Defining Sustainability Core Competencies in Business and Management Studies Based on Multinational Stakeholders’ Perceptions" Sustainability 11, no. 8: 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082303
APA StyleEizaguirre, A., García-Feijoo, M., & Laka, J. P. (2019). Defining Sustainability Core Competencies in Business and Management Studies Based on Multinational Stakeholders’ Perceptions. Sustainability, 11(8), 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082303





