A Dominance-Based Network Method for Ranking Efficient Decision-Making Units in Data Envelopment Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Ranking Methods Using Positional Features
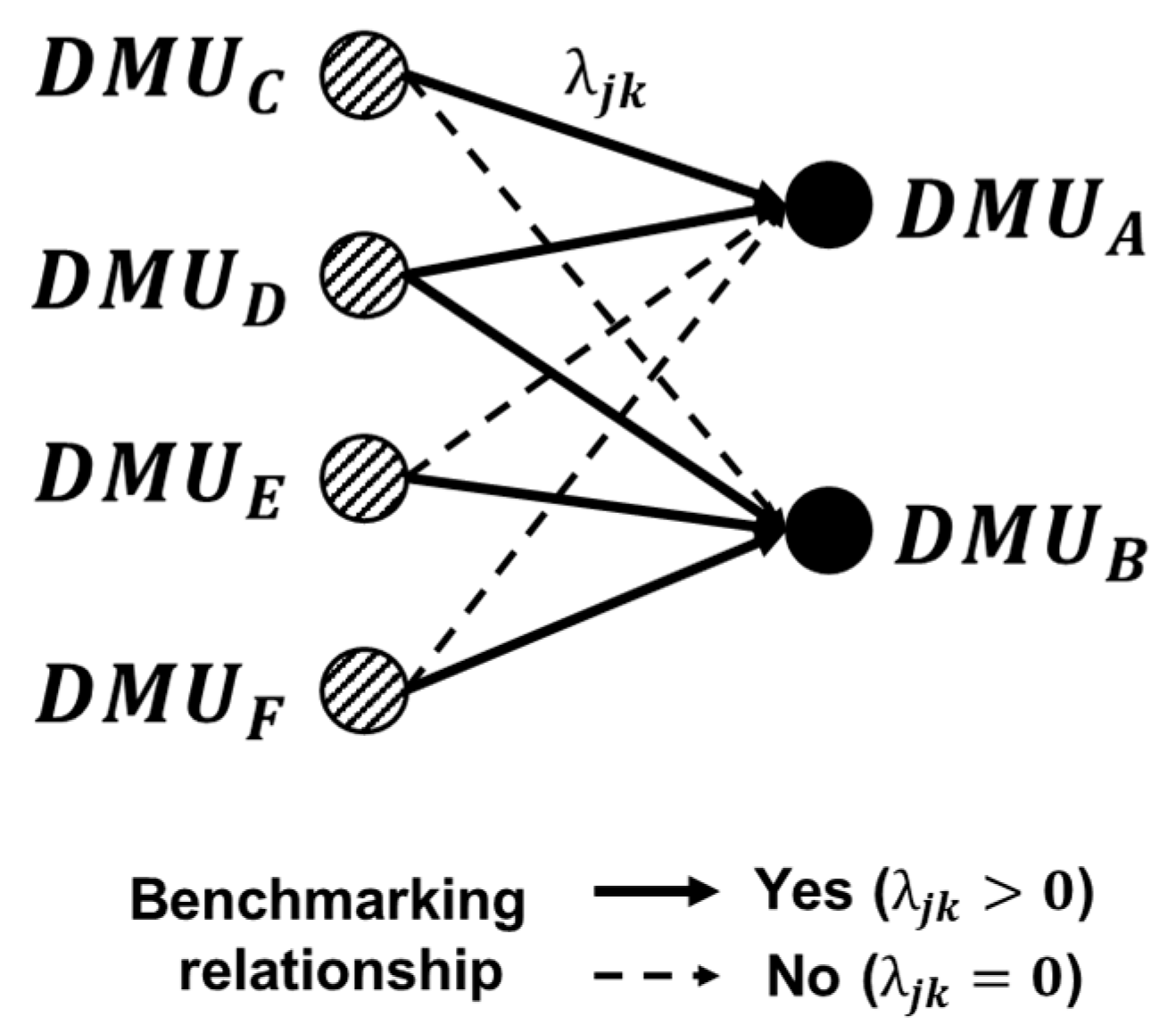
2.2. Network Representation for DEA
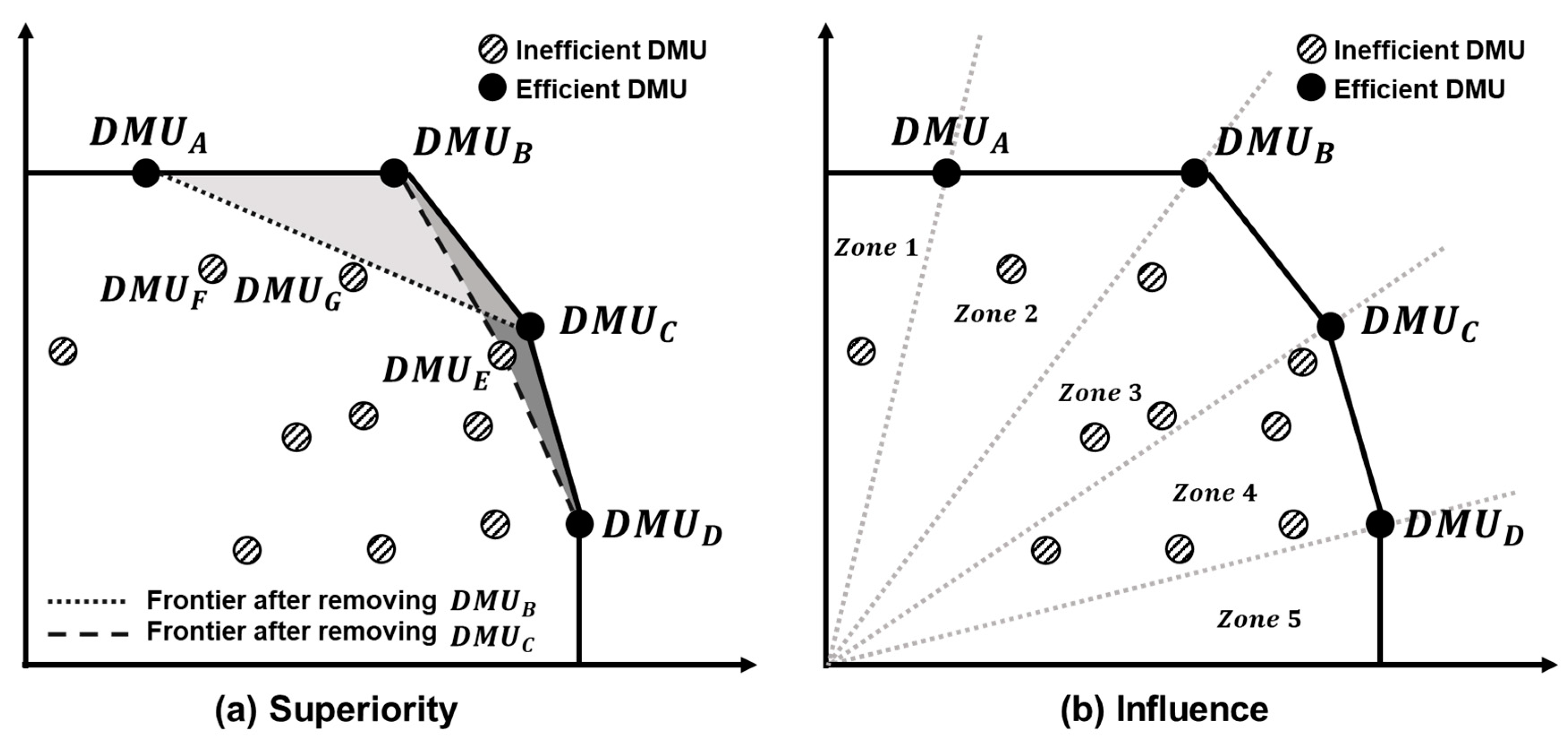
3. Dominance Value Using Centrality
4. Examples of the Dominance-Based Network Method
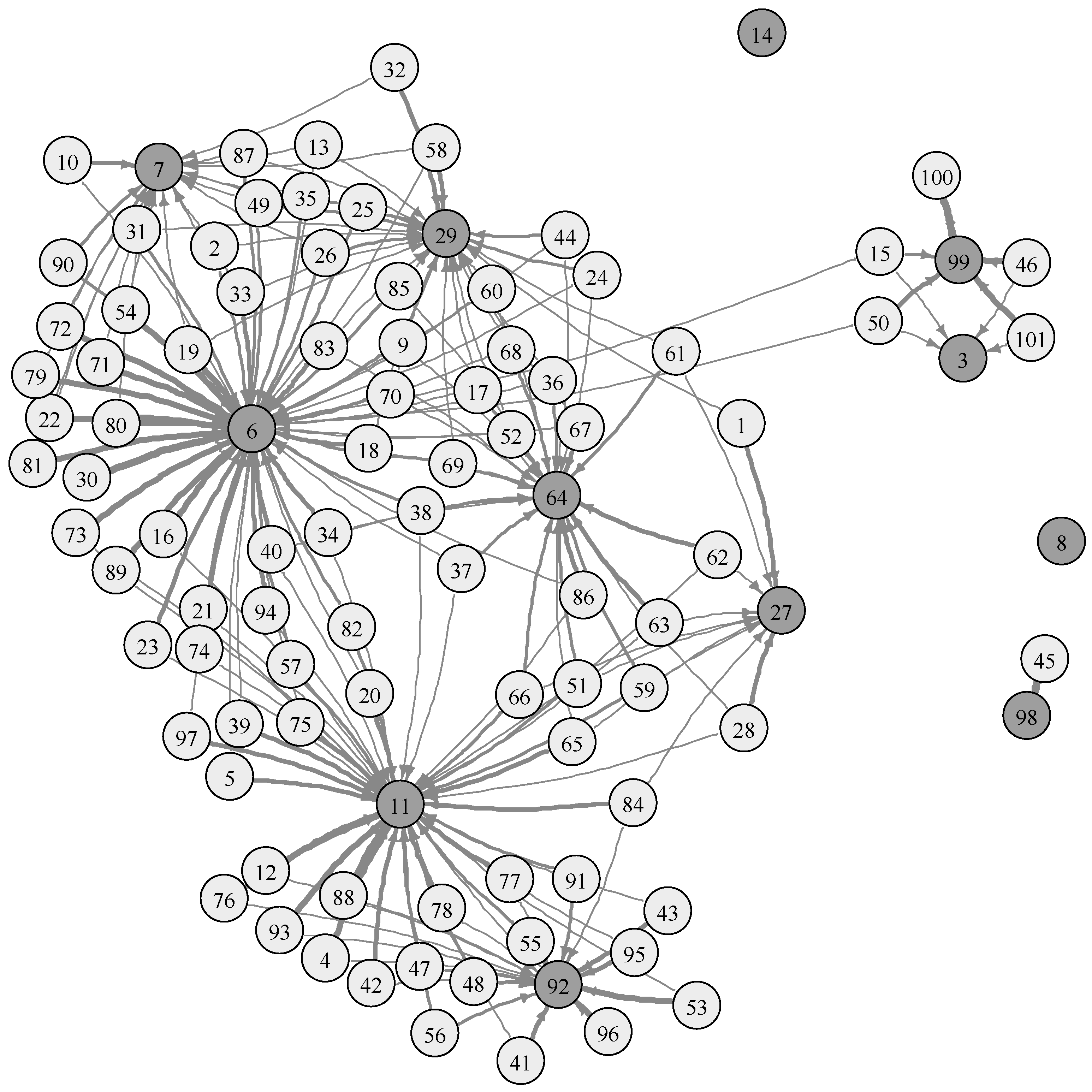
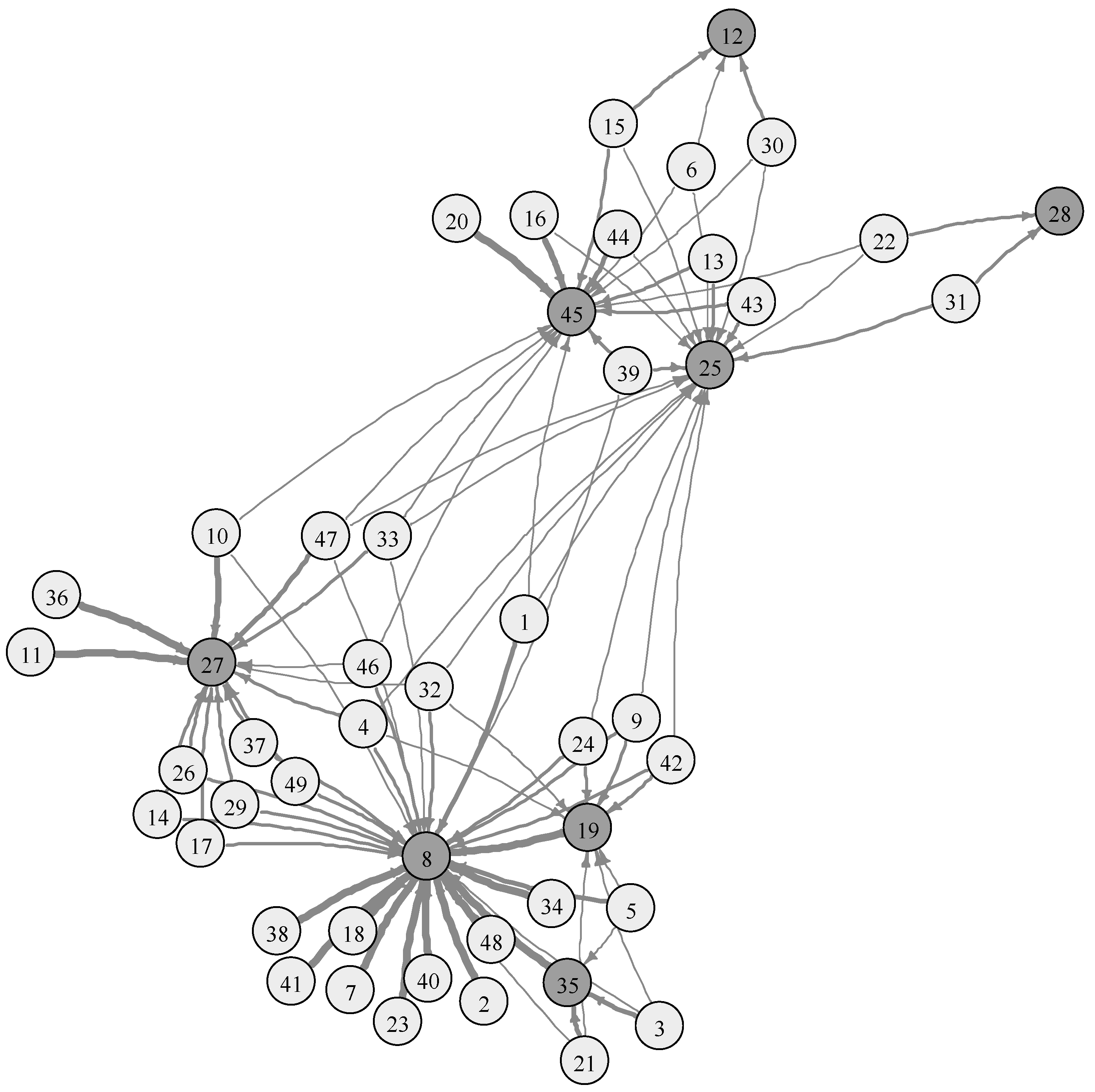
4.1. R&D Efficiency in SMEs
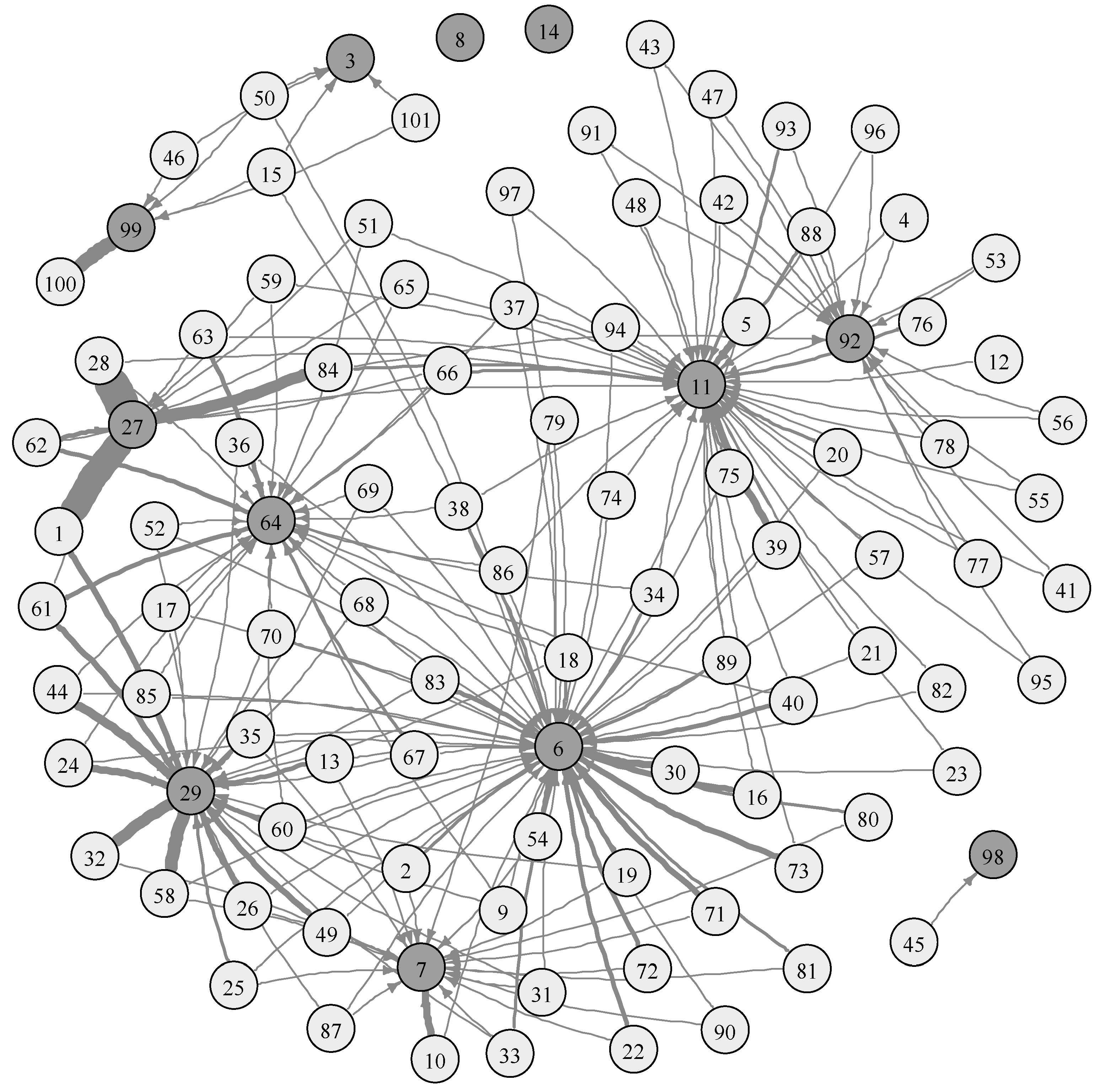
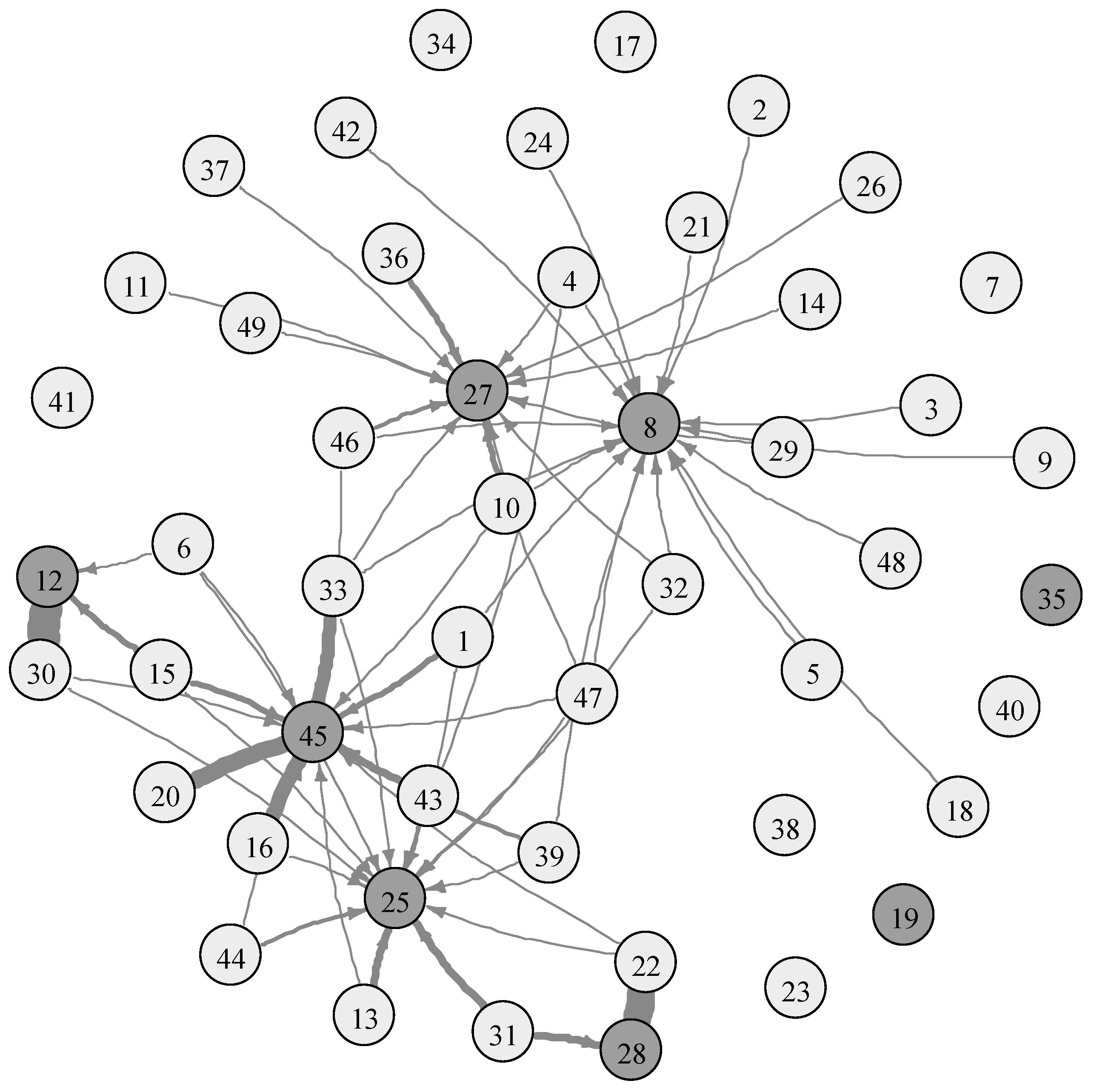
4.2. Efficiency of HEVs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witte, K.; Marques, R.C. Influential observations in frontier models, a robust non-oriented approach to the water sector. Ann. Oper. Res. 2010, 181, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Chen, B.; Xie, L.; Pan, H. Estimating energy consumption of transport modes in China using DEA. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4225–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Chen, K. Measuring the innovation production process: A cross-region empirical study of China’s high-tech innovations. Technovation 2010, 30, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Choi, G. Exploring data envelopment analysis for measuring collaborated innovation efficiency of small and medium-sized enterprises in Korea. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, P.; Marques, R.C. On the economic performance of the waste sector. A literature review. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 106, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Measuring eco-efficiency of agriculture in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, Z.; Liang, L. Using DEA-neural network approach to evaluate branch efficiency of a large Canadian bank. Expert Syst. Appl. 2006, 31, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrouznejad, A.; Yang, G.L. A survey and analysis of the first 40 years of scholarly literature in DEA: 1978–2016. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2018, 61, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Lu, L.Y.Y.; Lu, W.-M. Research fronts in data envelopment analysis. Omega 2016, 58, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldamak, A.; Zolfaghari, S. Review of efficiency ranking methods in data envelopment analysis. Measurement 2017, 106, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, N.; Friedman, L.; Sinuany-Stern, Z. Review of ranking methods in the data envelopment analysis context. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 140, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Sung, S.I. Integrated approach to construction of benchmarking network in DEA-based stepwise benchmark target selection. Sustainability 2016, 8, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, S.A.; Song, H.S.; Kim, Y.A.; Namn, S.H.; Kang, S.C. A method of stepwise benchmarking for inefficient DMUs based on the proximity-based target selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 11595–11604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.R.; Hollingsworth, K.; Inman, L. Assessing the rate of change in the enterprise database system market over time using DEA. In Proceedings of the Portland International Conference on Management of Engineering and Technology (PICMET), Portland, OR, USA, 29 July–2 August 2001; pp. 384–390. [Google Scholar]
- Po, R.-W.; Guh, Y.-Y.; Yang, M.-S. A new clustering approach using data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 199, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.H.F.; Hsuan Peng, H. Ranking of units on the DEA frontier with common weights. Comput. Oper. Res. 2008, 35, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, N.; Ruiz, J.L.; Sirvent, I. Common sets of weights as summaries of DEA profiles of weights: With an application to the ranking of professional tennis players. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 4882–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadad, Y.; Hanani, M.Z. Combining the AHP and DEA methodologies for selecting the best alternative. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2011, 9, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinuany-Stern, Z.; Mehrez, A.; Hadad, Y. An AHP/DEA methodology for ranking decision making units. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2000, 7, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.; Petersen, N.C. A Procedure for Ranking Efficient Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1993, 39, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Ranking efficient units in DEA. Omega 2004, 32, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahloo, G.R.; Hosseinzadeh Lotfi, F.; Shoja, N.; Tohidi, G.; Razavyan, S. Ranking using l1-norm in data envelopment analysis. Appl. Math. Comput. 2004, 153, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai Balf, F.; Zhiani Rezai, H.; Jahanshahloo, G.R.; Hosseinzadeh Lotfi, F. Ranking efficient DMUs using the Tchebycheff norm. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, T.R.; Silkman, R.H.; Hogan, A.J. Data Envelopment Analysis: Critique and Extensions. New Dir. Progr. Eval. 1986, 1986, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerafat Angiz, M.; Mustafa, A.; Kamali, M.J. Cross-ranking of Decision Making Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chu, J.; Yin, P.; Sun, J. DEA cross-efficiency evaluation considering undesirable output and ranking priority: A case study of eco-efficiency analysis of coal-fired power plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahloo, G.R.; Afzalinejad, M. A ranking method based on a full-inefficient frontier. Appl. Math. Model. 2006, 30, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H. The interval efficiency based on the optimistic and pessimistic points of view. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Chin, K.S.; Yang, J.B. Measuring the performances of decision-making units using geometric average efficiency. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2007, 58, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahloo, G.R.; Junior, H.V.; Lotfi, F.H.; Akbarian, D. A new DEA ranking system based on changing the reference set. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 181, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Deng, M. A cross-dependence based ranking system for efficient and inefficient units in DEA. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 9648–9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liang, L.; Yang, F.; Bi, G.B.; Yu, X.B. A new DEA-based method for fully ranking all decision-making units. Expert Syst. 2010, 27, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Luo, Y. DEA efficiency assessment using ideal and anti-ideal decision making units. Appl. Math. Comput. 2006, 173, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, U.; Pakkala, T.P.M. Ranking efficient DMUs based on single virtual inefficient DMU in DEA. OPSEARCH 2010, 47, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadikhah, M.; Farzipoor Saen, R. A new data envelopment analysis method for ranking decision making units: An application in industrial parks. Expert Syst. 2015, 32, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Yang, J.B. Measuring the performances of decision-making units using interval efficiencies. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2007, 198, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Wang, Y.M. Improved DEA models for measuring interval efficiencies of decision-making units. Measurement 2013, 46, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Lu, W.M.; Yang, C.; Chuang, M. A network-based approach for increasing discrimination in data envelopment analysis. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2009, 60, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Lu, W.M. DEA and ranking with the network-based approach: A case of R&D performance. Omega 2010, 38, 453–464. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.S.; Lu, W.M. Network-based method for ranking of efficient units in two-stage DEA models. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2012, 63, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, M.A.; Lozano, S.; Borrero, D.V.; Mármol, A.M. Ranking efficient DMUs using cooperative game theory. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 80, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, R.D.; Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W. Some Models for Estimating Technical and Scale Inefficiencies in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafarani, R.; Abbasi, M.A.; Liu, H. Social Media Mining: An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781139088510. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Cázares, C.; Bayona-Sáez, C.; García-Marco, T. You can’t manage right what you can’t measure well: Technological innovation efficiency. Res. Policy 2013, 42, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KOSIS (KOrean Statistical Information Service). Available online: http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1KI1556&conn_path=I2 (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Lim, D.J.; Jahromi, S.R.; Anderson, T.R.; Tudorie, A.A. Comparing technological advancement of hybrid electric vehicles (HEV) in different market segments. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2015, 97, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Inman, L.; Anderson, T. TFDEA: A New Approach for Technology Forecasting of New Product Development Targets. In Proceedings of the Portland International Conference on Management of Engineering and Technology (PICMET 04), Seoul, Korea, 1–4 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Akay, A.E.; Ertek, G.; Büyüközkan, G. Analyzing the solutions of DEA through information visualization and data mining techniques: SmartDEA framework. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 7763–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.B.; Marvel, J.H.; Roh, J.J. Three-stage performance modeling using DEA–BPNN for better practice benchmarking. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 71, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, N.; Ruiz, J.L.; Sirvent, I. Two-step benchmarking: Setting more realistically achievable targets in DEA. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 92, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiford, L.M.; Zhu, J. Context-dependent data envelopment analysis—Measuring attractiveness and progress. Omega 2003, 31, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Category | References | Descriptions | Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Super efficiency (SE) | Andersen and Petersen [21]; Chen [22]; Jahanshahloo et al. [23]; Rezai Balf et al. [24] | Drop a certain efficient DMU being evaluated from the reference set and evaluate efficiency | Distance-based superiority |
| Cross efficiency (CE) | Sexton et al. [25]; Zerafat Angiz et al. [26]; Liu et al. [27] | Efficiency of each DMU is compared one by one for all pairs and aggregated to derive the final efficiency | Distance-based superiority |
| Alternative frontier | Jahanshahloo and Afzalinejad [28]; Azizi [29]; Wang et al. [30] | Evaluate based on the least efficient frontier | Distance-based superiority |
| Efficiency change of Inefficient DMU | Jahanshahloo et al. [31]; Du et al. [33]; Chen and Deng [32] | Assess the efficiency change of inefficient DMUs that occurred by the exclusion of each efficient DMU | Distance-based superiority |
| Virtual DMU | Wang and Luo [34]; Shetty and Pakkala [35]; Izadikhah and Farzipoor Saen [36]; Wang and Yang [37]; Azizi and Wang [38] | Set a virtual DMU and compare the efficiency of DMUs with virtual DMU | Distance-based superiority |
| Benchmarking importance | Liu et al. [39]; Liu and Lu [40]; Liu and Lu [41] | Assess the benchmarking importance of efficient DMUs | Benchmarking importance-based influence |
| Average | 4.82 | 288.76 | 1989.54 | 2.20 |
| St.dev | 5.15 | 225.10 | 2257.34 | 1.34 |
| Influence | Superiority | Dominance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMU | Value | Rank | Value | Rank | Value | Rank |
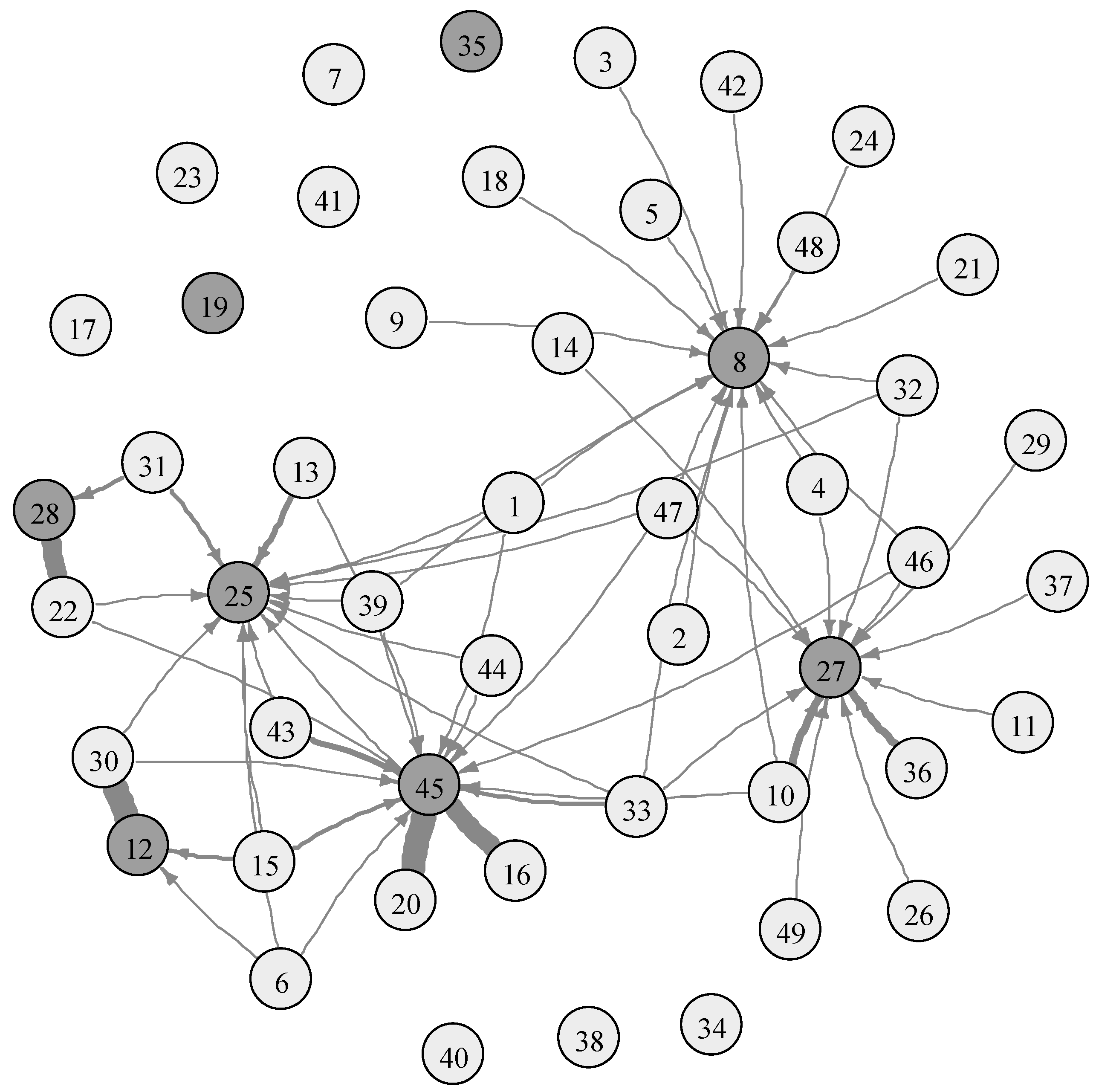
| 45 | 6.376 | 3 | 1.873 | 1 | 1.574 | 1 |
| 27 | 8.366 | 2 | 0.799 | 3 | 0.741 | 2 |
| 12 | 1.283 | 7 | 0.929 | 2 | 0.662 | 3 |
| 28 | 1.000 | 8 | 0.772 | 5 | 0.542 | 4 |
| 25 | 3.681 | 4 | 0.792 | 4 | 0.427 | 5 |
| 8 | 19.183 | 1 | 0.478 | 6 | 0.372 | 6 |
| 35 | 1.322 | 6 | 0.000 | 7 | 0.000 | 7 |
| 19 | 1.789 | 5 | 0.000 | 7 | 0.000 | 7 |
| Average | 40,762.71 | 12.53 | 34.63 | 39.63 |
| St.dev | 20,934.94 | 2.93 | 10.65 | 20.37 |
| Influence | Superiority | Dominance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMU | Value | Rank | Value | Rank | Value | Rank |
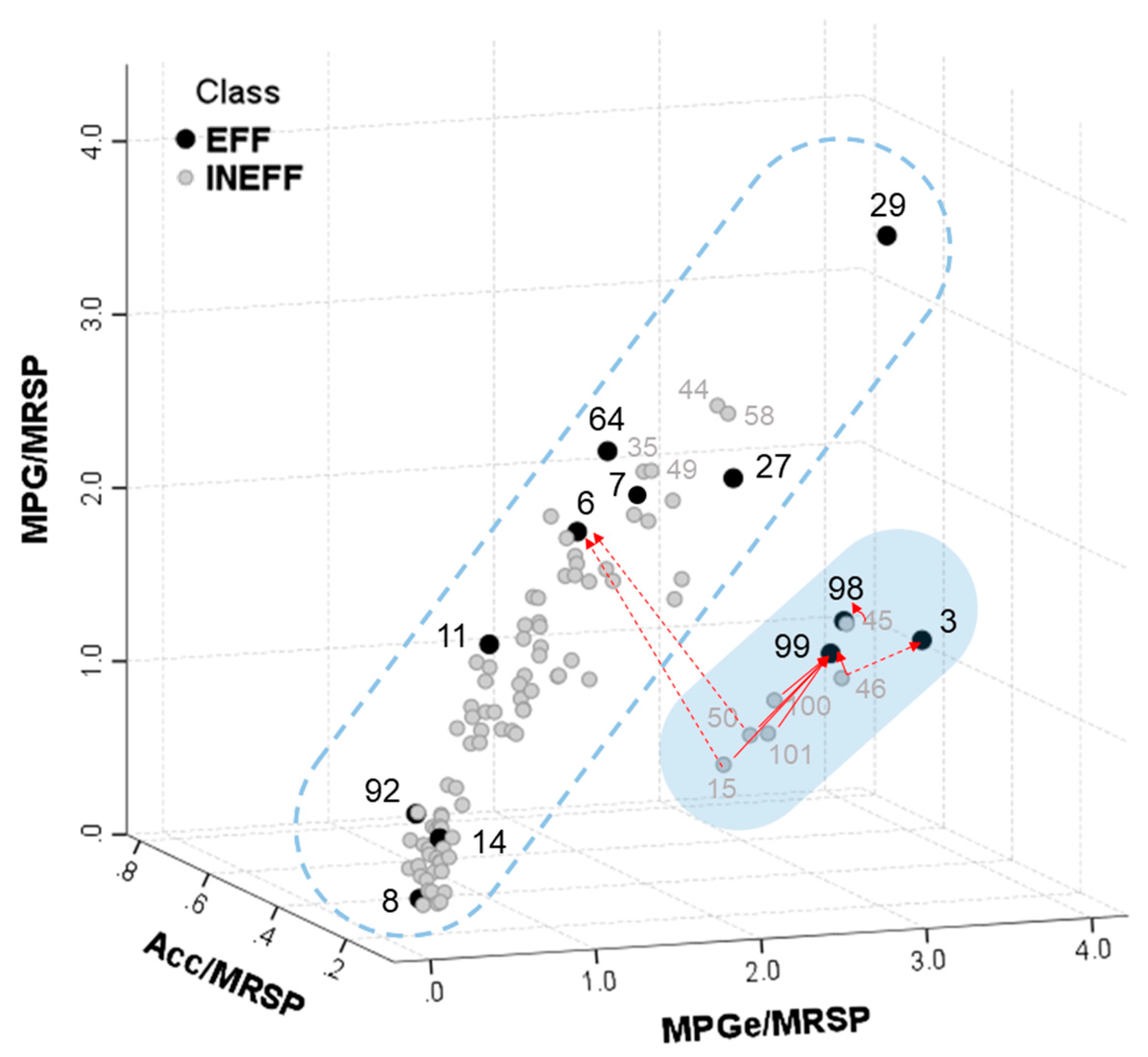
| 6 | 29.736 | 1 | 1.474 | 1 | 2.757 | 1 |
| 11 | 20.740 | 2 | 0.853 | 4 | 1.490 | 2 |
| 29 | 7.965 | 4 | 1.057 | 2 | 1.400 | 3 |
| 27 | 2.203 | 8 | 0.888 | 3 | 1.314 | 4 |
| 64 | 11.021 | 3 | 0.565 | 5 | 0.817 | 5 |
| 99 | 4.027 | 6 | 0.190 | 7 | 0.498 | 6 |
| 7 | 3.812 | 7 | 0.276 | 6 | 0.307 | 7 |
| 92 | 7.575 | 5 | 0.139 | 8 | 0.227 | 8 |
| 3 | 0.921 | 10 | 0.048 | 9 | 0.043 | 9 |
| 98 | 1.000 | 9 | 0.003 | 10 | 0.008 | 10 |
| 8 | 0.000 | 11 | 0.000 | 11 | 0.000 | 11 |
| 14 | 0.000 | 11 | 0.000 | 11 | 0.000 | 11 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Choi, G. A Dominance-Based Network Method for Ranking Efficient Decision-Making Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072059
Lee J, Choi G. A Dominance-Based Network Method for Ranking Efficient Decision-Making Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Sustainability. 2019; 11(7):2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jiyoung, and Gyunghyun Choi. 2019. "A Dominance-Based Network Method for Ranking Efficient Decision-Making Units in Data Envelopment Analysis" Sustainability 11, no. 7: 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072059
APA StyleLee, J., & Choi, G. (2019). A Dominance-Based Network Method for Ranking Efficient Decision-Making Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Sustainability, 11(7), 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072059





