Does Urbanization Improve Industrial Water Consumption Efficiency?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
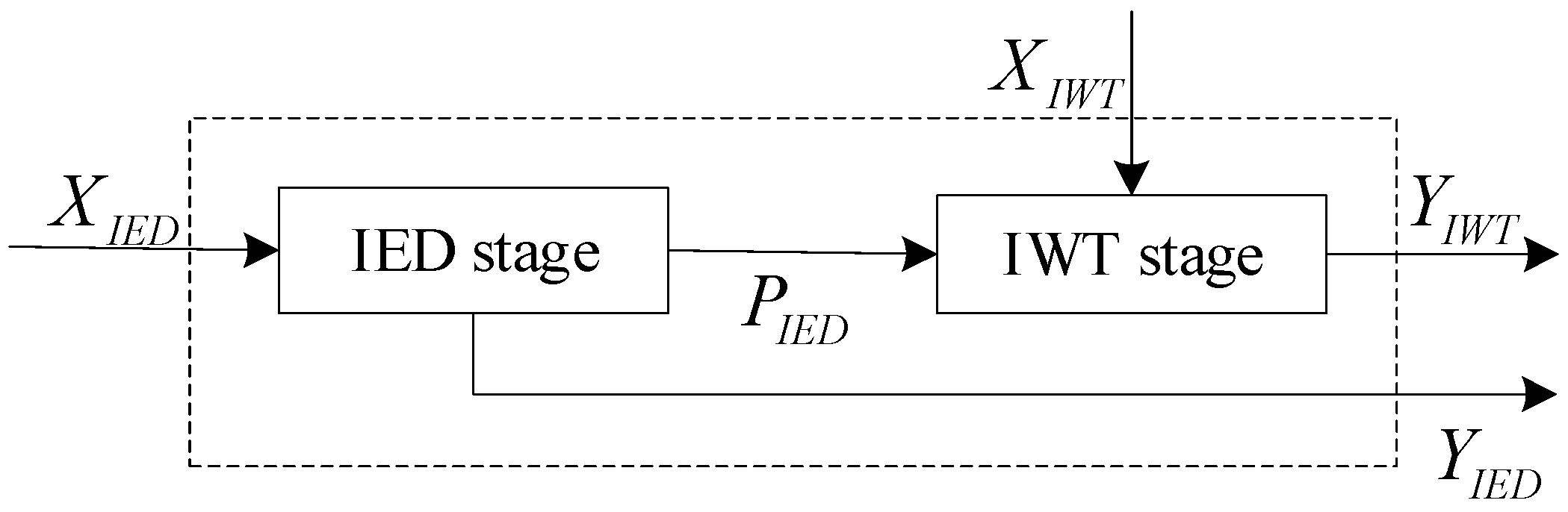
2.1. Two-Stage Efficiency Evaluation Model
- (1)
- If , the slack variables are equal to 0 in a given stage, and in the IED (or IWT) stage is efficient.
- (2)
- If , in the IED (or IWT) stage is inefficient.
- (3)
- If and only if and the slack variables are 0 in each stage, then is efficient.
2.2. Regression Analysis of Determinants
2.3. Variables and Data
3. Results and Discussion
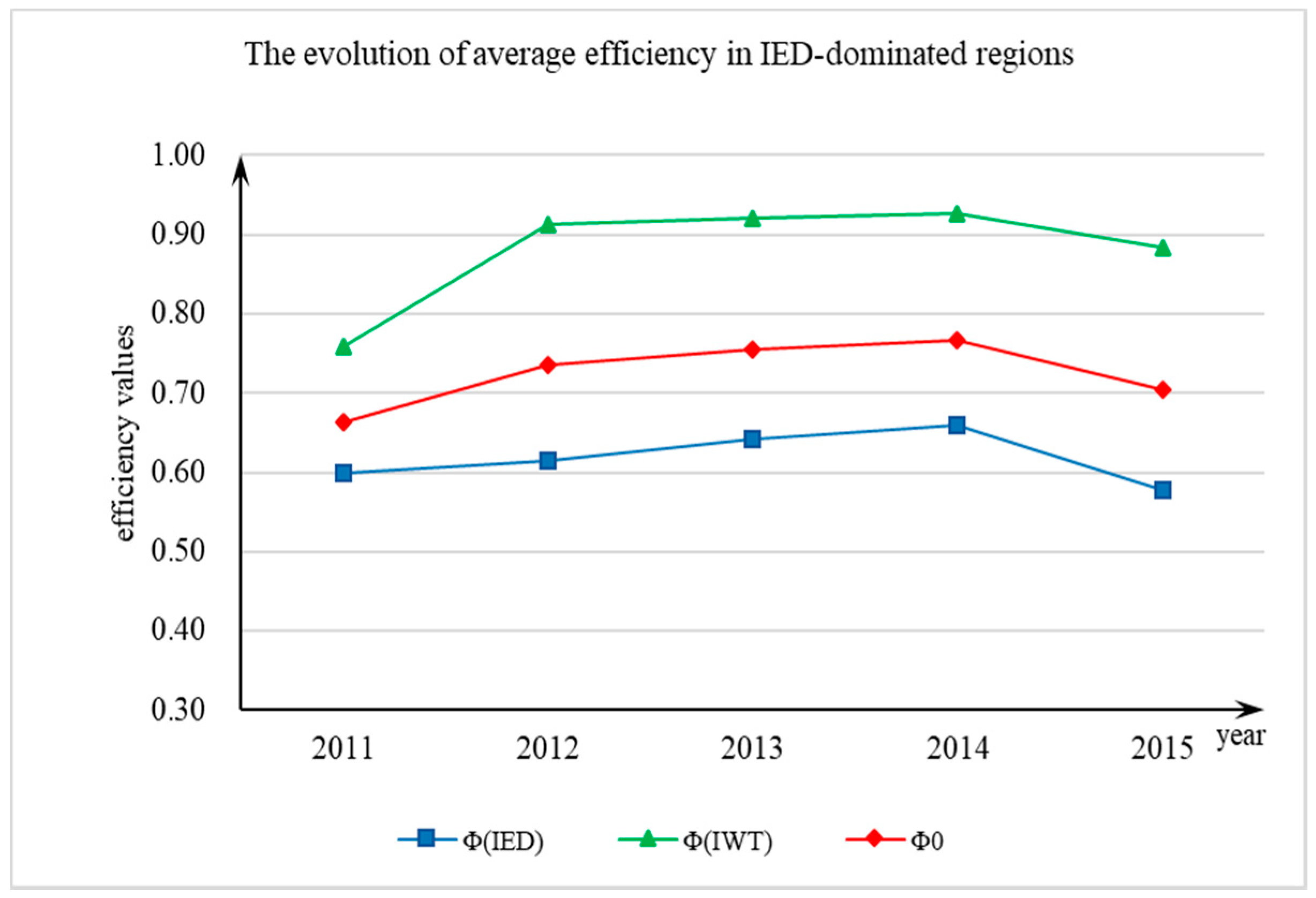
3.1. Measurement of the Efficiency of Industrial Water Consumption
3.2. Analysis of the Influential Factors
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistics PRC. China Statistical Yearbook (2011–2017); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011–2017.
- Guo, J.; Xu, Y.Z. The Coordinated Development between China’s Urbanization and Industrialization: Realistic Foundation and Level Measurement. Econ. Rev. 2016, 4, 39–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Marlow, R. Agriculture water consumption efficiency in the United States. In Proceedings of the U.S./China Water Resources Management Conference, Tucson, AZ, USA, 28 July 1999; pp. 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, B. Improving water use efficiency as part of integrated catchment management. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Grimble, R.J. Economic instruments for improving water use efficiency: Theory and practice. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, S.C.; Yeh, F.Y. Total-factor water efficiency of regions in China. Resour. Policy 2006, 31, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.W.; Yang, F. Resource and environment efficiency analysis of provinces in China: A DEA approach based on Shannon’s entropy. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Garrido, R.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Hernández-Sancho, F. Comparing the efficiency of wastewater treatment technologies through a DEA metafrontier model. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.Y.; Li, L.; Song, Y.N. Provincial water use efficiency measurement and factor analysis in China: Based on SBM-DEA model. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fare, R.; Grosskopf, S. Network dea. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2000, 34, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.W.; Yan, S.; Xu, H. Efficiency evaluation for regional urban water consumption and wastewater decontamination systems in China: A DEA approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.S.; Sun, C.Z.; Liu, F.C. Interprovincial two-stage water resource utilization efficiency under environmental constraint and spatial spillover effects in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Luo, R.; Yao, L.; Cao, S.; Wang, S.; Lev, B. Assessing integrated water consumption and wastewater treatment systems in China: A mixed network structure two-stage SBM DEA model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempenaar, A.; Westerink, J.; van Lierop, M.; Brinkhuijsen, M.; van den Brink, A. “Design makes you understand”-Mapping the contributions of designing to regional planning and development. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 149, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, R.; Pinilla, V.; Serrano, A. Is there an environmental Kuznets curve for water use? A panel smooth transition regression approach. Econ. Model. 2013, 31, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.S.; Pijanowski, B.C. Is there a relationship between water scarcity and water use efficiency in China? A national decadal assessment across spatial scales. Land Use Policy 2017, 69, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.L.; Wang, R.; Zeng, X.Q. Water resources utilization efficiency and influence factors under environmental restrictions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G. Estimation of eco-efficiency and its influencing factors in Guangdong province based on Super-SBM and panel regression models. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 86, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Z.; Shen, N. Energy efficiency and energy saving potential in China: A directional meta-frontier DEA approach. Sustainbility 2014, 6, 5476–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Folmer, H.; Bu, M.L. Interaction between output efficiency and environmental efficiency: Evidence from the textile industry in Jiangsu Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D. Do technological innovations promote urban green development?—A spatial econometric analysis of 105 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.L.; Geng, L.H.; Bian, J.Y. Driving Factor Analysis and the Spatial Regionalization on the Industrial Water Use Efficiency in China. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 2231–2239. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Shi, M.J. Urban transformation optimization model: How to evaluate industrial structure under water resource constraints? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 195, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, Ç. Efficiency and productivity (TFP) of the Turkish electricity distribution companies: An application of two-stage (DEA & Tobit) analysis. Energy Policy 2013, 63, 300–310. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, P.; Peter, U. Measuring the economic efficiency of airports: A Simar–Wilson methodology analysis. Transp. Res. Part E 2008, 44, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.C.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, Y.T. An analysis of the implications of China’s urbanization policy for economic growth and energy consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G. Transformation of water resource management: A case study of the South-to-North Water Diversion project. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Lovell, C.K.; Pasurka, C. Multilateral productivity comparisons when some outputs are undesirable: A nonparametric approach. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1989, 71, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, S.; Lovell, C.K.; Thijssen, G.J. Environmental efficiency with multiple environmentally detrimental variables; estimated with SFA and DEA. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 121, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A Slacks-Based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Bian, Y.W.; Xu, H. Water use efficiency and related pollutants’ abatement costs of regional industrial systems in China: A slacks-based measure approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 101, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Liang, L. Two-stage cooperation model with input freely distributed among the stages. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 205, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shi, Q.F. Two-stage DEA model with additional input in the second stage and part of intermediate products as final output. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 6570–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simar, L.; Wilson, P.W. Estimation and inference in two stage, semi-parametric models of productive efficiency. J. Econom. 2007, 136, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics PRC. China Environmental Statistics Yearbook (2011–2017); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011–2017.
- Cui, E.Q.; Ren, L.J.; Sun, H.Y. Evaluation of variations and affecting factors of eco-environmental quality during urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3958–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosskurth, J.; Rotmans, J. The Scene Model: Getting A Grip on Sustainable Development in Policy Making. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2005, 7, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T. A review of recent multi-region input–output models used for consumption-based emission and resource accounting. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 69, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.L.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Wang, W.J. The relationship between regional industrial organizing levels and ecological economic efficiency. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Bai, B.; Qiao, Q.; Kang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J. Study on eco-efficiency of industrial parks in China based on data envelopment analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Huang, Z.H.; Nie, P.Y. Industrial characteristics and consumption efficiency from a nexus perspective—Based on Anhui’s Empirical Statistics. Energy Policy 2018, 115, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Chu, F.; Ding, J.; Bi, G.; Liang, L. Carbon Emissions Abatement (CEA) allocation and compensation schemes based on DEA. Omega 2015, 53, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Indicator Types | Indicators | Variables and Units |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Investment | Industrial Development Investment (108 yuan) | |
| Industrial Labor | Industrial Employment Population (104) | |
| Industrial Water Consumption | Industrial Water Consumption (104 m3) | |
| Wastewater Discharge in the IED Stage | Initial Industrial Wastewater Discharge Amount (104 m3) | |
| Industrial Output | Industrial Economic Output (108 yuan) | |
| Government Investment | Wastewater Treatment Investment (108 yuan) | |
| Wastewater Treatment | Industrial Wastewater Treatment Amount (104 m3) |
| Influential Factors | Variable Names | Variable Meanings |
|---|---|---|
| Economic development | pdi | Per capita disposable income of urban residents (104 yuan) |
| Industrial structure | ins | Industrial development proportion (%) |
| iwp | Industrial water consumption proportion (%) | |
| Population growth | upd | Urban population density (100 people per square kilometer) |
| urp | Urban population (106) | |
| Spatial change | pba | Proportion of built-up areas (%) |
| Control variables | RD | R&D funds of industrial enterprises (108 yuan) |
| foi | Foreign investment (109 yuan) |
| Categories | Provinces |
|---|---|
| IED-dominated regions | Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Henan, Xinjiang, Gansu, Ningxia, Qinghai, Sichuan, Yunnan, Anhui, Hubei, Jiangxi, Hunan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Hainan |
| IWT-dominated regions | Liaoning, Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Heilongjiang, Chongqing, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong |
| IED-Dominated Regions | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Mongolia | 1.000 | 0.738 | 0.859 | 1.000 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.818 | 0.905 | 1.000 | 0.828 | 0.910 |
| Jilin | 0.637 | 0.707 | 0.671 | 0.680 | 0.910 | 0.787 | 1.000 | 0.774 | 0.880 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.646 | 0.767 | 0.704 |
| Anhui | 0.414 | 0.778 | 0.567 | 0.390 | 1.000 | 0.625 | 0.395 | 1.000 | 0.628 | 0.399 | 1.000 | 0.632 | 0.398 | 0.985 | 0.626 |
| Jiangxi | 0.440 | 0.716 | 0.561 | 0.458 | 1.000 | 0.677 | 0.458 | 0.908 | 0.645 | 0.459 | 1.000 | 0.678 | 0.445 | 0.893 | 0.631 |
| Henan | 1.000 | 0.707 | 0.841 | 1.000 | 0.780 | 0.883 | 0.935 | 0.766 | 0.846 | 1.000 | 0.767 | 0.876 | 0.770 | 0.778 | 0.774 |
| Hubei | 0.418 | 0.786 | 0.573 | 0.403 | 1.000 | 0.635 | 0.417 | 1.000 | 0.646 | 0.499 | 1.000 | 0.706 | 0.437 | 1.000 | 0.661 |
| Hunan | 0.439 | 0.740 | 0.570 | 0.440 | 1.000 | 0.664 | 0.489 | 0.998 | 0.699 | 0.554 | 1.000 | 0.744 | 0.448 | 1.000 | 0.669 |
| Guangxi | 0.486 | 0.818 | 0.630 | 0.507 | 1.000 | 0.712 | 0.484 | 1.000 | 0.696 | 0.459 | 0.993 | 0.675 | 0.452 | 1.000 | 0.672 |
| Hainan | 0.512 | 0.707 | 0.602 | 0.519 | 0.748 | 0.623 | 0.464 | 1.000 | 0.682 | 0.473 | 1.000 | 0.688 | 0.495 | 0.762 | 0.614 |
| Sichuan | 0.592 | 0.827 | 0.700 | 0.646 | 0.954 | 0.785 | 0.711 | 0.949 | 0.821 | 0.948 | 0.957 | 0.953 | 0.554 | 0.838 | 0.681 |
| Guizhou | 0.409 | 1.000 | 0.639 | 0.376 | 1.000 | 0.613 | 0.468 | 1.000 | 0.684 | 0.464 | 1.000 | 0.681 | 0.473 | 1.000 | 0.687 |
| Yunnan | 0.552 | 0.783 | 0.657 | 0.535 | 1.000 | 0.731 | 0.587 | 1.000 | 0.766 | 0.550 | 1.000 | 0.742 | 0.557 | 0.983 | 0.740 |
| Gansu | 0.451 | 0.710 | 0.566 | 0.478 | 0.776 | 0.609 | 0.545 | 0.780 | 0.652 | 0.496 | 0.755 | 0.612 | 0.470 | 0.760 | 0.597 |
| Qinghai | 0.803 | 0.716 | 0.758 | 1.000 | 0.911 | 0.955 | 0.937 | 1.000 | 0.968 | 0.983 | 1.000 | 0.992 | 0.793 | 1.000 | 0.890 |
| Ningxia | 0.687 | 0.707 | 0.697 | 0.661 | 0.762 | 0.710 | 0.657 | 0.780 | 0.716 | 0.609 | 0.756 | 0.678 | 0.655 | 0.765 | 0.708 |
| Xinjiang | 0.760 | 0.716 | 0.738 | 0.741 | 0.768 | 0.755 | 0.731 | 0.793 | 0.761 | 0.660 | 0.768 | 0.712 | 0.647 | 0.795 | 0.717 |
| Average | 0.600 | 0.760 | 0.664 | 0.615 | 0.912 | 0.735 | 0.642 | 0.922 | 0.756 | 0.660 | 0.926 | 0.767 | 0.577 | 0.885 | 0.705 |
| CV | 0.332 | 0.1 | 0.145 | 0.357 | 0.116 | 0.164 | 0.339 | 0.112 | 0.154 | 0.358 | 0.117 | 0.171 | 0.286 | 0.12 | 0.126 |
| IWT-Dominated Regions | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.972 | 0.885 | 0.927 | 0.964 | 0.973 | 0.969 | 0.967 | 0.843 | 0.903 | 0.979 | 0.962 | 0.970 | 0.908 | 0.969 | 0.938 |
| Tianjin | 0.991 | 0.947 | 0.969 | 0.998 | 0.957 | 0.977 | 0.963 | 0.934 | 0.948 | 0.954 | 0.895 | 0.924 | 0.985 | 0.963 | 0.974 |
| Hebei | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Shanxi | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.989 | 1.000 | 0.914 | 0.956 | 1.000 | 0.697 | 0.835 | 1.000 | 0.955 | 0.977 | 1.000 | 0.693 | 0.832 |
| Liaoning | 1.000 | 0.897 | 0.947 | 1.000 | 0.955 | 0.977 | 1.000 | 0.803 | 0.896 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.969 | 0.984 |
| Heilongjiang | 1.000 | 0.860 | 0.927 | 1.000 | 0.933 | 0.966 | 1.000 | 0.879 | 0.937 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.726 | 0.852 |
| Shanghai | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.996 | 0.998 | 0.994 | 0.813 | 0.899 | 0.996 | 0.684 | 0.826 | 0.985 | 0.720 | 0.842 |
| Jiangsu | 0.995 | 0.753 | 0.866 | 1.000 | 0.708 | 0.842 | 1.000 | 0.896 | 0.947 | 1.000 | 0.857 | 0.925 | 1.000 | 0.688 | 0.829 |
| Zhejiang | 1.000 | 0.682 | 0.826 | 1.000 | 0.715 | 0.845 | 1.000 | 0.681 | 0.825 | 1.000 | 0.695 | 0.834 | 1.000 | 0.687 | 0.829 |
| Fujian | 0.998 | 0.678 | 0.822 | 1.000 | 0.699 | 0.836 | 1.000 | 0.995 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 0.751 | 0.867 | 1.000 | 0.830 | 0.911 |
| Shandong | 0.999 | 0.715 | 0.845 | 1.000 | 0.695 | 0.834 | 1.000 | 0.694 | 0.833 | 1.000 | 0.725 | 0.851 | 1.000 | 0.854 | 0.924 |
| Guangdong | 0.999 | 0.973 | 0.986 | 0.995 | 0.760 | 0.869 | 0.993 | 0.768 | 0.873 | 0.997 | 0.807 | 0.897 | 0.999 | 0.902 | 0.949 |
| Chongqing | 0.997 | 0.948 | 0.972 | 1.000 | 0.831 | 0.912 | 1.000 | 0.707 | 0.841 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.954 | 0.976 |
| Shaanxi | 1.000 | 0.672 | 0.820 | 1.000 | 0.688 | 0.830 | 1.000 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.824 | 0.908 | 1.000 | 0.936 | 0.968 |
| Average | 0.996 | 0.856 | 0.921 | 0.997 | 0.845 | 0.915 | 0.994 | 0.836 | 0.910 | 0.995 | 0.868 | 0.927 | 0.991 | 0.849 | 0.915 |
| CV | 0.008 | 0.15 | 0.077 | 0.01 | 0.151 | 0.075 | 0.013 | 0.141 | 0.07 | 0.013 | 0.139 | 0.07 | 0.025 | 0.144 | 0.071 |
| Classifications | Indicators | IED-Dominated Regions | IWT-Dominated Regions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic development | pdi | −0.209 | −0.344 (***) | −0.088 (**) | 0.013 (***) | 0.159 (**) | 0.062 (**) |
| Industrial structure | ins | 0.03 (***) | 0.004 | 0.017 (*) | 0.001 (*) | −0.006 | −0.001 |
| iwp | −0.052 (***) | 0.018 (***) | −0.015 (**) | −0.008 (**) | 0.013 | 0.004 | |
| Population growth | upd | 0.045 | 0.015 | 0.024 | 0.009 (***) | 0.013 (*) | 0.005 (*) |
| urp | 0.010 | −0.007 | 0.002 | −0.011 (***) | 0.010 (**) | 0.003 (***) | |
| Spatial change | pba | −0.039 | −0.01 (***) | −0.010 (***) | 0.007 (*) | 0.018 (**) | 0.071 (*) |
| Control variables | R&D | 0.010 (*) | 0.011 (***) | 0.003 (***) | 0.002 (***) | 0.002 (**) | 0.003 (***) |
| foi | 0.016 (***) | −0.015 (*) | −0.011 (***) | −0.005 (**) | 0.008 (**) | 0.003 | |
| Cons. | 2.547 (*) | 2.169 (**) | 2.532 (*) | 1.147 | −0.288 (*) | 0.638 (**) | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Hou, R.; Wang, H. Does Urbanization Improve Industrial Water Consumption Efficiency? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061787
Liu B, Li Y, Hou R, Wang H. Does Urbanization Improve Industrial Water Consumption Efficiency? Sustainability. 2019; 11(6):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061787
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bingquan, Yongqing Li, Rui Hou, and Hui Wang. 2019. "Does Urbanization Improve Industrial Water Consumption Efficiency?" Sustainability 11, no. 6: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061787
APA StyleLiu, B., Li, Y., Hou, R., & Wang, H. (2019). Does Urbanization Improve Industrial Water Consumption Efficiency? Sustainability, 11(6), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061787




