Rural Tourism in Globalizing Beijing: Reproduction of the Mountainous Suburbs into a New Space of Leisure Consumption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Rise of Beijing’s Rural Tourism
2.1. Brief Review
2.2. Objectives and Current Economic Situation of Beijing’s Rural Sector
2.3. Role of Beijing Municipality: A Public-Led Transformation of the “Valley Economy”
3. Peasants’ Entrepreneurship in Rural Tourism
3.1. Boom of “Nongjiale”
3.2. Power Matrix of Rural Tourism Development
4. Survey Method and Materials Used
5. Results
5.1. Yanqi Valley: Spontaneous Market-Led Growth at Resourceful Sites
5.2. Miyun: Innovative Measures at Inferior Sites for Survival
6. Discussion
6.1. Widening the Rural–Urban Gap and Inter-Villlage Variance in the Globalization of Beijing
6.2. The More Balanced Framwork to Address the Rural–Urban and Inter-Village Inequality Issue
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beijing Municipal Commission of Rural Affairs. Beijing Rural Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Beijing Municipality. The Plan for Beijing’s Functional Zones. Available online: http://china.caixin.com/2012-09-18/100439011.html (accessed on 31 August 2018).
- Beijing Municipality. The Plan for the Integrative Development of Beijing’s Mountain Area (2006–2020). Available online: http://ghgtw.beijing.gov.cn/art/2009/8/6/art_4105_463631.html (accessed on 31 August 2018).
- Beijing Municipal Administration of Tourism. Beijing Tourism Yearbook; Beijing Tourism Bureau Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- He, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q. Rural Tourism in China: A Case Study of Nongjiale in the Chengdu Metropolitan Area. Mt. Res. Dev. 2004, 24, 260–262. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C. Delights in Farm Guesthouses: Nongjiale Tourism, Rural Development and the Regime of Leisure-Pleasure in Post-Mao China. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, S.; Miller, M. Power and Tourism: A Foucauldian Observation. Ann. Tourism Res. 2000, 27, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing Municipal Agricultural Committee. The Development Mode of Beijing’s ‘Valley Economy’; Official Paper of the 2011 Working Conference of Beijing Municipal Agricultural Committee; Beijing Municipal Agricultural Committee: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Gill, A.; Williams, P. Mindful deviation in creating a governance path towards sustainability in resort destinations. Tourism Geogr. 2014, 16, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacher, R.; Nepal, S. Dependency and development in northern Thailand. Ann. Tourism Res. 2010, 37, 947–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.; Hall, D.; Morag, M. New Directions in Rural Tourism; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley, D. Rural Tourism: A case of lifestyle-led opportunities. Aust. Geogr. 2003, 34, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.; Murphy, A. Regional Tourism and its Economic Development Links for Small Communities. In The Future of Australia’s Country Towns; Rogers, M., Collins, Y., Eds.; Centre for Sustainable Regional Communities, La Trobe University: Bendigo, Australia, 2001; p. 162. [Google Scholar]
- Kneafsey, M. Rural cultural economy: Tourism and social relations. Ann. Tourism Res. 2001, 28, 762–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waitt, G. Selling paradise and adventure: Representations of landscape in the tourist advertising of Australia. Aust. Geogr. Stud. 1997, 35, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L. Culture, economy, policy: Trends and developments. Geoforum 2000, 31, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; O’Connor, J.; Cohen, S. Local music policies within a global music industry: Cultural quarters in Manchester and Sheffield. Geoforum 2000, 31, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, E. Tourism Micro-Clusters. Tourism Econ. 2003, 9, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkach, D.; King, B. Strengthening Community-Based Tourism in a new resource-based island nation: Why and how? Tourism Manag. 2015, 48, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Filieri, R. Resident-tourist value co-creation: The role of residents’ perceived tourism impacts and life satisfaction. Tourism Manag. 2017, 61, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, T.; Zhou, Z. Community, governments and external capitals in China’s rural cultural tourism: A comparative study of two adjacent villages. Tourism Manag. 2007, 28, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinhuanet. Building up the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.xinhuanet.com/2018-03/15/c_1122538836.htm (accessed on 31 January 2019).
- Chen, S. Reform History of Beijing’s Rural Collective Property System: 1992–2013; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing Statistical Yearbook; Beijing Area Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Beijing Municipal Commission of Tourism Development. A Brief Review of 2014 Beijing Tourism Industry; Beijing Municipal Commission of Tourism Development: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Beijing Municipal Commission of Tourism Development. The Statistical Report on Tourism Industry of Beijing’s 16 Districts; Beijing Municipal Commission of Tourism Development: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Beijing Municipal Commission of Tourism Development. The Review of Beijing’s 2013 Tourism Industry and the Prediction for Trends of 2014. Official Paper of the 2014 Working Conference of Beijing’s Tourism Development; Beijing Municipal Commission of Tourism Development: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Xinhuanet. Guarding the Capital City’s Clean Water and Green Mountain. Available online: http://www.xinhuanet.com/politics/2018-11/01/c_1123648358.htm (accessed on 11 September 2018).
- Wang, B.; Luo, Z.; Hao, S. A study on the current situation of the development of rural tourism in Beijing. Tourism Trib. 2006, 21, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. A survey and analysis of Beijing’s rural tourism demands. J. Wenzhou Vocat. Tech. Coll. 2011, 11, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, M.; Porter, M.; Stern, S. Clusters and entrepreneurship. J. Econ. Geogr. 2010, 10, 495–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing Miyun Bureau of Statistics. Beijing Miyun Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Lin, G. Developing China: Land, Politics and Social Conditions; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, P. Who owns China’s land? Policies, property rights and deliberate institutional ambiguity. China Quart. 2001, 66, 394–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C. Policy and praxis of land acquisition in China. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, A.; Coles, T. Tourism, Power and Space; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Mentougou Bureau of Statistics. Beijing Mentougou Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wong, T.-C. Exploring sustainable tourism development in mountainous Guizhou Province, China. J. Hosp. Manag. Tourism 2015, 6, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, J. A Landscape of Travel: The Work of Tourism in Rural Ethnic China; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Chan, E.; Song, H. Social capital and entrepreneurial mobility in early-stage tourism development: A case from rural China. Tourism Manag. 2017, 63, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ryan, C.; Cave, J. Chinese rural tourism development: Transition in the case of Qiyunshan, Anhui—2008–2015. Tourism Manag. 2016, 55, 240–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Exploring community tourism in China: The case of Nanshan cultural tourism zone. J. Sustain. Tour. 2004, 12, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
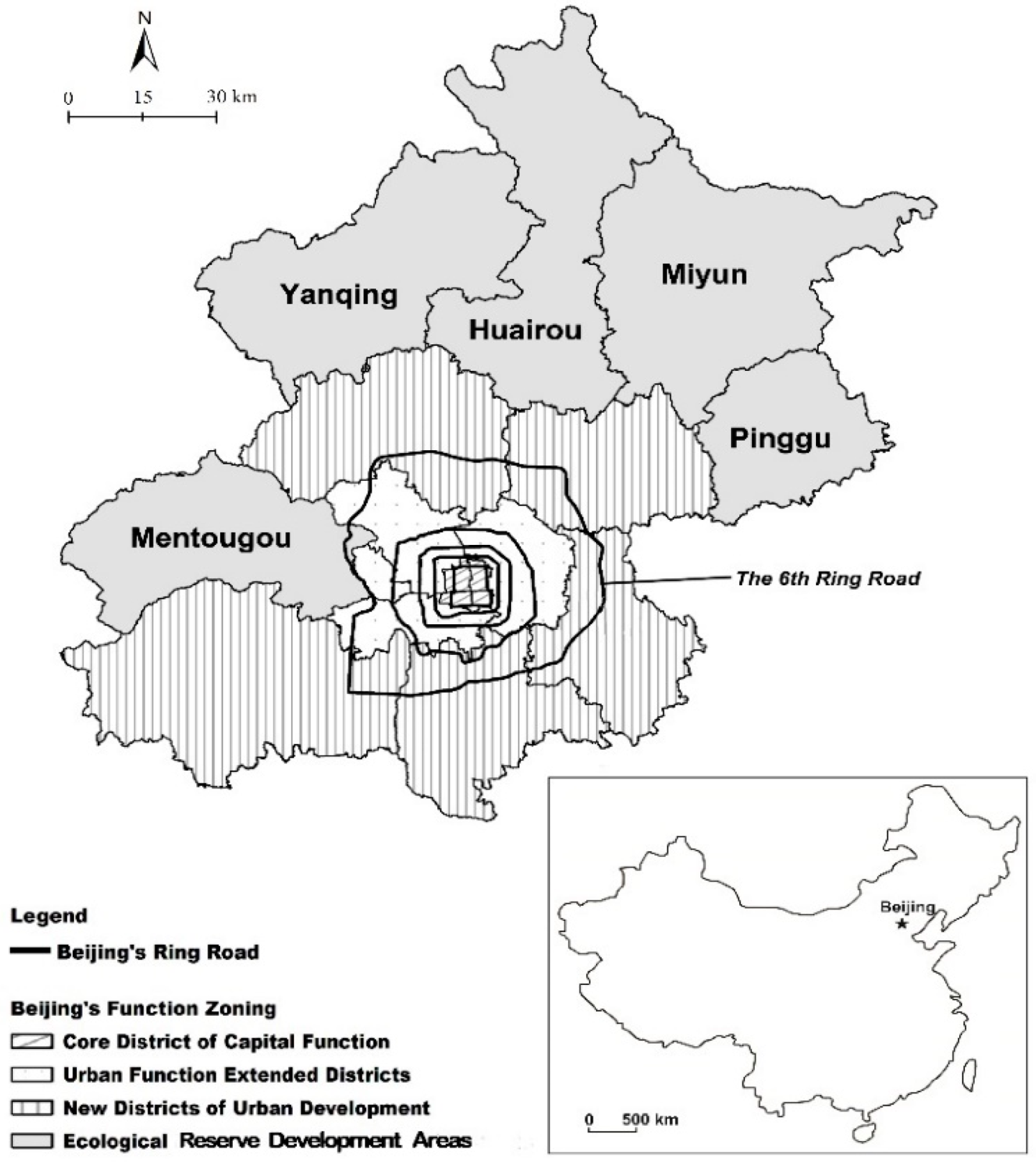
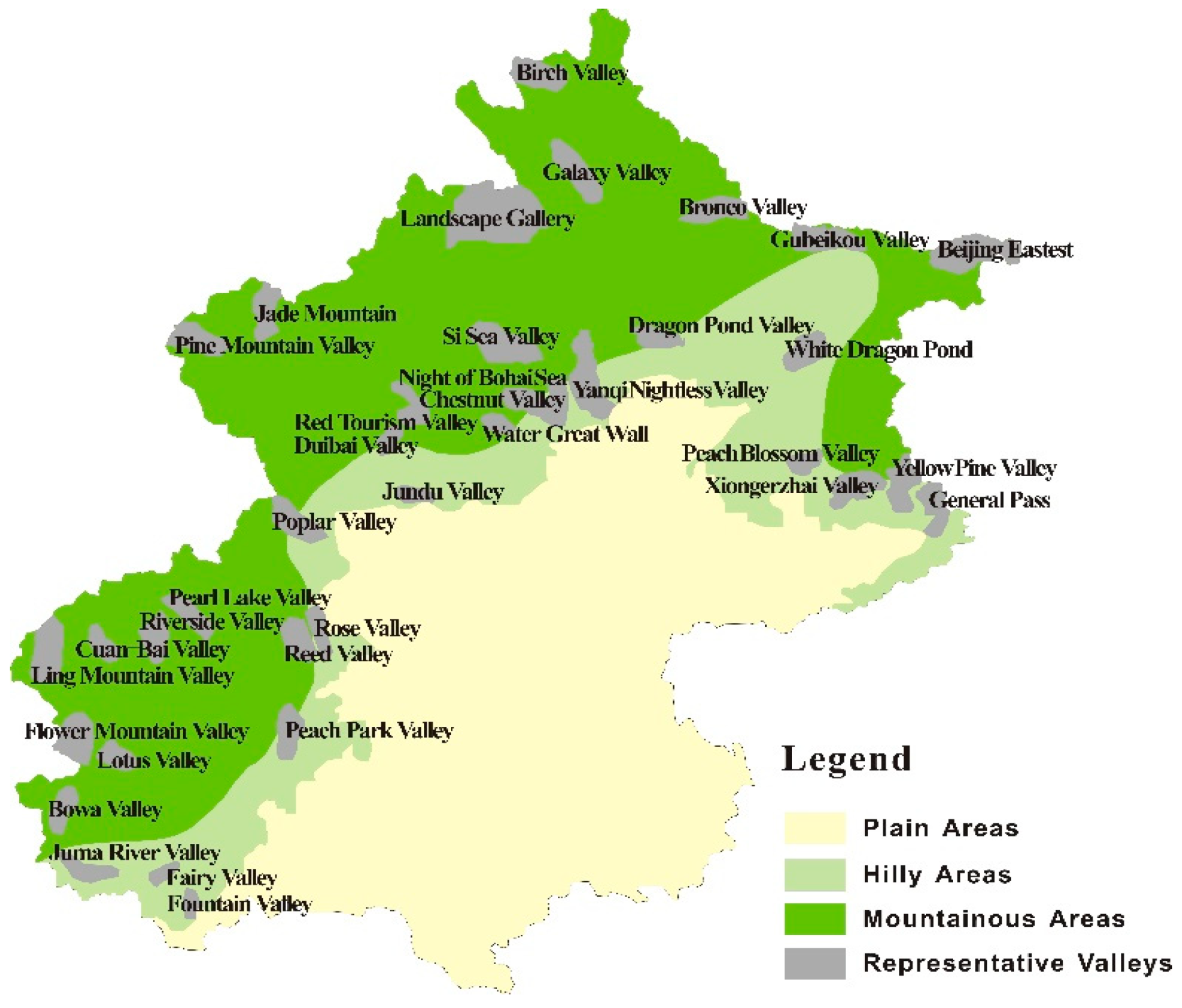

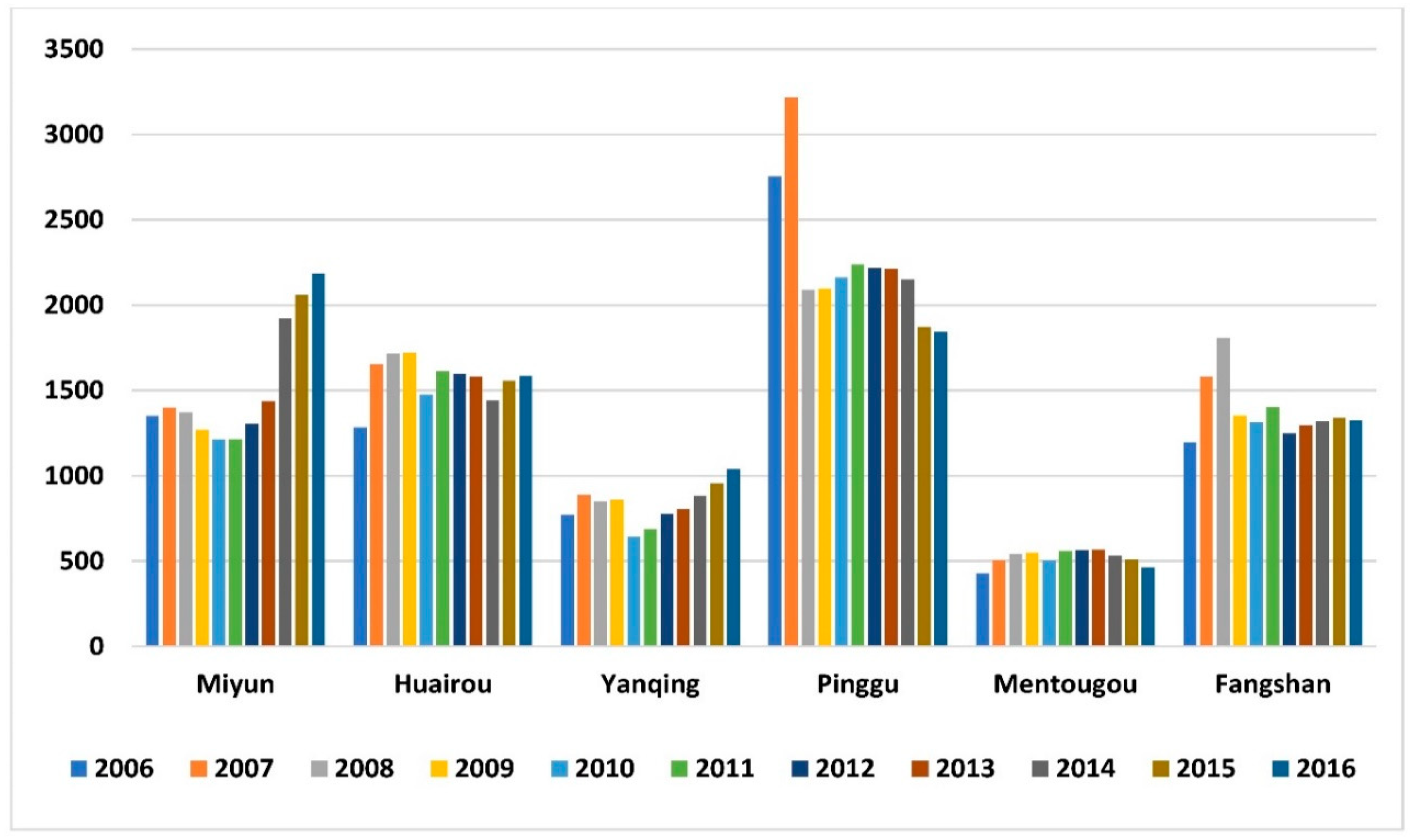





| Year | Rural Revenue | Year | Rural Revenue | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (billion RMB) | Composition | Total (billion RMB) | Composition | ||||||
| Collective % | Household % | Company * % | Collective % | Household % | Company * % | ||||
| 1983 | 5.1 | 87.6 | 12.4 | - | 1997 | 92.3 | 68.9 | 31.1 | - |
| 1984 | 7.0 | 84.9 | 15.1 | - | 1998 | 101.1 | 63.3 | 36.7 | - |
| 1985 | 8.8 | 84.0 | 16.0 | - | 1999 | 111.9 | 60.3 | 39.7 | - |
| 1986 | 9.9 | 84.5 | 15.5 | - | 2000 | 128.7 | 57.4 | 42.6 | - |
| 1987 | 12.4 | 84.1 | 15.9 | - | 2001 | 149.0 | 55.6 | 44.4 | - |
| 1988 | 17.9 | 82.4 | 17.6 | - | 2002 | 172.2 | 49.5 | 41.8 | 8.6 |
| 1989 | 21.9 | 81.9 | 18.1 | - | 2003 | 203.8 | 46.9 | 40.9 | 11.2 |
| 1990 | 25.6 | 81.3 | 18.7 | - | 2004 | 245.8 | 43.2 | 38.7 | 18.1 |
| 1991 | 30.4 | 67.7 | 32.2 | - | 2005 | 280.7 | 40.3 | 38.2 | 21.5 |
| 1992 | 38.6 | 69.7 | 30.3 | - | 2006 | 287.7 | 39.2 | 34.2 | 26.7 |
| 1993 | 61.4 | 72.6 | 27.4 | - | 2007 | 320.9 | 33.9 | 33.4 | 32.7 |
| 1994 | 103.5 | 72.7 | 27.3 | - | 2008 | 342.4 | 33.3 | 34.0 | 32.7 |
| 1995 | 71.3 | 81.6 | 18.4 | - | 2009 | 379.8 | 32.8 | 32.9 | 34.3 |
| 1996 | 82.7 | 71.7 | 28.3 | - | 2010 | 417.4 | 30.5 | 31.4 | 38.1 |
| Development Stages | Government Actions Taken | Socio-Economic Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Spontaneous initiatives (1980s–2002) |
|
|
| Regulatory measures (2003–2005) |
|
|
| Infrastructural improvement (2006–2012) |
|
|
| Reducing disparity between city and countryside (2013 until now) |
|
|
| Gender | Rural Hosts | City Guests |
|---|---|---|
| Male/Female | 44.4/55.6 | 47.1/52.9 |
| Age group (years) | % | % |
| Below 20 | 1.7 | 15.2 |
| 21–30 | 16.3 | 34.7 |
| 31–40 | 18.5 | 25.4 |
| 41–50 | 46.1 | 14.9 |
| Above 50 | 17.4 | 9.8 |
| Total | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Educational level | % | % |
| University and post-graduate | 10.7 | 79.5 |
| Senior high/vocational school | 54.5 | 11.4 |
| Junior high school | 30.3 | 9.0 |
| Elementary school and below | 4.5 | - |
| Total | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Employment type | % | % |
| Public sector | 0.0 | 19.1 |
| SOE or COE | 0.0 | 3.3 |
| Foreign capital/joint venture | 0.0 | 21.9 |
| Private enterprise | 16.3 | 35.3 |
| Family business | 83.8 | 0.0 |
| Young students | 0.0 | 20.5 |
| Total | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Disposable Rural Income per capita (yuan) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | |
| Villages in Cuan-Bai Valley Economy | |||
| • Cuandixia | 8581 | 14,012 | 29,178 |
| • Huanglingxi | 5802 | 7541 | 11,238 |
| • Shuangshitou | 4405 | 7180 | 10,649 |
| • Baiyucun | 4531 | 7703 | 11,938 |
| Average of Zhaitang Town, Mentougou District | 5086 | 7694 | 11,145 |
| Average of Rural Areas in Mentougou District | 6948 | 9982 | 14,582 |
| Average of Rural Beijing | 7860 | 13,262 | 20,569 |
| Year | Disposable Income per capita (yuan) | Urban–Rural Ratio | Year | Disposable Income per capita (yuan) | Urban–Rural Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| 1978 | 365 | 225 | 1.6 | 1998 | 8472 | 4029 | 2.1 | |
| 1979 | 415 | 250 | 1.7 | 1999 | 9183 | 4316 | 2.1 | |
| 1980 | 501 | 308 | 1.6 | 2000 | 10350 | 4687 | 2.2 | |
| 1981 | 514 | 361 | 1.4 | 2001 | 11578 | 5274 | 2.2 | |
| 1982 | 561 | 430 | 1.3 | 2002 | 12464 | 5880 | 2.1 | |
| 1983 | 591 | 520 | 1.1 | 2003 | 13883 | 6496 | 2.1 | |
| 1984 | 694 | 664 | 1.0 | 2004 | 15638 | 7172 | 2.2 | |
| 1985 | 908 | 775 | 1.2 | 2005 | 17653 | 7860 | 2.2 | |
| 1986 | 1068 | 823 | 1.3 | 2006 | 19978 | 8620 | 2.3 | |
| 1987 | 1182 | 916 | 1.3 | 2007 | 21989 | 9559 | 2.3 | |
| 1988 | 1437 | 1063 | 1.4 | 2008 | 24725 | 10,747 | 2.3 | |
| 1989 | 1597 | 1231 | 1.3 | 2009 | 26738 | 11,986 | 2.2 | |
| 1990 | 1787 | 1297 | 1.4 | 2010 | 29073 | 13,262 | 2.2 | |
| 1991 | 2040 | 1422 | 1.4 | 2011 | 32903 | 14,736 | 2.2 | |
| 1992 | 2364 | 1569 | 1.5 | 2012 | 36469 | 16,476 | 2.2 | |
| 1993 | 3296 | 1855 | 1.8 | 2013 | 40321 | 18,337 | 2.2 | |
| 1994 | 4731 | 2422 | 2.0 | 2014 | 43910 | 20,226 | 2.2 | |
| 1995 | 5868 | 3208 | 1.8 | 2015 | 52859 | 20,569 | 2.6 | |
| 1996 | 6886 | 3563 | 1.9 | 2016 | 57275 | 22,310 | 2.6 | |
| 1997 | 7813 | 3762 | 2.1 | 2017 | 62406 | 24,240 | 2.6 | |
| Functional Zones | Disposable Income per capita (yuan) | Consumption Expenditure per capita (yuan) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| 2005 | 2016 | 2005 | 2016 | 2005 | 2016 | 2005 | 2016 | |
| Urban function extended districts (inner suburbs) | ||||||||
| Chaoyang | 17,506 | 60,056 | 11,085 | - | 13,257 | 40,034 | 8017 | - |
| Fengtai | 15,795 | 51,173 | 8995 | - | 11,988 | 37,831 | 6848 | - |
| Haidian | 18,479 | 67,022 | 9987 | - | 12,942 | 46,630 | 8069 | - |
| New districts of urban development (outer suburbs) | ||||||||
| Fangshan | 15,175 | 39,486 | 7205 | 20,849 | 11,648 | 25,105 | 5204 | 15,470 |
| Tongzhou | 15,603 | 40,845 | 7661 | 23,538 | 11,077 | 29,238 | 4566 | 17,098 |
| Shunyi | 16,167 | 36,448 | 7459 | 24,649 | 10,208 | 23,810 | 5450 | 15,245 |
| Changping | 15,684 | 42149 | 7416 | 21,871 | 10,849 | 29,892 | 6735 | 18,949 |
| Daxing | 15,179 | 43932 | 7405 | 19,555 | 10,107 | 28,166 | 4426 | 17,389 |
| Ecological reserve development areas (mountainous areas) | ||||||||
| Mentougou | 16,006 | 45,872 | 7556 | 21,861 | 11,975 | 32,977 | 5532 | 20,271 |
| Huairou | 15,661 | 36,013 | 7201 | 21,620 | 10,549 | 23,633 | 4502 | 17,195 |
| Pinggu | 15,050 | 38,080 | 7336 | 21,866 | 10,478 | 24,539 | 4231 | 15,755 |
| Miyun | 15,106 | 36,631 | 7203 | 20,798 | 10,175 | 23,020 | 4716 | 15,300 |
| Yanqing | 15,596 | 38,442 | 6985 | 19,588 | 10,384 | 24,809 | 4383 | 14,500 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Wong, T.-C. Rural Tourism in Globalizing Beijing: Reproduction of the Mountainous Suburbs into a New Space of Leisure Consumption. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061719
Liu R, Wong T-C. Rural Tourism in Globalizing Beijing: Reproduction of the Mountainous Suburbs into a New Space of Leisure Consumption. Sustainability. 2019; 11(6):1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061719
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ran, and Tai-Chee Wong. 2019. "Rural Tourism in Globalizing Beijing: Reproduction of the Mountainous Suburbs into a New Space of Leisure Consumption" Sustainability 11, no. 6: 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061719
APA StyleLiu, R., & Wong, T.-C. (2019). Rural Tourism in Globalizing Beijing: Reproduction of the Mountainous Suburbs into a New Space of Leisure Consumption. Sustainability, 11(6), 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061719





