Emerging Location-Based Service Data on Perceiving and Measuring Multifunctionality of Rural Space: A Study of Suzhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
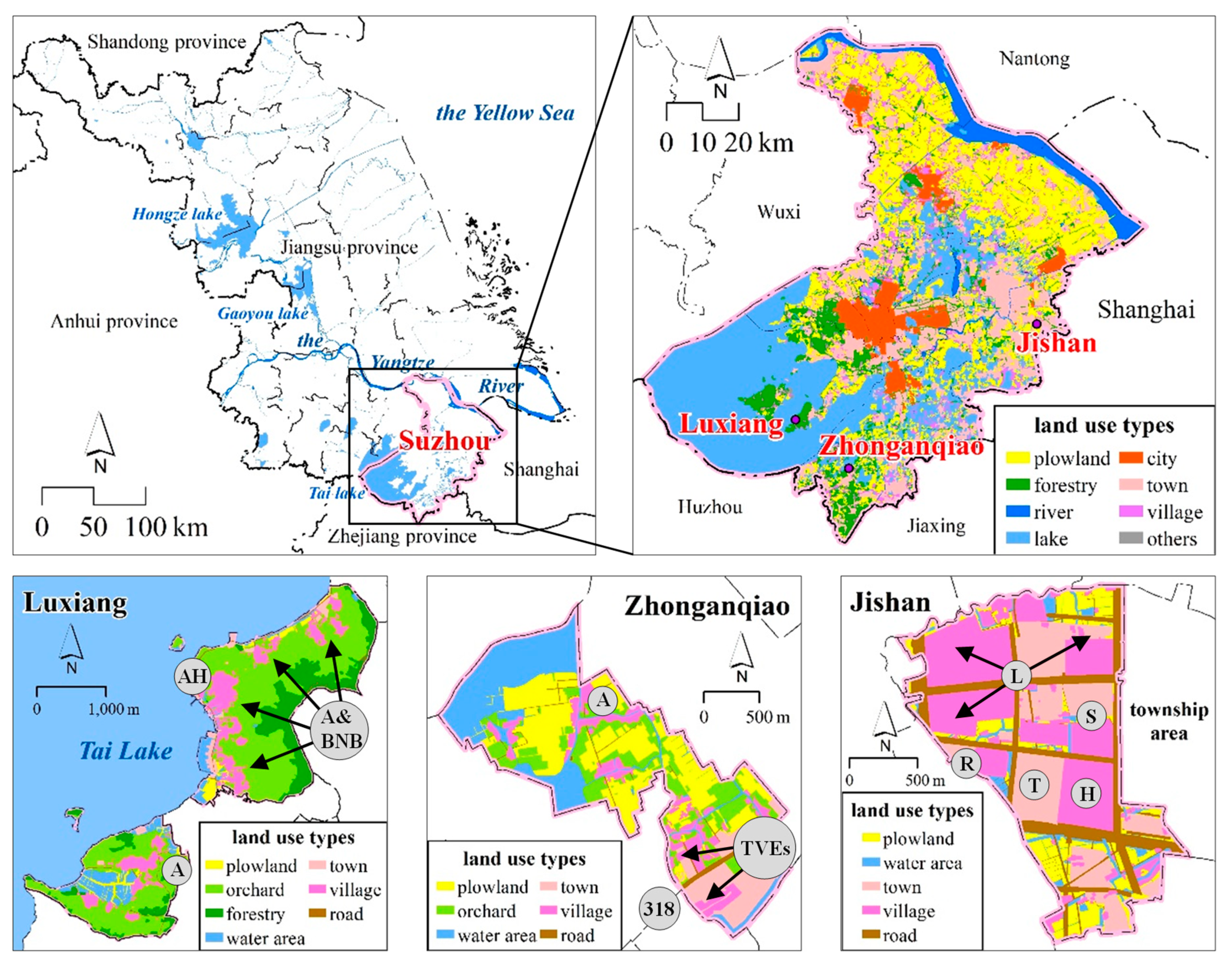
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Land Use Data
2.2.2. Tencent LBS Data
2.3. Function Index Built
- Ri is the index of residential function.
- Qdi and Qei, respectively, are the RTUQ in day and evening. In this study, i = 1, 2… 7, dates from 31 December 2018 to 6 January 2019.
- Ei is the index of employment function.
- Ci is the index of consumption function.
- m, n, and k, respectively, is the number of holidays, weekends and weekdays. In this study, a = 1 and 2, and dates from 31 December 2018 to 1 January 2019; b = 1 and 2, and dates from 5 to 6 January 2019; and c = 1, 2, and 3, and dates from 2 to 4 January 2019.
3. Results
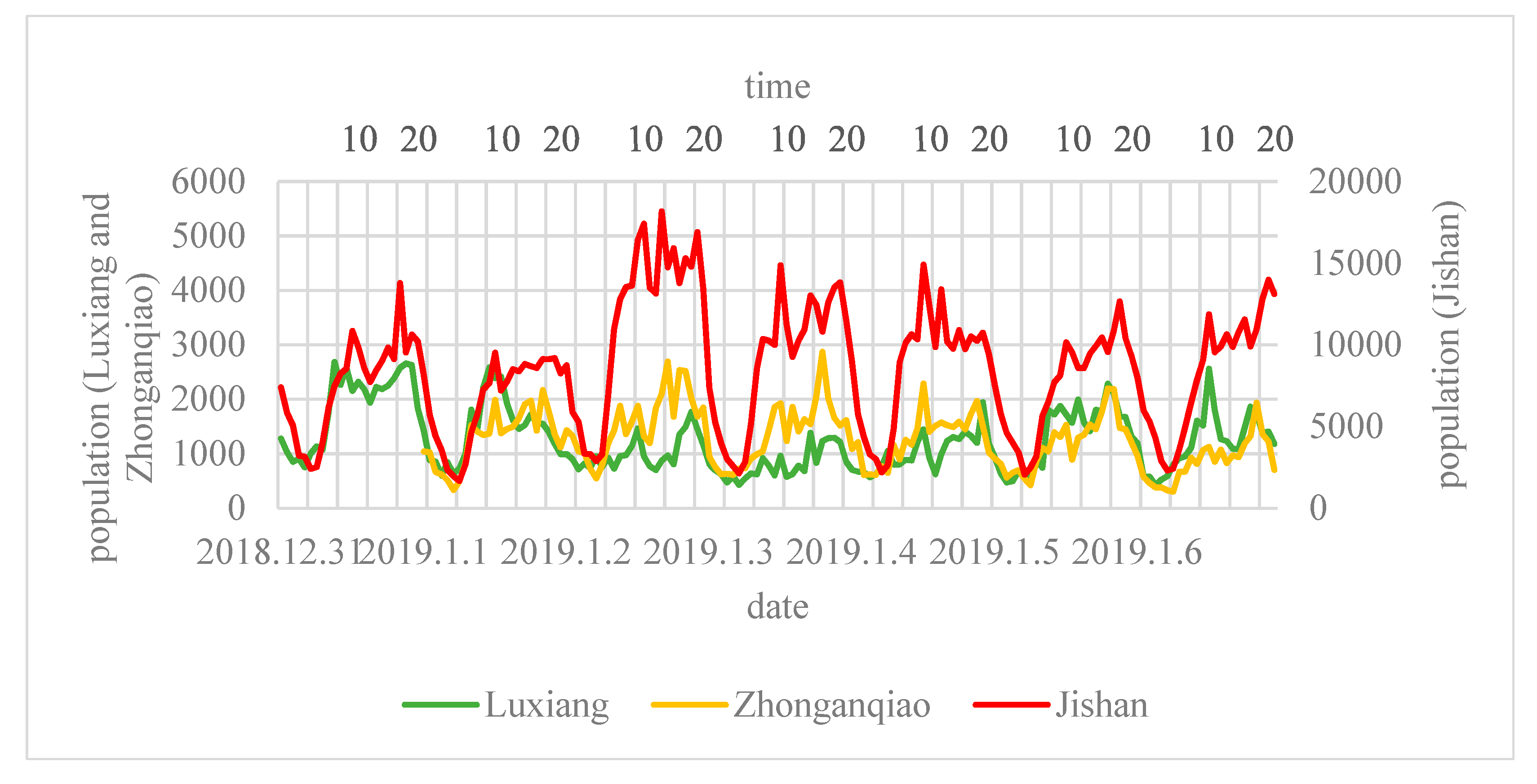
3.1. Perceiving Spatiotemporal Patterns of Human Mobilities
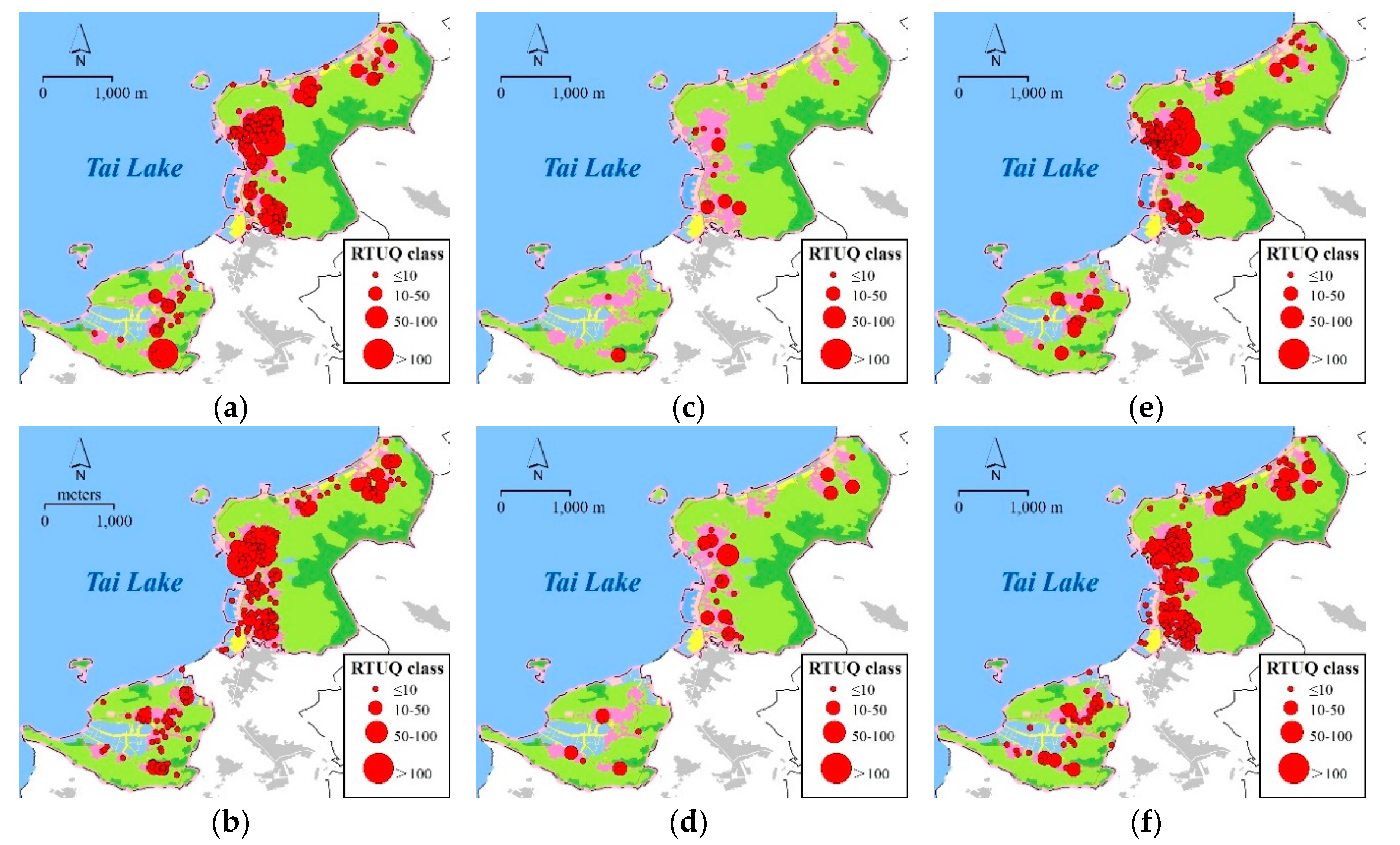
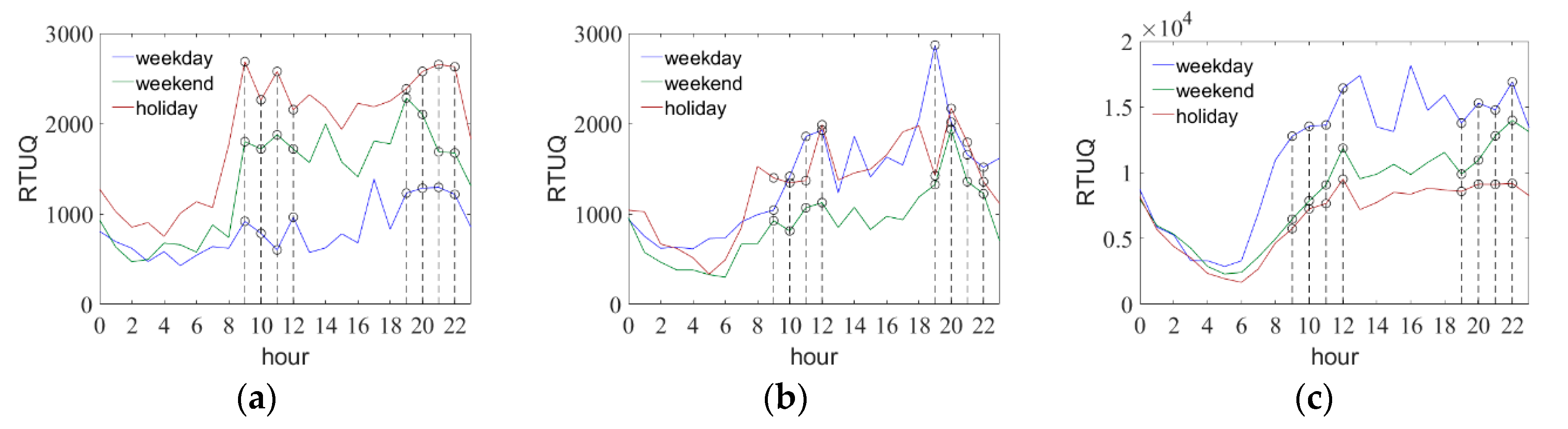
3.1.1. Prominent Holiday Economy in Luxiang
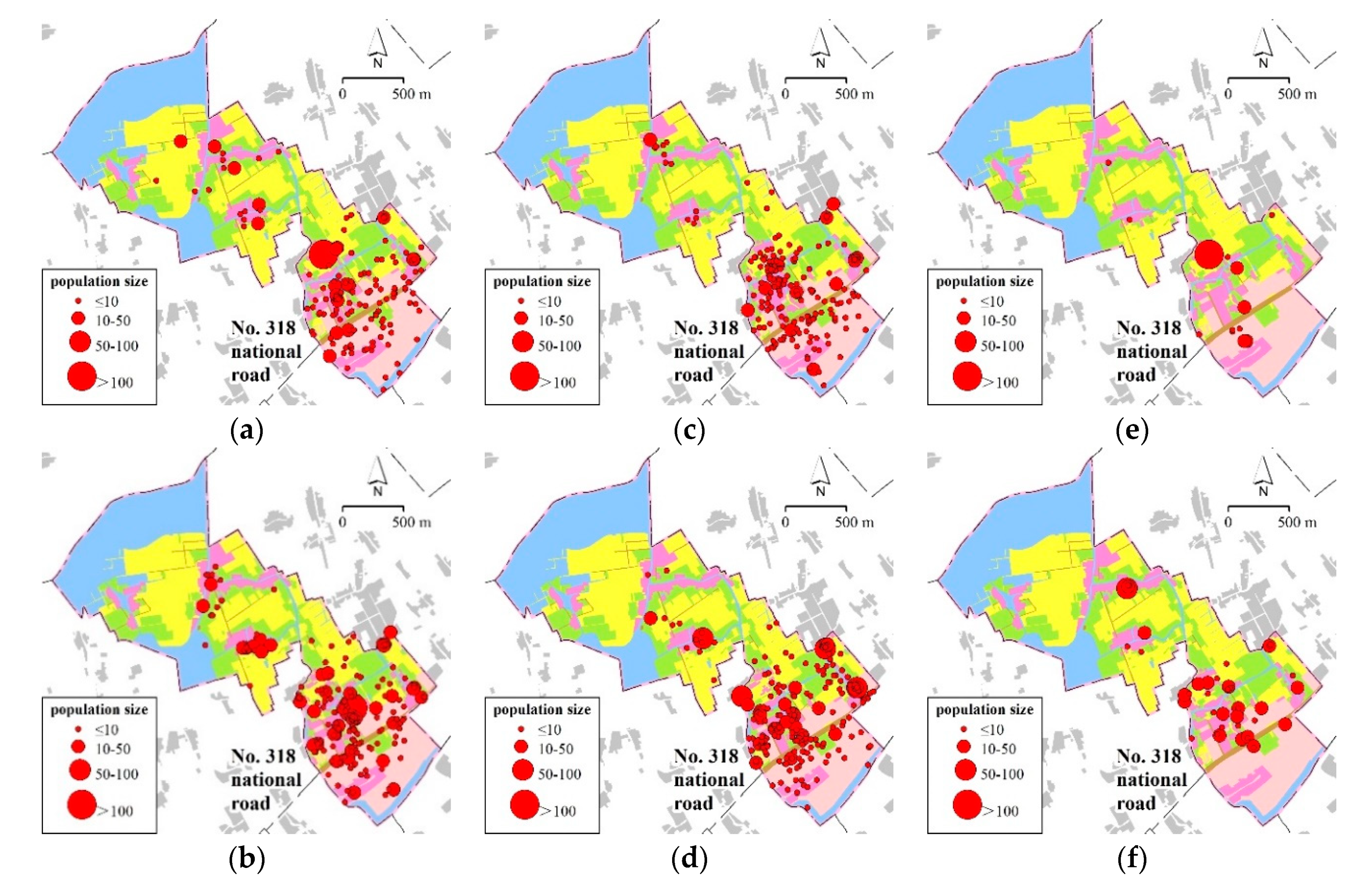
3.1.2. Transport-Oriented Development in Zhonganqiao
3.1.3. Seasonal Flow Out in Jishan
3.2. Measuring Multifunctionality Based on Function Index
3.2.1. Calculate RTUQ of Day and Evening
- Qdij and Qeij, respectively, are the hourly RTUQ data of day and evening.
- t1 and t2, respectively, are the hour of day and evening; t is the number of hours; j = 0, 1… t1… t2… 23. In this study, t1 = 9, t2 = 19, t = 4.
3.2.2. Evaluate Results of Function Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Methodological Contributions
4.2. Implications for Transitional Pathways of Decision-Making
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCarthy, J. Rural geography: Multifunctional rural geographies-reactionary or radical. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2005, 29, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, C.; Valdivia, C. Recreation and agroforestry: Examining new dimensions of multifunctionality in family farms. J. Rural Stud. 2010, 26, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.L.; Liu, Y.S. Rural restructuring in China. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribadi, D.O.; Zasada, I.; Müller, K.; Pauleit, S. Multifunctional adaption of farmers as response to urban growth in the Jabodetabek Metropolitan Area, Indonesia. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 55, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostindie, H. Unpacking Dutch multifunctional agrarian pathways as processes of peasantisation and agrarianisation. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 61, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosnell, H.; Abrams, J. Amenity migration: Diverse conceptualizations of drivers, socio-economic dimensions, and emerging challenges. GeoJournal 2011, 76, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J. Cape York Peninsula, Australia: A frontier region undergoing a multifunctional transition with indigenous engagement. J. Rural Stud. 2012, 28, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.A.; Hu, Z.; Rahman, S. Community resilience in rural China: The case of Hu Village, Sichuan Province. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 60, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.A. Multifunctional Agriculture: A Transition Theory Perspective; Cromwell Press: Trowbridge, UK, 2007; pp. 179–211. [Google Scholar]
- Marsden, T. New rural territories: Regulating the differentiated rural space. J. Rural Stud. 1998, 14, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.A. From productivism to post-productivism and back again? Exploring the (un)changed natural and mental landscapes of European agriculture. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2001, 26, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J. Impulses towards a multifunctional transition in rural Australia: Gaps in the research agenda. J. Rural Stud. 2006, 22, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, M. Engaging the global countryside: Globalization, hybridity and the reconstitution of rural place. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2007, 31, 485–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfacree, K. Trial by space for a ‘radical rural’: Introducing alternative localities, representations and lives. J. Rural Stud. 2007, 23, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunori, G.; Rossi, A. Differentiating countryside: Social representations and governance patterns in rural areas with high social density: The case of Chianti, Italy. J. Rural Stud. 2007, 23, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umans, L.; Arce, A. Fixing rural development cooperation? Not in situations involving blurring and fluidity. J. Rural Stud. 2014, 34, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peou, C. Negotiating rural-urban transformation and life course fluidity: Rural young people and urban sojourn in contemporary Cambodia. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 44, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, H.; Arentze, T.; Joh, C. Analysing space-time behaviour: New approaches to old problems. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2002, 26, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neutens, T.; Schwanen, T.; Witlox, F. The prism of everyday life: Towards a new research agenda for time geography. Transp. Rev. 2011, 31, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.W. Space-time behavior research in China: Recent development and future prospect. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2013, 103, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.L.; Yu, H.; Bombom, L. A Space-Time GIS Approach to Exploring Large Individual-based Spatiotemporal Datasets. Trans. GIS 2008, 12, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crease, P.; Reichenbacher, T. Linking time geography and activity theory to support the activities of mobile information seekers. Trans. GIS 2013, 17, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Arikawa, M.; Sugiyama, A. Location-based applications using analog maps for sustainable local tourism information services. Cartographica 2018, 53, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Ding, Y.; Wu, C.B.; Huang, J.; Hu, C.D. Measuring the spatial allocation rationality of service facilities of residential areas based on internet map and location-based service data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Capra, L.; Wolfson, O.; Yang, H. Urban computing: Concepts, methodologies, and applications. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2014, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, S.; Gong, L.; Kang, C.G.; Zhi, Y. Social sensing: A new approach to understanding our socioeconomic environments. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2015, 105, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.; Shelton, T. Geography and the future of big data, big data and the future of geography. Dialogues Hum. Geogr. 2013, 3, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y. Migration patterns in China extracted from mobile positioning data. Habitat Int. 2019, 86, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Niu, X.Y.; Song, X.D. Measuring the employment center system in Shanghai central city: A study using mobile phone signaling data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.W.; Liu, X.T.; Zhao, P.X.; Zhang, J.W.; Kwan, M.P. Interactions between bus, metro, and taxi use before and after the Chinese Spring Festival. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.G.; Qin, K. Understanding operation behaviors of taxicabs in cities by matrix factorization. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 60, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Wang, R.Y.; Li, Y.; Tu, W. Emerging social media data on measuring urban park use. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 31, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, M.L.; Keeler, B.L.; Wood, S.A.; Fisher, D.M.; Hamstead, Z.A.; McPhearson, T. Using social media to understand drivers of urban park visitation in the Twin Cities, MN. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 175, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, B.L.; Ratti, C.; Liu, Y. Discovering place-informative scenes and objects using social media photos. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Ratti, C. Using Google street view for street-level urban form analysis, a case study in Cambridge, Massachusetts. In The Mathematics of Urban Morphology: Modeling and Simulation in Science, Engineering and Technology; D’Acci, L., Ed.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 457–470. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.L. Conceptual exploration and practical application on flexibility and efficiency of territory spatial planning making from the perspective of big data. China Land Sci. 2019, 33, 9–16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lee, C. Global production networks and local institution building: The development of the information-technology industry in Suzhou, China. Environ. Plan. A 2007, 39, 1873–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.; Liefner, I.; Miao, C.H. Network configurations and R&D activities of the ICT industry in Suzhou Municipality, China. Geoforum 2011, 42, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, J.F.; Chung, C.K.L. City profile: Suzhou—A Chinese city under transformation. Cities 2015, 44, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, L.M. A comparative study on the quality of China’s eco-city: Suzhou vs Kitakyushu. Habitat Int. 2015, 50, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.H.; Hu, X.L. Evolution and transformation mechanism of the spatial structure of rural settlements from the perspective of long-term economic and social change: A case study of the Sunan region, China. J. Rural Stud. in press. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Dijst, M.; Weesep, J.V.; Jiao, Y.X. Residential choice among rural–urban migrants after Hukou reform: Evidence from Suzhou, China. Popul. Space Place 2017, 23, e2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lien, D. Union membership, union coverage and wage dispersion of rural migrants: Evidence from Suzhou industrial sector. China Econ. Rev. 2018, 49, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wei, Y.H.; Chen, W. Economic transition, industrial location and corporate networks: Remaking the Sunan Model in Wuxi City, China. Habitat Int. 2014, 42, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Z.; Zhang, L.P.; Qiu, F.D. Determinants of tourism ticket pricing for ancient villages and towns: Case studies from Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shanghai and Anhui provinces. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Rommel, J.; Feng, S.Y.; Hanisch, M. Can land transfer through land cooperatives foster off-farm employment in China? China Econ. Rev. 2017, 45, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.; Wang, H. Dilemmas of local governance under the development zone fever in China: A case study of the Suzhou region. Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Chan, R.C.K.; Qi, Z.X. Booming provincial-led north–south city-to-city cooperation in China: A case study of Suzhou-Suqian industrial park of Jiangsu province. Cities 2015, 46, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.S.; Wang, Y.R.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, L.G. Who are the stakeholders and how do they respond to a local government payments for ecosystem services program in a developed area: A case study from Suzhou, China. Habitat Int. 2015, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Zhang, C.M.; Cai, Y.Y. Varieties of agri-environmental schemes in China: A quantitative assessment. Land Use Policy 2018, 71, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M. Research on the development strategies of rural tourism in Suzhou based on SWOT analysis. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, X.P.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.B.; Liang, Z.T.; Mai, K.; Zhang, Y.T. Mapping fine-scale population distributions at the building level by integrating multisource geospatial big data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horanont, T.; Phithakkitnukoon, S.; Leong, T.W.; Sekimoto, Y.; Shibasaki, R. Weather effects on the patterns of people’s everyday activities: A study using GPS traces of mobile phone users. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widhalm, P.; Yang, Y.X.; Ulm, M.; Athavale, S.; González, M.C. Discovering urban activity patterns in cell phone data. Transportation 2015, 42, 597–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriman, P. Mobility, Space and Culture; Routledge: London, UK, 2012; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Milbourne, P. Re-populating rural studies: Migrations, movements and mobilities. J. Rural Stud. 2007, 23, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfacree, K. Heterolocal identities? Counter-urbanisation, second homes, and rural consumption in the era of mobilities. Int. J. Popul. Geogr. 2012, 18, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohíno, I.; Solís, E.; Urena, J. Changing commuting patterns in rural metro-adjacent regions: The case of Castilla-La Mancha in the context of Madrid, Spain. Reg. Stud. 2017, 51, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbourne, P.; Kitchen, L. Rural mobilities: Connecting movement and fixity in rural places. J. Rural Stud. 2014, 34, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieling, J.; Vermeij, L.; Haartsen, T. Beyond the local-newcomer divide: Village attachment in the era of mobilities. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 55, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aure, M.; Førdea, A.; Magnussen, T. Will migrant workers rescue rural regions? Challenges of creating stability through mobility. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 60, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H.; Gu, C.L. Industrial development and spatial dtructure in Changzhou city, China: The restructuring of the Sunan model. Urban Geogr. 2010, 31, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.H. Beyond the Sunan model: Trajectory and underlying factors of development in Kunshan, China. Environ. Plan A 2002, 34, 1725–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.S.; Long, H.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; Ge, D.Z.; Qu, Y. Rural restructuring at village level under rapid urbanization in metropolitan suburbs of China and its implications for innovations in land use policy. Habitat Int. 2018, 77, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigg, J. Land, farming, livelihoods, and poverty: Rethinking the links in the rural South. World Dev. 2006, 34, 180–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.A. Community resilience, globalization, and transitional pathways of decision-making. Geoforum 2012, 43, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Li, Z.G.; Jin, J. Pseudo-urbanization or real urbanization? Urban China’s mergence of administrative regions and its effects: A case study of Zhongshan city, Guangdong Province. China Rev. 2014, 14, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Li, Y.H. Revitalize the world’s countryside. Nature 2017, 548, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
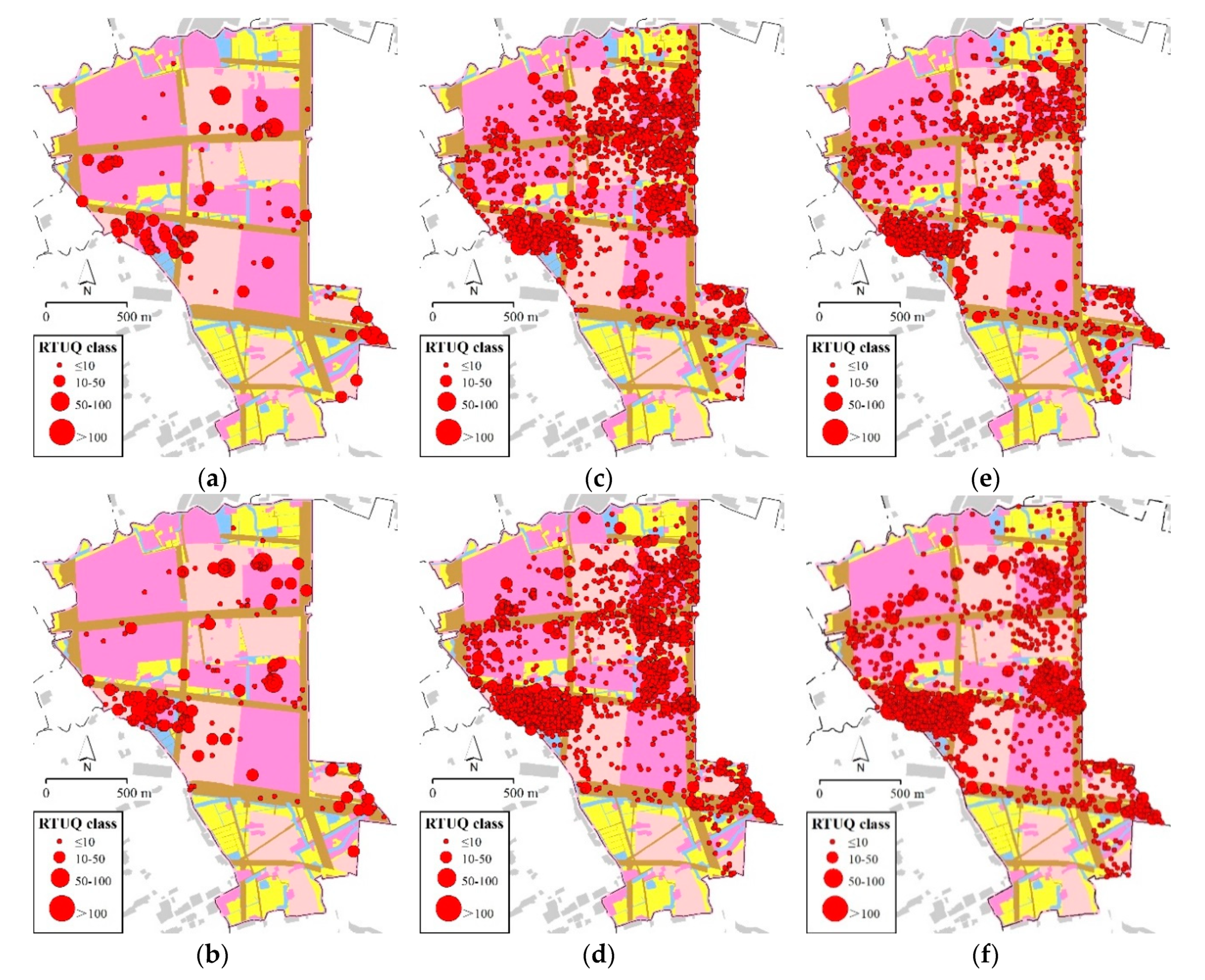

| Rural Space | Luxiang | Zhonganqiao | Jishan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | ||
| ecological space | subtotal | 1.7572 | 24.56 | 0.9555 | 27.21 | 0.1877 | 6.42 |
| forestry | 1.1629 | 16.25 | 0.0000 | 0.00 | 0.0000 | 0.00 | |
| water area | 0.5943 | 8.31 | 0.9555 | 27.21 | 0.1877 | 6.42 | |
| agricultural space | subtotal | 4.1897 | 58.56 | 1.6762 | 47.74 | 0.3806 | 13.03 |
| plowland | 0.2457 | 3.43 | 1.0374 | 29.55 | 0.3806 | 13.03 | |
| orchard | 3.9440 | 55.13 | 0.6387 | 18.19 | 0.0000 | 0.00 | |
| construction space | subtotal | 1.2072 | 16.87 | 0.8796 | 25.05 | 2.3529 | 80.55 |
| town | 0.1909 | 2.67 | 0.4083 | 11.63 | 0.6994 | 23.94 | |
| village | 0.9141 | 12.78 | 0.3934 | 11.21 | 1.0808 | 37.00 | |
| road | 0.1022 | 1.43 | 0.0778 | 2.22 | 0.5727 | 19.61 | |
| total | 7.1542 | 100.00 | 3.5112 | 100.00 | 2.9212 | 100.00 | |
| Name | Description | Type | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | serial number of area requested after approval | string | - |
| begin | time for beginning | integer | accurate to the second, begin and end both hourly, time span less than 2 days |
| end | time for ending | integer | the same as above |
| interval | granularity of time interval | choose from 5, 10, 30, or 60 min | |
| data | elements including time (string) and users quantity (integer) | array | for example: {“time”: “31 December 2018 12:05:00”, “quantity”: 18,746} |
| Village | Holiday | Weekday | Weekend | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:00 | 20:00 | 10:00 | 20:00 | 10:00 | 20:00 | |
| Luxiang | 2263 | 2578 | 785 | 1285 | 1719 | 2102 |
| Zhonganqiao | 1345 | 2169 | 1416 | 2016 | 812 | 1937 |
| Jishan | 7254 | 9134 | 13,534 | 15,298 | 7859 | 10,962 |
| Period | Date | Luxiang | Zhonganqiao | Jishan | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qd | Qe | Qd | Qe | Qd | Qe | ||
| vacation | 31 December 2018 | 2421 | 2562 | - 1 | - | 8772 | 10,769 |
| 1 January 2019 | 2162 | 1423 | 1525 | 1686 | 7543 | 9007 | |
| workday | 2 January 2019 | 1136 | 1517 | 1678 | 2188 | 14,097 | 15,193 |
| 3 January 2019 | 817 | 1257 | 1561 | 2014 | 11,372 | 12,687 | |
| 4 January 2019 | 1105 | 1468 | 1545 | 1663 | 11,505 | 10,303 | |
| weekend | 5 January 2019 | 1779 | 1937 | 1317 | 1827 | 8120 | 10,864 |
| 6 January 2019 | 1700 | 1599 | 983 | 1461 | 8818 | 11,914 | |
| Period | Date | Luxiang | Zhonganqiao | Jishan | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | E | C | R | E | C | R | E | C | ||
| holidays | 31 December 2018 | 1.0583 | 1.4699 | 4.3025 | - | - | - | 1.2277 | 1.1137 | 0.6022 |
| 1 January 2019 | 0.6583 | 1.1729 | 2.1358 | 1.1053 | 1.3260 | 0.8246 | 1.1940 | 0.8236 | 0.4331 | |
| weekdays | 2 January 2019 | 1.3351 | 0.3237 | 1.1954 | 1.3042 | 1.6050 | 1.1777 | 1.0778 | 2.8764 | 1.3654 |
| 3 January 2019 | 1.5379 | 0.1675 | 0.7125 | 1.2905 | 1.3891 | 1.0086 | 1.1156 | 1.8717 | 0.9197 | |
| 4 January 2019 | 1.3286 | 0.3063 | 1.1257 | 1.0764 | 1.3605 | 0.8239 | 0.8955 | 1.9159 | 0.7557 | |
| weekends | 5 January 2019 | 1.0891 | 0.7938 | 2.3911 | 1.3870 | 0.9896 | 0.7723 | 1.3379 | 0.9544 | 0.5624 |
| 6 January 2019 | 0.9407 | 0.7253 | 1.8871 | 1.4867 | 0.5506 | 0.4606 | 1.3511 | 1.1255 | 0.6698 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y. Emerging Location-Based Service Data on Perceiving and Measuring Multifunctionality of Rural Space: A Study of Suzhou, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5862. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205862
Yuan Y, Li H, Zhang X, Hu X, Wang Y. Emerging Location-Based Service Data on Perceiving and Measuring Multifunctionality of Rural Space: A Study of Suzhou, China. Sustainability. 2019; 11(20):5862. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205862
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yuan, Hongbo Li, Xiaolin Zhang, Xiaoliang Hu, and Yahua Wang. 2019. "Emerging Location-Based Service Data on Perceiving and Measuring Multifunctionality of Rural Space: A Study of Suzhou, China" Sustainability 11, no. 20: 5862. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205862
APA StyleYuan, Y., Li, H., Zhang, X., Hu, X., & Wang, Y. (2019). Emerging Location-Based Service Data on Perceiving and Measuring Multifunctionality of Rural Space: A Study of Suzhou, China. Sustainability, 11(20), 5862. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205862





