A CBR–AHP Hybrid Method to Support the Decision-Making Process in the Selection of Environmental Management Actions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
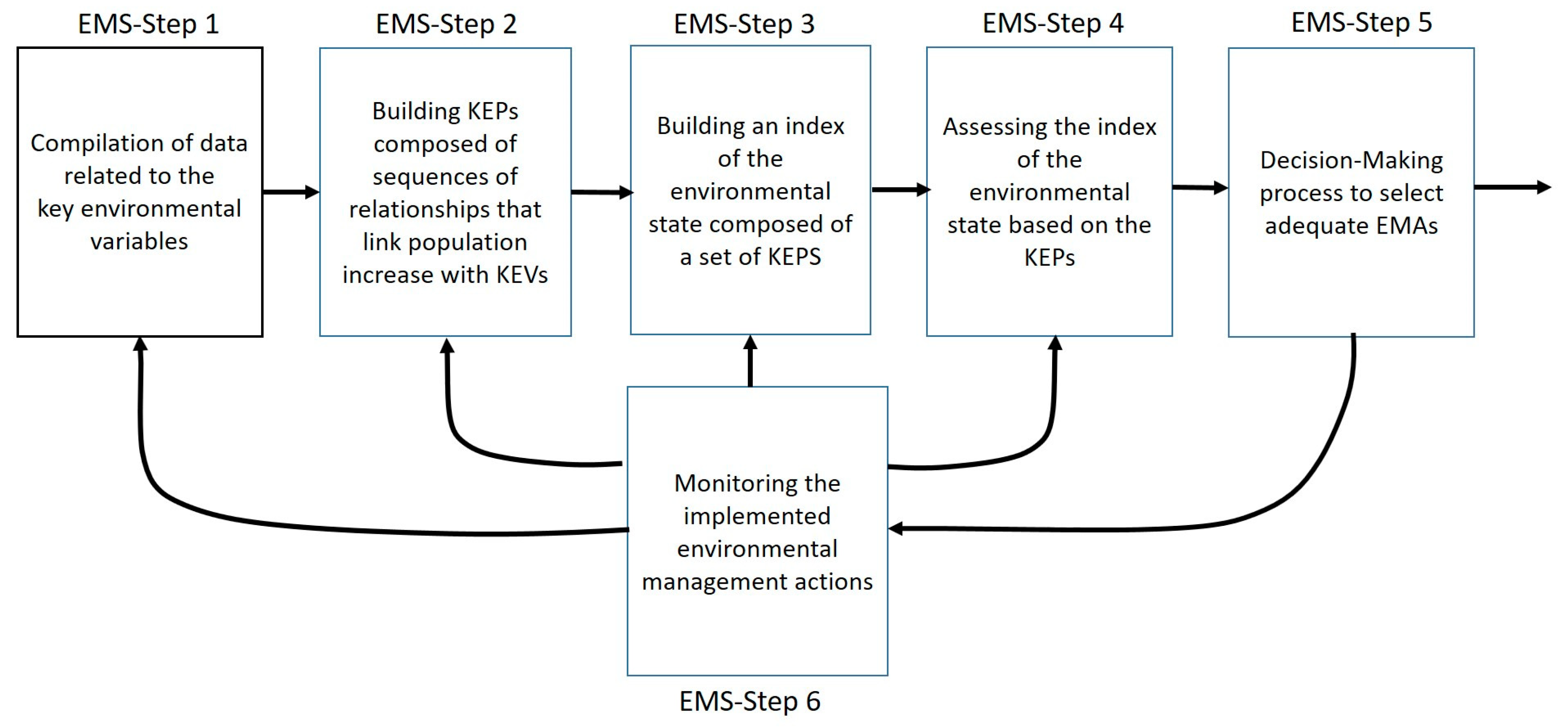
1.2. The Proposal: A Hybrid CBR–AHP Method Integrated into an EMS
1.3. Justification of the Proposed CBR–AHP Hybrid Method
1.4. The Scope of This Paper
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. The Compiled Data for the Period 2000–2010
2.1.2. Trends of Causal Relationships between Drivers and Pressure Variables
2.1.3. Integration of the CBR–AHP Hybrid Method into the EMS
2.1.4. Set of KEPs
2.1.5. A Set of EMAs to Improve the Environmental State
2.1.6. The OECD-Outlook to 2030
2.2. Methods
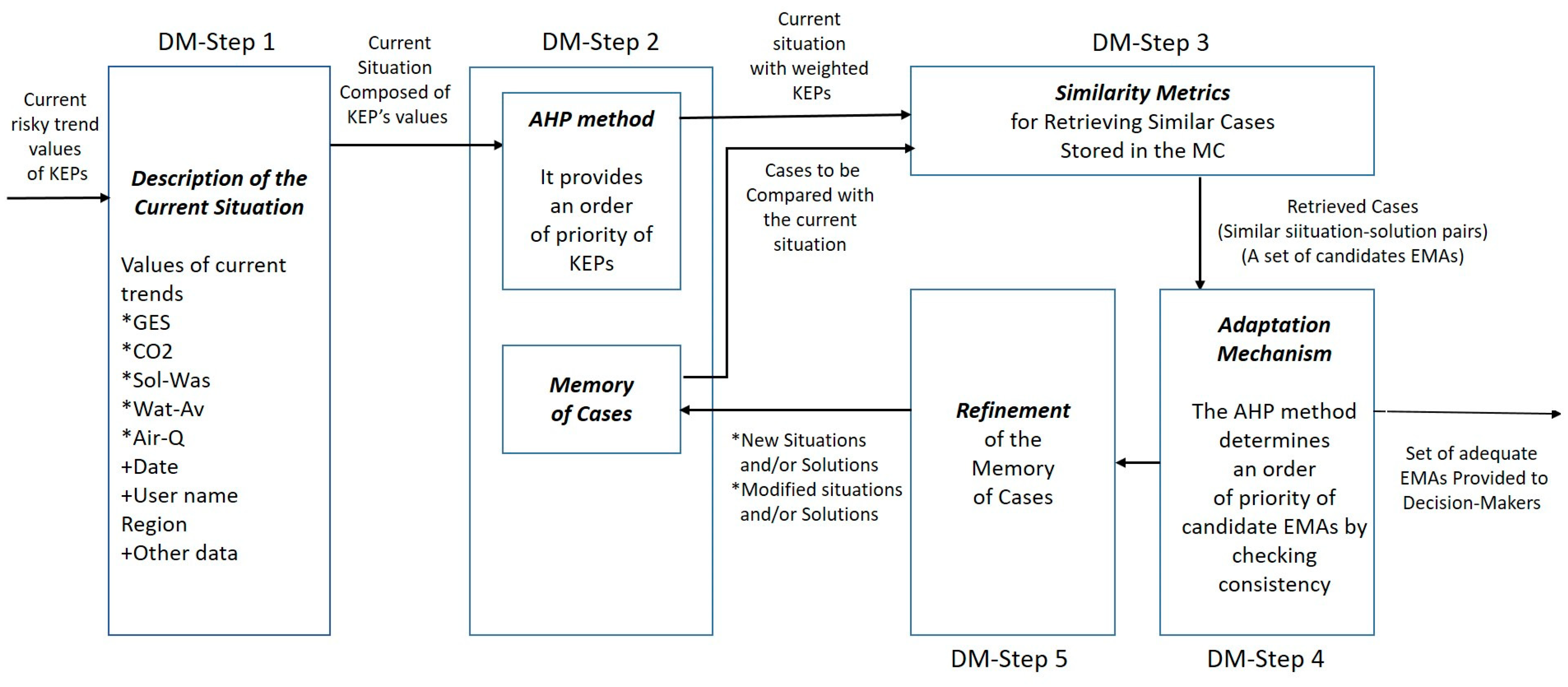
2.2.1. DM-Step 1: Description of the Current Situation
- Path_CO2: Angular value/Normalized value
- Path_Sol-Was: Angular value/Normalized value
- Path_Wat-Av: Angular value/Normalized value
- Path_LVC: Angular value/Normalized value
- Path_Air-Q: Angular value/Normalized value
- GES: Angular value/Normalized value
2.2.2. DM-Step 2: The MC and the Order of Priority of KEPs
Method to Define the Number of Potential Cases to Be Stored in the MC
A Pruning Method to Reduce the Number of Potential Cases to Be Stored in the MC
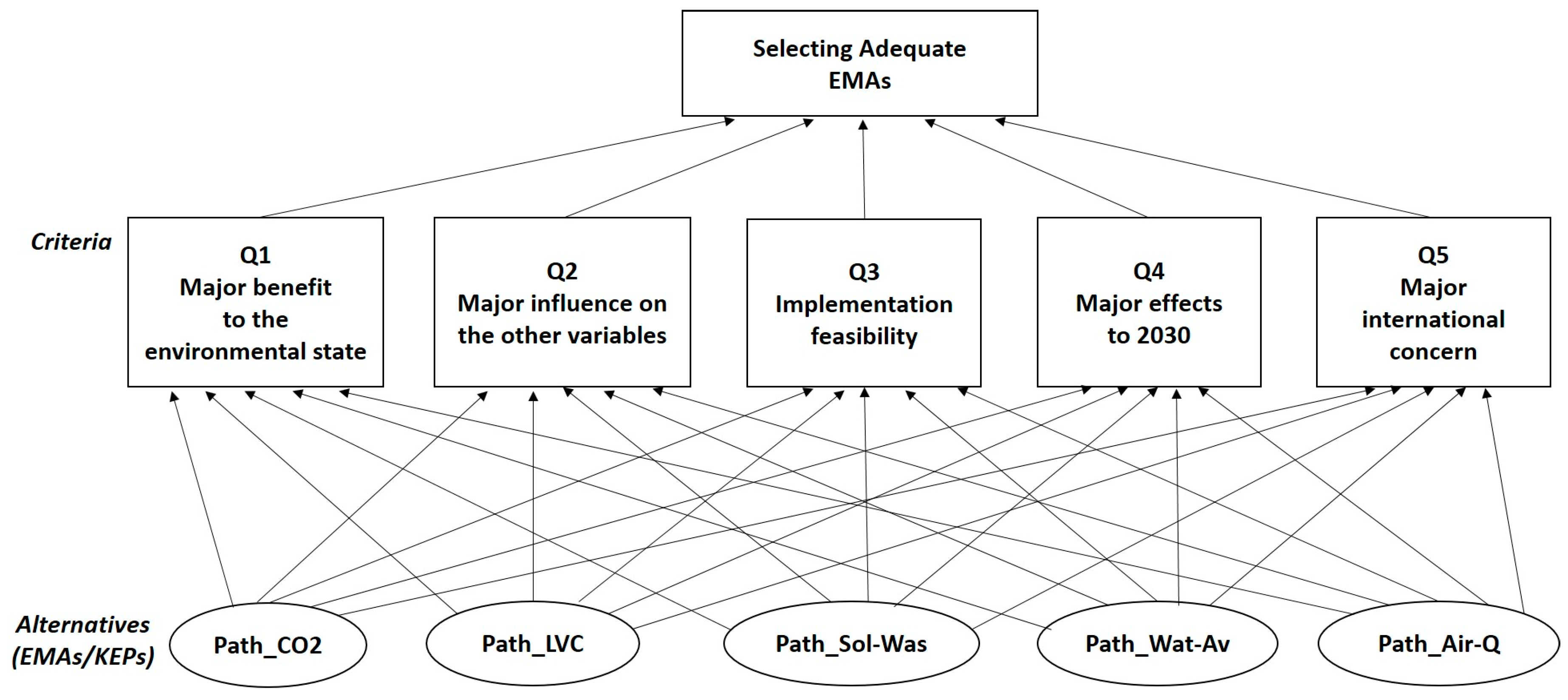
The AHP Method to Determine the Order of Importance Given to the Questions
| Qs | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 |
| Q1 | 1 | 1/3 | 3 | 5 | 1/5 |
| Q2 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 1/3 |
| Q3 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 1 | 3 | 1/7 |
| Q4 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/3 | 1 | 1/9 |
| Q5 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 9 | 1.0 |
| Sum of Columns | 9.533 | 4.675 | 16.333 | 25 | 1.786 |
| Qs | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Eigen Vector (x) or Criteria Weights |
| Q1 | 0.105 | 0.071 | 0.184 | 0.200 | 0.112 | 0.134 |
| Q2 | 0.314 | 0.214 | 0.306 | 0.280 | 0.186 | 0.260 |
| Q3 | 0.035 | 0.043 | 0.061 | 0.120 | 0.081 | 0.068 |
| Q4 | 0.021 | 0.030 | 0.020 | 0.040 | 0.064 | 0.035 |
| Q5 | 0.524 | 0.641 | 0.429 | 0.360 | 0.556 | 0.502 |
| Sum of Columns | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| RI | 0 | 0 | 0.52 | 0.88 | 1.1 | 1.25 | 1.35 |
The AHP Method to Determine the Order of Priority of the Alternatives (KEPs)
| EMAs Related to KEPs | Path_CO2 | Path_LVC | Path_Sol-Was | Path_Wat-Av | Path_Air-Q |
| Path_CO2 | 1 | 1/7 | 1/3 | 1/5 | 3 |
| Path_LVC | 7 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 9 |
| Path_Sol-Was | 3 | 1/5 | 1 | 1/3 | 5 |
| Path_Wat-Av | 5 | 1/3 | 3 | 1 | 7 |
| Path_Air-Q | 1/3 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1 |
| Sums of columns | 16.333 | 1.786 | 9.533 | 4.675 | 25 |
| EMAs Related to KEPs | Path_CO2 | Path_LVC | Path_Sol-Was | Path_Wat-Av | Path_Air-Q | Priority or Eigen Vector |
| Path_CO2 | 0.061 | 0.079 | 0.035 | 0.043 | 0.12 | 0.068 |
| Path_LVC | 0.428 | 0.559 | 0.524 | 0.642 | 0.36 | 0.503 |
| Path_Sol-Was | 0.183 | 0.112 | 0.105 | 0.071 | 0.20 | 0.134 |
| Path_Wat-Av | 0.306 | 0.186 | 0.315 | 0.213 | 0.28 | 0.260 |
| Path_Air-Q | 0.020 | 0.062 | 0.020 | 0.030 | 0.040 | 0.034 |
| Sums of columns | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| RI | 0 | 0 | 0.52 | 0.88 | 1.1 | 1.25 | 1.35 |
2.2.3. DM-Step 3: The Similarity Measure Method to Retrieve Similar Situations from the MC
2.2.4. DM-Step 4: The Adaptation Mechanism
2.2.5. DM-Step 5: The Refinement Process
- (1)
- If no similar situation to the current situation is found in the MC, then it is incorporated as a new situation in the MC;
- (2)
- If the adapted solution required more than five stored situations and their solutions need to be defined;
- (3)
- If the adapted solution is not yet included in the MC.
| CO2 | Waste | Water | LVC | Air-Q | GES | Region at Risk | |
| Current Situation | 0.720 | 0.83 | 0.630 | 0.882 | 0.500 | 0.7124 | high-risk |
3. Analysis and Discussion of Results
3.1. On the DM-Step 1: Description of the Current Situation
3.2. On the DM-Step 2: Memory of Cases and Priority of KEPs
3.2.1. Analysis of Cases to Be Stored in the MC
3.2.2. Analysis of the Method to Assign Weights to KEPs
3.3. Analysis Related to the Adaptation Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Year | Pop (Inhabitants) | CO2 (Gg) | Trans-Ro (Km) | FF (Ha) | LVC (Ha) | Wat-Av (m3/per) | Trans-Ve (Vehicles) | Sol-Was (tons) | Air-Q (PM2.5) (mass/m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Average | 1,555,296 | 2816.2 | 2001 | 12 | 90.4 | 2.818 | 155,600 | 459,000 | 1.016 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2001 | Average | 1,564,627 | 2865.2 | 2029 | 27 | 201.5 | 2.818 | 175,000 | 472,000 | Lack of data |
| % Increase | 0.600 | 1.742 | 1.399 | 125 | 122.9 | 0 | 12.468 | 2.832 | Lack of data | |
| 2002 | Average | 1,574.015 | 2974.88 | 2029 | 69 | 257.0 | 2.818 | 187,500 | 483,000 | 1.009 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 1.204 | 5.634 | 1.399 | 475 | 184.29 | 0 | 20.501 | 5.229 | 8.19 | |
| 2003 | Average | 1,583,459 | 3064.54 | 2029 | 69 | 329.7 | 2.713 | 192,500 | 493,000 | 1.117 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 1.811 | 8.818 | 1.399 | 475 | 264.71 | 3.726 | 23.715 | 7.407 | 9.95 | |
| 2004 | Average | 1,592,960 | 3231.57 | 2058 | 69 | 405.3 | 2.701 | 200,000 | 526,000 | 1.078 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 2.422 | 4.749 | 2.848 | 475 | 348.34 | 4.081 | 28.535 | 14.597 | 6.15 | |
| 2005 | Average | 1,612,899 | 3358.76 | 2080 | 69 | 476.1 | 2.746 | 212,500 | 538,000 | 1.137 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 3.704 | 19.265 | 3.948 | 475 | 426.65 | 2.555 | 36.568 | 17.211 | 11.99 | |
| 2006 | Average | 1,645,157 | 3530.68 | 2080 | 69 | 551.3 | 2.029 | 250,000 | 548,000 | 1.184 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 5.778 | 25.370 | 3.948 | 475 | 509.84 | 27.999 | 60.668 | 19.390 | 16.58 | |
| 2007 | Average | 1,678,060 | 4552.01 | 2112 | 72 | 613.7 | 2.055 | 270,000 | 551,000 | 1.285 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 7.893 | 26.127 | 5.547 | 500 | 578.87 | 27.076 | 73.522 | 20.044 | 26.49 | |
| 2008 | Average | 1,711,621 | 3652.88 | 2477 | 75.5 | 681.8 | 2.049 | 290,000 | 555,000 | 1.187 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 10.051 | 29.709 | 23.788 | 529.16 | 654.20 | 27.289 | 86.375 | 20.915 | 16.86 | |
| 2009 | Average | 1,745,854 | 3784.18 | 2477 | 77.5 | 762.7 | 2.040 | 310,000 | 558,000 | 1.049 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 12.252 | 34.371 | 23.788 | 545.83 | 743.69 | 27.608 | 99.229 | 21.569 | 3.31 | |
| 2010 | Average | 1,777,227 | 3859.22 | 2986 | 78.5 | 843.3 | 1.987 | 340,000 | 596,000 | 1.063 × 10−8 |
| % Increase | 14.269 | 37.036 | 49.325 | 554.16 | 832.85 | 29.489 | 118.509 | 29.847 | 4.66 | |
| Impacts: Percentage difference between 2010 and 2000 | The population increased 14,269% | The CO2 emissions increased 37.036% | The transport routes increased almost 50% | The forest fires increased 554% | The loss of vegetation cover increased 832% | Water availability decreased almost 30% | The number of vehicles increased 118.5% | The solid waste increased almost 30% | The PM2.5 increased almost 5% | |
Appendix B
| Key Environmental Variables | Environmental Management Actions |
|---|---|
| CO2 Emissions | (1) A program of road re-engineering along with an interstate vehicle verification with mobility restrictions, mainly within metropolitan zones; (2) modernization of the vehicle fleet; (3) hybrid and electric vehicles; (4) the use of alternative fuels such as ethanol and biodiesel; (5) the reorganization of loading and passenger transportation. |
| Solid Waste | (1) Construction of infrastructure for the separation, recycling, collection and disposal of waste; (2) construction of regional composting plants in areas of high organic waste generation and strategic areas for agriculture; (3) a formal inter-state program for the prevention and integral management of waste; (4) an ongoing awareness campaign for the reduction of the generation of solid waste. |
| Water Availability | (1) Modern infrastructure for an efficient management and monitoring of continuous operation of the existing waste-water treatment plants; (2) modern hydraulic infrastructure that ensures the extraction, the supply and adequate use of the liquid for domestic purposes; (3) the reuse of treated water to reduce the consumption of water of first quality; (4) a program of capture and use of rainwater in priority areas. |
| Loss of Vegetation Cover | (1) Protected natural areas; (2) payment of environmental services; (3) ecological zoning of the territory; (4) monitoring and control of forest fires; (5) reforestation. |
| Air Quality | (1) Vehicle transport control; (2) forest fires control; (3) environmental education; (4) clean production; (5) avoiding burning the residues of the sugarcane crop by using them for fertilizer, biodigesters, and power generation, among others. |
Appendix C
| Situations | Path CO2 | Path Waste | Path Water | Path LVC | Path Air-Q | GES (Norm) | GES (ang) | Regions at Risk of the GES | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.555 | 0.555 | say 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 50 | mid | It does not apply because the paths have the same value |
| 2 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.6 | 54 | mid | Air-Q |
| 3 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.6 | 54 | mid | LVC |
| 4 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6 | 54 | mid | Water |
| 5 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6 | 54 | mid | Waste |
| 6 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6 | 54 | mid | CO2 |
| 7 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.633 | 57 | mid | Air-Q |
| 8 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.633 | 57 | mid | LVC |
| 9 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.633 | 57 | mid | Water |
| 10 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.633 | 57 | mid | Waste |
| 11 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.633 | 57 | mid | CO2 |
| 12 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | LVC/Air-Q |
| 13 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | Air-Q/Water |
| 14 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | LVC/Water |
| 15 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | Waste/Air-Q |
| 16 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | Waste/LVC |
| 17 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | Waste/Water |
| 18 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | CO2/Air-Q |
| 19 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | CO2/LVC |
| 20 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | CO2/Water |
| 21 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.644 | 58 | mid | CO2/Waste |
| 22 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Air-Q/LVC |
| 23 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | LVC/Air-Q |
| 24 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Air-Q/Water |
| 25 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | LVC/Water |
| 26 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Water/Air-Q |
| 27 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Water/LVC |
| 28 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Waste/Air-Q |
| 29 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | LVC/Waste |
| 30 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Water/Waste |
| 31 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Waste/Air-Q |
| 32 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Waste/LVC |
| 33 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Waste/Water |
| 34 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Air-Q/CO2 |
| 35 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | LVC/CO2 |
| 36 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | CO2/Water |
| 37 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | Waste/CO2 |
| 38 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | CO2/Air-Q |
| 39 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | CO2/Waste |
| 40 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | CO2/Water |
| 41 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6772 | 61 | high | CO2/Waste |
| 42 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 43 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 44 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | Waste/Water/Air-Q |
| 45 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | Waste/Water/LVC |
| 46 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q |
| 47 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | CO2/Water/Air-Q |
| 48 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | CO2/Water/LVC |
| 49 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q |
| 50 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | CO2/Waste/Water |
| 51 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.6882 | 62 | high | CO2/Waste/Water |
| 52 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | LVC/Air-Q |
| 53 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | Water/Air-Q |
| 54 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | Water/LVC |
| 55 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | Waste/LVC |
| 56 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | Waste/LVC |
| 57 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | Waste/Water |
| 58 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | CO2/Air-Q |
| 59 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | CO2/LVC |
| 60 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | CO2/Water |
| 61 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.7106 | 64 | high | CO2/Waste |
| 62 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Air-Q/Water/LVC |
| 63 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | LVC/Water/Air-Q |
| 64 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 65 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Air-Q/Waste/LVC |
| 66 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | LVC/Waste/Air-Q |
| 67 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Air-Q/Waste/Water |
| 68 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | LVC/Waste/Water |
| 69 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Water/Waste/Air-Q |
| 70 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Water/Waste/LVC |
| 71 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 72 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Waste/Water/Air-Q |
| 73 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Waste/Water/LVC |
| 74 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Air-Q/CO2/LVC |
| 75 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | LVC/CO2/Air-Q |
| 76 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Air-Q/CO2/Water |
| 77 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | LVC/CO2/Water |
| 78 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Water/CO2/Air-Q |
| 79 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Water/CO2/LVC |
| 80 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Air-Q/CO2/Waste |
| 81 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | LVC/CO2/Waste |
| 82 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Water/CO2/Waste |
| 83 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Waste/CO2/Air-Q |
| 84 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Waste/CO2/LVC |
| 85 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | Waste/CO2/Water |
| 86 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q |
| 87 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | CO2/Water/Air-Q |
| 88 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | CO2/Water/LVC |
| 89 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q |
| 90 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC |
| 91 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.7216 | 65 | high | CO2/Waste/Water |
| 92 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7326 | 66 | high | Waste/Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 93 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7326 | 66 | high | CO2/Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 94 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7326 | 66 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 95 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7326 | 66 | high | CO2/Waste/Water/Air-Q |
| 96 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7326 | 66 | high | CO2/Waste/Water/LVC |
| 97 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 98 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Water/Air-Q/LVC |
| 99 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.755 | 68 | high | LVC/Water/Air-Q |
| 100 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | LVC/Air-Q/Waste |
| 101 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Air-Q/Water/Waste |
| 102 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | LVC/Water/Waste |
| 103 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/Air-Q/LVC |
| 104 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 105 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/Air-Q/Water |
| 106 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/LVC/Water |
| 107 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/Water/Air-Q |
| 108 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/Water/LVC |
| 109 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | LVC/Air-Q/CO2 |
| 110 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Air-Q/Water/CO2 |
| 111 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | LVC/Water/CO2 |
| 112 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/Air-Q/CO2 |
| 113 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/LVC/CO2 |
| 114 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | Waste/Water/CO2 |
| 115 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q |
| 116 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q |
| 117 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Water |
| 118 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/LVC/Water |
| 119 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/Water/Air-Q |
| 120 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/Water/LVC |
| 121 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Waste |
| 122 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/LVC/Waste |
| 123 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/Water/Waste |
| 124 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q |
| 125 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC |
| 126 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.755 | 68 | high | CO2/Waste/Water |
| 127 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Air-Q/Waste/Water/LVC |
| 128 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | LVC/Waste/Water/Air-Q |
| 129 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Water/Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 130 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Waste/Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 131 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Air-Q/CO2/LVC/Water |
| 132 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | LVC/CO2/Water/Air-Q |
| 133 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Water/CO2/LVC/Air-Q |
| 134 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Air-Q/CO2/Waste/LVC |
| 135 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | LVC/CO2/Waste/Air-Q |
| 136 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Air-Q/CO2/Waste/Water |
| 137 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.766 | 69 | high | LVC/CO2/Waste/Water |
| 138 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Water/CO2/Waste/Air-Q |
| 139 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Water/CO2/Waste/LVC |
| 140 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Waste/CO2/LVC/Air-Q |
| 141 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Waste/CO2/Water/Air-Q |
| 142 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.766 | 69 | high | Waste/CO2/Water/LVC |
| 143 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | CO2/Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 144 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 145 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.766 | 69 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Water |
| 146 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.766 | 69 | high | CO2/Waste/Water/LVC/ |
| 147 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 70 | high | CO2/Waste/Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 148 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | LVC/Water/Air-Q |
| 149 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | LVC/Waste/Air-Q |
| 150 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | Waste/Air-Q/Water |
| 151 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | LVC/Waste/Water |
| 152 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q |
| 153 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Water |
| 154 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | CO2/LVC/Water |
| 155 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q |
| 156 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | CO2/Waste/Water |
| 157 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.555 | 0.7884 | 71 | high | CO2/Waste/Water |
| 158 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | LVC/Air-Q/Waste/Water |
| 159 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Air-Q/Water/Waste/LVC |
| 160 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | LVC/Water/Waste/Air-Q |
| 161 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/Air-Q/LVC/Water |
| 162 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 163 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 164 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | LVC/Air-Q/CO2/Water |
| 165 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | LVC/Water/CO2/Air-Q |
| 166 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | LVC/Air-Q/CO2/Waste |
| 167 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Air-Q/Water/CO2/Waste |
| 168 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | LVC/Water/CO2/Waste |
| 169 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/Air-Q/CO2/LVC |
| 170 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/LVC/CO2/Air-Q |
| 171 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/Air-Q/CO2/Water |
| 172 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/LVC/CO2/Water |
| 173 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/Water/CO2/Air-Q |
| 174 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Waste/Water/CO2/LVC |
| 175 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Air-Q/LVC/Water |
| 176 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 177 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 178 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Waste/LVC |
| 179 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/LVC/Waste/Air-Q |
| 180 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Waste/Water |
| 181 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/LVC/Waste/Water |
| 182 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Water/Waste/Air-Q |
| 183 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Water/Waste/LVC |
| 184 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 185 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Waste/Water/Air-Q |
| 186 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Water |
| 187 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.7994 | 72 | high | Air-Q/Water/CO2/LVC |
| 188 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8104 | 73 | high | Air-Q/CO2/LVC/Waste/Water |
| 189 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8104 | 73 | high | LVC/ CO2/Waste/Air-Q/Water |
| 190 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.8104 | 73 | high | Water/CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 191 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.8104 | 73 | high | Waste/ CO2/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 192 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.8104 | 73 | high | CO2/LVC/Waste/Air-Q/Water |
| 193 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | LVC/Air-Q/Water/Waste |
| 194 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | LVC/Waste/Air-Q/Water |
| 195 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | Waste/Air-Q/Water/LVC |
| 196 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | Waste/LVC/Water/Air-Q |
| 197 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | LVC/Air-Q/Water// CO2 |
| 198 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | Waste/LVC/Air-Q/ CO2 |
| 199 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | Waste/Air-Q/Water/ CO2 |
| 200 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | Waste/LVC/Water/ CO2 |
| 201 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 202 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Water/LVC |
| 203 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/LVC/Water/Air-Q |
| 204 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q/Waste |
| 205 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Water/Waste |
| 206 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/LVC/Water/Waste |
| 207 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q/LVC |
| 208 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 209 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q/Water |
| 210 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Water |
| 211 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/Waste/Water/Air-Q |
| 212 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.8328 | 75 | high | CO2/Waste/Water/LVC |
| 213 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | LVC/Air-Q/CO2/Waste/Water |
| 214 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | Air-Q/Water/CO2/Waste/LVC |
| 215 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | LVC/Water/CO2/Waste/Air-Q |
| 216 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | Waste/Air-Q/CO2/LVC/Water |
| 217 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | Waste/LVC/CO2/Air-Q/Water |
| 218 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | Waste/Water/CO2/LVC/Air-Q |
| 219 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Waste/LVC/Water |
| 220 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | CO2/LVC/Waste/Air-Q/Water |
| 221 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | CO2/Water/Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 222 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.8438 | 76 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 223 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8662 | 78 | high | Waste/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 224 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8662 | 78 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 225 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8662 | 78 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q |
| 226 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.8662 | 78 | high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q/Water |
| 227 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.8662 | 78 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Water |
| 228 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | LVC/Air-Q/Water/CO2/Waste |
| 229 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | Waste/LVC/Air-Q/CO2/Water |
| 230 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | Waste/Air-Q/Water/CO2/LVC |
| 231 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | Waste/LVC/Water/CO2/Air-Q |
| 232 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q/Waste/Water |
| 233 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | CO2/Air-Q/Water/Waste/LVC |
| 234 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | CO2/LVC/Water/Waste/Air-Q |
| 235 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q/LVC/Water |
| 236 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 237 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.8772 | 79 | high | CO2/Waste/Water/LVC/Air-Q |
| 238 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.9106 | 82 | very high | Waste/LVC/Air-Q/Water/CO2 |
| 239 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.9106 | 82 | very high | CO2/LVC/Air-Q/Water/Waste |
| 240 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.9106 | 82 | very high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
| 241 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.9106 | 82 | very high | CO2/Waste/Air-Q/Water/LVC |
| 242 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.9106 | 82 | very high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Water/Air-Q |
| 243 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 85 | very high | CO2/Waste/LVC/Air-Q/Water |
References
- Dyson, B.; Chang, N. Forecasting municipal solid waste generation in a fast-growing urban region with system dynamics modeling. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, D.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Kennedy, C. Waste production must peak this century. Nature 2013, 502, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Solid Waste Management; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, T.; Mookerjee, R. Population growth and global CO2 emissions: A secular perspective. Energy Policy 1996, 24, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neill, B.C.; Dalton, M.; Fuchs, R.; Jiang, L.; Pachauri, S.; Zigova, K. Global demographic trends and future carbon emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17521–17526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, A. Population growth and global carbon dioxide emissions. In Proceedings of the IUSSP Conference in Brazil/Session-s09, Salvador, Brazil, 18–24 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Niu, D.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Factors Affecting Transportation Sector CO2 Emissions Growth in China: An LMDI Decomposition Analysis. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsina, G.R.; Shrestha, A. Transport sector CO2 emissions growth in Asia: Underlying factors and policy options. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 4523–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyette, R.P.; Muzika, R.M.; Dey, D.C. Dynamics of an anthropogenic fire regime. Ecosystems 2002, 5, 472–486. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras-MacBeath, T.; Ongay-Delhumeau, E.; Sorani, D.V. Programa Estatal de Ordenamiento Territorial Sustentable de Morelos. Fases I,I y III; Incluyendo los Subsistemas Natural, Social y Económico: Cuernavaca, Morelos, México, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Environmental Indicators, Development, Measurement and Use. 2003. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/env/indicators-modelling-outlooks/24993546.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Kohsaka, R. Developing biodiversity indicators for cities: Applying the DPSIR model to Nagoya and integrating social and ecological aspects. Ecol. Res. 2010, 25, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristersen, P. The DPSIR framework. In Proceedings of the Workshop on a Comprehensive/Detailed Assessment of the Vulnerability of Water Resources to Environmental Change in Africa Using River Basin Approach, Nairobi, Kenya, 27–29 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Maureen, C.; Charles, G. The interaction of population growth and environmental quality. Am. Econ. Rev. 1994, 84, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Maxim, L.; Spangenberg, J.H.; O’Connor, M. An analysis of risks for biodiversity under the DPSIR framework. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 69, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezami, R.S.; Nazariha, M.; Moridi, A.; Baghvand, A. Environmentally sound water resources management in catchment level using DPSIR model and scenario analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2013, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Environmental Indicators: Towards Sustainable Development Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development; OECD Publicaction: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner, J.L. Improving human decision making through Case-Based Decision Aiding. AI Mag. 1991, 12, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner, J.L. An introduction to Case-Based Reasoning. Artif. Intell. Rev. 1992, 6, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansar, S.L.; Marir, F.; Reijers, H.A. Case-based reasoning as a technique for knowledge management in business process redesign. Electron. J. Knowl. Manag. 2003, 1, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.-H. Expert system methodologies and applications—A decade review from 1995 to 2004. Expert Syst. Appl. 2005, 28, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechitov, A.I.; Moshkovich, H.M.; Olson, D.L.; Killingsworth, B. Knowledge acquisition tool for case-based reasoning systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 1995, 9, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, R.; Kolodner, J.; Plaza, E. Representation in case-based reasoning. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2005, 20, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamodt, A. Knowledge-intensive case-based reasoning in creek. In European Conference on Case-Based Reasoning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Brink, P.J.; Roelsma, J.; Van Nes, E.H.; Scheffer, M.; Brock, T.C. Perpest model, a case-based reasoning approach to predict ecological risks of pesticides. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2002, 21, 2500–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, A.E.; El-Bendary, N.; Sweidan, A.H.; Mohamed, A.E.K.; Hegazy, O.M. Hybrid-biomarker case-based reasoning system for water pollution assessment in Abou Hammad Sharkia, Egypt. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2015, 46, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, J.; Guo, L.; Shi, B.; Liu, J.; Du, Z.; Wang, P. Screening of pollution control and clean-up materials for river chemical spills using the multiple case-based reasoning method with a difference-driven revision strategy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11247–11256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avesani, P.; Perini, A.; Ricci, F. Interactive case-based planning for forest fire management. Appl. Intell. 2000, 13, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, C.; Feng, X. Research on a soft measurement model of sewage treatment based on a case-based reasoning approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 3181–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazara, P.; Negny, S.; Montastruc, L. Flexible knowledge representation and new similarity measure: Application on case based reasoning for waste treatment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 58, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolodner, J.L.; Simpson, R.L.; Sycara-Cyranski, K. A Process Model of Cased-Based Reasoning in Problem Solving; School of Information and Computer Science, Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Aamodt, A.; Plaza, E. Case-based reasoning: Foundational issues, methodological variations, and system approaches. AI Commun. 1994, 7, 35–59. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés, U.; Sànchez-Marrè, M.; Ceccaroni, L.; Roda, I.R.; Poch, M. Artificial intelligence and environmental decision support systems. Appl. Intell. 2000, 13, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Jakeman, A.J.; Norton, J.P. Artificial Intelligence techniques: An introduction to their use for modelling environmental systems. Math. Comput. Simul. 2008, 78, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Ahmed, M.U.; Funk, P.; Xiong, N.; Folke, M. Case-Based Reasoning Systems in the Health Sciences: A Survey of Recent Trends and Developments. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2011, 41, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiker, G.A.; Bridges, T.S.; Varghese, A.; Seager, T.P.; Linkov, I. Application of multicriteria decision analysis in environmental decision making. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. Int. J. 2005, 1, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daengdej, J.; Lukose, D.; Murison, R. Using statistical models and case-based reasoning in claims prediction: Experience from a real-world problem. Knowl. Based Syst. 1999, 12, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Xu, X.; Dey, P.K. Multi-criteria decision making approaches for supplier evaluation and selection: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 202, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.L.; Lee, W.B.; Lo, V. A knowledge-based supplier intelligence retrieval system for outsource manufacturing. Knowl. Based Syst. 2005, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, M.; Hester, P.T. An analysis of multi-criteria decision making methods. Int. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 10, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Kang, S. A Method of assigning weights using a ranking and nonhierarchy comparison. Adv. Decis. Sci. 2016, 2016, 8963214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahroodi, K.; Amin, K.; Shabnam, A.; Elnaz, S.; Najibzadeh, M. Application of analytical hierarchy process (ahp) technique to evaluate and selecting suppliers in an effective supply chain. Kuwait Chapter Arab. J. Bus. Manag. Rev. 2012, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Environmental Outlook to 2030. 2008. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/env/indicators-modelling-outlooks/40200582.pdf. (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Ramos-Quintana, F.; Sotelo-Nava, H.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.; Tovar-Sánchez, E. Assessing the Environmental Quality Resulting from Damages to Human-Nature Interactions Caused by Population Increase: A Systems Thinking Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEGI. Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía; Perspectiva estadística: Aguascalientes, Mexico, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI. Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. 2016. Available online: http://www3.inegi.org.mx (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- SCT. Secretaría de Comunicaciones y Transportes. Anuario Estadístico 2011. Mexico. 2012. Available online: http://www.sct.gob.mx/planeacion/estadistica/anuario-estadistico-sct/ (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- SEMARNAT. Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales, Comisión Nacional Forestal, Gerencia de Incendios Forestales (SEMARNAT). 2012. Available online: http://www.conafor.gob.mx/web/temas-forestales/ (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- GFW. Global Forest Watch. 2014. Available online: http://www.globalforestwatch.org (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales—Comisión Nacional del Agua (SEMARNAT-CONAGUA). Programa Hídrico Visión 2030 del Estado de Morelos; Comisión Nacional del Agua: Mexico City, Mexico, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- SNIARNF-SEMARNAT. Sistema Nacional de Información Ambiental y de Recursos Naturales (Módulo de Consulta Temática, Dimensión Ambiental, Generación de Residuos Sólidos Urbanos. 2012. Available online: http://dgeiawf.semarnat.gob.mx (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- UNFCCC. United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. 2014. Available online: http://unfccc.int/national_reports/nonannex_i_natcom/training_material/methodological_documents/items/349.php (accessed on 15 January 17).
- Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D. HYSPLIT—Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory Model. Available online: http://www.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- Núnez, H.; Sánchez-Marré, M.; Cortez, U.; Comas, J.; Martínez, M.; Rodríguez-Roda, I.; Poch, M. A comparative study on the use of similarity measures in case-based reasoning to improve the classification of environmental systems situations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 19, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, N.J. Varieties of knowledge elicitation techniques. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 1994, 41, 801–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, J.E. Knowledge Elicitation Tool Classification; Artificial Intelligence Research Group, Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Haruhiko, K.; Saeki, M. Using domain ontology as domain knowledge for requirements elicitation. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Requirements Engineering Conference (RE’06), Minneapolis/St. Paul, MN, USA, 11–15 September 2006; pp. 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilova, T.; Andreeva, T. Knowledge elicitation techniques in a knowledge management context. J. Knowl. Manag. 2012, 16, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalbolt, N.; Smart, P.R.; Wilson, J.R.; Sharples, S. Knowledge elicitation. Eval. Hum. Work 2015, 163–200. [Google Scholar]
- Laurinen, P.; Siirtola, P.; Röning, J. Efficient Algorithm for Calculating Similarity between Trajectories Containing an Increasing Dimension. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2006, 392–399. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/2865/98957a6fddd986849401dc39a22888f48713.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2019).
- García Romero, H. Payments for Environmental Services: Can They Work? Field Actions Science Reports [Online]. 2012. Available online: http://journals.openedition.org/factsreports/1711 (accessed on 27 June 2012).
- Marie, A.G.; de Janvry, A.; Sadoulet, E. Payments for Environmental Services: To whom, where, and how much? Am. Agric. Econ. Assoc. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevochtchikova, M.; Tamayo, O.; Milena, A. Avances y limitantes del programa de pago de servicios ambientales hidrológicos en México, 2003–2009. Rev. Mex. Cienc. For. 2012, 3, 89–112. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia-Silva, F.O. Advances in Geomatics and Geospatial Technologies to Solve Water Problems in Mexico. In Water Resources in Mexico. Scarcity, Degradation, Stress, Conflicts, Management, and Policy; Oswald-Spring, U., Ed.; Springer: Belinn/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; p. 524. [Google Scholar]
- Tortajada, C. Water management in Mexico City metropolitan area. Water Resour. Dev. 2006, 22, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Arias, M.; Riojas-Rodríguez, H.; Catalan-Vázquez, M.; Terrazas-Meraz, M.A.; Rosas, I.; Espinosa-García, A.C.; Santo-Luna, R.; Siebe, C. Socio-environmental assessment of a landfill using a mixed study design: A case study from México. Waste Manag. 2019, 85, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, L.E.; Torres, V.; Bolongaro, A.; Reyna, J.A.; Pohle, O.; Hernández-Espriú, A.; Tabla, H.F.P. Identifying suitable sanitary landfill locations in the state of Morelos, México, using a Geographic Information System. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2012, 37, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefson, J. Clock ticking in climate action. Nature 2018, 562, 172–173. Available online: https://www.nature.com/magazine-assets/d41586-018-06876-2/d41586-018-06876-2.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2019). [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers of IPCC Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C approved by governments. Available online: https://archive.ipcc.ch/pdf/session48/pr_181008_P48_spm_en.pd (accessed on 12 June 2019).
| Causal Relationships | Equations of the Interpolated Straight Line | B1 Expressed in Tangent Values | B1 Expressed in Angular Values | B1 Expressed in Normalized Values | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔPop → ΔCO2 | y = 4.7 + 2.5x | 2.5 | 68.4° | 0.76 | 0.92 |
| ΔPop → ΔTrans-Ve | y = 8.45 + 7.8x | 7.8 | 82.7° | 0.92 | 0.99 |
| ΔPop → ΔSol-Was | y = 5.14 + 1.7x | 1.7 | 59.7° | 0.66 | 0.83 |
| ΔPop → −ΔWat-Av | y = 0.03 + 2.5x | 2.5 | 68.1° | 0.76 | 0.81 |
| ΔPop → ΔAir-Q | y = 7.2 + 0.4x | 0.4 | 22.7° | 0.25 | 0.07 |
| ΔPop → ΔFF | y = 294 + 23.3x | 23.3 | 87.5° | 0.97 | 0.41 |
| ΔPop → ΔTrans-Ro | y = 4.4 + 2.8x | 2.8 | 70.2° | 0.78 | 0.80 |
| ΔTrans-Ve → ΔCO2 | y = 1.8 + 0.3x | 0.3 | 17.6° | 0.20 | 0.94 |
| ΔFF → ΔLVC | y = 57 + 1.1x | 1.1 | 48.8° | 0.54 | 0.61 |
| ΔTrans-Ro → ΔLVC | y = 276 + 13.9x | 13.9 | 85.9° | 0.95 | 0.65 |
| KEPs | Sequence of Relationships Representing the KEPs |
|---|---|
| Path_Sol-Was | ΔPop → ΔSol-Was → GES |
| Path_Water-Av | ΔPop →-ΔWat-Av → GES |
| Path_Air-Q | ΔPop → ΔAir-Q → GES |
| Path_CO2 | (((ΔPop → Trans-Ve) ∧ (ΔTrans-Ve → ΔCO2)) + (ΔPop → ΔCO2)) → GES |
| Path_LVC | (((ΔPop → ΔFF) ∧ (ΔFF → ΔLVC)) + ((ΔPop → ΔTrans-Ro) ∧ (ΔTrans-Ro → LVC))) → GES |
| Regions at Risk | Ranges in Angular Values | Centroid in Angular Values | Ranges in Normalized Values | Centroid in Normalized Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region at very low risk | (0°, 20°) | 10° | (0, 0.222) | 0.111 |
| Region at low risk | (20°, 40°) | 30° | (0.222, 0.444) | 0.333 |
| Region at medium risk | (40°, 60°) | 50° | (0.444,0.666) | 0.555 |
| Region at high risk | (60°, 80°) | 70° | (0.666, 0.888) | 0.777 |
| Region at very high risk | (80°, ∞) | 85° | (0.888, 1] | 0.944 |
| Questions |
|---|
| Question 1. What implementable EMAs related to the different environmental variables provide the major benefit to the current environmental quality of the region? |
| Question 2. What key environmental variable has the major influence or effects on the remaining key environmental variables being considered? |
| Question 3. Based on the real situation of the region under study: which of the EMAs associated with key environmental variables are more feasible to be implemented, from the socioeconomic, sociopolitical and technical point of view? |
| Question 4. In the case of the implementation of EMAs, what key environmental variable would have a major positive effect on the improvement of the environmental quality, considering the OECD-Outlook toward the future (2030)? |
| Question 5. What KEV of this study represents the most international concern? |
| Questions | Path_CO2 | Path_Air-Q | Path_LVC | Path_Sol-Waste | Path_Wat-Av | Average of the Points Assigned to Questions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Question 1 | 2.48 | 1.92 | 3.92 | 2.72 | 3.92 | 2.992 |
| Question 2 | 2.84 | 2.00 | 4.32 | 2.32 | 3.56 | 3.008 |
| Question 3 | 2.08 | 1.76 | 4.16 | 3.80 | 3.08 | 2.976 |
| Question 4 | 2.40 | 1.60 | 4.28 | 2.80 | 3.76 | 2.968 |
| Question 5 | 3.92 | 1.84 | 2.96 | 2.32 | 4.24 | 3.056 |
| Average of KEPs | 2.744 | 1.824 | 3.928 | 2.792 | 3.712 |
| Situation | CO2 | Waste | Water | LVC | Air-Q | GES (Angular Value) | Similarity Value | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Situation Norm. values | 0.720 | 0.830 | 0.630 | 0.882 | 0.500 | 0.712 | ||
| Current Situation Angular values | 64.8° | 74.7° | 56.7° | 79.38° | 45° | 64.11° | ||
| S81 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 65° | 0.0628 | LVC/CO2/Waste |
| S50 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 62° | 0.0682 | CO2/Waste/Water |
| S113 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 68° | 0.0734 | Waste/LVC/CO2 |
| S84 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 65° | 0.0780 | Waste/CO2/LVC |
| S29 | 0.555 | 0.777 | 0.555 | 0.944 | 0.555 | 61° | 0.0925 | LVC/Waste |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramos-Quintana, F.; Tovar-Sánchez, E.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.; Sotelo-Nava, H.; Sánchez-Hernández, J.P.; Castrejón-Godínez, M.-L. A CBR–AHP Hybrid Method to Support the Decision-Making Process in the Selection of Environmental Management Actions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5649. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205649
Ramos-Quintana F, Tovar-Sánchez E, Saldarriaga-Noreña H, Sotelo-Nava H, Sánchez-Hernández JP, Castrejón-Godínez M-L. A CBR–AHP Hybrid Method to Support the Decision-Making Process in the Selection of Environmental Management Actions. Sustainability. 2019; 11(20):5649. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205649
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos-Quintana, Fernando, Efraín Tovar-Sánchez, Hugo Saldarriaga-Noreña, Héctor Sotelo-Nava, Juan Paulo Sánchez-Hernández, and María-Luisa Castrejón-Godínez. 2019. "A CBR–AHP Hybrid Method to Support the Decision-Making Process in the Selection of Environmental Management Actions" Sustainability 11, no. 20: 5649. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205649
APA StyleRamos-Quintana, F., Tovar-Sánchez, E., Saldarriaga-Noreña, H., Sotelo-Nava, H., Sánchez-Hernández, J. P., & Castrejón-Godínez, M.-L. (2019). A CBR–AHP Hybrid Method to Support the Decision-Making Process in the Selection of Environmental Management Actions. Sustainability, 11(20), 5649. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205649








