Does Urban Sprawl Inhibit Urban Eco-Efficiency? Empirical Studies of Super-Efficiency and Threshold Regression Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review of the Mechanisms of the Impact of Urban Sprawl on Eco-Efficiency
3. Methods and Data Collection
3.1. Measurement of the Eco-Efficiency by Data Envelopment Analysis
3.1.1. Methods
3.1.2. Indicators for the Super-Efficiency DEA Model
3.2. Factors that Influence Eco-Efficiency in the Tobit Model
3.2.1. Model Construction
3.2.2. Variable Selection for the Tobit Model
3.3. Threshold Model Setting
4. Results
4.1. The Overall Urban Sprawl Situation in China
4.2. Eco-Efficiency Results
4.3. Results of the Panel Tobit Model
4.3.1. Establishment of the Benchmark Regression Model
4.3.2. Regional Analysis of the Panel Tobit Model
4.4. Threshold Regression Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistical Bulletin of National Economic and Social Development; National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- National New-Type Urbanization Plan (2014–2020); National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Outline of the Thirteenth Five Year Plan for Nationality Law of the People’s Republic of China; National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Hao, J.; Wang, L. Improving Urban Air Quality in China: Beijing Case Study. J. Air Waste Manag. 2005, 9, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulletin on the State of Ecological Environment in China; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Whyte, W.H. Urban Sprawl: The Exploding Metropolis; Doubleday: New York, NY, USA, 1958; pp. 133–156. [Google Scholar]
- Gottmann, J.; Robert, A.H. Metropolis on the Move: Geographers Look at Urban Sprawl. In New York: Twentieth Century Fund; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Downs, A. New Visions for Metropolitan America, The Brookings Institution and Lincoln Institution of Land Policy; Lincoln Institute of Land Policy: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Burchell, R.W. The Costs of Sprawl-Revisited; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, W.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Driving Forces of Urban Sprawl in China During 2003–2017. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, F. Urban sprawl in China: Differences and socioeconomic drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, B.; Saurí, D.; Serra, P. Urban sprawl in the Mediterranean? Patterns of growth and change in the Barcelona Metropolitan Region 1993–2000. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 85, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Aggarwal, S.P.; Netzband, M.; Fazal, S. Monitoring urban sprawl using remote sensing and gis techniques of a fast growing urban centre, India. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, B.N.; Partridge, M.D.; Olfert, M.R. Urban sprawl and productivity: Evidence from US metropolitan areas. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2011, 90, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behan, K.; Maoh, H.; Kanaroglou, P. Smart growth strategies, transportation and urban sprawl: Simulated futures for Hamilton, Ontario. Can. Geograph. 2010, 52, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Xia, Z.G.; Clarke, K.C.; Frei, A. Impact of urban sprawl on water quality in eastern Massachusetts, USA. Environ. Manag. 2007, 40, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eco-Efficiency Indicators: Measuring Resource-Use Efficiency and the Impact of Economic Activities on the Environment. United Nations, Economic and Social Commission for Asia and Pacific (ESCAP); ESCAP: Bangkok, Thailand, 2009.
- Burritt, R.L.; Saka, C. Environmental management accounting applications and eco-efficiency: Case studies from Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, R.; An, Q.; Yao, L.; Liang, J. Using eco-efficiency as an indicator for sustainable urban development: A case study of Chinese provincial capital cities. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Hao, S.; Sun, C.; Lyu, L. Spatial Correlation and Convergence Analysis of Eco-Efficiency in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, D.; Yin, J.; Chen, X.; Bao, A.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X. The effects of ecological policy of Kyrgyzstan based on data envelope analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Arp, H.P. Examination of the relationship between urban form and urban eco-efficiency in China. Habitat Int. 2012, 36, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Liu, Y.; Stein, A.; Jiao, L. Characterization and Spatial modeling of urban sprawl in the Wuhan Metropolitan Area, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform. 2015, 34, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaigné, C.; Riou, S.; Thisse, J. Are compact cities environmentally friendly? J. Urban Econ. 2012, 72, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, M.V.; Hilber, C.A.L.; Schöni, O. Institutional Settings and Urban Sprawl: Evidence from Europe. J. Hous. Econ. 2018, 42, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckner, J.K.; Largey, A.G. Social interaction and urban sprawl. J. Urban Econ. 2008, 64, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, M.; Hong, H.; Sajjad, H. Analyzing urban spatial patterns and trend of urban growth using urban sprawl matrix: A study on Kolkata urban agglomeration, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holcombe, R.G.; Williams, D.W. Urban sprawl and transportation externalities. Rev. Reg. Stud. 2010, 40, 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Q.; DeSalvo, J.S. The effect of transportation subsidies on urban sprawl. J Regional Sci. 2008, 48, 567–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshi, F.; Ji-Hwan, H.; Akihiko, K.; Hiroshi, N.; Motoki, T.; Kazuo, S.Y. JBIR-44, a new bromotyrosine compound from a marine sponge Psammaplysilla purpurea. J. Antibiotics. 2009, 62, 393–395. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, B.; Tousi, S.N. An explanation of urban sprawl phenomenon in shiraz metropolitan area (SMA). Cities 2018, 73, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandelli, D.I.; Dupas, F.A.; Dias, P.N.A. Dynamics of urban sprawl, vacant land, and green spaces on the metropolitan fringe of São Paulo, Brazil. J. Urban Plan Dev. 2013, 139, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Yu, M. Discerning fragmentation dynamics of tropical forest and wetland during reforestation, urban sprawl, and policy shifts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Dijkema, G.P.J.; de Jong, M.; Shi, H. From an eco-industrial park towards an eco-city: A case study in Suzhou, China. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 102, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. The effects of urban sprawl and industrial agglomeration on environmental efficiency: Evidence from the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Baležentis, T.; Tian, Z.; Shao, S.; Geng, Y.; Wu, R. Environmental performance and regulation effect of China’s atmospheric pollutant emissions: Evidence from “three regions and ten urban agglomerations”. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 74, 211–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, P.; Yue, W.; Song, Y. Impacts of land finance on urban sprawl in China: The case of Chongqing. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, S. Spatiotemporal dynamics of urban expansion in 13 cities across the jing-jin-ji urban agglomeration from 1978 to 2015. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sickles, R.C.; Zelenyuk, V. Measurement of Productivity and Efficiency; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-107-03616-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Hansson, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, R. Implementing stricter environmental regulation to enhance eco-efficiency and sustainability: A case study of Shandong Province’s pulp and paper industry, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, P.; Guo, S. Assessing the Eco-Efficiency of a Circular Economy System in China’s Coal Mining Areas: Emergy and Data Envelopment Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Cheng, B. The eco-efficiency of pulp and paper industry in china: An assessment based on slacks-based measure and Malmquist–Luenberger index. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liang, L.; Zhu, J. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis: A comment. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 204, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.J.; Omrani, H.; Abdollahzadeh, S.; Alinaghian, M.; Mohammadi, H. A Robust Super-Efficiency Data Envelopment Analysis Model for Ranking of Provincial Gas Companies in Iran. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 10875–10881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, W.D.; Tone, K.; Zhu, J. Data envelopment analysis: Prior to choosing a model. Omega 2014, 44, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 44, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper Res. 1979, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, R.; Meghir, C. Bivariate alternatives to the Tobit model. J. Econometrics 1987, 34, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B.; Saraswati, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Urban sprawl measurement from remote sensing data. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 30, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feranec, J.; Jaffrain, G.; Soukup, T.; Hazeu, G. Determining changes and flows in European landscapes 1990–2000 using CORINE land cover data. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batisani, N.; Yarnal, B. Urban expansion in Centre County, Pennsylvania: Spatial dynamics and landscape transformations. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.; Pendall, R.; Chen, D. Measuring Sprawl and Its Impacts; Smart Growth America: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 57, pp. 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ren, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M. Quantifying urban land sprawl and its driving forces in Northeast China from 1990 to 2015. Sustainability 2018, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Inference when a nuisance parameter is not identified under the null hypothesis. J. Econ. Soc. 1996, 2, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notice on Adjusting the Standards for the Division of City Size; State Council of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Wu, B.; Qian, J.; Zeng, Y.; Qian, J.K. Land Cover Atlas of the People’s Republic of China (1:1,000,000); Sino Maps Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, N.; Friedman, L.; Sinuany-Stern, Z. Review of ranking methods in the data envelopment analysis context. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 140, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Qi, W.; Jin, H. Urban sprawl among Chinese cities of different population sizes. Habitat Int. 2018, 79, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, P. Measuring urban sprawl and its drivers in large Chinese cities: The case of Hangzhou. Land Use Policy 2013, 31, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.V. Marshall’s scale economies. J. Urban Econ. 2001, 53, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, J.E.; Lathrop, R.G. Land Resource Impact Indicators of Urban Sprawl. Appl. Geogr. 2003, 23, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garouani, A.E.; Mulla, D.J.; Garouani, S.E.; Knight, J. Analysis of urban growth and sprawl from remote sensing data: Case of Fez, Morocco. Int. J. Sust. Built Environ. 2017, 6, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
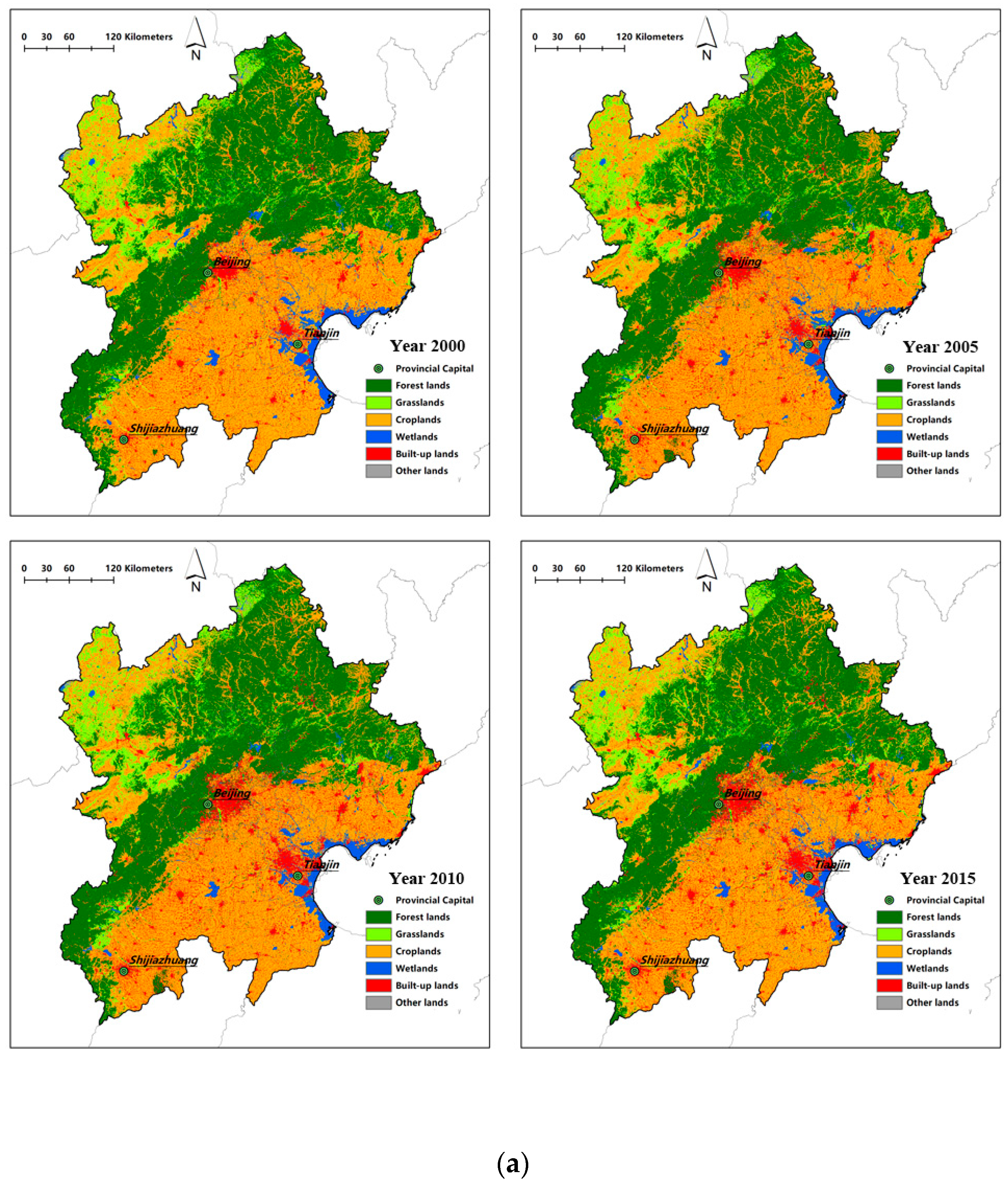
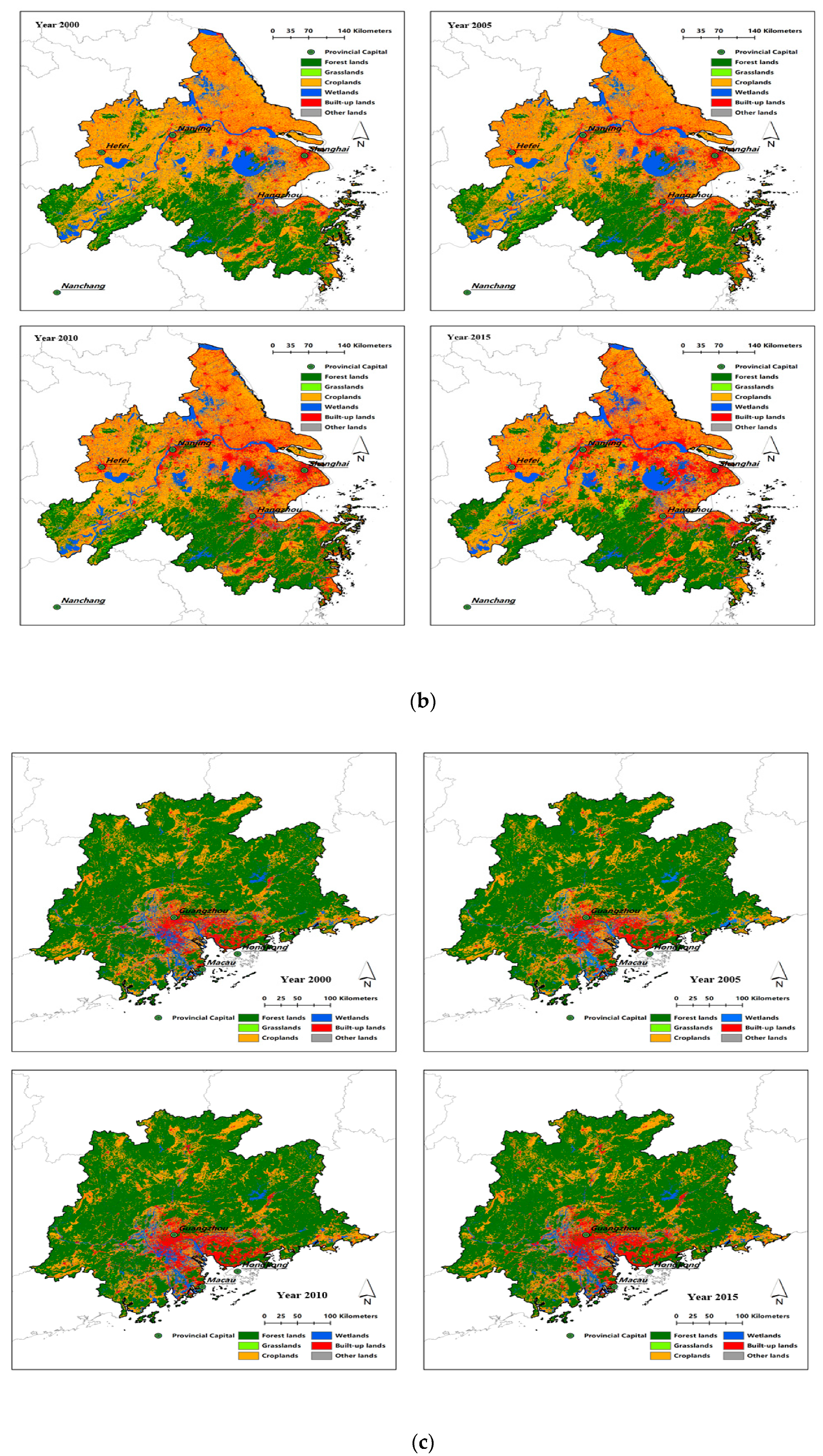

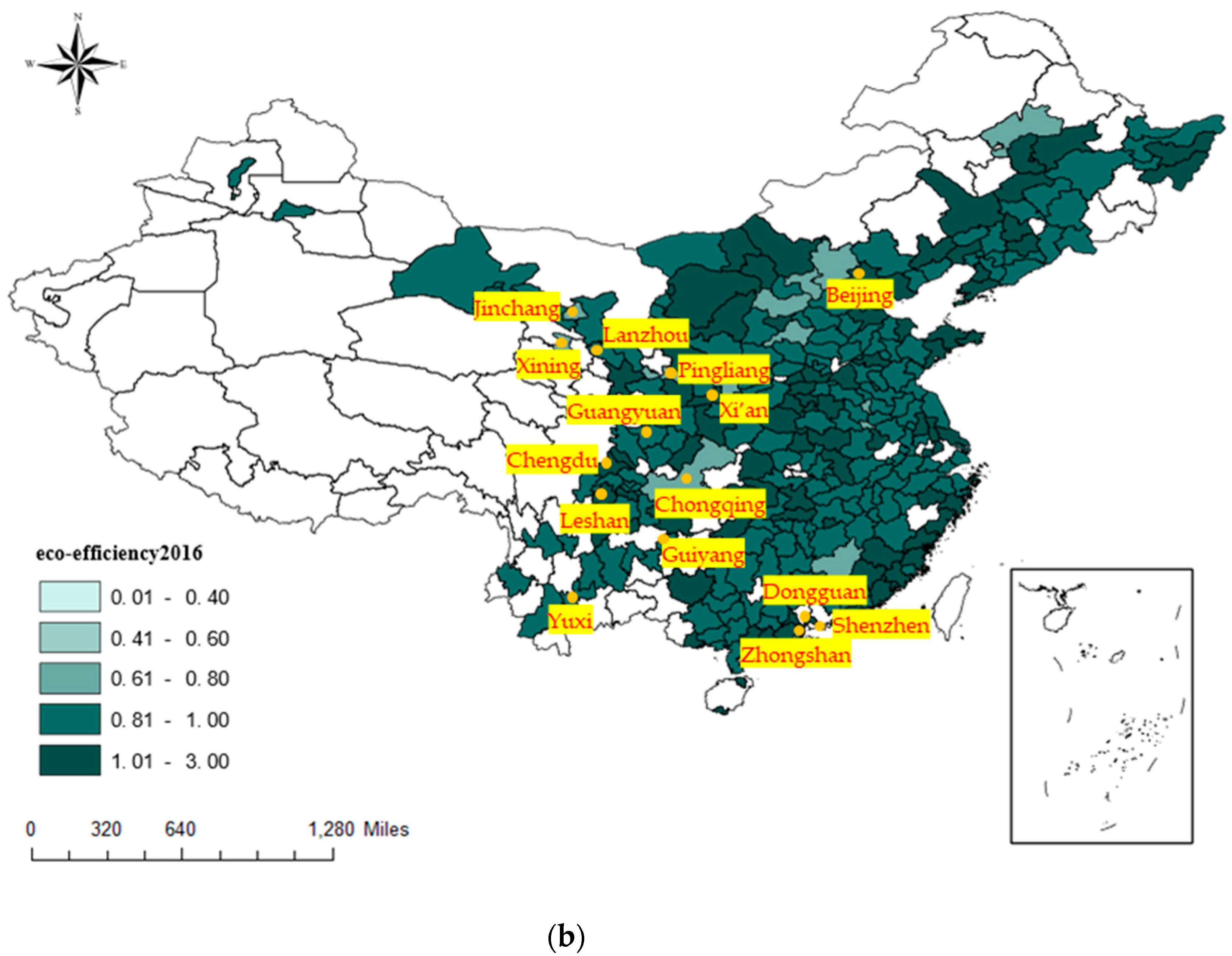
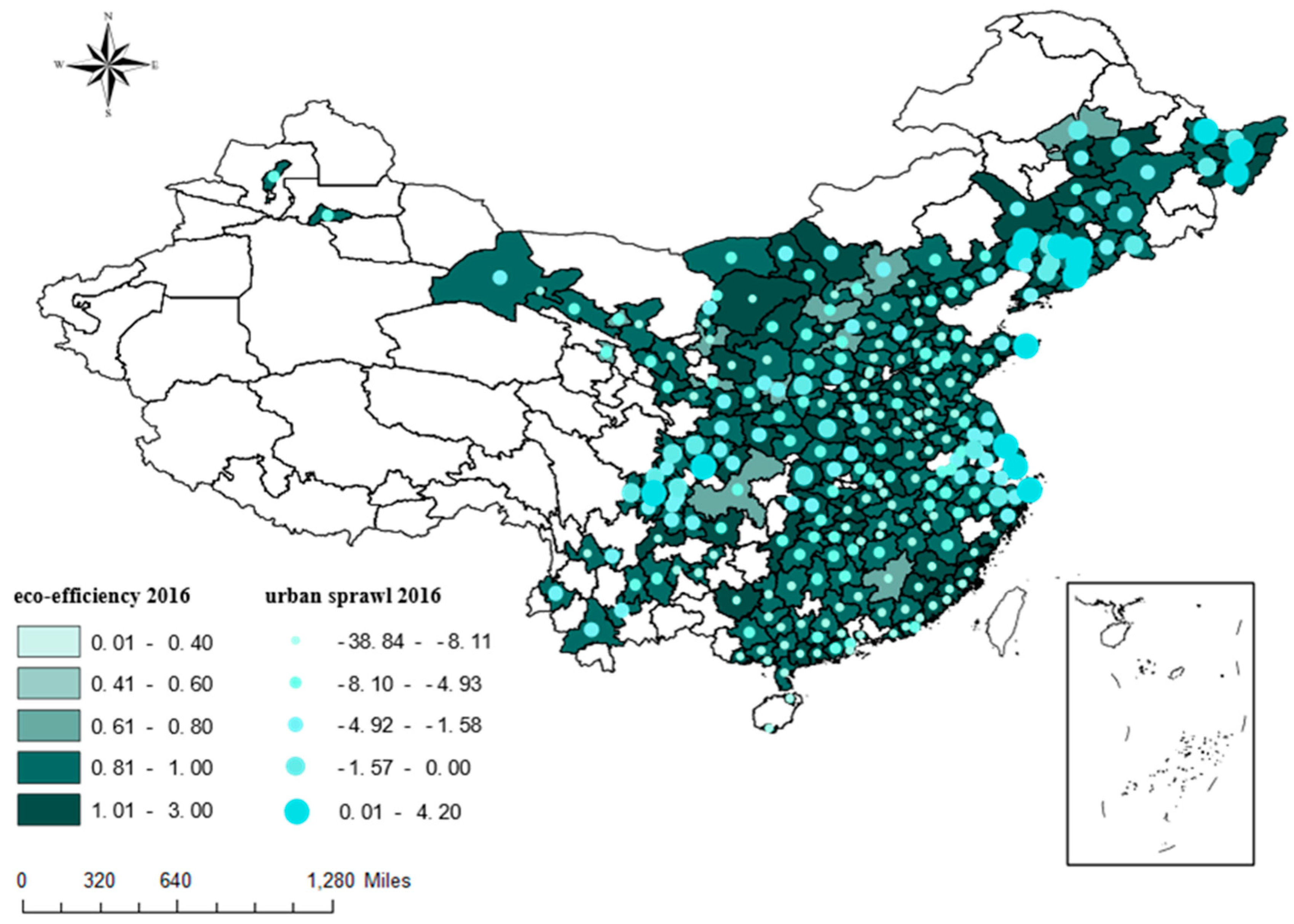

| Variable Classification | Variable Name | Variable Explanation | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | ecoit | Eco-efficiency | DEA model results |
| Independent variable | cityit | Urban sprawl level | China Urban Database |
| Control variable | rgdpit | Growth rate of GDP | China Regional Economic Database |
| pgpdit | GDP per capita | China Regional Economic Database | |
| technoit | Number of scientific researchers and technical service personnel | China Urban Database | |
| perrelecit | Electricity consumption per unit output | China Urban Database | |
| pepit | Year-end population | China Regional Economic Database | |
| fdiit | Foreign direct investment | China Regional Economic Database |
| Model | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | National Level | Eastern Cities | Central Cities | Western Cities | |
| city | −0.00701 *** | −0.0100 *** | −0.00570 * | −0.00455 | |
| (−3.33) | (−2.63) | (−1.96) | (−1.21) | ||
| pgdp | 0.0211 *** | −0.00222 | 0.0464 *** | 0.0454 *** | |
| (6.87) | (−0.42) | (10.72) | (5.99) | ||
| techno | 0.0995 *** | 0.104 *** | 0.0395 * | 0.120 *** | |
| (15.24) | (12.18) | (1.74) | (4.74) | ||
| pep | −0.0354 *** | −0.0668 *** | 0.00465 | −0.0588 *** | |
| (−4.65) | (−4.16) | (0.47) | (−4.14) | ||
| fdi | 0.0159 *** | 0.00996 ** | −0.00705 | 0.0542 *** | |
| (4.35) | (2.00) | (−0.77) | (5.52) | ||
| rgdp | −0.00186 | −0.00810 ** | 0.00760 *** | −0.000480 | |
| (−0.96) | (−2.29) | (3.18) | (−0.12) | ||
| perelec | −0.0149 *** | −0.0561 *** | −0.00948 * | −0.00578 | |
| (−4.53) | (−4.91) | (−1.69) | (−1.41) | ||
| _cons | 0.946 *** | 0.966 *** | 0.927 *** | 0.960 *** | |
| (126.76) | (73.15) | (111.15) | (51.03) | ||
| N | 3668 | 1484 | 1414 | 770 | |
| Critical Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Value | P Value | 1% | 5% | 10% | |
| Single threshold test | 8.646 ** | 0.017 | 10.489 | 5.522 | 3.266 |
| Double threshold test | 29.963 *** | 0.000 | 10.753 | 6.674 | 4.645 |
| Variables | Results | |
|---|---|---|
| K1 | −0.0408 *** (−3.60) | |
| City | K2 | −0.00846 *** (−3.56) |
| K3 | −0.0747 *** (−5.34) | |
| pgdp | 0.0215 *** (6.77) | |
| techno | 0.0442 *** (6.66) | |
| fdi | −0.000746 (−0.19) | |
| rgdp | −0.00202 (−0.91) | |
| Perelec | −0.0311 *** (−11.38) | |
| pep | −0.0273 *** (−7.58) | |
| _cons | 0.945 *** (485.44) | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, B.; Yu, C.; Yang, Y. Does Urban Sprawl Inhibit Urban Eco-Efficiency? Empirical Studies of Super-Efficiency and Threshold Regression Models. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5598. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205598
Zhang Q, Zhang H, Zhao D, Cheng B, Yu C, Yang Y. Does Urban Sprawl Inhibit Urban Eco-Efficiency? Empirical Studies of Super-Efficiency and Threshold Regression Models. Sustainability. 2019; 11(20):5598. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205598
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qian, Huaxing Zhang, Dan Zhao, Baodong Cheng, Chang Yu, and Yanli Yang. 2019. "Does Urban Sprawl Inhibit Urban Eco-Efficiency? Empirical Studies of Super-Efficiency and Threshold Regression Models" Sustainability 11, no. 20: 5598. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205598
APA StyleZhang, Q., Zhang, H., Zhao, D., Cheng, B., Yu, C., & Yang, Y. (2019). Does Urban Sprawl Inhibit Urban Eco-Efficiency? Empirical Studies of Super-Efficiency and Threshold Regression Models. Sustainability, 11(20), 5598. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205598




