A Spatio-Temporal Autowave Model of Shanghai Territory Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
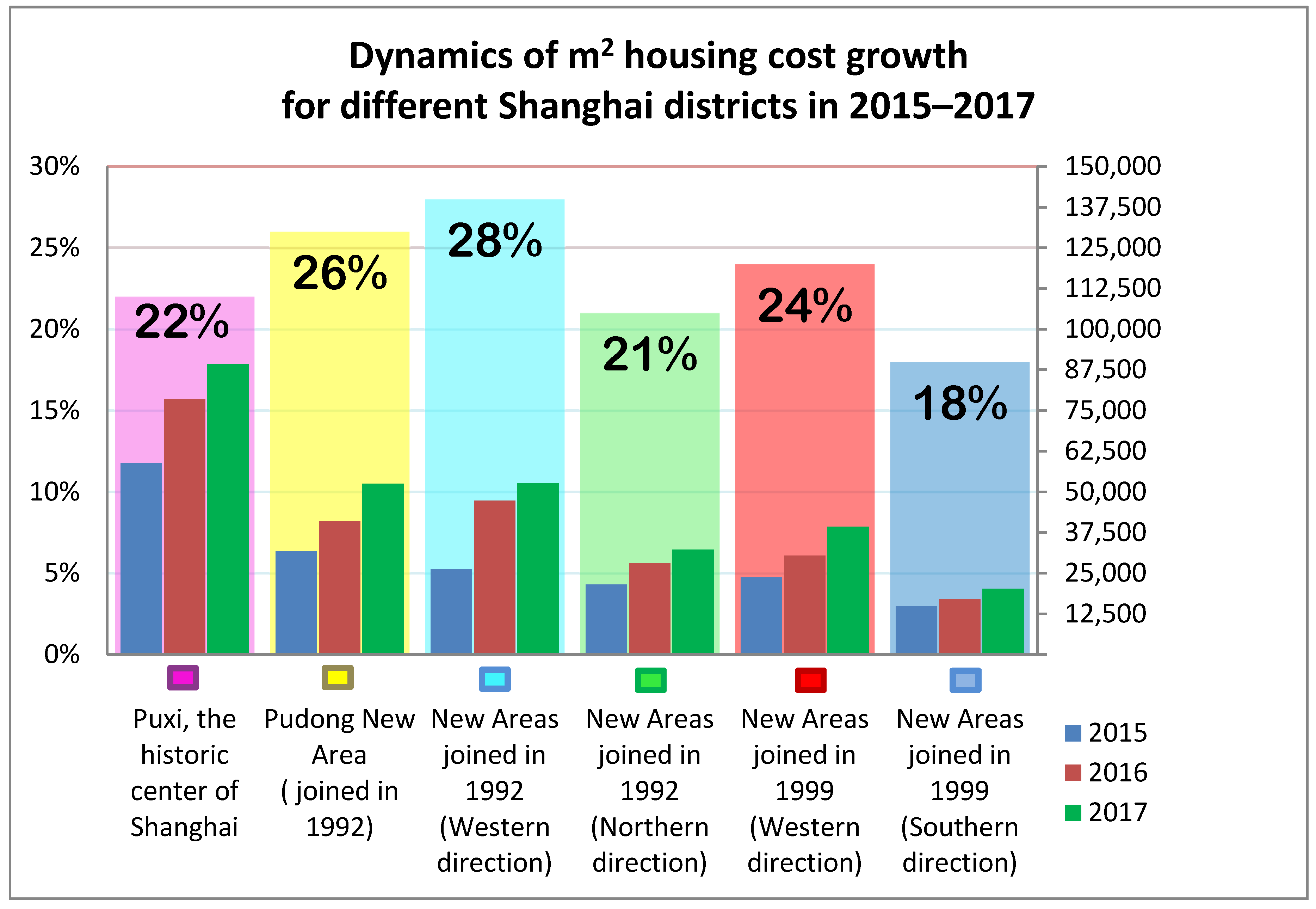
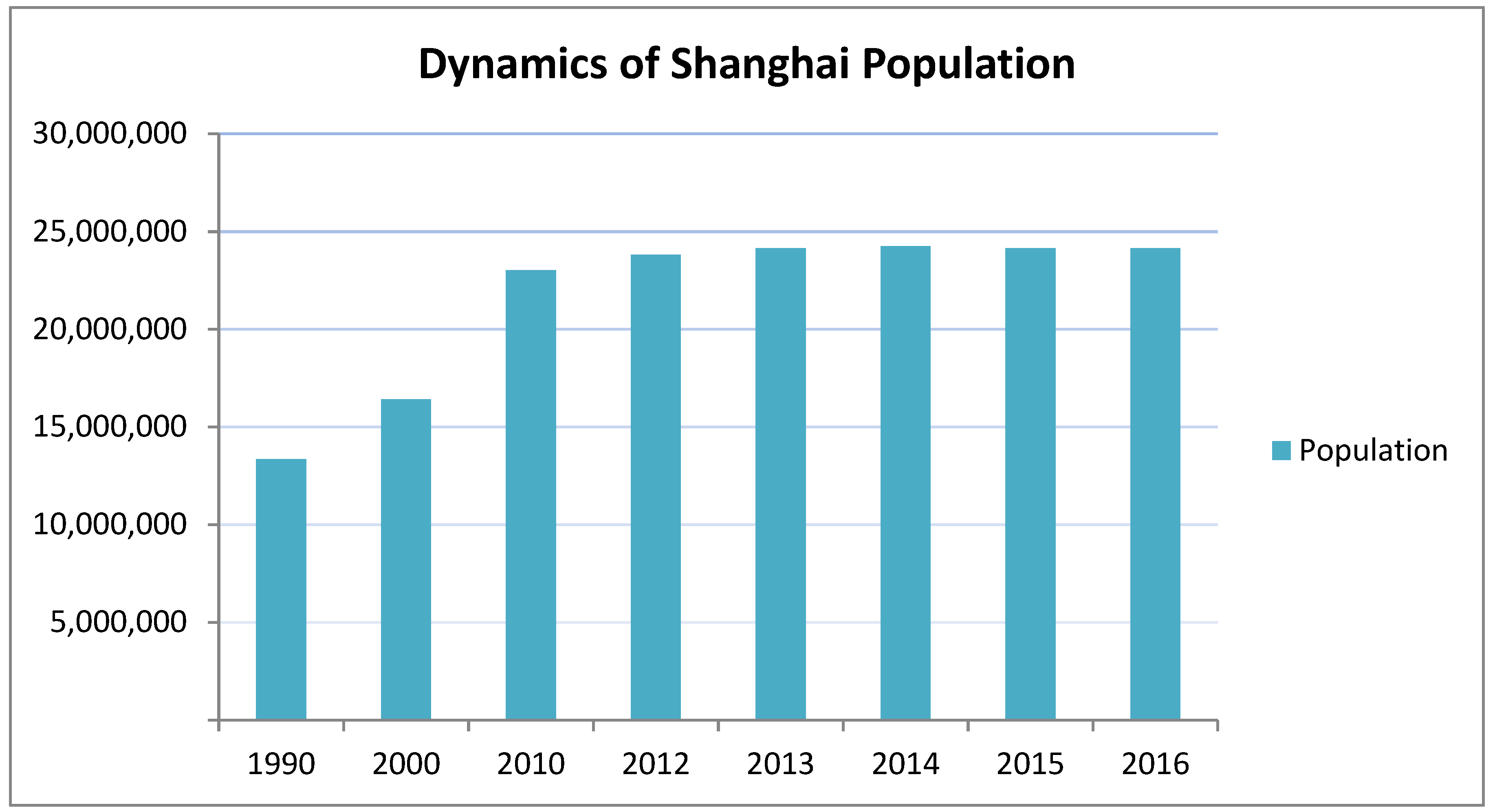
2.1. Object of Study
The Choice of the Inhibitor
2.2. Theoretical Background of a Spatio-Temporal Model of Shanghai Development
2.3. The Study Methodology
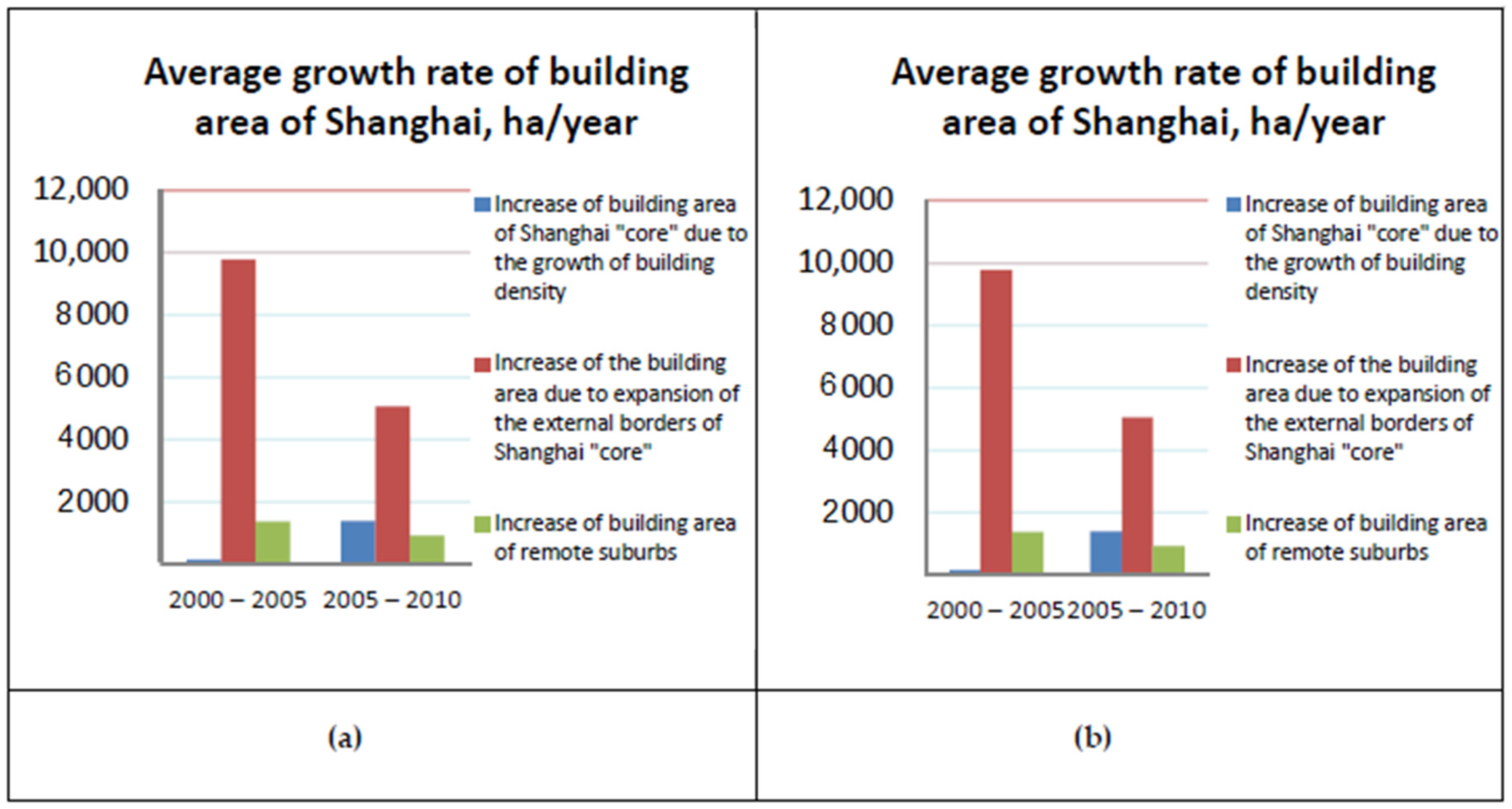
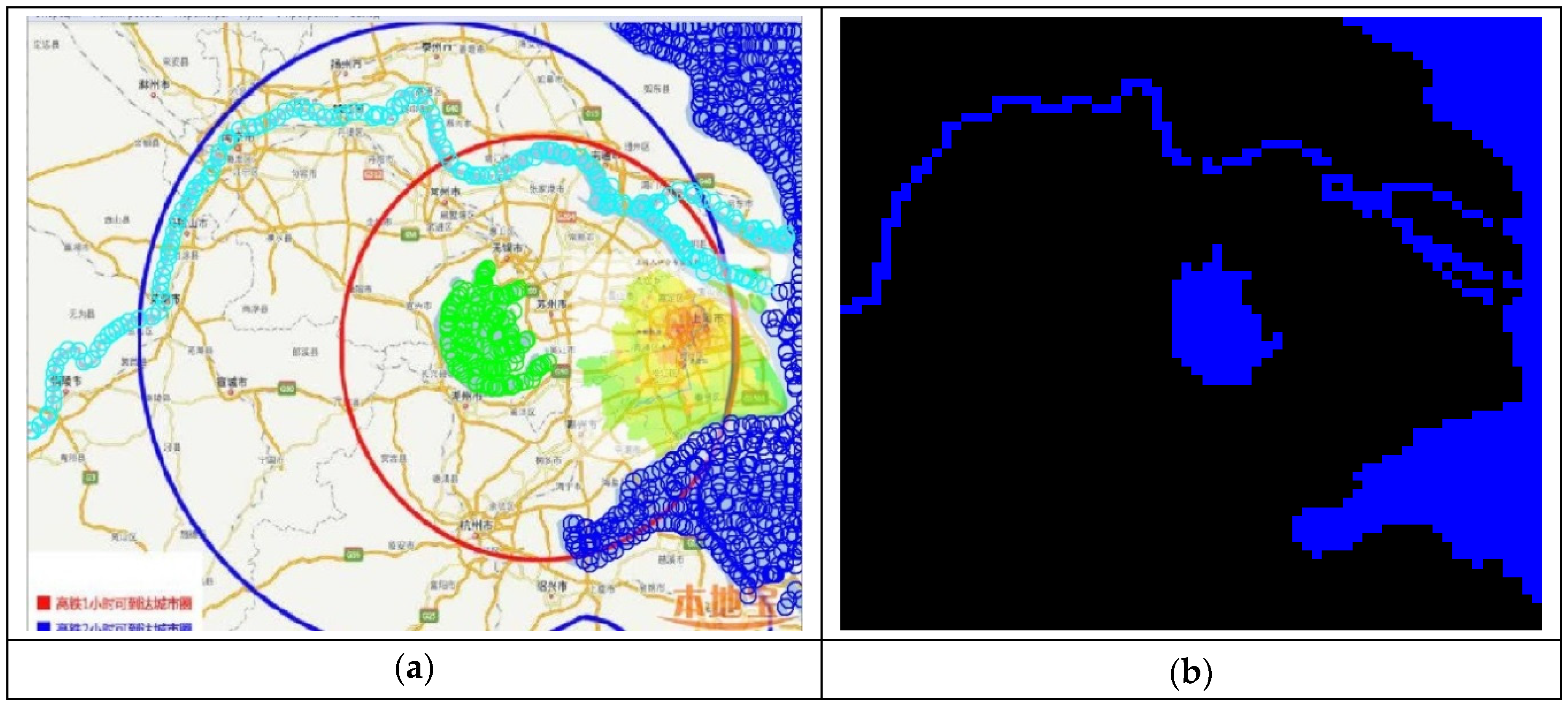
2.3.1. Map Data Processing
2.3.2. The Choice of Model Parameters
2.3.3. The Method of Numerical Solution
3. Results
4. Discussion
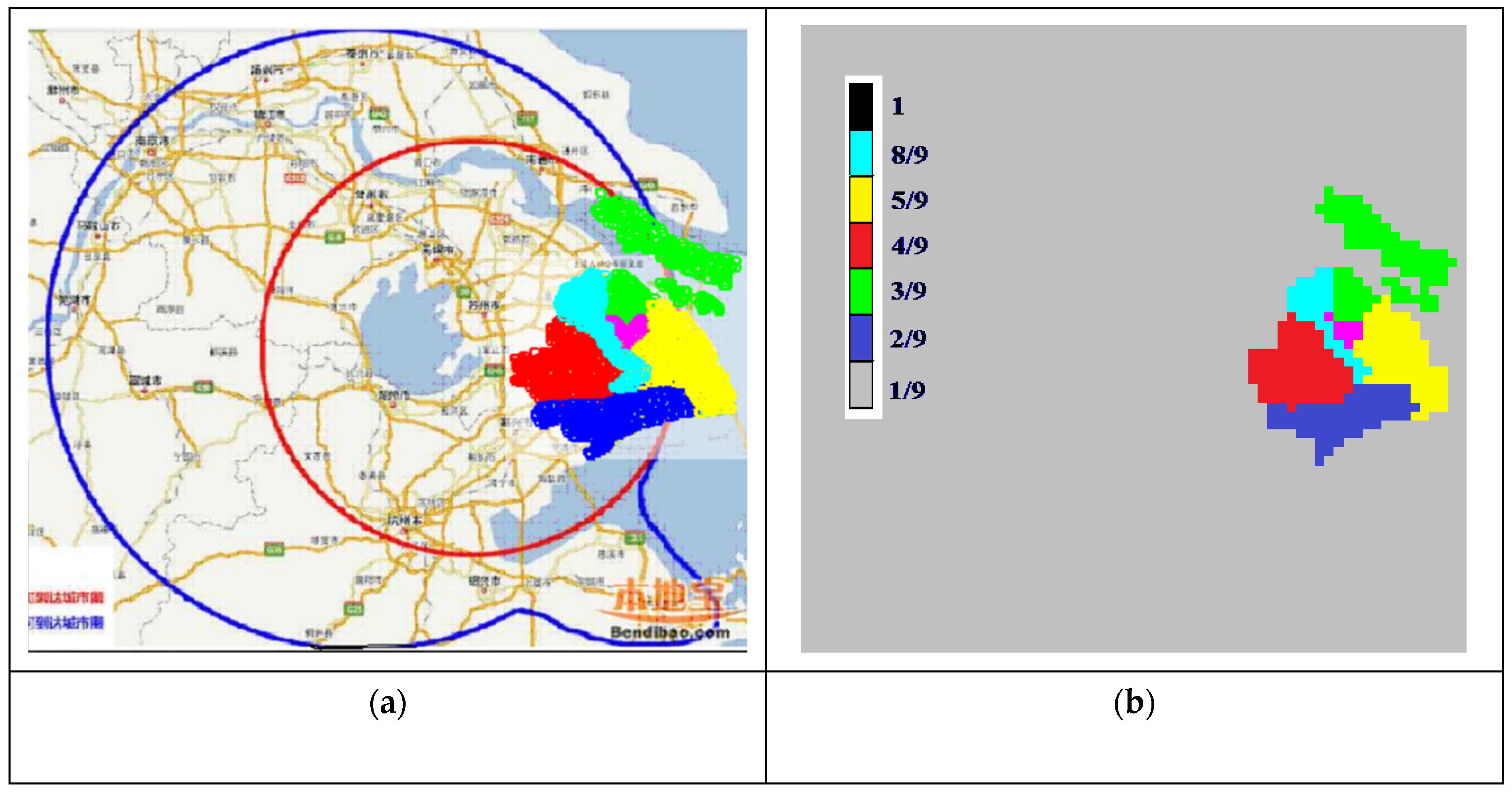
4.1. Model Reliability
4.2. Development Outlook for Shanghai and the Surrounding Areas
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helbich, M.; Leitner, M. Postuburban Spatial Evolution of Vienna’s Urban Fringe: Evidence from Point Process Modeling. Urban Geogr. 2010, 31, 1100–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, Y.Y. Population density in a central-place system. J. Reg. Sci. 2014, 54, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, D.; Hazam, S. Intra-Urban Mobility and Changing Density Functions in Tel Aviv, 1995–2006. In Societies in Motion: Regional Development, Industrial Innovation and Spatial Mobility; Frenkel, A., McCann, P., Nijkamp, P., Eds.; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2012; pp. 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; David, J.L. A spatially explicit hierarchical approach to modeling complex ecological systems: Theory and applications. Ecol. Model. 2002, 153, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankhauser, P. Fractal geometry of urban patterns and their morphogenesis. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 1998, 2, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changlin, Y.; Dingquan, Y.; Honghui, Z.; Shengjing, Y.; Guanghui, C. Simulation of urban growth using a cellular automata-based model in a developing nation’s region. Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2008, 7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizhong, H.; Lina, T.; Shenghui, C.; Kai, Y. Simulating Urban Growth Using the SLEUTH Model in a Coastal Peri-Urban District in China. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3899–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihamta, N.; Soffianian, A.; Fakheran, S.; Gholamalifard, M. Using the SLEUTH Urban Growth Model to Simulate Future Urban Expansion of the Isfahan Metropolitan Area, Iran. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2015, 43, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, E.; Arsanjani, J.J. Predicting Urban Growth of the Greater Toronto Area-Coupling a Markov Cellular. Automata with Document Meta-Analysis. J. Environ. Inform. 2015, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Deal, B. Reporting on the Performance and Usability of Planning Support Systems—Towards a Common Understanding. Appl. Spat. Anal. 2019, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, L.; Cong, C.; Deal, B.; Wang, Y. A dynamic and spatially explicit modeling approach to identify the ecosystem service implications of complex urban systems interactions. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf Alkheder, S.; Shan, J. Urban Growth Simulation Using Remote Sensing Imagery and Neural Networks. School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University, USA. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.125.8120&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 12 June 2019).
- Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H.; Asghari, A.; Tayyebi, A.; Taleai, M. Coupling machine learning, tree-based and statistical models with cellular automata to simulate urban growth. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 64, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolund, P.; Hunhammar, S. Ecosystem services in urban areas. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y. Infrastructure Development and Urbanization in China. In China’s Urbanization and Socioeconomic Impact; Tang, Z., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 91–107. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin, A.; Huxley, A. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. Bltn. Mathcal Biol. 1990, 52, 25–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.N. Platelet-coagulant protein interactions. In Hemostasis and Thrombosis, 2nd ed.; Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1987; pp. 689–709. [Google Scholar]
- Zaikin, A.N.; Zhabotinsky, A.M. Concentration wave propagation in two-dimensional liquid-phase self-oscillating system. Nature 1970, 225, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanag, V.K.; Epstein, I.R. Segmented spiral waves in a reaction-diffusion system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14635–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.D. Mathematical Biology II: Spatial Models and Biomedical Applications, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 72–252. [Google Scholar]
- FitzHugh, R. Mathematical models of threshold phenomena in the nerve membrane. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1955, 17, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagumo, J.; Arimoto, S.; Yoshizawa, S. An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proc. IRE. 1962, 50, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzHugh, R. Impulses and Physiological States in Theoretical Models of Nerve Membrane. Biophys. J. 1961, 1, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, A.E.; Levashova, N.T.; Semina, A.E.; Melnikovа, А.А. The Application of a Distributed Model of Active Media for the Analysis of Urban Ecosystems Development. Math. Biol. Bioinform. 2018, 13, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, A.E.; Levashova, N.T.; Semina, A.E. Autowave Model of Megapolis Morphogenesis in the Context of Inhomogeneous Active Media. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 2019, 83, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Wang, H. Driving force of urban growth and regional planning: A case study of China’s Guangdong Province. Habitat Int. 2013, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Statistics. Available online: www.stats.gov.cn/english/Statisticaldata/AnnualData (accessed on 15 July 2018).
- Sharinov, D.O. About housing reform in China (on the example of Shanghai). Probl. Far East 1997, 5, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, W.; Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Sun, C. Spatio-temporal patterns and driving forces of urban expansion in Beijing Central City since 1932. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 4, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortgage Experience in Developing Countries. Available online: www.2016.mosurbanforum.ru/files/pdf/analiticheskie_obzory/masterplan_book_2_chast.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2018).
- Yang Lin Shanghai Plan, Materials of the Moscow Urban Forum, 278-304. Available online: https://issuu.com/mosurbanforum/docs/masterplan (accessed on 6 July 2017).
- Li, J.; Fang, W.; Wang, T.; Qureshi, S.; Alatalo, J.M.; Bai, Y. Correlations between Socioeconomic Drivers and Indicators of Urban Expansion: Evidence from the Heavily Urbanised Shanghai Metropolitan Area, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Guneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A meta-analysis of global urban land expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.L.; Gao, J.L.; Chen, W. Urban land expansion and the transitional mechanisms in Nanjing, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 53, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.D. Zone fever, project fever: Development policy, economic transition, and urban expansion in China. Geogr. Rev. 2015, 105, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, D.; Larondelle, N.; Andersson, E.; Artmann, M.; Borgström, S.; Breuste, J.; Gomez-Baggethun, E.; Gren, Å.; Hamstead, Z.; Hansen, R.; et al. Quantitative review of urban ecosystem services assessment: Concepts, models and implementation. Ambio 2014, 43, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larondelle, N.; Lauf, S. Balancing demand and supply of multiple urban ecosystem services on Different spatial scales. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 22, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.; Haase, D. Compact, eco-, hybrid or teleconnected? Novel aspects of urban ecological research seeking compatible solutions to socio-ecological complexities. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.J. Landscape Ecology: Pattern, Process, Scale and Hierarchy, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Bowling, L.C.; Cherkauer, K.A.; Pijanowski, B.C. The impact of urban development on hydrologic regime from catchment to basin scales. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 103, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Ding, Y.H.; He, J.H.; Tang, X. Study of relationship between urbanization speed and change of spatial distribution of rainfall over Shanghai. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2011, 4, 475–483. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, A.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.C. Decadal changes of air temperature in Shanghai in recent 50 years and its relation to urbanization. China J. Geophys. 2008, 51, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Sidorova, A.E.; Mukhartova, Y.V.; Yakovenko, L.V. An Urban Ecosystem as a Superposition of Interrelated Active Media. Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 2014, 69, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, A.E.; Levashova, N.T.; Melnikova, A.A.; Deryugina, N.N.; Semina, A.E. Autowave self-organization in heterogeneous natural–anthropogenic ecosystems. Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 2016, 71, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, A.E.; Levashova, N.T.; Melnikova, A.A.; Yakovenko, L.V. A model of a human dominated urban ecosystem as an active medium. Biophysics 2015, 60, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levashova, N.; Melnikova, A.; Semina, A.; Sidorova, A. Autowave mechanisms of structure formation in urban ecosystems as the process of self-organization in active media. Commun. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 31, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Barenblatt, G.I.; Librovich, V.B.; Makhviladze, G.M. The Mathematical Theory of Combustion and Explosions; Plenum: New York, NY USA, 1985; pp. 79–100. [Google Scholar]
- Levashova, N.T.; Mel’nikova, A.A. Step-like contrast structure in a singularly perturbed system of parabolic equations. Differ. Equ. 2015, 51, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedov, N.N.; Levashova, N.T.; Orlov, A.O. The asymptotic stability of a stationary solution with an internal transition layer to a reaction–diffusion problem with a discontinuous reactive term. Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 2018, 73, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levashova, N.T.; Nefedov, N.N.; Orlov, A.O. Asymptotic Stability of a Stationary Solution of a Multidimensional Reaction–Diffusion Equation with a Discontinuous Source. Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 2019, 59, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distribution of Prices Per Square Meter of Housing in Shanghai. Available online: http://m.focus.cn/sh/daogou/11042556 (accessed on 15 July 2018).
- Shanghai Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shanghai (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Complex Urban Policy and the Construction of the City of Moscow. Available online: https://stroi.mos.ru/infographics/novoi-moskvie-piat-liet-1/ (accessed on 22 November 2018).
- Moscow Map. Available online: https://yandex.ru/maps/213/moscow/ (accessed on 22 November 2018).




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levashova, N.; Sidorova, A.; Semina, A.; Ni, M. A Spatio-Temporal Autowave Model of Shanghai Territory Development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133658
Levashova N, Sidorova A, Semina A, Ni M. A Spatio-Temporal Autowave Model of Shanghai Territory Development. Sustainability. 2019; 11(13):3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133658
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevashova, Natalia, Alla Sidorova, Anna Semina, and Mingkang Ni. 2019. "A Spatio-Temporal Autowave Model of Shanghai Territory Development" Sustainability 11, no. 13: 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133658
APA StyleLevashova, N., Sidorova, A., Semina, A., & Ni, M. (2019). A Spatio-Temporal Autowave Model of Shanghai Territory Development. Sustainability, 11(13), 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133658