The Impact of Labor Union Influence on Corporate Social Responsibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Labor Unions
2.2. Corporate Social Responsibility
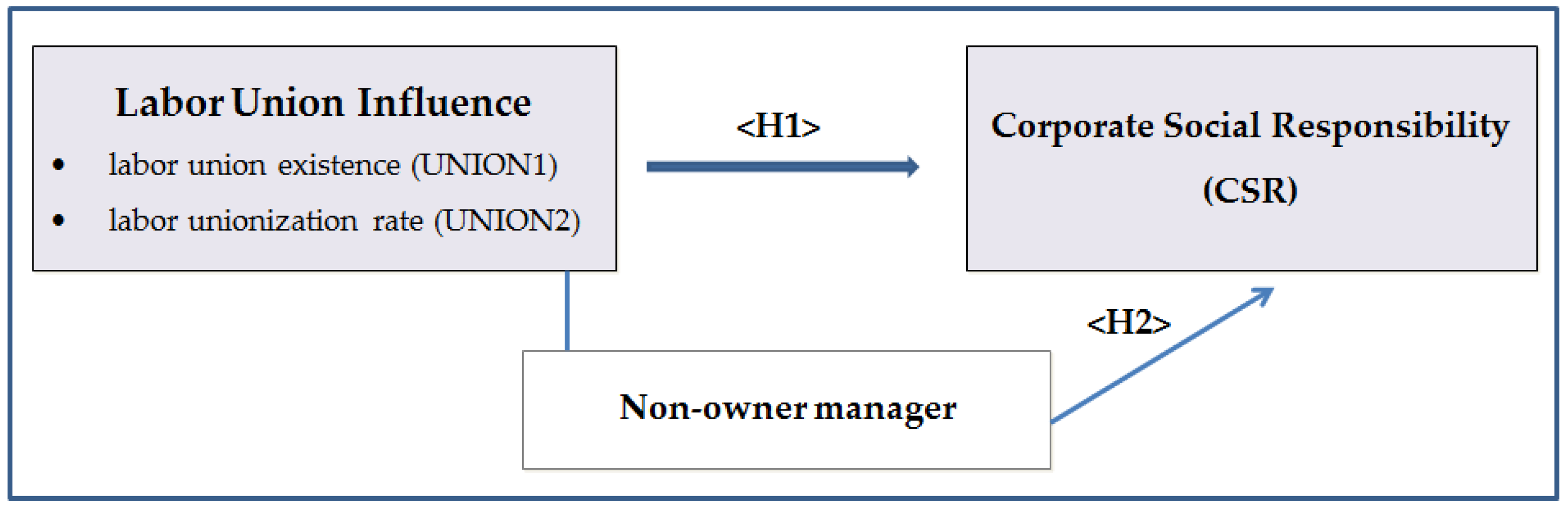
2.3. Hypotheses Development
3. Research Methodology
3.1. CSR Activity Measures
3.2. Empirical Model
+ β6FORi,t + Industry & Year Fixed Effects + ε,
3.3. Sample
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Univariate Analysis
4.3. Multivariate Analysis
4.4. Robustness Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.B. A three-dimensional conceptual model of corporate performance. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1979, 4, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgrom, P.; Roberts, J. Price and advertising signals of product quality. J. Polit. Econ. 1986, 94, 796–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, R.P.; Ritter, J.R. Investment banking, reputation and the underpricing of initial public offering. J. Financ. Econ. 1986, 15, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoul, S.; Guedhami, O.; Kwok, C.; Mishra, D. Does corporate social responsibility affect the cost of capital? J. Bank. Financ. 2011, 35, 2388–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fombrun, C.; Shanley, M. What’s in a name? Reputation building and corporate strategy. Acad. Manag. J. 1990, 33, 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Waddock, S.A.; Graves, S.B. The corporate social performance-financial performance link. Strat. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Greening, D. The effects of corporate governance and institutional ownership types on corporate social performance. Acad. J. Manag. J. 1999, 42, 564–576. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, W.Y.; Chang, Y.K.; Martynov, A. The effect of ownership structure on corporate social responsibility: Empirical evidence from Korea. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 104, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnea, A.; Rubin, A. Corporate social responsibility as a conflict between shareholders. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 97, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulkowski, A.J.; Edwards, M.; Freeman, R.E. Shake Your Stakeholder: Firms Leading Engagement to Cocreate Sustainable Value. Org. Environ. 2017, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Medoff, J. The Two Faces of Unionism; NBER working papers; The NBER Labor Studies Program: Cambridge, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.J.; Kacperczyk, M.; Ortiz-Molina, H. Labor unions, operating flexibility, and the cost of equity. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 2011, 46, 25–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyz, J.A.; Leung, W.S.; Li, O.Z.; Rui, O.M. Labor unions and tax aggressiveness. J. Financ. Econ. 2013, 180, 675–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Tian, X.; Yang, H. Labor Unions and Payout Policy: A Regression Discontinuity Approach; Working paper; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, UAS, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hilary, G. Organized labor and information asymmetry in the financial markets. Rev. Account. Stud. 2016, 11, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.; Kim, I.; Tian, X. Do unions affect innovation? Manag. Sci. 2016, 63, 2251–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.; Shin, S. Labor union and real earnings management. Glob. Bus. Financ. Rev. 2017, 22, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M. Value maximization, stakeholder theory, and the corporate objective function. J. Appl. Corp. Financ. 2010, 22, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banning, K.; Chiles, T. Trade-offs in the labor union-CEO compensation relationship. J. Labor Res. 2007, 28, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Tinaikar, S.; Zhang, Y. The Impact of Labor Unionization on Corporate Overinvestment and Underinvestment; Working paper; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bryan, D.B. Influence of Organized Labor on Audit Quality and Internal Control; Working paper; Florida State University: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, R.; Lee, B.B.; Lee, W.J.; Sohn, B.C. Do managers withhold good news from labor unions? Inst. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2015, 62, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirch, T. Firm investment behavior and collective bargaining strategy. Ind. Relat. 1991, 31, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Lee, B.; Lee, W.; Sohn, B. Do labor unions always lead to under-investment? J. Manag. Account. Res. 2017, 29, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karier, T. Unions and monopoly profits. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1985, 67, 1335–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruback, R.S.; Zimmerman, M.B. Unionization and profitability: Evidence from the capital market. J. Polit. Econ. 1984, 92, 1134–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, H.G. Union Relative Wage Effects: A Survey; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, R.A.; Hirsch, B.T.; Hirschey, M. Union rent seeking, intangible capital and market value of the firm. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1986, 68, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.C.; Meckling, W.H. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. J. Financ. Econ. 1976, 3, 305–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, S.J.; Thomas, R. Realigning corporate governance: Shareholder activism by labor unions. Mich. Law Rev. 1998, 96, 1018–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, R.V.; Rupp, D.E.; Williams, C.A.; Ganapathi, J. Putting the S back in corporate social responsibility: A Multilevel Theory of Social Change in Organizations. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2007, 32, 836–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Hong, A.; Hwang, J. An analysis of CSR on firm financial performance in stakeholder perspectives. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, H.H.; Tang, J. The impacts of social responsibility and ownership structure on sustainable financial development of China’s energy industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matten, D.; Moon, J. “Implicit” and “Explicit” CSR: A Conceptual Framework for a Comparative Understanding of Corporate Social Responsibility. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2008, 33, 404–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L. Why would corporations behave in socially responsible ways? An institutional theory of corporate social responsibility. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2007, 32, 946–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.; Mark, K. The Big Idea: Creating Shared Value. How to reinvent capitalism—And unleash a wave of innovation and growth. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2011, 89, 2–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kinderman, D.P.; Lutter, M. Explaining the Growth of CSR within OECD Countries: The Role of Institutional Legitimacy in Resolving the Institutional Mirror vs. Substitute Debate; Max Planck Institute for the Study of Societies Discussion Paper; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins, C.E. A test of labor union social responsibility: Effects on union member attachment. Bus. Soc. 2016, 55, 214–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amihud, Y.; Lev, B. Risk reduction as a managerial motive for conglomerate mergers. Bell J. Econ. 1981, 12, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salancik, G.R.; Pfeffer, J. Effects of ownership and performance on executive tenure in U.S. Corporations. Acad. Manag. J. 1980, 23, 653–664. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, H.M. Corporate international diversification and corporate social responsibility: Evidence from Korean firms. Asian Soc. Sci. 2014, 21, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hategan, C.-D.; Sirghi, N.; Curea-Pitorac, R.-I.; Hategan, V.-P. Doing Well or Doing Good: The Relationship between Corporate Social Responsibility and Profit in Romanian Companies. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.J.; Kwon, I. Corporate social responsibility as a strategic means to attract foreign investment: Evidence from Korea. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M. Estimating Standard Errors in Finance Panel Data Sets: Comparing Approaches. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2009, 22, 435–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Lee, C.F.; Huang, C.M. The effects of corporate social responsibility on equity fund returns: Evidence from China. Int. J. Econ. Financ. 2016, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, J.J. The common structure of statistical models of truncation, sample selection and limited dependent variables and a sample estimator for such models. Ann. Econ. Soc. Meas. 1979, 5, 475–492. [Google Scholar]
| Panel A. Summary statistics | |||||||||
| Variables | N | Mean | Std. dev. | 25th | Median | 75th | |||
| KEJI index score | 675 | 47.429 | 2.468 | 45.380 | 47.060 | 49.030 | |||
| CSR | 675 | 0.632 | 0.032 | 0.605 | 0.627 | 0.653 | |||
| UNION1 | 675 | 0.714 | 0.452 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| UNION2 | 675 | 0.300 | 0.277 | 0 | 0.267 | 0.559 | |||
| LNSIZE | 675 | 26.989 | 1.571 | 25.754 | 26.530 | 27.768 | |||
| LEV | 675 | 0.389 | 0.169 | 0.249 | 0.384 | 0.520 | |||
| ROA | 675 | 0.070 | 0.054 | 0.032 | 0.061 | 0.099. | |||
| MB | 675 | 1.295 | 0.978 | 0.631 | 0.982 | 1.609 | |||
| FOR | 675 | 0.178 | 0.175 | 0.031 | 0.113 | 0.286 | |||
| Panel B. High vs. Low Union Samples | |||||||||
| High Unionization | Low Unionization | Difference | |||||||
| Variables | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p-Value | ||||
| UNION2 | 0.548 | 0.008 | 0.052 | 0.004 | 0.00 | ||||
| CSR | 0.628 | 0.001 | 0.635 | 0.001 | 0.00 | ||||
| LNSIZE | 27.206 | 0.088 | 26.590 | 0.080 | 0.00 | ||||
| LEV | 0.407 | 0.009 | 0.371 | 0.009 | 0.00 | ||||
| ROA | 0.069 | 0.003 | 0.071 | 0.002 | 0.71 | ||||
| MB | 1.183 | 0.047 | 1.408 | 0.058 | 0.00 | ||||
| FOR | 0.181 | 0.009 | 0.175 | 0.009 | 0.68 | ||||
| Variables | CSR | UNION1 | UNION2 | LNSIZE | LEV | ROA | MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNION1 | 0.004 (0.913) | ||||||
| UNION2 | −0.073 (0.054) | 0.680 (0.00) | |||||
| LNSIZE | 0.348 (0.000) | 0.253 (0.693) | 0.248 (0.928) | ||||
| LEV | −0.075 (0.049) | 0.152 (0.000) | 0.141 (0.000) | 0.351 (0.000) | |||
| ROA | 0.243 (0.000) | −0.047 (0.222) | 0.004 (0.901) | 0.118 (0.002) | −0.227 (0.000) | ||
| MB | 0.323 (0.000) | 0.050 (0.188) | −0.069 (0.070) | 0.298 (0.000) | −0.177 (0.000) | 0.369 (0.000) | |
| FOR | 0.269 (0.000) | 0.095 (0.013) | 0.061 (0.113) | 0.464 (0.000) | −0.049 (0.198) | 0.297 (0.000) | 0.314 (0.000) |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNION1 | −0.006 ** | −0.006 * | ||
| (−2.495) | (−1.781) | |||
| UNION2 | −0.016 *** | −0.016 *** | ||
| (−3.757) | (−2.975) | |||
| LNSIZE | 0.007 *** | 0.008 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.008 *** |
| (8.098) | (8.329) | (6.716) | (7.354) | |
| MB | 0.007 *** | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.006 *** |
| (5.039) | (4.506) | (4.847) | (4.155) | |
| LEV | −0.038 *** | −0.036 *** | −0.038 *** | −0.036 *** |
| (−4.664) | (−4.406) | (−3.543) | (−3.394) | |
| ROA | 0.015 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.025 |
| (0.642) | (1.075) | (0.541) | (0.880) | |
| FOR | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
| (1.083) | (1.083) | (0.918) | (0.933) | |
| Constant | 0.489 *** | 0.486 *** | 0.489 *** | 0.486 *** |
| (28.834) | (28.751) | (23.727) | (24.642) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Firm cluster | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 675 | 675 | 675 | 675 |
| R-squared | 0.351 | 0.358 | 0.351 | 0.358 |
| Panel A: Owner Manager | ||||
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
| UNION1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| (0.422) | (0.271) | |||
| UNION2 | −0.011 | −0.011 | ||
| (−1.632) | (−1.469) | |||
| LNSIZE | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** |
| (3.558) | (3.830) | (2.997) | (3.201) | |
| MB | 0.006 ** | 0.005 * | 0.006 ** | 0.005 * |
| (2.225) | (1.784) | (2.324) | (1.834) | |
| LEV | −0.045 *** | −0.039 *** | −0.045 ** | −0.039 ** |
| (−3.654) | (−3.120) | (−2.405) | (−2.096) | |
| ROA | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.014 |
| (0.397) | (0.424) | (0.321) | (0.320) | |
| FOR | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| (0.058) | (0.014) | (0.051) | (0.012) | |
| Constant | 0.504 *** | 0.501 *** | 0.504 *** | 0.501 *** |
| (15.593) | (15.621) | (14.153) | (14.189) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Firm cluster | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 304 | 304 | 304 | 304 |
| R-squared | 0.319 | 0.325 | 0.319 | 0.325 |
| Panel B: Non-Owner Manager | ||||
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
| UNION1 | −0.015 *** | −0.015 *** | ||
| (−3.722) | (−3.558) | |||
| UNION2 | −0.025 *** | −0.025 *** | ||
| (−4.157) | (−3.610) | |||
| LNSIZE | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** |
| (6.356) | (6.341) | (5.625) | (6.007) | |
| MB | 0.009 *** | 0.008 *** | 0.009 *** | 0.008 *** |
| (5.012) | (4.597) | (5.280) | (5.071) | |
| LEV | −0.040 *** | −0.038 *** | −0.040 *** | −0.038 *** |
| (−3.589) | (−3.402) | (−3.481) | (−3.248) | |
| ROA | 0.016 | 0.037 | 0.016 | 0.037 |
| (0.473) | (1.127) | (0.408) | (0.994) | |
| FOR | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.011 |
| (1.357) | (1.139) | (1.094) | (0.957) | |
| Constant | 0.505 *** | 0.501 *** | 0.505 *** | 0.501 *** |
| (23.845) | (23.747) | (19.473) | (20.571) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Firm cluster | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 371 | 371 | 371 | 371 |
| R-squared | 0.424 | 0.429 | 0.424 | 0.429 |
| CSR Quintile Regression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Q10 | Q25 | Q50 | Q75 | Q90 |
| UNION2 | −0.002 | −0.010 ** | −0.017 *** | −0.018 *** | −0.020 ** |
| (−0.379) | (−2.513) | (−4.318) | (−3.678) | (−2.549) | |
| LNSIZE | 0.003 * | 0.006 *** | 0.008 *** | 0.009 *** | 0.008 *** |
| (1.717) | (5.529) | (8.170) | (6.924) | (4.601) | |
| LEV | −0.012 | −0.025 ** | −0.020 * | −0.043 *** | −0.070 *** |
| (−1.561) | (−2.473) | (−1.899) | (−4.536) | (−5.134) | |
| ROA | −0.012 | −0.017 | 0.028 | 0.037 | 0.018 |
| (−0.349) | (−0.626) | (0.856) | (0.980) | (0.434) | |
| MB | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.006 ** | 0.010 *** |
| (3.283) | (5.542) | (2.965) | (2.346) | (5.806) | |
| FOR | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0.002 | −0.013 |
| (0.299) | (0.974) | (1.634) | (0.295) | (−0.927) | |
| Constant | 0.537 *** | 0.491 *** | 0.463 *** | 0.477 *** | 0.503 *** |
| (16.075) | (26.392) | (27.833) | (19.294) | (14.629) | |
| Industry fixed effect | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Year fixed effect | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Observations | 675 | 675 | 675 | 675 | 675 |
| Pseudo R2R | 0.130 | 0.183 | 0.250 | 0.249 | 0.292 |
| Panel A. First-Stage Regressions | ||
| (1) | (2) | |
| Variables | UNION1 | UNION2 |
| WORKAGE | 0.006 ** | 0.010 *** |
| (2.033) | (5.264) | |
| LNSIZE | 0.060 *** | 0.035 *** |
| (4.252) | (4.085) | |
| LEV | 0.167 | 0.178 ** |
| (1.438) | (2.574) | |
| ROA | −0.495 | 0.374 * |
| (−1.384) | (1.752) | |
| MB | −0.003 | −0.050 *** |
| (−0.168) | (−4.214) | |
| FOR | 0.044 | 0.001 |
| (0.380) | (0.008) | |
| Constant | −0.560 ** | −0.479 *** |
| (−2.226) | (−3.185) | |
| Observations | 675 | 675 |
| R-squared | 0.078 | 0.130 |
| Panel B. Second Stage Regression: The Relation between CSR and Union Strength | ||
| Dep. Var. | CSR | |
| (1) | (2) | |
| Union | UNION1 | UNION2 |
| Fitted value of union | −0.177 ** | −0.128 *** |
| (−2.236) | (−3.784) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES |
| Year fixed effects | YES | YES |
| Industry fixed effects | YES | YES |
| Observations | 675 | 675 |
| OLS | Heckman Two-Step | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (UNION1 = 1) | First Stage | Second Stage | |
| VARIABLES | CSR | UNION1 | CSR |
| WORKAGE | 0.034 ** | ||
| (2.132) | |||
| UNION2 | −0.018 *** | −0.018 *** | |
| (−2.927) | (−3.004) | ||
| LNSIZE | 0.007 *** | 0.280 *** | 0.007 *** |
| (6.546) | (5.232) | (4.598) | |
| LEV | −0.037 *** | 0.817 * | −0.036 *** |
| (−3.867) | (1.787) | (−3.673) | |
| ROA | 0.058 ** | −2.503 ** | 0.055 * |
| (2.114) | (−1.966) | (1.902) | |
| MB | 0.005 *** | 0.058 | 0.005 *** |
| (3.259) | (0.721) | (3.359) | |
| FOR | 0.009 | 0.190 | 0.009 |
| (1.015) | (0.444) | (1.055) | |
| Constant | 0.498 *** | 0.488 *** | |
| (24.595) | (15.140) | ||
| IMR (Inverse Mills ratio) | 0.004 | ||
| (0.367) | |||
| Year fixed effects | YES | YES | YES |
| Industry fixed effects | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 482 | 675 | 482 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chun, H.-M.; Shin, S.-Y. The Impact of Labor Union Influence on Corporate Social Responsibility. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10061922
Chun H-M, Shin S-Y. The Impact of Labor Union Influence on Corporate Social Responsibility. Sustainability. 2018; 10(6):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10061922
Chicago/Turabian StyleChun, Hong-Min, and Sang-Yi Shin. 2018. "The Impact of Labor Union Influence on Corporate Social Responsibility" Sustainability 10, no. 6: 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10061922
APA StyleChun, H.-M., & Shin, S.-Y. (2018). The Impact of Labor Union Influence on Corporate Social Responsibility. Sustainability, 10(6), 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10061922




