Immediate Effects of Multiple Ischemic Compression Applications on Pain Sensitivity and Biomechanical Properties of Myofascial Trigger Points
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aim of the Study
2. Material and Methods
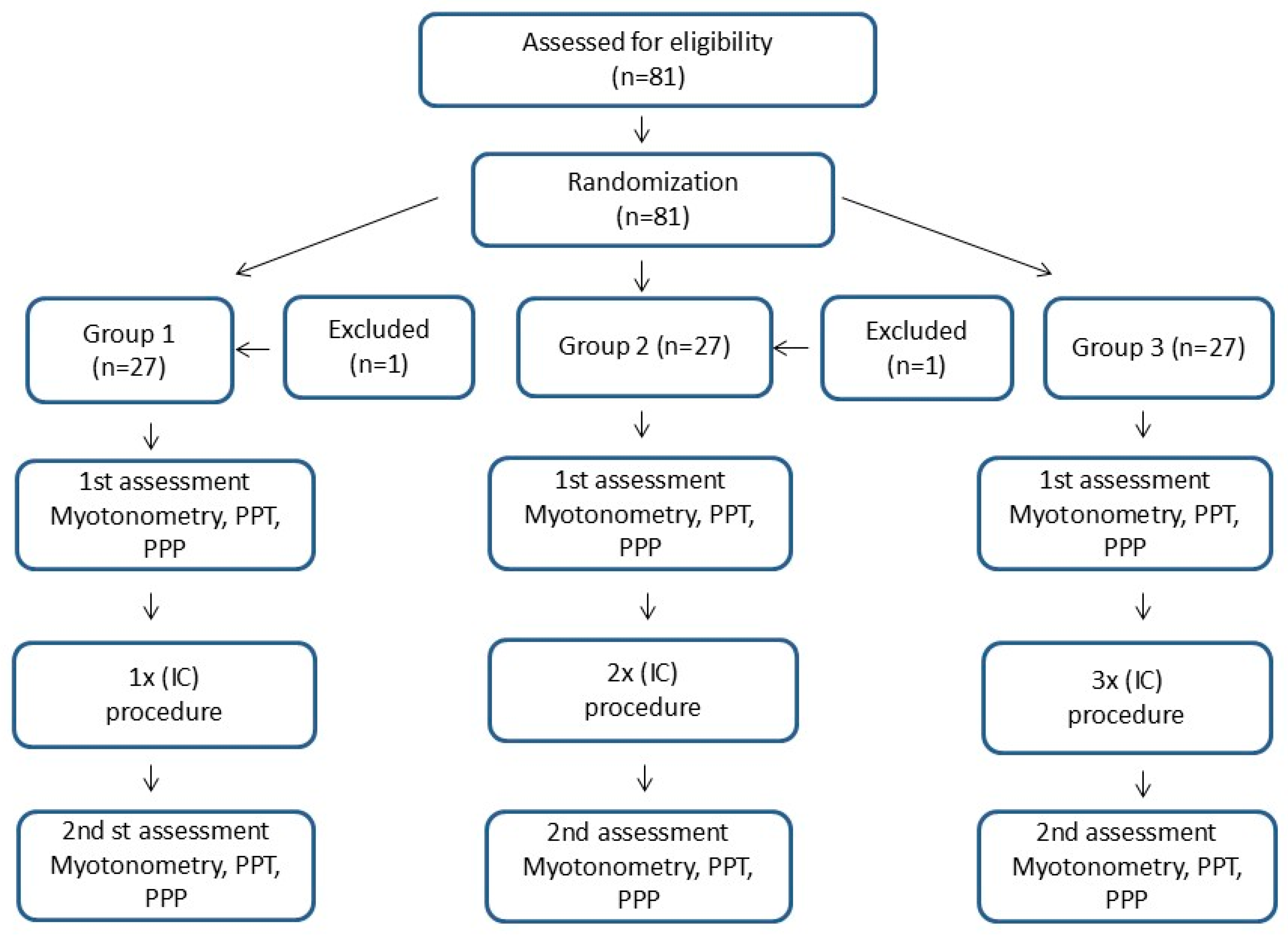
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.2.1. Myotonometric Measurements of Muscle Mechanical Properties
2.2.2. Ischemic Compression (IC) Procedure
2.2.3. Protocols in Individual Groups
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Study Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MTrPs | Myofacial Trigger Points |
| IC | Ischemic compression |
| PPT | Pressure Pain Threshold |
| PPP | Pressure Pain Perception |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide |
| UCS | Upper Cervical Syndrome |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| MET | Muscle Energy Technique |
| PS | Passive Stretching |
| EMG | Electromyography |
References
- Simons, D.G.; Travell, J.G.; Simons, L.S. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction, Vol. 1: The Trigger Point Manual. The Upper Extremities, 2nd ed.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Dommerholt, J. International consensus on diagnostic criteria and clinical considerations of myofascial trigger points: A delphi study. Pain Med. 2018, 19, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosman-Rimon, L.; Parkinson, W.; Upadhye, S.; Clarke, H.; Katz, J.; Flannery, J.; Peng, P.; Kumbhare, D. Circulating biomarkers in acute myofascial pain: A case-control study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos-Calderon, Y.T.; Martínez-Merinero, P.; Nunez-Nagy, S.; Pecos-Martín, D.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Romero-Morales, C.; Abuín-Porras, V.; Serrano-Imedio, A. Myofascial trigger points and central sensitization signs, but no anxiety, are shown in women with dysmenorrhea: A case-control study. Biology 2022, 11, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupska, E.; Dybek, T.; Rychlik, M.; Jokiel, M.; Dobrakowski, P.; Szczerba, A.; Wotzka, D.; Jankowska, A.; Herrero, P. A Potential objective sign of central sensitization: Referred pain elicited by manual gluteus minimus muscle exploration is coincident with pathological autonomic response provoked by noxious stimulation. Pain Res. Manag. 2023, 2023, e4030622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.P.; Phillips, T.M.; Danoff, J.V.; Gerber, L.H. An in vivo microanalytical technique for measuring the local biochemical milieu of human skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecos-Martin, D.; Ponce-Castro, M.J.; Jiménez-Rejano, J.J.; Nunez-Nagy, S.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Gallego-Izquierdo, T. Immediate effects of variable durations of pressure release technique on latent myofascial trigger points of the levator scapulae: A double-blinded randomized clinical trial. Acupunct. Med. 2019, 37, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzack, R.; Wall, P.D. Pain mechanisms: A new theory. Science 1965, 150, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnie, B.; Castelein, F.; Pollie, L.; Steelant, H.; Verhoeyen, A.; Cools, B. Evidence for the use of ischemic compression and dry needling in the management of trigger points of the upper trapezius in patients with neck pain. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 94, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraska, A.F.; Hickner, R.C.; Kohrt, W.M.; Brewer, A. Changes in blood flow and cellular metabolism at a myofascial trigger point with trigger point release (ischemic compression): A proof-of-principle pilot study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Lobo, C.; Diez-Vega, I.; Martınez-Pascual, B. Tensiomyography, sonoelastography, and mechanosensitivity differences between active, latent, and control low back myofascial trigger points: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2017, 96, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bellmunt, A.; Casasayas-Cos, O.; López-de-Celis, C.; Rodríguez-Sanz, J.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, J.; Ortiz-Miguel, S.; Meca-Rivera, T.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C. Effects of Dry Needling of latent trigger points on viscoelastic and muscular contractile properties: Preliminary results of a randomized within-participant clinical trial. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisilewicz, A.; Janusiak, M.; Szafraniec, R.; Smoter, M.; Ciszek, B.; Madeleine, P.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Kawczyński, A. Changes in muscle stiffness of the trapezius muscle after application of ischemic compression into myofascial trigger points in professional basketball players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 64, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesiejuk, M.; Marusiak, J.; Chalimoniuk, M. Myofascial Trigger Points therapy decreases myotonometric tone and stiffness of trapezius muscle, benefits headaches and muscle pain in migraine. NeuroRehabilitation 2023, 52, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Campelo, N.M.; de Melo, C.A.; Alburquerque-Sendín, F.; Machado, J.P. Short- and medium-term effects of manual therapy on cervical active range of motion and pressure pain sensitivity in latent myofascial pain of the upper trapezius muscle: A randomized controlled trial. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2013, 36, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, J.; Tian, Y.; Lu, X. Effect of ischemic compression on myofascial pain syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chiropr. Man. Ther. 2022, 30, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Huang, Q.; Rong, J.; Wu, X.; Deng, M.; Ji, L. Effectiveness of ischemic compression on myofascial trigger points in relieving neck pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2023, 36, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.C.; De Noronha, M.; Liberatori-Junior, R.M.; Aily, J.B.; Gonçalves, G.H.; Arrais-Lima, C.; Vieira, L.M.S.M.d.A.; Mattiello, S.M. The effectiveness of ischemic compression technique on pain and function in individuals with shoulder pain: A systematic review. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2020, 43, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Tahara, S.; Mitsuda, M.; Izumi, H.; Ikeda, S.; Seki, K.; Nishida, N.; Funaba, M.; Imajo, Y.; Yukata, K.; et al. Current Concept of Quantitative Sensory Testing and Pressure Pain Threshold in Neck/Shoulder and Low Back Pain. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervullens, S.; Haenen, V.; Meert, L.; Meeus, M.; Smeets, R.J.E.M.; Baert, I.; Mertens, M.G.C.A.M. Personal influencing factors for pressure pain threshold in healthy people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 139, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcioglu, O.; Topacoglu, H.; Dikme, O.; Dikme, O. A systematic review of the pain scales in adults: Which to use? Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticone, M.; Ferrante, S.; Rocca, B.; Nava, T.; Parini, C.; Cerri, C. Chronic pain acceptance questionnaire: Confirmatory factor analysis, reliability, and validity in Italian subjects with chronic low back pain. Spine Phila Pa 1976 2013, 38, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettner, J.; Królikowska, A.; Ramadanov, N.; Oleksy, Ł.; Hakam, H.T.; Becker, R.; Prill, R. Evaluating the reliability of MyotonPro in assessing muscle properties: A systematic review of diagnostic test accuracy. Medicina 2024, 60, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, S.; Yaşar, Ü.; Kaynak, B.A. Interrater and intrarater reliability of a handheld myotonometer in measuring mechanical properties of the neck and orofacial muscles. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2021, 44, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corum, M.; Aydin, T.; Medin Ceylan, C.; Kesiktas, F.N. The comparative effects of spinal manipulation, myofascial release and exercise in tension-type headache patients with neck pain: A randomized controlled trial. Complement Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 43, 101319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travell, J.G.; Simons, D.G.; Simons, L.S. Travell & Simons’ Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual; Wolters & Kluwer Health: Waltham, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, C.R.; Tsai, L.C.; Cheng, K.F.; Chung, K.C.; Hong, C.Z. Immediate effects of various physical therapeutic modalities on cervical myofascial pain and trigger-point sensitivity. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H. Sample size determination and power analysis using the G*Power software. J. Educ. Eval. Health 2021, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, F.J.; Martín, D.P.; Masanet, R.A. Immediate effect of ultrasound and ischemic compression techniques for the treatment of trapezius latent myofascial trigger points in healthy subjects: A randomized controlled study. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2009, 32, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Penãs, C.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Fernández- Carnero, J.; Miangolarra-Page, J.C. The immediate effect of ischemic compression technique and transverse friction massage on tenderness of active and latent myofascial trigger points: A pilot study. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2006, 10, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczarzyk, D.; Jamka, K.; Mikołajczyk, E.; Zając, B. Comparing the Effects of a Series of Ischaemic Compression Therapy and Muscle Energy Techniques on Pain Threshold and Muscle Tension in People with Upper Crossed Syndrome. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 27, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczarzyk, D.; Kurowski, P. Comparison of the effect of two methods of ischemic compression of trigger points on the change of pain threshold and electromyographic parameters of the trapezius muscle. Physiother. Rev. 2020, 24, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudaut, Y.; Lonigro, A.; Coste, B.; Hao, J.; Delmas, P.; Crest, M. Touch sense: Functional organization and molecular determinants of mechano-sensitive receptors. Channels 2012, 6, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p ** | η2 | ||
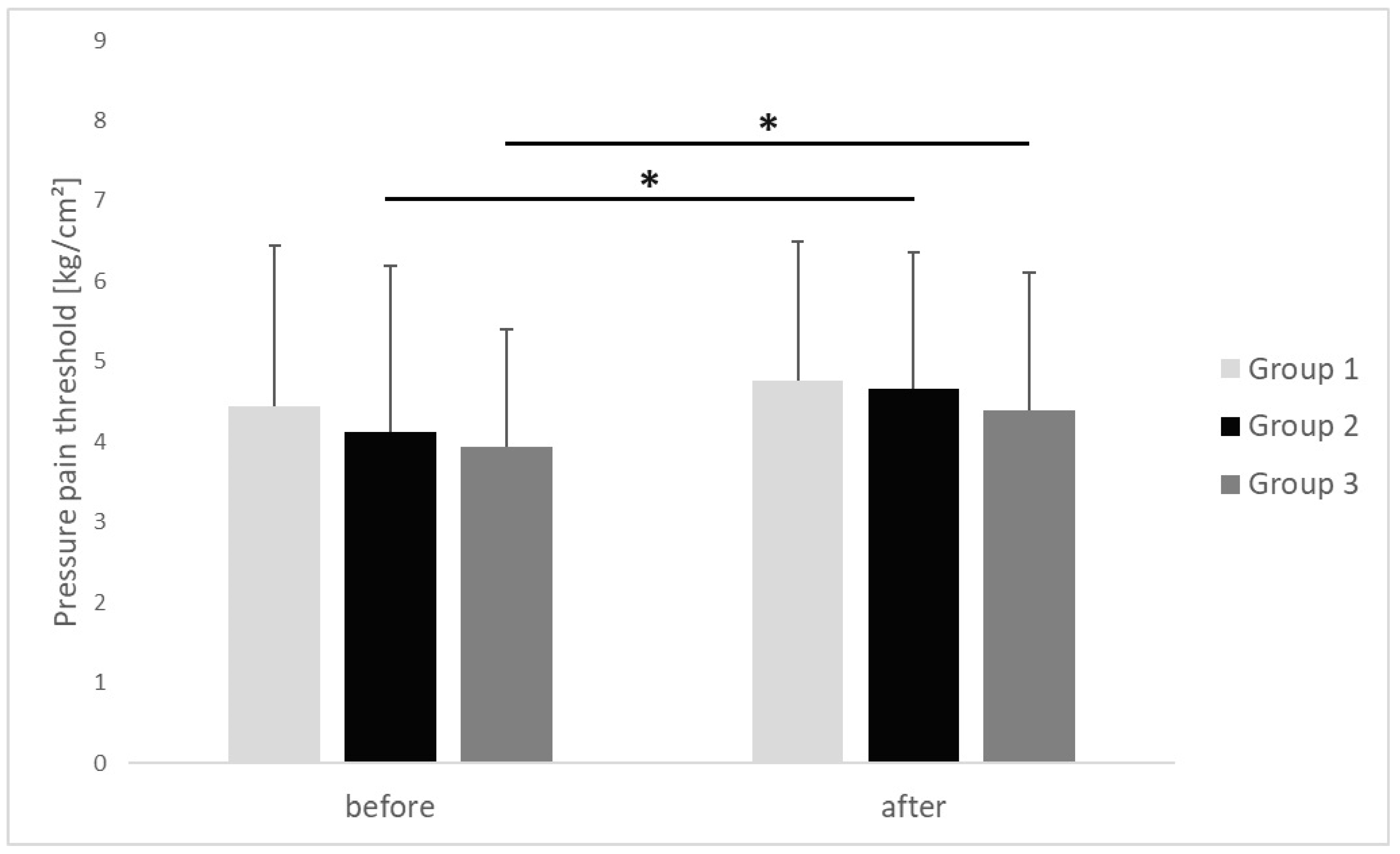
| Pressure pain threshold [kg/cm2] | before | 4.44 ± 2 | 4.12 ± 2.06 | 3.94 ± 1.45 | 0.703 | 0.01 |
| after | 4.76 ± 1.72 | 4.66 ± 1.69 | 4.38 ± 1.72 | 0.574 | 0.02 | |
| p * | 0.053 | 0.009 | 0.009 | |||
| r | 0.43 | 0.53 | 0.44 | |||
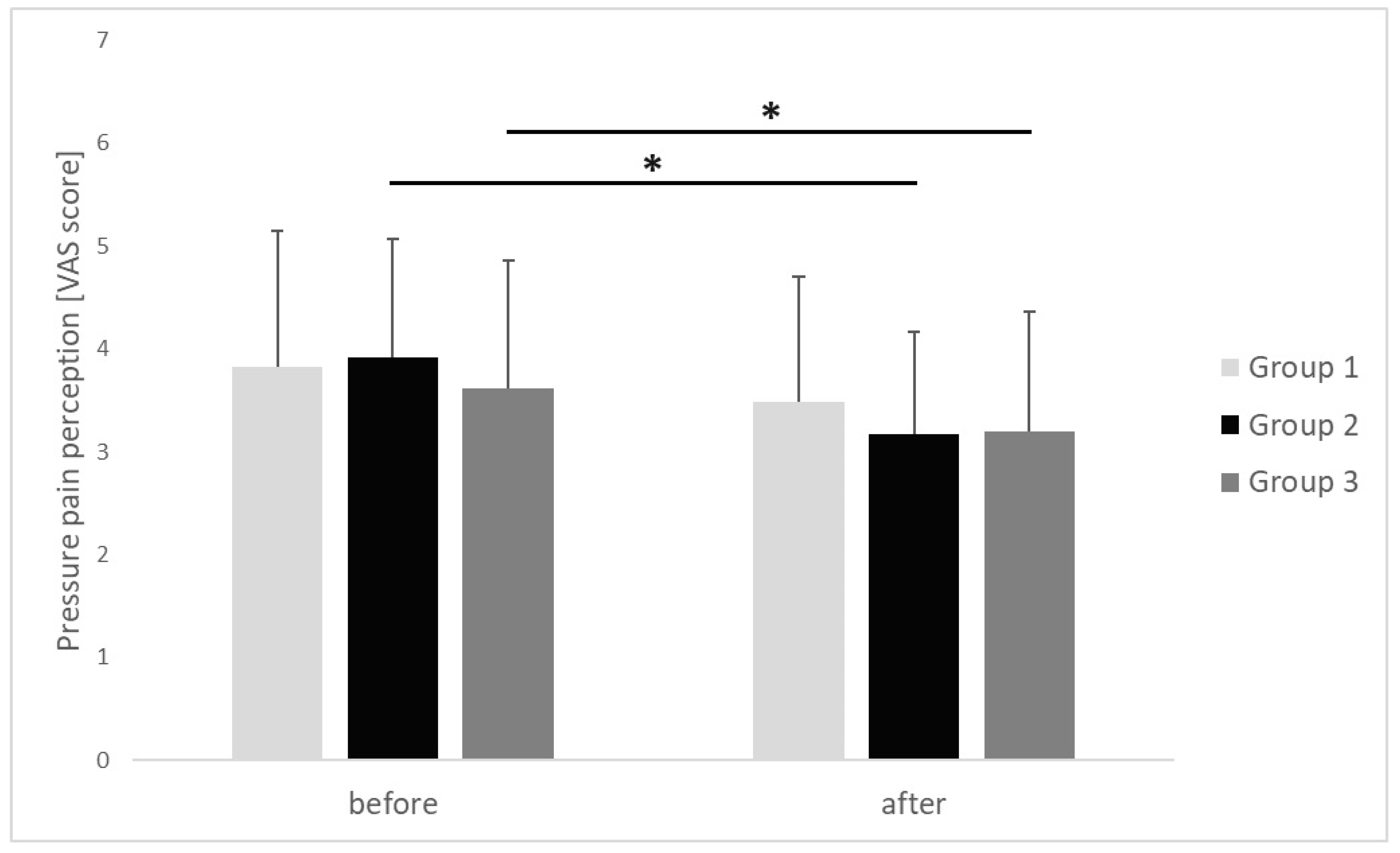
| Pressure pain perception [VAS score] | before | 3.82 ± 1.33 | 3.92 ± 1.15 | 3.62 ± 1.24 | 0.685 | 0.02 |
| after | 3.49 ± 1.21 | 3.17 ± 1 | 3.2 ± 1.16 | 0.761 | 0.01 | |
| p | 0.623 | 0.016 | 0.041 | |||
| r | 0.24 | 0.56 | 0.48 | |||
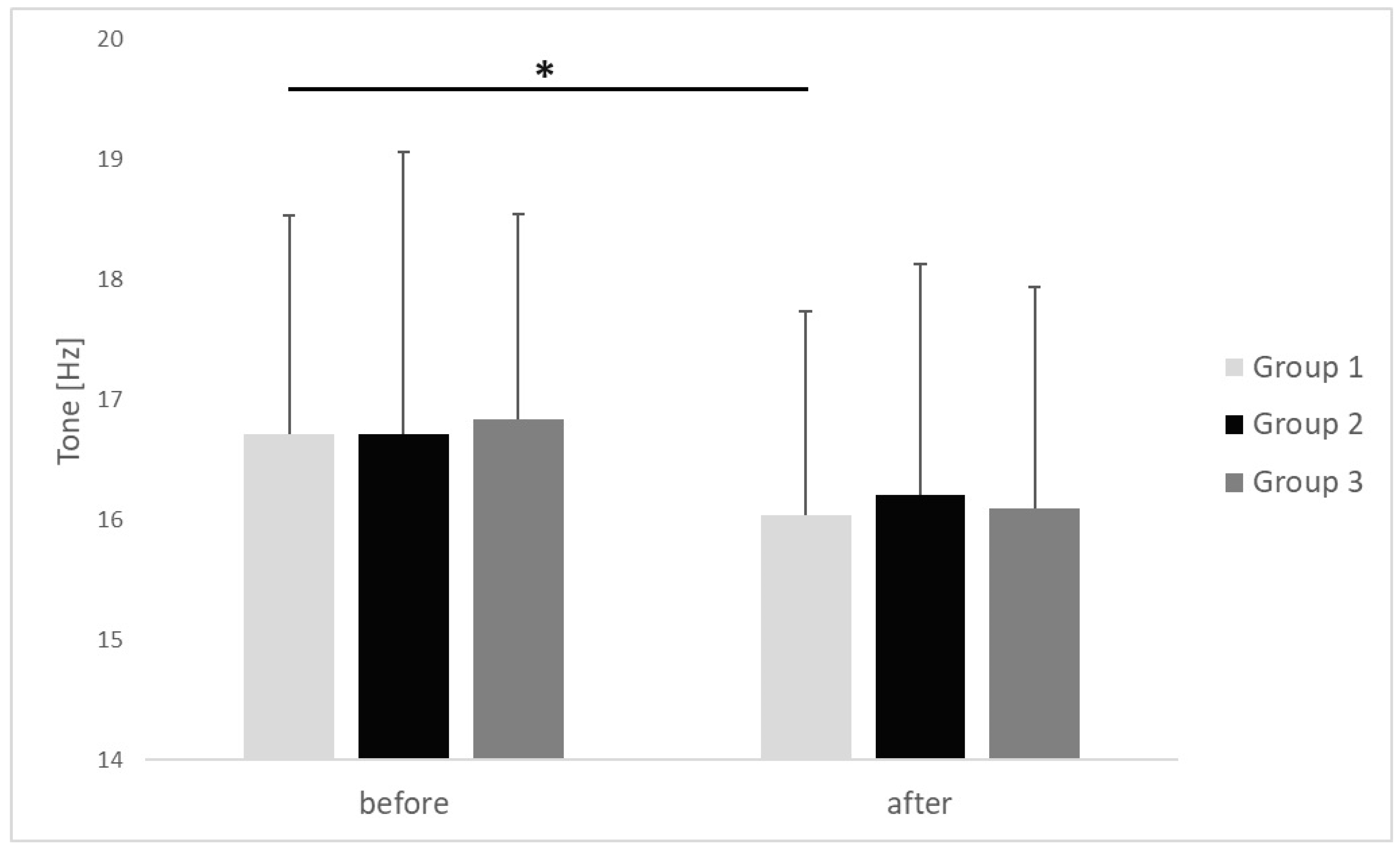
| Tone [Hz] | before | 16.71 ± 1.82 | 16.72 ± 2.34 | 16.84 ± 1.71 | 0.912 | 0.02 |
| after | 16.03 ± 1.7 | 16.21 ± 1.93 | 16.10 ± 1.84 | 0.856 | 0.01 | |
| p | <0.001 | 0.082 | 0.068 | |||
| r | 0.66 | 0.51 | 0.69 | |||
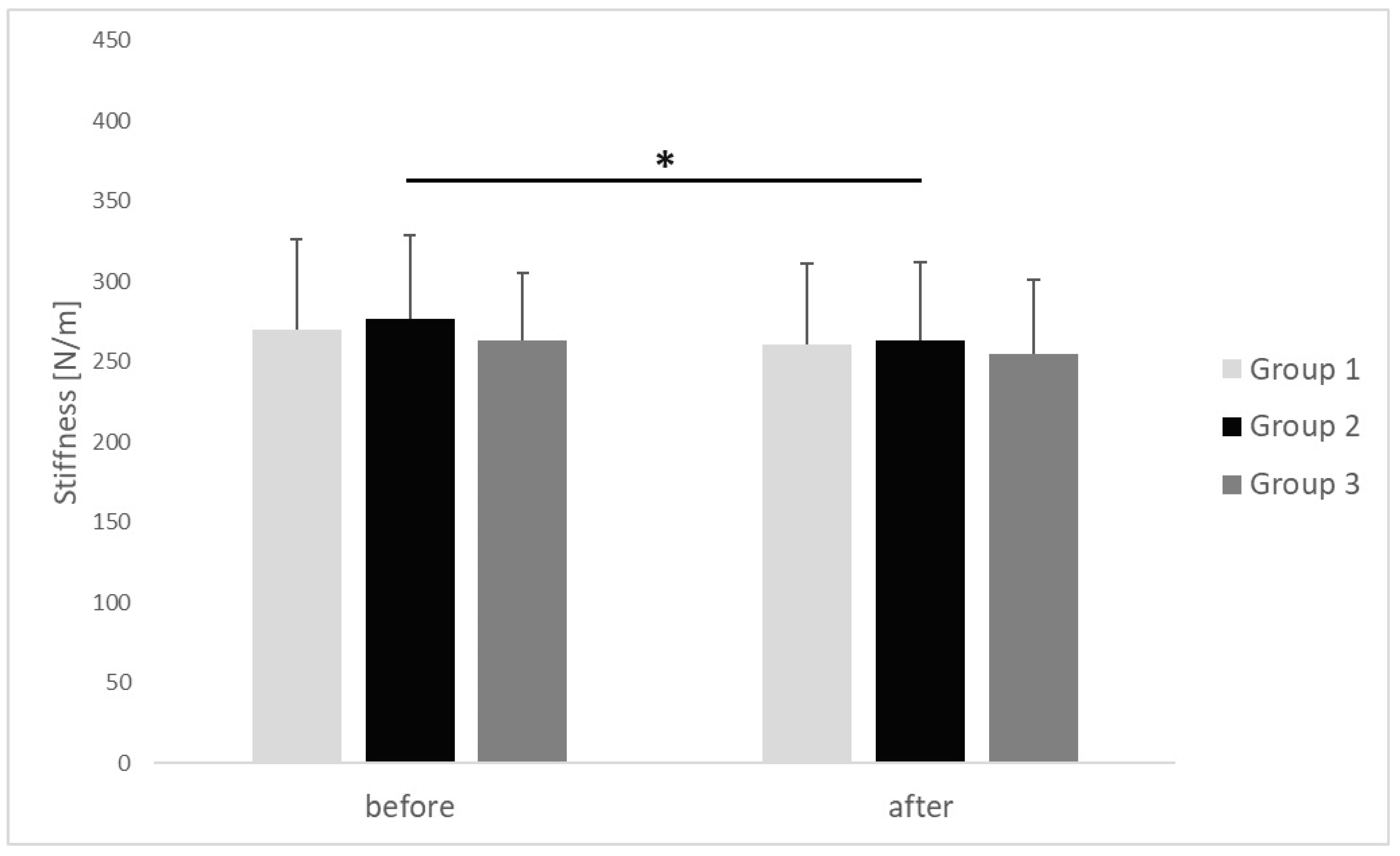
| Stiffness [N/m] | before | 270.31 ± 56.29 | 276.46 ± 52.43 | 263.33 ± 42.29 | 0.924 | 0.01 |
| after | 260.92 ± 50.36 | 263.15 ± 48.49 | 254.67 ± 46.45 | 0.821 | 0.02 | |
| p | 0.059 | 0.036 | 0.071 | |||
| r | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.29 | |||
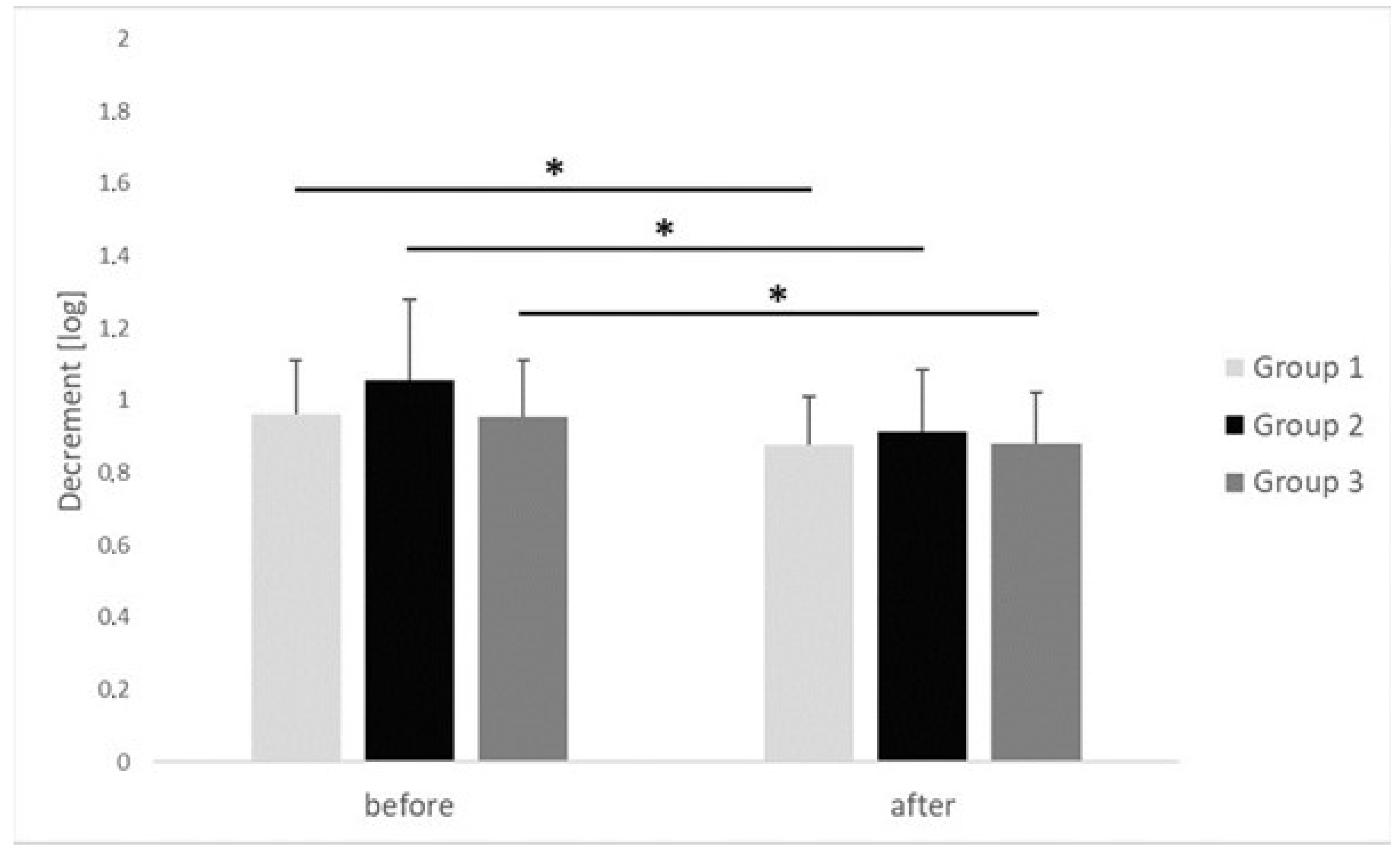
| Decrement [log] | before | 0.96 ± 0.15 | 1.05 ± 0.22 | 0.95 ± 0.15 | 0.882 | 0.02 |
| after | 0.87 ± 0.13 | 0.91 ± 0.17 | 0.88 ± 0.014 | 0.709 | 0.01 | |
| p | 0.022 | 0.001 | 0.042 | |||
| r | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.38 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szajkowski, S.; Pasek, J.; Cieślar, G. Immediate Effects of Multiple Ischemic Compression Applications on Pain Sensitivity and Biomechanical Properties of Myofascial Trigger Points. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15070125
Szajkowski S, Pasek J, Cieślar G. Immediate Effects of Multiple Ischemic Compression Applications on Pain Sensitivity and Biomechanical Properties of Myofascial Trigger Points. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(7):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15070125
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzajkowski, Sebastian, Jarosław Pasek, and Grzegorz Cieślar. 2025. "Immediate Effects of Multiple Ischemic Compression Applications on Pain Sensitivity and Biomechanical Properties of Myofascial Trigger Points" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 7: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15070125
APA StyleSzajkowski, S., Pasek, J., & Cieślar, G. (2025). Immediate Effects of Multiple Ischemic Compression Applications on Pain Sensitivity and Biomechanical Properties of Myofascial Trigger Points. Clinics and Practice, 15(7), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15070125







