Abstract
Thiamethoxam (TMX), a second-generation neonicotinoid insecticide, is one of the most widely used insecticides in Algeria. The present study assessed the effects of repeated subchronic exposure to the commercial formulation of thiamethoxam (Actara®, 25% WG) in albino male rats. The toxic effects of thiamethoxam (TMX) were studied biochemically and histopathologically. Twenty-eight male albino rats weighing between 226 and 243 g were randomly assigned to four groups. One group served as control, and the other three were served as experimental groups administered a neonicotinoid thiamethoxam (TMX; 26, 39 and 78 mg/kg/day) for 6 weeks. The effects of the insecticide on various biochemical parameters were evaluated at 2, 4 and 6 weeks. Histopathological studies were carried out in the liver, kidney, cerebellum and hippocampus at the end of the experiment. Changes in biochemical parameters glucose, ALT (alanine aminotransferase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), γGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase) ALP (alkaline phosphatase) urea and creatinine were observed in treated-groups in a dose dependent manner when compared to the control. Histopathological alterations were more intense in male rats from the TMX high dose group than those from group 2 and 3. Based on these results, subchronic oral administration of thiamethoxam altered the biochemical parameters, which correlated with histopathological changes in the liver kidney and brain.
Introduction
Nowadays, acute pesticide poisoning is an important public health problem worldwide and inappropriate use of those chemical products can lead to adverse effects to humans and the environment. The research on the risk of diseases associated with occupational and environmental exposures are primarily drawing on studies in human populations, along with supportive findings from experimental studies. Lifelong cumulative exposure to pesticides may produce lasting toxic effects on various organs including the central nervous system and contribute to the development of pathologies like systemic lupus erythematosus[1] and Alzheimer’s disease.[2]
Neonicotinoids insecticides have been registered globally in more than 120 countries, [3] in major markets acetamiprid, imidacloprid, thiacloprid, clothianidin, thiamethoxam, and dinotefuran.[4] These six neonicotinoids have distinct structural features compared with nicotine and at high doses were associated with evidence of systemic toxicity.[5] Animal studies indicate relatively low toxicity of neonicotinoides to birds, fish and mammals[6,7] because they have resistant nicotinic receptor subtypes compared to insects, as well as the protection of the central nervous system (CNS) by the blood-/brain barrier.[8] However, Rodrigues et al. (2010)[9] demonstrate that administration of the neonicotinoid insecticide may provoke alterations on the cholinergic system of rats, producing biochemical and behavioral effects that can be correlated to the toxicity produced by other kinds of pesticides that are linked to the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s type dementia.
Thiamethoxam (TMX), a second-generation neonicotinoid insecticide, developed both for foliar/soil applications and as a seed treatment for use in most agricultural crops all over the world.[10] Clothianidin and thiamethoxam are extremely toxic to winter worker honey bees, they act like endocrine disrupting chemicals.[11] It has been shown that TMX is a much better substrate for mouse liver microsomal CYPs than the corresponding rat or human enzymes in forming desmethyl-TMX (dm-TMX), which is also hepatotoxic, and clothianidin (CLO), which is not hepatotoxic or hepatocarcinogenic. [12] Systemic administration of 20 mg/kg/b.w./TMX in mice has shown that at least 44% of this substance is metabolized and that its metabolites are found in the brain.[13] Comparisons of the major metabolic pathways of thiamethoxam in vitro using mouse, rat, and human liver fractions has shown that metabolic rates in humans are lower than those in the rat. Though, the insecticide, thiamethoxam, has been found to cause a reduction in serum cholesterol an earlier sign of liver dysfunction that may be causally associated with the later pathological changes, and eventually cell death, increased cell proliferation and tumor formation[14] suggesting that thiamethoxam is unlikely to pose a hazard to humans exposed to this chemical at the low concentrations found in the environment or during its use as an insecticide.
In Algeria, the two formulations of Thiamethoxam Actara® for foliar application and Cruiser® for seed treatment are largely commercialized. The aim of this study was to determine the potential effects of the commercial formulation of thiamethoxam named Actara® in multiple organs of rats. For this purpose, biochemical and histopathological analysis were investigated in this setting.
Materials and Methods
A commercial formulation of thiamethoxam [3-2-Cloro 1,3-tiazol-5-ilmetil- 1,3,5- oxadiazinan-4-ilideno-Nnitroamine], named Actara® (25 WG) 25% purity of active compound was purchased from Syngenta Crop Protection Agrochemicals, Greensboro, USA. All other biochemical reagents used were obtained from commercial sources (BIOLABO SA, France).
Experimental animals and research design
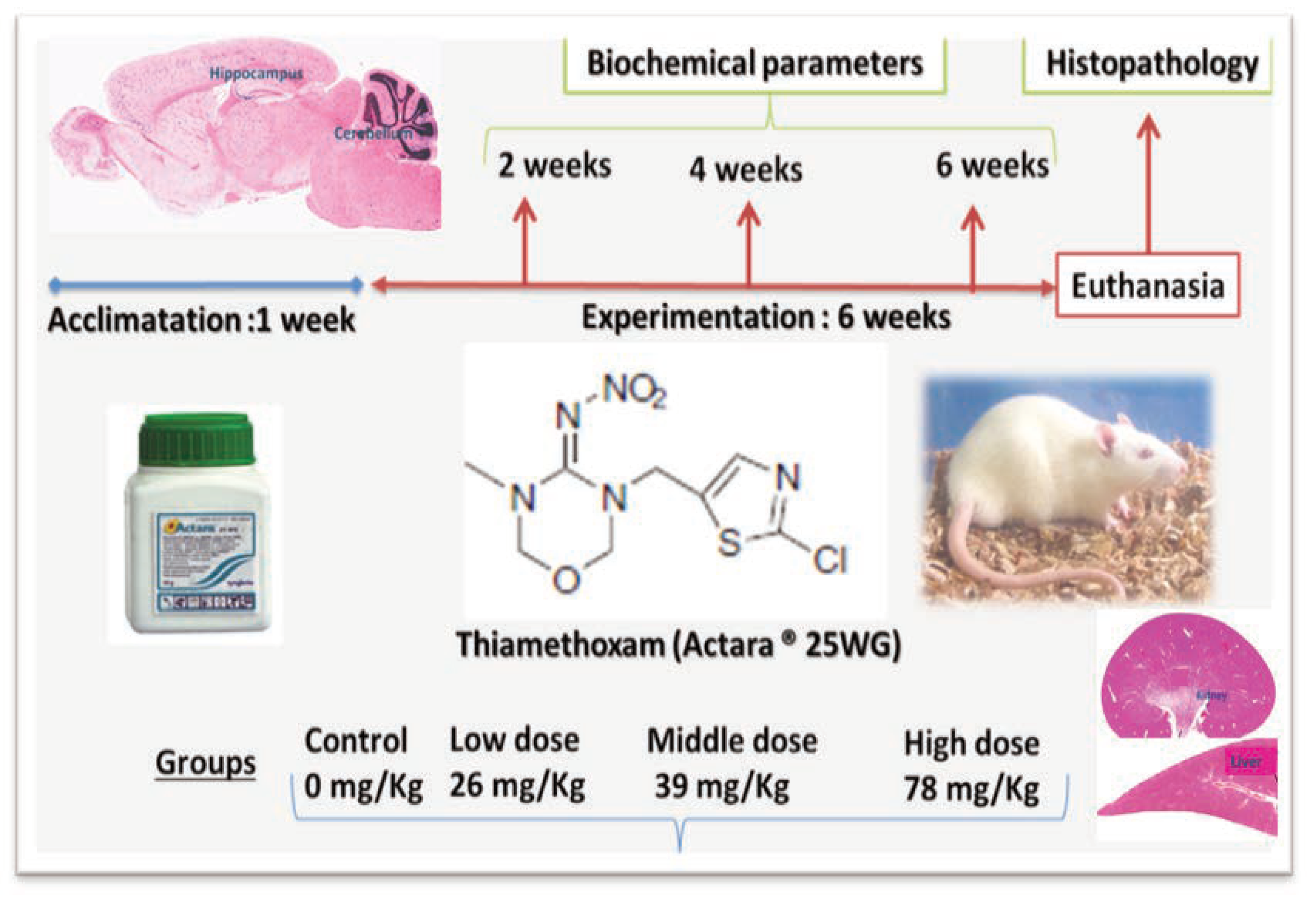
Male Wistar rats, weighing 226-243 g, were housed in four groups of seven animals under controlled conditions of temperature and photoperiod of 12 h light/dark, with free access to food and water. Treated animals received, by gavage three different doses of TMX dissolved in distilled water, 1/60, 1/40 and 1/20 TMX-LD50 respectively 26, 39 and 78 mg/kg/b.w. The oral LD50 value of thiamethoxam was 1563 mg/kg/b.w.[10] Control animals received vehicle (H[2]OD) in the same volume as treated animals. All rats were allowed to acclimate to their home cages for a week prior to the initiation of experiments.
The experiment was performed in accordance with the OCDE guidelines.[15] The research design involves treatment of the rats with the chemicals for 6 weeks. At the end of the 6 weeks experiment, the overnight-fasted rats were anesthetized using anesthetic ether than sacrificed by cervical dislocation.[16] The following organs liver, kidney, brain, testes, thymus and adrenal glands were collected. All these organs were weighed individually and organ body weight ratio was calculated (Figure 1).
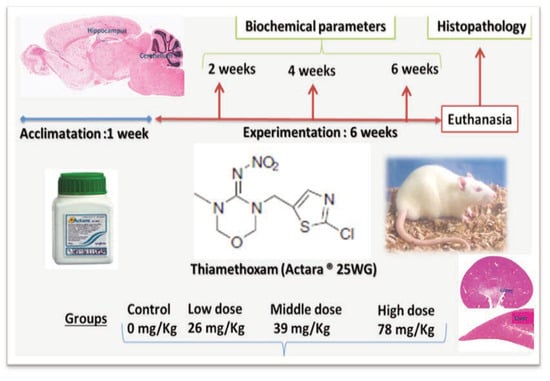
Figure 1.
Experimental animals and research design.
Biochemical measurements
At 2, 4 and 6 weeks after treatment, blood was collected by retro-orbital bleeding. Plasma samples were separated from blood cells by centrifugation at 3000 g for 10 min. Subsequently, plasma samples were used to determine creatinine, urea, ALT (alanine aminotransferase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), γGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase) ALP (alkaline phosphatase) and glucose levels using standard kits marketed by BIOLABO SA, France.
Histopathological examination
For selective investigation, the liver, kidney, brain were quickly excised and fixed in 10% normal buffered formalin. The samples were afterward paraffin-embedded, sectioned and stained with haematoxylin and eosin for microscopic examination.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare the experimental groups followed by Duncan’s post-hoc test to identify significantly different groups (Statistica version 10.0, StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, USA). P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Body weight
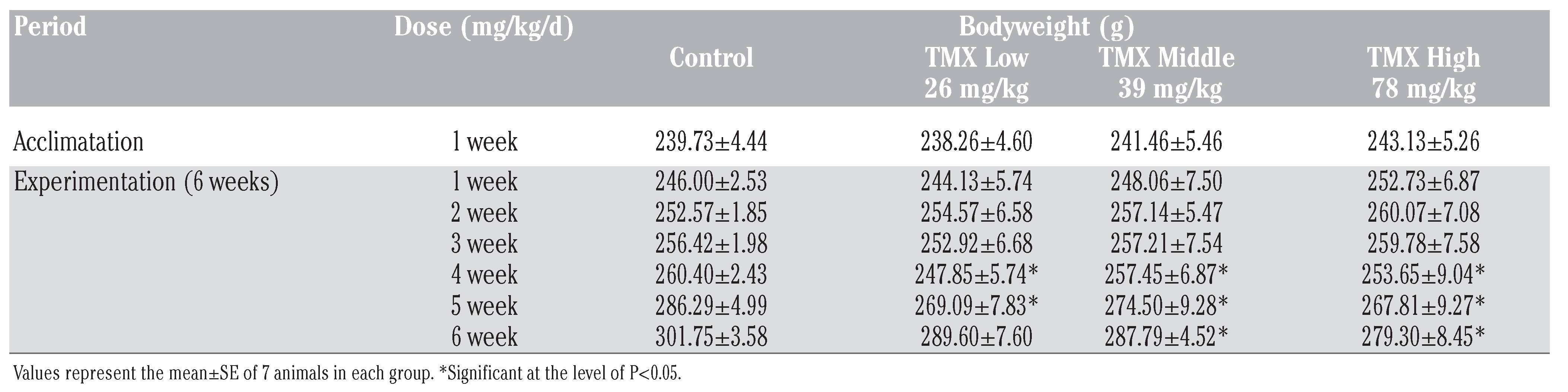
No deaths occurred in any group throughout the experiment. The body weight of the control and the TMX-treated rats during the experiment are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Body weight gain in rats after oral administration of thiamethoxam (26, 39 and 78 mg/Kg/b.w.of TMX) for 6 weeks.
Body weight of rats significantly decreases after TMX exposure for 6 weeks in a dose dependent manner. Comparison of the final body weight with the initial body weight revealed a significant difference and hence the increase of about 22 %, 18% and 15% was considerable in the control and TMX low and middle dose-groups respectively compared with an increase of about 10% in the TMX high dose group.
Absolute and relative organ weights
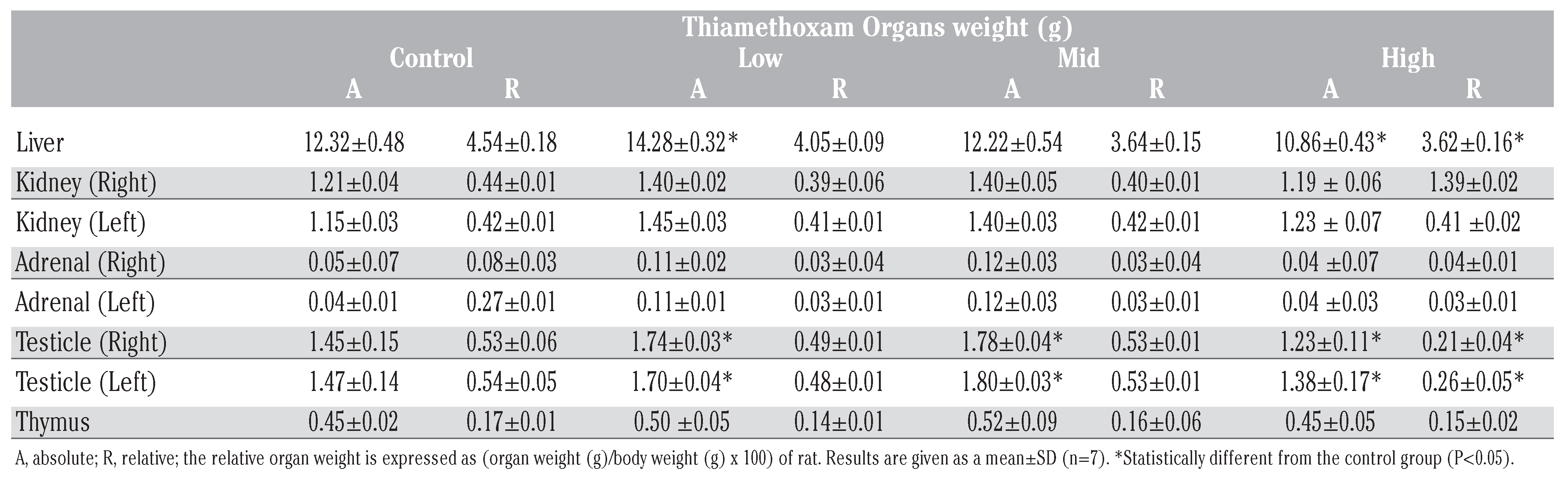
The relative and absolute organ weights are shown in Table 2. The organs like adrenals, kidneys and thymus of rats did not illustrate any significant change in their weights at any doses as compared to controls. However, relative weight of liver and testicles were significantly reduced (P<0.05) at 78 mg/kg/b.w.

Table 2.
Effects of thiamethoxam (TMX) on absolute and relative organ weights in the control and TMX-treated groups.
Biochemical parameters
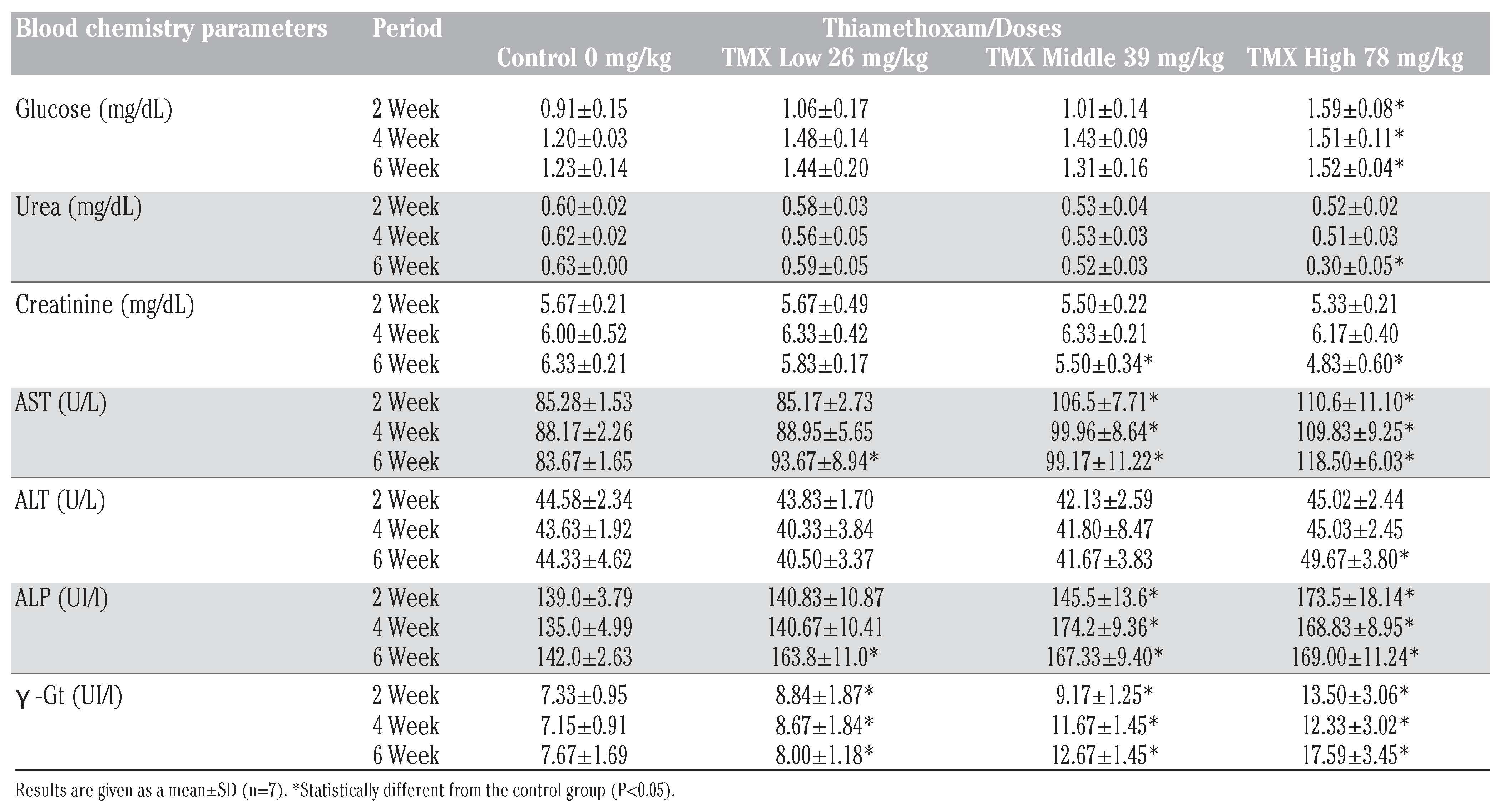
Plasma biochemical data after subchronic toxicity in rats, treated with three doses of thiamethoxam 26, 39, 78 mg/Kg/b.w at 2, 4 and 6 weeks, are presented on Table 3.

Table 3.
Biochemical data of male rats orally administered thiamethoxam for 6 weeks.
After six weeks of treatment, TMX at higher dose caused significant increase (P<0.05) in plasma glucose, urea and creatinine levels as compared with control group. While, AST, ALT, PAL and γ -GT levels significantly increased (P<0.05) in dose dependent manner.
Histopathological finding
The results of microscopic examination of the organs are summarized as follows. The liver, kidney, cerebellum and hippocampus of control rats appeared structurally and functionally normal without any visible lesion. However, pathological changes were observed in all cited organs of rats exposed to TMX at 26, 39 and 78 mg/kg/d in a dose dependent manner (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5).
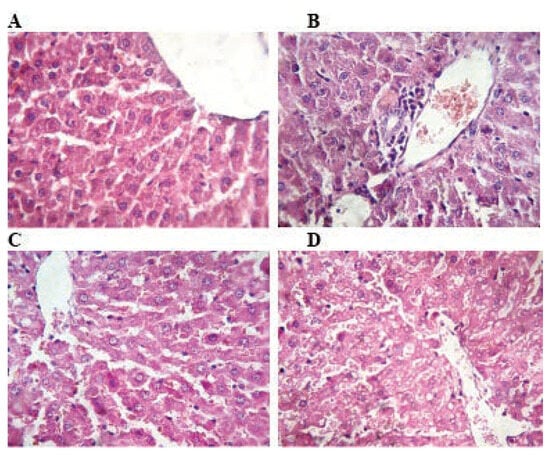
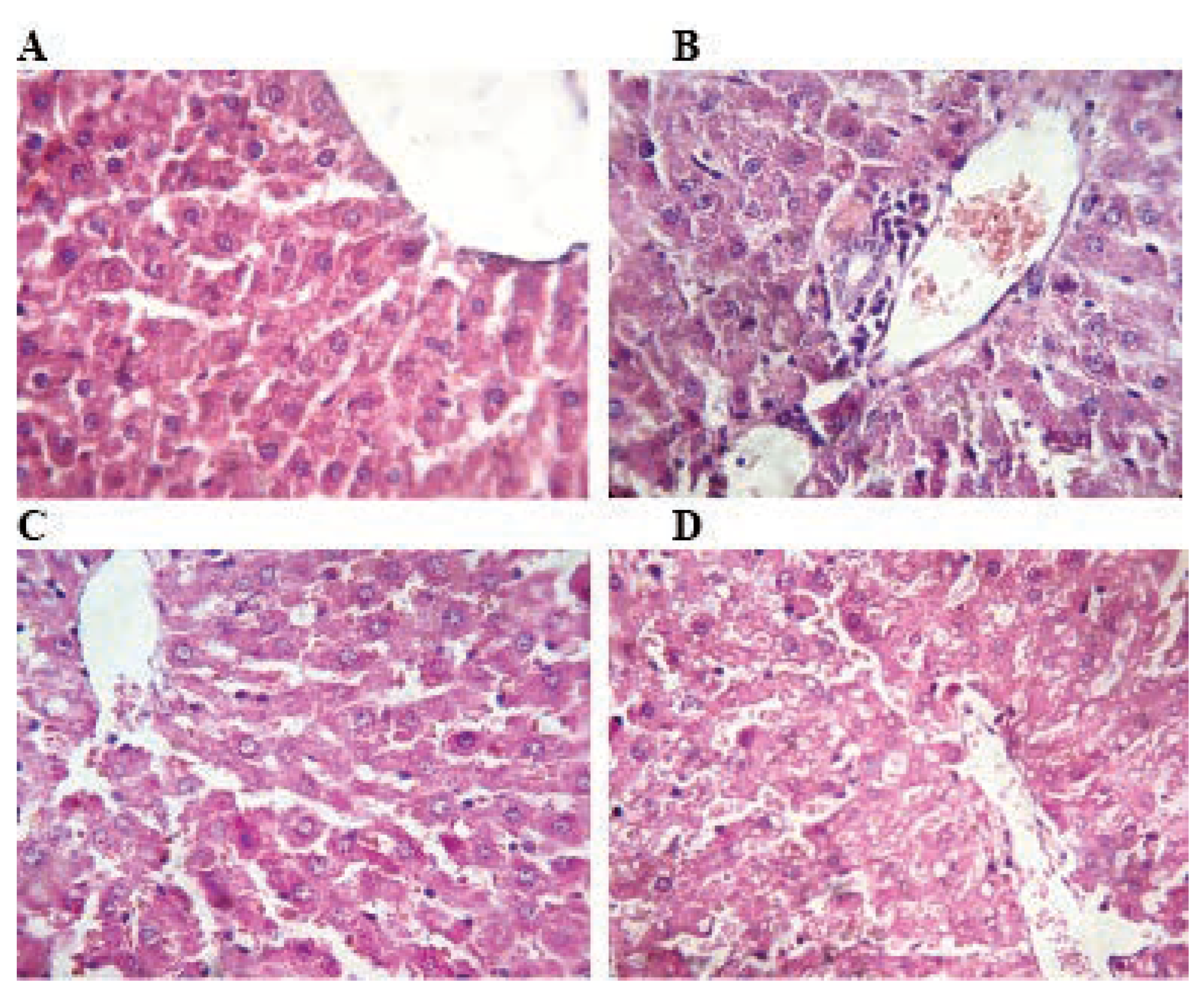
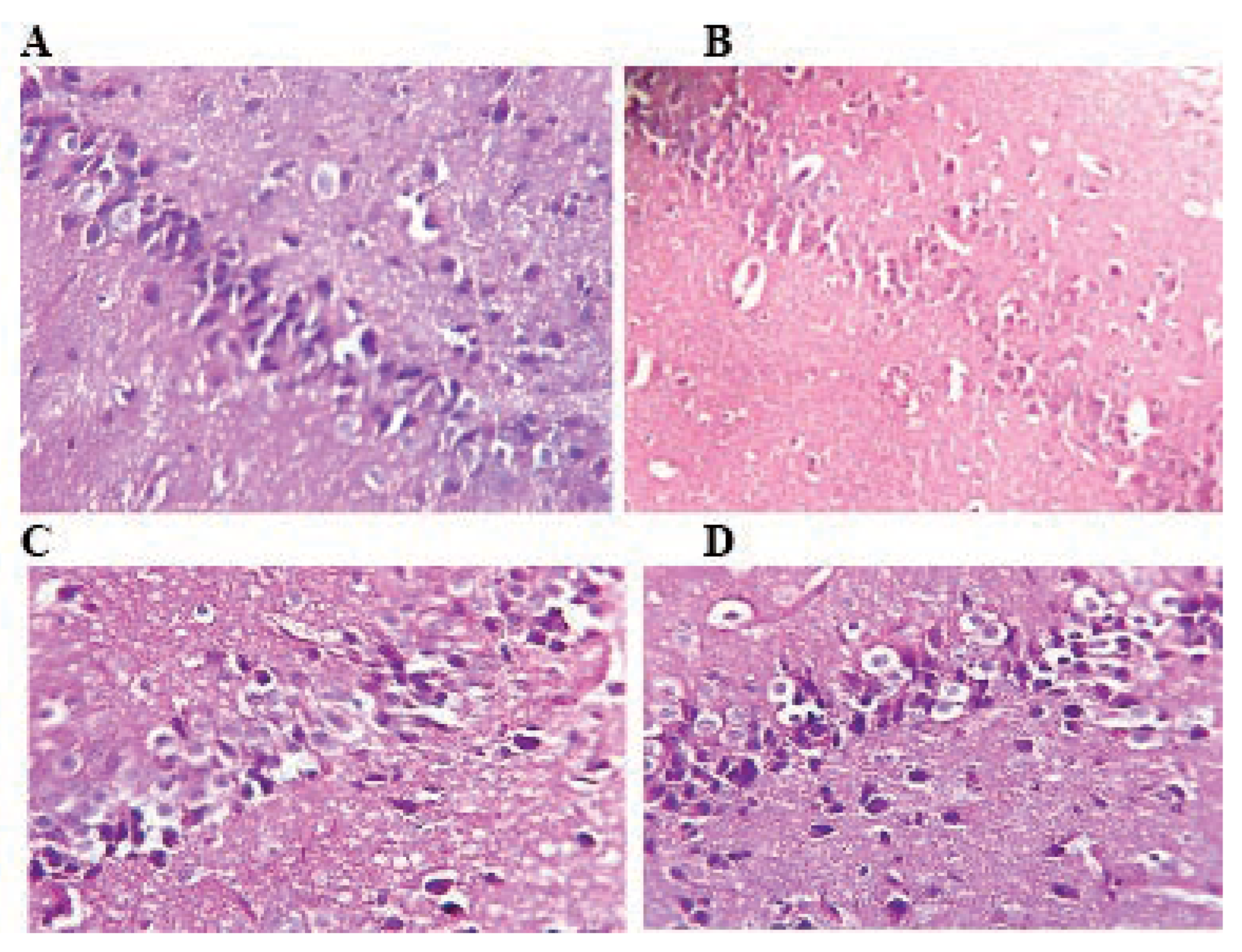
Figure 2.
Photomicrograph of rat liver stained with hematoxylin and eosin: A) the histoarchitecture of the liver is intact in control rats. B) Rats treated with TMX at 26 mg/Kg/b.w show few inflammatory cells infiltration and congestion. C and D) Rats treated with TMX 39 mg/Kg/b.w and 78 mg/Kg/b.w respectively shows disorganization of hepatic cords and degeneration of the hepatocytes with swollen cellular nuclei (A, B, C and D: H&E; Gr x400).
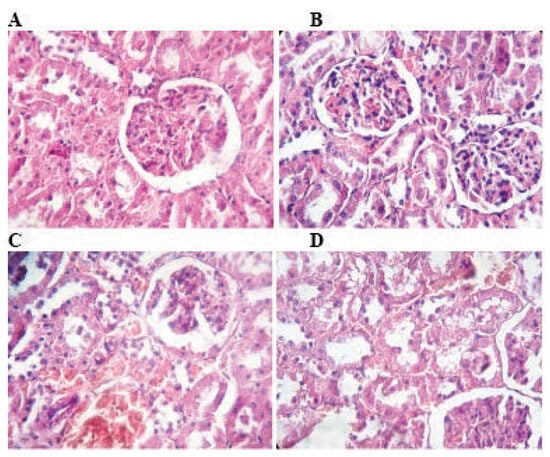
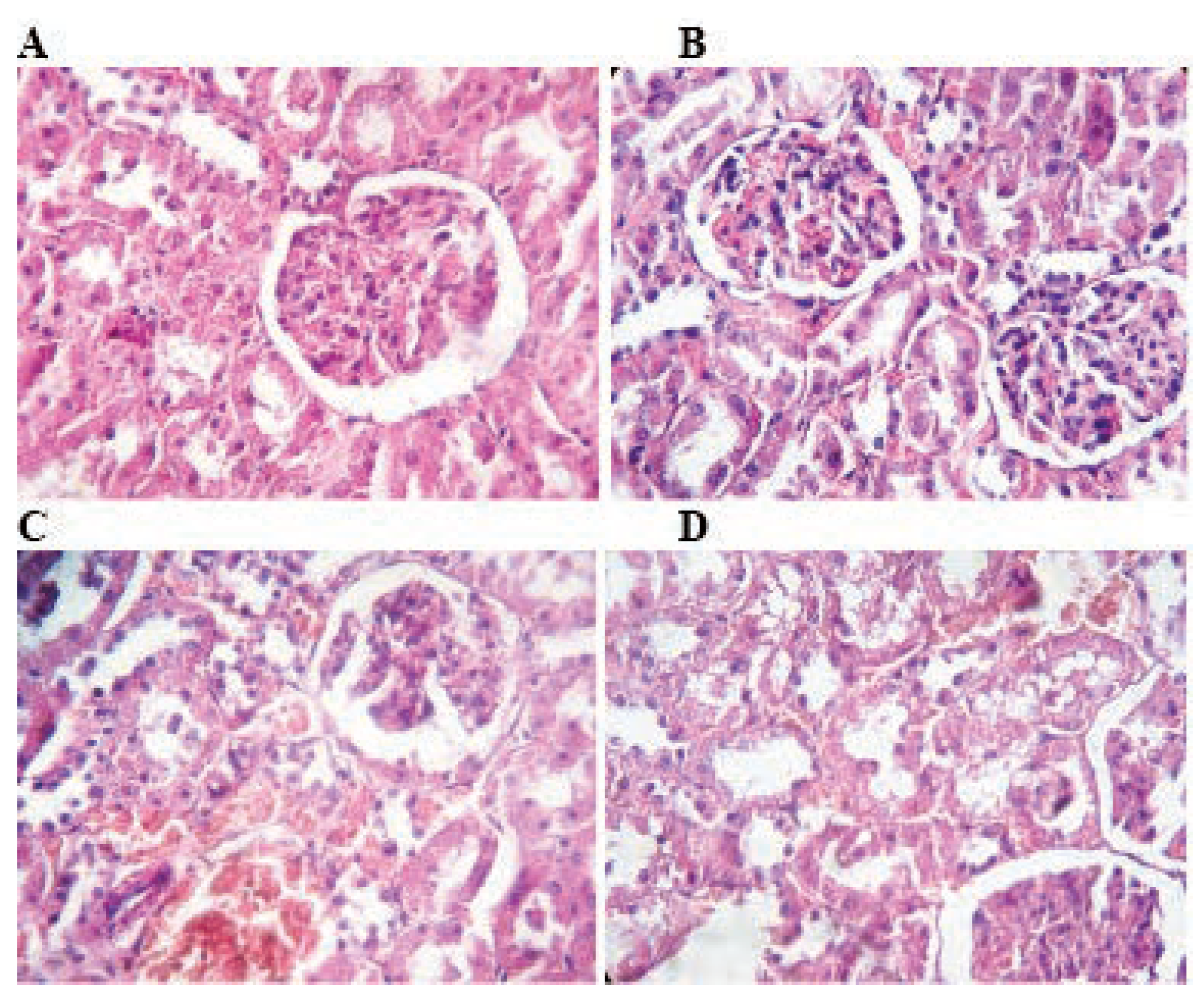
Figure 3.
Photomicrograph of rat kidney stained with hematoxylin and eosin: The histological structure of the renal cortex is intact in control rats and TMX low dose (A and B). Rats treated with TMX at 39 mg/Kg/b.w and 78 mg/Kg/b.w respectively (C and D) shows mild congestion in the glumeroli, and vacuolar degeneration of tubular cells (A, B, C and D H&E; 400).
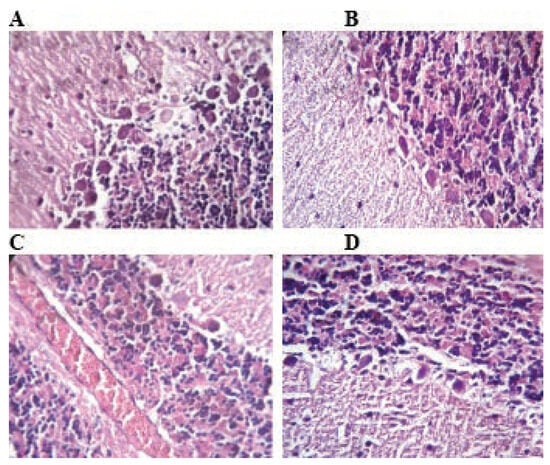
Figure 4.
Histological architecture of the cerebellum in the control and TMX-treated groups. In control group (A) normal histological architecture of cerebellum shows intact Purkinje layer, molecular layer, granular layer and gray matter. Rats treated with TMX at 26 mg/Kg/b.w shows Purkinje layer with few necrotic Purkinje cells (B). Cerebellum of TMX-treated rats at 39 and 78 mg/Kg/b.w respectively (C and D) showing congestion severe vacuolation in the molecular layer with degeneration and detachment of pyramidal cell layer degeneration of Purkinje cell layer (A, B, C and D H&E; 400).
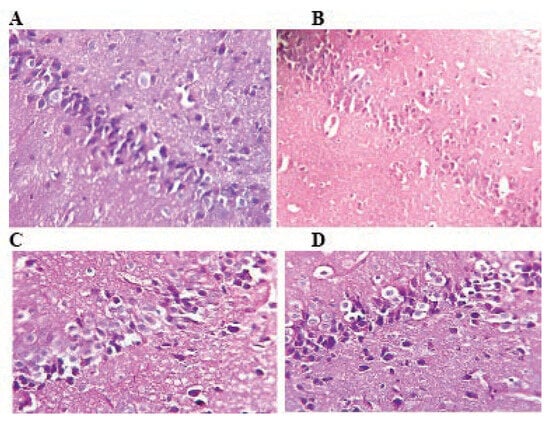
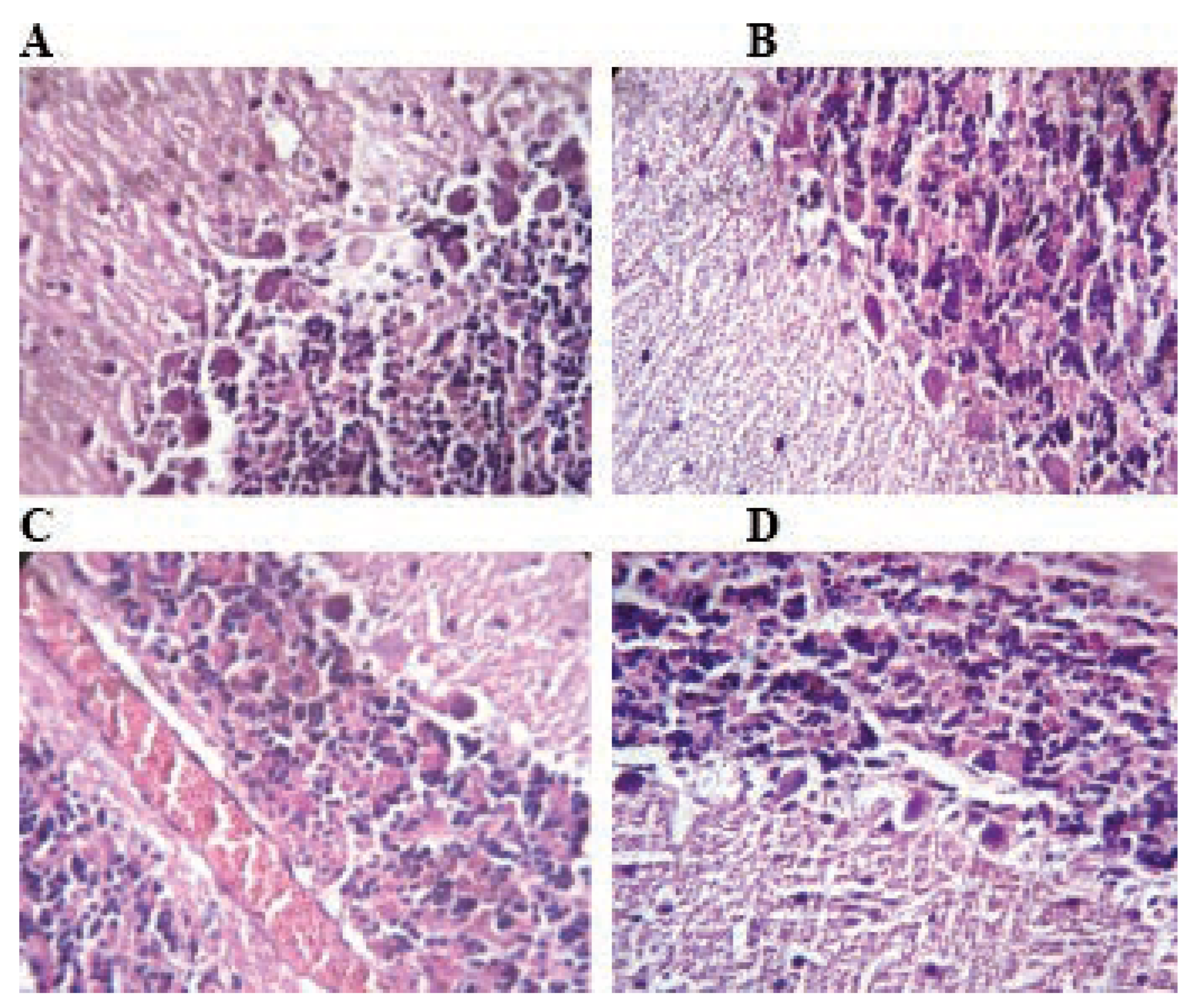
Figure 5.
Histological architecture of the hippocampus in the control and TMX-treated groups (H&E: 400). In control group (A), normal histological architecture of hippocampus. Rats treated with TMX shows neurodegradation states of pyramidal neurons and granule cells and foam structure between neurons (B, C and D) (A, B, C and D H&E; 400).
Effect of thiamethoxam on histological structure of the liver
In the liver, TMX lower dose (26 mg/kg/d) treatment for 6 weeks resulted in congestion of vessels and mild periportal infiltration by inflammatory cells. While, hepatocytes of liver at middle and high doses 39 and 78 mg/Kg/b.w respectively showed mild focal necrosis with swollen cellular nuclei and cytoplasmic lesions as compared to control (Figure 2).
Effect of thiamethoxam on histological structure of the kidneys
There were no pathological changes in the kidney of rats exposed to TMX at 26 mg/Kg/b.w. as compared with control. However, administration of TMX at 39 and 78 mg/Kg/b.w respectively caused renal necrosis, congestion of renal vessels and degeneration of the tubular cells (Figure 3).
Effect of thiamethoxam on histological structure of the cerebellum
The histological structure of the cerebellum in TMX exposed rats at low (Figure 4B) and middle (Figure 4C) doses showed congestion in cerebrum and degenerative changes in Purkinje cells as compared to control (Figure 4A). Whereas, repeated exposure of thiamethoxam at higher (Figure 4D) dose for 6 weeks, produced necrosed Purkinje cells with loss of dendrites and granules in the granular layer of cerebellum.
Effect of thiamethoxam on histological structure of the hippocampus
Histological structure of the hippocampus of the control group show normal pyramidal and multilateral cells forming the molecular layer (Figure 5A). In hippocampus of rats treated with TMX a decrease of degenerative changes can be observed (Figure 5B, C and D). It concerns all hippocampus zones of pyramidal cells as well as cells of granular and molecular layers. Degenerative changes in the structure of the hippocampus layers consist principally in various degree of cytoplasmic vacuolation, which result in foam structure.
Discussion and Conclusions
There is epidemiological and experimental evidence that environmental factors, like pesticides, influence a diverse array of molecular mechanisms and consequently alter disease risk not only for metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and immune system diseases but also for psychiatric and neurobehavioral disorders.[1,2,17]
In the present study, we examined the toxic effects of three doses of thiamethoxam 26, 39 and 78 mg/Kg/b.w. respectively for six weeks on hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity by using biochemical and histological techniques in rat.
Exposure to TMX caused a significant decrease in the body weight gain. This result is in agreement with the findings of Arfat et al. (2014),[18] who indicate that exposure to imidacloprid a neonicotinoide insecticide decreased body weight in male albino mice at 15 mg/kg/day together with significant toxicity symptoms.
The organ weights are important criteria for evaluation the toxicity of xenobiotics. Our results showed insignificant changes in the relative weights of kidney and thymus of rats. But, treatment with high dose TMX induced a significant reduction in relative liver and testes weights compared to respective control. Considering that thiamethoxam is metabolized to clothianidin in mammals, these findings agree with other several previous studies.[19,20]
The liver and kidney play an important role in the detoxification and elimination of numerous xenobiotics and are prone to various disorders as a consequence of exposure to environmental pollutants. Conventional liver biochemical parameters provide information about the integrity of hepatocytes, such as serum transaminases ALT and AST, with ALT being considered as the gold standard clinical chemistry marker of liver injury. In addition, the integrity of the biliary system is commonly assessed by measuring gamma-glutamyl transferase and alkaline phosphatase.[21,22,23]
Our result shows that six weeks oral exposure of high dose of thiamethoxam to rat has produced significant toxic effects. The activities of AST, ALT, ALP, γGT and glucose levels in the plasma of TMX exposed rats were significantly elevated, and the activity of creatinine and uric acid was significantly decreased, indicating that TMX disturbs the hepatic and renal functions. This effect was more pronounced in the TMX mild and high dose-groups. TMX provoke an increase in glucose levels those results are in agreement with the study of Khalil et al. (2017)[24] who show that imidacloprid perturbed the glucose regulation through hyperglycemic activity in both developing and adult rats.
The present study shows that subchronic oral administration of thiamethoxam lead to systemic biochemical but also histopathological damages of kidney, liver and brain. The renal tissue showed in TMXtreated groups glomerular and tubular lesions both in proximal and distal parts. Besides, the hepatic tissue showed mild focal necrosis with swollen cellular nuclei and cytoplasmic lesions in the TMX-treated groups. Consequently, thiamethoxam like imidacloprid disturb liver and kidney functions. Similar results have been found in animals exposed to neonicotinoid compound imidacloprid, thiamethoxam and clothianidin who demonstrate oxidative stress and inflammation in organs like liver, kidney and brain in mice and rats.[13,18,25,26]
The hippocampus is importantly and directly involved in the mediation of untrained anxiety reactions in animals.[21] Numerous works show that Alzheimer’s disease is a consequence of neuron loss, decrease of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), sodium- dependent choline transporter, and AChE activities, and a decreased level of acetylcholine in the hippocampal and cortical regions of the brain.[2,27,28] Potential concern that the neonicotinoid insecticides could affect the developing nervous system is associated with their nicotinic mode of insecticidal action and recognition of nicotine as a likely developmental neurotoxicant in humans and laboratory animals.[5] Nicotine is believed to interfere with neuronal development, with adverse effects on various brain regions, including cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, and/or the limbic system.[28]
Rodrigues et al. (2010)[9] indicate that mice 7 days exposure to high doses of thiamethoxam 100 mg/Kg/b.w. produces AChE inhibition in three cerebral regions, the hippocampus, striatum and cortex, that persists some days after exposure ceases and that it is accompanied by deficits in behavioral performance. According to the histopathological findings in this study, exposure to thiamethoxam led to destructive effects on the hippocampus and cerebellum of rat showing neuro-degradation states of pyramidal neurons and granule cells, foam structure between neurons of the hippocampus, degeneration and detachment of pyramidal cell layer and degeneration of Purkinje cell layer in the cerebellum of rats treated with TMX at middle and high doses.
Kimura-Kuroda et al. (2012)[29] show that acetamiprid and imidacloprid (two insecticides neonicotinoids), and nicotine exert similar excitatory effects on mammalian nAChRs at concentrations greater than 1 μM. Therefore, the neonicotinoids may adversely affect human health, especially the developing brain. The present investigation is the first to assess the impact of the TMX on the brain hippocampus and cerebellum, kidney and liver of male rats, and thus, contributes to the existing literature on the potential correlation between neonicotinoids and neurodegenerative disease and neurotoxicity.
References
- Parks, C.G.; De Roos, A.J. Pesticides, chemical and industrial exposures in rela- tion to systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2014, 23, 527–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yana, H. Pesticide exposure and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 322–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Selective toxici- ty of neonicotinoids attributable to speci- ficity of insect and mammalian nicotinic receptors. Ann Rev Entomol 2003, 48, 339–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensley, S.M. Chapter 48: Neonicotinoids. Veterinary Toxicology (Second Edition); 2012. pp 596-598.
- Sheets, L.P.A.A.; Lib, D.J.; Minnemac, R.H.; Collierd, M.R.; Creeke, R.C.; Pefferc, A. Critical review of neonicotinoids insecti- cides for developmental neurotoxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol 2016, 46, 153–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: mechanisms of selective action. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxical 2005, 45, 247–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, D.; George, I.A.; Peter, J.V. Toxicology of the newer neonicotinoid insecticides: imidacloprid poisoning in a human. Clin Toxicol 2007, 45, 485–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.M.; Meier, K.H. Acute Confidor® (imidacloprid-N-methyl pyrrolidone) insecticides intoxication with mimicking cholinergic syndrome. Toxicol Ind Health 2005, 21, 137–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.J.; Santana, M.B.; Do Nascimento, J.L.; Picanço-Diniz, D.L.; Maués, L.A.; Santos, S.N.; et al. Behavioral and bio- chemical effects of neonicotinoid thi- amethoxam on the cholinergic system in rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2010, 73, 101–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maienfisch, P.; Huerlimann, H.; Rindlisbacher, A.; Gsell, L.; Dettwiler, H.; Haettenschwiler, J.; et al. The discovery of thiamethoxam: a second-generation neon- icotinoid. Pest Manage Science 2001, 57, 165–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, D.; Wilton, E.; Pawluk, A.; Gorter Md Chomistek, N. Neonicotinoids act like endocrine disrupting chemicals in newly- emerged bees and winter bees. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 109–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tami, L.; Swenson, J.; Casida, E. Neonicotinoid formaldehyde generators: possible mechanism of mouse-specific hepatotoxicity/hepatocarcinogenicity of thiamethoxam. Toxicol Lett 2013, 216, 139–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, K.A.; Casida, J.E. Unique and common metabolites of thiamethoxam, clothiani- din, and dinotefuran in mice. Chem Res Toxicol 2006, 19, 1549–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.; Toghill, A.; Lee, R.; Waechter, F.; Weber, E.; Peffer, R.; et al. Thiamethoxam induced mouse liver tumors and their rele- vance to humans. Part 2: species differ- ences in response. Toxicol Sci 2005, 86, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Repeated dose 90 day oral toxicity study in rodents. Guideline No. 408.; 2010.
- Directive 2010/63/EU of The European Parliament And Of The Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of ani- mals used for scientific purposes (Text with EEA relevance). Official Journal of the European Union.
- Dubovický, M. Neurobehavioral manifestations of developmental impairment of the brain. Interdisc Toxicol 2010, 3, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfat, Y.; Mahmood, N.; Tahir, M.U.; Rashid, M.; Fan Zhao, S.A.; Li, D.-J.; et al. Effect of imidacloprid on hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in male albino mice. Toxicol Rep 2014, 1, 554–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Yanai, S.; Omotehara, T.; Hashimoto, R.; Umemura, Y.; Kubota, N.; et al. The combined effect of clothianidin and environmental stress on the behavioral and reproductive function in male mice. J Vet Med Sci 2015, 77, 1207–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, R.; Türk, G.; Tuzcu, M.; Yılmaz, Ö.; Kuloğlu, T.; Baydaş, G.; et al. Effects of the neonicotinoid insecticide, clothianidin, on the reproductive organ system in adult male rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 2013, 36, 421–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, E.; Treit, D. The role of hippocampus in anxiety: intracerebral infusion studies. Behav Pharmacol 2007, 18, 365–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, J.; Ratner, M.; Shaw, M.; Bailey, W.; Schomarker, S. The current state of serum biomarkers of hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 2008, 245, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Gil, F.; Lacasaña, M.; Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Tsatsakis, A.; Tesifón Parrón, M.R.; et al. Pesticide expo- sure and genetic variation in xenobiotic- metabolizing enzymes interact to induce biochemical liver damage. Food Chem Toxicol 2013, 61, 144–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.R.; Hesham, A.A.; AbdoNassan, H.M. Imidacloprid insecticide exposure induces stress and disrupts glucose home- ostasis in male rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2017, 55, 165–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzguner, V.; Erdogan, S. Acute oxidant and inflammatory effects of imidacloprid on the mammalian central nervous system and liver in rats. Pestic Biochem Physiol 2010, 97, 13–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, U.; Srivastava, M.K.; Bhardwaj, S.; Srivastava, L.P. Effect of imidacloprid on antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxida- tion in female rats. J Toxicol Sci 2010, 35, 577–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, D.H.; Lin, C.C.; Wu, M.L.; Deng, J.F.; Yang, C.C. Neonicotinoid insecticides: an emerg- ing cause of acute pesticide poisoning. Clin Toxicol 2009, 47, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.B.; Mcquown, S.C.; Leslie, F.M. The dynamic effects of nicotine on the devel- oping brain. Pharmacol Ther 2009, 122, 125–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura-Kuroda, J.; Komuta, Y.; Kuroda, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Kawano, H. Nicotine-like effects of the neonicotinoid insecticides acetamiprid and imidacloprid on cerebel- lar neurons from neonatal Rats. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© Copyright H. Khaldoun-Oularbi et al., 2017 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 License (CC BY-NC 4.0).