Biomarkers Study in Rainbow Trout Exposed to Industrially Contaminated Groundwater
Abstract
:Introduction
Materials and methods
Fish
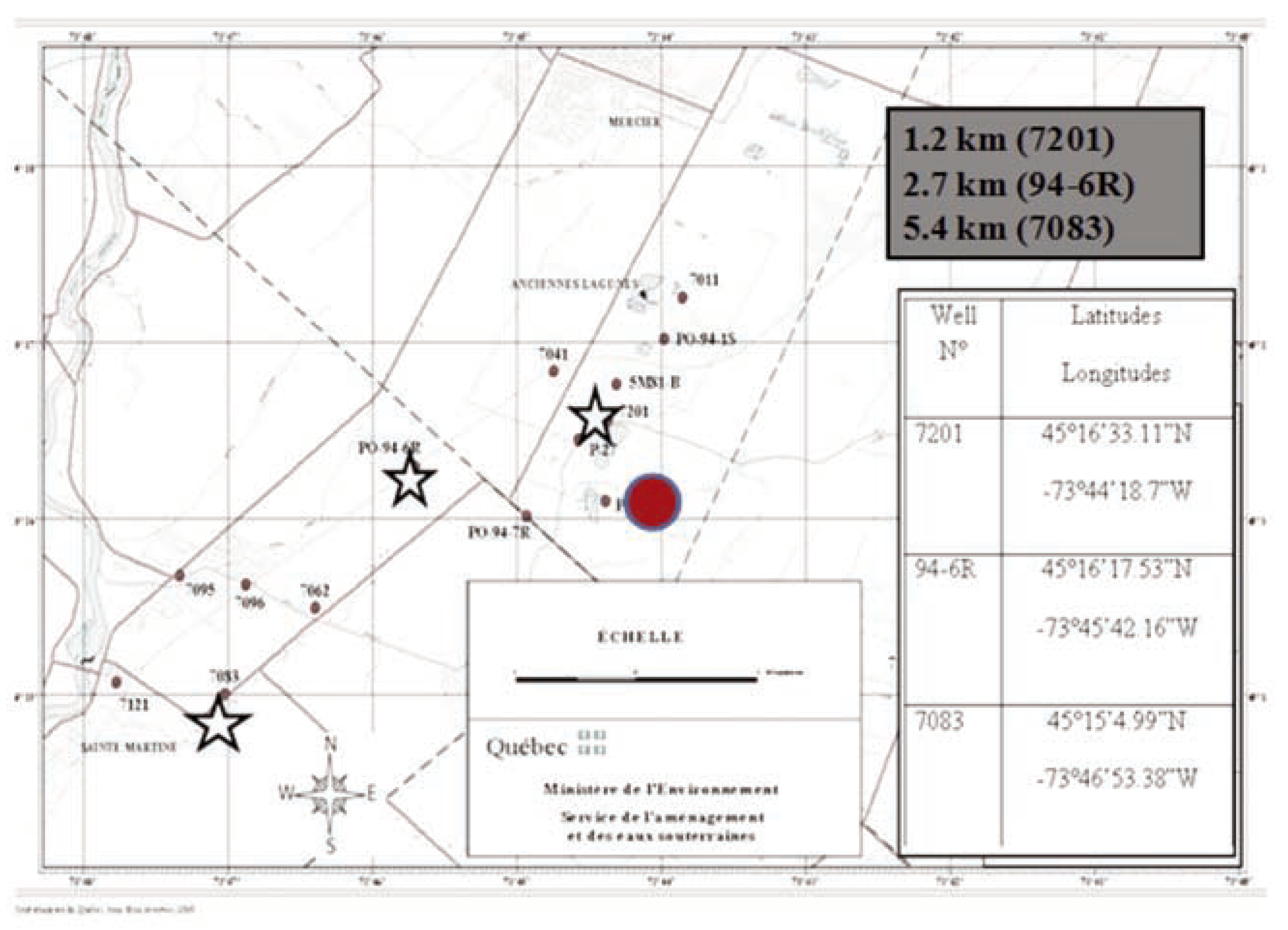
Groundwater exposure experiments
Biochemical analyses
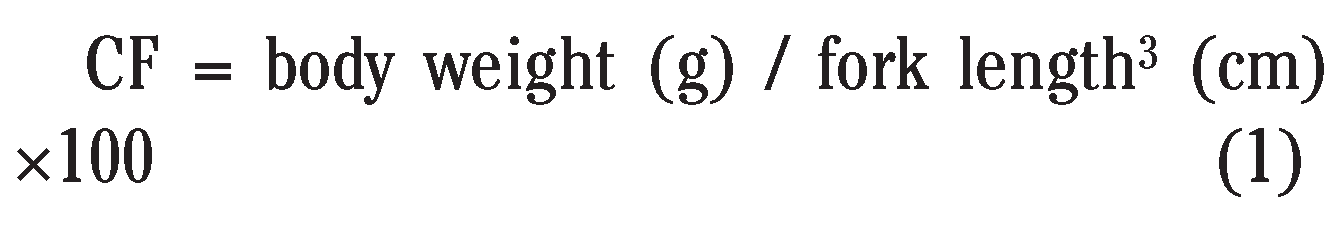 |
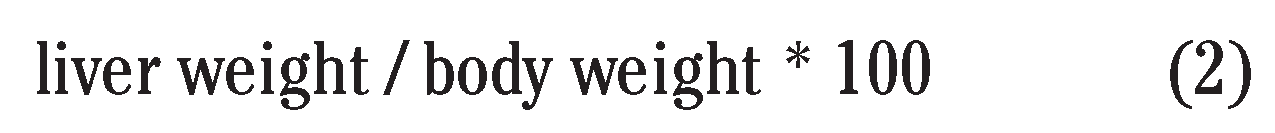 |
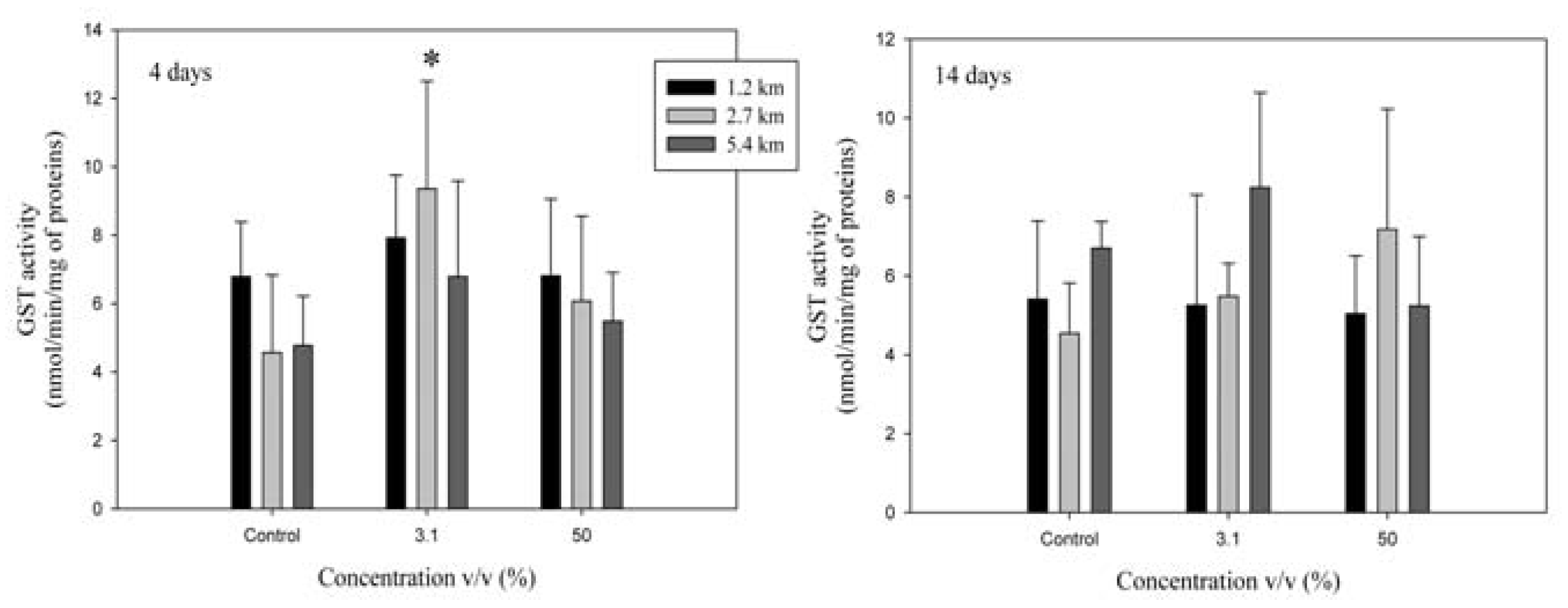
7-Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase
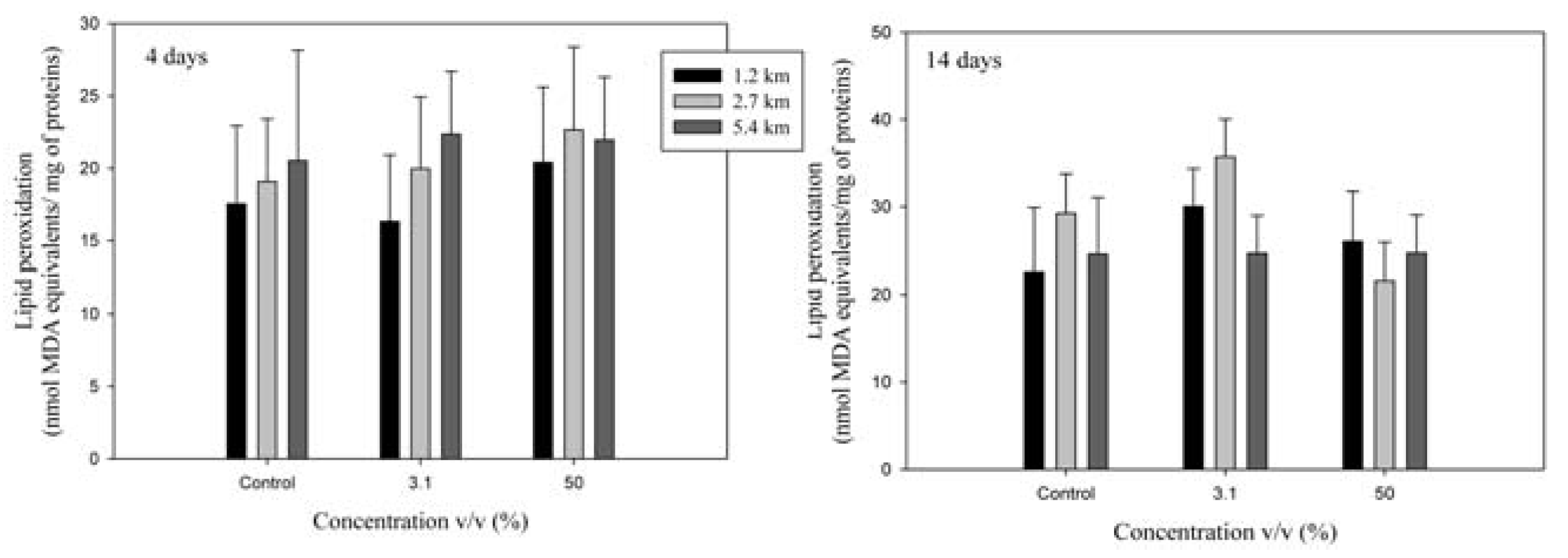
Lipid peroxidation
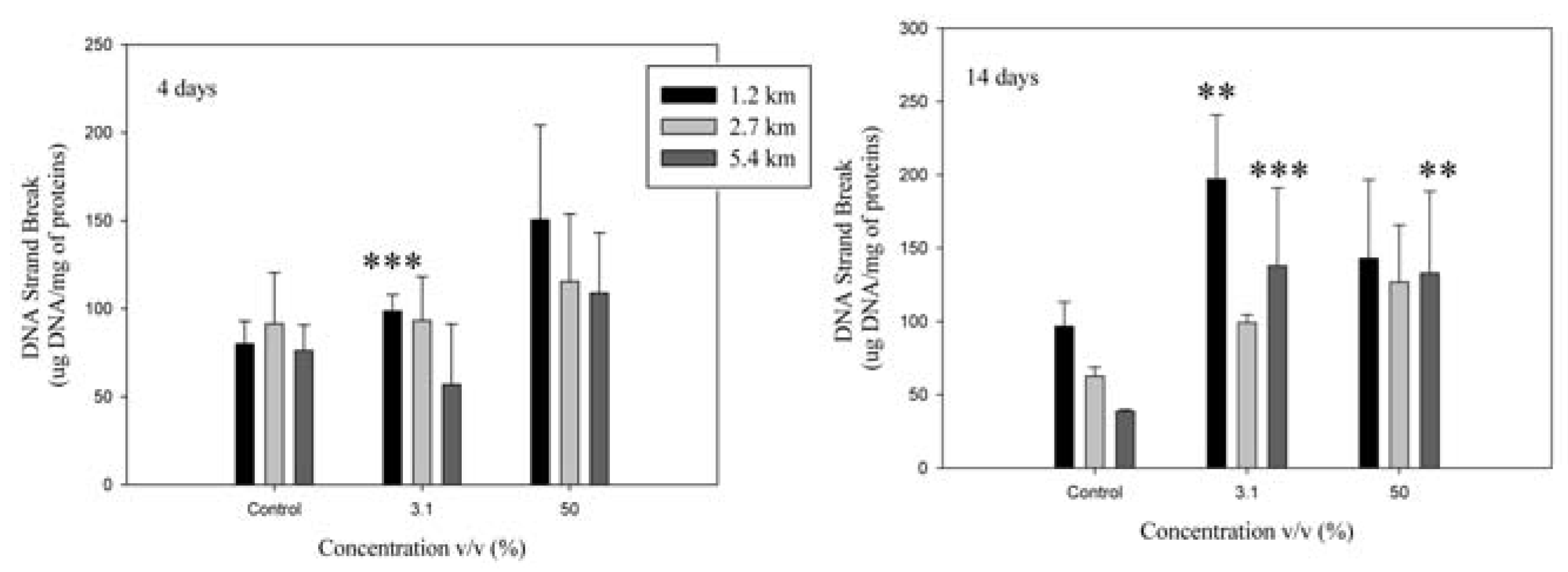
DNA strand breaks
Glutathione S-transferase
Statistical analyses
Results
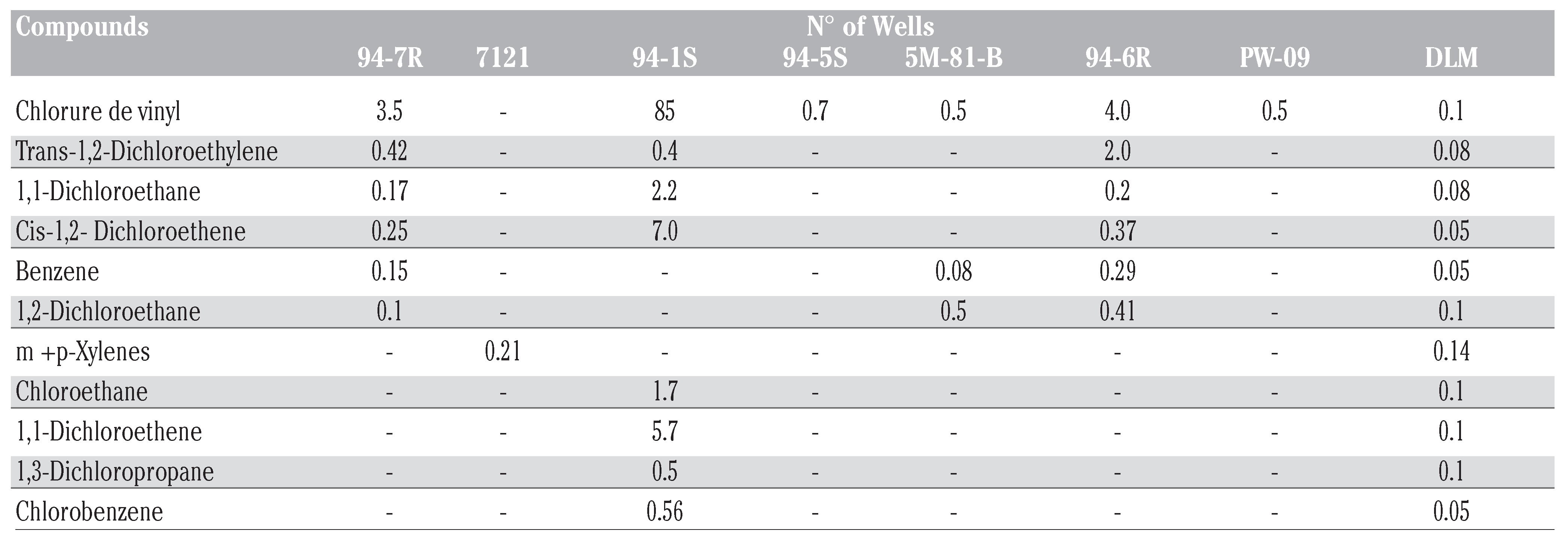
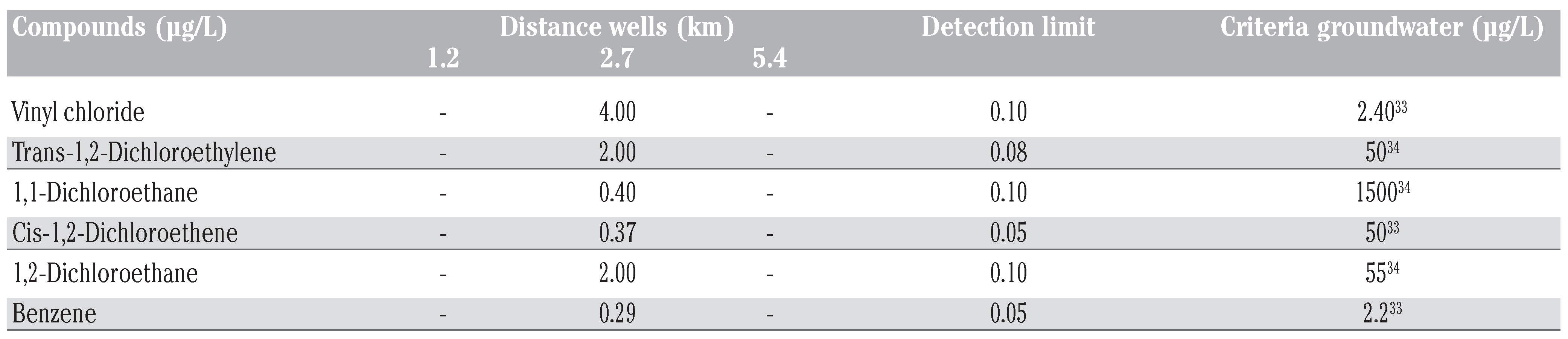
Chemical analysis
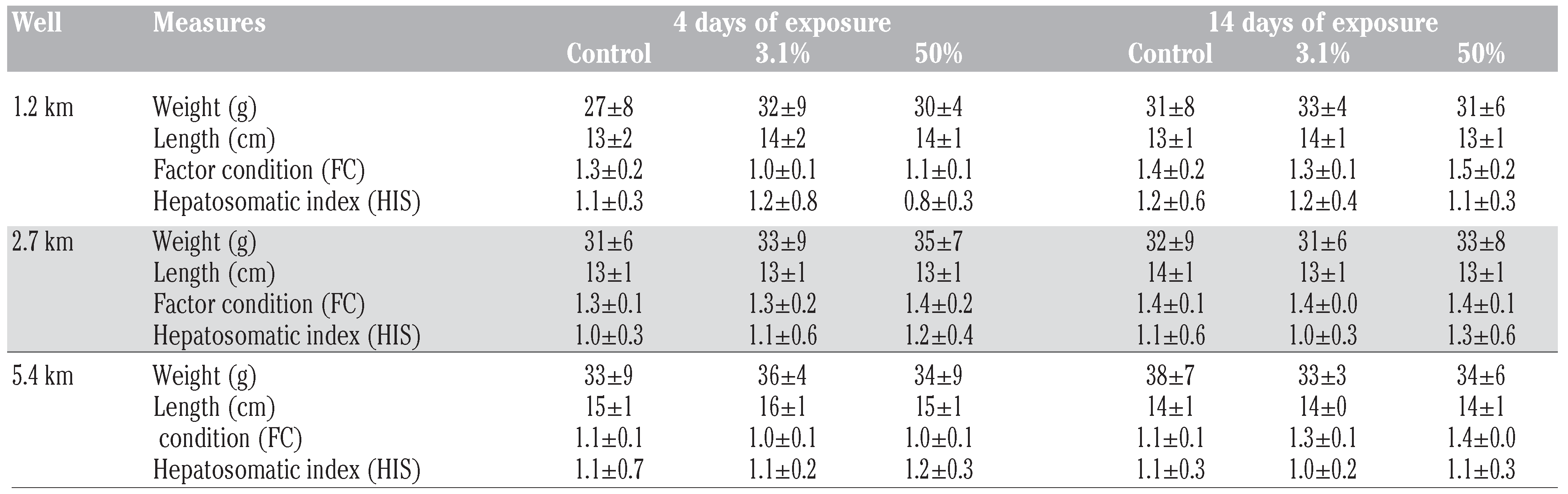
Morphological parameters
Biomarker responses
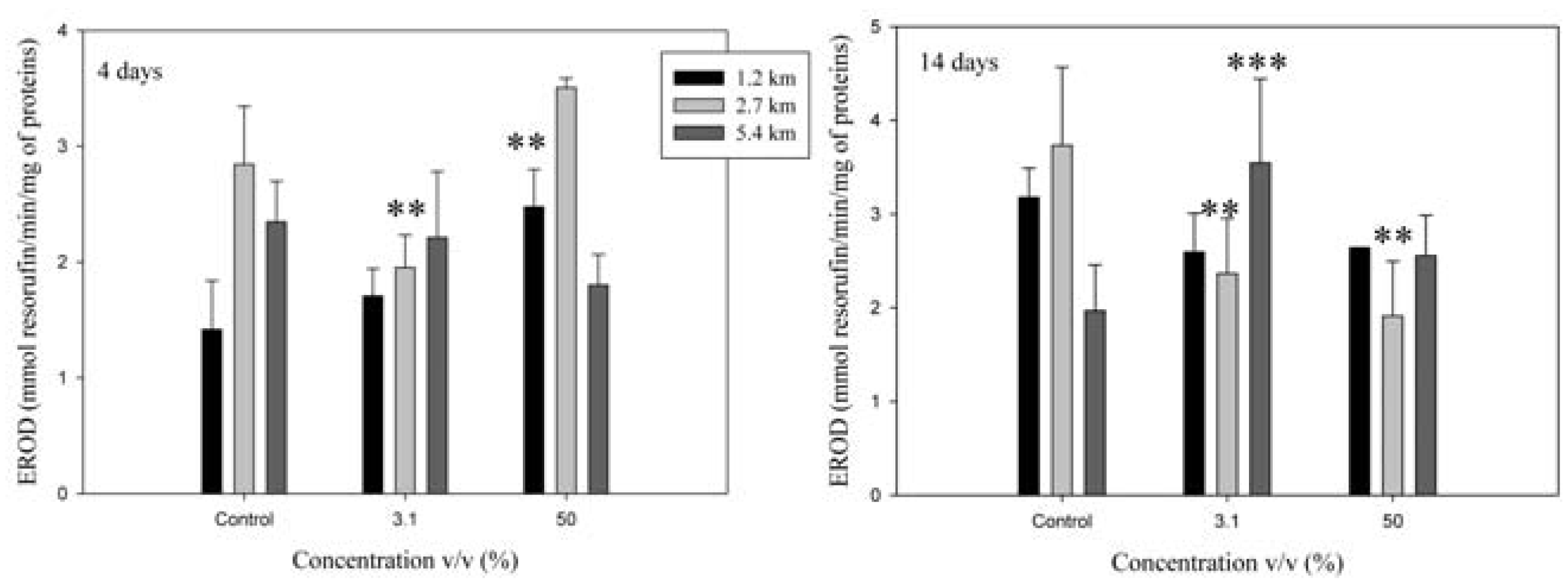
Phase I and II biotransformation activities
Biomarkers of tissue damage
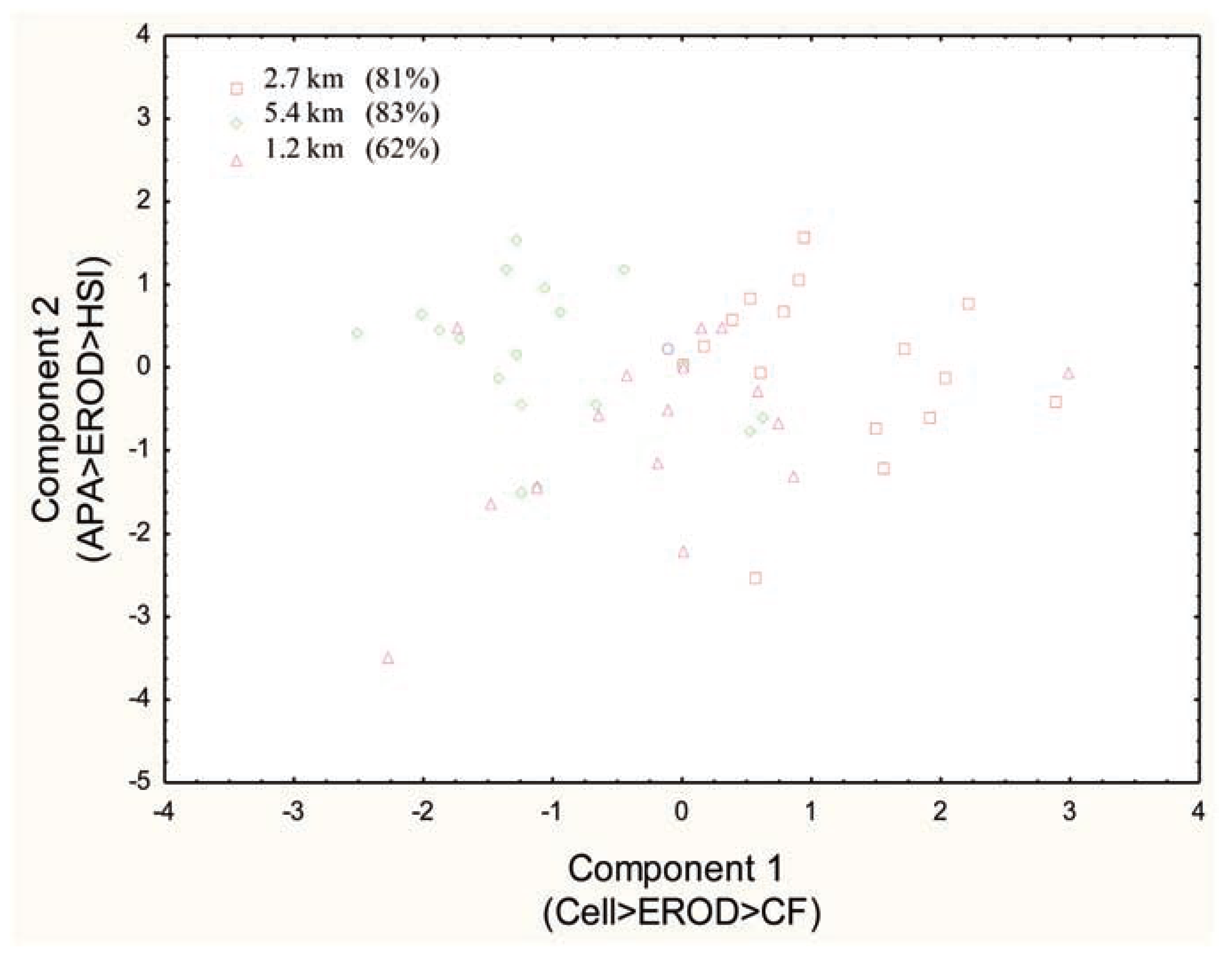
Discriminant function analysis
Discussion
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bureau d’Audiences Publiques sur l’Environnement du Québec (BAPE). Restauration du lieu contaminé de Mercier; Bureau d’Audiences Publiques sur l’Environnement du Québec (BAPE): Montréal, 1994; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Poulin, M.; Simard, G.; Sylvestre, M. Pollution des eaux souterraines par les composés organiques à Mercier, Québec [Ground- water pollution by organic compounds at Mercier, Quebec]. Hydrogéologie. 1985, 2, 125–31. [Google Scholar]
- Centre d’expertise en analyse environ- nementale (CAEQ). Certificat d’analyse: Eaux souterraines de la région de Mercier. Projet 5534; Centre d’expertise en analyse environnementale (CAEQ): Montréal, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Prime, J.; Fournier, M. Création d’un réseau de recherche interuniversitaire et multi- disciplinaire sur les problématiques envi- ronnementales associées au site des lagunes de Mercier: Rapport préparé par le Centre interinstitutionnel de recherche en écotoxicologie (CIRÉ). 2008; 224. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, H.R.; Scinicariello, F. The impact of CYP2E1 genetic variability on risk assess- ment of VOC mixtures. Regulat Toxicol Pharmacol 2011, 59, 364–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, M.; Fournier, M.; Brousseau, P.; Morin, A. Effects of volatile aromatics, aldehydes, and phenols in tobacco smoke on viability and proliferation of mouse lymphocytes. J Toxicol Environ Health - Part A 2002, 65, 1437–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabrodskii, P.F.; Mandych, V.G.; Germanchuk, V.G. Inhibition of cytochrome P-450 with 2- diethylaminoethyl-2,2-diphenylpropylac- etate (SKF-525A) reduces immunotoxicity of chlorinated carbohydrates. Bull Exper Biol Med 2006, 142, 324–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattes, T.E.; Alexander, A.K.; Coleman, N.V. Aerobic biodegradation of the chloro- ethenes: pathways, enzymes, ecology, and evolution. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2010, 34, 445–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gwinn, M.R.; Johns, D.O.; Bateson, T.F.; Guyton, K.Z. A review of the genotoxicity of 1,2- dichloroethane (EDC). Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 2011, 727, 42–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Sushama, A.; Rohil, V.; Manral, S.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Prasad, A.; et al. Preven- tion of benzene-induced genotoxicity in bone marrow and lung cells: superiority of polyphenolic acetates to polyphenols. Archiv Toxicol 2011, 85, 1141–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozzi, G.; De Bartolomeo, A.; Fabiani, R.; Rosignoli, P.; Lepore, L. Induction of DNA- damage and apoptosis by volatile organic compounds and by benzene metabolites. Igiene Moderna 1999, 112, 1503–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gros, M.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelo, D. Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for aquatic contamination by pharmaceuticals in the ebro river basin (northeast Spain). Environ Toxicol Chem 2007, 26, 1553–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Mishra, M.; Sharma, A.; Shukla, A.K.; Mudiam, M.K.R.; Patel, D.K.; et al. Genotoxicity and apoptosis in Drosophila melanogaster exposed to benzene, toluene and xylene: attenuation by quercetin and curcumin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2011, 253, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couillard, C.M.; Lee, K.; Légaré, B.; King, T.L. Effect of dispersant on the composition of the water-accommodated fraction of crude oil and its toxicity to larval marine fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 2005, 24, 1496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, L.; Kumaraguru, A.K.; Ramakritinan, C.M.; Anand, M. Biochemical response of anthracene and benzo [a] pyrene in milkfish Chanos chanos. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 2012, 75, 187–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, P.D.; Thornton-Manning, J.R.; Gargas, M.L.; Clewell, H.J.; Andersen, M.E.; Manning, J.R.T. Kinetic characterization of CYP2E1 inhibition in vivo and in vitro by the chloroethylenes. Archiv Toxicol 1998, 72, 609–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, M.; Gonzalez de Canales, M.L.; Gravato, C.; Guilhermino, L.; Perales, J.A. Biochemical effects and polycyclic aromatic hydrocar- bons (PAHs) in senegal sole (Solea sene- galensis) from a Huelva estuary (SW Spain). Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 2010, 73, 1842–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otitoloju, A.; Olagoke, O. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense enzymes in Clarias gariepinus as useful biomarkers for monitoring exposure to polycyclic aro- matic hydrocarbons. Environ Monit Assess 2011, 182, 205–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gomez, C.; Vethaak, A.D.; Hylland, K.; Burgeot, T.; Kohler, A.; Lyons, B.P.; et al. A guide to toxicity assessment and monitor- ing effects at lower levels of biological organization following marine oil spills in European waters. ICES J Marine Sci 2010, 67, 1105–18. [Google Scholar]
- Eseigbe, F.; Doherty, V.; Sogbanmu, T.; Otitoloju, A. Histopathology alterations and lipid peroxidation as biomarkers of hydro- carbon-induced stress in earthworm, Eudrilus eugeniae. Environ Monit Assess 2013, 185, 2189–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, N.; Larsson, Ã. Experiences from a biomarker study on farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) used for environ- mental monitoring in a Swedish river. Environ Toxicol Chem 2009, 28, 1536–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, J.J.; Jung, R.E.; Schmitt, C.J.; Tillitt, D.E. Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity in fish as a biomarker of chemical exposure. Crit Rev Toxicol 2000, 30, 347–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bols, N.C.; Brubacher, J.L.; Ganassin, R.C.; Lee, L.E.J. Ecotoxicology and innate immunity in fish. Develop Comparat Immunol 2001, 25, 853–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Oost, R.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, J.F.; Reimschuessel, R.; Shaikh, B.; Kane, A.S. Kinetics of hepatic phase I and II biotransformation reactions in eight fin- fish species. Marine Environ Res 2009, 67, 183–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazenave, J.; Bistoni, M.D.L.A.; Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Differential detoxification and antioxidant response in diverse organs of Corydoras paleatus experimen- tally exposed to microcystin-RR. Aquatic Toxicol 2006, 76, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monferran, M.V.; Galanti, L.N.; Bonansea, R.I.; Amé, M.V.; Wunderlin, D.A. Integrated survey of water pollution in the SuquÃa River basin (Cordoba, Argentina). J Environ Monit 2011, 13, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, X.R.; Wu, J.C.; Xue, Y.Q. Responses of the antioxidant defenses of the Goldfish Carassius aura- tus, exposed to 2,4-dichlorophenol. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2005, 19, 185–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Zlabek, V.; Velisek, J.; Grabic, R.; Machova, J.; Kolarova, J.; et al. Acute toxicity of carbamazepine to juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Effects on antioxidant responses, hematological parameters and hepatic EROD. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 2011, 74, 319–27. [Google Scholar]
- Nigro, M.; Frenzilli, G.; Scarcelli, V.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Induction of DNA strand breakage and apoptosis in the eel Anguilla anguilla. Marine Environ Res 2002, 54, 517–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.F.; Saga, A.; Akasaka, M.; Ishibashi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Su, Y.Q.; et al. Detection of in vivo genotoxicity of haloalkanes and haloalkenes carcinogenic to rodents by the alkaline single cell gel electrophoresis (comet) assay in multiple mouse organs. Mutat Res. 1998, 419, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchalgo, N.; Gagné, F.; Fournier, M. Immunotoxic effects of an industrial waste incineration site on groundwater in rain- bow trout (oncorhynchus mykiss). J Environ Sci, 2014; [In press]. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. 2006 Edition of the drinking water standards and health advisories (EPA 822-R-06-013). Office of Water, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, 2006; Available online: http://water.epa.gov/action/advisories/drinking/upload/2009_04_27_criteria_drinking_dwstandards.
- WHO. Guidelines for drinking-water quali- ty recommendations. Vol. 1: Recom - mendations, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2006; Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/gdwq3rev/en/.
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Analyt Biochem 1976, 72, 248–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagne, F.; Blaise, C. Hepatic metallothionein level and mixed function oxidase activity in fingerling rainbow trout (Oncorhyn- chus mykiss) after acute exposure to pulp and paper mill effluents. Water Res 1993, 27, 1669–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; Trottier, S.; Blaise, C.; Sproull, J.; Ernst, B. Genotoxicity of sediment extracts obtained in the vicinity of a creosote-treat- ed wharf to rainbow trout hepatocytes. Toxicol Lett 1995, 78, 175–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roose, P.; Brinkman, U.A.T. Volatile organic compounds in various marine organisms from the Southern North Sea. Marine Pollut Bull 2000, 40, 1167–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraku, Y.; Karwanishi, S. Oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis induced by benzene metabolites. Cancer Res 1996, 56, 5172–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kopecka-Pilarczyk, J.; Correia, A.D. Biochemical response in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) to in vivo expo- sure to pyrene and fluorene. J Exper Marine Biol Ecol 2009, 372, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, J.J.; Jung, R.E.; Schmitt, C.J.; Tillitt, D.E. Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity in fish as a biomarker of chemical exposure. Crit Rev Toxicol 2000, 30, 347–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Huang, K.-L.; Cheng, T.-J.; Wang J-, D.; Hsieh, L.-L. The GST T1 and CYP2E1 genotypes are possible factors causing vinyl chloride induced abnormal liver func- tion. Archiv Toxicol 1997, 71, 482–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Wang, R.S.; Elovaara, E.; Park, S.S.; Gelboin, H.V.; Hietanen, E.; et al. Monoclonal antibody-directed characterization of cytochrome P450 isozymes responsible for toluene metabolism in rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol 1991, 41, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filser, J.G.; Bolt, H.M. Pharmacokinetics of halogenated ethylenes in rats. Archiv Toxicol 1978, 42, 123–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, V.L.; Correia, A.C.; Santos, M.A. Genotoxic and biochemical responses in caged eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) after short-term exposure to harbour waters. Environ Int 2004, 29, 923–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and teratogenicity of marine sediments from Qingdao coastal areas using in vitro fish cell assay, comet assay and zebrafish embryo test. Toxicol Vitro 2010, 24, 2003–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Yin, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, S. Effects of four chlorobenzenes on serum sex steroids and hepatic microsome enzyme activities in crucian carp, Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 127–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, A.D.; Gongalves, R.; Scholze, M.; Ferreira, M.; Henriques, M.A.-R. Biochemical and behavioral responses in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) to phenan- threne. J Exper Marine Biol Ecol 2007, 347, 109–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Neuparth, T.S.; Caeiro, S.; Lobo, J.; Martins, M.; Ferreira, A.M.; et al. Assessment of the genotoxic potential of contaminated estuarine sediments in fish peripheral blood: Laboratory versus in situ studies. Environ Res 2011, 111, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, A.; Flammarion, P.; Bernardon, V.; Garric, J.; Monod, G. Monitoring of the chemical pollution of the river Rhone through measurement of DNA damage and cytochrome P4501A induction in Chub (Leuciscus cephalus). Marine Environ Res 1998, 46, 257–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 |
 |
 |
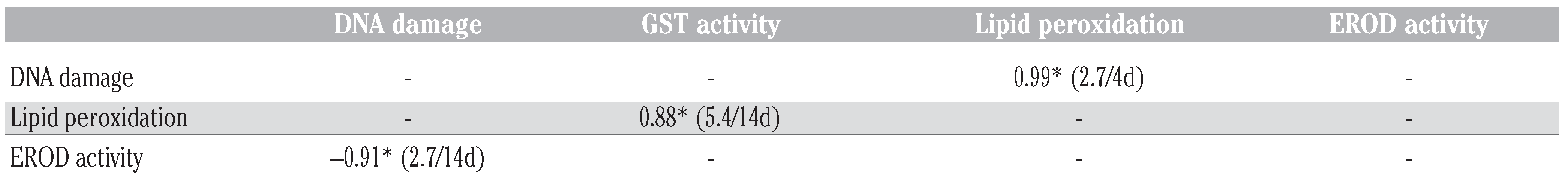 |
© Copyright N. Benchalgo et al., 2014. Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 License (CC BYNC 3.0).
Share and Cite
Benchalgo, N.; Gagné, F.; Fournier, M. Biomarkers Study in Rainbow Trout Exposed to Industrially Contaminated Groundwater. J. Xenobiot. 2014, 4, 1991. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.1991
Benchalgo N, Gagné F, Fournier M. Biomarkers Study in Rainbow Trout Exposed to Industrially Contaminated Groundwater. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2014; 4(1):1991. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.1991
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenchalgo, Nadjet, François Gagné, and Michel Fournier. 2014. "Biomarkers Study in Rainbow Trout Exposed to Industrially Contaminated Groundwater" Journal of Xenobiotics 4, no. 1: 1991. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.1991
APA StyleBenchalgo, N., Gagné, F., & Fournier, M. (2014). Biomarkers Study in Rainbow Trout Exposed to Industrially Contaminated Groundwater. Journal of Xenobiotics, 4(1), 1991. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.1991




