Abstract
Background/Objectives: The progressive increase in the aging population highlights the need for interventions aimed at preserving cognitive health and overall well-being in older adults. This study aimed to assess the impact of a structured cognitive training program on psychological well-being, executive function performance, and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor levels (BDNF) in older adults from a Mexican geriatric center. Methods: A quasi-experimental pretest–posttest design with a nonequivalent control group was conducted. Thirty-two older adults were assigned either to a cognitive stimulation intervention group or a control group. The intervention consisted of 120 individually structured sessions, each lasting approximately 60 min, delivered five times per week over 24 weeks. Independent neuropsychologists, blinded to group allocation, assessed executive function (BANFE-3), depressive symptoms (Yesavage Geriatric Depression Scale), autonomy in daily living (Barthel Index), and quality of life (WHOQOL-OLD) before and after the intervention. Serum BDNF levels were also measured. Results: The intervention group showed significant improvements in executive function, depressive symptoms, independence in daily activities, and quality of life, while the control group showed no changes. Additionally, the intervention group showed an increase in BDNF expression post-intervention. Conclusions: The cognitive stimulation program effectively improved cognitive performance, emotional well-being, autonomy, and quality of life in older adults. These findings highlight the importance of integrating structured cognitive stimulation into geriatric care. For nursing practice, this underscores the key role nurses can play in delivering cognitive interventions to promote cognitive health, independence, and emotional stability among institutionalized and non-institutionalized older adults.
1. Introduction
Population aging, resulting from increased life expectancy and declining birth rates, is a global phenomenon that presents significant challenges for health systems and public policy. Worldwide, the proportion of individuals over the age of sixty is rising rapidly, with estimates indicating that by 2030, one in six people will belong to this age group [1]. This demographic shift poses substantial public health challenges, particularly due to the cognitive changes associated with aging [2]. One of the most affected cognitive domains in this process is executive functions, a specialized subset of cognitive functions primarily associated with the brain’s prefrontal cortex, which are crucial for goal-directed behavior and self-regulation [3].
Cognitive decline, particularly in executive functions, can significantly impact the well-being of older adults [4]. The decline of these abilities can significantly impair the capacity to perform basic activities of daily living, thereby reducing functional autonomy [5]. This loss of autonomy is closely associated with an increased risk of developing depressive symptoms, as functional dependence and perceived incapacity negatively impact emotional health [6]. Collectively, cognitive decline, reduced autonomy, and the presence of depression contribute to a marked decrease in quality of life among older adults [7]. These relationships highlight the importance of developing interventions aimed at preserving and enhancing cognitive functions to promote healthy aging and sustained well-being.
Cognitive stimulation (CS) has emerged as a promising non-pharmacological intervention for preserving and enhancing cognitive functions in older adults. It involves a structured set of activities and exercises specifically designed to promote, maintain, and improve several cognitive domains, including memory, attention, and executive functions [8,9]. However, studies analyzing the effects of cognitive stimulation on cognitive functions have yielded inconsistent results. While some studies found a significant increase in participants’ cognitive function after the intervention compared to the control group [10,11,12,13,14], others failed to find an improvement in cognitive function [15,16,17], and some even found an increase in cognitive decline [18].
Furthermore, most CS programs are of short duration, highlighting the relevance of prolonged interventions as a key factor in optimizing their effectiveness. Longer interventions enable more comprehensive follow-up of participants and provide sufficient time for the consolidation and stabilization of cognitive improvements in older adults [13,19]. In support, Chiu et al. [20] suggested that the intervention characteristics of ≧3 times each week, ≧8 total training weeks, and ≧24 total training sessions yield a higher effect size. In addition, several considerations could enhance the scope and effectiveness of CS programs: (1) the use of gamification in delivering interventions may increase participant adherence and engagement [21]; (2) implementing the intervention in an individual format could better accommodate each participant’s pace and provide access for those unable to participate in group settings due to personal preferences, health conditions, behavioral issues, or fear of stigmatization [21,22] and (3) analyzing predictors of intervention outcomes and adherence could contribute to the optimization and personalization of future interventions [21].
CS has been shown to play a significant role in promoting neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize in response to new experiences and learning throughout the lifespan. This neuroplastic process is supported by several molecular mechanisms, among which the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) is particularly important [23]. BDNF is a neurotrophin that facilitates neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and the formation of new neural connections, all of which are essential for cognitive function and learning [23]. Evidence suggests that engaging in structured cognitive stimulation activities can increase BDNF levels [24], thereby enhancing neuroplasticity and contributing to the maintenance and improvement of cognitive functions in older adults [24].
Given the imminent inversion of the population pyramid and the growing need to address the cognitive needs of this vulnerable population, effective strategies to improve or mitigate cognitive deficiencies in older adults are essential. Therefore, the primary aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of a cognitive training program on older adults, specifically assessing its effects on psychological well-being, executive function performance, and serum BDNF levels. The secondary aim was to explore the potential association between these cognitive changes and variations in BDNF expression, contributing to a better understanding of the neurobiological mechanisms underlying cognitive stimulation and their role in promoting healthy aging.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
A quasi-experimental, pretest–posttest design was conducted with a nonequivalent control group, with a 1:2 allocation.
Participants were randomly assigned to one of two study groups: the experimental group (participants who received the intervention) and control group (participants with similar characteristics who did not receive the intervention). Throughout the study period, both groups continued to receive their usual medical and therapeutic care. All assessment instruments were administered simultaneously to both groups to ensure consistency in evaluation conditions.
The study design, data collection, analysis, and reporting were conducted in accordance with the STROBE (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) guidelines [25] (see Supplementary Material Table S1). Regarding ethical considerations, this research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, the General Health Law on Research, and was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the San Luis de la Paz General Hospital (CONBIOÉTICA Registry: CONBIOÉTICA-11-CEI-003-20200312). Participation was entirely voluntary, without any financial or other incentives.
2.2. Sample Size
Based on a previous study [26], a sample size of 36 participants in total was estimated to be sufficient to detect a mean difference of 1.05 between the experimental and control groups, assuming an α of 0.05 and a power (1 − β) of 0.8. Considering a 10% dropout rate, the recruitment target was set at 12 participants per group, maintaining a 2:1 ratio of experimental to control participants.
2.3. Participants
Older adults who attended the Gerontological Centers of the National System for the Integral Development of Families (DIF) in Guanajuato, Mexico, were invited to participate. (DIF is a Mexican decentralized agency attached to the Ministry of Health, responsible for directing social assistance at the national level.) Participants were randomly assigned to either the intervention or control group. To ensure comparability, randomization was stratified based on gender, age, educational level, and pre-intervention cognitive function score. This approach aimed to balance key characteristics between groups, minimizing potential confounding factors. To participate in the study, participants had to meet the following selection criteria:
Inclusion:
- ○
- Adults (of any gender) over 60 years of age.
- ○
- Willingness to participate in all intervention and assessment sessions.
- ○
- Ability to communicate verbally.
- ○
- Ability to participate in simple games/activities.
Exclusion
- ○
- Impairments or behavioral problems that could prevent participation in activities.
- ○
- Have received psychological or psychiatric care in the last two months.
- ○
- Presenting any condition that requires immediate intervention (i.e., suicidal ideation) or that interferes with participation in the study (i.e., severe hearing loss).
- ○
- Inability to communicate that limits participation in the intervention, as determined by the researchers.
- ○
- Presence of any medical condition that endangered survival during the project.
Elimination
- ○
- Change in residence.
- ○
- Participant or family member’s decision to withdraw from the study.
- ○
- Participating in less than 80% of the intervention sessions.
2.4. Blood Sample Collection and Measurement of BDNF Serum Levels
Venous blood samples were obtained from participants after an overnight fast of at least 8 to 12 h by puncture of the antecubital vein. Collection was performed using yellow tubes (tubes with separating gel and without anticoagulant; BD Vacutainer® SST™, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). The samples were allowed to stand at room temperature for 30 min to allow clotting and then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min. The resulting serum was processed by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA technique) using a commercial kit (Human BDNF ELISA Kit (ab212166, Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA)) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5. Cognitive Assessment
After the blood sample was collected, participants were allowed to have breakfast and consume their regular medication. Subsequently, and after a minimum period of one hour had elapsed, the cognitive assessment was conducted. Two neuropsychologists who were unaware of the study aims and the condition assigned to each participant conducted assessments at both pre-intervention (baseline) and post-intervention (6 months). The Neuropsychological Executive Functions and Frontal Lobes battery-3 (in Spanish, Batería Neuropsicológica de Funciones Ejecutivas y Lóbulos Frontales, BANFE-3), a neuropsychological battery that had been designed and validated for the Mexican population, was used [27], ensuring its applicability and accuracy in assessing executive functions in the population studied.
This instrument comprises a comprehensive set of tests with high reliability and validity for cognitive processes evaluation that depend mainly on the prefrontal cortex. It provides a global performance index of the functioning of the three prefrontal areas evaluated: the orbitofrontal cortex, anterior prefrontal cortex, and the dorsolateral cortex; it indicates the abilities and inabilities of participants in each of these cognitive areas. These areas are linked to cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, working memory, planning and organization, problem-solving, reasoning, attention, concentration, processing speed, and decision-making [28].
The interpretation of the total score and each of the areas enables classification of an individual’s performance as follows: high normal (116 and above), normal (85–115), moderate mild impairment (70–84), or severe impairment (<69), with high reliability and a Cronbach’s alpha greater than 0.80.
2.6. Measuring Well-Being Indicators
The day after the cognitive assessment was conducted, well-being indicators were assessed. Similar to the cognitive assessment, the assessments were conducted by two neuropsychologists who were unaware of the study aims and the condition assigned to each participant.
To assess symptoms of depression in the past 15 days, the Yesavage Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-15) was used. The score ranges from 0 to 15, where a score <5 indicates a normal range, 5 to 9 suggests mild depression, and more than 10 indicates moderate to severe depression [29]. This scale was validated in the Mexican population and is considered reliable and valid for measuring depression in older Mexican adults (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.84) [30].
In addition, to assess autonomy in activities of daily living (ADL), the Barthel Index was used, which has been widely validated and used in the geriatric population. This index analyses 10 aspects: bowel, bladder, personal hygiene, bathroom use, feeding, transferring, mobility, dressing, stairs, and bathing. The total score ranges from 0 to 100 points. The higher the score, the greater the functional independence [31]. This instrument has been validated in Mexican older adults and is recognized for its strong psychometric properties, making it a reliable and valid tool for assessing functional independence in the Mexican geriatric population (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.89) [32,33].
Finally, to assess quality of life, the World Health Organization Quality of Life-Old scale (WHOQOL-OLD) was used, an instrument developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) specifically to measure quality of life in older people. It is an instrument made up of 24 items that are answered on a five-point Likert scale, enabling the assessment of various degrees of satisfaction and perceived quality of life; divided into 6 areas: sensory skills, autonomy, past, present and future activities, social participation, death and intimacy [34]. The WHOQOL-OLD was validated in Mexican older adults, determining it suitable for application in the Mexican population to evaluate the construct of quality of life Cronbach’s alpha = 0.89) [35].
2.7. Cognitive Stimulation Intervention
A cognitive stimulation program was designed based on the following principles: (1) Cognitive stimulation therapy principles are person-centered, respect, participation, inclusion, choice, fun, maximizing potential, and strengthening individual social relationships between the therapist and each participant [36]; (2) Cognitive reserve is understood as the brain’s ability to cope with and/or tolerate brain changes associated with normal aging or due to a pathological process, delaying or decreasing the symptoms or clinical manifestations [37]. Cognitive reserve is dynamic and multifactorial, which enables participants to maintain functionality despite age-related brain changes [38]; (3) Neuroplasticity, according to which the brain could change as a result of experience [39]; and (4) this intervention followed the guidelines proposed by Dreer et al. [40] to maximize the success of interventions with elderly patients based on their neuropsychological functioning. This includes a higher frequency of sessions with shorter duration, a clear structure, and adaptations to the pace of each participant and the slower information processing speed often observed in older adults.
The main aim of this intervention was to enhance cognitive domains, primarily targeting cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, working memory, planning, reasoning, attention, concentration, and processing speed. All sessions followed the basic structure of the individual cognitive stimulation program suggested by Justo-Henriques, 2021 [41], as described in Table 1.

Table 1.
Structure of the individual cognitive stimulation program.
During the time allocated for cognitive stimulation, cognitive domains were trained through two cognitive stimulation tools:
1. Paper activities: A cognitive training manual was developed for the paper-based activities, which included 28 types of activities. Each activity comprised 30 exercises, divided into three predefined levels of complexity (basic, intermediate, and advanced), designed to provide a progressive challenge to cognitive functions: level 1 with 10 basic exercises, level 2 with 10 intermediate exercises, and level 3 with 10 advanced exercises (Table 2). In total, the manual contained 840 exercises (28 activities × 30 exercises). For reference, Supplementary Material File S1 includes an example of a Level 1 exercise for each of the 28 activities.

Table 2.
Structure of the cognitive training manual.
2. Board games: Several board games were used as a tool for cognitive stimulation in older adults (Table 3). Cognitive flexibility was stimulated through games that promoted adaptation to changes and the generation of new strategies. For inhibitory control, activities were implemented that challenged participants to regulate impulses and maintain focus on established rules. Working memory was exercised through games that facilitated the retention and manipulation of short-term information. Planning was stimulated through activities that required players to anticipate moves and develop strategies. Reasoning was promoted through games that encouraged problem-solving and logical decision-making. Attention was targeted through tasks that required sustained focus and precision in task execution. Finally, concentration and processing speed were enhanced through activities that incentivized quick and efficient responses. These games were integrated to create a dynamic cognitive stimulation program.

Table 3.
Board game uses in the intervention.
The intervention was applied during 120 individual sessions of 60 min duration, with a frequency of five times a week (total duration = 6 months or 24 weeks). Appendix A shows the exercise schedule used during the 120 sessions. The intervention was applied from January to July 2024, by the principal investigators as well as by nursing and midwifery students, previously trained by two experts in clinical psychology with six years of experience in cognitive stimulation, at the Gerontological Center.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS v.26. Descriptive statistics were computed to analyze the results of the assessment instruments, including measures of central tendency and dispersion. To evaluate changes in cognitive performance before and after the cognitive stimulation program, paired-sample comparison tests were applied, including Student’s t-test for related samples or the Wilcoxon signed-rank test when parametric assumptions were not met. Additionally, a comparative analysis of cognitive assessment results and well-being variables before and after the intervention was performed. To account for multiple comparisons and reduce the risk of Type I error, the Bonferroni correction was applied where appropriate.
To assess baseline homogeneity of categorical variables across conditions, the χ2 test was used. When expected values were below 5, Fisher’s exact test or the Fisher–Freeman–Halton exact test was applied. For continuous variables, the Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare two independent samples. The analyses followed the intention-to-treat principle, with all participants analyzed in their originally assigned groups. Missing data related to cognitive performance, depressive symptoms, and autonomy in daily living activities were addressed using the last observation carried forward approach.
To examine inter-group differences in cognitive performance, depressive symptoms, and autonomy at pre- and post-intervention, as well as therapist-related outcome variations, the Mann–Whitney U test for independent samples was performed. Intra-group changes from pre- to post-intervention were assessed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Effect sizes were calculated using Cohen’s d, with interpretation thresholds set at d = 0.2 (small), d = 0.5 (moderate), and d = 0.8 (large).
Adherence to the intervention was evaluated by analyzing the frequency distribution of participant dropouts and comparing dropout rates between groups using the Mann–Whitney U test. Additionally, descriptive statistics and frequency distributions were computed to assess the number of attended sessions.
3. Results
As presented in Table 4, the final sample comprised 36 participants, with 24 participants in the intervention group and 12 in the control group. The analysis revealed no statistically significant differences between the groups concerning the sociodemographic variables examined. This suggests that the groups were comparable at baseline, enhancing the validity of subsequent comparisons.

Table 4.
Sociodemographic characterization of the sample.
3.1. Adherence to the Intervention
Out of the 120 sessions that comprised the intervention, participants in the intervention group attended an average of 114.8 ± 5.2 sessions. A total of 28 participants (87.5%) attended all scheduled sessions, while 4 participants (12.5%) attended more than 80% of the sessions.
3.2. Cognitive Assessments
3.2.1. Intragroup Differences
As illustrated in Table 5, a comparison of pre-intervention and post-intervention scores demonstrated statistically significant improvements in the total executive functions score and across all subdomains within the intervention group. Additionally, regarding performance classification, the findings indicated significant differences, with an increase in the number of participants exhibiting higher performance levels. In contrast, no significant differences were found in the control group, underscoring the effectiveness of the cognitive stimulation intervention.

Table 5.
Intragroup comparison between cognitive assessments.
3.2.2. Intergroup Differences
A comparison of post-evaluation data revealed a significant improvement in the total executive function score and all individual domains in the intervention group, compared to the control group. Furthermore, regarding performance classification, significant differences were observed, with an increase in the number of participants attaining higher performance levels within the intervention group (Table 6). These results highlight the effectiveness of the cognitive stimulation program in improving executive function in older adults.

Table 6.
Intergroup comparison between post-cognitive assessment.
3.3. Well-Being Indicators
3.3.1. Depression
In relation to the Yesavage scale, a significant difference was observed between the intervention and control groups (t = 2.45, p = 0.027). This finding suggests that the intervention had an effect in reducing depression-related symptoms in the evaluated population (Figure 1).
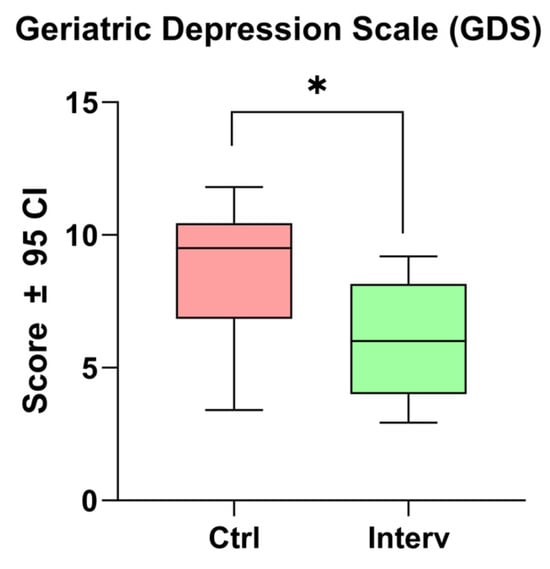
Figure 1.
Comparison of depression scores before and after the cognitive stimulation program using the Yesavage Scale. Unpaired t-tests were used to measure statistical significance * p < 0.05.
3.3.2. Autonomy in Activities of Daily Living (ADL)
A significant increase in the Barthel Index score was observed between the intervention and control groups (t = 3.534, p < 0.01). These results indicate that the cognitive stimulation program effectively enhances the level of independence in activities of daily living (ADL) within this population (Figure 2).
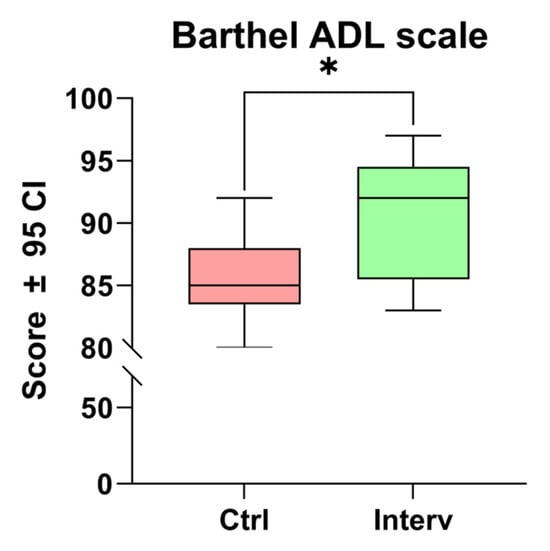
Figure 2.
Comparison of autonomy scores in ADL before and after the cognitive stimulation program using the Barthel Index. Unpaired t-tests were used to measure statistical significance * p < 0.05.
3.3.3. Quality of Life
Quality of life in older adults was assessed using the WHOQOL-OLD questionnaire. Significant differences were found between the intervention and control group comparisons for sensory abilities (t = 2.823, p = 0.014), social participation (t = 2.173, p = 0.027), and autonomy (t = 3.758, p = 0.007). These findings suggest that the intervention had a positive impact on specific aspects of quality of life in older adults (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Comparison of quality of life scores between the intervention and control groups using the WHOQOL-OLD questionnaire to assess the impact of the cognitive stimulation program. Unpaired t-tests were used to measure statistical significance * p < 0.05.
3.4. BDNF Serum Levels
As shown in Figure 4, the intervention group exhibited a significantly higher BDNF expression (362.75 ± 68.79 pg/mL) compared to the control group of older adults (243.17 ± 84.49 pg/mL; t = 3.248, df = 46, p = 0.001).
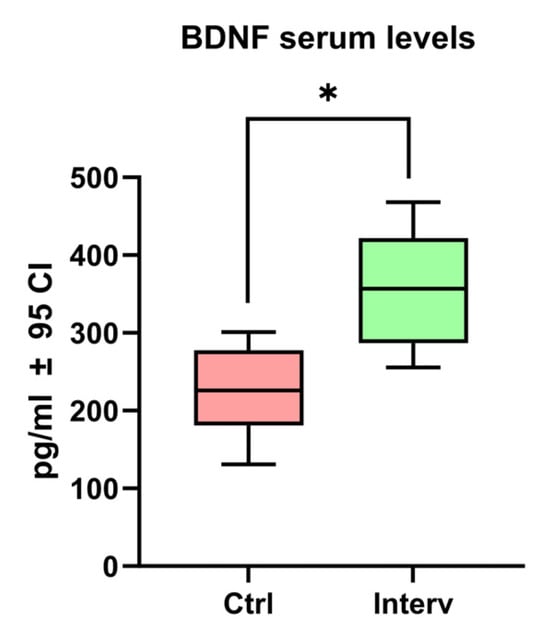
Figure 4.
BDNF serum levels among both older adult groups. Unpaired t-tests were used to measure statistical significance * p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
This study evaluated the efficacy of a cognitive stimulation program in an individual format with continued exposure to cognitive stimulation activities in Mexican older adults. Findings show that long-term cognitive stimulation intervention led to significant improvements in executive function within the intervention group. Intragroup comparisons showed a marked increase in the total executive function score and all individual domains, along with a higher proportion of participants achieving higher performance classifications. In contrast, the control group exhibited no significant changes in any of the measured outcomes. Furthermore, intergroup analysis confirmed that the intervention group outperformed the control group in post-intervention assessments, with statistically significant differences in both the overall executive function score and the classification of participants into higher performance categories. These results indicate the intervention’s effectiveness in enhancing cognitive performance and highlight the strength of these effects, suggesting potential clinical relevance in improving functional outcomes. Distinguishing between statistical significance and the actual magnitude of the changes observed will be important for understanding the real-world impact of these improvements.
Our findings are consistent with the idea that cognitive stimulation programs lead to improvements in several areas of cognitive functioning. For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis by Gómez-Soria et al. [42] suggest that cognitive stimulation can increase general cognitive functioning, memory, orientation, praxis, and calculation in older adults. Similarly, the systematic review and meta-analysis by Yun et al. [43] concluded that cognitive-based interventions were effective in improving the cognitive function of older adults, both in those without cognitive impairment and in those with mild impairment, which supports the results of our study by demonstrating significant improvements in these functions after the intervention in the experimental group [9]. These observed benefits may be explained by cognitive-based interventions stimulating neural plasticity, leading to enhanced cognitive performance. Additionally, such interventions might improve mood and motivation, further contributing to cognitive enhancement.
Several mechanisms can explain the neurobiological basis for these cognitive improvements. Cognitive stimulation has been shown to enhance neuroplasticity, which refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections [39]. This process is crucial for maintaining and improving cognitive functions in aging. Research indicates that cognitive training can increase the density of gray matter in brain regions associated with executive functions, such as the prefrontal cortex. Moreover, such interventions may boost synaptic density and connectivity, contributing to more efficient cognitive processing. Additionally, cognitive stimulation can help mitigate age-related declines in brain volume and support the preservation of cognitive reserves, which are vital for maintaining cognitive abilities despite the effects of aging [37,38]. These neurobiological changes likely underlie the observed improvements in cognitive performance and executive functions in our study.
In this study, a significant increase in serum BDNF levels was observed in the intervention group compared to the control group. BDNF is a key neurotrophic factor that plays an essential role in synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival, and its increased expression is associated with increased cognitive resilience. These findings are consistent with previous studies that have shown that cognitive training can favor BDNF upregulation, thus promoting cognitive function and contributing to the slowing of neurodegenerative processes [24,44]. For instance, a study by Ledreux et al. demonstrated that cognitive training over a 5-week period was associated with increased serum BDNF levels in older adults, suggesting benefits for brain health with aging [44]. Similarly, recent studies have shown that traditional Chinese exercises may improve BDNF levels in older populations, although variations in study designs necessitate further confirmation. However, differences in BDNF elevation across studies may be attributed to variations in training intensity, duration, and participant characteristics [45,46,47]. While some research indicates that combining physical and cognitive activities produces greater BDNF increases, our study demonstrates that cognitive training alone can have a significant neurotrophic effect. Additionally, methods of BDNF assessment and timing of sample collection may influence results, as some studies have used plasma BDNF measurements, while ours focused on serum levels, which may yield different sensitivities in detecting changes [48,49]
A plausible explanation for these observations is that cognitive exercises may stimulate neuroplasticity, leading to increased BDNF secretion. This elevation in BDNF could support neuronal growth and maintenance, thereby enhancing cognitive functions and offering neuroprotective benefits. Studies have demonstrated that cognitive training, especially when combined with physical exercise, can lead to significant increases in BDNF levels, which are associated with improvements in cognitive performance. Moreover, aerobic exercises such as brisk walking and high-intensity interval training, as well as activities like yoga and dancing, have been shown to improve cognitive function and increase BDNF levels. These activities promote neuroplasticity and may alleviate symptoms associated with cognitive decline [50].
A particularly relevant finding was the increase in the number of participants who reached higher performance levels after the intervention. This improvement in functional classification suggests that training not only optimizes performance in specific tasks but may also contribute to greater autonomy in activities of daily living [11]. This finding aligns with previous studies, including that of [9], who reported that cognitive stimulation programs can translate into long-term functional benefits in older adults, especially if they already have some type of cognitive impairment.
In this sense, the findings have a clear implication in indicators of well-being such as depression, a significant difference was observed when comparing scores before and after cognitive stimulation (t = 2.45, p = 0.027). This finding suggests that the intervention had an effect in reducing depression-related symptoms in the population assessed. Such a result is in agreement with previous research that has shown that cognitive stimulation may play a key role in improving emotional well-being in older adults [8].
In relation to quality of life, the findings of this study reinforce the idea that cognitive training not only impacts cognitive function per se but also improves key components of subjective well-being in this population. Recent studies have shown that strengthening autonomy and social interaction contribute to a better perception of quality of life in older adults [10]. Thus, the implementation of this type of program could be integrated into public health strategies aimed at promoting active and healthy aging [51,52].
4.1. Perspectives for Clinical Practice
The results of this study underscore the relevance of structured cognitive stimulation programs as an effective strategy to promote cognitive health, psychological well-being, autonomy, and quality of life in older adults. The cognitive stimulation program developed and implemented in this study could represent a practical tool that can be integrated into routine geriatric nursing care.
From a clinical perspective, nursing professionals play a key role in identifying cognitive decline, initiating preventive interventions, and supporting sustained engagement in cognitive activities. The structured nature of the program allows nurses to plan and deliver sessions systematically, adapting the pace to each participant’s abilities while maintaining standardization of content [53]. This model, inspired by chronic disease management frameworks, allows for ongoing monitoring, progressive challenge, and personalized support, like approaches used in managing conditions like diabetes and hypertension, where adherence and patient-centered care are crucial [54].
Incorporating this cognitive training program into nursing practice contributes not only to cognitive and emotional improvements but also reduces the risk of functional decline and dependence, potentially lowering long-term care costs. Furthermore, by promoting active participation in cognitive, social, and recreational activities, these interventions help prevent isolation and depression among older adults [55].
Nurses are therefore positioned as central facilitators in the delivery of cognitive stimulation, ensuring that such programs are accessible, effective, and sustainable in institutional and community settings. The program presented in this study offers a structured, replicable framework that nursing professionals can use to enhance cognitive resilience, support healthy aging, and strengthen social integration in geriatric populations.
4.2. Limitations
While the results of this study are encouraging and provide preliminary evidence of the benefits of an individual-based cognitive stimulation program for older Mexican adults, there are some limitations that should be considered. Although participants were randomized, the small sample size and recruitment from a single gerontological center may not fully represent the broader older adult population, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the pretest–posttest design and the lack of long-term follow-up restrict the ability to assess the durability of the observed effects. Further research with larger and more diverse samples is necessary, along with studies that explore the long-term outcomes of these interventions and evaluate their scalability across different healthcare settings to ensure their effectiveness and sustainability at a population level. Finally, the control group did not receive any type of session, which could influence the results, given the lack of control over the effect of simple participation or interaction. Consequently, the observed positive effects on autonomy and quality of life might be partially attributed to increased motivation or expectation effects rather than actual cognitive improvements. For future studies, it is important for the control group to receive structured interventions with the same frequency and duration but without cognitive training in order to better isolate the specific effect of the intervention.
In terms of cost-effectiveness, the implemented face-to-face cognitive stimulation program requires significant investment in human resources, printed materials, and physical spaces. However, it promotes social interaction and close support, which can be beneficial in populations with limited digital literacy. In contrast, computerized cognitive training offers a more adaptable and lower-cost option, with automatic difficulty adjustments, scalability, and reduced operational costs. Nevertheless, technological barriers in older adults may limit its applicability. Future studies should compare the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of both approaches, considering contextual factors that affect their real-world implementation.
5. Conclusions
The findings of this study suggest that the cognitive stimulation program used represents a promising strategy for improving executive functions, psychological well-being, autonomy in activities of daily living, and quality of life in older adults. The observed increase in serum BDNF levels in the intervention group provides a potential neurobiological explanation for these improvements, supporting the hypothesis that cognitive stimulation promotes neuroplasticity and brain health.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nursrep15050151/s1, Table S1: STROBE Statement—checklist. File S1. Example of a Level 1 Exercise for Each of the 28 Activities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O. and A.L.-M.; methodology, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O. and A.L.-M.; validation, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O. and A.L.-M.; formal analysis, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O. and A.L.-M.; investigation, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O. and A.L.-M.; data curation, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O. and A.L.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O., L.G.M.-M., E.S.-D. and A.L.-M.; writing—review and editing, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O., L.G.M.-M., E.S.-D. and A.L.-M.; project administration, N.Y.C.-Á., C.R.V.-O. and A.L.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by IDEA GTO (IDEAGTO/CONV/101/2023).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, the General Health Law on Research, and was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the San Luis de la Paz General Hospital (CONBIOÉTICA Registry: CONBIOÉTICA-11-CEI-003-20200312, approval date 1 January 2024). Participation was entirely voluntary, without any financial or other incentives.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained in person from each participant prior to the start of the study. During this process, participants were thoroughly informed about the study’s purpose, procedures, and potential risks, ensuring they fully understood the information provided. Participants were given the opportunity to ask questions and express any concerns.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Material.
Public Involvement Statement
No public involvement in any aspect of this research.
Guidelines and Standards Statement
This manuscript was drafted against the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement [25], for improving the reporting quality of nonrandomized evaluations of behavioral and public health interventions research.
Use of Artificial Intelligence
AI or AI-assisted tools were not used in drafting any aspect of this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the university students of XXVIII and XXIX Summer of Science at the University of Guanajuato for their valuable support. Thanks also to the staff of the Gerontological Centers of the National System for the Integral Development of Families, Guanajuato (DIF) provided for the facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BDNF | Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| BANFE-3 | Neuropsychological Executive Functions and Frontal Lobes battery-3 |
| GDS-15 | Yesavage Geriatric Depression Scale |
| ADL | Autonomy in activities of daily living |
| WHOQOL-OLD | World Health Organization Quality of Life-Old |
| WM | Working memory |
Appendix A. Exercise Schedule Used During the 120 Sessions

Table A1.
LEVEL 1.
Table A1.
LEVEL 1.
| 1st Week | 2nd Week | 3rd Week | 4th Week | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper activities | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 | S17 | S18 | S19 | S20 |
| 10.5 | 14.5 | 25.7 | 6.5 | 18.9 | 13.8 | 17.3 | 22.4 | 21.7 | 23.1 | 16.5 | 12.10 | 22.5 | 24.3 | 10.3 | 25.1 | 11.10 | 15.1 | 5.1 | 9.10 | |
| 3.1 | 11.3 | 8.5 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 14.10 | 3.2 | 2.3 | 26.7 | 9.5 | 23.7 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 16.7 | 1.4 | 7.6 | 21.1 | 19.7 | 9.8 | 28.3 | |
| 6.4 | 21.4 | 10.7 | 22.3 | 8.4 | 9.1 | 18.10 | 2.1 | 18.3 | 17.6 | 15.2 | 22.10 | 27.8 | 2.8 | 27.3 | 12.3 | 9.2 | 24.7 | 26.4 | 12.9 | |
| 19.3 | 20.8 | 27.1 | 10.2 | 19.8 | 22.2 | 19.10 | 8.10 | 23.10 | 12.6 | 26.8 | 5.2 | 10.8 | 16.4 | 4.7 | 3.5 | 18.7 | 21.3 | 3.10 | 5.3 | |
| 19.1 | 9.7 | 20.10 | 13.3 | 20.4 | 27.4 | 14.7 | 6.8 | 2.10 | 28.4 | 16.1 | 26.10 | 28.6 | 13.5 | 7.7 | 3.6 | 26.6 | 5.10 | 1.5 | 7.5 | |
| 21.10 | 23.6 | 26.9 | 27.6 | 20.3 | 26.2 | 17.2 | 22.6 | 7.1 | 7.3 | 8.9 | 24.6 | 24.8 | 9.9 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 28.5 | 21.6 | 24.10 | 15.6 | |
| 20.1 | 12.4 | 8.3 | 2.5 | 7.9 | 13.7 | 14.4 | 4.9 | 17.9 | 23.5 | 1.10 | 27.9 | 16.2 | 6.6 | 12.1 | 2.4 | 4.3 | 28.9 | 20.6 | 11.9 | |
| Board games | Dominoes | Take it all | Loteria | Snakes and ladders | Foosball | Bowling | Jenga® | Lottery | Golfito | Uno® | Jenga | Chinese chopsticks | Marbles | The game of the goose | Dominoes | Take it all | Loteria | Snakes and ladders | Foosball | Bowling |
| 5th Week | 6th Week | 7th Week | 8th Week | |||||||||||||||||
| Paper activities | S21 | S22 | S23 | S24 | S25 | S26 | S27 | S28 | S29 | S30 | S31 | S32 | S33 | S34 | S35 | S36 | S37 | S38 | S39 | S40 |
| 17.10 | 23.3 | 7.4 | 12.7 | 20.5 | 5.7 | 23.4 | 27.2 | 15.9 | 12.2 | 3.7 | 7.8 | 26.5 | 18.4 | 11.4 | 10.6 | 15.5 | 18.2 | 2.9 | 23.2 | |
| 25.9 | 5.8 | 8.6 | 3.3 | 9.6 | 22.9 | 17.1 | 1.3 | 20.7 | 19.6 | 4.6 | 26.3 | 23.8 | 11.8 | 15.4 | 1.8 | 8.8 | 27.5 | 19.9 | 25.3 | |
| 13.1 | 14.8 | 21.9 | 4.8 | 2.7 | 28.2 | 21.5 | 26.1 | 13.9 | 15.8 | 12.8 | 24.5 | 11.2 | 24.9 | 1.7 | 13.10 | 15.3 | 11.5 | 17.5 | 17.8 | |
| 10.4 | 14.2 | 11.7 | 28.1 | 14.3 | 22.8 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 22.7 | 17.4 | 25.4 | 16.8 | 10.9 | 16.10 | 1.6 | 18.6 | 14.9 | 14.6 | 16.3 | 1.2 | |
| 20.2 | 23.9 | 10.1 | 5.6 | 25.10 | 24.1 | 13.4 | 18.1 | 6.7 | 21.8 | 5.9 | 4.4 | 13.2 | 25.5 | 1.9 | 6.9 | 25.8 | 3.4 | 6.10 | 25.2 | |
| 19.2 | 19.5 | 15.7 | 9.4 | 4.5 | 13.6 | 10.10 | 3.8 | 9.3 | 2.2 | 28.10 | 28.8 | 18.8 | 6.2 | 25.6 | 19.4 | 5.5 | 24.4 | 24.2 | 14.1 | |
| 11.1 | 7.2 | 27.10 | 15.10 | 1.1 | 4.1 | 4.10 | 27.7 | 17.7 | 2.6 | 16.6 | 16.9 | 6.3 | 20.9 | 8.2 | 18.5 | 7.10 | 28.7 | 21.2 | 22.1 | |
| Board games | Dominoes | Take it all | Loteria | Snakes and ladders | Foosball | Bowling | Jenga® | Lottery | Golfito | Uno® | Jenga | Chinese chopsticks | Marbles | The game of the goose | Dominoes | Take it all | Loteria | Snakes and ladders | Foosball | Bowling |
The table presents the distribution of manual exercises for Level 1 across weeks 1 to 8. S denotes the corresponding week number.

Table A2.
LEVEL 2.
Table A2.
LEVEL 2.
| 9th Week | 10th Week | 11th Week | 12th Week | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper activities | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 | S17 | S18 | S19 | S20 |
| 10.12 | 21.11 | 6.16 | 1.18 | 15.13 | 26.18 | 19.12 | 10.14 | 21.15 | 18.14 | 18.20 | 3.14 | 25.12 | 16.18 | 28.12 | 15.18 | 8.12 | 9.19 | 16.11 | 22.17 | |
| 20.14 | 17.16 | 5.15 | 18.13 | 10.11 | 13.12 | 19.17 | 3.15 | 20.12 | 15.17 | 2.17 | 13.14 | 5.17 | 4.18 | 16.19 | 14.14 | 7.18 | 12.20 | 27.18 | 25.11 | |
| 21.12 | 17.15 | 17.14 | 2.14 | 27.14 | 5.11 | 18.12 | 14.16 | 12.18 | 27.19 | 17.12 | 4.19 | 22.15 | 21.19 | 1.12 | 14.20 | 1.17 | 9.13 | 20.13 | 28.20 | |
| 28.16 | 14.12 | 13.13 | 1.16 | 17.20 | 22.13 | 6.12 | 5.14 | 4.17 | 8.16 | 10.16 | 13.17 | 13.19 | 16.17 | 13.20 | 1.15 | 15.15 | 12.16 | 19.13 | 26.14 | |
| 10.19 | 7.13 | 15.16 | 6.20 | 15.11 | 10.18 | 23.18 | 24.18 | 14.18 | 19.18 | 25.14 | 3.12 | 12.15 | 19.16 | 24.14 | 4.11 | 8.17 | 1.20 | 14.13 | 24.20 | |
| 9.17 | 20.17 | 25.20 | 15.20 | 11.15 | 24.17 | 16.14 | 8.18 | 3.20 | 2.20 | 27.20 | 21.16 | 24.13 | 16.20 | 8.19 | 26.17 | 26.15 | 11.16 | 23.14 | 23.11 | |
| 23.17 | 27.13 | 28.18 | 8.14 | 27.11 | 14.11 | 28.14 | 27.16 | 4.13 | 19.19 | 17.19 | 26.19 | 23.13 | 4.16 | 16.13 | 19.11 | 5.20 | 21.17 | 23.16 | 28.17 | |
| Board games | UNO® | Dominoes | Loteria | Chinese chopsticks | Snakes and ladders | The game of the goose | Marbles | Bowling | Take it all | Foosball | Fenga® | Golfito | UNO® | Dominoes | Loteria | Chinese chopsticks | Snakes and ladders | The game of the goose | Marbles | Bowling |
| 13th Week | 14th Week | 15th Week | 16th Week | |||||||||||||||||
| Paper activities | S21 | S22 | S23 | S24 | S25 | S26 | S27 | S28 | S29 | S30 | S31 | S32 | S33 | S34 | S35 | S36 | S37 | S38 | S39 | S40 |
| 19.20 | 12.14 | 3.11 | 2.18 | 18.18 | 14.15 | 4.12 | 11.20 | 11.13 | 23.20 | 24.16 | 17.17 | 17.11 | 21.20 | 7.12 | 6.11 | 21.14 | 17.18 | 21.18 | 13.11 | |
| 16.15 | 16.16 | 28.15 | 12.19 | 22.11 | 26.12 | 7.16 | 6.14 | 4.20 | 2.12 | 6.15 | 7.19 | 12.11 | 20.16 | 16.12 | 10.15 | 10.13 | 12.17 | 18.15 | 12.13 | |
| 24.15 | 4.15 | 7.15 | 4.14 | 8.15 | 5.19 | 8.11 | 3.16 | 22.19 | 9.11 | 26.11 | 2.16 | 28.11 | 21.13 | 17.13 | 13.16 | 3.17 | 19.14 | 15.14 | 25.16 | |
| 9.15 | 7.14 | 20.15 | 9.12 | 9.20 | 1.19 | 3.13 | 19.15 | 9.16 | 11.11 | 8.13 | 1.11 | 28.19 | 26.13 | 6.17 | 5.18 | 14.19 | 22.16 | 11.19 | 11.14 | |
| 10.17 | 11.17 | 27.15 | 8.20 | 26.20 | 28.13 | 2.19 | 24.11 | 22.18 | 22.12 | 20.19 | 3.19 | 27.17 | 6.19 | 20.11 | 22.20 | 25.13 | 6.13 | 2.13 | 18.16 | |
| 2.11 | 5.12 | 7.11 | 13.18 | 27.12 | 20.20 | 18.19 | 14.17 | 23.19 | 11.18 | 26.16 | 24.19 | 5.13 | 11.12 | 3.18 | 5.16 | 2.15 | 9.14 | 6.18 | 7.17 | |
| 18.17 | 1.14 | 12.12 | 15.19 | 24.12 | 10.20 | 7.20 | 25.19 | 20.18 | 1.13 | 18.11 | 25.17 | 15.12 | 25.18 | 9.18 | 13.15 | 23.15 | 23.12 | 22.14 | 25.15 | |
| Board games | Take it all | Foosball | Jenga® | Golfito | UNO® | Dominoes | Loteria | Chinese chopsticks | Snakes and ladders | The game of the goose | Marbles | Bowling | Take it all | Foosball | Jenga® | Golfito | UNO® | Dominoes | Loteria | Chinese chopsticks |
The table presents the distribution of manual exercises for Level 2 across weeks 9 to 16. S denotes the corresponding week number.

Table A3.
LEVEL 3.
Table A3.
LEVEL 3.
| 17th Week | 18th Week | 19th Week | 20th Week | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper activities | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 | S17 | S18 | S19 | S20 |
| 22.29 | 8.21 | 7.21 | 14.23 | 5.26 | 10.30 | 15.26 | 20.21 | 17.27 | 6.24 | 2.25 | 13.23 | 14.25 | 19.26 | 1.21 | 14.30 | 7.24 | 13.30 | 15.23 | 11.29 | |
| 10.28 | 24.28 | 3.27 | 13.26 | 11.23 | 10.29 | 23.25 | 2.30 | 16.29 | 20.29 | 24.21 | 15.22 | 15.29 | 14.21 | 8.24 | 2.26 | 4.25 | 15.27 | 21.23 | 28.22 | |
| 25.21 | 7.25 | 12.28 | 26.28 | 11.21 | 11.22 | 9.29 | 5.30 | 28.27 | 11.27 | 22.24 | 7.26 | 15.30 | 11.28 | 26.21 | 17.21 | 28.23 | 24.30 | 5.21 | 28.21 | |
| 20.26 | 26.30 | 26.27 | 25.28 | 21.25 | 24.27 | 4.22 | 23.22 | 8.22 | 14.28 | 12.26 | 4.28 | 20.24 | 26.22 | 1.23 | 25.26 | 22.25 | 1.26 | 8.23 | 1.27 | |
| 26.24 | 23.21 | 17.22 | 13.28 | 10.26 | 8.29 | 2.21 | 16.21 | 19.28 | 13.21 | 17.23 | 10.21 | 8.27 | 9.25 | 18.28 | 5.27 | 3.29 | 8.30 | 14.26 | 9.23 | |
| 6.26 | 3.25 | 17.28 | 18.25 | 18.29 | 23.23 | 3.21 | 5.24 | 5.29 | 3.30 | 24.24 | 2.27 | 19.23 | 24.26 | 10.23 | 11.26 | 6.23 | 11.30 | 20.30 | 17.30 | |
| 25.27 | 9.21 | 21.24 | 26.29 | 16.24 | 24.25 | 21.30 | 1.30 | 12.24 | 2.28 | 23.30 | 13.29 | 12.30 | 21.28 | 10.25 | 19.25 | 23.27 | 12.21 | 27.24 | 6.27 | |
| Board games | Dominoes | Take it all | Loteria | Snakes and ladders | Foosball | Bowling | Jenga® | Lottery | Golfito | UNO® | Jenga | Chinese chopsticks | Marbles | The game of the goose | Dominoes | Take it all | Loteria | Snakes and ladders | Foosball | Bowling |
| 21th Week | 22th Week | 23th Week | 24th Week | |||||||||||||||||
| Paper activities | S21 | S22 | S23 | S24 | S25 | S26 | S27 | S28 | S29 | S30 | S31 | S32 | S33 | S34 | S35 | S36 | S37 | S38 | S39 | S40 |
| 1.24 | 18.30 | 20.23 | 23.26 | 1.22 | 6.25 | 2.24 | 9.27 | 27.29 | 5.23 | 12.23 | 9.24 | 27.28 | 6.22 | 12.29 | 19.27 | 19.29 | 24.29 | 27.30 | 11.24 | |
| 4.29 | 25.30 | 26.23 | 3.28 | 1.28 | 2.23 | 20.27 | 8.28 | 15.25 | 7.29 | 17.29 | 18.24 | 3.26 | 13.25 | 22.30 | 3.24 | 6.30 | 16.22 | 21.27 | 18.23 | |
| 28.24 | 17.25 | 7.22 | 14.22 | 13.27 | 26.26 | 22.22 | 12.22 | 22.27 | 7.23 | 19.30 | 15.28 | 16.25 | 20.22 | 16.23 | 6.28 | 10.22 | 19.22 | 25.22 | 27.26 | |
| 28.25 | 19.21 | 4.24 | 10.24 | 23.24 | 1.29 | 12.27 | 21.26 | 18.27 | 21.21 | 28.29 | 22.23 | 6.29 | 4.27 | 6.21 | 7.27 | 22.26 | 24.22 | 5.22 | 8.25 | |
| 15.24 | 16.30 | 25.23 | 3.22 | 25.29 | 15.21 | 14.24 | 20.28 | 8.26 | 13.24 | 24.23 | 22.21 | 27.25 | 4.21 | 16.26 | 21.29 | 27.22 | 7.30 | 28.26 | 28.28 | |
| 12.25 | 18.22 | 27.27 | 9.28 | 13.22 | 4.26 | 21.22 | 17.26 | 5.28 | 23.29 | 27.21 | 5.25 | 4.30 | 28.30 | 18.26 | 7.28 | 9.22 | 14.27 | 20.25 | 26.25 | |
| 16.27 | 25.24 | 19.24 | 16.28 | 4.23 | 23.28 | 22.28 | 2.22 | 1.25 | 9.26 | 10.27 | 2.29 | 17.24 | 18.21 | 9.30 | 27.23 | 14.29 | 3.23 | 11.25 | 25.25 | |
| Board games | Jenga® | Lottery | Golfito | UNO® | Jenga | Chinese chopsticks | Marbles | The game of the goose | Dominoes | Take it all | Toteria | Snakes and ladders | Foosball | Bowling | Jenga® | Lottery | Golfito | UNO® | Jenga | Chinese chopsticks |
The table presents the distribution of manual exercises for Level 3 across weeks 17 to 24. S denotes the corresponding week number.
References
- Rudnicka, E.; Napierała, P.; Podfigurna, A.; Męczekalski, B.; Smolarczyk, R.; Grymowicz, M. The World Health Organization (WHO) Approach to Healthy Ageing. Maturitas 2020, 139, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PAHO. La Demencia en América Latina y el Caribe: Prevalencia, Incidencia, Repercusiones y Tendencias a lo Largo del Tiempo; PAHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, N.P.; Robbins, T.W. The Role of Prefrontal Cortex in Cognitive Control and Executive Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, M.I.; Szameitat, A.J. Executive Function Abilities in Cognitively Healthy Young and Older Adults-A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 976915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimo, S.; Maggi, G.; Ilardi, C.R.; Cavallo, N.D.; Torchia, V.; Pilgrom, M.A.; Cropano, M.; Roldán-Tapia, M.D.; Santangelo, G. The Relation between Cognitive Functioning and Activities of Daily Living in Normal Aging, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 2427–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Xue, Z.; Hao, X. The Association between Falls and Depressive Symptoms among Older Adults: Evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1248551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.G.; Zhou, Y.; Marti, C.N.; Kunik, M.E. Associations between Changes in Depression/Anxiety Symptoms and Fall Worry among Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Appl. Gerontol. 2022, 41, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcelén-Fraile, M.D.C.; Llera-Delatorre, A.M.; Aibar-Almazán, A.; Afanador-Restrepo, D.F.; Baena-Marín, M.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Brandão-Loureiro, V.; García-Garro, P.A.; Castellote-Caballero, Y. Cognitive Stimulation as Alternative Treatment to Improve Psychological Disorders in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares-Pereira, G.; Silva-Nunes, M.V.; Spector, A. Validation of the Cognitive Stimulation Therapy (CST) Program for People with Dementia in Portugal. Aging Ment. Health 2021, 25, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, T.B.L.; Dos Santos, G.; Moreira, A.P.B.; Ishibashi, G.A.; Verga, C.E.R.; De Moraes, L.C.; Lessa, P.P.; Cardoso, N.P.; Ordonez, T.N.; Brucki, S.M.D. Cognitive Interventions in Mature and Older Adults, Benefits for Psychological Well-Being and Quality of Life: A Systematic Review Study. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2021, 15, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuwan, P.; Nakawiro, D.; Chansirikarnjana, S.; Kuha, O.; Chaikongthong, P.; Suwannagoot, T. Effects of a Group-Based 8-Week Multicomponent Cognitive Training on Cognition, Mood and Activities of Daily Living among Healthy Older Adults: A One-Year Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 7, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuán, M.; Navarro, E.; Dolores Calero, M. Effectiveness of Cognitive Interventions in Older Adults: A Review. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2020, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Soria, I.; Peralta-Marrupe, P.; Plo, F. Cognitive Stimulation Program in Mild Cognitive Impairment A Randomized Controlled Trial. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2020, 14, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, B.; Rai, H.K.; Elliott, E.; Aguirre, E.; Orrell, M.; Spector, A. Cognitive Stimulation to Improve Cognitive Functioning in People with Dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD005562. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, M.; Gills, J.L.; Glenn, J.M.; Vincenzo, J.L.; Walter, C.S.; Madero, E.N.; Hall, A.; Fuseya, N.; Bott, N.T. Cognitive Decline Negatively Impacts Physical Function. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 143, 111164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowski, D.R.; Hansen, T.I.; Rise, H.H.; Reitlo, L.S.; Wisløff, U.; Stensvold, D.; Håberg, A.K. 5 Years of Exercise Intervention Did Not Benefit Cognition Compared to the Physical Activity Guidelines in Older Adults, but Higher Cardiorespiratory Fitness Did. A Generation 100 Substudy. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 742587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandison, H.; Callan, N.G.L.; Rao, R.V.; Phipps, J.; Bradley, R. Observed Improvement in Cognition During a Personalized Lifestyle Intervention in People with Cognitive Decline. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 94, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinius, C.J.; Pocknell, C.E.; Caffrey, M.P.; Roche, R.A.P. Cognitive Interventions for Memory and Psychological Well-Being in Aging and Dementias. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1070012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo-Henriques, S.I.; Marques-Castro, A.E.; Otero, P.; Vázquez, F.L.; Torres, Á.J. Long-Term Individual Cognitive Stimulation Program in Patients with Mild Neurocognitive Disorder: A Pilot Study. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 68, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, H.L.; Chu, H.; Tsai, J.C.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.R.; Yang, H.L.; Chou, K.R. The Effect of Cognitive-Based Training for the Healthy Older People: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo-Henriques, S.I.; Otero, P.; Torres, Á.J.; Vázquez, F.L. Effect of Long-Term Individual Cognitive Stimulation Intervention for People with Mild Neurocognitive Disorder. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 73, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Ebrahimi, O.V. Gamification: A Novel Approach to Mental Health Promotion. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2023, 25, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, A.; Paciello, F.; Del Vecchio, V.; Malesci, R.; De Corso, E.; Cantone, E.; Fetoni, A.R. The Role of BDNF as a Biomarker in Cognitive and Sensory Neurodegeneration. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastri, C.M.; McFeeley, B.M.; Simon, S.S.; Ledreux, A.; Håkansson, K.; Granholm, A.C.; Mohammed, A.H.; Daffner, K.R. BDNF Mediates Improvement in Cognitive Performance after Computerized Cognitive Training in Healthy Older Adults. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2022, 8, e12337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, C.O.; Palacio, R.R.; Cortez, J.; Echeverría, S.B.; Rodríguez-Fórtiz, M.J. Effects of a Cognitive Stimulation Software on Attention, Memory, and Activities of Daily Living in Mexican Older Adults. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2022, 21, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragón-Maya, A.; Flores-Medina, Y.; López-Arreaga, G.; López-Ramírez, S.; Paz-Rodríguez, F. Funciones Ejecutivas En Estudiantes Universitarios Con Patrón de Consumo Excesivo de Alcohol. Psicol. Salud 2021, 31, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, M.J.; Sachdev, P. Brain Reserve and Dementia: A Systematic Review. Psychol. Med. 2006, 36, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda de Jesus, Y.; Álvarez Orozco, M.E.; Álvarez Hernández, H.J.; Jaimes Cortés, D.; Alvarado Reyes, E.R. Factores Que Desencadenan Depresión En El Adulto Mayor de La Comunidad de Santiaguito Maxda, Estado de México. Dilemas Contemp. Educ. Política Valores 2020, 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystal Salgado Cedano, Y.; Andrade Palos, P.; Hernández Galván, A.; Ivonne González-Arriata López-Fuentes, N.; en Psicología, D.; Eduardo Velasco Rojano, Á. Validación de La Escala de Depresión Geriátrica de Yesavage En Adultos Mayores Mexicanos. Inf. Psicol. 2024, 24, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.A.M.; Barajas, M.E.S.; Ordóñez, J.A.G.; Alpirez, H.Á.; Fhon, J.R.S.; Duran-Badillo, T. Quality of Life Related to Functional Dependence, Family Functioning and Social Support in Older Adults*. Rev. Esc. Enferm. 2022, 56, e20210482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, N.F.; Figueiredo, F.C.X.S.; Biscaro, R.R.M.; Lunardelli, E.B.; Maurici, R. Psychometric Properties of the Barthel Index Used at Intensive Care Unit Discharge. Am. J. Crit. Care 2022, 31, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizabeth Duarte-Ayala, R.; Ángel Eduardo Velasco-Rojano, D.; Elizabeth Duarte Ayala Dirección postal, R.; de Las Aves, P.; Mateo Nopala, S.; de Juárez, N.; de México, C.; Mayor, A. Validación Psicométrica Del Índice de Barthel En Adultos Mayores Mexicanos. Horiz. Sanit. 2022, 21, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Pekçetin, E.; Pekçetin, S.; Sağlamoğlu, E.; Ekici, G. Urban versus Rural Older Adults: Occupational Balance and Quality of Life Comparison. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz de León Castañeda, C.; Anguiano-Morán, A.C.; Valtierra-Oba, E.R.; Lemus-Loeza, B.M.; Galván-Villalobos, G.; Rodríguez-Orozco, A.R. Psychometric Properties of the World Health Organization Quality of Life Scale for Older Adults (WHO-QoL-Old) in a Mexican Population. Geriatrics 2024, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, L.A. Individual Cognitive Stimulation Therapy (ICST). In Cognitive Stimulation Therapy for Dementia; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, Y. What Is Cognitive Reserve? Theory and Research Application of the Reserve Concept. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2002, 8, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loenhoud, A.C.; Van Der Flier, W.M.; Wink, A.M.; Dicks, E.; Groot, C.; Twisk, J.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Ossenkoppele, R. Cognitive Reserve and Clinical Progression in Alzheimer Disease: A Paradoxical Relationship. Neurology 2019, 93, e334–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.; Spampinato, D. Alzheimer Disease and Neuroplasticity. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2022, 184, 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Dreer, L.E.; Copeland, J.N.; Cheavens, J.S. Integrating Neuropsychological Functioning into Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Implications for Older Adults. In Cognitive Behavior Therapy with Older Adults: Innovations Across Care Settings; Springer Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 317–365. [Google Scholar]
- Justo-Henriques, S.I. Individual Intervention Protocol Based on Cognitive Stimulation Therapy for Older Adults with Mild Neurocognitive Disorder. Rev. Enferm. Ref. 2021, 2021, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Soria, I.; Iguacel, I.; Aguilar-Latorre, A.; Peralta-Marrupe, P.; Latorre, E.; Zaldívar, J.N.C.; Calatayud, E. Cognitive Stimulation and Cognitive Results in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 104, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Ryu, S. The Effects of Cognitive-Based Interventions in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Iran. J. Public Health 2022, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledreux, A.; Håkansson, K.; Carlsson, R.; Kidane, M.; Columbo, L.; Terjestam, Y.; Ryan, E.; Tusch, E.; Winblad, B.; Daffner, K.; et al. Differential Effects of Physical Exercise, Cognitive Training, and Mindfulness Practice on Serum BDNF Levels in Healthy Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Intervention Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 71, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Garavito, A.; Díaz Martínez, V.; Juárez Cortés, E.; Negrete Díaz, J.V.; Montilla Rodríguez, L.M. Impact of Physical Exercise on the Regulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in People with Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurol. 2025, 15, 1505879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukkahatai, N.; Ong, I.L.; Benjasirisan, C.; Saligan, L.N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Marker of Physical Exercise or Activity Effectiveness in Fatigue, Pain, Depression, and Sleep Disturbances: A Scoping Review. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, F.; Mesrabadi, J.; Iranpour, M.; Donyaei, A. Exercise Training Alters Resting Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Concentration in Older Adults: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Randomized-Controlled Trials. Exp. Gerontol. 2025, 199, 112658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; He, J.; Zhou, K.; Shang, Z.; Dong, G.; Bao, D.; Zhou, J. Effects of Traditional Chinese Exercises on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2025, 23, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossberg, A.N.; Bettcher, B.M.; Gorgens, K.A.; Ledreux, A. Curiosity-Based Interventions Increase Everyday Functioning Score But Not Serum BDNF Levels in a Cohort of Healthy Older Adults. Front. Aging 2021, 2, 700838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaeifar, F.; Pourranjbar, S.; Pourranjbar, M.; Ramezani, S.; Mehr, S.R.; Wadan, A.H.S.; Khazeifard, F. Beneficial Effects of Physical Exercise on Cognitive-Behavioral Impairments and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Alteration in the Limbic System Induced by Neurodegeneration. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 195, 112539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivanek, T.J.; Gale, S.A.; McFeeley, B.M.; Nicastri, C.M.; Daffner, K.R. Promoting Successful Cognitive Aging: A Ten-Year Update. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 81, 871–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi-Mahani, S.; Eghbali-Babadi, M.; Farajzadegan, Z.; Keshvari, M.; Farokhzadian, J. Active Aging Needs from the Perspectives of Older Adults and Geriatric Experts: A Qualitative Study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1121761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifa, A.L.B.; Alrø, A.B.; Holm, A.; Dreyer, P. Nurses’ Experiences of Managing Cognitive Problems in Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Qualitative Study. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2023, 79, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangelosi, G.; Mancin, S.; Pantanetti, P.; Thi, C.; Nguyen, T.; Palomares, S.M.; Biondini, F.; Sguanci, M.; Petrelli, F. Lifestyle Medicine Case Manager Nurses for Type Two Diabetes Patients: An Overview of a Job Description Framework—A Narrative Review. Diabetology 2024, 5, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Pradhan, J. Impact of Social Isolation and Leisure Activities on Cognition and Depression: A Study on Middle-Aged and Older Adults in India. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2023, 38, e5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).