The Teaching and Learning Cultural Competence in a Multicultural Environment (CCMEn) Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
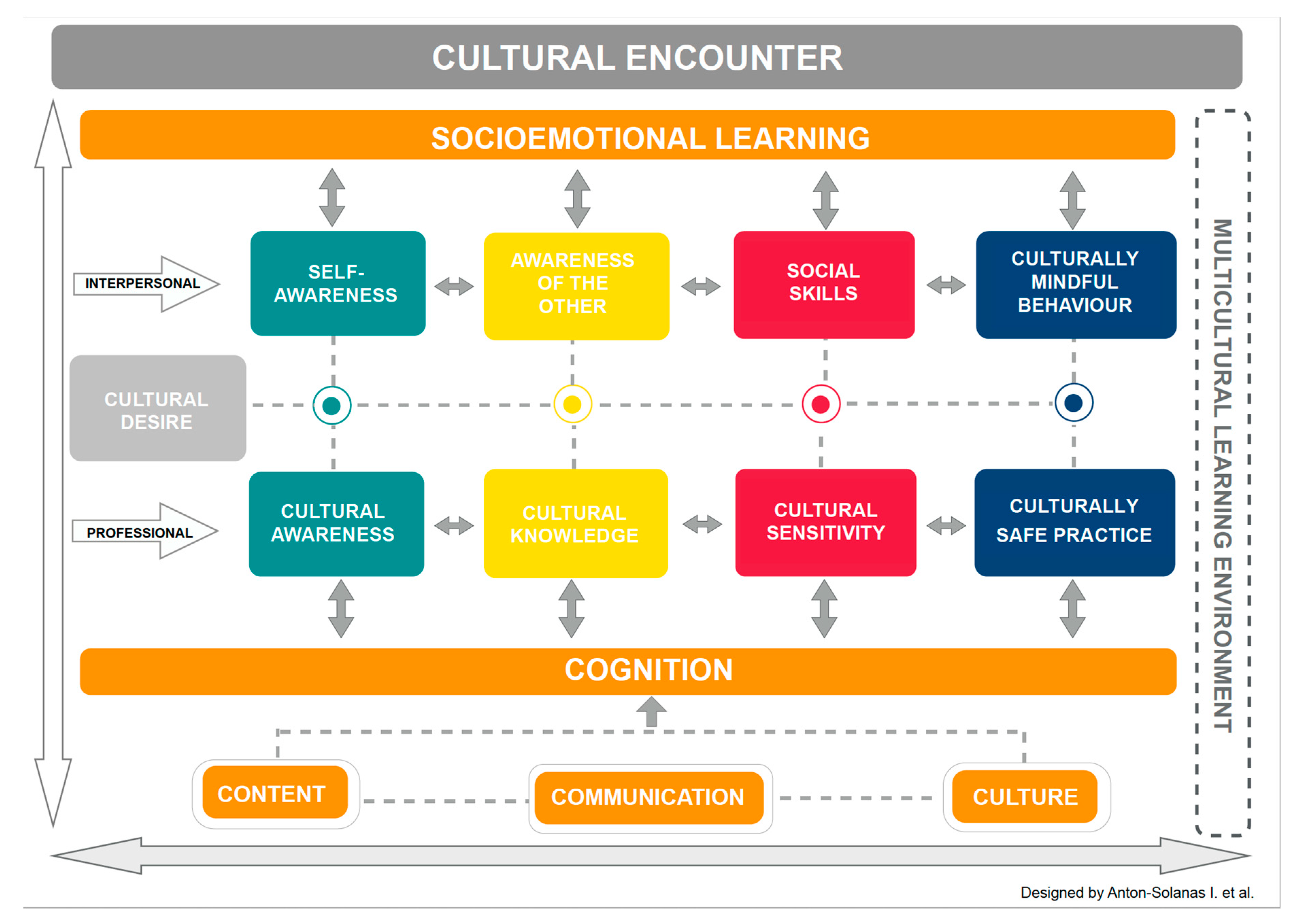
2. The CCMEn Model
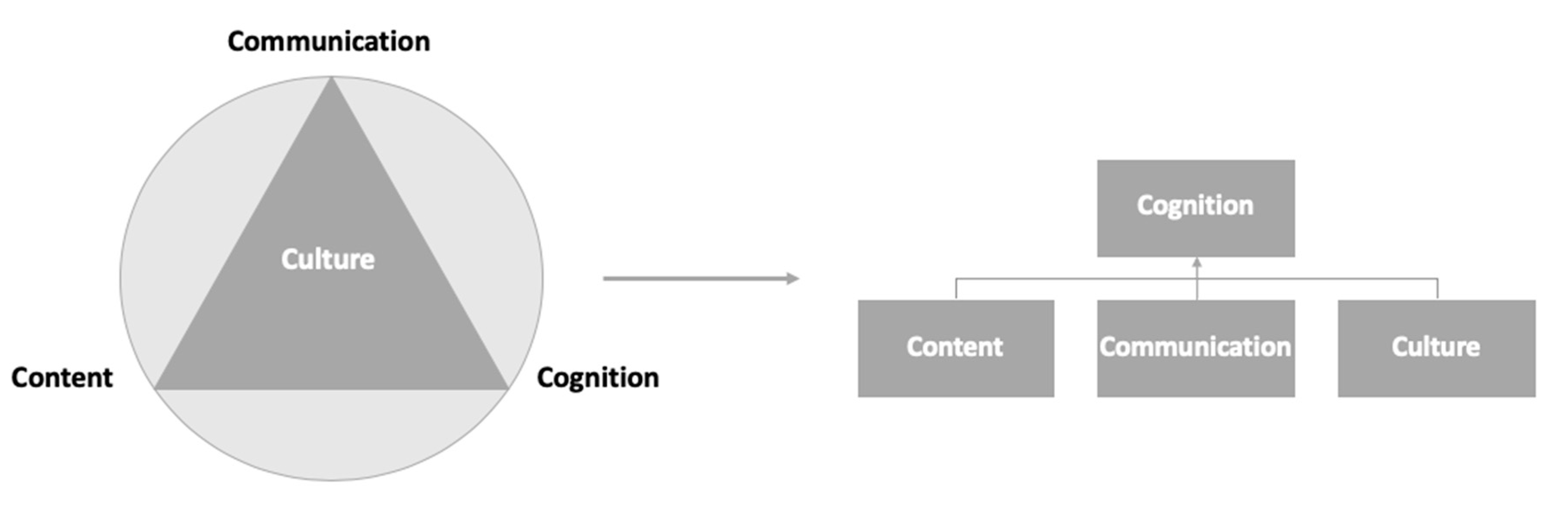
2.1. A CLIL Approach
- Content: What the students need to know.
- Communication: The language skills that the students need to have in order to work on the content both autonomously and in the classroom.
- Culture: The students’ cultural heritage that shapes their experiences, personal values, reflective processes and behaviours.
- Cognition: The thinking processes that the students need to use in order to engage with and understand course content.
2.2. Socioemotional Learning
2.3. A Five-Stage Process
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- European Commission Social Inclusion. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/europeaid/sectors/human-development/social-inclusion_en (accessed on 26 February 2019).
- Cowan, D.T.; Norman, I. Cultural competence in nursing: New meanings. J. Transcult. Nurs. 2006, 17, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, L.; Munkhondya, B.; Myhre, K. Similarities and mutual understanding: Exchange experiences in Malawi for host and guest students. Int. Nurs. Rev. 2009, 56, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohman, D.M.; Borglin, G. Student exchange for nursing students: Does it raise cultural awareness’? A descriptive, qualitative study. Nurse Educ. Pract. 2014, 14, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campinha-Bacote, J. The Process of Cultural Competence in the Delivery of Healthcare Services: A Model of Care. J. Transcult. Nurs. 2002, 13, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffreys, M.R. Teaching Cultural Competence in Nursing and Health Care, Third Edition: Inquiry, Action, and Innovation, 3rd ed.; Springer Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-8261-1996-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.C.-Y.; Sy, P.Y. The Relationships Among Personality, Intercultural Communication, and Cultural Self-Efficacy in Nursing Students. J. Nurs. Res. 2016, 24, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, I.; Tilki, M.; Taylor, G. Transcultural Care: A Guide for Health Care Professionals; Quay Books: Dinton, UK, 1998; ISBN 978-1-85642-051-8. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, J.A.; Cookson, P.; Gay, G.; Hawley, W.D.; Irvine, J.J.; Nieto, S.; Schofield, J.W.; Stephan, W.G. Diversity within Unity: Essential Principles for Teaching and Learning in a Multicultural Society. Phi Delta Kappan 2001, 83, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnardi, M.; Bryant, L.; Colin, J. Banks Multicultural Model: A Framework for Integrating Multiculturalism Into Nursing Curricula. J. Prof. Nurs. 2009, 25, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, E.; McKenna, L. International clinical placements for undergraduate students. J. Clin. Nurs. 2003, 12, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, L.; Tossavainen, K. Study abroad as a process of learning intercultural competence in nursing. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2004, 10, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Transcultural Nursing: A European Priority, a Professional Responsibility. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/programmes/erasmus-plus/projects/eplus-project-details_en (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Arunasalam, N.D.; Burton, R. Investigating Malaysian Nurses’ perspectives of intercultural teaching in transnational higher education learning environments. Nurse Educ. Today 2018, 69, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, B.; Harding, T.; Jurlina, L.; Scobie, N.; Khan, R. Utilising the Hand Model to promote a culturally safe environment for international nursing students. Nurs. Prax. N Z 2011, 27, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, D. Supporting students in content and language integrated contexts: Planning for effective classrooms. In Learning through a Foreign Language—Models, Methods and Outcomes; Masih, J., Ed.; Centre for Information on Language Teaching and Research (CILT): London, UK, 1999; pp. 46–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shriver, T.P.; Buffett, J.; Comer, J.P.; Goleman, D.; Darling-Hammond, L. Handbook of Social and Emotional Learning: Research and Practice; Durlak, J.A., Domitrovich, C.E., Weissberg, R.P., Gullotta, T.P., Eds.; Edición: Reprint; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4625-2791-5. [Google Scholar]
- Garone, A.; Van de Craen, P. The role of language skills and internationalization in nursing degree programmes: A literature review. Nurse Educ. Today 2017, 49, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, D. Content and Language Integrated Learning—Motivating Learners and Teachers. Scott. Lang. Rev. 2006, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, O. Towards quality-CLIL: Successful planning and teaching strategies. Pulso 2010, 33, 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Frydenberg, E.; Liang, R.; Muller, D. Assessing Students’ Social and Emotional Learning: A Review of the Literature on Assessment Tools and Related Issues. In Social and Emotional Learning in Australia and the Asia-Pacific: Perspectives, Programs and Approaches; Frydenberg, E., Martin, A.J., Collie, R.J., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2017; pp. 55–82. ISBN 978-981-10-3394-0. [Google Scholar]
- O’Conner, R.; De Feyter, J.; Carr, A.; Luo, J.L.; Romm, H. A Review of the Literature on Social and Emotional Learning for Students Ages 3-8: Characteristics of Effective Social and Emotional Learning Programs (Part 1 of 4). REL 2017-245; Regional Educational Laboratory Mid-Atlantic: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2017.
- Mortimore, L. The importance of developing social and emotional learning (SEL) within the CLIL classroom, with special reference to Spain. Encuentro, Revista de investigación e Innovación en la Classe de Idiomas 2017, 26, 126–140. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, C.; Alcalay, L.; Torretti, A.; Milicic, N. Socio-emotional well-being and academic achievement: Evidence from a multilevel approach. Psicologia: Reflexão e Crítica 2011, 24, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujitani, E.; Volet, S. Socio-emotional challenges in international education: Insight into reciprocal understanding and intercultural relational development. J. Res. Intern. Educ. 2008, 7, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, J. Cultural competency in baccalaureate US nursing education: Hybrid course. Holist. Nurs. Pract. 2012, 26, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of Europe Educational Culture. Available online: https://www.coe.int/en/web/lang-migrants/educational-culture-/-tradition-/-background (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Foronda, C. A Theory of Cultural Humility. J. Transcult. Nurs. 2019, 31, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Brown, L.; Duff, C.; Nesbitt, P.; Hepner, A. Development and evaluation of a teaching and learning approach in cross-cultural care and antidiscrimination in university nursing students. Nurse Educ. Today 2013, 33, 1592–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, A. Transcultural nursing: How do nurses respond to cultural needs? Br. J. Nurs. 2003, 12, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, I. Culturally Competent Compassion, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-138-67490-5. [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Miller, C.A.; Leak, A.; Harlan, C.A.; Dieckmann, J.; Sherwood, G. “Leaving the Comfort of the Familiar”: Fostering Workplace Cultural Awareness Through Short-Term Global Experiences. Nurs. Forum. 2010, 45, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-M.; Chen, G.M.; Starosta, W.J. The development and validation of the intercultural communication sensitivity scale. Hum. Commun. 2000, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, I.; Tilki, M.; Ayling, S. Cultural competence in action for CAMHS: Development of a cultural competence assessment tool and training programme. Contemp. Nurse 2008, 28, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CSI Resources: Professional Learning. Available online: https://casel.org/csi-resources-professional-learning/ (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Biggs, J.; Tang, C. Teaching for Quality Learning at University, 3rd ed.; Open University Press: Maidenhead, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Repo, H.; Vahlberg, T.; Salminen, L.; Papadopoulos, I.; Leino-Kilpi, H. The Cultural Competence of Graduating Nursing Students. J. Transcult. Nurs. 2017, 28, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañado, M.L.P. Teacher training needs for bilingual education: In-service teacher perceptions. Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 2016, 19, 266–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehisto, P.; Marsh, D.; Frigols, M.J. Uncovering CLIL: Content and Language Integrated Learning in Bilingual and Multilingual Education; Macmillan Education: London, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-0-230-02719-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nursing Council of New Zealand. Guidelines for Cultural Safety, the Treaty of Waitangi and Maori Health in Nursing Education and Practice.; Nursing Council of New Zealand: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011; ISBN 978-0-908662-38-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-C.; Jensen, F.; Measom, G.; Bennett, S.; Nichols, N.D.; Wiggins, L.; Anderton, A. Factors Influencing the Development of Cultural Competence in Undergraduate Nursing Students. J. Nurs. Educ. 2018, 57, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaihlanen, A.-M.; Hietapakka, L.; Heponiemi, T. Increasing cultural awareness: Qualitative study of nurses’ perceptions about cultural competence training. BMC Nurs. 2019, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A. Linking Content and Language-Integrated Learning (CLIL) and Task-based Language Teaching (TBLT) in an effective way: A methodological proposal. Onomázein: Revista de lingüística, filología y traducción de la Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile 2020, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, A.J.; Guillot, C.P. Beyond the CEFR: Towards Standardization of Language Competence Recognition in Europe. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 178, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antón-Solanas, I.; Coelho, M.; Huércanos-Esparza, I.; Vanceulebroeck, V.; Kalkan, I.; Cordeiro, R.; Kömürkü, N.; Soares-Coelho, T.; Hamam-Alcober, N.; Dehaes, S.; et al. The Teaching and Learning Cultural Competence in a Multicultural Environment (CCMEn) Model. Nurs. Rep. 2020, 10, 154-163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep10020019
Antón-Solanas I, Coelho M, Huércanos-Esparza I, Vanceulebroeck V, Kalkan I, Cordeiro R, Kömürkü N, Soares-Coelho T, Hamam-Alcober N, Dehaes S, et al. The Teaching and Learning Cultural Competence in a Multicultural Environment (CCMEn) Model. Nursing Reports. 2020; 10(2):154-163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep10020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntón-Solanas, Isabel, Margarida Coelho, Isabel Huércanos-Esparza, Valérie Vanceulebroeck, Indrani Kalkan, Raul Cordeiro, Nuran Kömürkü, Teresa Soares-Coelho, Nadia Hamam-Alcober, Shana Dehaes, and et al. 2020. "The Teaching and Learning Cultural Competence in a Multicultural Environment (CCMEn) Model" Nursing Reports 10, no. 2: 154-163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep10020019
APA StyleAntón-Solanas, I., Coelho, M., Huércanos-Esparza, I., Vanceulebroeck, V., Kalkan, I., Cordeiro, R., Kömürkü, N., Soares-Coelho, T., Hamam-Alcober, N., Dehaes, S., Casa-Nova, A., & Sagarra-Romero, L. (2020). The Teaching and Learning Cultural Competence in a Multicultural Environment (CCMEn) Model. Nursing Reports, 10(2), 154-163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep10020019






