What’s in an App? Scoping Review and Quality Assessment of Clinically Available Hearing-Aid-Connected Apps
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources
2.4. Search Terms
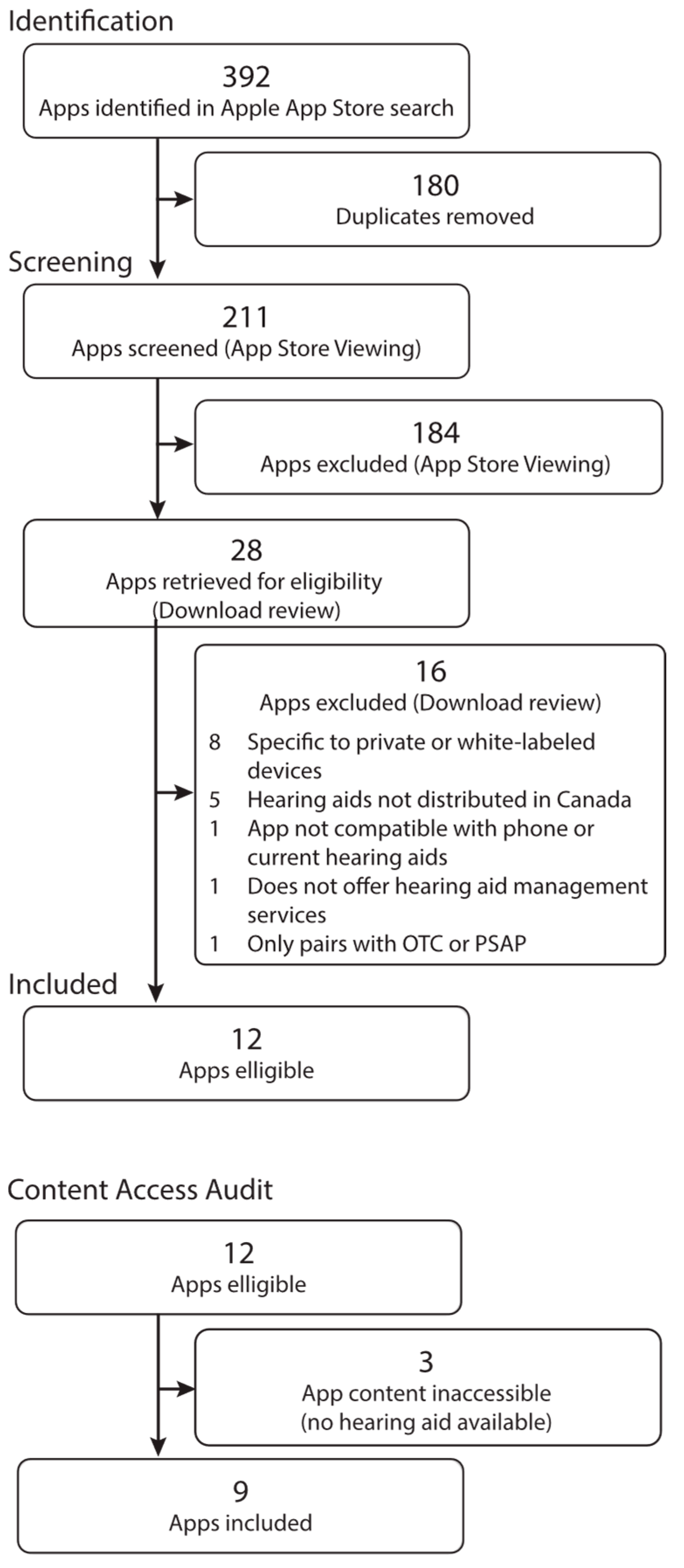
2.5. Selection of Sources of Evidence
2.6. Data Charting Process and Data Items
2.7. Data Synthesis
Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Apps
3.2. Metadata
3.3. App Features
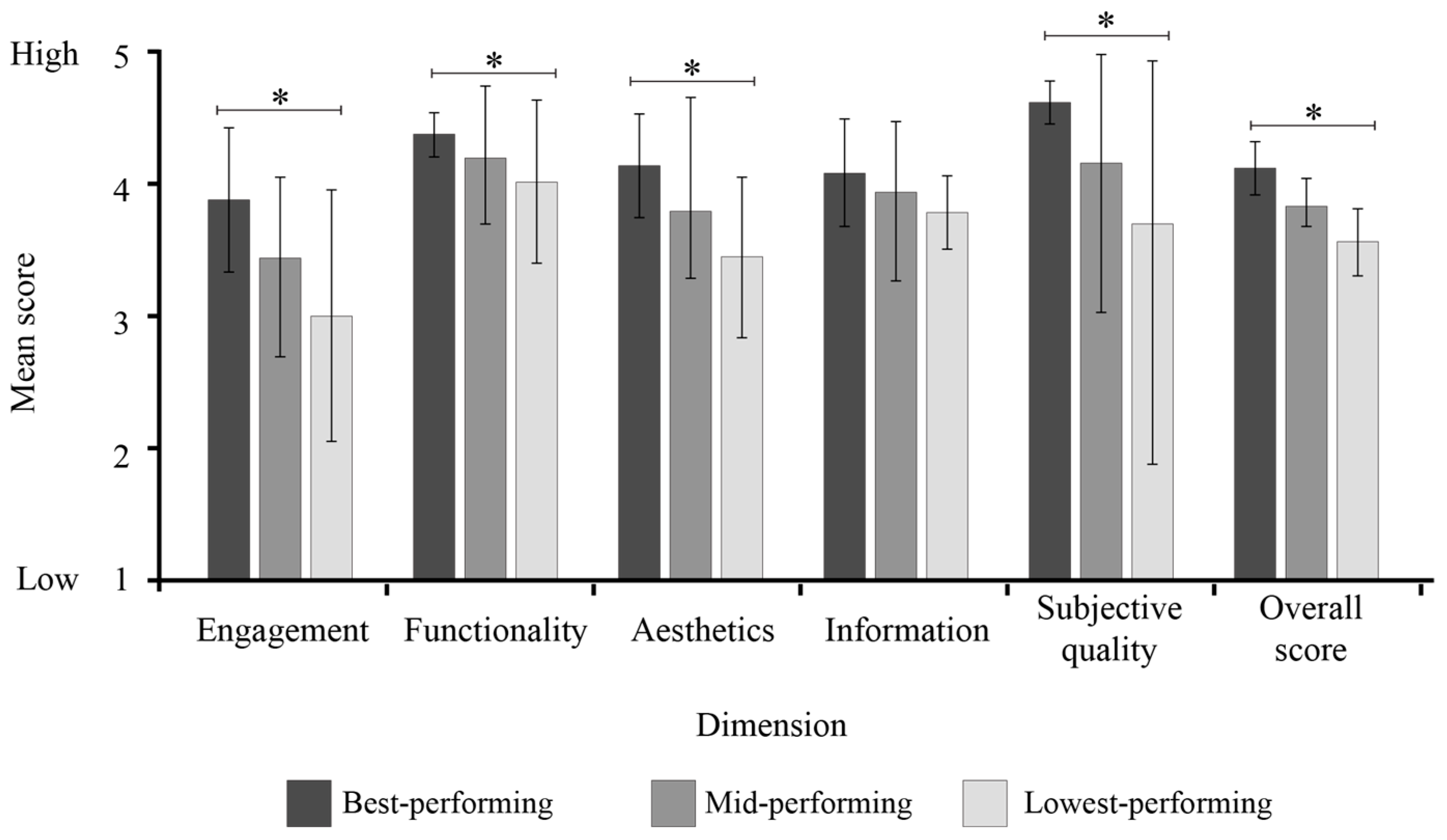
3.4. Quality Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. MARS Quality Ratings
4.2. Summary of Included Apps and Key Study Findings
4.3. Future Directions
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MARS | Mobile Application Rating Scale |
| PRISMA-ScR | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews |
Appendix A
| Dimension | Items | Response Options |
|---|---|---|
| Metadata | Manufacturer | Open-text |
| iOS rating | Open-text | |
| Age classification | Open-text | |
| App version | Open-text | |
| Date of last update | Open-text | |
| Data privacy | ||
| Analytics | Health and fitness, location, identifiers, usage data, diagnostics, and other data | |
| App functionality | Health and fitness, location, identifiers, usage data, contact information, diagnostics, and other data | |
| Other purposes | Contact information | |
| Privacy notice | Yes/No | |
| User manual | Yes/No | |
| App features | Remote control | |
| Volume | Yes/No | |
| Mute | Yes/No | |
| Noise reduction | Yes/No | |
| Directional microphone | Yes/No | |
| Loud/soft adjustments | Yes/No | |
| Equalizer | Yes/No | |
| Program toggling | Yes/No | |
| Program management | Yes/No | |
| Bluetooth functionality | Yes/No | |
| User supports | Yes/No | |
| User guide | ||
| Tutorials/videos | Yes/No | |
| Information icons | Yes/No | |
| Technical support | Yes/No | |
| Tinnitus management | Yes/No | |
| Health tracking | ||
| Step count | Yes/No | |
| Activity tracking | Yes/No | |
| Falls alerts | Yes/No | |
| Stand time | Yes/No | |
| Remote support | ||
| Synchronous support | Yes/No | |
| Asynchronous support | Yes/No | |
| Video | Yes/No | |
| Messaging | Yes/No | |
| Other | ||
| Wearing time | Yes/No | |
| Listening goals | Yes/No | |
| Notifications & reminders | Yes/No | |
| Find my hearing aids | Yes/No | |
| Remote connection | ||
| Does the app allow the user to connect with their hearing healthcare professional? | Yes/No |
Appendix B
| App Name (Manufacturer) | Developer | iOS App Rating (Number of Ratings) | Age | App Version | Date Last Updated 1 | Data Linked to End-User 2 | Data Not Linked to End-User 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bernafon App (Bernafon) | Bernafon AG | 1.6 (8) | 4+ | 1.3.1 | 3 months | None | Analytics: Identifiers (user ID, device ID), usage data (product interaction) App functionality: Location (coarse location), contact info (email address), identifiers (user ID), diagnostics (crash data, performance data) |
| myPhonak (Phonak) | Sonova AG | 4.4 (6600) | 17+ | 6.8.0 | 1 day | None | Analytics: Identifiers (device ID); usage data (product interaction); diagnostics (crash data, performance data) App functionality: Identifiers (device ID); usage data (product interaction); diagnostics (crash data, performance data) |
| myPhonak JR (Phonak) | Sonova AG | 4.4 (33) | 4+ | 1.3.0 | 5 months | None | Analytics: Identifiers (device ID); usage data (product interaction); diagnostics (crash data, performance data) App functionality: Identifiers (device ID); usage data (product interaction); diagnostics (crash data, performance data) |
| My Starkey (Starkey) | Starkey Laboratories | 3.8 (9) | 12+ | 2.1.0 | 2 months | Analytics: Health and fitness App functionality: Health and fitness, contact info (email address, name) | Analytics: Usage data (product interaction); diagnostics (performance data) App functionality: Location (precise location), usage data (product information), diagnostics (crash data, performance data, other diagnostic data) |
| Oticon Companion (Oticon) | Oticon A/S | 2.2 (81) | 4+ | 1.3.1 | 3 months | None | Analytics: Identifiers (user ID, device ID), usage data (product information) App functionality: Location (coarse location), contact info (email address), identifiers (user ID), diagnostics (crash data, performance data) |
| Resound Smart 3D (ReSound) | ReSound | 4.5 (2200) | 4+ | 1.35.1 | 4 months | None | Analytics: Health & fitness (health), identifiers (user ID, device ID), usage data (product interaction), sensitive info (sensitive info), diagnostics (crash data); app functionality (user content (customer support), diagnostics (crash data) |
| Signia App (Signia) | Sivantos Pte. Ltd. | 4.1 (839) | 17+ | 2.6.71 | 3 months | Analytics: Identifiers (user ID) App functionality: Identifiers (user ID) | Analytics: Usage data (product interaction); diagnostics (crash data; performance data; other diagnostic data) App functionality: Usage data (product interaction) |
| Unitron Remote Plus (Unitron) | Sonova AG | 4.4 (309) | 17+ | 5.1.0 | 2 months | Analytics: Other data App functionality: Other data, other (contact info-email address & name) | Analytics: Usage data (product interaction), diagnostics (crash data, performance data) |
| Widex Moment (Widex) | Widex A/S | 3.2 (43) | 17+ | 1.8.0 | 6 months | Analytics: Health and fitness (health), location (coarse location), user content (other user content), identifiers (user ID, device ID), usage data (product interaction, other usage data), diagnostics (crash data, performance data), other data (other data types) App functionality: Diagnostics (crash data) | None |
References
- Ferrari, A.J.; Santomauro, D.F.; Aali, A.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abdelmasseh, M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdollahi, A.; et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2133–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage-Morin, P.; Banks, R.; Pineault, D.; Atrach, M. Heather Gilmour Hypertension Associated with Hearing Health Problems Among Canadian Adults Aged 19 to 79 Years. Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/82-003-x/2021010/article/00002-eng.htm (accessed on 21 March 2024).
- Dawes, P.; Emsley, R.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Moore, D.R.; Fortnum, H.; Edmondson-Jones, M.; McCormack, A.; Munro, K.J. Hearing loss and cognition: The role of hearing aids, social isolation and depression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-Y.; Seo, H.W.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, J.H. Physical Inactivity and Sedentariness in Older Hearing Loss patients: Restoration With Hearing Aids. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 5109–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, N.E.; Woodside, J.V. Factors affecting hearing aid adoption and use: A qualitative study. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2018, 29, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, B.H.B.; Launer, S.; Hickson, L. Using smartphone technology to support the adult audiologic rehabilitation journey. Int. J. Audiol. 2021, 60, S61–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisby, C.; Eikelboom, R.; Mahomed-Asmail, F.; Kuper, H.; Swanepoel, D.W. m-Health applications for hearing loss: A scoping review. Telemed. e-Health 2022, 28, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, F. Hearing aid accompanying smartphone apps in hearing healthcare. A systematic review. Appl. Med. Inform. 2020, 42, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Stoyanov, S.R.; Hides, L.; Kavanagh, D.J.; Zelenko, O.; Tjondronegoro, D.; Mani, M. Mobile App Rating Scale: A new tool for assessing the quality of health mobile apps. JMIR MHealth UHealth 2015, 3, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.M.; McInerney, P.; Munn, Z.; Trico, A.; Khalil, H. Chapter 11: Scoping reviews. In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. Prisma extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, D.; Colquhoun, H.; O’Brien, K.K. Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement. Sci. 2010, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfingstgraef, K.; O’Hagan, R.; Glista, D. Scoping Review and Quality Assessment Protocol for Clinically-Available Hearing Aid Connected Apps; Open Science Framework: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research; Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada; Social Sciences and Humanities Research. Tri-Council Policy Statement: Ethical Conduct for Research Involving Humans; Canadian Institutes of Health Research: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2018; Available online: http://publications.gc.ca/collections/collection_2019/irsc-cihr/RR4-2-2019-eng.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Azad-Khaneghah, P.; Neubauer, N.; Miguel Cruz, A.; Liu, L. Mobile health app usability and quality rating scales: A systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2021, 16, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualtrics. 2023. Available online: https://www.qualtrics.com (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Hajesmaeel-Gohari, S.; Khordastan, F.; Fatehi, F.; Samzadeh, H.; Bahaadinbeigy, K. The most used questionnaires for evaluating satisfaction, usability, acceptance, and quality outcomes of mobile health. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, A.; de Sola, H.; Failde, I.; Moral-Munoz, J.A. Measuring the quality of mobile apps for the management of pain: Systematic search and evaluation using the mobile app rating scale. JMIR MHealth UHealth 2018, 6, e10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, M.; Kavanagh, D.J.; Hides, L.; Stoyanov, S.R. Review and evaluation of mindfulness-based iPhone apps. JMIR MHealth UHealth 2015, 3, e4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, N.; Høie, N.M.; Nguyen, M.H.; Smit, E.S. Customization in mobile health apps: Explaining effects on physical activity intentions by the need for autonomy. Digit. Health 2019, 5, 2055207619888074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzipavlou, I.A.; Christoforidou, S.A.; Vlachopoulou, M. A recommended guideline for the development of mHealth Apps. mHealth 2016, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changizi, M.; Kaveh, M.H. Effectiveness of the mHealth technology in improvement of healthy behaviors in an elderly population-a systematic review. mHealth 2017, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdowar, H.; Khedo, K.K.; Chooramun, N. A comprehensive review of mobile user interfaces in mHealth applications for elderly and the related ageing barriers. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2024, 23, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazard, A.J.; Brennen, J.S.B.; Belina, S.P. App designs and interactive features to increase mHealth adoption: User expectation survey and experiment. JMIR MHealth UHealth 2021, 9, e29815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, S.P.; Fitzgerald, J.E.; Holme, T.; Powell, J.; McGregor, A. What is the clinical value of mHealth for patients? NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glista, D.; O’Hagan, R.; Jalilian, N.; Servais, M. Adolescent-centred mHealth applications in a collaborative care model: A virtual focus group study with audiologists. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2024, 67, 2794–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Dimension | Items |
|---|---|
| Objective Quality | |
| Engagement | Entertainment, interest, customization, interactivity, target group |
| Functionality | Performance, ease of use, navigation, gestural design |
| Aesthetics | Layout, graphics, visual appeal |
| Information | Accuracy, goals, quality, quantity, visual information, credibility, evidence-based |
| Subjective Quality | Personal interest level of the app (recommendation of the app to others, how often they would use it, if they would pay for the app) |
| Evaluator Star Rating | The overall star rating the individual would give the app |
| Category | App | Overall Quality | Objective Quality Dimensions | Objective Quality | Subjective Quality | Evaluators’ Star Rating | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engagement | Functionality | Aesthetics | Information | ||||||
| High-performing | 1 | 4.49 | 4.15 | 4.38 | 4.17 | 4.25 | 4.24 | 4.75 | 4.00 |
| 2 | 4.38 | 3.70 | 4.38 | 4.33 | 4.17 | 4.14 | 4.63 | 3.50 | |
| 3 | 4.35 | 3.85 | 4.50 | 4.00 | 3.92 | 4.07 | 4.63 | 3.50 | |
| Mid-performing | 4 | 4.09 | 3.35 | 4.38 | 3.83 | 4.17 | 3.93 | 4.25 | 3.50 |
| 5 | 4.33 | 3.67 | 4.00 | 4.33 | 3.67 | 3.92 | 4.75 | 4.00 | |
| 6 | 3.77 | 3.10 | 4.38 | 3.83 | 3.83 | 3.79 | 3.75 | 3.00 | |
| Low-performing | 7 | 4.03 | 2.95 | 4.25 | 3.67 | 3.83 | 3.68 | 4.38 | 3.00 |
| 8 | 3.71 | 3.40 | 3.75 | 3.17 | 3.90 | 3.55 | 3.88 | 3.00 | |
| 9 | 3.17 | 2.60 | 4.13 | 3.50 | 3.67 | 3.47 | 2.88 | 2.50 | |
| Mean | 4.04 | 3.42 | 4.24 | 3.87 | 3.93 | 3.86 | 4.21 | 3.33 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pfingstgraef, K.; O’Hagan, R.; Bataineh, J.N.; Glista, D. What’s in an App? Scoping Review and Quality Assessment of Clinically Available Hearing-Aid-Connected Apps. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060157
Pfingstgraef K, O’Hagan R, Bataineh JN, Glista D. What’s in an App? Scoping Review and Quality Assessment of Clinically Available Hearing-Aid-Connected Apps. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(6):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060157
Chicago/Turabian StylePfingstgraef, Kate, Robin O’Hagan, Jana N. Bataineh, and Danielle Glista. 2025. "What’s in an App? Scoping Review and Quality Assessment of Clinically Available Hearing-Aid-Connected Apps" Audiology Research 15, no. 6: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060157
APA StylePfingstgraef, K., O’Hagan, R., Bataineh, J. N., & Glista, D. (2025). What’s in an App? Scoping Review and Quality Assessment of Clinically Available Hearing-Aid-Connected Apps. Audiology Research, 15(6), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15060157







