Self-Motion Misperception Induced by Neck Muscle Fatigue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Subjects
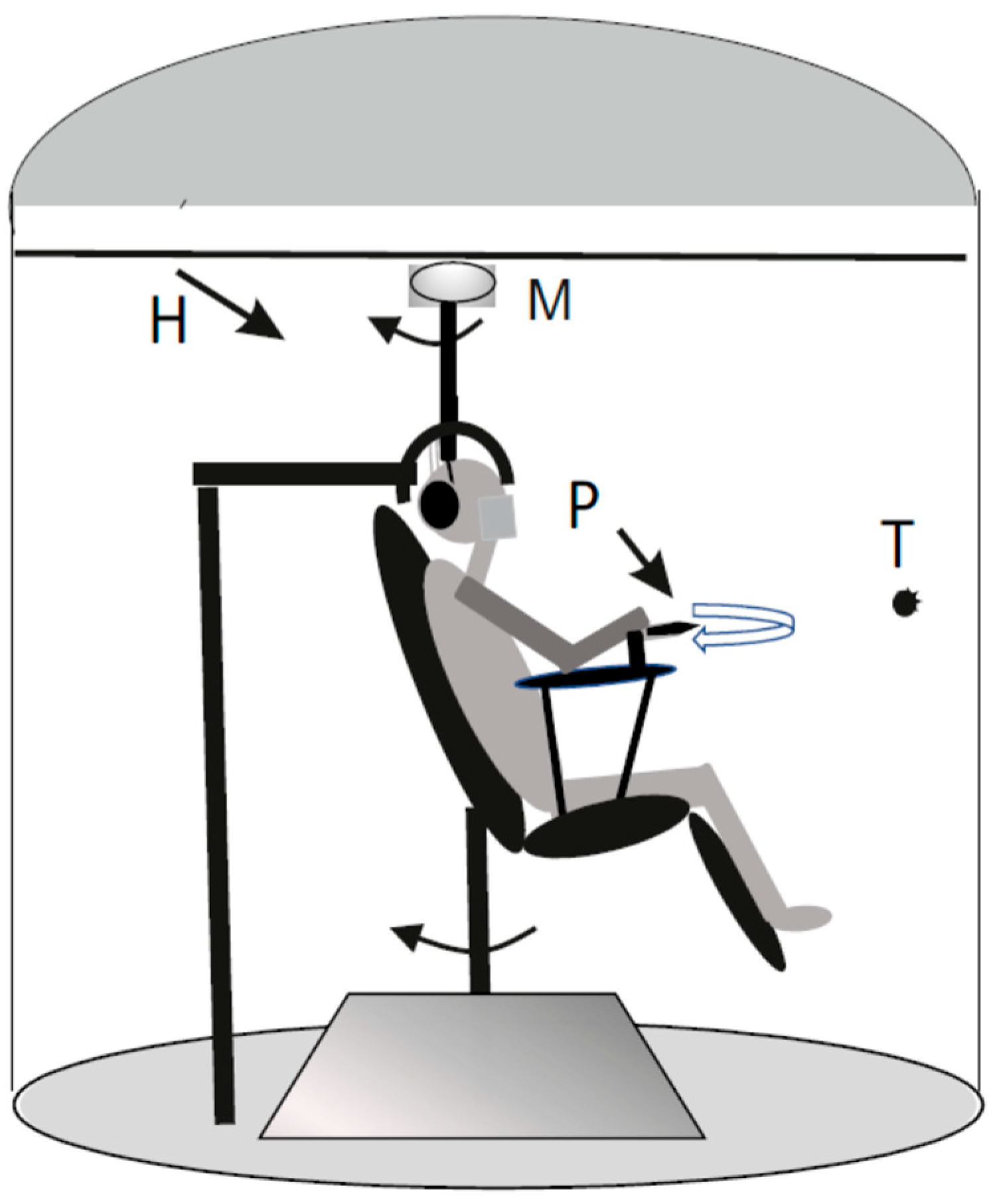
2.2. Experimental Setting
2.2.1. Neck Proprioceptive and Vestibular Sinusoidal Rotation
2.2.2. Symmetric Rotation
2.2.3. Asymmetric Rotation
2.2.4. Self-Motion Perception Recording
2.2.5. Neck Extensor Muscle Fatigue
2.2.6. Experimental Protocol
2.2.7. Data Acquisition and Analysis
3. Results
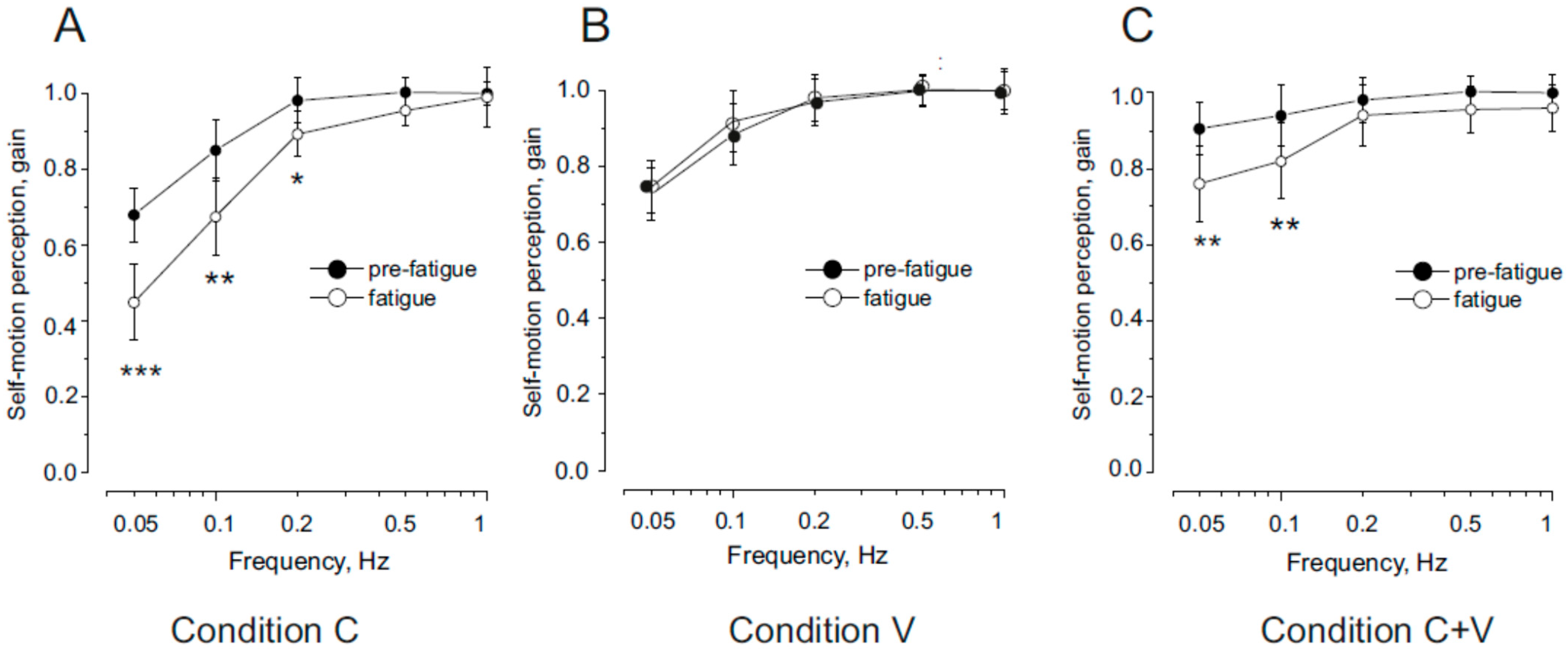
3.1. Effect of Neck Muscle Fatigue on Self-Motion Perceptual Gain in Response to Head and Trunk Symmetric Sinusoidal Rotation
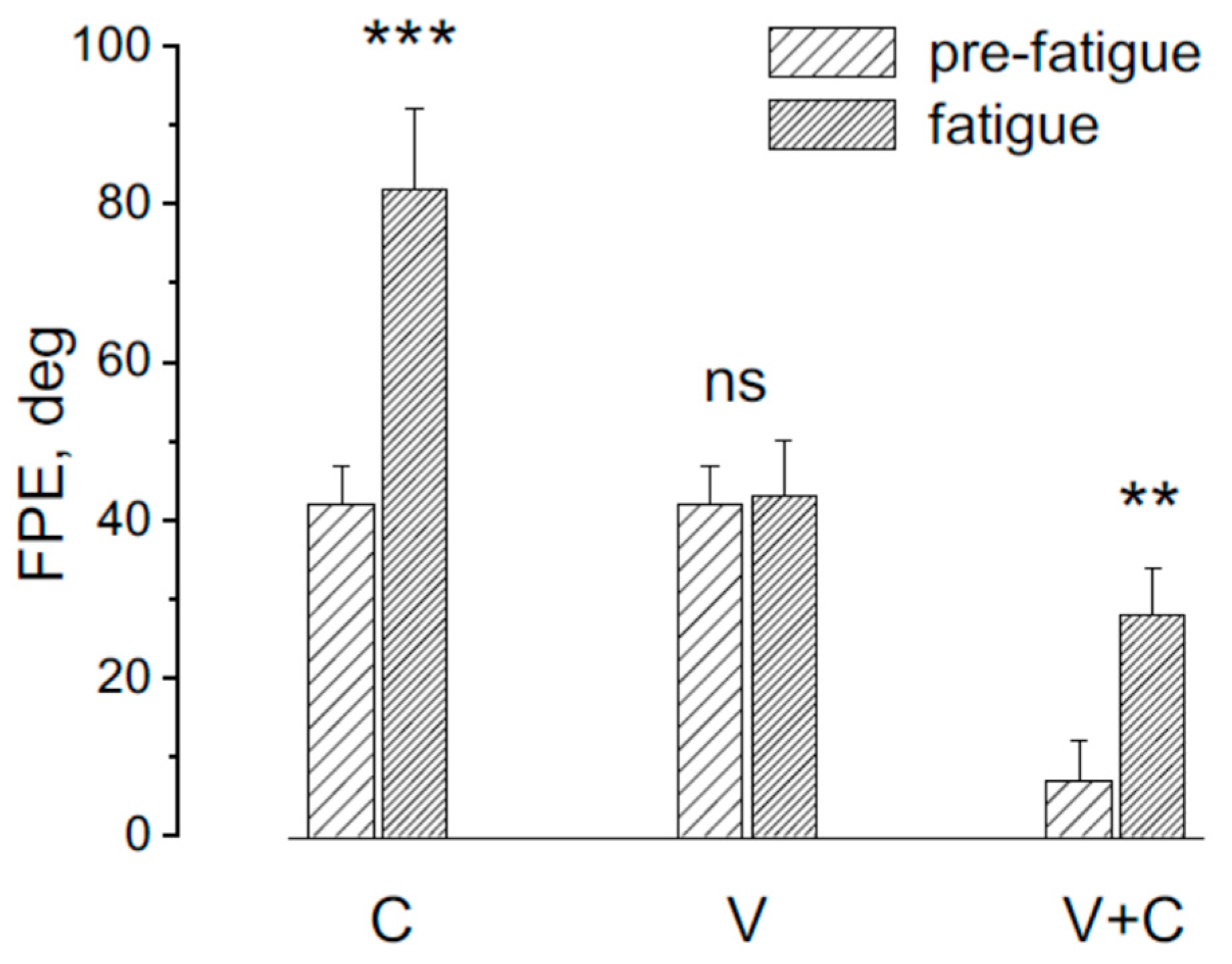
3.2. Effect of Light on the Induction of FPE During Asymmetric Rotation
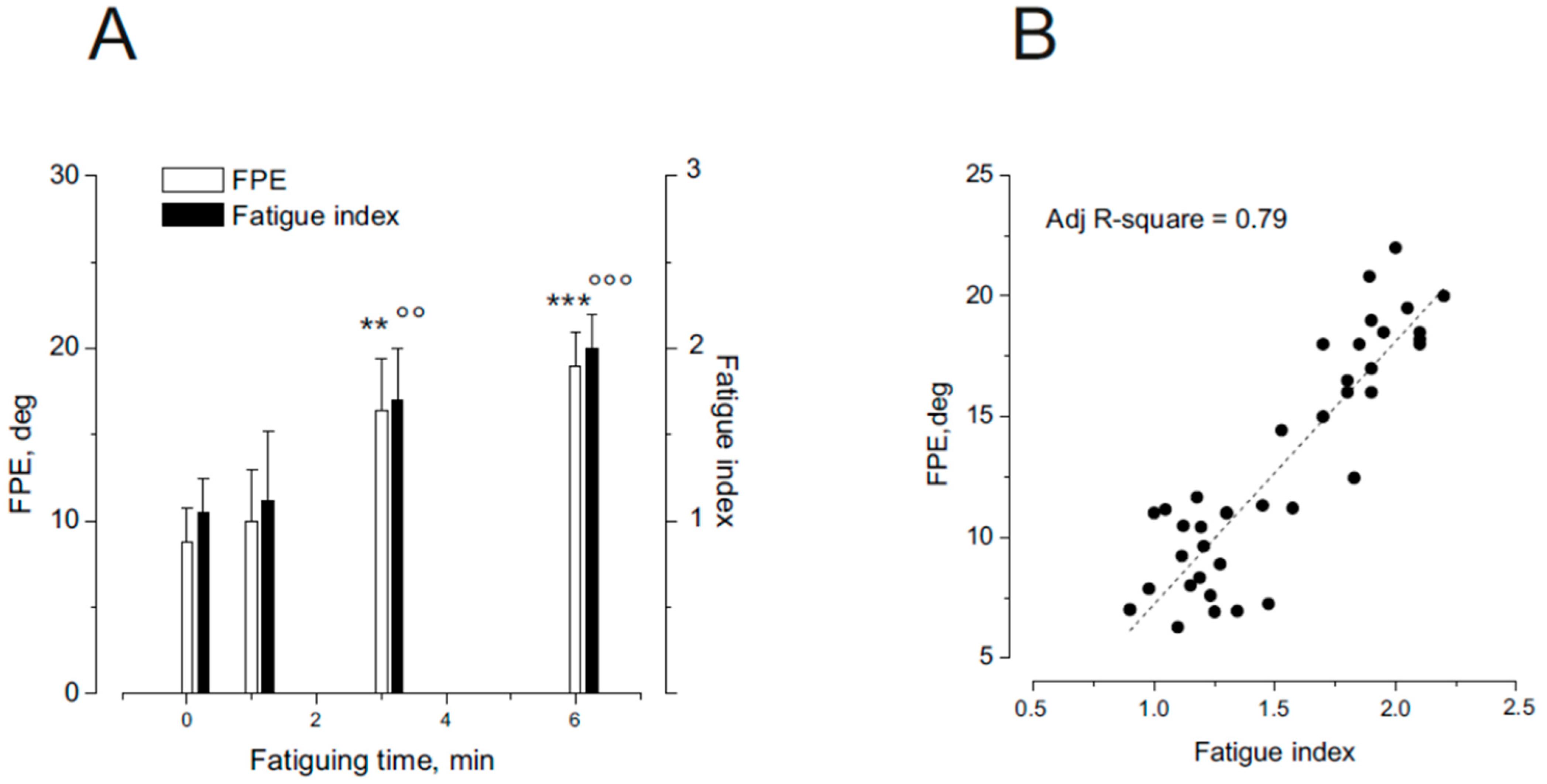
3.3. Effect of Different Fatigue Levels on FPE Induction During Asymmetric Rotation
4. Discussion
4.1. Perceptual Impairment by Neck Muscle Fatigue During Head and/or Trunk Rotation
4.2. Persistence of Perceptual Impairment Under Lighted Conditions
4.3. Fatigue-Induced Errors at Moderate Levels of Muscle Fatigue
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schweigart, G.; Heimbrand, S.; Mergner, T. Becker W Role of neck input for the perception of horizontal head and trunk rotation in patients with loss of vestibular function. Exp. Brain Res. 1993, 95, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweigart, G.; Chien, R.D.; Mergner, T. Neck proprioception compensates for age-related deterioration of vestibular self-motion perception. Exp. Brain Res. 2002, 147, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottini, G.; Karnath, H.O.; Vallar, G.; Sterzi, R.; Frith, C.D.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Paulesu, E. Cerebral representations for egocentric space: Functional anatomical evidence from caloric vestibular stimulation and neck vibration. Brain 2001, 124, 1182–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bove, M.; Courtine, G.; Schieppati, M. Neck muscle vibration and spatial orientation during stepping in place in humans. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorossi, V.E.; Schieppati, M. Neck proprioception shapes body orientation and perception of motion. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 4, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, K.E. The neural encoding of self-generated and externally applied movement: Implications for the perception of self-motion and spatial memory. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, K.; Leplaideur, S.; Leblanche, F.; Moulinet Raillon, A.; Honoré, T.; Bonan, I. The effects of neck muscle vibration on postural orientation and spatial perception: A systematic review. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2020, 50, 227–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselin, G.; Rassoulian, H.; Brown, I. Effects of neck extensor muscles fatigue on balance. Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, G.; Fagan, M.J. Effects of cervical muscle fatigue on the perception of the subjective vertical and horizontal. SpringerPlus 2014, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihhosseinian, M.; Holmes, M.W.; Murphy, B. Neck muscle fatigue alters upper limb proprioception. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieppati, M.; Nardone, A.; Schmid, M. Neck muscle fatigue affects postural control in man. Neuroscience 2003, 121, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccini, M.; Risaliti, I.; Rinaldi, L.A.; Paci, M. Head position and neck muscle fatigue: Effects on postural stability. Gait Posture 2006, 24, S9–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Schieppati, M. Neck muscle fatigue and spatial orientation during stepping in place in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Schieppati, M.; Pozzo, T. Effect of fatigue on the precision of a whole-body pointing task. Neuroscience 2006, 139, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botti, F.M.; Guardabassi, M.; Ferraresi, A.; Faralli, M.; Filippi, G.M.; Marcelli, V.; Occhigrossi, C.; Pettorossi, V.E. Neck muscle fatigue disrupts self-motion perception. Exp. Brain Res. 2025, 243, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardabassi, M.; Botti, F.M.; Rodio, A.; Fattorini, L.; Filippi, G.M.; Ferraresi, A.; Occhigrossi, C.; Pettorossi, V.E. Prolonged neck proprioceptive vibratory stimulation prevents the self-motion misperception induced by neck muscle fatigue: Immediate and sustained effects. Exp. Brain Res. 2025, 243, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, O.; Della Torre, G.; Lucchi, M.L.; Chiocchetti, R.; Bortolami, R.; Pettorossi, V.E. Inhibition of muscle spindle afferent activity during masseter muscle fatigue in the rat. Exp. Brain Res. 2003, 152, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettorossi, V.E.; Della Torre, G.; Bortolami, R.; Brunetti, O. The role of capsaicin-sensitive muscle afferents in fatigue-induced modulation of the monosynaptic reflex in the rat. J. Physiol. 2004, 515, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, H.B.; Wyatt, M.P.; Hodgdon, J.A. Effects of fatigue on joint position sense of the knee. J. Orthop. Res. 1986, 4, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shape, M.H.; Miles, T.S. Position sense at the elbow after fatiguing contractions. Exp. Brain Res. 1993, 94, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, S.J.; Kaufman, M.P. Role of muscle afferents in the inhibition of motoneurons during fatigue. In Fatigue: Neural and Muscular Mechanisms; Gandevia, S.C., Enoka, R.M., McComas, A.J., Stuart, D.G., Thomas, C.K., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1995; Volume 384, pp. 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia, S.C.; Enoka, R.M.; McComas, A.J.; Stuart, D.G.; Thomas, C.K. Fatigue: Neural and Muscular Mechanisms; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1995; Volume 384. [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth, K.E.; Macefield, V.G. The fusimotor system. Its role in fatigue. In Fatigue: Neural and Muscular Mechanisms; Gandevia, S.C., Enoka, R.M., McComas, A.J., Stuart, D.G., Thomas, C.K., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1995; Volume 384, pp. 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Lattanzio, P.J.; Petrella, R.J.; Sproule, J.R.; Fowler, P.J. Effects of fatigue on knee proprioception. Clin. J. Sports Med. 1997, 7, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, J.M.; Ljubislavlevic, M.; Bergenheim, M.; Johansson, H. Alterations in information transmission in ensemble of primary muscle spindle afferents after muscle fatigue in heteronymous muscle. Neuroscience 1998, 84, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, J.M.; Lonn, J.; Hellstrom, F.; Djupsjobacka, M.; Johansson, H. Localised muscle fatigue decreases the acuity of the movement sense in the human shoulder. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestier, N.; Teasdale, N.; Nougier, V. Alteration of the position sense at the ankle induced by muscular fatigue in humans. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.K.; Duchateau, J.; Enoka, R.M. Muscle fatigue and the mechanisms of task failure. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2004, 32, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Ishibashi, Y.; Tsuda, E.; Okamura, Y.; Otsuka, H.; Toh, S. The effect of local and general fatigue on knee proprioception. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2004, 20, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proske, U.; Gandevia, S.C. Kinaesthetic Senses. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 4139–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proske, U.; Gandevia, S.C. The proprioceptive senses: Their roles in signaling body shape, body position and movement, and muscular force. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1651–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elfattah, H.M.; Abdelazeim, F.H.; Elshennawy, S. Physical and cognitive consequences of fatigue: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proske, U. Exercise, fatigue and proprioception: A retrospective. Exp. Brain Res. 2019, 237, 2447–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proske, U.; Allen, T.J. The neural basis of the senses of effort, force and heaviness. Exp. Brain Res. 2019, 237, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannopoulos, C.; Watson, J.; Kahan, S.; Lawler, D. The effect of muscle fatigue on wrist joint position sense in healthy adults. J. Hand Ther. 2020, 33, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyadi, P.; Minoonejad, H.; Seifi, F.; Sheikhhoseini, R.; Arghadeh, R. The effectiveness of fatigue on repositioning sense of lower extremities: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, R.H.; Curthoys, I.S.; Markham, C.H. Planar relationships of the semicircular canals in man. Acta Otolaryngol. 1975, 80, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorossi, V.E.; Panichi, R.; Botti, F.M.; Kyriakareli, A.; Ferraresi, A.; Faralli, M.; Schieppati, M.; Bronstein, A.M. Prolonged asymmetric vestibular stimulation induces opposite, long-term effects on self-motion perception and ocular responses. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemungal, B.M.; Gunaratne, I.A.; Fleming, I.O.; Gresty, M.A.; Bronstein, A.M. Perceptual and nystagmic thresholds of vestibular function in yaw. J. Vestib. Res. 2004, 14, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panichi, R.; Botti, F.M.; Ferraresi, A.; Faralli, M.; Kyriakareli, A.; Schieppati, M.; Pettorossi, V.E. Self-motion perception and vestibulo ocular reflex during whole body yaw rotation in standing subjects: The role of head position and neck proprioception. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2011, 30, 314–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorossi, V.E.; Panichi, R.; Botti, F.M.; Biscarini, A.; Filippi, G.M.; Schieppati, M. Long-lasting effects of neck muscle vibration and contraction on self-motion perception of vestibular origin. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1886–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegle, J.H.; Campos, J.L.; Mohler, B.J.; Loomis, J.M.; Bülthoff, H.H. Measurement of instantaneous perceived self-motion using continuous pointing. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 195, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Lo Conte, L.R. Surface EMG signal processing during isometric contractions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1997, 7, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergner, T.; Siebold, C.; Schweigart, G.; Becker, W. Human perception of horizontal trunk and head rotation in space during vestibular and neck stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 1991, 85, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergner, T.; Rosemeier, T. Interaction of vestibular, somatosensory and visual signals for postural control and motion perception under terrestrial and microgravity conditions—A conceptual model. Brain Res. Rev. 1998, 28, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettorossi, V.E.; Occhigrossi, C.; Panichi, R.; Botti, F.M.; Ferraresi, A.; Ricci, G.; Faralli, M. Induction and Cancellation of Self-Motion Misperception by Asymmetric Rotation in the Light. Audiol. Res. 2023, 13, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Botti, F.M.; Guardabassi, M.; Occhigrossi, C.; Faralli, M.; Ferraresi, A.; Draicchio, F.; Pettorossi, V.E. Self-Motion Misperception Induced by Neck Muscle Fatigue. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050128
Botti FM, Guardabassi M, Occhigrossi C, Faralli M, Ferraresi A, Draicchio F, Pettorossi VE. Self-Motion Misperception Induced by Neck Muscle Fatigue. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(5):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050128
Chicago/Turabian StyleBotti, Fabio Massimo, Marco Guardabassi, Chiara Occhigrossi, Mario Faralli, Aldo Ferraresi, Francesco Draicchio, and Vito Enrico Pettorossi. 2025. "Self-Motion Misperception Induced by Neck Muscle Fatigue" Audiology Research 15, no. 5: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050128
APA StyleBotti, F. M., Guardabassi, M., Occhigrossi, C., Faralli, M., Ferraresi, A., Draicchio, F., & Pettorossi, V. E. (2025). Self-Motion Misperception Induced by Neck Muscle Fatigue. Audiology Research, 15(5), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050128







