Early Cochlear Implant Promotes Global Development in Children with Severe-to-Profound Hearing Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sampling Criteria
- -
- Diagnosis of severetoprofound deafness by 24 months age;
- -
- Age at activation of the CI being within 36 months;
- -
- Absence of pathologies associated with deafness (e.g., severe hypotonia or neuromotor disorders);
- -
- Hearing parents;
- -
- Exposure to an oral communication habilitation program before and after implantation;
- -
- No exposure to sign language;
- -
- Signing of informed consent.
- -
- Presence of associated pathologies and neuromotor delays;
- -
- Non-Italian-speaking parents.
2.3. Participants
2.4. Materials
- -
- Foundations of Learning (scale A): Assesses critical aspects of learning during the early childhood years. These aspects include basic cognitive skills for learning, such as attention and processing speed; thinking skills, such as reasoning, organizing information, and planning solutions; different types of memory (working memory, visual memory, auditory memory, etc.); and playing skills.
- -
- Language and Communication (scale B): Measures overall language development. This includes expressive language, receptive language, and use of language to communicate socially with others.
- -
- Eye and Hand Coordination (scale C): Tests fine motor skills, manual dexterity, and visual perception skills.
- -
- Personal–Social–Emotional (scale D): Measures constructs relating to the child’s developing sense of self and growing independence, interactions with others, plus many aspects of emotional development.
- -
- Gross Motor (scale E): Assesses postural control, balance, and gross body coordination, among other abilities.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Cochlear Implant |
| CIs | Cochlear Implants |
| HL | Hearing Loss |
| PTA | Pure Tone Average |
| HAs | Hearing Aids |
| DQ | Development Quotient |
| GDQ | Global Development Quotient |
References
- Yoshinaga-Itano, C.; Sedey, A.L.; Wiggin, M.; Mason, C.A. Language outcomes improved through early hearing detection and earlier cochlear implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, J.G.; Geers, A.E. Will they catch up? The role of age at cochlear implantation in the spoken language development of children with severe to profound hearing loss. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geers, A.E.; Brenner, C.; Tobey, E.A. Long-Term outcomes of cochlear implantation in early childhood: Sample characteristics and data collection methods. Ear Hear 2011, 32, 2S–12S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niparko, J.K.; Tobey, E.A.; Thal, D.J.; Eisenberg, L.S.; Wang, N.Y.; Quittner, A.L.; Fink, N.E. Spoken language development in children following cochlear implantation. JAMA 2010, 303, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerzoni, L.; Mancini, P.; Nicastri, M.; Fabrizi, E.; Giallini, I.; Cuda, D. Does early cochlear implantation promote better reading comprehension skills? Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 133, 109976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerzoni, L.; Falzone, C.; Ghiselli, S.; Nicastri, M.; Mancini, P.; Fabrizi, E.; Cuda, D. Corrigendum to “Speech Perception in noise in adolescents with cochlear implant”. Int. J. Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 193, 11231, Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, P.; Nicastri, M.; Giallini, I.; Odabaşi, Y.; Greco, A.; D’Alessandro, H.D.; Portanova, G.; Mariani, L. Long-term speech perception and morphosyntactic outcomes in adolescents and young adults implanted in childhood. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 167, 111514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geers, A.E. Speech, language, and reading skills after early cochlear implantation. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesJardin, J.L.; Eisenberg, L.S. Maternal contributions: Supporting language development in young children with cochlear implants. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, A.; Yusuf, P.A.; Land, R. Higher-order auditory areas in congenital deafness: Top-down interactions and corticocortical decoupling. Hear Res. 2017, 343, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.S.; Hamel, B.L.; Wichert, K.; Kozlowski, K.; Mleziva, S.; Ray, C.; Pisoni, D.B.; Kronenberger, W.G.; Moberly, A.C. Contribution of Verbal Learning & Memory and Spectro-Temporal Discrimination to Speech Recognition in Cochlear Implant Users. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, L.; Wouters, J.; van Wieringen, A. Speech perception in noise, working memory, and attention in children: A scoping review. Hear Res. 2023, 439, 108883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreery, R.W.; Walker, E.A.; Spratford, M.; Lewis, D.; Brennan, M. Auditory, Cognitive, and Linguistic Factors Predict Speech Recognition in Adverse Listening Conditions for Children with Hearing Loss. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almomani, F.; Al-Momani, M.O.; Garadat, S.; Alqudah, S.; Kassab, M.; Hamadneh, S.; Rauterkus, R.; Gans, R. Cognitive functioning in Deaf children using Cochlear implants. BMC Pediatrics 2021, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.B.; Monshizadeh, L. The effect of cochlear implantation in development of intelligence quotient of 6–9 deaf children in comparison with normal hearing children (Iran, 2009–2011). Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 76, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, P.; Shehata-Dieler, W.; Huestegge, L.; Hagen, R.; Kühn, H. Longitudinal Development of Verbal and Nonverbal Intelligence After Cochlear Implantation According to Wechsler Tests in German-speaking Children: A Preliminary Study. Ear Hear. 2023, 44, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Association for Research in Infant and Child Development. Griffiths III Year Four Items Grouped by Quartile Level of Difficulty. 2018. Available online: https://www.aricd.ac.uk/ (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Lanfranchi, S.; Rea, M.; Ferri, R.; Vianello, R. Studio di Validazione e Standardizzazione Italiana delle Griffiths III; Hogrefe Editore: Florence, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2023. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Luchkina, E.; Waxman, S. Talking About the Absent and the Abstract: Referential Communication in Language and Gesture. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2024, 19, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltefleiter, L.J.; Sodian, B.; Kristen-Antonow, S.; Grosse Wiesmann, C.; Schuwerk, T. Does syntax play a role in Theory of Mind development before the age of 3 years? Infant Behav. Dev. 2021, 64, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelemon, C.; Necula, V.; Berghe, A.S.; Livinț-Popa, L.; Palade, S.; Văcăraș, V.; Mureșanu, I.A.; Strilciuc, S.; Mureșanu, F.D. Neurodevelopmental Aspects and Cortical Auditory Maturation in Children with Cochlear Implants. Medicina 2020, 56, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colletti, L.; Mandalà, M.; Zoccante, L.; Shannon, R.V.; Colletti, V. Infants versus older children fitted with cochlear implants: Performance over 10 years. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 75, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, A.; Kronenberger, W.G.; Pison, D.B.; O’Donoghue, G.M. Neurocognitive factors in sensory restoration of early deafness: A connectome model. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirsky, M.A.; Teoh, S.W.; Neuburger, H. Development of language and speech perception in congenitally, profoundly deaf children as a function of age at cochlear implantation. Audiol. Neuro-Otol. 2004, 9, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomblin, J.B.; Peng, S.C.; Spencer, L.J.; Lu, N. Long-term trajectories of the development of speech sound production in pediatric cochlear implant recipients. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2008, 51, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spencer, L.J.; Tomblin, B. Evaluating phonological processing skills in children with prelingual deafness who use cochlear implants. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2009, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, A.; Sharma, A. Developmental neuroplasticity after cochlear implantation. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 280293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, S.E.; Walker, E.A.; Unflat-Berry, L.M.; Oleson, J.J.; Moeller, M.P. Quantity and quality of caregivers’ linguistic input to 18-month and 3-year-old children who are hard of hearing. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 10771091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cejas, I.; Mitchell, C.M.; Barker, D.H.; Sarangoulis, C.; Eisenberg, L.S.; Quittner, A.L. Parenting Stress, Self-Efficacy, and Involvement: Effects on Spoken Language Ability Three Years After Cochlear Implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, S11–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, L.; Adkins, D.; Kao, A.; Munyemana, M.A.; Kallogjeri, D.; Lieu, J.E. Social Determinants of Health and Language and Academic Outcomes in Pediatric Cochlear Implantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2025, 151, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittrouer, S. The changing face of spoken language development in children with hearing loss. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2021, 26, 293304. [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberger, W.G.; Pisoni, D.B. Neurocognitive functioning in deaf children with cochlear implants. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 28, 509515. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, L.S.; Geers, A.E.; Blamey, P.J.; Tobey, E.A.; Brenner, C.A. Factors contributing to speech perception scores in long-term pediatric cochlear implant users. Ear Hear 2011, 32 (Suppl. S1), 19S–26S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarkowski, A.; Dirks, E. Fathers of Young Deaf or Hard-of-Hearing Children: A Systematic Review. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2021, 26, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, R.; Low, S. Early social-emotional, language and academic development in children with hearing loss: Families with and without fathers. Am. Ann. Deaf 1998, 143, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingber, S.; Most, T. Fathers’ involvement in preschool programs for children with and without hearing loss. Am. Ann. Deaf 2012, 157, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majorano, M.; Guidotti, L.; Guerzoni, L.; Murri, A.; Morelli, M.; Cuda, D.; Lavelli, M. Spontaneous language production of Italian children with cochlear implants and their mothers in two interactive contexts. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2018, 53, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Son, S.E.; Moon, I.J.; Chung, W.H.; Cho, Y.S.; Hong, S.H.; Cho, Y.S. The role of socioeconomic factors and third-party support in language development for children with cochlear implants. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinzen-Derr, J.; Wiley, S.; Grether, S.; Choo, D.I.; Murray, J. Home intervention and early language outcomes in young children with hearing loss. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2021051797. [Google Scholar]

| n. Subjects | Gender | Median Age at Diagnosis (Months) | Median Age at CI Activation (Months) | Mean Age at t0 (Months) | Mean Age at t1 (Months) | Mother’s Schooling Mean Age (Years) | Father’s Schooling Mean Age (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 12 females 12 males | 3 | 14 | 13.7 | 24.4 | 15.2 | 14 |
| t0 Mean (sd) | t1 Mean (sd) | Test Statistic | p. Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale A (DQ) | 98.3 (19.7) | 99.04 (11.5) | −0.23575 | 0.816 |
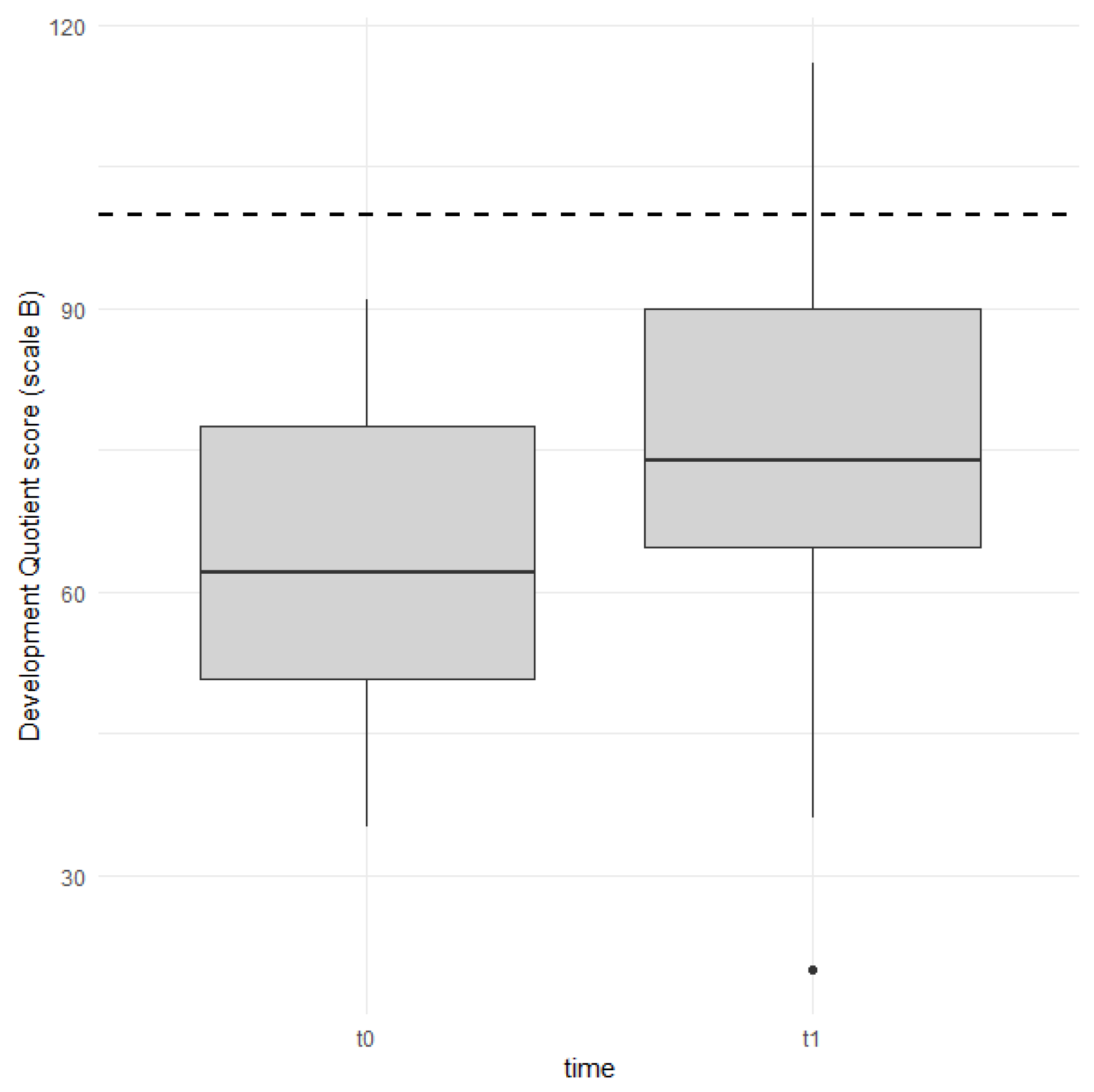
| Scale B (DQ) | 63.6 (16.2) | 78.9 (19.8) | −2.76644 | 0.011 |
| Scale C (DQ) | 98.1 (16.1) | 93.2 (15) | 1.408743 | 0.172 |
| Scale D (DQ) | 98 (13.2) | 92.6 (15.2) | 1.685367 | 0.105 |
| Scale E (DQ) | 96.7 (17.1) | 96.6 (14.6) | 0.041407 | 0.967 |
| GDQ | 84.5 (16.3) | 87.4 (18.1) | −0.99263 | 0.331 |
| Response | Estimate | std. Error | Statistic | p. Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale A_DQ | 2.433852 | 0.908866 | 2.6779 | 0.013 * |
| Scale B_DQ | 2.038208 | 0.966431 | 2.10901 | 0.045 * |
| Scale C_DQ | 2.348758 | 0.842754 | 2.797 | 0.009 ** |
| Scale D_DQ | 1.914092 | 0.764038 | 2.50523 | 0.019 * |
| Scale E_DQ | 1.758525 | 0.99993 | 1.75865 | 0.091 (.) |
| GDQ | 2.202218 | 0.986047 | 2.23338 | 0.035 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falzone, C.; Guerzoni, L.; Ghiselli, S.; Franchomme, L.; Nicastri, M.; Mancini, P.; Fabrizi, E.; Cuda, D. Early Cochlear Implant Promotes Global Development in Children with Severe-to-Profound Hearing Loss. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050121
Falzone C, Guerzoni L, Ghiselli S, Franchomme L, Nicastri M, Mancini P, Fabrizi E, Cuda D. Early Cochlear Implant Promotes Global Development in Children with Severe-to-Profound Hearing Loss. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(5):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050121
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalzone, Chiara, Letizia Guerzoni, Sara Ghiselli, Laura Franchomme, Maria Nicastri, Patrizia Mancini, Enrico Fabrizi, and Domenico Cuda. 2025. "Early Cochlear Implant Promotes Global Development in Children with Severe-to-Profound Hearing Loss" Audiology Research 15, no. 5: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050121
APA StyleFalzone, C., Guerzoni, L., Ghiselli, S., Franchomme, L., Nicastri, M., Mancini, P., Fabrizi, E., & Cuda, D. (2025). Early Cochlear Implant Promotes Global Development in Children with Severe-to-Profound Hearing Loss. Audiology Research, 15(5), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050121








