Feasibility of Early Vestibular Screening and Developmental Changes in Air- and Bone-Conducted Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Infants and Children with Normal Hearing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Methods
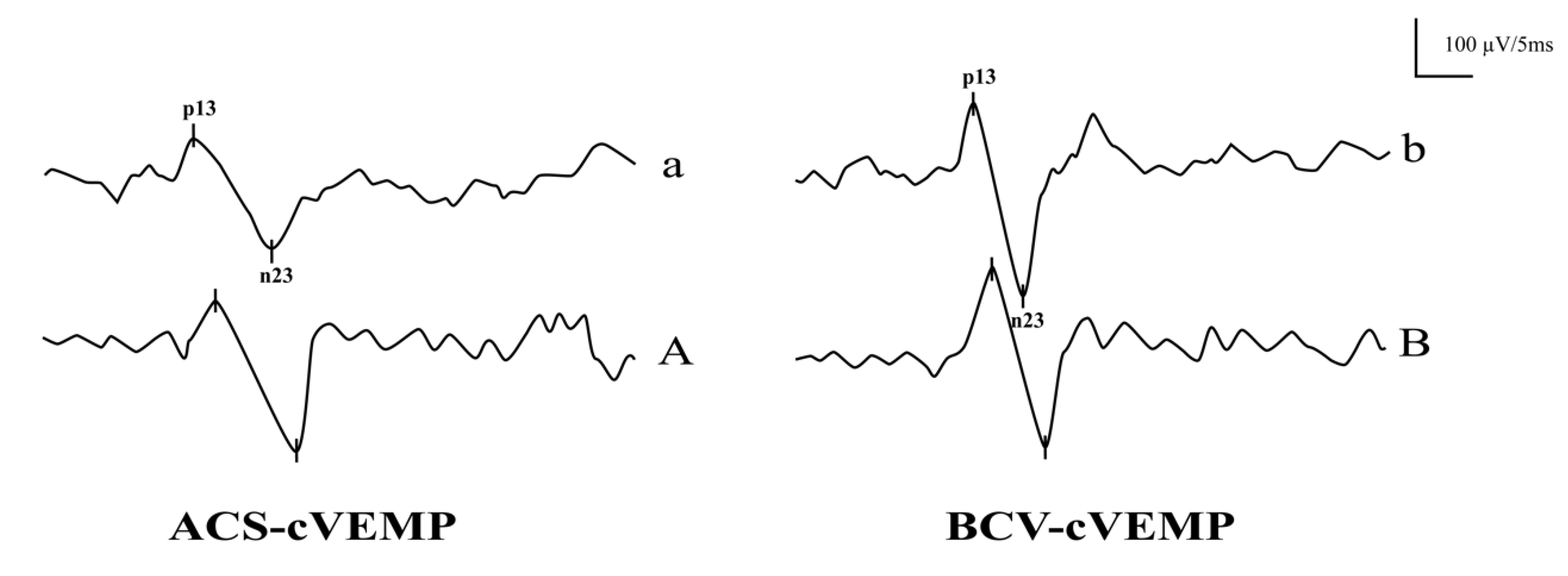
2.2.1. ACS-cVEMP, BCV-cVEMP Measurement
2.2.2. Audiological Assessment
2.2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Response Rates and Waveforms of ACS-cVEMP and BCV-cVEMP in Different Age Groups with Normal Hearing
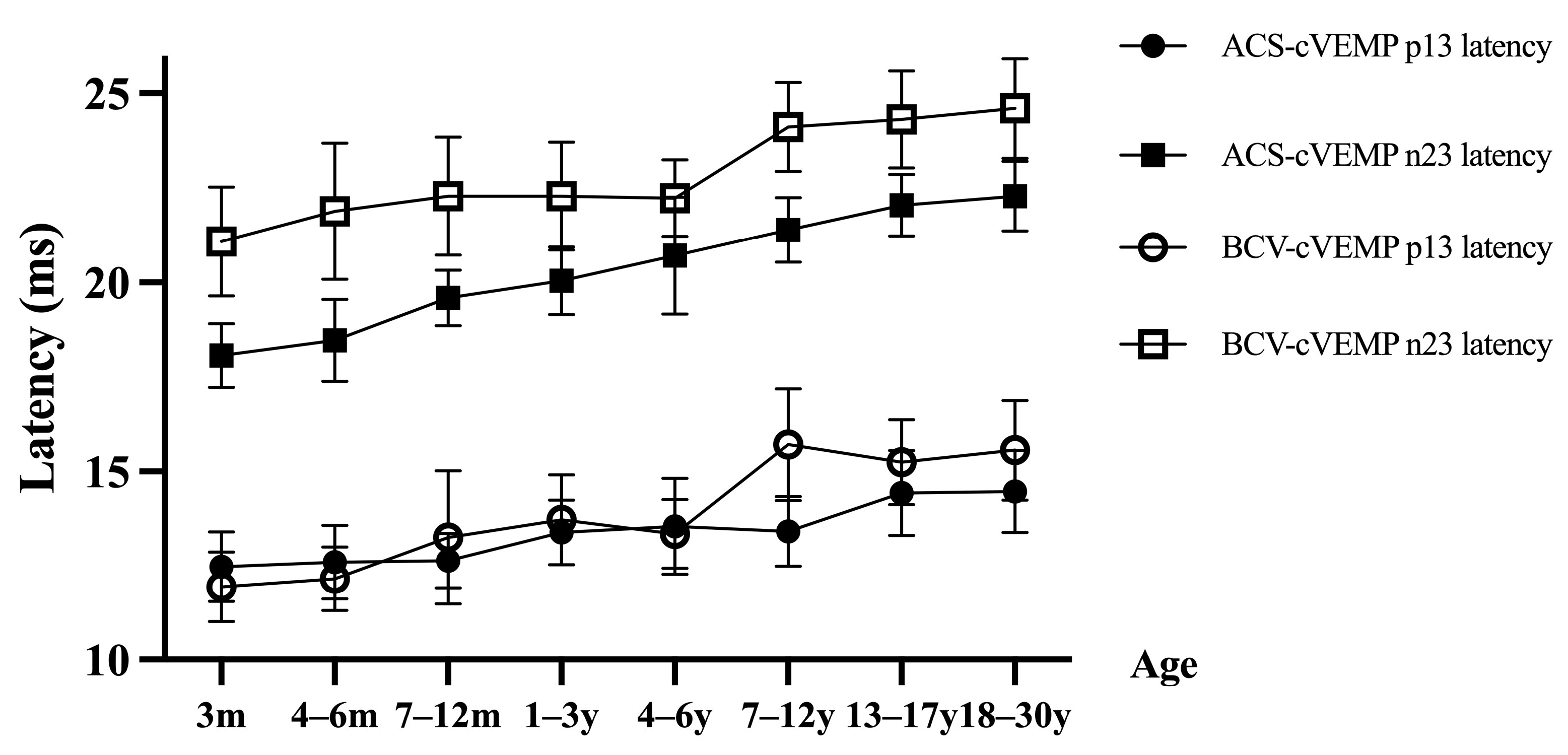
3.2. ACS-cVEMP Latency in Different Age Groups with Normal Hearing
3.3. BCV-cVEMP Latency in Different Age Groups with Normal Hearing
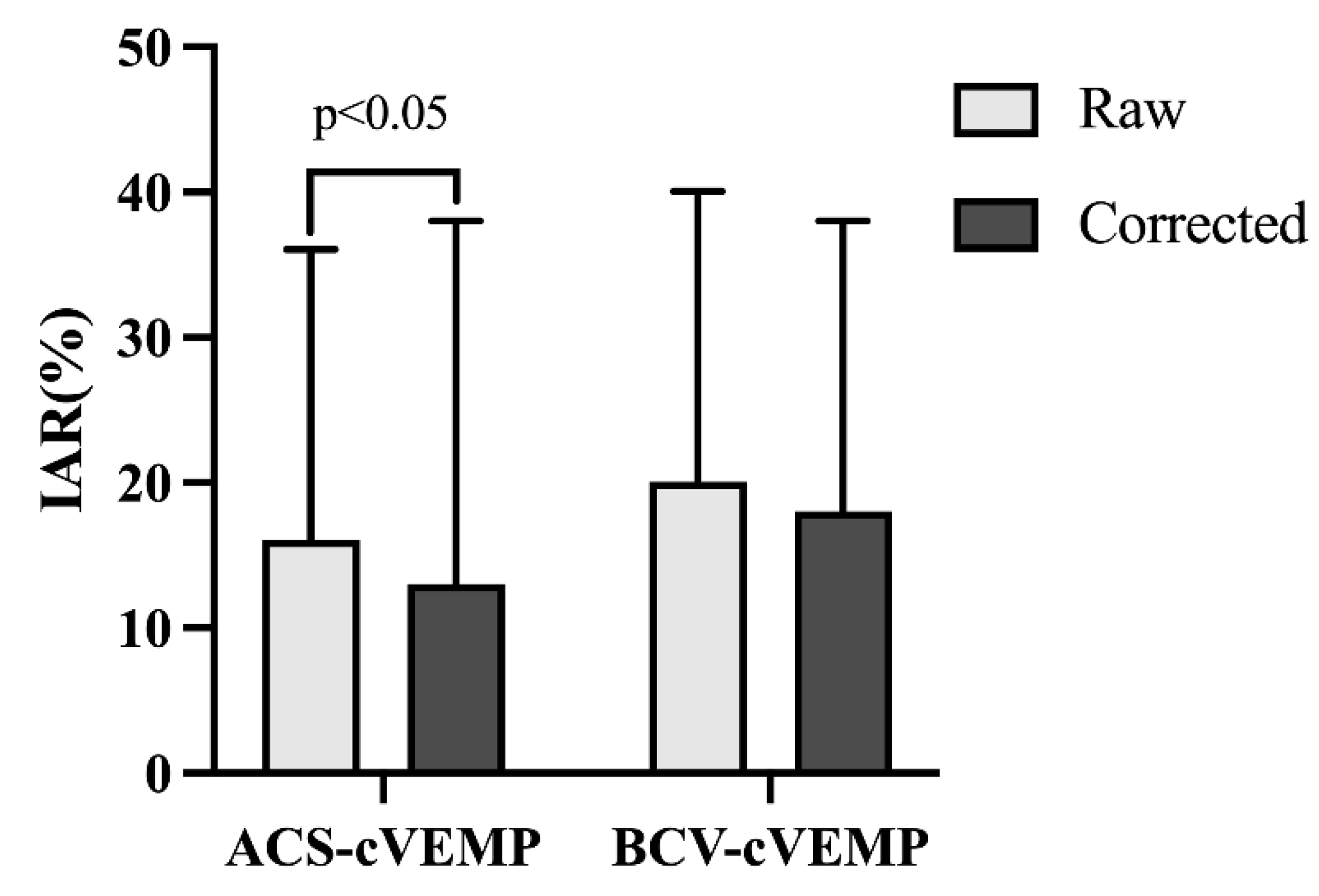
3.4. Amplitude and IAR of ACS-cVEMP and BCV-cVEMP in Different Age Groups with Normal Hearing
4. Discussion
4.1. The Response Rates in Different Age Groups with Normal Hearing
4.2. Latencies in Different Age Groups with Normal Hearing
4.3. Amplitudes and IAR in Different Age Groups with Normal Hearing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cushing, S.L.; Papsin, B.C. Special Considerations for the Pediatric Patient. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 82, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, Y.H. Assessment of functional development of the otolithic system in growing children: A review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, S.; Dhooge, I.; Dhondt, C.; Leyssens, L.; Sucaet, M.; Vanaudenaerde, S.; Rombaut, L.; Maes, L. Vestibular Infant Screening-Flanders: The implementation of a standard vestibular screening protocol for hearing-impaired children in Flanders. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 120, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; He, K.; Wang, W.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in 3-month-old infants: Comparative characteristics and feasibility for infant vestibular screening. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 992392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, S.Z.; Abdul Wahat, N.H. Effects of Age on Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials and Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials Using 750 Hz Tone Burst Stimuli among Healthy Adults. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 29, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbecque, E.; Marijnissen, T.; De Belder, N.; Van Rompaey, V.; Boudewyns, A.; Van de Heyning, P.; Vereeck, L.; Hallemans, A. Vestibular (dys) function in children with sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review. Int. J. Audiol. 2017, 56, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, L.; Galle Barrett, K.; Karltorp, E. The feasibility, validity and reliability of a child friendly vestibular assessment in infants and children candidates to cochlear implant. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 135, 110093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykholeslami, K.; Megerian, C.A.; Arnold, J.E.; Kaga, K. Vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in infancy and early childhood. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.N.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, C.T.; Hsieh, W.S.; Young, Y.H. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in newborns. Audiol. Neurootol. 2007, 12, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbek, S.; Erbek, S.S.; Gokmen, Z.; Ozkiraz, S.; Tarcan, A.; Ozluoglu, L.N. Clinical application of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in healthy newborns. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 71, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kegel, A.; Maes, L.; Baetens, T.; Dhooge, I.; Van Waelvelde, H. The influence of a vestibular dysfunction on the motor development of hearing-impaired children. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.F.; Moreira, F.C.; Menezes, A.S.; Costa, I.E.; Azevedo, C.; Vilarinho, S.; Dias, L. Vestibular Disorders in the Pediatric Age: Retrospective Analysis and Review of the Literature. Acta Med. Port. 2021, 34, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, S.; Dhooge, I.; Dhondt, C.; Vanaudenaerde, S.; Sucaet, M.; Rombaut, L.; Boudewyns, A.; Desloovere, C.; Janssens de Varebeke, S.; Vinck, A.S.; et al. Vestibular Infant Screening (VIS)-Flanders: Results after 1.5 years of vestibular screening in hearing-impaired children. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrecchia, L.; Karpeta, N.; Westin, M.; Johansson, A.; Aldenklint, S.; Brantberg, K.; Duan, M. Methodological aspects of testing vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in infants at universal hearing screening program. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alde, M.; Fancello, V.; Di Mauro, P.; Canelli, R.; Zaouche, S.; Falanga, C. Audiological and Vestibular Follow-Up for Children with Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: From Current Limitations to Future Directions. Children 2024, 11, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M. Maturational effects of the vestibular system: A study of rotary chair, computerized dynamic posturography, and vestibular evoked myogenic potentials with children. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2007, 18, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribukait, A.; Brantberg, K.; Bergenius, J. Function of semicircular canals, utricles and saccules in deaf children. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004, 124, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsch, T.A.; Schaefer, L.A.; Esquivel, C.R. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in young children: Test parameters and normative data. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinjo, Y.; Jin, Y.; Kaga, K. Assessment of vestibular function of infants and children with congenital and acquired deafness using the ice-water caloric test, rotational chair test and vestibular-evoked myogenic potential recording. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007, 127, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, S.M.; Govender, S.; Colebatch, J.G. Ocular and cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials produced by air- and bone-conducted stimuli: Comparative properties and effects of age. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhondt, C.; Dhooge, I.; Maes, L. Vestibular assessment in the pediatric population. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener-Vacher, S.R.; Campi, M.; Boizeau, P.; Thai-Van, H. Cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in healthy children: Normative values for bone and air conduction. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1157975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, E.S.; Murofushi, T.; Akin, F.W.; Colebatch, J.G. International guidelines for the clinical application of cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials: An expert consensus report. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, S.; Dhooge, I.; Dhondt, C.; Vanaudenaerde, S.; Sucaet, M.; Rombaut, L.; Maes, L. Pediatric Vestibular Assessment: Clinical Framework. Ear Hear. 2023, 44, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, S.; Dhooge, I.; Dhondt, C.; Vanaudenaerde, S.; Sucaet, M.; Van Hoecke, H.; De Leenheer, E.; Rombaut, L.; Boudewyns, A.; Desloovere, C.; et al. Three Years of Vestibular Infant Screening in Infants With Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2021055340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinard, C.G.; Piker, E.G.; Thorne, A.P.; Surface, E.N.; Anderson, A.E.; Beacham, V.A.; Crouse, M.C.; Whitney, V.H.; Depaolis, R.A. Maximum Output and Low-Frequency Limitations of B71 and B81 Clinical Bone Vibrators: Implications for Vestibular Evoked Potentials. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwalt, N.L.; Patterson, J.N.; Rodriguez, A.I.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Gordon, K.R.; Janky, K.L. Bone Conduction Vibration Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential (VEMP) Testing: Reliability in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults. Ear Hear. 2021, 42, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.D.; Welgampola, M.S.; Carey, J.P. Test-retest reliability and age-related characteristics of the ocular and cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential tests. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, I.S.; Vulovic, V.; Burgess, A.M.; Cornell, E.D.; Mezey, L.E.; Macdougall, H.G.; Manzari, L.; McGarvie, L.A. The basis for using bone-conducted vibration or air-conducted sound to test otolithic function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1233, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.C.; Young, Y.H. Eliciting Cervical Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potentials by Bone-Conducted Vibration via Various Tapping Sites. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, I.S.; Grant, J.W. How does high-frequency sound or vibration activate vestibular receptors? Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, L.; Dhooge, I.; D’Haenens, W.; Bockstael, A.; Keppler, H.; Philips, B.; Swinnen, F.; Vinck, B.M. The effect of age on the sinusoidal harmonic acceleration test, pseudorandom rotation test, velocity step test, caloric test, and vestibular-evoked myogenic potential test. Ear Hear. 2010, 31, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowetzky, K.; Yoon, K.H.; Mackowetzky, E.J.; Waskiewicz, A.J. Development and evolution of the vestibular apparatuses of the inner ear. J. Anat. 2021, 239, 801–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, L.; De Kegel, A.; Van Waelvelde, H.; Dhooge, I. Rotatory and collic vestibular evoked myogenic potential testing in normal-hearing and hearing-impaired children. Ear Hear. 2014, 35, e21–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Young, Y.H.; Murofushi, T. Tone burst-evoked myogenic potentials in human neck flexor and extensor. Acta Otolaryngol. 1999, 119, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Yeh, T.H.; Chang, C.H.; Young, Y.H. Consistent latencies of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials. Ear Hear. 2008, 29, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janky, K.L.; Rodriguez, A.I. Quantitative Vestibular Function Testing in the Pediatric Population. Semin. Hear. 2018, 39, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janky, K.L.; Thomas, M.; Patterson, J.; Givens, D. Using Functional Outcomes to Predict Vestibular Loss in Children. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.S.B.; Cabral, A.M.L.; Britto, D. Vestibular assessment in children aged zero to twelve years: An integrative review. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 88 (Suppl. S3), S212–S224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Danasoury, I.; El Sirafy, G.; Taha, H.; Hegazy, S. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMPs) in young children: Test parameters and normative data. Egypt. J. Ear Nose Throat Allied Sci. 2015, 16, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Xue, S.; Wei, X.; Chen, B.; Kong, Y.; Li, Y. Characteristics of vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in children with vestibular malformation and severe sensorineural hearing loss. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 176, 111781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Kim, M.S.; Son, E.J.; Lim, H.J.; Bang, J.H.; Kang, J.G. The Usefulness of Rectified VEMP. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 1, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosengren, S.M.; Todd, N.P.; Colebatch, J.G. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials evoked by brief interaural head acceleration: Properties and possible origin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosengren, S.M.; Colebatch, J.G.; Young, A.S.; Govender, S.; Welgampola, M.S. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in practice: Methods, pitfalls and clinical applications. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2019, 4, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.L.A.; Fitzpatrick, D.; McCreery, R.; Janky, K.L. Big Stimulus, Little Ears: Safety in Administering Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Children. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2017, 28, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.I.; Thomas, M.L.A.; Janky, K.L. Air-Conducted Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential Testing in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults: Thresholds, Frequency Tuning, and Effects of Sound Exposure. Ear Hear. 2019, 40, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaslin, D.L.; Jacobson, G.P.; Hatton, K.; Fowler, A.P.; DeLong, A.P. The effects of amplitude normalization and EMG targets on cVEMP interaural amplitude asymmetry. Ear Hear. 2013, 34, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age Group | Number of Subjects | Average Age (Mean ± SD) | Gender (Male/Female) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 months | 31 | 3.0 ± 0.00 | 19/12 |
| 4–6 months | 25 | 5.12 ± 0.85 | 12/13 |
| 7–12 months | 20 | 9.05 ± 1.74 | 10/10 |
| 1–3 years | 20 | 24.20 ± 8.96 | 12/8 |
| 4–6 years | 20 | 58.80 ± 9.33 | 10/10 |
| 7–12 years | 23 | 105.91 ± 19.15 | 13/10 |
| 13–17 years | 20 | 180.00 ± 13.86 | 10/10 |
| 18–30 years | 20 | 250.80 ± 27.15 | 10/10 |
| Age Group | Number of Ears | p13 Latency (ms) | n23 Latency (ms) | p13–n23 Interval (ms) | Corrected Amplitude (μV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACS-cVEMP | 3 months | 54 | 12.48 ± 0.92 | 18.08 ± 0.84 | 5.60 ± 0.95 | 1.11 ± 0.29 |
| 4–6 months | 44 | 12.61 ± 0.97 | 18.47 ± 1.09 | 5.86 ± 1.04 | 1.18 ± 0.31 | |
| 7–12 months | 38 | 12.64 ± 0.72 | 19.59 ± 0.73 | 6.95 ± 0.98 | 1.17 ± 0.51 | |
| 1–3 years | 40 | 13.39 ± 0.85 | 20.05 ± 0.90 | 6.66 ± 1.01 | 1.63 ± 0.32 | |
| 4–6 years | 40 | 13.55 ± 1.27 | 20.71 ± 1.55 | 7.16 ± 1.67 | 2.21 ± 0.54 | |
| 7–12 years | 46 | 13.42 ± 0.92 | 21.39 ± 0.86 | 7.96 ± 1.01 | 2.49 ± 0.56 | |
| 13–17 years | 40 | 14.43 ± 1.12 | 22.05 ± 0.82 | 7.62 ± 1.10 | 2.77 ± 0.59 | |
| 18–30 years | 40 | 14.47 ± 1.08 | 22.29 ± 0.92 | 7.82 ± 1.14 | 2.91 ± 0.80 | |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| F value | 26.072 | 140.497 | 34.606 | 97.983 | ||
| BCV-cVEMP | 3 months | 60 | 11.95 ± 0.92 | 21.09 ± 1.44 | 9.14 ± 1.10 | 1.14 ± 0.60 |
| 4–6 months | 48 | 12.16 ± 0.85 | 21.89 ± 1.81 | 9.74 ± 1.58 | 1.39 ± 0.78 | |
| 7–12 months | 40 | 13.26 ± 1.76 | 22.28 ± 1.56 | 9.02 ± 1.63 | 1.73 ± 0.71 | |
| 1–3 years | 40 | 13.72 ± 1.19 | 22.28 ± 1.43 | 8.56 ± 0.97 | 2.36 ± 1.00 | |
| 4–6 years | 40 | 13.35 ± 0.91 | 22.23 ± 1.01 | 8.88 ± 1.01 | 3.29 ± 2.37 | |
| 7–12 years | 46 | 15.71 ± 1.48 | 24.11 ± 1.18 | 8.39 ± 1.28 | 2.86 ± 1.59 | |
| 13–17 years | 40 | 15.25 ± 1.13 | 24.31 ± 1.29 | 9.06 ± 1.39 | 2.28 ± 0.56 | |
| 18–30 years | 40 | 15.57 ± 1.32 | 24.61 ± 1.32 | 9.04 ± 1.28 | 2.25 ± 0.90 | |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| F value | 80.310 | 42.342 | 4.063 | 23.998 |
| Age Group | ACS-cVEMP | BCV-cVEMP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p13 Latency (ms) | n23 Latency (ms) | Corrected Amplitude (μV) | p13 Latency (ms) | n23 Latency (ms) | Corrected Amplitude (μV) | |
| 3 months | 12.24–12.73 | 17.85–18.30 | 1.03–1.19 | 11.72–12.19 | 20.72–21.46 | 0.99–1.30 |
| 4–6 months | 12.33–12.89 | 18.16–18.79 | 1.09–1.27 | 11.91–12.40 | 21.37–22.42 | 1.16–1.61 |
| 7–12 months | 12.40–12.88 | 19.35–19.83 | 1.01–1.34 | 12.70–13.82 | 21.79–22.78 | 1.50–1.95 |
| 1–3 years | 13.12–13.66 | 19.76–20.33 | 1.52–1.73 | 13.34–14.10 | 21.83–22.74 | 2.04–2.68 |
| 4–6 years | 13.14–13.96 | 20.21–21.20 | 1.85–2.15 | 13.06–13.65 | 21.91–22.56 | 2.53–4.04 |
| 7–12 years | 13.15–13.70 | 21.13–21.64 | 2.32–2.65 | 15.27–16.15 | 23.76–24.46 | 2.39–3.33 |
| 13–17 years | 14.07–14.79 | 21.79–22.31 | 2.58–2.96 | 14.89–15.62 | 23.90–24.72 | 2.10–2.46 |
| 18–30 years | 14.13–14.82 | 22.00–22.58 | 2.66–3.17 | 15.15–16.00 | 24.19–25.03 | 1.96–2.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, M.; Jin, Y.; Yang, J. Feasibility of Early Vestibular Screening and Developmental Changes in Air- and Bone-Conducted Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Infants and Children with Normal Hearing. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030067
Shen J, Ma X, Wang L, Wang W, Chen J, Zhang Q, Duan M, Jin Y, Yang J. Feasibility of Early Vestibular Screening and Developmental Changes in Air- and Bone-Conducted Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Infants and Children with Normal Hearing. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jiali, Xiaobao Ma, Lu Wang, Wei Wang, Jianyong Chen, Qing Zhang, Maoli Duan, Yulian Jin, and Jun Yang. 2025. "Feasibility of Early Vestibular Screening and Developmental Changes in Air- and Bone-Conducted Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Infants and Children with Normal Hearing" Audiology Research 15, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030067
APA StyleShen, J., Ma, X., Wang, L., Wang, W., Chen, J., Zhang, Q., Duan, M., Jin, Y., & Yang, J. (2025). Feasibility of Early Vestibular Screening and Developmental Changes in Air- and Bone-Conducted Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Infants and Children with Normal Hearing. Audiology Research, 15(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030067







