Balance Rehabilitation with Peripheral Visual Stimulation in Patients with Panic Disorder and Agoraphobia: An Open-Pilot Intervention Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
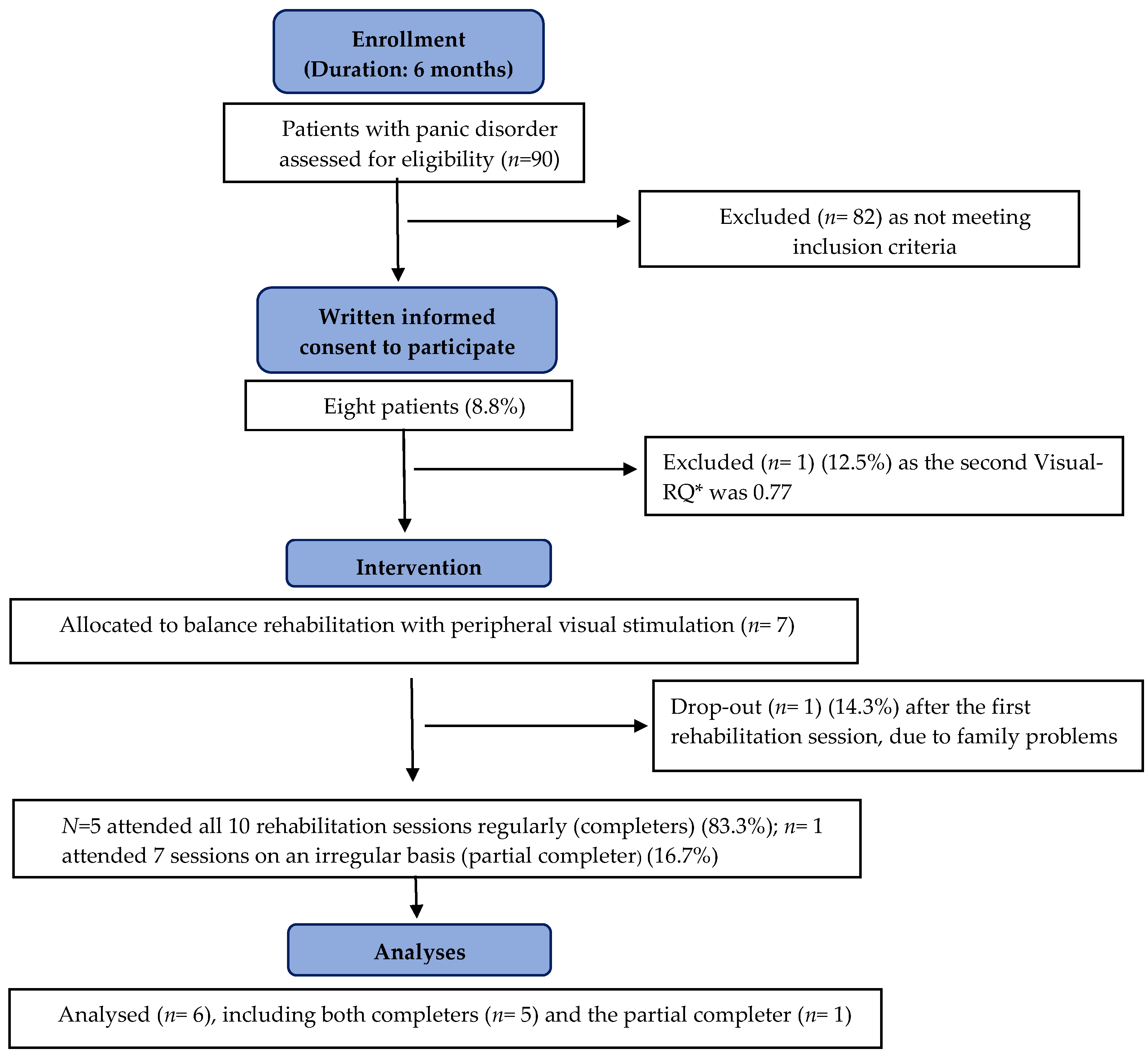
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Procedure and Measures
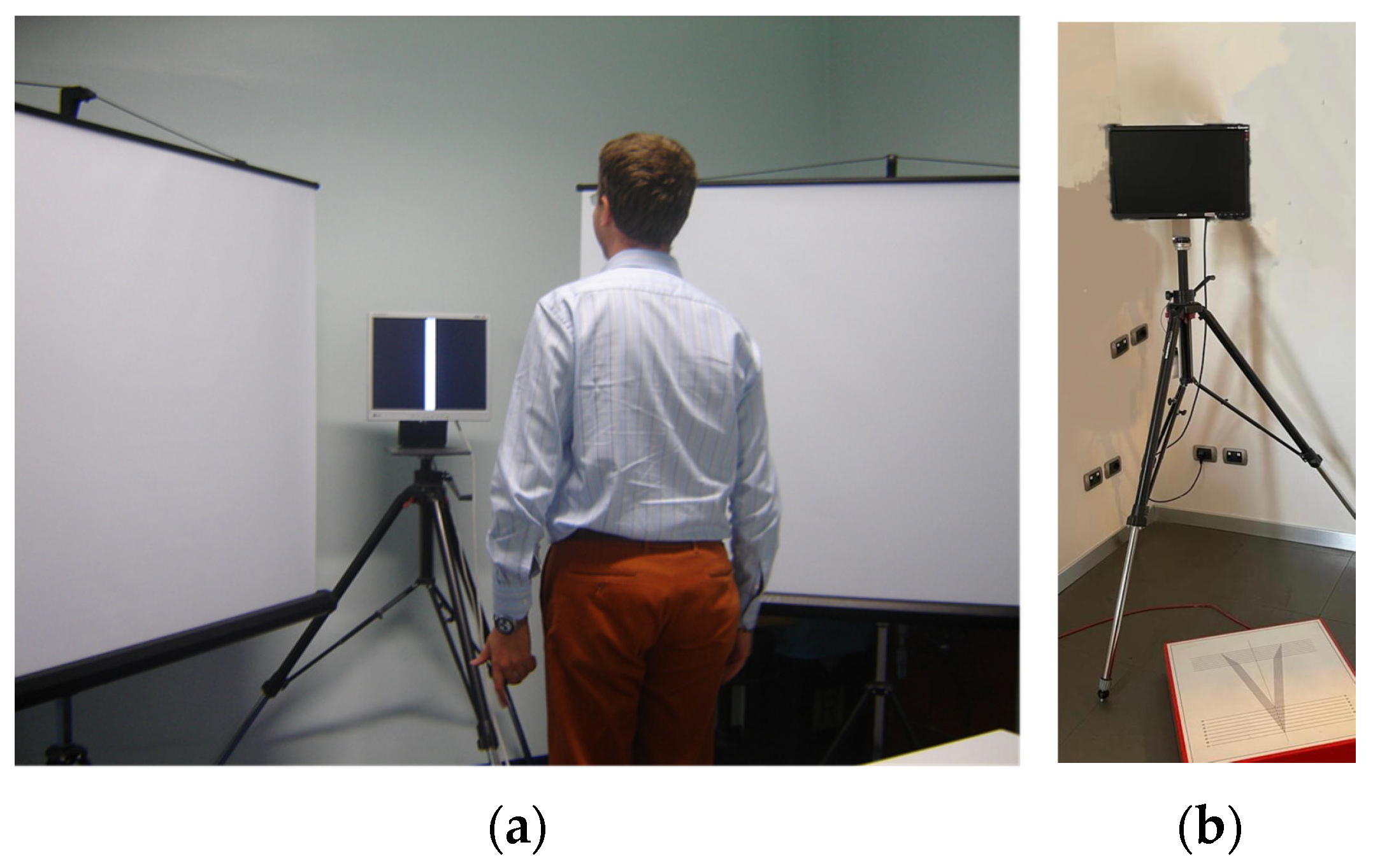
2.2.1. Balance System Function Evaluation
2.2.2. Panic-Agoraphobic Symptom and Dizziness Evaluation
2.3. Balance Rehabilitation with Peripheral Visual Stimulation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Balance System Function Evaluation
3.2. Dizziness and Panic–Agoraphobic Symptom Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | anticipatory anxiety |
| AG | agoraphobia |
| BR-PVS | balance rehabilitation with peripheral visual stimulation |
| CBT | cognitive–behavioral therapy |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| LS-PAs | limited symptom panic attacks |
| MIA | mobility inventory for agoraphobia |
| MIA-D | mobility inventory for agoraphobia, modified for dizziness |
| PA(s) | panic attacks |
| PASS | panic-associated symptom scale |
| PD-AG | panic disorder with agoraphobia |
| PVS | peripheral visual stimulation |
| RQ | Romberg Quotient |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SP | static posturography |
| SP-PVS | static posturography with peripheral visual stimulation |
| SSRI(s) | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor(s) |
| VAS-A | visual analog scale for anxiety |
| VAS-D | visual analog scale for dizziness |
References
- Furman, J.M.; Jacob, R.G. A Clinical Taxonomy of Dizziness and Anxiety in the Otoneurological Setting. J. Anxiety Disord. 2001, 15, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibold, N.K.; Schruers, K.R. Assessing Panic: Bridging the Gap Between Fundamental Mechanisms and Daily Life Experience. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, G.; Dario, A.; Caldirola, D.; Stefania, B.; Cesarani, A.; Bellodi, L. Panic Disorder: The Role of the Balance System. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2001, 35, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, L.; Britton, J.; Lear, S.; Bird, J.; Luxon, L.M. Relationship between Balance System Function and Agoraphobic Avoidance. Behav. Res. Ther. 1995, 33, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.G.; Furman, J.M.; Durrant, J.D.; Turner, S.M. Panic, Agoraphobia, and Vestibular Dysfunction. Am. J. Psychiatry 1996, 153, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teggi, R.; Caldirola, D.; Bondi, S.; Perna, G.; Bellodi, L.; Bussi, M. Vestibular Testing in Patients with Panic Disorder and Chronic Dizziness. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2007, 27, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Teggi, R.; Caldirola, D.; Colombo, B.; Perna, G.; Comi, G.; Bellodi, L.; Bussi, M. Dizziness, Migrainous Vertigo and Psychiatric Disorders. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2010, 124, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecer, A.; Tükel, R.; Erdamar, B.; Sunay, T. Audiovestibular Functioning in Patients with Panic Disorder. J. Psychosom. Res. 2004, 57, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.G.; Furman, J.M.; Durrant, J.D.; Turner, S.M. Surface Dependence: A Balance Control Strategy in Panic Disorder with Agoraphobia. Psychosom. Med. 1997, 59, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfern, M.S.; Furman, J.M.; Jacob, R.G. Visually Induced Postural Sway in Anxiety Disorders. J. Anxiety Disord. 2007, 21, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.L.; Azevedo, T.M.; Imbiriba, L.A.; Freire, R.C.; Valença, A.M.; Caldirola, D.; Perna, G.; Volchan, E.; Nardi, A.E. Freezing Reaction in Panic Disorder Patients Associated with Anticipatory Anxiety. Depress. Anxiety 2009, 26, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angov, G.; Mihaylova-Angelova, E.; Petrova, D.; Stambolieva, K. Vestibular Function in Panic Disorder Patients: A Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potentials and Video Head Impulse Test Study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stambolieva, K.; Angov, G. Balance Control in Quiet Upright Standing in Patients with Panic Disorder. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 267, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiaz, R.; Kimel Naor, S.; Caspi, A.; Czerniak, E.; Noy, S.; Pelc, T.; Mintz, M.; Plotnik, M. Responses to Balance Challenges in Persons with Panic Disorder: A Pilot Study of Computerized Static and Dynamic Balance Measurements. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldirola, D.; Teggi, R.; Bondi, S.; Lopes, F.L.; Grassi, M.; Bussi, M.; Perna, G. Is There a Hypersensitive Visual Alarm System in Panic Disorder? Psychiatry Res. 2011, 187, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkirov, S.; Staab, J.P.; Stone, J. Persistent Postural-Perceptual Dizziness (PPPD): A Common, Characteristic and Treatable Cause of Chronic Dizziness. Pract. Neurol. 2018, 18, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterston, J.; Chen, L.; Mahony, K.; Gencarelli, J.; Stuart, G. Persistent Postural-Perceptual Dizziness: Precipitating Conditions, Co-Morbidities and Treatment With Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 795516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.M.; Balaban, C.D. Visuo-Vestibular Contributions to Anxiety and Fear. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 48, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, G.; Caldirola, D. Is Panic Disorder a Disorder of Physical Fitness? A Heuristic Proposal. F1000Research 2018, 7, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldirola, D.; Alciati, A.; Cuniberti, F.; Perna, G. Experimental Drugs for Panic Disorder: An Updated Systematic Review. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 13, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.G.; Whitney, S.L.; Detweiler-Shostak, G.; Furman, J.M. Vestibular Rehabilitation for Patients with Agoraphobia and Vestibular Dysfunction: A Pilot Study. J. Anxiety Disord. 2001, 15, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, G.A.; Thabane, L. Guidelines for Reporting Non-Randomised Pilot and Feasibility Studies. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2019, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, T.C.; Glasziou, P.P.; Boutron, I.; Milne, R.; Perera, R.; Moher, D.; Altman, D.G.; Barbour, V.; Macdonald, H.; Johnston, M.; et al. Better Reporting of Interventions: Template for Intervention Description and Replication (TIDieR) Checklist and Guide. BMJ 2014, 348, g1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.L. A Website for Pilot and Feasibility Studies: Giving Your Research the Best Chance of Success. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2019, 5, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; ISBN 0890423342. [Google Scholar]
- Bandelow, B.; Michaelis, S.; Wedekind, D. Treatment of Anxiety Disorders. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 19, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagey, P.M.; Weber, B.G. Posturologie. Regulation et Dereglements de La Station Debout; Masson: Paris, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gagey, P.M. Non-Vestibular Dizziness and Static Posturography. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Belg. 1991, 45, 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Bizzo, G.; Guillet, N.; Patat, A.; Gagey, P.M. Specifications for Building a Vertical Force Platform Designed for Clinical Stabilometry. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1985, 23, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wewers, M.E.; Lowe, N.K. A Critical Review of Visual Analogue Scales in the Measurement of Clinical Phenomena. Res. Nurs. Health 1990, 13, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyle, N.; Deltito, J.; Allerup, P.; Maier, W.; Albus, M.; Nutzinger, D.; Ayuso, J.L.; Bech, P.; Rasmussen, S. The Panic-Associated Symptom Scale: Measuring the Severity of Panic Disorder. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1991, 83, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambless, D.L.; Caputo, G.C.; Jasin, S.E.; Gracely, E.J.; Williams, C. The Mobility Inventory for Agoraphobia. Behav. Res. Ther. 1985, 23, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambless, D.L.; Sharpless, B.A.; Rodriguez, D.; McCarthy, K.S.; Milrod, B.L.; Khalsa, S.R.; Barber, J.P. Psychometric Properties of the Mobility Inventory for Agoraphobia: Convergent, Discriminant, and Criterion-Related Validity. Behav. Ther. 2011, 42, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, G.P.; Newman, C.W. The Development of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1990, 116, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppelaar-van Eijsden, H.M.; Schermer, T.R.; Bruintjes, T.D. Measurement Properties of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory: A Systematic Review. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, e282–e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, E.B.; Freeman, M.; Penner-Goeke, L.; Reynolds, K.; Lebel, C.; Giesbrecht, G.F.; Rioux, C.; MacKinnon, A.; Sauer-Zavala, S.; Roos, L.E.; et al. Building Emotional Awareness and Mental Health (BEAM): An Open-Pilot and Feasibility Study of a Digital Mental Health and Parenting Intervention for Mothers of Infants. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2023, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempert, T.; Olesen, J.; Furman, J.; Waterston, J.; Seemungal, B.; Carey, J.; Bisdorff, A.; Versino, M.; Evers, S.; Newman-Toker, D. Vestibular Migraine: Diagnostic Criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2012, 22, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cort, K.; Schroijen, M.; Hurlemann, R.; Claassen, S.; Hoogenhout, J.; Van den Bergh, O.; Goossens, L.; Van Diest, I.; Schruers, K. Modeling the Development of Panic Disorder with Interoceptive Conditioning. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 27, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domschke, K.; Stevens, S.; Pfleiderer, B.; Gerlach, A.L. Interoceptive Sensitivity in Anxiety and Anxiety Disorders: An Overview and Integration of Neurobiological Findings. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viziano, A.; Micarelli, A.; Augimeri, I.; Micarelli, D.; Alessandrini, M. Long-Term Effects of Vestibular Rehabilitation and Head-Mounted Gaming Task Procedure in Unilateral Vestibular Hypofunction: A 12-Month Follow-up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2019, 33, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micarelli, A.; Viziano, A.; Micarelli, B.; Augimeri, I.; Alessandrini, M. Vestibular Rehabilitation in Older Adults with and without Mild Cognitive Impairment: Effects of Virtual Reality Using a Head-Mounted Display. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 83, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiak, O.; Krajewski, K.; Woszczak, M.; Jozefowicz-Korczynska, M. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Virtual Reality-Based Exercise Program for Unilateral Peripheral Vestibular Deficit. J. Vestib. Res. 2018, 28, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, G.; Grassi, M.; Caldirola, D.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Revolution of Personalized Psychiatry: Will Technology Make It Happen Sooner? Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| T0 (Completer, n = 5; Partial Completer (PC), n = 1) | T1 (Completer, n = 5; Partial Completer (PC), n = 1) | 100 × (T1 − T0)/T0 (Completer, n = 5; Partial Completer (PC), n = 1) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristics | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Min Value | Max Value | Value of the PC | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Min Value | Max Value | Value of the PC | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Min Change | Max Change | Value of the PC |
| Visual-RQ | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.71 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.96 | 0.18 | 1.00 | 0.21 | 0.76 | 1.21 | 0.59 | 37.9 | 21.4 | 39.7 | 14.1 | 7.0 | 65.8 | −22.4 |
| VAS-A before SP-PVS | 37.4 | 20.5 | 46.0 | 26.0 | 7 | 56 | 45 | 16.8 | 15.6 | 24.0 | 28.2 | 0 | 32 | 33 | −67.2 | 30.5 | −53.8 | 56.7 | −39 | −100 | −27 |
| VAS-A during SP-PVS | 46.4 | 31.0 | 51.0 | 45.0 | 12 | 86 | 75 | 17.6 | 20.3 | 12.0 | 29.0 | 0 | 47 | 54 | −75.3 | 25.2 | −76.5 | 45.3 | −45 | −100 | −28 |
| VAS-A after SP-PVS | 44.2 | 31.3 | 50.0 | 38.0 | 6 | 85 | 55 | 18.4 | 20.2 | 17.0 | 27.0 | 0 | 48 | 21 | −72.8 | 26.1 | −66.0 | 45.8 | −44 | −100 | −62 |
| VAS-D before SP-PVS | 40.8 | 26.0 | 45 | 40.0 | 12 | 73 | 47 | 22.0 | 23.2 | 23.0 | 32.0 | 0 | 55 | 24 | −63.5 | 34.5 | −48.9 | 56.1 | −25 | −100 | −49 |
| VAS-D during SP-PVS | 48.0 | 22.9 | 56 | 36.0 | 22 | 74 | 73 | 14.6 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 28.0 | 0 | 30 | 68 | −77.5 | 21.6 | −73.2 | 40.5 | −55 | −100 | −7 |
| VAS-D after SP-PVS | 46.8 | 25.7 | 57 | 36.0 | 15 | 76 | 71 | 13.8 | 13.5 | 19.0 | 19.0 | 0 | 31 | 63 | −78.9 | 19.5 | −68.9 | 33.3 | −59 | −100 | −11 |
| PASS, total score | 9.0 | 2.8 | 8 | 5.0 | 6 | 12 | 8 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 7 | −75.5 | 13.6 | −75.0 | 19.0 | −58.3 | −91.7 | −13 |
| PASS, unexpected PAs | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PASS, expected PAs | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | −83.3 | 28.9 | −100.0 | 25.0 | −50.0 | −100.0 | 0 |
| PASS, AA | 2.4 | 0.5 | 2 | 1.0 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −76.7 | 22.4 | −66.7 | 33.3 | −50 | −100 | −50 |
| PASS, LS-PAs | 1.8 | 0.4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | −70.0 | 27.4 | −50.0 | 50.0 | −50 | −100 | 0 |
| PASS, AG | 2.8 | 0.8 | 3 | 1.0 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | −78.3 | 21.7 | −75.0 | 23.3 | −50 | −100 | 0 |
| MIA-AAC | 2.1 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 2.9 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 2.3 | 1.5 | −21.4 | 23.4 | −16.5 | 28.9 | 7.3 | −51.6 | −3.3 |
| MIA-AAL | 3.3 | 1.1 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 1.77 | 1.61 | 1.1 | 3.4 | 2.2 | −37.2 | 19.0 | −34.0 | 32.6 | −17.1 | −59.5 | −7.6 |
| MIA-D | 56.8 | 30.5 | 72 | 50 | 20 | 86 | 42 | 28.8 | 22.8 | 32.0 | 36.0 | 6 | 58 | 39 | −55.7 | 21.7 | −62.8 | 28.3 | −25.6 | −78.6 | −7 |
| DHI | 64.8 | 24.9 | 74 | 18.0 | 24 | 88 | 48 | 49.6 | 25.5 | 58 | 22 | 8 | 72 | 44 | −29.7 | 21.1 | −21.6 | 8.5 | −15.4 | −66.7 | −8.3 |
| First Session of the BR-PVS (Completer, n = 5; Partial Completer (PC), n = 1) | Last Session of the BR-PVS (completer, n = 5; Partial Completer (PC), n = 1) | 100 × (T1 − T0)/T0 (Completer, n = 5; Partial Completer (PC), n = 1) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Characteristics | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Min Value | Max Value | Value of the PC | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Min Value | Max Value | Value of the PC | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Min Change | Max Change | Value of the PC |
| VAS-A before | 38.8 | 31.0 | 28.0 | 30.0 | 5 | 85 | 47 | 30.0 | 31.2 | 20 | 11.0 | 5 | 84 | 38 | −22.3 | 24.7 | −13.0 | 45.3 | 0 | −51 | −19 |
| VAS-A during | 52.0 | 24.4 | 60 | 39 | 20 | 75 | 56 | 29.2 | 27.1 | 26 | 43.0 | 0 | 63 | 45 | −43.8 | 37.5 | −21.2 | 48.3 | −16 | −100 | −20 |
| VAS-A after | 40.0 | 20.1 | 42.0 | 8.0 | 10 | 66 | 30 | 22.0 | 30.9 | 0 | 45.0 | 0 | 65 | 27 | −60.3 | 54.4 | −100 | 98.5 | 0 | −100 | −10 |
| VAS-D before | 37.6 | 24.1 | 40 | 28.0 | 5 | 67 | 69 | 29.4 | 23.0 | 23 | 20.0 | 5 | 65 | 57 | −16.4 | 28.6 | −4.2 | 4.5 | 0 | −67 | −17 |
| VAS-D during | 60.0 | 26.3 | 59 | 32.0 | 25 | 92 | 77 | 19.2 | 11.7 | 26 | 10.0 | 0 | 28 | 60 | −71.5 | 16.7 | −66.7 | 4.3 | −56 | −100 | −22 |
| VAS-D after | 44.0 | 21.4 | 50 | 20 | 10 | 64 | 50 | 30.0 | 21.5 | 29 | 27.0 | 10 | 62 | 54 | −25.2 | 35.9 | −3.1 | 42.0 | 0 | −81 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caldirola, D.; Carminati, C.; Daccò, S.; Grassi, M.; Perna, G.; Teggi, R. Balance Rehabilitation with Peripheral Visual Stimulation in Patients with Panic Disorder and Agoraphobia: An Open-Pilot Intervention Study. Audiol. Res. 2023, 13, 314-325. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres13030027
Caldirola D, Carminati C, Daccò S, Grassi M, Perna G, Teggi R. Balance Rehabilitation with Peripheral Visual Stimulation in Patients with Panic Disorder and Agoraphobia: An Open-Pilot Intervention Study. Audiology Research. 2023; 13(3):314-325. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres13030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaldirola, Daniela, Claudia Carminati, Silvia Daccò, Massimiliano Grassi, Giampaolo Perna, and Roberto Teggi. 2023. "Balance Rehabilitation with Peripheral Visual Stimulation in Patients with Panic Disorder and Agoraphobia: An Open-Pilot Intervention Study" Audiology Research 13, no. 3: 314-325. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres13030027
APA StyleCaldirola, D., Carminati, C., Daccò, S., Grassi, M., Perna, G., & Teggi, R. (2023). Balance Rehabilitation with Peripheral Visual Stimulation in Patients with Panic Disorder and Agoraphobia: An Open-Pilot Intervention Study. Audiology Research, 13(3), 314-325. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres13030027








