Percentile Distribution of Habitual-Correction Visual Acuity in a Sample of 1500 Children Aged 5 to 15 Years in Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Visual Acuity Measurements
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCVA | Best-Corrected Visual Acuity |
| HCVA | Habitual-Correction Visual Acuity |
| OD | Right Eye |
| OS | Left Eye |
| OU | Oculus Uterque |
| VA | Visual Acuity |
References
- Cotter, S.A.; Cyert, L.A.; Miller, J.M.; Quinn, G.E.; National Expert Panel to the National Center for Children’s Vision and Eye Health. Vision Screening for Children 36 to <72 Months: Recommended Practices. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2015, 92, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmucker, C.; Grosselfinger, R.; Riemsma, R.; Antes, G.; Lange, S.; Lagrèze, W.; Kleijnen, J. Diagnostic Accuracy of Vision Screening Tests for the Detection of Amblyopia and Its Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 247, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsahn, M. International Vision Screening: Results from Alexandria, Egypt. Curr. Ophthalmol. Rep. 2014, 2, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Donahue, S.P.; Arnold, R.W.; Ruben, J.B. Preschool Vision Screening: What Should We Be Detecting and How Should We Report It? Uniform Guidelines for Reporting Results of Preschool Vision Screening Studies. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus (JAAPOS) 2003, 7, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsing, I.T.; Hansraj, R.; Jacobs, W.; Nel, E.W. Review of School Vision Screening Guidelines. Afr. Vis. Eye Health 2018, 77, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, M.; Keyes, M.; Wright, M. A Review of the Evidence on the Effectiveness of Children’s Vision Screening. Child 2010, 36, 756–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstice, N.S.; Thompson, B. The Measurement of Visual Acuity in Children: An Evidence-based Update. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2014, 97, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Navia, B.; Garcia-Montero, L.; Pérez-Sanchez, B.; Villa-Collar, C. Visual Acuity Percentile Curves in a Spanish Paediatric Population. J. Optom. 2022, 15, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, S.; Sampson, G.P.; Hendicott, P.; Wood, J.M. Review of Guidelines for Children’s Vision Screenings. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2013, 96, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leat, S.J.; Yadav, N.K.; Irving, E.L. Development of Visual Acuity and Contrast Sensitivity in Children. J. Optom. 2009, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8596:2017; Ophthalmic Optics—Visual Acuity Testing—Standard and Clinical Optotypes and Their Presentation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Ferris, F.L.; Kassoff, A.; Bresnick, G.H.; Bailey, I. New Visual Acuity Charts for Clinical Research. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1982, 94, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgett, Y.; Siderov, J. Crowding in Children’s Visual Acuity Tests—Effect of Test Design and Age. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarko, V.M.; Semenov, L.A. Visual Acuity and the Crowding Effect in 8- to 17-Year-Old Schoolchildren. Hum. Physiol. 2005, 31, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, L.; Näsänen, R.; Laurinen, P. New Visual Acuity Test for Pre-School Children. Acta Ophthalmol. 1980, 58, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo Dall’Orto, G.; Facchin, A.; Bellatorre, A.; Maffioletti, S.; Serio, M. Measurement of Visual Acuity with a Digital Eye Chart: Optotypes, Presentation Modalities and Repeatability. J. Optom. 2021, 14, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.; Hübsch, S.; Gräf, M.H.; Kaufmann, H. Examination of Young Children with Lea Symbols. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, V.; Clifford-Donaldson, C.E.; Green, T.K.; Miller, J.M.; Harvey, E.M. Normative Monocular Visual Acuity for Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Charts in Emmetropic Children 5 to 12 Years of Age. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.R.; Garthwaite, P.H. Percentiles Please: The Case for Expressing Neuropsychological Test Scores and Accompanying Confidence Limits as Percentile Ranks. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2009, 23, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, L.D.; Kraemer, H.C.; Wilson, D.M.; Ritter, P.L.; Dornbusch, S.M. Standardized Percentile Curves of Body-Mass Index for Children and Adolescents. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1991, 145, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L. The Precision of Percentiles in Establishing Normal Limits in Medicine. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1958, 52, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, I.L. Chapter 7—Visual Acuity. In Borish’s Clinical Refraction, 2nd ed.; Benjamin, W.J., Borish, I.M., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Saint Louis, MO, USA, 2006; pp. 217–246. ISBN 978-0-7506-7524-6. [Google Scholar]
- Facchin, A.; Maffioletti, S.; Martelli, M.; Daini, R. Different Trajectories in the Development of Visual Acuity with Different Levels of Crowding: The Milan Eye Chart (MEC). Vis. Res. 2019, 156, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y. Statistical Notes for Clinical Researchers: Assessing Normal Distribution (2) Using Skewness and Kurtosis. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2013, 38, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenmakers, E.-J.; Farrell, S. AIC Model Selection Using Akaike Weights. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2004, 11, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle. In Selected Papers of Hirotugu Akaike; Parzen, E., Tanabe, K., Kitagawa, G., Eds.; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 199–213. ISBN 978-1-4612-7248-9. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, Version: 4.4.4; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024.
- Wade, A.M.; Salt, A.T.; Proffitt, R.V.; Heavens, S.J.; Sonksen, P.M. Likelihood-Based Modelling of Age-Related Normal Ranges for Ordinal Measurements: Changes in Visual Acuity through Early Childhood. Stat. Med. 2004, 23, 3623–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, B.; West, S.K.; Rodriguez, J.; Sanchez, R.; Broman, A.T.; Snyder, R.; Klein, R. Blindness, Visual Impairment and the Problem of Uncorrected Refractive Error in a Mexican-American Population: Proyecto VER. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 608–614. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Sankaridurg, P.; Naduvilath, T.; Wang, J.; Xiong, S.; Weng, R.; Du, L.; Chen, J.; Zou, H.; Xu, X. Normative Data and Percentile Curves for Axial Length and Axial Length/Corneal Curvature in Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 4–18 Years. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, Ö.; Despriet, D.D.G.; van der Meulen-Schot, H.M.; Romers, A.; Slot, X.; Sang, M.T.F.; Fronius, M.; Kelderman, H.; Simonsz, H.J. Comparison of Optotypes of Amsterdam Picture Chart with Those of Tumbling-E, LEA Symbols, ETDRS, and Landolt-C in Non-Amblyopic and Amblyopic Patients. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 252, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonksen, P.M.; Wade, A.M.; Proffitt, R.; Heavens, S.; Salt, A.T. The Sonksen logMAR Test of Visual Acuity: II. Age Norms from 2 Years 9 Months to 8 Years. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2008, 12, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health: Children & Youth Version: ICF-CY; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
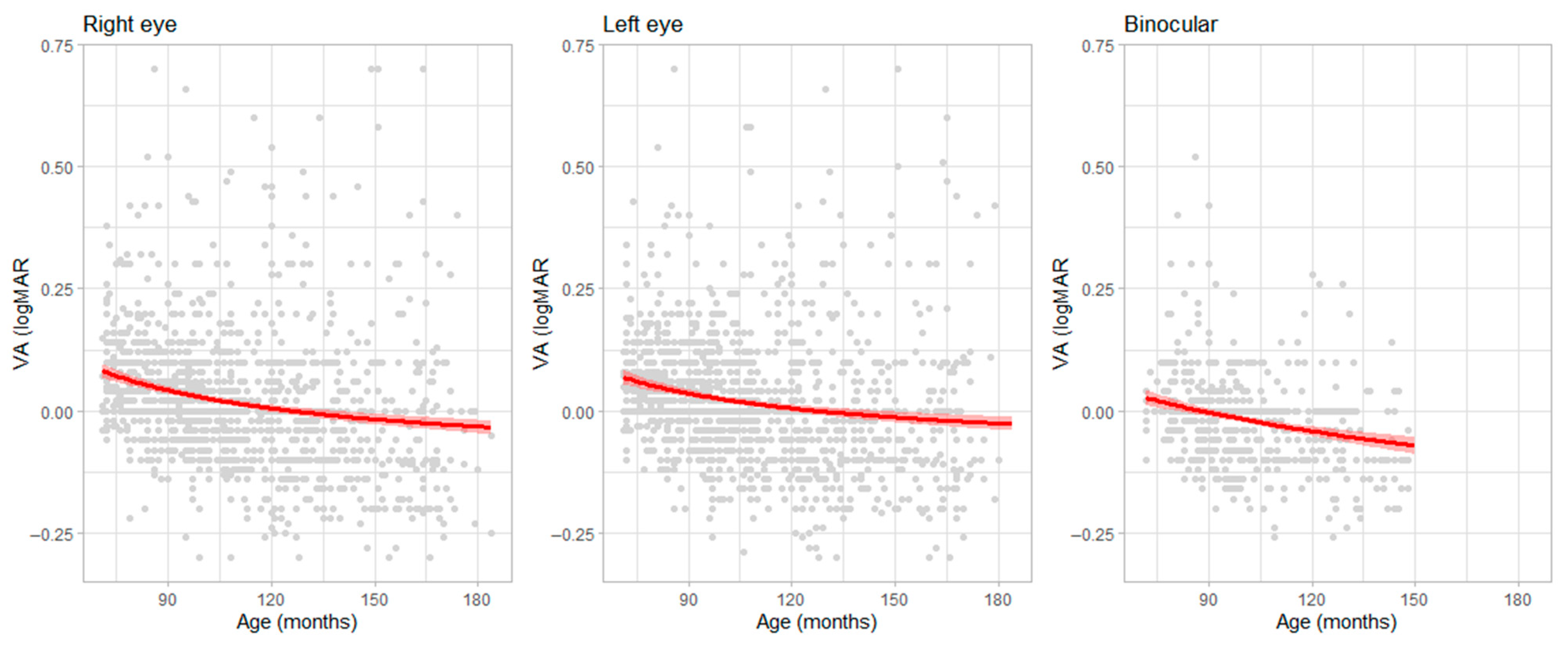
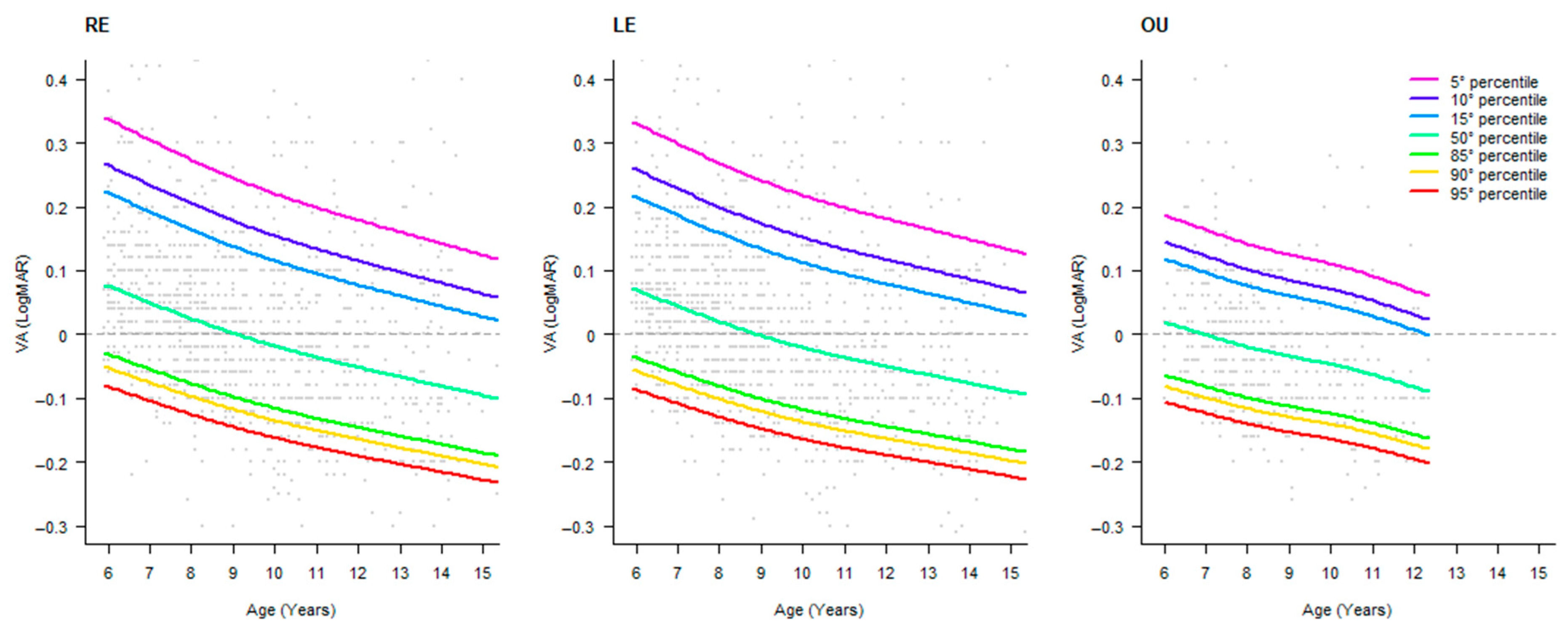
| Age (Years) | Frequency | Percent | Cumulative Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 7 | 0.46 | 0.46 |
| 6 | 235 | 15.56 | 16.03 |
| 7 | 275 | 18.21 | 34.24 |
| 8 | 287 | 19.01 | 53.25 |
| 9 | 175 | 11.59 | 64.83 |
| 10 | 233 | 15.43 | 80.26 |
| 11 | 108 | 7.15 | 87.42 |
| 12 | 72 | 4.77 | 92.19 |
| 13 | 80 | 5.30 | 97.48 |
| 14 | 35 | 2.32 | 99.80 |
| 15 | 3 | 0.20 | 100.00 |
| Missing | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Total | 1510 | 100.0 |
| OD | OS | OU | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valid | 1510 | 1510 | 631 |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 879 |
| Mean | 0.02 | 0.02 | −0.02 |
| SD | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.09 |
| Minimum | −0.30 | −0.30 | −0.26 |
| Maximum | 0.74 | 0.92 | 0.52 |
| Age (Years) | Percentile Rank | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 50 | 85 | 90 | 95 | |
| 6 | 0.337 | 0.265 | 0.222 | 0.076 | −0.031 | −0.052 | −0.082 |
| 7 | 0.305 | 0.234 | 0.192 | 0.050 | −0.055 | −0.075 | −0.104 |
| 8 | 0.274 | 0.205 | 0.164 | 0.025 | −0.077 | −0.097 | −0.125 |
| 9 | 0.245 | 0.178 | 0.138 | 0.002 | −0.098 | −0.118 | −0.145 |
| 10 | 0.220 | 0.154 | 0.115 | −0.018 | −0.116 | −0.135 | −0.162 |
| 11 | 0.198 | 0.134 | 0.095 | −0.036 | −0.132 | −0.151 | −0.177 |
| 12 | 0.179 | 0.115 | 0.077 | −0.052 | −0.146 | −0.165 | −0.191 |
| 13 | 0.160 | 0.097 | 0.060 | −0.067 | −0.159 | −0.178 | −0.203 |
| 14 | 0.142 | 0.080 | 0.044 | −0.081 | −0.173 | −0.191 | −0.216 |
| 15 | 0.124 | 0.063 | 0.027 | −0.096 | −0.186 | −0.204 | −0.228 |
| Age (Years) | Percentile Rank | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 50 | 85 | 90 | 95 | |
| 6 | 0.330 | 0.258 | 0.215 | 0.070 | −0.036 | −0.058 | −0.087 |
| 7 | 0.299 | 0.228 | 0.186 | 0.044 | −0.059 | −0.080 | −0.108 |
| 8 | 0.268 | 0.200 | 0.159 | 0.020 | −0.081 | −0.101 | −0.129 |
| 9 | 0.241 | 0.174 | 0.134 | −0.002 | −0.101 | −0.121 | −0.148 |
| 10 | 0.218 | 0.152 | 0.112 | −0.021 | −0.118 | −0.137 | −0.164 |
| 11 | 0.198 | 0.133 | 0.094 | −0.037 | −0.132 | −0.151 | −0.178 |
| 12 | 0.181 | 0.117 | 0.079 | −0.050 | −0.145 | −0.163 | −0.189 |
| 13 | 0.165 | 0.102 | 0.064 | −0.063 | −0.156 | −0.175 | −0.200 |
| 14 | 0.148 | 0.086 | 0.049 | −0.077 | −0.168 | −0.186 | −0.212 |
| 15 | 0.132 | 0.070 | 0.034 | −0.090 | −0.180 | −0.198 | −0.223 |
| Age (Years) | Percentile Rank | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | 50 | 85 | 90 | 95 | |
| 6 | 0.185 | 0.143 | 0.116 | 0.017 | −0.066 | −0.083 | −0.108 |
| 7 | 0.162 | 0.121 | 0.095 | −0.003 | −0.084 | −0.101 | −0.125 |
| 8 | 0.140 | 0.100 | 0.074 | −0.021 | −0.101 | −0.118 | −0.141 |
| 9 | 0.123 | 0.084 | 0.059 | −0.036 | −0.114 | −0.131 | −0.154 |
| 10 | 0.109 | 0.070 | 0.045 | −0.048 | −0.126 | −0.142 | −0.165 |
| 11 | 0.089 | 0.051 | 0.027 | −0.065 | −0.141 | −0.157 | −0.180 |
| 12 | 0.066 | 0.029 | 0.005 | −0.085 | −0.159 | −0.175 | −0.197 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Facchin, A.; Mazzilli, M.; Maffioletti, S. Percentile Distribution of Habitual-Correction Visual Acuity in a Sample of 1500 Children Aged 5 to 15 Years in Italy. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17040085
Facchin A, Mazzilli M, Maffioletti S. Percentile Distribution of Habitual-Correction Visual Acuity in a Sample of 1500 Children Aged 5 to 15 Years in Italy. Pediatric Reports. 2025; 17(4):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17040085
Chicago/Turabian StyleFacchin, Alessio, Marilena Mazzilli, and Silvio Maffioletti. 2025. "Percentile Distribution of Habitual-Correction Visual Acuity in a Sample of 1500 Children Aged 5 to 15 Years in Italy" Pediatric Reports 17, no. 4: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17040085
APA StyleFacchin, A., Mazzilli, M., & Maffioletti, S. (2025). Percentile Distribution of Habitual-Correction Visual Acuity in a Sample of 1500 Children Aged 5 to 15 Years in Italy. Pediatric Reports, 17(4), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17040085







