Postoperative Respiratory Failure in US Pediatric Care: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Are specific hospital characteristics (region, teaching status, rurality, ownership, size) associated with the likelihood of pediatric PORF?
- Are specific patient characteristics (age, gender, payer, race/ethnicity, service line of care, or major surgical procedure) associated with PORF?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PICO Framework
- Population: Pediatric inpatients aged 0–20 years included in the 2019 HCUP KID database.
- Intervention/Exposure: Patient and hospital characteristics (e.g., region, teaching status, payer, service line, prior major surgery).
- Comparison: Groups stratified by hospital features (e.g., public vs. private, rural vs. urban) and patient factors (e.g., male vs. female, different service lines).
- Outcome: Occurrence of postoperative respiratory failure, defined by AHRQ’s PDI 09 measure.
2.2. Variables
- Hospital characteristics: region (Northeast, Midwest, South, West), location and teaching status (rural, urban non-teaching, urban teaching), bed size (small, medium, large), and ownership (public, private non-profit, private for-profit).
- Patient demographics: age, sex (male = 0, female = 1), race/ethnicity (White, Black, Hispanic, Asian/Pacific Islander, Native American, Other), payer type (government, private, self-pay), and surgical procedure (Yes/No).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Review
3. Results
Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Public Health Implications and Recommendations
6. Strengths and Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHRQ | Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality |
| HCUP | Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project |
| UPI | unplanned endotracheal tube intubation |
| KID | Kids’ Inpatient Databases |
| PDI09 | Postoperative Respiratory Failure indicator |
| PDI | Pediatric Quality Indicator |
| PCLASS_ORPROC | Procedure Classes Refined for ICD-10-PCS |
| PORF | Post Operative Respiratory Failure |
| MDCs | Major Diagnostic Categories |
| DRG | Diagnosis-Related Group |
| QI | Quality Improvement |
| ICD | International Classification of Diseases |
Appendix A. Classification of Major Operating Room Procedures (PCLASS_ORPROC)
Appendix A.1. The Data Element PCLASS_ORPROC Indicates Whether a Major Operating Room Procedure Was Reported on the Discharge Record [10]
- Minor Diagnostic: Non-operating-room procedures that are diagnostic (e.g., BW2800Z CT scan of head using high osmolar contrast);
- Minor Therapeutic—Non-operating-room procedures that are therapeutic (e.g., 079030Z drainage of head lymph, percutaneous approach);
- Major Diagnostic—All procedures considered valid operating room procedures by the Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) grouper and that are performed for diagnostic reasons (e.g., 00B00ZX excision of brain, open approach, diagnostic);
- Major Therapeutic—All procedures considered valid operating room procedures by the Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) grouper and that are performed for therapeutic reasons (e.g., 021008W bypass coronary artery, one artery from aorta with zooplastic tissue, open approach).
| Variable | Description | Value | Value Description |
| PCLASS_ORPROC | Major operating room ICD-10-PCS procedure indicator | 0 | No major operating room procedure reported on discharge record |
| 1 | Major operating room procedure reported on discharge record |
- A.
- All discharges were categorized into five hospitalization types (i.e., service lines) in the following hierarchical order: Maternal/Neonatal, Mental health/Substance abuse, Injury, Surgical, and Medical. The criteria for identifying the hospitalization types varies across data years.
Appendix A.2. Beginning in Data Year 2019
- MDC 14 Pregnancy, Childbirth, and Puerperium;
- MDC 15 Newborn and Other Neonates (Perinatal Period).
- MDC 19 Mental Diseases and Disorders;
- MDC 20 Alcohol/Drug Use or Induced Mental Disorders.
- Clinical Classification Software-Refined categories for the principal ICD-10-CM diagnosis:
- ○
- INJ001–INJ027;
- ○
- INJ032.
References
- Canet, J.; Gallart, L. Postoperative respiratory failure: Pathogenesis, prediction, and prevention. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Pediatric Quality Indicator 09 (Postoperative Respiratory Failure)—Technical Specifications. AHRQ Quality Indicators, v2020. 2020. Available online: https://qualityindicators.ahrq.gov/measures/pdi_resources.aspx (accessed on 29 October 2022).
- Parikh, K.; Hall, M.; Tieder, J.S.; Dixon, G.; Ward, M.C.; Hinds, P.S.; Goyal, M.K.; Rangel, S.J.; Flores, G.; Kaiser, S.V. Disparities in racial, ethnic, and payer groups for pediatric safety events in US hospitals. Pediatrics 2024, 153, e2023063714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizamuddin, S.L.; Gupta, A.; Latif, U.; Nizamuddin, J.; Tung, A.; Minhaj, M.M.; Apfelbaum, J.; Shahul, S.S. A predictive model for pediatric postoperative respiratory failure: A National Inpatient Sample study. J. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 36, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odetola, F.O.; Gebremariam, A. Epidemiology of acute respiratory failure in US children: Outcomes and resource use. Hosp. Pediatr. 2024, 14, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, E.C.; Palac, H.L.; Paik, K.H.; Hajduk, J.; De Oliveira, G.S.; Jagannathan, N.; Suresh, S. Unplanned postoperative intubation in pediatric surgical patients: Development and validation of a multivariable prediction model. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisler, L.D.; Hua, M.; Li, G.; Sun, L.S.; Kim, M. A multivariable model predictive of unplanned postoperative intubation in infant surgical patients. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbuta, C.; Mason, K.P. Recognizing risks and optimizing perioperative care to reduce respiratory complications in the pediatric patient. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samawi, M.; Shah, G.H.; Kimsey, L.; Waterfield, K.C.; Hendrix, S. Hospital and patient characteristics associated with neonatal bloodstream infection in inpatient care: Insights from the 2019 HCUP KID database. Children 2024, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). Kids’ Inpatient Database (KID)—Overview of the KID Database. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. 2022. Available online: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/kidoverview.jsp (accessed on 29 October 2022).
- Guth, M.; Garfield, R.; Rudowitz, R. The effects of Medicaid expansion under the ACA: Updated findings from a literature review (2014–2020). Kaiser Family Foundation Report. 2023 Feb 17. Available online: https://www.kff.org/report-section/the-effects-of-medicaid-expansion-under-the-aca-updated-findings-from-a-literature-review-report/ (accessed on 29 October 2022).
| Variable | Attributes | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| PORF (PDI 09) | Absent | 4,214,198 | 92.31% |
| Present | 351,201 | 7.69% | |
| Hospital bed size | Small | 470,770 | 15.20% |
| Medium | 742,057 | 24.00% | |
| Large | 1,876,456 | 60.70% | |
| Hospital location | Rural | 189,298 | 6.10% |
| Urban nonteaching | 356,963 | 11.60% | |
| Urban teaching | 2,543,022 | 82.30% | |
| Hospital region | Northeast | 529,073 | 17.10% |
| Midwest | 696,645 | 22.60% | |
| South | 1,183,705 | 38.30% | |
| West | 679,860 | 22.00% | |
| Hospital ownership | Public | 365,784 | 11.80% |
| Private, not for profit | 2,382,758 | 77.10% | |
| Private, investor owned | 340,741 | 11.00% | |
| Gender | Female | 1,587,394 | 51.40% |
| Male | 1,500,745 | 48.60% | |
| Race | White | 1,407,652 | 45.60% |
| Black | 513,619 | 16.60% | |
| Hispanic | 607,329 | 19.70% | |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 123,698 | 4.00% | |
| Native American | 26,306 | 0.90% | |
| Other | 188,042 | 6.10% | |
| Service line | Maternal and Neonatal | 1,716,825 | 55.60% |
| Mental health/substance use | 209,939 | 6.80% | |
| Injury | 97,434 | 3.20% | |
| Surgical | 219,576 | 7.10% | |
| Medical | 845,509 | 27.40% | |
| Payment source | Medicare | 10,554 | 0.30% |
| Medicaid | 1,567,452 | 50.70% | |
| Private insurance | 1,270,547 | 41.10% | |
| Self-pay | 131,918 | 4.30% | |
| No charge | 3,843 | 0.10% | |
| Other | 100,660 | 3.30% | |
| Operation on record | No operation in record | 2,718,390 | 88.00% |
| Major operating on record | 370,893 | 12.00% | |
| Variable | Attributes | Mean | Std Dev |
| Age | N = 4,571,036 | 5.76 | 7.82 |
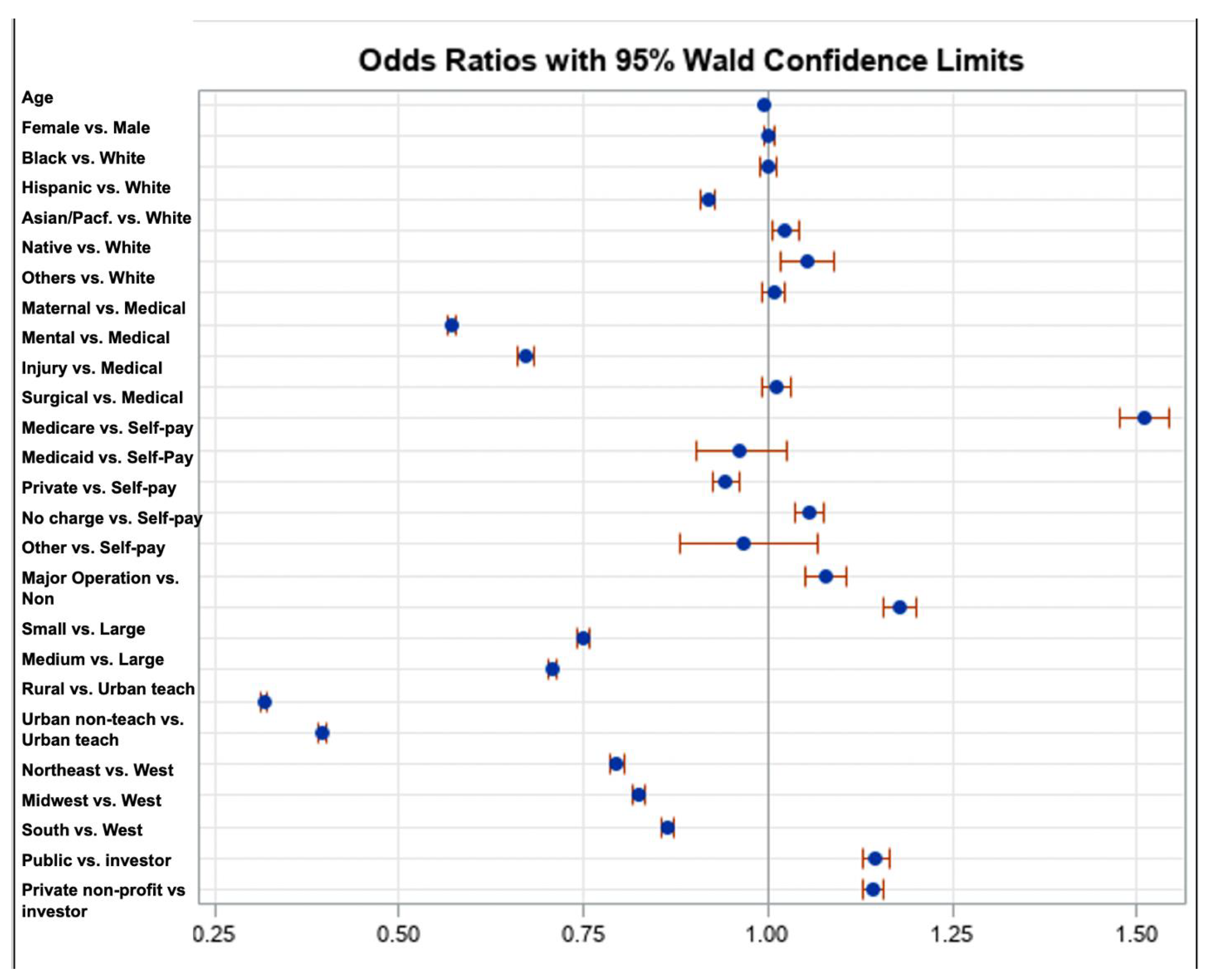
| Variable | Estimate | SE | Wald Test | p-Value | Adjusted OR | Wald 95% CI for AOR Lower Upper | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −1.7917 | 0.0124 | 20,964.6656 | <0.0001 | 0.167 | - | - | |
| AGE | −0.00418 | 0.000298 | 196.0796 | <0.0001 | 0.996 | 0.995 | 0.996 | |
| SEX | Female | 0.00150 | 0.00379 | 0.1571 | 0.6919 | 1.002 | 0.994 | 1.009 |
| Male * | ||||||||
| RACE | White | |||||||
| Black | 0.000486 | 0.00536 | 0.0082 | 0.9278 | 1.000 | 0.990 | 1.011 | |
| Hispanic | −0.0850 | 0.00521 | 266.0689 | <0.0001 | 0.918 | 0.909 | 0.928 | |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 0.0226 | 0.00914 | 6.1137 | 0.0134 | 1.023 | 1.005 | 1.041 | |
| Native American | 0.0508 | 0.0177 | 8.1824 | 0.0042 | 1.052 | 1.016 | 1.089 | |
| Others * | 0.00803 | 0.00789 | 1.0349 | 0.3090 | 1.008 | 0.993 | 1.024 | |
| Service line | Maternal and Neonatal | −0.5617 | 0.00471 | 14,217.7550 | <0.0001 | 0.570 | 0.565 | 0.576 |
| Mental health/substance use | −0.3991 | 0.00884 | 2040.6849 | <0.0001 | 0.671 | 0.659 | 0.683 | |
| Injury | 0.0112 | 0.0102 | 1.2020 | 0.2729 | 1.011 | 0.991 | 1.032 | |
| Surgical | 0.4124 | 0.0111 | 1385.5081 | <0.0001 | 1.510 | 1.478 | 1.544 | |
| Medical * | ||||||||
| Payment Source | Medicare | −0.0385 | 0.0329 | 1.3729 | 0.2413 | 0.962 | 0.902 | 1.026 |
| Medicaid | −0.0589 | 0.00927 | 40.3335 | <0.0001 | 0.943 | 0.926 | 0.960 | |
| Private insurance | 0.0533 | 0.00937 | 32.3885 | <0.0001 | 1.055 | 1.036 | 1.074 | |
| No charge | −0.0325 | 0.0492 | 0.4366 | 0.5088 | 0.968 | 0.879 | 1.066 | |
| Other | 0.0759 | 0.0130 | 33.9742 | <0.0001 | 1.079 | 1.052 | 1.107 | |
| Self-pay * | ||||||||
| Operation on record | Major operating room procedure on record | 0.1643 | 0.00953 | 297.2510 | <0.0001 | 1.179 | 1.157 | 1.201 |
| Hospital bed size | Small | −0.2887 | 0.00501 | 3321.6974 | <0.0001 | 0.749 | 0.742 | 0.757 |
| Medium | −0.3458 | 0.00470 | 5408.6080 | <0.0001 | 0.708 | 0.701 | 0.714 | |
| Large * | ||||||||
| Hospital location | Rural | −1.1499 | 0.00777 | 21,923.3961 | <0.0001 | 0.317 | 0.312 | 0.322 |
| Urban nonteaching | −0.9302 | 0.00692 | 18,057.0116 | <0.0001 | 0.394 | 0.389 | 0.400 | |
| Urban teaching * | ||||||||
| Hospital region | Northeast | −0.2290 | 0.00603 | 1443.3234 | <0.0001 | 0.795 | 0.786 | 0.805 |
| Midwest | −0.1925 | 0.00570 | 1138.1736 | <0.0001 | 0.825 | 0.816 | 0.834 | |
| South | −0.1477 | 0.00499 | 875.6528 | <0.0001 | 0.863 | 0.854 | 0.871 | |
| West * | ||||||||
| Hospital ownership | Public | 0.1361 | 0.00784 | 301.7575 | <0.0001 | 1.146 | 1.128 | 1.164 |
| Private, not-profit | 0.1328 | 0.00637 | 435.0090 | <0.0001 | 1.142 | 1.128 | 1.156 | |
| Private, investor-owned * | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samawi, M.; Shah, G.H.; Kimsey, L. Postoperative Respiratory Failure in US Pediatric Care: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Database. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17030058
Samawi M, Shah GH, Kimsey L. Postoperative Respiratory Failure in US Pediatric Care: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Database. Pediatric Reports. 2025; 17(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamawi, Michael, Gulzar H. Shah, and Linda Kimsey. 2025. "Postoperative Respiratory Failure in US Pediatric Care: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Database" Pediatric Reports 17, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17030058
APA StyleSamawi, M., Shah, G. H., & Kimsey, L. (2025). Postoperative Respiratory Failure in US Pediatric Care: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Database. Pediatric Reports, 17(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17030058








