Measuring Community and Home Participation and Environmental Factors in Children with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Outcome Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Community Participation Frequency, Involvement, and Desire to Change the Current Level of Participation
3.3. Home Participation Frequency, Involvement, and Desire to Change the Current Level of Participation
3.4. Home Environment Perceived Availability and Adequacy of Resources
3.5. Community Environment Perceived Availability and Adequacy of Resources
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, G.; Law, M.; King, S.; Rosenbaum, P.; Kertoy, M.K.; Young, N.L. A conceptual model of the factors affecting the recreation and leisure participation of children with disabilities. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2003, 23, 63–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health; Children and Youth Version: ICF-CY; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Coster, W.; Khetani, M.A. Measuring participation of children with disabilities: Issues and challenges. Disabil. Rehabil. 2008, 30, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjessing, B.; Jahnsen, R.B.; Strand, L.I.; Natvik, E. Adaptation for participation! Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2018, 13, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palisano, R.J.; Kang, L.J.; Chiarello, L.A.; Orlin, M.; Oeffinger, D.; Maggs, J. Social and community participation of children and youth with cerebral palsy is associated with age and gross motor function classification. Phys. Ther. 2009, 89, 1304–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milićević, M.; Nedović, G. Comparative study of home and community participation among children with and without cerebral palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 80, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imms, C.; Reilly, S.; Carlin, J.; Dodd, K.J. Characteristics influencing participation of Australian children with cerebral palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2009, 31, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodmansee, C.; Hahne, A.; Imms, C.; Shields, N. Comparing participation in physical recreation activities between children with disability and children with typical development: A secondary analysis of matched data. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 49–50, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Reilly, S.; Reddihough, D.; Mensah, F.; Green, J.; Pennington, L.; Morgan, A.T. Activities and participation of children with cerebral palsy: Parent perspectives. Disabil. Rehabil. 2015, 37, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, C.; Van Kruijsbergen, M.; Ketelaar, M.; Hurks, P.; Adair, B.; Imms, C.; De Kloet, A.; Piskur, B.; Van Heugten, C. Assessing participation of children with acquired brain injury and cerebral palsy: A systematic review of measurement properties. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, C.; McDowell, B.; McDonough, S. The relationship between gross motor function and participation restriction in children with cerebral palsy: An exploratory analysis. Child Care Health Dev. 2007, 33, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solish, A.; Perry, A.; Minnes, P. Participation of Children with and without Disabilities in Social, Recreational and Leisure Activities. J. Appl. Res. Intellect. Disabil. 2010, 23, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, A.; Ressler, K.J.; Bradley, R.G. The protective role of friendship on the effects of childhood abuse and depression. Depress. Anxiety 2009, 26, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bult, M.K.; Verschuren, O.; Jongmans, M.J.; Lindeman, E.; Ketelaar, M. What influences participation in leisure activities of children and youth with physical disabilities? A systematic review. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; O’Keefe, S.; Stagnitti, K. Activity preferences and participation of school-age children living in urban and rural environments. Occup. Ther. Health Care 2011, 25, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylov, S.I.; Jarvis, S.N.; Colver, A.F.; Beresford, B. Identification and description of environmental factors that influence participation of children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2004, 46, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, H. Built environment accessibility in the eastern province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia as seen by persons with disabilities. J. Access. Des. All 2021, 11, 115–147. [Google Scholar]
- Alsolami, A. The Educational Journey of Students with Disabilities in Saudi Arabia: From Isolation to Inclusive Education. Remedial Spec. Educ. 2024, 45, 07419325241240058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhoweris, H.; Efthymiou, E. Inclusive and Special Education in the Middle East; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, M.S.; Alharbi, E.; Alghamdi, R.; Alhowimel, A.S.; Alenazi, A.M.; Alshehri, M.M.; Alqahtani, B.A.; Awali, A. Arabic Patient-Reported Measures of Activity and Participation for Children: A Systematic Review of Psychometric Properties. Children 2023, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaad, E.; Alborno, N. Social inclusion for individuals with developmental disabilities in the Middle East. Int. J. Dev. Disabil. 2024, 70, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coster, W.; Bedell, G.; Law, M.; Khetani, M.A.; Teplicky, R.; Liljenquist, K.; Gleason, K.; Kao, Y.-C. Psychometric evaluation of the Participation and Environment Measure for Children and Youth. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.; Boyd, R.N.; Chatfield, M.D.; Ziviani, J.; Sakzewski, L. Self-care performance in children with cerebral palsy: A longitudinal study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.; Sakzewski, L.; Whittingham, K.; Wotherspoon, J.; Chatfield, M.D.; Ware, R.S.; Boyd, R.N. Development of social functioning in children with cerebral palsy: A longitudinal study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, M.; Anaby, D.; Teplicky, R.; Khetani, M.A.; Coster, W.; Bedell, G. Participation in the Home Environment among Children and Youth with and without Disabilities. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2013, 76, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.Y.; Law, M.; Khetani, M.; Pollock, N.; Rosenbaum, P. Participation in Out-of-Home Environments for Young Children with and Without Developmental Disabilities. OTJR Occup. Ther. J. Res. 2016, 36, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedell, G.; Coster, W.; Law, M.; Liljenquist, K.; Kao, Y.C.; Teplicky, R.; Anaby, D.; Khetani, M.A. Community participation, supports, and barriers of school-age children with and without disabilities. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsakos, E.M.; Patel, S.; Simpson, R.; Nelson, M.L.A.; Penner, M.; Perrier, L.; Bayley, M.T.; Munce, S.E.P. Conceptualization, use, and outcomes associated with compassion in the care of youth with childhood-onset disabilities: A scoping review. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1365205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, D.Z.; Houtrow, A.J.; Arango, P.; Kuhlthau, K.A.; Simmons, J.M.; Neff, J.M. Family-centered care: Current applications and future directions in pediatric health care. Matern. Child Health J. 2012, 16, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piškur, B.; Beurskens, A.J.H.M.; Jongmans, M.J.; Ketelaar, M.; Norton, M.; Frings, C.A.; Hemmingsson, H.; Smeets, R.J.E.M. Parents’ actions, challenges, and needs while enabling participation of children with a physical disability: A scoping review. BMC Pediatr. 2012, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaby, D.; Avery, L.; Gorter, J.W.; Levin, M.F.; Teplicky, R.; Turner, L.; Cormier, I.; Hanes, J. Improving body functions through participation in community activities among young people with physical disabilities. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.H.; Messiah, S.E.; Hansen, E.; D’Agostino, E.M. The relationship between transportation vulnerability, school attendance, and free transportation to an afterschool program for youth. Transportation 2021, 48, 2315–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, F.; Ullenhag, A.; Jahnsen, R.; Dolva, A.S. Perceived facilitators and barriers for participation in leisure activities in children with disabilities: Perspectives of children, parents and professionals. Scand. J. Occup. Ther. 2021, 28, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.M.; Bogart, K.R.; Logan, S.W.; Case, L.; Fine, J.; Thompson, H. Physical Activity Participation of Disabled Children: A Systematic Review of Conceptual and Methodological Approaches in Health Research. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollin, I.L.; Bonilla, B.; Bagley, A.; Tucker, C.A. Social and environmental determinants of health among children with long-term movement impairment. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2022, 3, 831070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, B.; Ederer, F.; Amann, R.; Morgenthaler, T.; Schulze, C.; Dawal, B. Translation and cross-cultural adaptation of the young children participation and environment measure for its use in Austria, Germany, and Switzerland. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1258377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, B.; Schulze, C.; Boyd, J.; Amann, R.; Piškur, B.; Beurskens, A.; Teplicky, R.; Moser, A. Cross-cultural adaptation of the Participation and Environment Measure for Children and Youth (PEM-CY) into German: A qualitative study in three countries. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.Y.; Law, M.; Khetani, M.; Pollock, N.; Rosenbaum, P. Establishing the Cultural Equivalence of the Young Children’s Participation and Environment Measure (YC-PEM) for Use in Singapore. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2016, 36, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruijsen-Terpstra, A.J.; Ketelaar, M.; Boeije, H.; Jongmans, M.J.; Gorter, J.W.; Verheijden, J.; Lindeman, E.; Verschuren, O. Parents’ experiences with physical and occupational therapy for their young child with cerebral palsy: A mixed studies review. Child Care Health Dev. 2014, 40, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salloom, H. Education in Saudi Arabia; Amana Publication: Belleville, MD, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, L.; Almatroodi, N.; AlAngari, D.; AlShehri, R.; Alshammari, S. Disability inclusion assessment in primary healthcare centers in Eastern Saudi Arabia: A way forward. J. Med. Life 2023, 16, 1813–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, K.L.; FitzGerald, T.L.; Albesher, R.A.; McGinley, J.L.; Allison, K.; Lee, K.J.; Cheong, J.L.Y.; Spittle, A.J. Barriers and facilitators to community participation for preschool age children born very preterm: A prospective cohort study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushta, S.M.; Alghamdi, R.; Almalki, H.; Waqas, S.; Alawwadh, A.; Barasheed, O.; Garnan, M.; McIntyre, S.; Rashid, H.; Badawi, N.; et al. Saudi Cerebral Palsy Register (SCPR): Protocol on the Methods and Technical Details. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2024, 14, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Children with CP (n = 50) | Typically Developing Children (n = 50) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.841 | ||
| Female | 22 (44%) | 23 (46%) | |
| Male | 28 (56%) | 27 (54%) | |
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 10.1 ± 2.426 | 10.56 ± 2.314 | 0.3344 |
| Type of School | |||
| Public school | 16 (32%) | 33 (66%) | <0.001 |
| Inclusion education | 6 (12%) | - | |
| Private school | 7 (14%) | 17 (34%) | |
| Do not attend any school | 21 (42%) | - | |
| Type of Cerebral Palsy | - | ||
| Spastic hemiplegia | 7 (14%) | - | |
| Spastic diplegia | 18 (36%) | - | |
| Spastic quadriplegia | 15 (30%) | - | |
| Spastic paraplegia | 6 (12%) | - | |
| Ataxia | 4 (8%) | - | |
| Gross Motor Function Classification System | |||
| Level I | 2 (4%) | ||
| Level II | 19 (38%) | ||
| Level III | 18 (36%) | ||
| Level IV | 8 (16%) | ||
| Level V | 3 (6%) | ||
| Father Education level | 0.448 | ||
| Elementary | 2 (4%) | 1 (2%) | |
| Middle | 6 (12%) | 4 (8%) | |
| High school | 25 (50%) | 22 (44%) | |
| Higher education | 14 (28%) | 22 (44%) | |
| Other * | 3 (6%) | 1 (2%) | |
| Mother Education level | 0.002 | ||
| Elementary | 4 (8%) | 2 (4%) | |
| Middle | 7 (14%) | 18 (36%) | |
| High school | 14 (28%) | 22 (44%) | |
| Higher education | 21 (42%) | 8 (16%) | |
| Other | 4 (8%) | 0 |
| Variable | Children with CP, n (%) | Typically Developing Children, n (%) | Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) | 95% CI | Adjusted p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
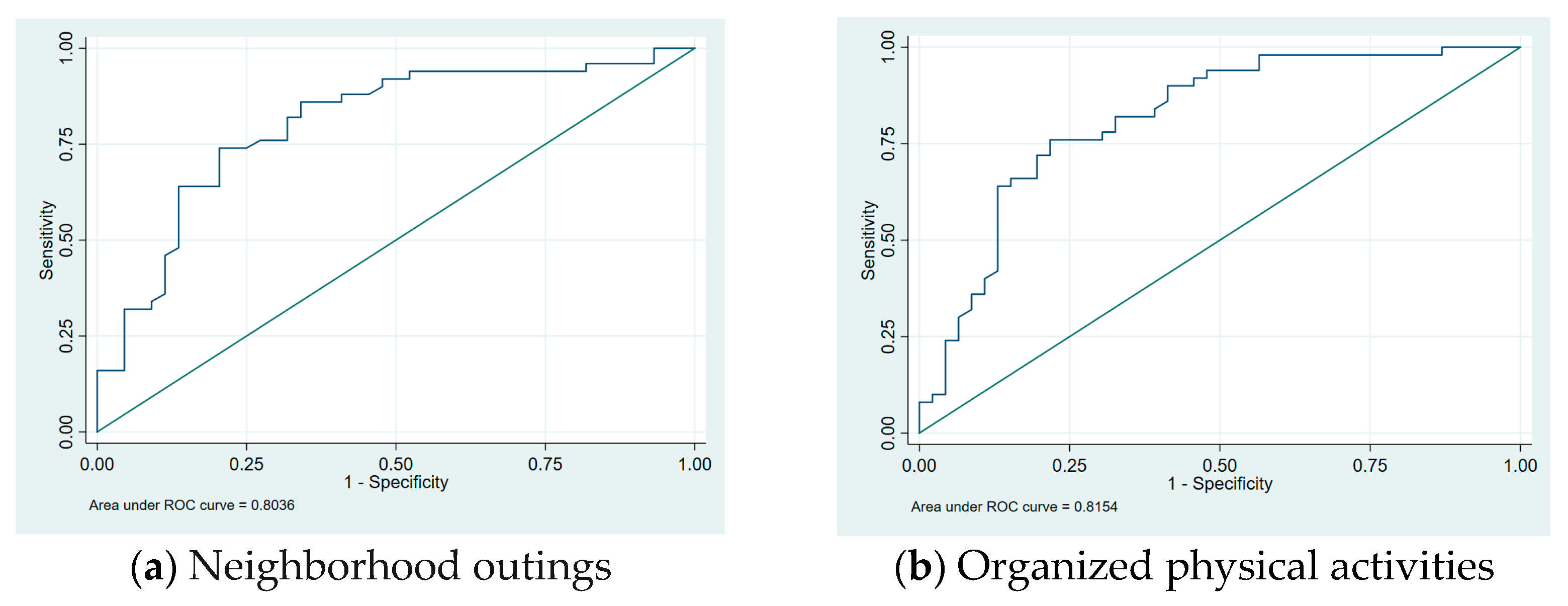
| Neighborhood outings (e.g., shopping at the store/mall, going to a movie, eating out at a restaurant, visiting the local library/bookstore) | Daily | 2 (4) | 0 | 1 | - | - |
| Weekly | 11 (22) | 25 (50) | 0.105 | (0.020–0.539) | 0.007 | |
| Monthly | 24 (48) | 22 (44) | 0.167 | (0.035–0.799) | 0.025 | |
| Never | 13 (26) | 3 (6) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Community events (e.g., attending a play, concert, sports game, parade) | Daily | 0 | 1 (2) | 1 | - | - |
| Weekly | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | 2.873 | (0.283–29.135) | 0.372 | |
| Monthly | 5 (10) | 16 (32) | 0.300 | (0.079–1.137) | 0.077 | |
| Never | 43 (86) | 31 (62) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Organized physical activities (e.g., sports teams or classes such as baseball, hockey, martial arts, dance, horseback riding, swimming, gymnastics) | Daily | 1 (2) | 12 (24) | 0.024 | (0.005–0.671) | 0.002 |
| Weekly | 8 (16) | 15 (30) | 0.184 | (0.054–0.628) | 0.007 | |
| Monthly | 1 (2) | 6 (12) | 0.059 | (0.002–256) | 0.022 | |
| Never | 40 (80) | 17 (34) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Unorganized physical activities (e.g., walking in nature, riding a bike, skiing, skateboarding, playing hide-and-seek or running, playing basketball) | Daily | 4 (8) | 4 (8) | 0.876 | (0.141–5.436) | 0.212 |
| Weekly | 8 (16) | 15 (30) | 0.252 | (0.069–0.924) | 0.038 | |
| Monthly | 8 (16) | 13 (26) | 0.460 | (0.136–1.559) | 0.887 | |
| Never | 30 (60) | 18 (36) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Unsupported classes by the school (e.g., music, art, computer languages) | Daily | 5 (10) | 12 (24) | 0.251 | (0.059–1.059) | 0.060 |
| Weekly | 6 (12) | 17 (34) | 0.132 | (0.036–0.480) | 0.002 | |
| Monthly | 4 (8) | 6 (12) | 0.180 | (0.032–0.994) | 0.049 | |
| Never | 35 (70) | 15 (30) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Religious or spiritual gatherings and activities (e.g., attending places of worship, religion classes, groups) | Daily | 7 (14) | 23 (46) | 0.149 | (0.048–0.463) | 0.001 |
| Weekly | 3 (6) | 8 (16) | 0.197 | (0.038–1.026) | 0.054 | |
| Monthly | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | 0.235 | (0.012–4.436) | 0.334 | |
| Never | 38 (76) | 17 (34) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Getting together with friends in the community (e.g., hanging out, informal gatherings outside of home or school, BBQ, going out on a date) | Daily | 4 (8) | 9 (18) | 0.047 | (0.004–0.619) | 0.020 |
| Weekly | 22 (44) | 29 (58) | 0.071 | (0.007–0.688) | 0.022 | |
| Monthly | 11 (22) | 11 (22) | 0.061 | (0.005–0.699) | 0.025 | |
| Never | 13 (26) | 1 (2) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Overnight visits or trips (e.g., sleepovers, camp, vacations) | Daily | 0 | 5 (10) | 1 | - | - |
| Weekly | 4 (8) | 2 (4) | 2.407 | (0.310–18.659) | 0.401 | |
| Monthly | 8 (16) | 11 (22) | 0.781 | (0.250–2.434) | 0.669 | |
| Never | 38 (76) | 32 (64) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Variable | Children with CP, n (%) | Typically Developing Children, n (%) | Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) | 95% CI | Adjusted p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computer and video games | Daily | 37 (74) | 39 (78) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Weekly | 3 (6) | 10 (20) | 0.177 | (0.026–1.193) | 0.075 | |
| Monthly | 9 (18) | 1 (2) | 14.371 | (1.468–140.730) | 0.022 | |
| Never | 1 (2) | 0 | 1 | - | - | |
| Arts, crafts, music, and hobbies (e.g., participating in arts and crafts, listening to music, playing an instrument, collecting, reading for leisure, cooking for fun) | Daily | 6 (12) | 21 (42) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Weekly | 18 (36) | 21 (42) | 2.536 | (0.686–9.375) | 0.163 | |
| Monthly | 19 (38) | 3 (6) | 16.420 | (3.156–85.443) | 0.001 | |
| Never | 7 (14) | 5 (10) | 2.827 | (0.515–15.501) | 0.231 | |
| Getting together with other people (e.g., interacting with peers, family, other houseguests) OR Socializing using technology (e.g., telephone, computer) | Daily | 24 (48) | 34 (68) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Weekly | 8 (16) | 10 (20) | 1.392 | (0.407–4.764) | 0.286 | |
| Monthly | 14 (28) | 4 (8) | 4.598 | (1.138–18.575) | 0.032 | |
| Never | 4 (8) | 2 (4) | 4.353 | (0.606–31.242) | 0.144 | |
| Household chores (e.g., unloading/loading the dishwasher, cleaning room or other areas of the house, cooking, taking out the garbage, setting the table, caring for the household pet) | Daily | 2 (4) | 15 (30) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Weekly | 7 (14) | 27 (54) | 2.344 | (0.313–17.551) | 0.407 | |
| Monthly | 39 (78) | 0 | 1 | - | - | |
| Never | 2 (4) | 8 (16) | 3.208 | (0.252–40.837) | 0.369 | |
| Personal care management (e.g., getting dressed, choosing clothing, brushing hair or teeth, applying makeup) | Daily | 21 (42) | 45 (90) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Weekly | 7 (14) | 5 (10) | 2.413 | (0.585–9.961) | 0.223 | |
| Monthly | 21 (42) | 0 | 1 | - | - | |
| Never | 1 (2) | 0 | 1 | - | - | |
| Homework (e.g., daily reading, homework assignments, school projects) | Daily | 45 (90) | 45 (90) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Weekly | 5 (10) | 5 (10) | 1.004 | (0.213–4.745) | 0.996 | |
| Monthly | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | |
| Never | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Variable | Children with CP, n (%) | Typically Developing Children, n (%) | Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) | 95% CI | Adjusted p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The physical layout or amount of space and furniture in your home | Usually helps | 11 (22) | 26 (52) | 0.166 | (0.052–0.527) | 0.002 |
| Usually makes hard | 12 (24) | 11 (22) | 0.378 | (0.107–1.337) | 0.131 | |
| Not an issue | 27 (54) | 13 (26) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The sensory qualities of the home environment (e g. amount and/or type of sound, light, temperature, textures of objects) | Usually helps | 25 (50) | 33 (66) | 0.480 | (0.156–2.301) | 0.199 |
| Usually makes hard | 9 (18) | 7 (14) | 0.513 | (0.115–2.301) | 0.384 | |
| Not an issue | 16 (32) | 10 (20) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The physical demands of typical activities in the home (e.g., strength, endurance, coordination) | Usually helps | 23 (46) | 37 (74) | 0.407 | (0.113–1.466) | 0.169 |
| Usually makes hard | 17 (34) | 7 (14) | 1.694 | (0.361–7.958) | 0.504 | |
| Not an issue | 10 (20) | 6 (12) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The cognitive demands of typical activities in the home (e.g., concentration, attention, problem solving) | Usually helps | 22 (44) | 40 (80) | 0.116 | (0.020–0.685) | 0.017 |
| Usually makes hard | 17 (34) | 8 (16) | 0.398 | (0.060–2.693) | 0.345 | |
| Not an issue | 11 (22) | 2 (4) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The social demands of typical activities in the home (e.g., communication, interacting with others) | Usually helps | 34 (68) | 47 (94) | 0.075 | (0.007–0.771) | 0.029 |
| Usually makes hard | 6 (12) | 2 (4) | 0.175 | (0.009–3.235) | 0.242 | |
| Not an issue | 10 (20) | 1 (2) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Variable | Children with CP, n (%) | Typically Developing Children, n (%) | Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) | 95% CI | Adjusted p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The physical layout or amount of space outside and inside buildings (e.g., distances to stores, presence of sidewalks, availability of ramps or elevators) | Usually helps | 23 (46) | 24 (48) | 1.075 | - | 0.905 |
| Usually makes it hard | 16 (32) | 15 (30) | 1.124 | (0.318–3.979) | 0.856 | |
| Not an issue | 11 (22) | 11 (22) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The sensory qualities of community settings (e.g., noise, crowds, lighting) | Usually helps | 10 (20) | 10 (20) | 0.982 | (0.248–3.892) | 0.979 |
| Usually makes it hard | 26 (52) | 29 (58) | 0.695 | (0.236–2.048) | 0.509 | |
| Not an issue | 14 (28) | 11 (22) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The physical demands of typical activities (e.g., strength, endurance, coordination) | Usually helps | 19 (38) | 34 (68) | 0.907 | (0.245–3.357) | 0.884 |
| Usually makes it hard | 22 (44) | 7 (14) | 3.593 | (0.787–16.409) | 0.099 | |
| Not an issue | 9 (18) | 9 (18) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The cognitive demands of typical activities (e.g., focus, attention, problem solving) | Usually helps | 25 (50) | 40 (80) | 0.834 | (0.153–4.537) | 0.834 |
| Usually makes it hard | 20 (40) | 6 (12) | 2.618 | (0.399–17.141) | 0.315 | |
| Not an issue | 5 (10) | 4 (8) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The social demands of typical activities (e.g., communication, interaction with others) | Usually helps | 31 (62) | 41 (82) | 1.451 | (0.273–7.707) | 0.662 |
| Usually makes it hard | 14 (28) | 5 (10) | 2.867 | (0.420–19.589) | 0.282 | |
| Not an issue | 5 (10) | 4 (8) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Child’s relationship with their friends | Usually helps | 32 (64) | 46 (92) | 0.230 | (0.040–1.338) | 0.102 |
| Usually makes it hard | 7 (14) | 2 (4) | 0.577 | (0.053–6.279) | 0.652 | |
| Not an issue | 11 (22) | 2 (4) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| The attitudes and actions of community members toward your child (e.g., shop owner, supervisor, trainers, other families) | Usually helps | 25 (50) | 35 (70) | 0.741 | (0.239–2.303) | 0.605 |
| Usually makes it hard | 12 (24) | 6 (12) | 1.835 | (0.401- 8.388) | 0.434 | |
| Not an issue | 13 (26) | 9 (18) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| External weather conditions (e.g., climate, temperature) | Usually helps | 18 (36) | 21 (42) | 0.480 | (0.154–1.497) | 0.206 |
| Usually makes it hard | 14 (28) | 17 (34) | 0.395 | (0.123–1.266) | 0.118 | |
| Not an issue | 18 (36) | 12 (24) | Ref | Ref | Ref | |
| Safety in society (e.g., traffic, crime, violence) | Usually helps | 18 (36) | 17 (34) | 0.834 | (0.482–1.445) | 0.517 |
| 0.678 | (0.197–2.338) | 0.539 | ||||
| Usually makes it hard | 14 (28) | 25 (50) | 0.261 | (0.077–0.893) | 0.032 | |
| Not an issue | 18 (36) | 8 (16) | Ref | Ref | Ref |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljuhani, T.; Alzahrani, S.A.; Aldosary, A.M.; Alzamil, L.A.; Alshehri, R.K.; Gmmash, A.S.; Albesher, R.A. Measuring Community and Home Participation and Environmental Factors in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17010017
Aljuhani T, Alzahrani SA, Aldosary AM, Alzamil LA, Alshehri RK, Gmmash AS, Albesher RA. Measuring Community and Home Participation and Environmental Factors in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatric Reports. 2025; 17(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljuhani, Turki, Shaden A. Alzahrani, Abeer M. Aldosary, Lana A. Alzamil, Rakan K. Alshehri, Afnan S. Gmmash, and Reem A. Albesher. 2025. "Measuring Community and Home Participation and Environmental Factors in Children with Cerebral Palsy" Pediatric Reports 17, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17010017
APA StyleAljuhani, T., Alzahrani, S. A., Aldosary, A. M., Alzamil, L. A., Alshehri, R. K., Gmmash, A. S., & Albesher, R. A. (2025). Measuring Community and Home Participation and Environmental Factors in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatric Reports, 17(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17010017






