Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Clinical Course and Complications of Varicella—A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Group
3.2. Clinical Presentation
3.3. Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gershon, A. Varicella Zoster Virus. In Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 7th ed.; Cherry, J., Harrison, G., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 2021–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Varela, F.H.; Pinto, L.A.; Scotta, M.C. Global impact of varicella vaccination programs. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzola, E.; Spina, G.; Russo, R.; Bozzola, M.; Corsello, G.; Villani, A. Mandatory vaccinations in European countries, undocumented information, false news and the impact on vaccination uptake: The position of the Italian pediatric society. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impfkalendar 2023. Available online: https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Kommissionen/STIKO/Empfehlungen/Aktuelles/Impfkalender.pdf?__blob=publicationFile (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Kalendarz Szczepień Ochronnych 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/psse-walcz/kalendarz-obowiazkowych-szczepien-ochronnych-na-rok-2024 (accessed on 19 May 2024).
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Barnett, E.D.; Lynfield, R.; Sawyer, M.H. (Eds.) Varicella Zoster Virus Infections. In Red Book 2021–2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases; American Academy of Pediatrics: Itasca, IL, USA, 2021; p. 834. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, R.; Ashman, M.; Taha, M.K.; Varon, E.; Angoulvant, F.; Levy, C.; Rybak, A.; Ouldali, N.; Guiso, N.; Grimprel, E. Pediatric Infectious Disease Group (GPIP) position paper on the immune debt of the COVID-19 pandemic in childhood, how can we fill the immunity gap? Infect. Dis. Now 2021, 51, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, H.J.; Menegale, F.; Preziosi, G.; Pariani, E.; Migliari, M.; Pellegrinelli, L.; Sechi, G.M.; Buoro, S.; Merler, S.; Cereda, D.; et al. Reconstructing the impact of COVID-19 on the immunity gap and transmission of respiratory syncytial virus in Lombardy, Italy. EBioMedicine 2023, 95, 104745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldunki Epidemiologiczne. Available online: https://wwwold.pzh.gov.pl/oldpage/epimeld/index_p.html (accessed on 19 May 2024).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Intensified Circulation of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and Associated Hospital Burden in the EU/EEA—12 December 2022; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022.
- Seward, J.; Jumaan, A. VSV: Persistence in the population. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A., Campadelli-Fiume, G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; Chapter 40. [Google Scholar]
- NIZP-PZH. Choroby Zakaźne i Zatrucia w Polsce w 2019 Roku. Available online: http://wwwold.pzh.gov.pl/oldpage/epimeld/2019/Ch_2019.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- NIZP-PZH. Choroby Zakaźne i Zatrucia w Polsce w 2022 Roku. Available online: http://wwwold.pzh.gov.pl/oldpage/epimeld/2022/Ch_2022_Wstepne_dane.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Available online: https://www.unicef.org/press-releases/two-million-refugee-children-flee-war-ukraine-search-safety-across-borders (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Warsaw City Council. Warszawa w Kryzysie Uchodźczym. Available online: https://um.warszawa.pl/documents/39703/26880339/Warszawa+w+kryzysie+uchod%C5%BAczym+-+raport+za+pierwsze+trzy+miesi%C4%85ce.pdf/5f08dc64-1037-cc30-7835-6193c643b0ab?t=1655819297071 (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Varicella and Herpes Zoster Vaccines: WHO Position Paper. 2014. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/242227/WER8925_265-287.PDF (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Naeimi, R.; Sepidarkish, M.; Mollalo, A.; Parsa, H.; Mahjour, S.; Safarpour, F.; Almukhtar, M.; Mechaal, A.; Chemaitelly, H.; Sartip, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in children worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 56, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franczak, J.; Moppert, J.; Sobolewska-Pilarczyk, M.; Pawłowska, M. The Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies in Children Hospitalized for Reasons Other Than COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuter, B.J.; Weibel, R.E.; Guess, H.A.; Matthews, H.; Morton, D.H.; Neff, B.J.; Provost, P.J.; Watson, B.A.; Starr, S.E.; Plotkin, S.A. Oka/Merck varicella vaccine in healthy children: Final report of a 2-year efficacy study and 7-year follow-up studies. Vaccine 1991, 9, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawaskar, M.; Méroc, E.; Samant, S.; Flem, E.; Bencina, G.; Riera-Montes, M.; Heininger, U. Economic burden of varicella in Europe in the absence of universal varicella vaccination. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelcwajg, A.; Quinet, B.; Castello, B.; Parez, N.; Grimprel, E. Motifs d’hospitalisation des patients atteints de varicelle dans un établissement pédiatrique parisien: Évolution entre 1990 et 2001. Arch. De Pédiatrie 2006, 13, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubos, F.; Grandbastien, B.; Hue, V.; Martinot, A. Epidemiology of hospital admissions for paediatric varicella infections: A one-year prospective survey in the pre-vaccine era. Epidemiol. Infect. 2007, 135, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gier, B.; Marchal, N.; de Beer-Schuurman, I.; Te Wierik, M.; Hooiveld, M.; de Melker, H.E.; van Sorge, N.M. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal (Streptococcus pyogenes) infections (iGAS) in young children in the Netherlands, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babiker, A.; Li, X.; Lai, Y.L.; Strich, J.R.; Warner, S.; Sarzynski, S.; Dekker, J.P.; Danner, R.L.; Kadri, S.S. Effectiveness of adjunctive clindamycin in β-lactam antibiotic-treated patients with invasive β-haemolytic streptococcal infections in US hospitals: A retrospective multicentre cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreoni, F.; Zürcher, C.; Tarnutzer, A.; Schilcher, K.; Neff, A.; Keller, N.; Marques Maggio, E.; Poyart, C.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Zinkernagel, A.S. Clindamycin Affects Group A Streptococcus Virulence Factors and Improves Clinical Outcome. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
| Total n = 221 | 2019 n = 59 | 2022 n = 162 | p Value (2019 vs. 2022) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | Male | 112 (51) | 29 (49) | 83 (51) | 0.78 | |
| Female | 109 (49) | 30 (51) | 79 (49) | |||
| Median age in years (IQR) | 3.5 (1.0; 6.0) | 3.0 (0.5; 5.4) | 4.0 (1.0–6.0) | 0.02 | ||
| Infants, n (%) | 40 (18) | 16 (27.1) | 24(14.8) | 0.03 | ||
| Ukrainian refugee, n (%) | 8 (3.6) | 0 | 8 (4.9) | 0.08 | ||
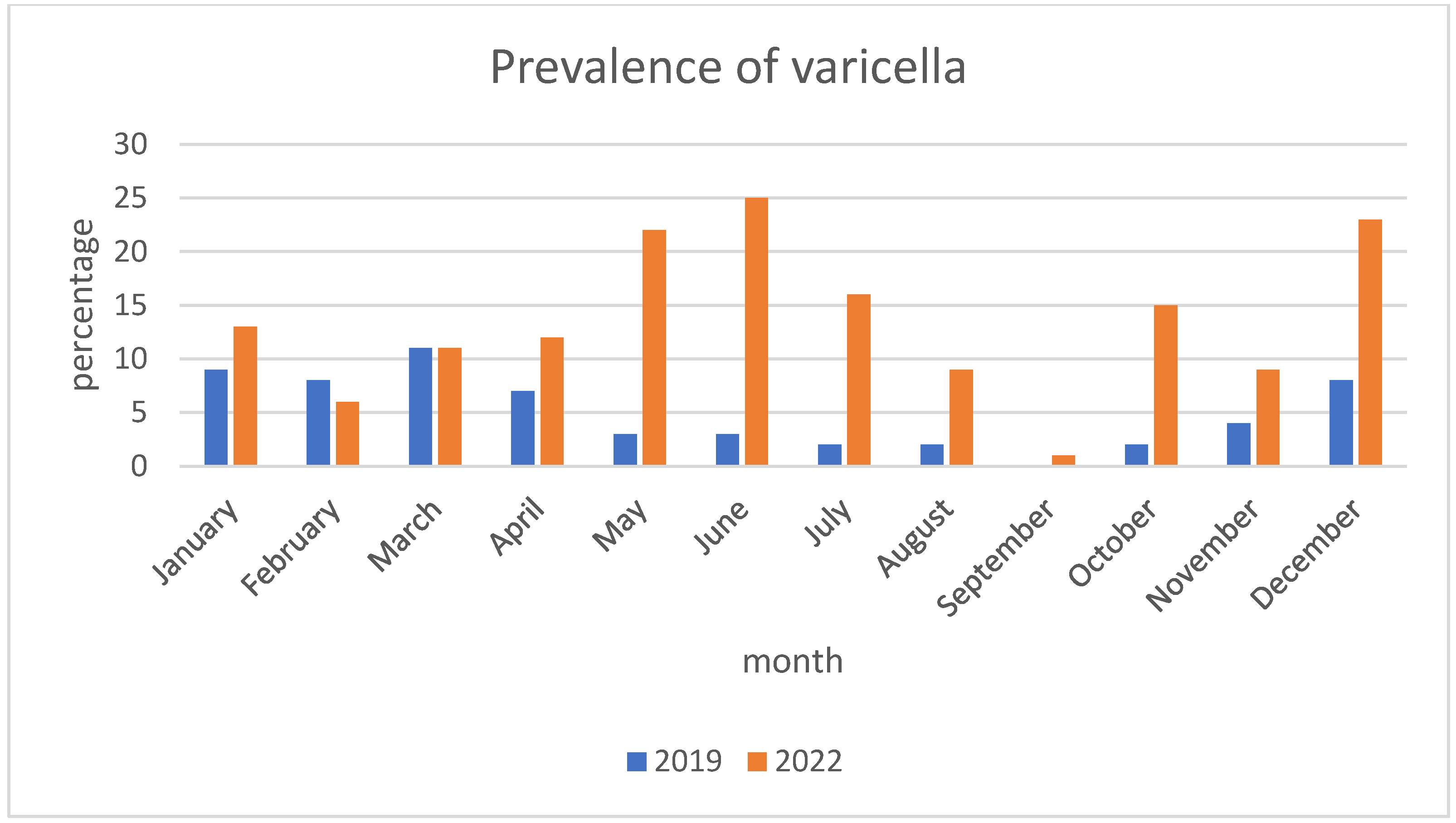
| Month of infection, n (%) | Winter-spring (December–May) | 133 (60.2) | 46 (78) | 87 (53.7) | 0.0011 | |
| Summer-fall (June–November) | 88 (39.8) | 13 (22) | 75 (46.3) | |||
| Coronavirus disease 2019, n (%) | Vaccinated | Not applicable | 2 (1.2) | Not applicable | ||
| Not vaccinated | 64 (39.5) | |||||
| Not qualified for vaccination | 96 (59.3) | |||||
| Varicella immunization, n (%) | Not vaccinated | 219 (99.1) | 58 (98.3) | 161 (99.4) | 0.45 | |
| 1 dose/postexposure | 2 (0.9) | 1 (1.7) | 1 (0.6) | |||
| Fully vaccinated | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Immunosuppression, n (%) | 5 (2.3) | 2 (3.4) | 3 (1.9) | 0.49 | ||
| Source of infection, n (%) | Unknown | 61 (27.6) | 11 (18.6) | 50 (30.9) | 0.007 | |
| Household | 79 (35.7) | 23 (39) | 56 (34.6) | |||
| Daycare/Schools.py | 73 (33) | 19 (32.2) | 54 (33.3) | |||
| Refugee camp | 8 (3.6) | 6 (10.2) | 2 (1.3) | |||
| Comorbidities, n (%) | 48 (21.7) | 14 (23.7) | 34 (21) | 0.66 | ||
| Total (n = 221) | 2019 (n = 59) | 2022 (n = 162) | p Value (2019 vs. 2022) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General condition, n (%) | Good | 55 (24.9) | 15 (25.4) | 40 (24.7) | 0.52 |
| Fair | 138 (62.4) | 39 (66.1) | 99 (61.1) | ||
| Serious | 28 (12.7) | 5 (8.5) | 23 (14.2) | ||
| Median Time of (in days), IQR | Lesions | 6 (5–8) | 6 (5–7) | 7 (5–8) | 0.17 |
| Fever | 3 (1–4) | 2 (0–3) | 4 (2–5) | <0.0001 | |
| hospitalization | 4 (4–6) | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–7) | 0.01 | |
| Skin complications, n (%) | 159 (71.9) | 31 (52.5) | 129 (79.6) | 0.0001 | |
| Bacterial superinfection, n (%) | 156 (70.6) | 30 (50.8) | 126 (77.8) | 0.0001 | |
| Etiology, n (%) | S. pyogenes | 29 (13.1) | 3 (5.1) | 26 (16.0) | 0.03 |
| S. aureus | 27 (12.2) | 1 (1.7) | 26 (16.0) | 0.004 | |
| S. pyogenes + S. aureus | 3 (1.4) | 0 | 3 (1.9) | 0.29 | |
| Scarlet fever, n (%) | 40 (18.1) | 10 (16.9) | 30 (18.5) | 0.79 | |
| Cellulitis, n (%) | 24 (10.9) | 2 (3.4) | 22 (13.6) | 0.03 | |
| Sepsis, n (%) | 29 (13.1) | 2 (3.4) | 27 (16.7) | 0.009 | |
| Neurological complications n (%) | Total | 12 (5.4) | 5 (8.5) | 7 (4.3) | 0.01 |
| Meningitis | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| Cerebellitis | 6 (2.7) | 3 (5.1) | 3 (1.9) | 0.19 | |
| encephalitis | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 1 (0.6) | 0.54 | |
| Seizures | 5 (2.3) | 4 (6.8) | 1 (0.6) | 0.006 | |
| Eye involvement, n (%) | 84 (38) | 21 (35.6) | 63(38.9) | 0.65 | |
| Other complications, n (%) | Total | 58 (26.2) | 21 (35.6) | 37 (22.8) | 0.05 |
| syncope/unconsciousness | 7 (3.2) | 2 (3.4) | 5 (3.1) | 0.9 | |
| otitis media | 19 (8.6) | 7 (11.9) | 12 (7.4) | 0.29 | |
| Pneumonia | 16(7.2) | 5 (8.5) | 11 (6.8) | 0.66 | |
| Other | 13 (5.8) | 6 (1.0) | 7 (4.3) | 0.02 | |
| Total | 2019 | 2022 | p Value (2019 vs. 2022) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leukocytes Median (IQR) | 8.8 (6.7–12.3) | 9.5 (7.4–13.6) | 8.5 (6.5–11.9) | 0.13 |
| CRP Median (IQR) | 14.0 (6.3–28.8) | 9.5 (6.0–30.0) | 16 (7.0–28.3) | 0.27 |
| PCT Median (IQR) | 0.29 (0.16–0.88) | 0.26 (0.16–1.24) | 0.31 (0.16–0.87) | 0.79 |
| Total (n = 221) | 2019 (n = 59) | 2022 (n = 162) | p Value (2019 vs. 2022) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of antibiotics, n (%) | None | 41 (18.6) | 17 (28.8) | 24 (14.8) | 0.01 |
| One | 150 (67.9) | 40 (67.8) | 110 (67.9) | 0.98 | |
| Two | 27 (12.2) | 2 (3.4) | 25 (15.4) | 0.01 | |
| Three | 3 (1.3) | 0 | 3 (1.9) | 0.29 | |
| Route of administration, n (%), | Oral | 20 | 7 | 13 | 0.19 |
| Intravenous | 27 | 8 | 19 | 0.24 | |
| Sequential | 133 | 27 | 106 | 0.10 | |
| Acyclovir, n (%) | Total | 133 (60.1) | 33 (55.9) | 100 (61.7) | 0.43 |
| Oral | 116 (52.5) | 24 (40.7) | 92 (56.8) | 0.01 | |
| Intravenous | 10 (4.5) | 5 (8.5) | 5 (3.1) | ||
| Sequential | 7 (3.2) | 4 (6.8) | 3 (1.9) | ||
| Antihistamines, n (%) | 126 (57.0) | 28 (47.5) | 98 (60.5) | 0.08 | |
| Antipyretics, n (%) | 175 (79.2) | 37 (62.7) | 138 (85.2) | 0.0003 | |
| Intravenous fluids, n (%) | 189 (85.5) | 45 (76.3) | 144 (88.9) | 0.01 | |
| Mannitol, n (%) | 8 (3.6) | 3 (5.1) | 5 (3.1) | 0.48 | |
| Steroid, n (%) | 10 (4.5) | 3 (5.1) | 7 (4.3) | 0.80 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietrzak, M.; Pokorska-Śpiewak, M. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Clinical Course and Complications of Varicella—A Retrospective Cohort Study. Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16, 451-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020039
Pietrzak M, Pokorska-Śpiewak M. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Clinical Course and Complications of Varicella—A Retrospective Cohort Study. Pediatric Reports. 2024; 16(2):451-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020039
Chicago/Turabian StylePietrzak, Maja, and Maria Pokorska-Śpiewak. 2024. "Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Clinical Course and Complications of Varicella—A Retrospective Cohort Study" Pediatric Reports 16, no. 2: 451-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020039
APA StylePietrzak, M., & Pokorska-Śpiewak, M. (2024). Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Clinical Course and Complications of Varicella—A Retrospective Cohort Study. Pediatric Reports, 16(2), 451-460. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16020039







