The Fakir Child: Clinical Observation or Invasive Treatment?
Abstract
1. Introduction
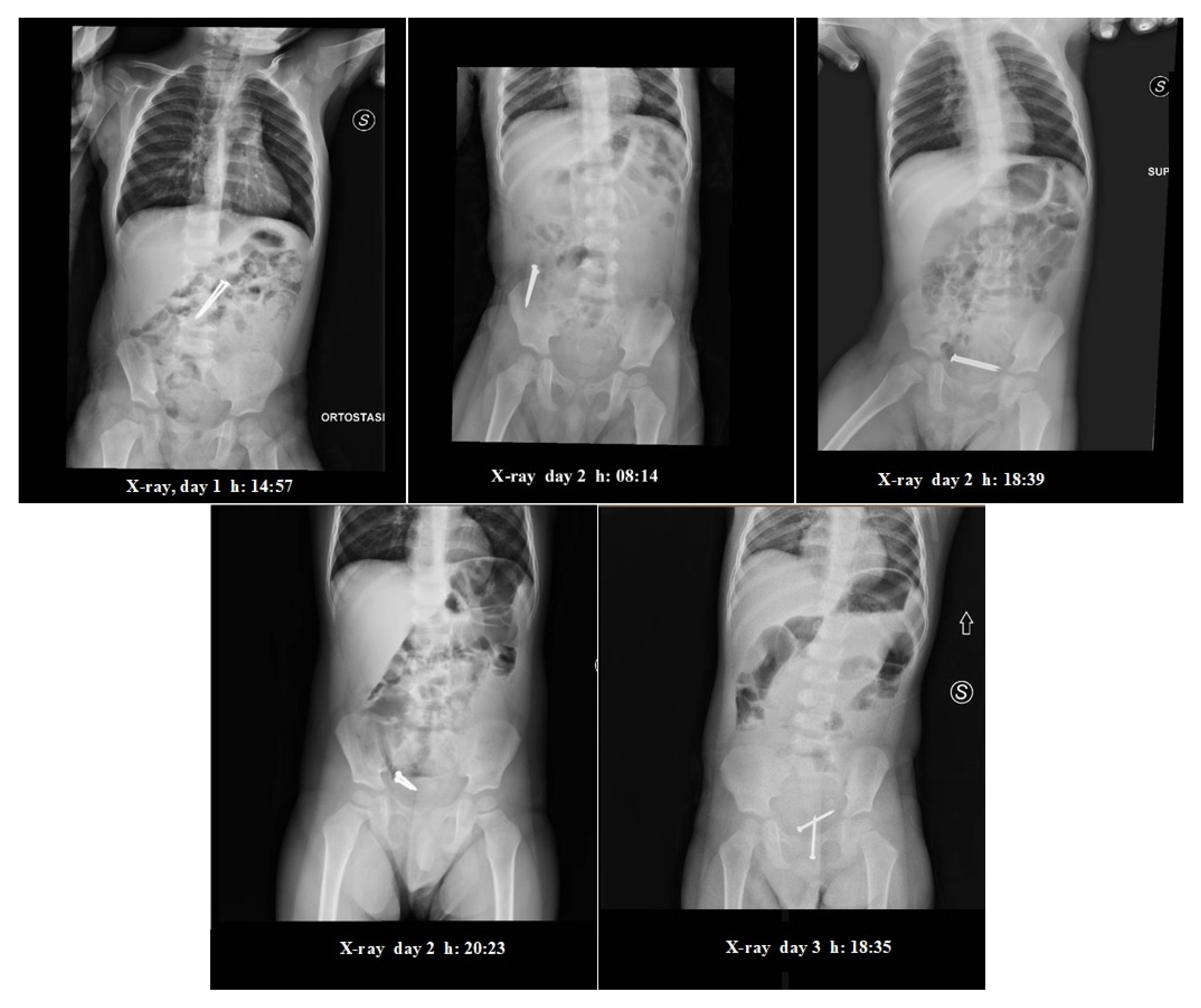
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| FB | foreign body |
References
- Litovitz, T.L.; Klein-Schwartz, W.; White, S.; Cobaugh, D.J.; Youniss, J.; Omslaer, J.C.; Drab, A.; Benson, B.E. 2000 annual report of the American association of poison control centers toxic exposure surveillance system. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2001, 19, 337–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.K. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal foreign bodies in children. Indian J. Pediatr. 1999, 66, S75–S80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Ikenberry, S.O.; Jue, T.L.; Anderson, M.A.; Appalaneni, V.; Banerjee, S.; Ben-Menachem, T.; Decker, G.A.; Fanelli, R.D.; Fisher, L.R.; et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies and food impactions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 73, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandra, S.; Eslick, G.D. A systematic review of paediatric foreign body ingestion: Presentation, complications, and management. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Tam, P.K. Foreign-body ingestion in children: Experience with 1265 cases. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1999, 34, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachimi-Idrissi, S.; Corne, L.; Vandenplas, Y. Management of ingested foreign bodies in childhood: Our experience and review of the literature. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 1998, 5, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokar, B.; Cevik, A.A.; Ilhan, H. Ingested gastrointestinal foreign bodies: Predisposing factors for complications in children having surgical or endoscopic removal. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2007, 23, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, W. Management of foreign bodies of the upper gastrointestinal tract: Update. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1995, 41, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, R. Foreign bodies in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2006, 18, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamary, K.R.; Davis, J.W.; Ament, E.E.; Dirks, R.C.; Garry, J.E. This too shall pass: A study of ingested sharp foreign bodies. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 82, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, Y.; Sahn, B.; Weinstein, T. Foreign body ingestion in pediatric patients. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018, 30, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaretti, A.; Pierri, F.; Valentini, P.; Russo, I.; Gargiullo, L.; Riccardi, R. Current practice and recent advances in pediatric pain management. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17 (Suppl. S1), 112–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khorana, J.; Tantivit, Y.; Phiuphong, C.; Pattapong, S.; Siripan, S. Foreign Body Ingestion in Pediatrics: Distribution, Management and Complications. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019, 55, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, R.E.; Lerner, D.G.; Lin, T.; Manfredi, M.; Shah, M.; Stephen, T.C.; Gibbons, T.E.; Pall, H.; Sahn, B.; McOmber, M.; et al. North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Endoscopy Committee. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: A clinical report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomson, M.; Tringali, A.; Dumonceau, J.M.; Tavares, M.; Tabbers, M.M.; Furlano, R.; Spaander, M.; Hassan, C.; Tzvinikos, C.; Ijsselstijn, H.; et al. Paediatric Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition and European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Guidelines. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyemura, M.C. Foreign body ingestion in children. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gatto, A.; Angelici, S.; Di Pangrazio, C.; Nanni, L.; Buonsenso, D.; Paradiso, F.V.; Chiaretti, A. The Fakir Child: Clinical Observation or Invasive Treatment? Pediatr. Rep. 2020, 12, 103-107. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric12030023
Gatto A, Angelici S, Di Pangrazio C, Nanni L, Buonsenso D, Paradiso FV, Chiaretti A. The Fakir Child: Clinical Observation or Invasive Treatment? Pediatric Reports. 2020; 12(3):103-107. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric12030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleGatto, Antonio, Serenella Angelici, Claudia Di Pangrazio, Lorenzo Nanni, Danilo Buonsenso, Filomena Valentina Paradiso, and Antonio Chiaretti. 2020. "The Fakir Child: Clinical Observation or Invasive Treatment?" Pediatric Reports 12, no. 3: 103-107. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric12030023
APA StyleGatto, A., Angelici, S., Di Pangrazio, C., Nanni, L., Buonsenso, D., Paradiso, F. V., & Chiaretti, A. (2020). The Fakir Child: Clinical Observation or Invasive Treatment? Pediatric Reports, 12(3), 103-107. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric12030023






