Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from a Watershed Section of Ameca River in Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Microbiological Assessments
2.3. Statistical Analysis
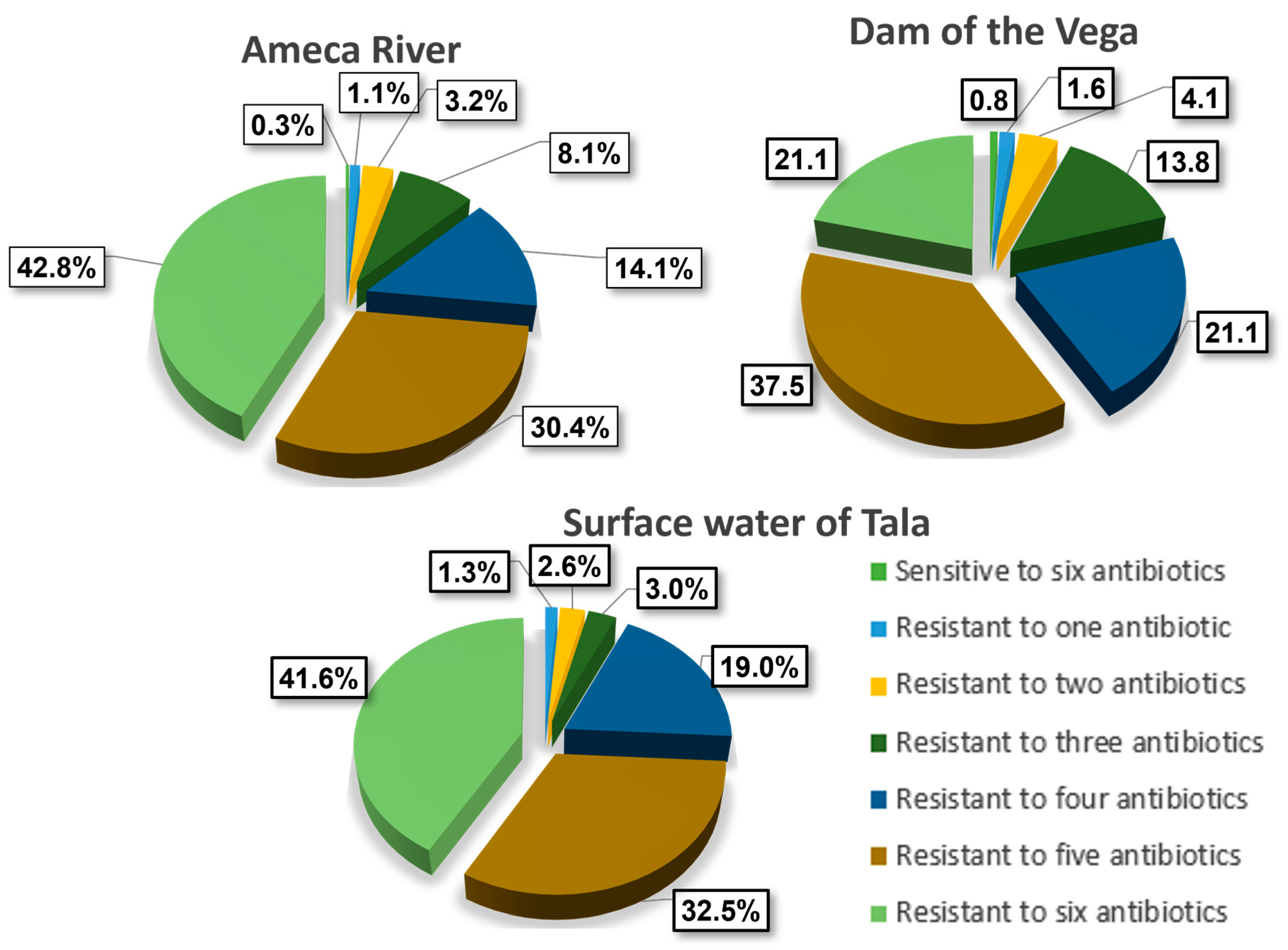
3. Results
3.1. AR in E. coli
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance (AR) Profile by Zone
- Ameca: 6 × 12 (six antibiotics for each month over 12 months) and 5 × 12 (five sampling points for each month over 12 months);
- Presa la Vega: 6 × 12 (six antibiotics for each month over 12 months) and 6 × 12 (six sampling points for each month over 12 months);
- Tala: 6 × 12 (six antibiotics for each month over 12 months) and 5 × 12 (five sampling points for each month over 12 months).
3.2.1. Tala
3.2.2. La Vega Wetland
3.2.3. Ameca
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Antibiotic resistance |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| GLASS | Global Antimicrobial Surveillance System |
| ESKAPE | Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp. |
| CFU/mL | Colony-forming units per milliliter |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| AMP | Ampicillin |
| AMC | Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid |
| GE | Gentamicin |
| TE | Tetracycline |
| STX | Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim |
| S | Streptomycin |
| NMX | Norma Mexicana |
| NOM | Norma Oficial Mexicana |
| USEPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| SNII | Sistema Nacional de Investigadores e Investigadoras/National System of Researchers |
| SNCA | Sistema Nacional de Creadores de Arte/National System of Art Creators |
| PROSNII | Programa de Apoyo a la Mejora en las Condiciones de Producción de los Miembros del SNII y SNCA/Improvement in Production Conditions of SNII and SNCA Members |
| JIMAV | Junta Intermunicipal para la Gestión Integral del Medio Ambiente de la Región Valles/Intermunicipal Board for Environmental Management in the Valley Region |
| PRODEP | Programa para el Desarrollo Profesional Docente para el Tipo Superior/Support Program for the Incorporation of New Full-Time Professors |
| SEP | Secretaría de Educación Pública/Ministry of Public Education |
References
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Selection and Transmission of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Microb. Transm. 2017, 5, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Wermuth, H.R.; Calhoun, C.; Hall, G.A. Antibiotics. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535443/ (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance Found Worldwide, New Data Shows. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-01-2018-high-levels-of-antibiotic-resistance-found-worldwide-new-data-shows (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. P T 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- European Comission. A European One Health Action Plan against Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) European Comission; European Comission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; pp. 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Laxminarayan, R. The overlooked pandemic of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2022, 399, 606–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, Z.; Goodarzi, F.; Dalir, A.; Sholeh, M. Comments on the published meta-analysis of antibiotic resistance in hospital-acquired ESKAPE-E infections in low- and lower-middle-income countries. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1602–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadimurthy, R.; Mayegowda, S.B.; MNayak, S.C.; Mohan, C.D.; Rangappa, K.S. Escaping mechanisms of ESKAPE pathogens from antibiotics and their targeting by natural compounds. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 34, e00728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, I.M.; Bal, A.M. New antibiotic agents in the pipeline and how they can help overcome microbial resistance. Virulence 2013, 4, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkman, A.; Do, T.T.; Walsh, F.; Virta, M.P.J. Antibiotic-Resistance Genes in Waste Water. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, P.R.; Balasubramanium, R. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; Report WHO/HSE/PED/AIP/2014.2; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 9–34. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.; Aguilar, C.; Estrada, M.A.; Echániz, G.; Carnalla, N.; Soto, A.; López-Antuñano, F.J. Susceptibility to new beta-lactams of enterobacterial extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producers and penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in Mexico. J. Chemother. 1998, 10, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Torres, J.I.; Ocaña-Munguía, M.A.; Madero Morales, P.A.; Ruiz-Galindo, E.; Garza-González, E.; Gómez-Guerra, L. Antimicrobial resistance and extended spectrum beta-lactamases in urinary tract infections: A serious problem in Northern Mexico. Rev. Mex. De Urol. 2020, 80, e02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-González, E.; Morfín-Otero, R.; Mendoza-Olazarán, S.; Bocanegra-Ibarias, P.; Flores-Treviño, S.; Rodríguez-Noriega, E.; Ponce-de-León, A.; Sanchez-Francia, D.; Franco-Cendejas, R.; Arroyo-Escalante, S.; et al. A snapshot of antimicrobial resistance in Mexico. Results from 47 centers from 20 states during a six-month period. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiratisin, P.; Chongthaleong, A.; Tan, T.Y.; Lagamayo, E.; Roberts, S.; Garcia, J.; Davies, T. Comparative in vitro activity of carbapenems against major Gram-negative pathogens: Results of Asia-Pacific surveillance from the COMPACT II study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, S.A.; Ramachandran, A.; Perron, G.G. Antibiotic Pollution in the Environment: From Microbial Ecology to Public Policy. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.G.; de Pedro, C.; Paxeus, N. Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breathnach, A.S.; Cubbon, M.D.; Karunaharan, R.N.; Pope, C.F.; Planche, T.D. Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa outbreaks in two hospitals: Association with contaminated hospital waste-water systems. J. Hosp. Infect. 2012, 82, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.B.; Graham, J.P.; Lackey, L.G.; Roess, A.; Vailes, R.; Silbergeld, E. Elevated risk of carrying gentamicin-resistant Escherichia coli among U.S. poultry workers. Environ. Health Perspect 2007, 115, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielen, A.; Šimatović, A.; Kosić-Vukšić, J.; Senta, I.; Ahel, M.; Babić, S.; Jurina, T.; González Plaza, J.J.; Milaković, M.; Udiković-Kolić, N. Negative environmental impacts of antibiotic-contaminated effluents from pharmaceutical industries. Water Res. 2017, 126, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushniak, B.D. Antibiotic resistance: A public health crisis. Public Health Rep. 2014, 129, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossolini, G.M.; Arena, F.; Pecile, P.; Pollini, S. Update on the antibiotic resistance crisis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, E.W.; Zimbler, D.; Callahan, E.; Plomaritis, E. Patterns and persistence of antibiotic resistance in faecal indicator bacteria from freshwater recreational beaches. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diario Oficial de la Federación. Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-034-SCFI-2015. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/normasOficiales/5959/seeco12_C/seeco12_C.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Yang, Y.; Song, W.; Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Du, L.; Xing, W. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in global lakes: A review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.; Hughes, D. Microbiological effects of sublethal levels of antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Joung, Y.; Han, J.H.; Jung, W.; Kim, S.B. Antibiotic resistance among aquatic bacteria in natural freshwater environments of Korea. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, C.W.; Dolfing, J.; Ehlert, P.A.; Graham, D.W. Evidence of increasing antibiotic resistance gene abundances in archived soils since 1940. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruden, A.; Arabi, M.; Storteboom, H.N. Correlation between upstream human activities and riverine antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11541–11549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekalski, N.; Gascón Díez, E.; Bürgmann, H. Wastewater as a point source of antibiotic-resistance genes in the sediment of a freshwater lake. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, C.E.; Fox, J.T.; Dougherty, E.R.; Cameron, A.D.S.; Alexander, K.A. The Changing Face of Water: A Dynamic Reflection of Antibiotic Resistance Across Landscapes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Jackson, C.R.; Frye, J.G. The prevalence and antimicrobial resistance phenotypes of Salmonella, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus sp. in surface water. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouki, C.; Venieri, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Detection and fate of antibiotic resistant bacteria in wastewater treatment plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadozie, C.F.; Odume, O.N. Freshwater environments as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their role in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragón, V.A.; Llamas-Pérez, D.F.; González-Guzmán, G.E.; Márquez-González, A.R.; Padilla-Noriega, R.; Durán-Avelar, M.d.J.; Franco, B. Identification of Enterococcus faecalis bacteria resistant to heavy metals and antibiotics in surface waters of the Mololoa River in Tepic, Nayarit, Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 183, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Rojas, G.; Mazari-Hiríart, M.; Ponce de León, S.; Amieva-Fernández, R.I.; Agis-Juárez, R.A.; Huebner, J.; López-Vidal, Y. Comparison of Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis Strains isolated from water and clinical samples: Antimicrobial susceptibility and genetic relationships. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Gardea, M.C.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Gomez-Flores, R.; Zavala-Díaz de la Serna, F.J.; Eroza-de la Vega, G.; Nevárez-Moorillón, G.V.; Pérez-Recoder, M.C.; Sánchez-Ramírez, B.; Del González-Horta, M.C.; Infante-Ramírez, R. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Surface Water in Bassaseachic Falls National Park, Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magaña-Lizárraga, J.A.; Gómez-Gil, B.; Rendón-Maldonado, J.G.; Delgado-Vargas, F.; Vega-López, I.F.; Báez-Flores, M.E. Genomic Profiling of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from Surface Water of Agricultural Drainage in North-Western Mexico: Detection of the International High-Risk Lineages ST410 and ST617. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Lenczewski, M.; Leal-Bautista, R.M.; Duvall, M. Groundwater microbial diversity and antibiotic resistance linked to human population density in Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Can. J. Microbiol. 2020, 66, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugo-Melchor, Y.; Quiñones, B.; Amézquita-López, B.A.; León-Félix, J.; García-Estrada, R.; Chaidez, C. Characterization of tetracycline resistance in Salmonella enterica strains recovered from irrigation water in the Culiacan Valley, Mexico. Microb. Drug Resist. 2010, 16, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, I.; Salinas, E.; Martínez, L.; Cruz-Córdova, A.; González-Pedrajo, B.; Espinosa, N.; Amábile-Cuevas, C.F. Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates from an Urban Lake Receiving Water from a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Mexico City: Fecal Pollution and Antibiotic Resistance. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo-Ariyama, H.A.; García-Heredia, A.; Heredia, N.; García, S.; León, J.; Jaykus, L.; Solís-Soto, L. Phylogroups, pathotypes, biofilm formation and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolates in farms and packing facilities of tomato, jalapeño pepper and cantaloupe from Northern Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizalez-Roman, A.; Velazquez-Roman, J.; Valdez-Flores, M.A.; Flores-Villaseñor, H.; Vidal, J.E.; Muro-Amador, S.; Guadrón-Llanos, A.M.; Gonzalez-Nuñez, E.; Medina-Serrano, J.; Tapia-Pastrana, G.; et al. Detection of antimicrobial-resistance diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains in surface water used to irrigate food products in the northwest of Mexico. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 304, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Google Maps. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Diario Oficial de la federación. Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-230-SSA1-2002. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=2081772&fecha=12/07/2005#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- EPA 821-R-02-024; Method 1604: Total Coliforms and Escherichia coli in Water by Membrane Filtration Using a Simultaneous Detection Technique (MI Medium). USEPA—United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Diario Oficial de la Federación. Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-102-SCFI-2006. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/normasOficiales/8303/seeco14_C/seeco14_C.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Diario Oficial de la Federación. Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-113-SSA1-1994. Available online: https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=4880115&fecha=25/08/1995#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Rekha, R.; Alam-Rizvi, M.; Jaishree, P. Designing and validation of genus-specific primers for human gut flora study. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 9, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candrian, U.; Furrer, B.; Höfelein, C.; Meyer, R.; Jermini, M.; Lüthy, J. Detection of Escherichia coli and identification of enterotoxigenic strains by primer-directed enzymatic amplification of specific DNA sequences. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1991, 12, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesapane, R.; Ponder, M.; Alexander, K.A. Tracking pathogen transmission at the human–wildlife interface: Banded mongooses (Mungos mungo) and Escherichia coli. EcoHealth 2013, 10, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- My, T.T.; Thien, L.V.; Manh, V.D.; My, B.T.P.; Lan, D.T.M.; Binh, D.X.; Duc, V.M. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular characterization of Escherichia coli isolated from bovine mastitis samples in Nghe An province, Vietnam. Vet. World 2023, 16, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemer, J.J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing by the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1973, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI M100-S24; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-fourth Informational Supplement. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014.
- Skof, A.; Koller, M.; Baumert, R.; Hautz, J.; Treiber, F.; Kittinger, C.; Zarfel, G. Comparison of the Antibiotic Resistance of Escherichia coli Populations from Water and Biofilm in River Environments. Pathogens 2024, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W147–W153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsar Sites Information Service. Available online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/ris/2026 (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Holcomb, D.A.; Stewart, J.R. Microbial Indicators of Fecal Pollution: Recent Progress and Challenges in Assessing Water Quality. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, A.B.; Grant, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Mowbray, S.L.; McGee, C.D.; Clark, C.D.; Foley, D.M.; Wellman, D.E. Decadal and shorter period variability of surf zone water quality at Huntington Beach, California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Watanabe, N.; Xiao, C.; Harter, T.; McCowan, B.; Liu, Y.; Atwill, E.R. Antibiotic-resistant E. coli in surface water and groundwater in dairy operations in Northern California. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.H.; Lv, X.; Han, B.; Gu, X.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C.; He, Z. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolates in surface water of Taihu Lake Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 11412–11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.L.; Grant, S.B.; Mrse, R.D.; Copil Oancea, C.M.; Sanders, B.F.; Boehm, A.B. Scaling and management of fecal indicator bacteria in runoff from a coastal urban watershed in southern California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2637–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, S.L.; Hollis, E.J.; Depas, M.M.; Van Dyke, M.; Harris, J.; Scopel, C.O. Distribution and fate of Escherichia coli in Lake Michigan following contamination with urban stormwater and combined sewer overflows. J. Great Lakes Res. 2007, 33, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaia, C.M.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Nunes, O.C. Antibiotic Resistance in Waste Water and Surface Water and Human Health Implications. In Emerging Organic Contaminants and Human Health; Barceló, D., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 20, pp. 173–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.V.; Wilson, S.; Sanjay Preeth, R.S.; Prakash, P.; Sathiyasree, M.; Saigeetha, S.; Shobana, N.; Pachiyappan, S.; Rajesh, V.V. Sources of Antibiotic Contamination in Wastewater and Approaches to Their Removal—An Overview. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayan, R.A. Pharmaceutical effluent evokes superbugs in the environment: A call to action. Biosaf. Health 2023, 5, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Savin, M.C. Populations of antibiotic-resistant coliform bacteria change rapidly in a wastewater effluent dominated stream. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6192–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Obayiuwana, A.C.; Murinda, S.E. Enterococcus Species and Their Antimicrobial Resistance in an Urban Watershed Affected by Different Anthropogenic Sources. Water 2024, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pratap, S.G.; Raj, A. Occurrence and dissemination of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in aquatic environment and its ecological implications: A review. Environ. Sci Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 47505–47529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homeier-Bachmann, T.; Heiden, S.E.; Lübcke, P.K.; Bachmann, L.; Bohnert, J.A.; Zimmermann, D.; Schaufler, K. Antibiotic-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Wastewater of Abattoirs. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Murinda, S.E.; Graves, A.K. Genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli from human and animal sources uncovers multiple resistances from human sources. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothrock, M.J.; Min, B.R.; Castleberry, L.; Waldrip, H.; Parker, D.; Brauer, D.; Pitta, D.; Indugu, N. Antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial residues, and bacterial community diversity in pasture-raised poultry, swine, and beef cattle manures. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Pharmaceutical Drugs; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1990; (IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, No. 50) Ampicillin. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526244/ (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Chaves, B.J.; Tadi, P. Gentamicin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557550/ (accessed on 3 May 2025).
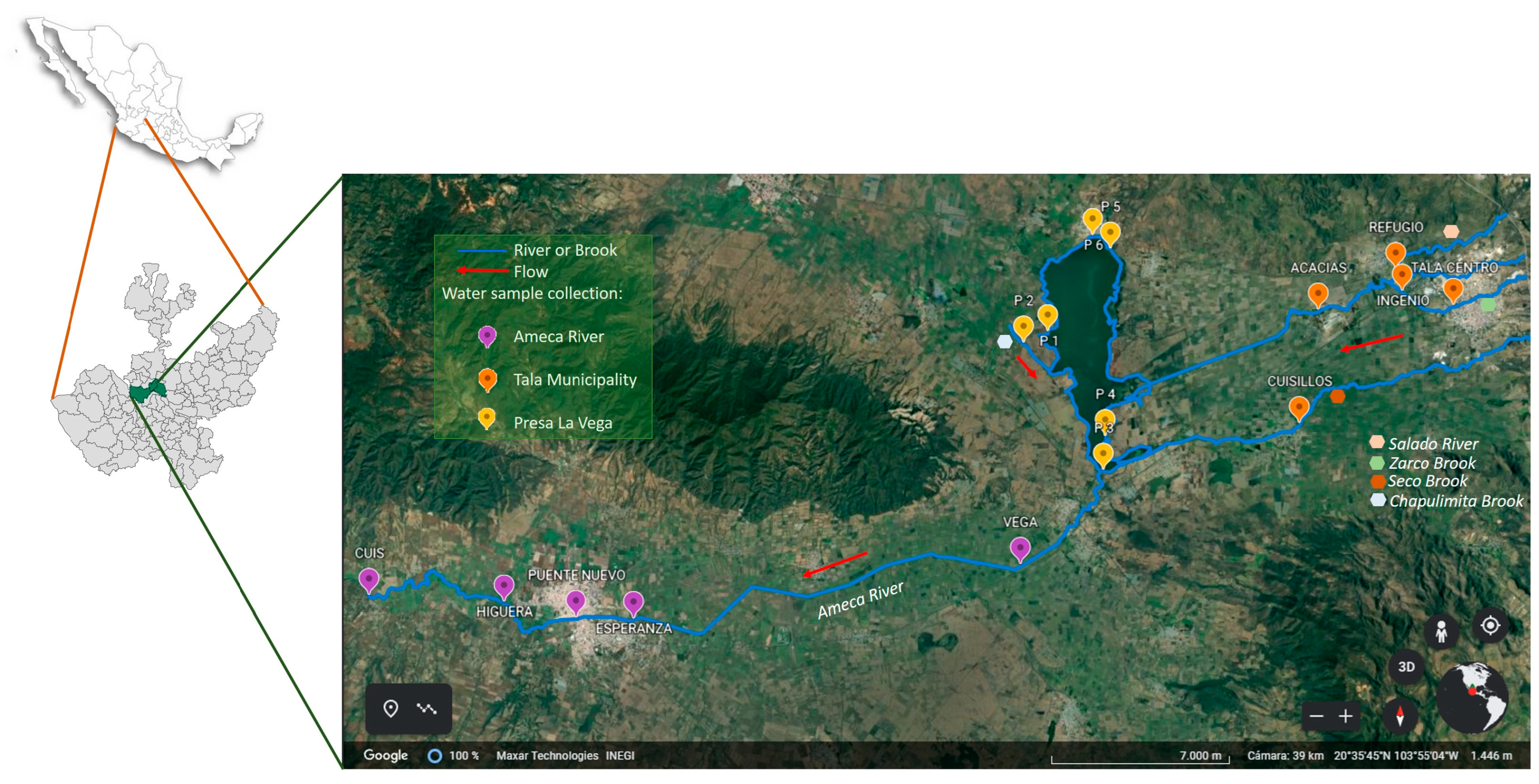
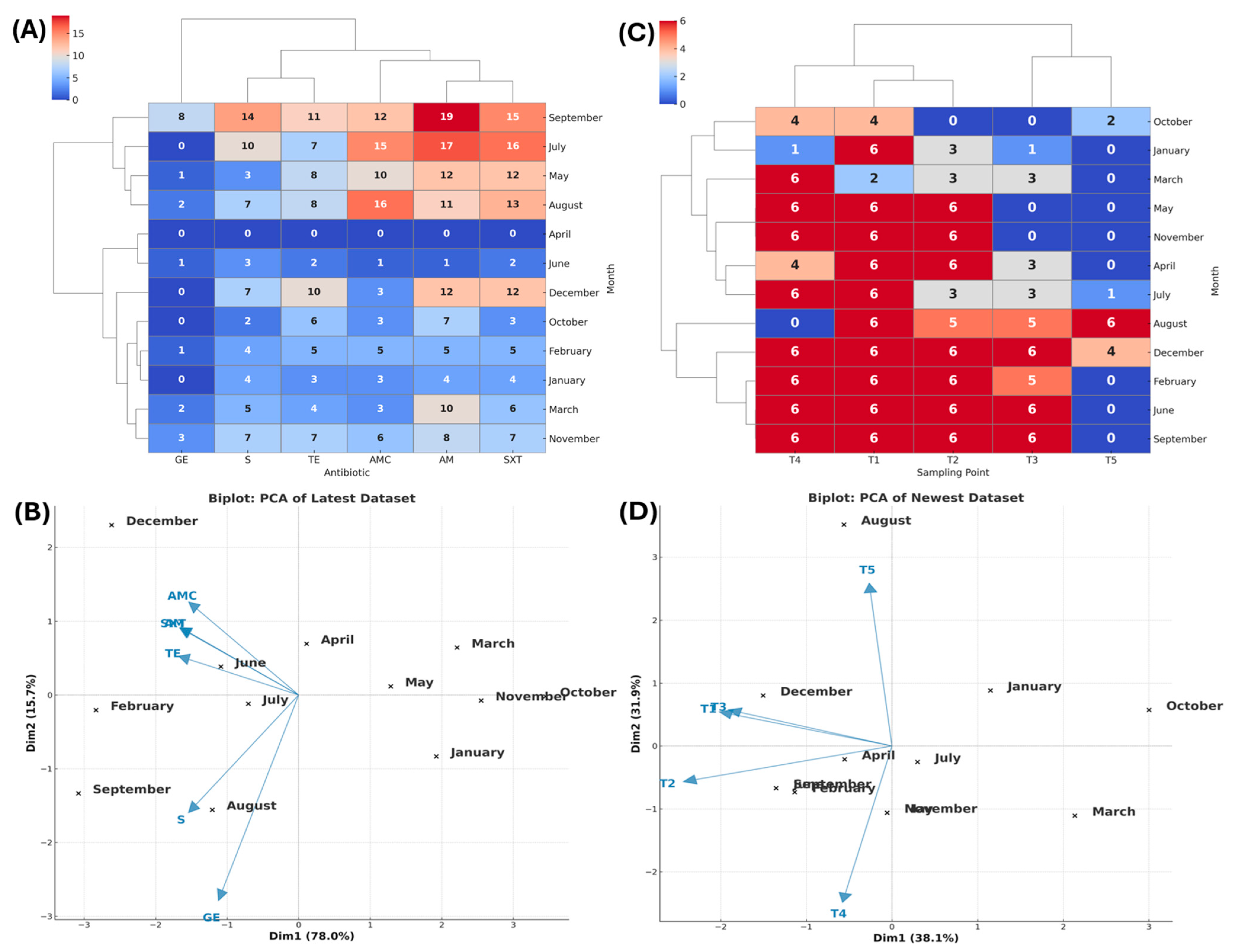
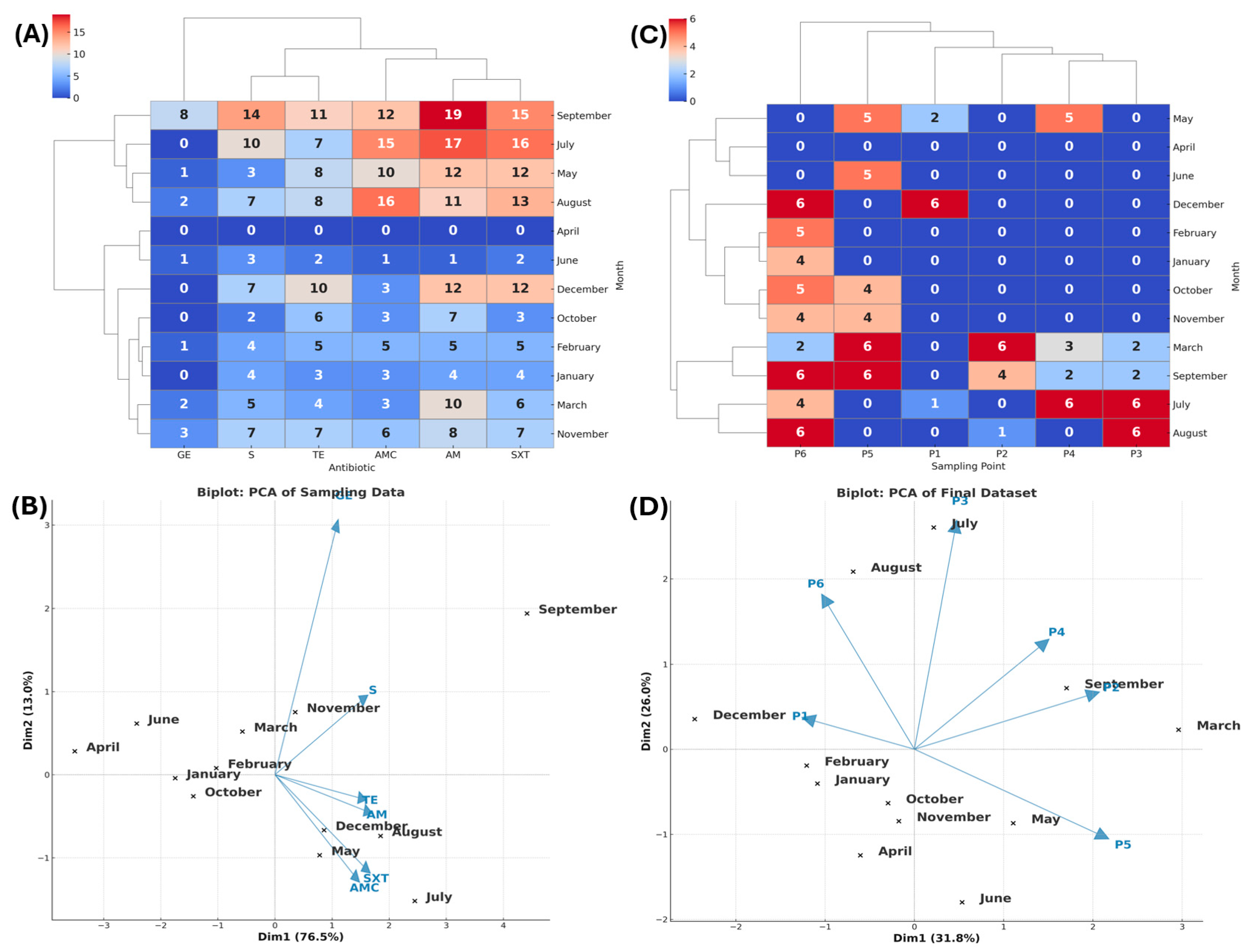
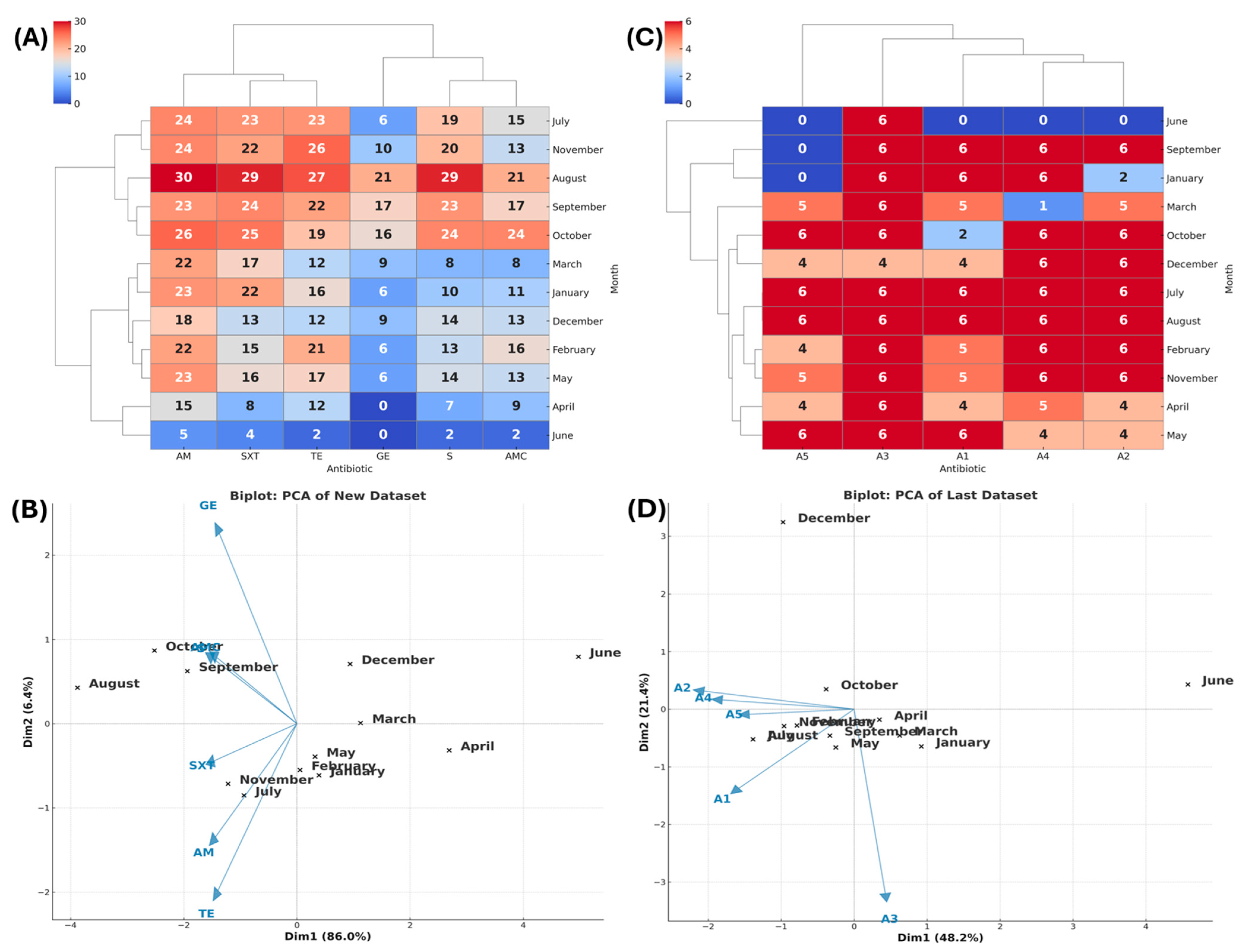
| Tala | La Vega | Ameca | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic | E. coli n = 231 | E. coli n = 123 | E. coli n = 287 | |
| Ampicillin | 220 (95.2%) | 114 (92.7%) | 272 (94.8%) | 0.586 |
| Streptomycin | 211 (91.3%) | 103 (83.7%) | 261 (90.9%) | 0.050 * |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid | 200 (86.5%) | 94 (76.4%) | 229 (79.7%) | 0.103 |
| Gentamicin | 118 (51.0%) | 37 (30.1%) | 159 (55.4%) | ˂0.001 * |
| Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim | 192 (83.1%) | 99 (80.5%) | 239 (83.3%) | 0.800 |
| Tetracycline | 221 (95.7%) | 106 (86.2%) | 261 (90.9%) | 0.024 * |
| Rainy Season | Dry Season | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic | E. coli n = 273 | E. coli n = 362 | |
| Ampicillin | 261 (95.6%) | 339 (93.6%) | 0.471 |
| Streptomycin | 261 (95.6%) | 308 (85.1%) | ˂0.001 * |
| Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid | 234 (85.7%) | 283 (78.2%) | 0.086 |
| Gentamicin | 171 (62.6%) | 140 (38.7%) | ˂0.001 * |
| Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim | 238 (87.3%) | 286 (79.0%) | 0.006 * |
| Tetracycline | 259 (94.8%) | 323 (89.2%) | 0.050 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Zaragoza, M.; Rodriguez-Preciado, S.Y.; Hernández-Ventura, L.; Ortiz-Covarrubias, A.; Castellanos-García, G.; Sifuentes-Franco, S.; Pereira-Suárez, A.L.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Montoya-Buelna, M.; Macias-Barragan, J. Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from a Watershed Section of Ameca River in Mexico. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080186
Díaz-Zaragoza M, Rodriguez-Preciado SY, Hernández-Ventura L, Ortiz-Covarrubias A, Castellanos-García G, Sifuentes-Franco S, Pereira-Suárez AL, Muñoz-Valle JF, Montoya-Buelna M, Macias-Barragan J. Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from a Watershed Section of Ameca River in Mexico. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(8):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080186
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Zaragoza, Mariana, Sergio Yair Rodriguez-Preciado, Lizeth Hernández-Ventura, Alejandro Ortiz-Covarrubias, Gustavo Castellanos-García, Sonia Sifuentes-Franco, Ana Laura Pereira-Suárez, José Francisco Muñoz-Valle, Margarita Montoya-Buelna, and Jose Macias-Barragan. 2025. "Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from a Watershed Section of Ameca River in Mexico" Microbiology Research 16, no. 8: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080186
APA StyleDíaz-Zaragoza, M., Rodriguez-Preciado, S. Y., Hernández-Ventura, L., Ortiz-Covarrubias, A., Castellanos-García, G., Sifuentes-Franco, S., Pereira-Suárez, A. L., Muñoz-Valle, J. F., Montoya-Buelna, M., & Macias-Barragan, J. (2025). Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from a Watershed Section of Ameca River in Mexico. Microbiology Research, 16(8), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080186








