Novel Reoviruses of Waterfowl Origin in Northern Vietnam: A Laboratory Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Detection of nWRVs by RT-PCR
2.3. Detection of Co-Infecting Viruses
2.4. Virus Isolation and Titration
2.5. Pathogenicity Assessment of Isolated Strains in Ducklings
2.6. Genetic Classification Based on the Sigma C-Encoding Gene
2.7. Immunoinformatic Analysis of the Sigma C Protein Amino Acid Sequence of nWRVs
2.8. Evolutionary Analysis of the Sigma C-Encoding Gene
3. Results
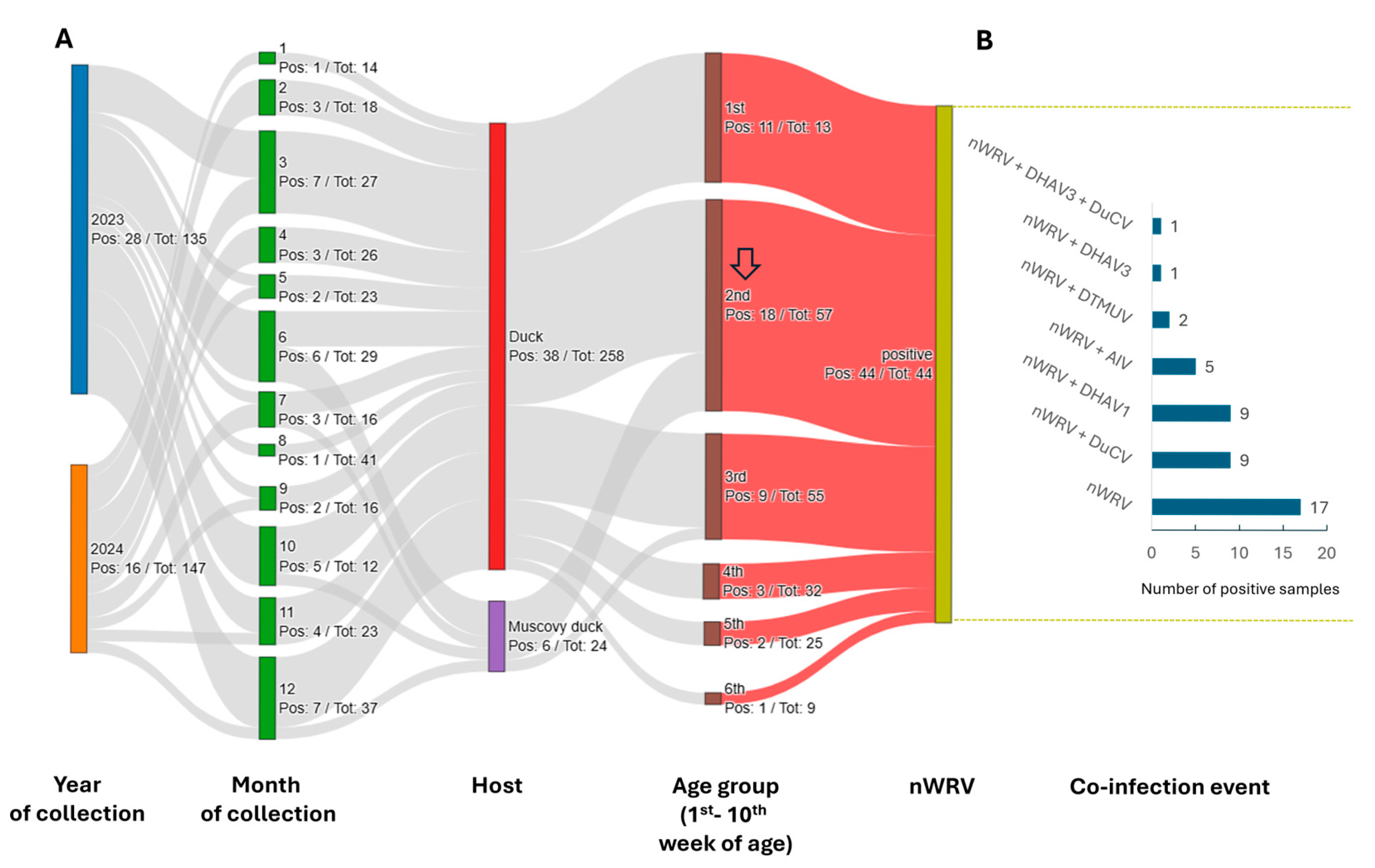
3.1. Detection of nWRVs and Co-Infection Status
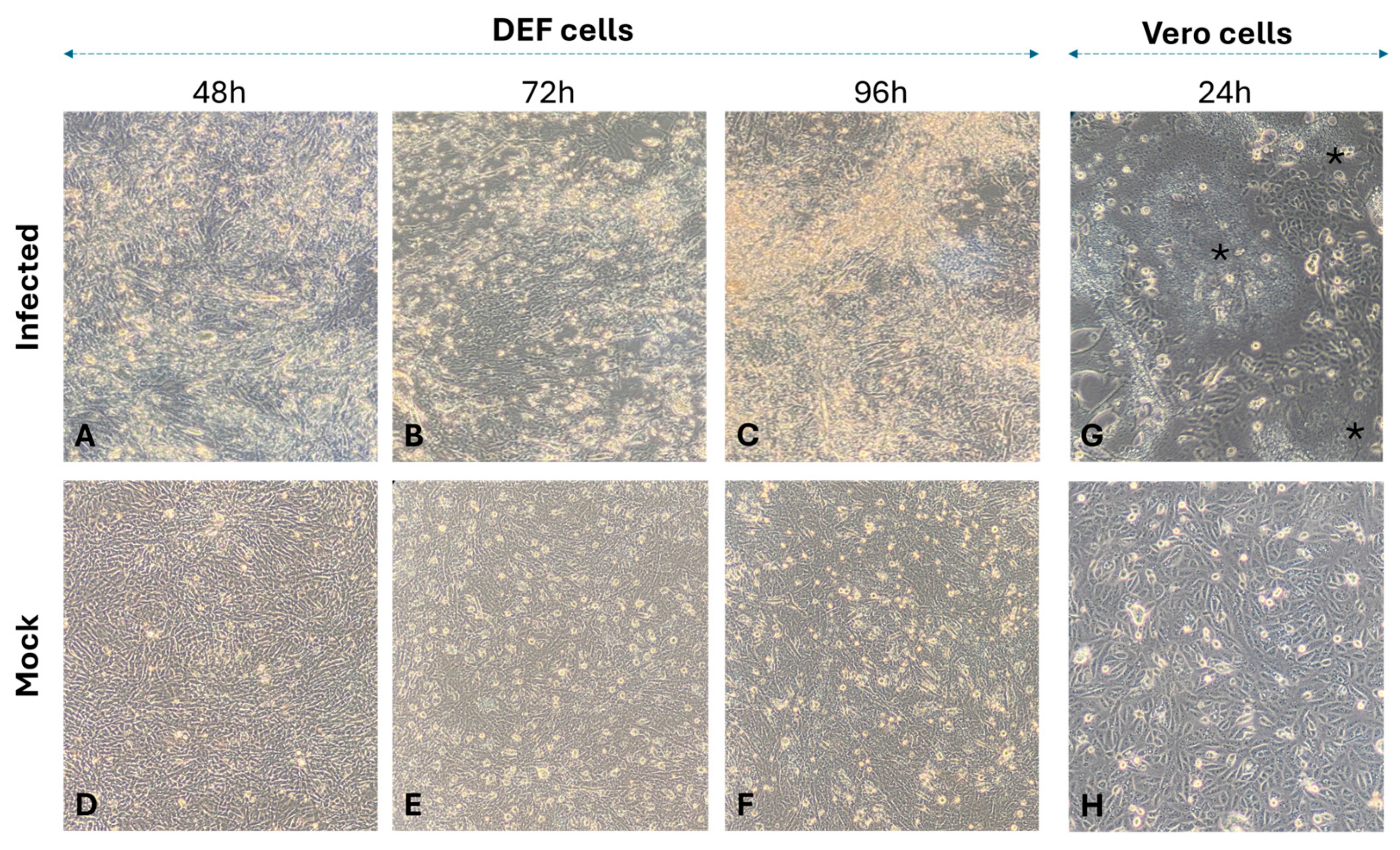
3.2. Isolation of nWRV Strains
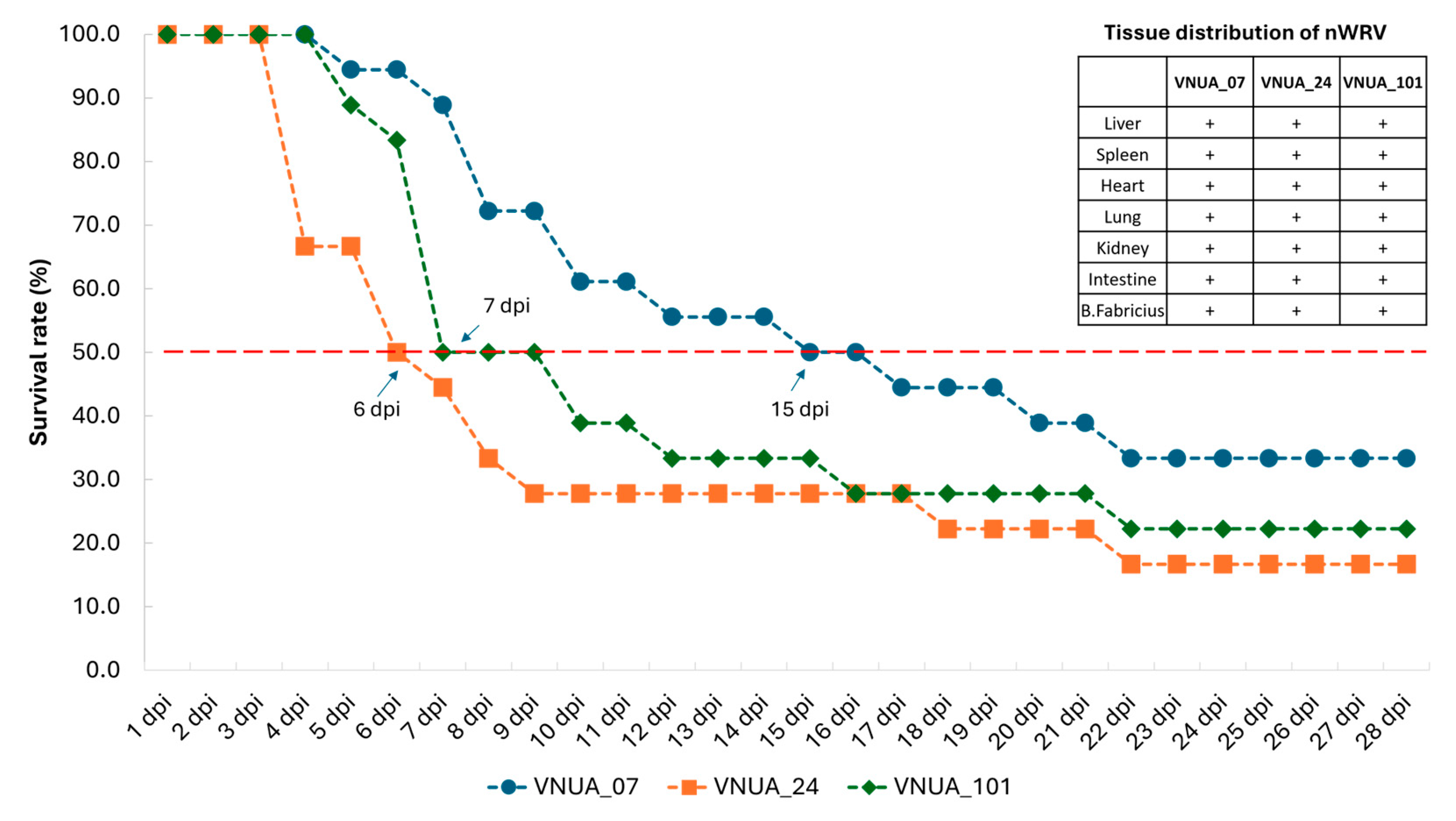
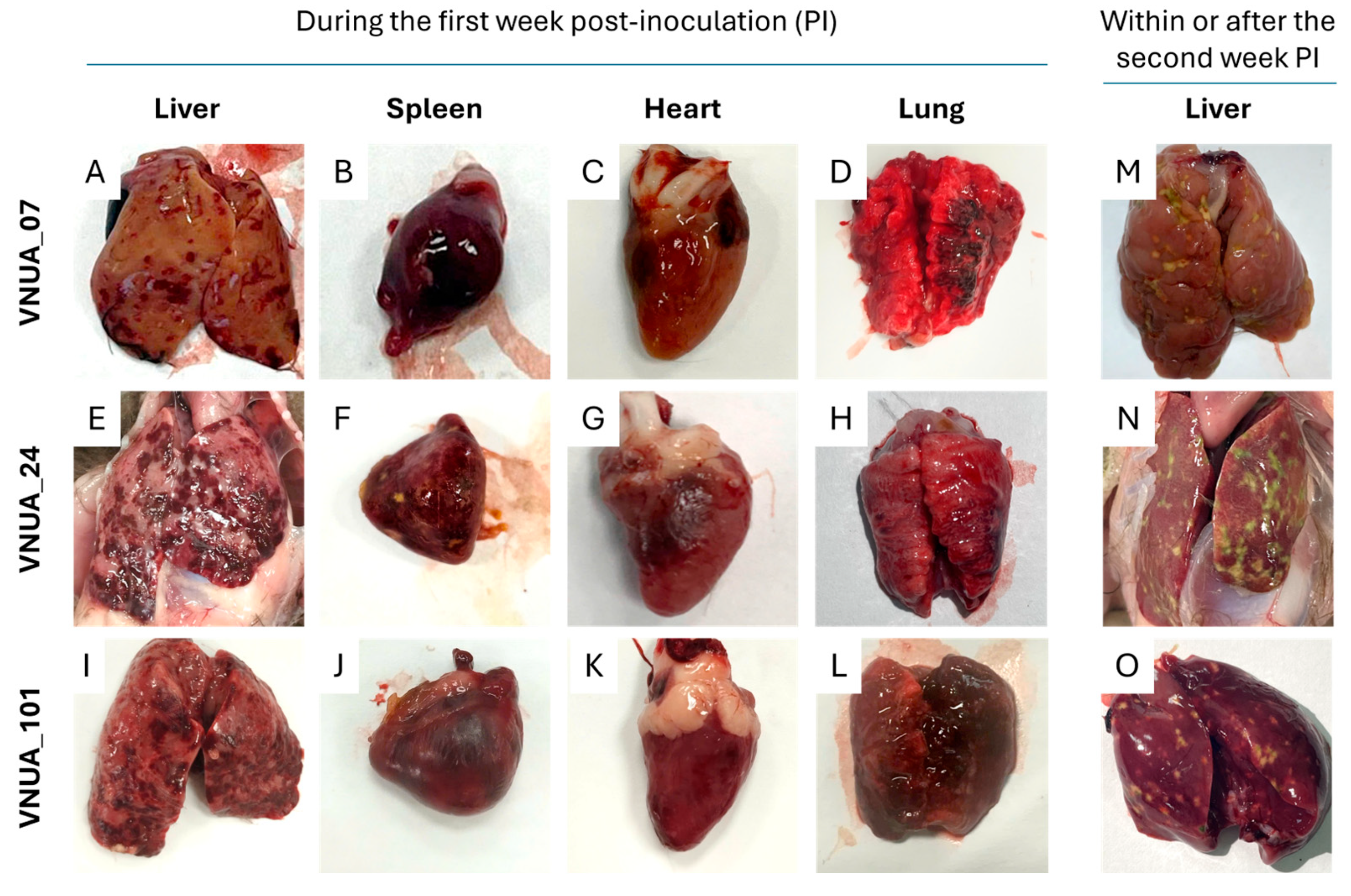
3.3. Pathogenicity in One-Day-Old Ducklings
3.4. Genetic Classification Based on the sC Gene
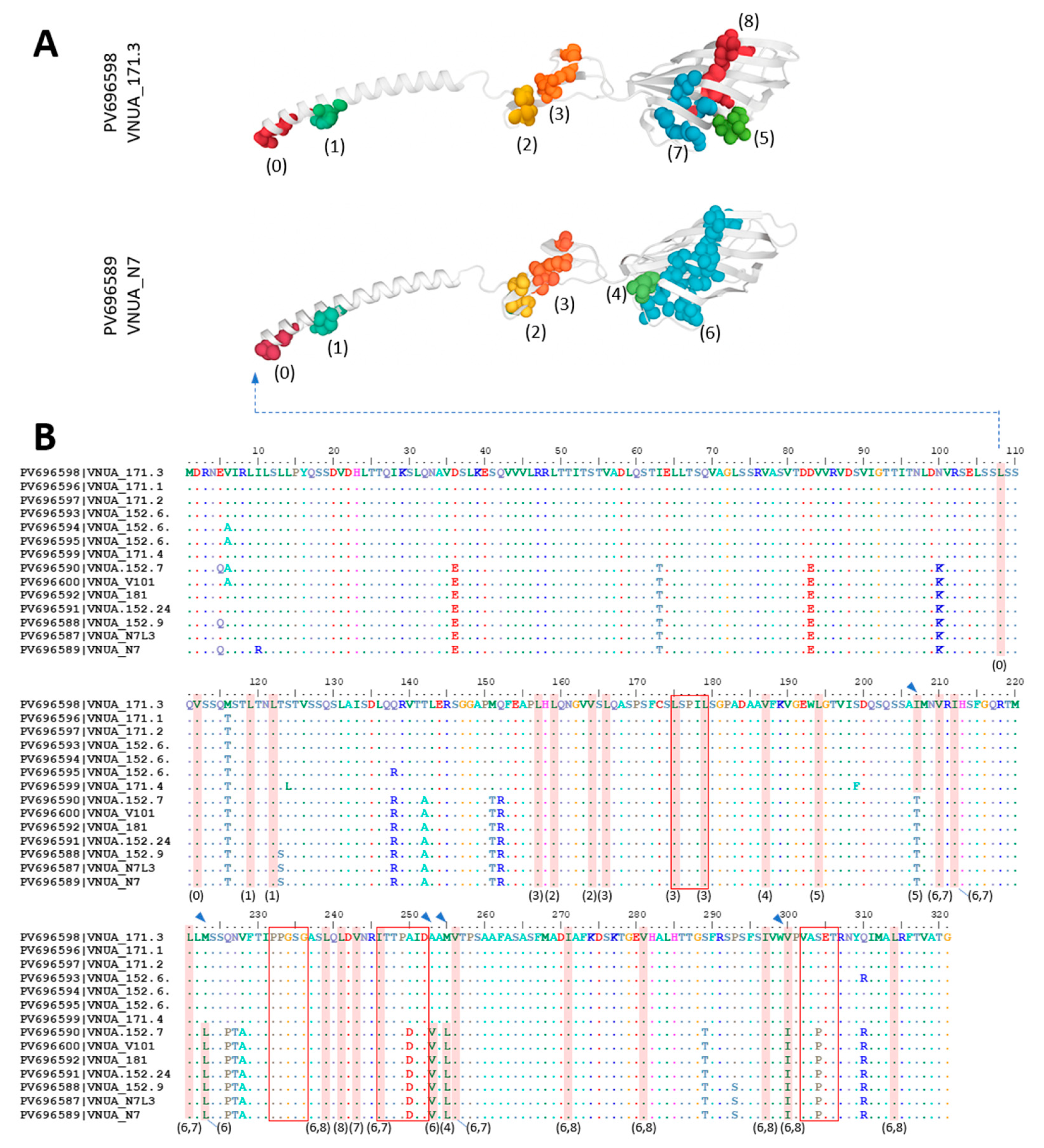
3.5. Characterization of the Amino Acid Sequence of the nWRSs’ sC Protein
3.6. Molecular Evolution of the nWRSs’ sC Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Forward /Reverse * | Sequences (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| nWRV-368F | TGAGACGCCTGACTACGATT | 368 | [44] |
| /nWRV-368R | ATGCTTGGAGTGAGACGACT |
| Forward /Reverse * | Sequences (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| DHAV1.714F | GCCCCACTCTATGGAAATTTG | 714 | [66] |
| /DHAV1.714R | ATTTGGTCAGATTCAATTTCC | ||
| DHAV3.720F | ATGCGAGTTGGTAAGGATTTTCAG | 720 | [66] |
| /DHAV3.720R | GATCCTGATTTACCAACAACCAT | ||
| AIV.147F | CTTCTAACCGAGGTCGAAACGTA | 147 | [67] |
| /AIV.147R | GGATTGGTCTTGTCTTTAGCCA | ||
| DTMUV.350F | TTTGGTACATGTGGCTCG | 350 | [68] |
| /DTMUV.350R | ACTGTTTTCCCATCACGTCC | ||
| DuCV.230F | ATGGCGAAGAGCGGCAACTAC | 230 | [69] |
| /DuCV.230R | TCAGTAGTTTATTGGGAACGG |
| Forward /Reverse * | Sequences (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| nWRV-sC1001F | ACGATGGATCGCAACGAGGTG | 1001 | [21] |
| /nWRV-sC1001R | GATGAATAGCTCTTCTCATYGC |
| Model | sC Gene | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of codons | 321 | |
| Omega (dN/dS) value | M1a | 0.255 |
| Likelihood logarithm (lnL) | M1a | −6290.59 |
| M2a | −6232.39 | |
| M7 | −6230.07 | |
| M8 | −6225.15 | |
| LRT | M2a vs. M1a | 116.40 ** |
| M8 vs. M7 | 9.85 ** |
References
- Malkinson, M.; Perk, K.; Weisman, Y. Reovirus infection of young Muscovy ducks (Cairina moschata). Avian Pathol. 1981, 10, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffels-Redmann, U.; Muller, H.; Kaleta, E.F. Structural and biological characteristics of reoviruses isolated from Muscovy ducks (Cairina moschata). Avian Pathol. 1992, 21, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palya, V.; Glavits, R.; Dobos-Kovacs, M.; Ivanics, E.; Nagy, E.; Banyai, K.; Reuter, G.; Szucs, G.; Dan, A.; Benko, M. Reovirus identified as cause of disease in young geese. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, T.; Ye, W.; Ni, Z.; Chen, L.; Yu, B.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Complete genomic sequence of goose-origin reovirus from China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, G. Outbreak-associated novel duck Reovirus, China, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Ren, G.; Chen, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, D.; Han, B.; Su, W.; Zhao, J.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a reovirus causing spleen necrosis in Pekin ducklings. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Li, Y.; Han, H.; Song, M.; Ma, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, B.; Li, F. Complete genome sequence of an avian reovirus isolated from wild mallard ducks in china. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00813-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniakowski, G.; Samorek-Salamonowicz, E.; Gawel, A. Occurrence of reovirus infection in Muscovy ducks (Cairina moschata) in south western Poland. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 17, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Hong, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K.; Cai, Y.; Liu, S.; Wei, L.; Chai, T. The pathogenicity of novel duck reovirus in Cherry Valley ducks. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 192, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Lu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Xu, H.; Mei, K.; Huang, S. Isolation and identification of a novel goose-origin reovirus GD218 and its pathogenicity experiments. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1423122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, D.; Ning, K.; Liang, T.; Wang, M.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, D. A duck reovirus variant with a unique deletion in the sigma C gene exhibiting high pathogenicity in Pekin ducklings. Virus Res. 2016, 215, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Guo, J.; Shen, J.; Guan, M.; Liu, L.; Xie, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Ren, A.; Li, W.; et al. Genetics and biological characteristics of duck reoviruses isolated from ducks and geese in China. Vet. Res. 2025, 56, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Shao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.; Feng, K.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Q. Molecular characterization, complete genome sequencing, and pathogenicity of Novel Duck Reovirus from South Coastal Area in China. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z. Isolation and characterization of a duck reovirus strain from mature ducks in China. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; He, W.; Su, J. Phenotypic and genetic characterisation of an emerging reovirus from Pekin ducks in China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, S.L.; Varga-Kugler, R.; Marton, S.; Lengyel, G.; Palya, V.; Banyai, K. Genomic sequence and phylogenetic analyses of two novel orthoreovirus strains isolated from Pekin ducks in 2014 in Germany. Virus Res. 2018, 257, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga-Kugler, R.; Marton, S.; Thuma, A.; Szentpali-Gavaller, K.; Balint, A.; Banyai, K. Candidate ‘Avian orthoreovirus B’: An emerging waterfowl pathogen in Europe and Asia? Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e3386–e3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Attoui, H.; Banyai, K.; Brussaard, C.P.D.; Danthi, P.; Del Vas, M.; Dermody, T.S.; Duncan, R.; Fang, Q.; Johne, R.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Spinareoviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, D. Complete sequence of a reovirus associated with necrotic focus formation in the liver and spleen of Muscovy ducklings. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Shao, J.W.; Li, X.W.; Mei, M.M.; Guo, J.Y.; Li, W.F.; Huang, W.J.; Chi, S.H.; Yuan, S.; Li, Z.L.; et al. Molecular characterization of two novel reoviruses isolated from Muscovy ducklings in Guangdong, China. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.; Yu, B.; Ni, Z.; Ye, W.; Chen, L.; Hua, J.; Zhang, C. Genomic characteristics of a novel reovirus from Muscovy duckling in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, J.M. The diversity of the orthoreoviruses: Molecular taxonomy and phylogentic divides. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banyai, K.; Palya, V.; Benko, M.; Bene, J.; Havasi, V.; Melegh, B.; Szucs, G. The goose reovirus genome segment encoding the minor outer capsid protein, sigma1/sigmaC, is bicistronic and shares structural similarities with its counterpart in Muscovy duck reovirus. Virus Genes 2005, 31, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntz-Simon, G.; Le Gall-Recule, G.; de Boisseson, C.; Jestin, V. Muscovy duck reovirus sigmaC protein is atypically encoded by the smallest genome segment. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Xu, F.; Ma, G.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, D. Complete genomic sequence of a new Muscovy duck-origin reovirus from China. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Costas, J.; Grande, A.; Varela, R.; Garcia-Martinez, C.; Benavente, J. Protein architecture of avian reovirus S1133 and identification of the cell attachment protein. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, R.; Meanger, J.; Enriquez, C.E.; Wilcox, G.E. Avian reovirus proteins associated with neutralization of virus infectivity. Virology 1993, 194, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, W.L.; Hsu, H.W.; Liao, M.H.; Lee, L.H.; Liu, H.J. Avian reovirus σC protein induces apoptosis in cultured cells. Virology 2004, 321, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Lee, L.H.; Hsu, H.W.; Kuo, L.C.; Liao, M.H. Molecular evolution of avian reovirus: Evidence for genetic diversity and reassortment of the S-class genome segments and multiple cocirculating lineages. Virology 2003, 314, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasserman, Y.; Eliahoo, D.; Hemsani, E.; Kass, N.; Ayali, G.; Pokamunski, S.; Pitcovskiad, J. The influence of reovirus sigma C protein diversity on vaccination efficiency. Avian Dis. 2004, 48, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelón, G.; Labrada, L.; Martínez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J. The Avian Reovirus Genome Segment S1 Is a Functionally Tricistronic Gene That Expresses One Structural and Two Nonstructural Proteins in Infected Cells. Virology 2001, 290, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gaspard, G.; McMullen, N.; Duncan, R. Polycistronic Genome Segment Evolution and Gain and Loss of FAST Protein Function during Fusogenic Orthoreovirus Speciation. Viruses 2020, 12, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Ding, M.; Wu, Q.; Li, C.H.; Guo, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, Z. Characterization of a P18 protein in the S1 segment of the novel duck reovirus genome. Acta Virol. 2020, 64, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandar, E.; Farkas, S.L.; Marton, S.; Oldal, M.; Jakab, F.; Mato, T.; Palya, V.; Banyai, K. The complete genome sequence of a European goose reovirus strain. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2165–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, S.L.; Dandár, E.; Marton, S.; Fehér, E.; Oldal, M.; Jakab, F.; Mató, T.; Palya, V.; Bányai, K. Detection of shared genes among Asian and European waterfowl reoviruses in the whole genome constellations. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 28, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J.; Li, L.; Kuang, R.; Sun, M.; Liao, M. Isolation and characterization of a new goose orthoreovirus causing liver and spleen focal necrosis in geese, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3028–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Liu, R.; Guo, J.; Mei, K.; Qin, L.; Li, Z.; Yuan, S.; Huang, S.; Wen, F. Identification, pathological, and genomic characterization of novel goose reovirus associated with liver necrosis in geese, China. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, F.; Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Xiao, S.; Zheng, M.; Huang, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, S. The genomic constellation of a novel duck reovirus strain associated with hemorrhagic necrotizing hepatitis and splenitis in Muscovy ducklings in Fujian, China. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 53, 101604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Liu, R.; Weng, L.; Li, K.; Qi, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Pan, Q.; et al. Genomic sequences and pathogenic characteristics of two variant duck reoviruses associated with spleen necrosis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 92, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Lv, Y.; Bian, C. Identification and molecular characterization of novel duck reoviruses in Henan Province, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1137967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Chen, H.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. Isolation and characterization of a variant duck orthoreovirus causing spleen necrosis in Peking ducks, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sabry, M.I.; Almasri, O. Global waterfowl production: Stocking rate is a key factor for improving productivity and well-being-a review. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Banerjee, R.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Patra, G.; Das, A.K.; Das, S.K. Technological investigation into duck meat and its products-A potential alternative to chicken. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2019, 75, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Dou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Preparation and evaluation of goose reovirus inactivated vaccine. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, X. On the Calculation of TCID(50) for Quantitation of Virus Infectivity. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, M.; Torrents, D.; Bork, P. PAL2NAL: Robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W609–W612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, J.N.; Høie, M.H.; Deleuran, S.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M.; Marcatili, P. BepiPred-3.0: Improved B-cell epitope prediction using protein language models. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, e4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Bui, H.H.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Bourne, P.E.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. ElliPro: A new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, H.R.; Islam, S.A.; David, A.; Sternberg, M.J.E. Phyre2.2: A Community Resource for Template-based Protein Structure Prediction. J. Mol. Biol. 2025, 437, 168960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruz, N.; Schmidt, S.; Höcker, B. ProteinTools: A toolkit to analyze protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W559–W566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savojardo, C.; Manfredi, M.; Martelli, P.L.; Casadio, R. DDGemb: Predicting protein stability change upon single- and multi-point variations with embeddings and deep learning. Bioinformatics 2025, 41, btaf019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Carretero, S.; Kapli, P.; Yang, Z. Beginner’s Guide on the Use of PAML to Detect Positive Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diller, J.R.; Halloran, S.R.; Koehler, M.; Natividade, R.d.S.; Alsteens, D.; Stehle, T.; Dermody, T.S.; Ogden, K.M. Reovirus σ1 Conformational Flexibility Modulates the Efficiency of Host Cell Attachment. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01163-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wen, F.; Guo, J.; Mei, K.; Huang, S.; Li, Z. Characterization and pathogenicity evaluation of recombinant novel duck reovirus isolated from Southeast China. Front. Veter. Sci. 2023, 10, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, T.; Kwiecinski, A.; Kwiecinski, P.; Tomczyk, G.; Wodz, K. Detection and Identification of Avian Reovirus in Young Geese (Anser anser domestica) in Poland. Animals 2022, 12, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liao, L.; Su, J.; Liu, Z.; Pan, S.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y. Interactions of Muscovy duck reovirus, gut microbiota, and host innate immunity: Transcriptome and gut microbiota analysis. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 264, 109286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Wang, A.; Zhu, S.; Wu, S. From obscurity to urgency: A comprehensive analysis of the rising threat of duck circovirus. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Fan, X.; Liu, N.; Miao, R.; Zhai, X.; Wei, L.; Jiao, P.; Jiang, S. Genetic characterization of novel duck reoviruses from Shandong Province, China in 2022. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Wu, Q.; Jia, W.; Zhang, J.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. Isolation and Pathogenicity Analysis of a Novel Orthoreovirus Caused the Outbreak of Duck Viral Arthritis in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2023, 2023, 8179312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, D.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Pirak, M.; Kass, N.; Lublin, A.; Yeheskel, A.; Heller, D.; Pitcovski, J. Genetic and antigenic characterization of sigma C protein from avian reovirus. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R.; Goldman, N.; Pedersen, A.-M.K. Codon-Substitution Models for Heterogeneous Selection Pressure at Amino Acid Sites. Genetics 2000, 155, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, H.T.; Le, X.T.; Do, R.T.; Hoang, C.T.; Nguyen, K.T.; Le, T.H. Molecular genotyping of duck hepatitis A viruses (DHAV) in Vietnam. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Trani, L.; Bedini, B.; Donatelli, I.; Campitelli, L.; Chiappini, B.; De Marco, M.A.; Delogu, M.; Buonavoglia, C.; Vaccari, G. A sensitive one-step real-time PCR for detection of avian influenza viruses using a MGB probe and an internal positive control. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Yin, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. Adapted Tembusu-like virus in chickens and geese in China. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2807–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fringuelli, E.; Scott, A.N.; Beckett, A.; McKillen, J.; Smyth, J.A.; Palya, V.; Glavits, R.; Ivanics, E.; Mankertz, A.; Franciosini, M.P.; et al. Diagnosis of duck circovirus infections by conventional and real-time polymerase chain reaction tests. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vu, T.-N.; Le, V.-T.; Cao, T.-B.-P.; Nguyen, V.-G.; Huynh, T.-M.-L. Novel Reoviruses of Waterfowl Origin in Northern Vietnam: A Laboratory Investigation. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080187
Vu T-N, Le V-T, Cao T-B-P, Nguyen V-G, Huynh T-M-L. Novel Reoviruses of Waterfowl Origin in Northern Vietnam: A Laboratory Investigation. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(8):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080187
Chicago/Turabian StyleVu, Thi-Ngoc, Van-Truong Le, Thi-Bich-Phuong Cao, Van-Giap Nguyen, and Thi-My-Le Huynh. 2025. "Novel Reoviruses of Waterfowl Origin in Northern Vietnam: A Laboratory Investigation" Microbiology Research 16, no. 8: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080187
APA StyleVu, T.-N., Le, V.-T., Cao, T.-B.-P., Nguyen, V.-G., & Huynh, T.-M.-L. (2025). Novel Reoviruses of Waterfowl Origin in Northern Vietnam: A Laboratory Investigation. Microbiology Research, 16(8), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080187





