AiiA Lactonase Suppresses ETEC Pathogenicity Through 3OC12-HSL Quenching in a Murine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Growth Kinetics and Gene Expression Analysis
2.3. In Vitro Polymicrobial Culture Model
2.4. Mouse Experiments
2.5. Histopathology and Apoptosis Assays
2.6. ELISA and Barrier Function Markers
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
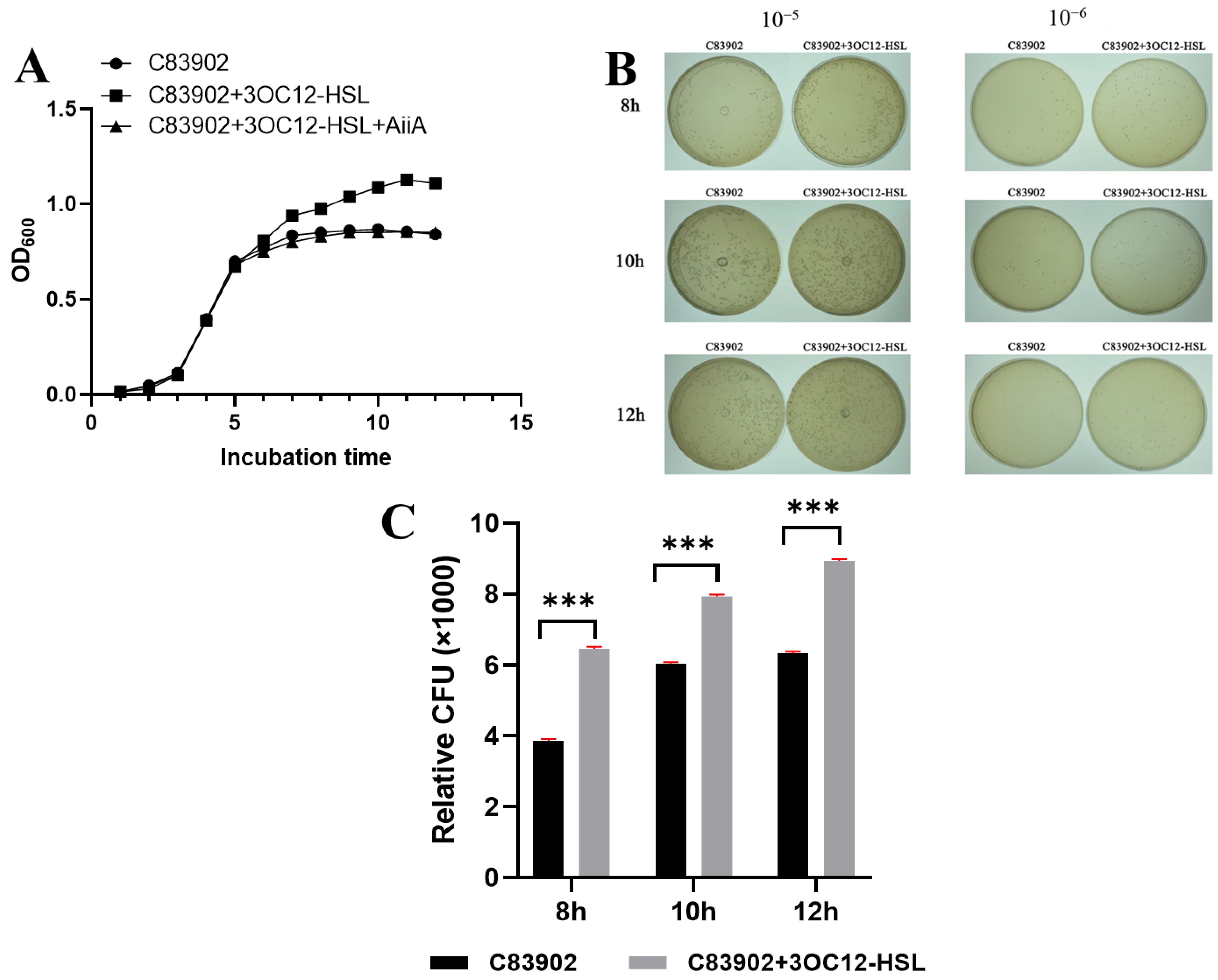
3.1. AiiA Reverses Quorum-Sensing Induced Growth Stimulation in ETEC
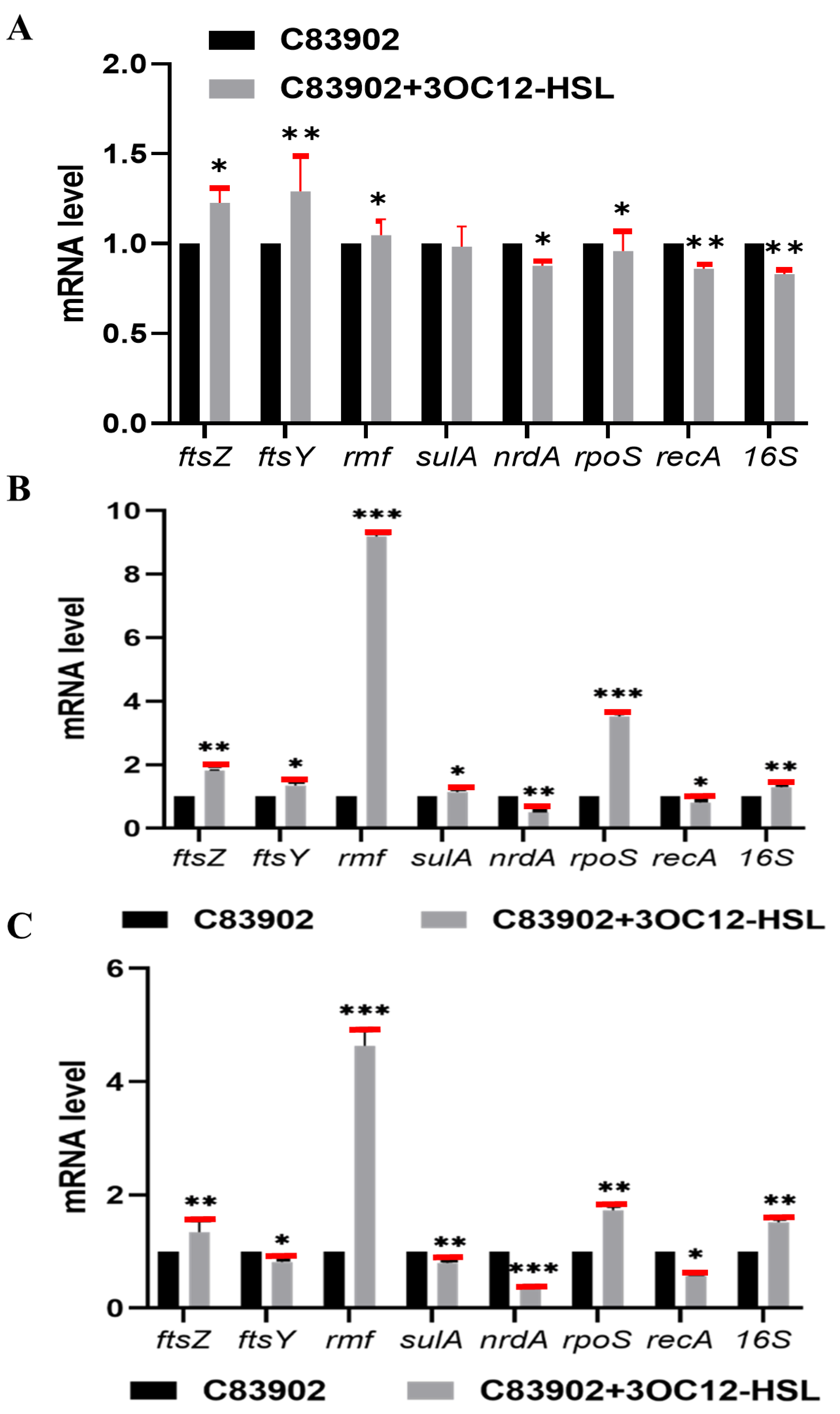
3.2. 3OC12-HSL Modulates Key Gene Transcription in Diverse Growth Conditions
3.3. 3OC12-HSL Specifically Enhances E. coli in a Simulated Gut Microbiota Model
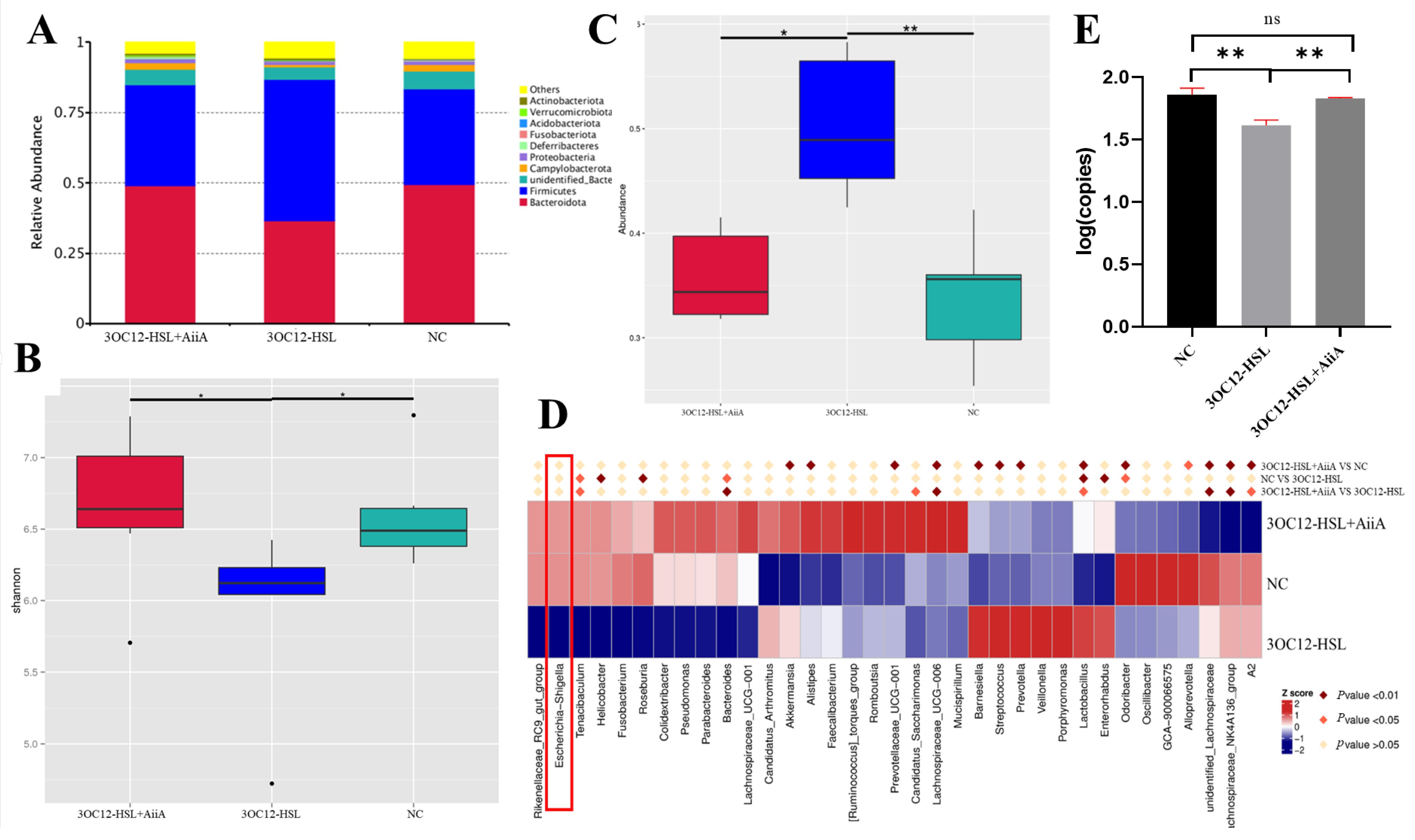
3.4. AiiA Enzyme Reverses 3OC12-HSL-Induced Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Mice
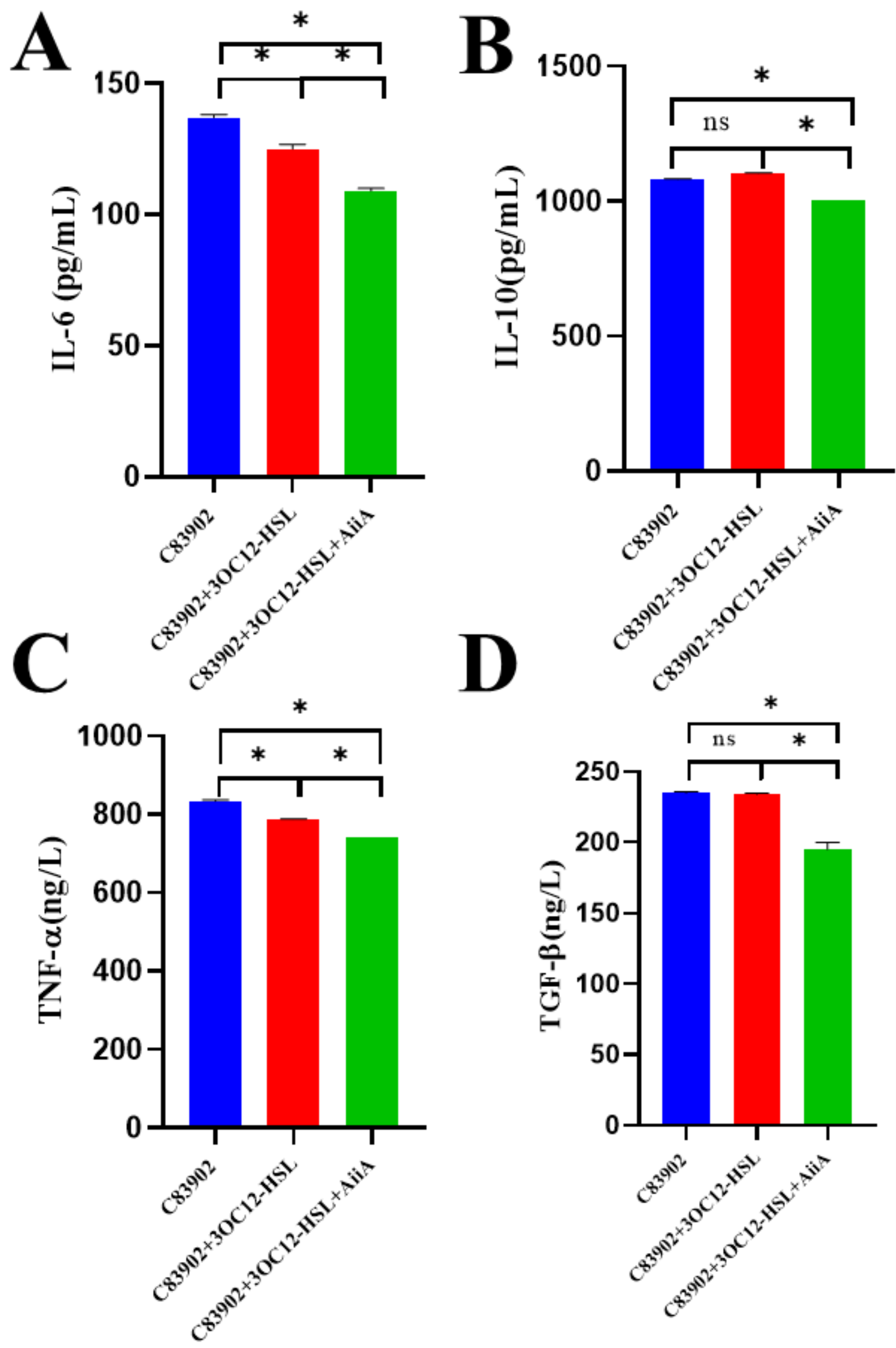
3.5. AiiA Modulates 3OC12-HSL-Induced Serum Cytokine Profiles in Mice
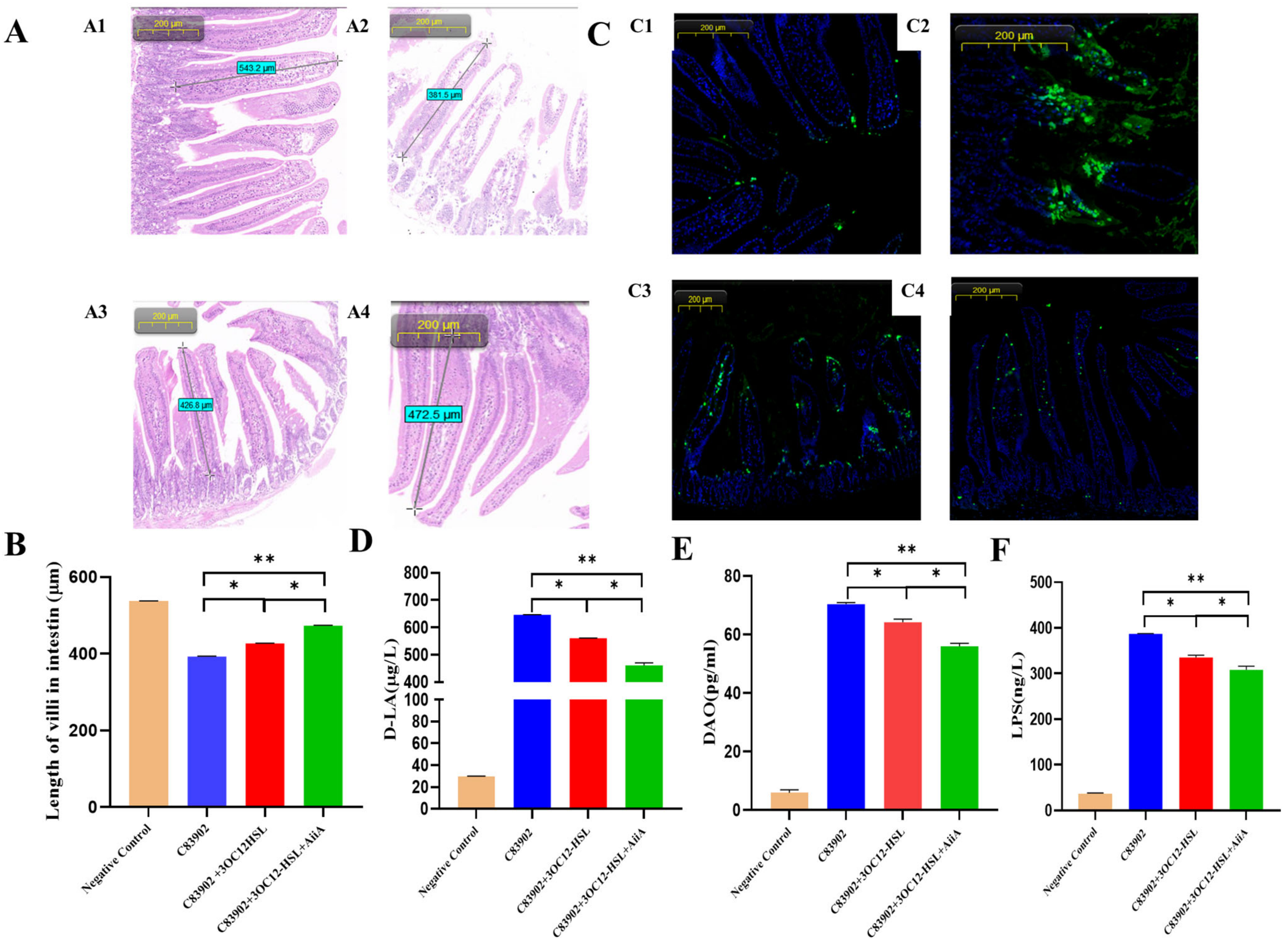
3.6. Synergistic Enhancement of Intestinal Recovery by AiiA and 3OC12-HSL in ETEC-Infected Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.; Blacker, B.F.; Rao, P.C.; Brown, A.; Atherly, D.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Engmann, C.M.; Houpt, E.R.; Kang, G.; et al. Morbidity and mortality due to shigella and enterotoxigenic escherichia coli diarrhoea: The global burden of disease study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.; Anderson, J.D.; Bagamian, K.H.; Baqar, S.; Giersing, B.; Hausdorff, W.P.; Marshall, C.; Porter, C.K.; Walker, R.I.; Bourgeois, A.L. Vaccine value profile for enterotoxigenic escherichia coli (ETEC). Vaccine 2023, 41, S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Park, B.C.; Han, J.H. Effects of dietary supplementation of bacteriophages against enterotoxigenic escherichia coli (ETEC) k88 on clinical symptoms of post-weaning pigs challenged with the ETEC pathogen. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondakindi, V.R.; Nalam, R.S.S.; Pabbati, R.; Maddela, N.R. Quorum quenching a sustainable biofilm mitigation strategy. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 17, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, R.; Elias, M. Quorum quenching enzymes and their effects on virulence, biofilm, and microbiomes: A review of recent advances. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmati, F.; Salehi, R.; Ghotaslou, R.; Samadi, K.H.; Hasani, A.; Gholizadeh, P.; Nouri, R.; Ahangarzadeh, R.M. Quorum quenching: A potential target for antipseudomonal therapy. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Yoshida, K.; Ikegame, M.; Okamura, H. Quorum sensing molecule n-(3-oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone: An all-rounder in mammalian cell modification. J. Oral Biosci. 2020, 62, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Yadav, D.K.; Bisht, S.C.; Yadav, N.; Singh, V.; Dubey, K.K.; Jawed, A.; Wahid, M.; Dar, S.A. Quorum sensing pathways in gram-positive and -negative bacteria: Potential of their interruption in abating drug resistance. J. Chemother. 2019, 31, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Fratamico, P.M.; Yan, X. Eavesdropping by bacteria: The role of SdiA in escherichia coli and salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium quorum sensing. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieters, A.; Ahmer, B. Role of the LuxR solo, SdiA, in eavesdropping on foreign bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 49, fuaf015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Chai, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Intestinal mucus components and secretion mechanisms: What we do and do not know. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Song, R.; Meng, C.; Zhu, G. N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-homoserine lactone induces intestinal barrier damage in piglets via the lipid raft-mediated apoptosis pathway. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Xiao, Q.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, W.; Long, Y.; Zheng, D.; Huang, B.; et al. SdiA improves the acid tolerance of e. Coli by regulating GadW and GadY expression. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Y.; Nguyen, N.X.; Rogers, J.L.; Liao, J.; MacMillan, J.B.; Jiang, Y.; Sperandio, V. Structural and mechanistic roles of novel chemical ligands on the SdiA quorum-sensing transcription regulator. mBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lou, W.; Liu, F. Transcriptomics analysis of the role of SdiA in desiccation tolerance of cronobacter sakazakii in powdered infant formula. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 426, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, P.; Tang, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Zhu, G. Intestinal microbiota mediates enterotoxigenic escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in piglets. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Yin, J.; Xiao, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, G.; Tan, B.; Li, N.; Peng, Y.; Li, T.; Zeng, B.; et al. Intestinal microbiota-derived GABA mediates interleukin-17 expression during enterotoxigenic escherichia coli infection. Front. Immunol. 2017, 7, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturbelle, R.T.; de Avila, L.F.D.C.; Roos, T.B.; Borchardt, J.L.; Da Conceicao, R.D.C.D.; Dellagostin, O.A.; Leite, F.P.L. The role of quorum sensing in escherichia coli (ETEC) virulence factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Ye, C. Dihydromyricetin alleviates ETEC k88-induced intestinal inflammatory injury by inhibiting quorum sensing-related virulence factors. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, A.D.R.; Martins, M.L.; de Araujo, E.F.; Mantovani, H.C.; Vanetti, M.C.D. AiiA quorum-sensing quenching controls proteolytic activity and biofilm formation by enterobacter cloacae. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 758. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ou, J. Targeting n-acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) on the quorum quenching AiiA protein to eradicate biofilm formation in vibrio parahaemolyticus. CyTA-J. Food 2024, 22, 2383763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhou, M.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, G. Effects of quorum sensing AHL signaling on the biological characteristics of porcine derived f4ac+ enterotoxigenic escherichia coli. Pak. J. Zool. 2022, 54, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bao, W.; Wu, S.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G. Flagella from f18+escherichia coli play a role in adhesion to pig epithelial cell lines. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 55, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Duan, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Zhu, G. Membrane cholesterol plays an important role in enteropathogen adhesion and the activation of innate immunity via flagellin-TLR5 signaling. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Xia, P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhu, G. RyhB paralogs downregulate the expressions of multiple survival-associated genes and attenuate the survival of salmonella enteritidis in the chicken macrophage HD11. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassall, J.; Cheng, J.K.J.; Unnikrishnan, M. Erratum for Hassall et al., “Dissecting individual interactions between pathogenic and commensal bacteria within a multispecies gut microbial community”. mSphere 2024, 9, e0089324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videnska, P.; Smerkova, K.; Zwinsova, B.; Popovici, V.; Micenkova, L.; Sedlar, K.; Budinska, E. Stool sampling and DNA isolation kits affect DNA quality and bacterial composition following 16s rRNA gene sequencing using MiSeq illumina platform. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, J.; Pelckmann, L.; Drewes, B. Preservation and Processing of Intestinal Tissue for the Assessment of Histopathology; Nagamoto-Combs, K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; p. 267. [Google Scholar]
- Patankar, J.V.; Becker, C. Cell death in the gut epithelium and implications for chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilev, G.; Manolova, I.; Ivanova, M.; Stanilov, I.; Miteva, L.; Stanilova, S. The role of IL-18 in addition to th17 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis development and treatment in women. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillet, S.; Hamdallah, I.; Majdalani, N.; Tripathi, A.; Gottesman, S. A negative feedback loop is critical for recovery of RpoS after stress in escherichia coli. PLoS Genet. 2024, 20, e1011059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellhorn, H.E. Function, evolution, and composition of the RpoS regulon in escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 560099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.H.; King, C.G.; Wingreen, N.S.; Gitai, Z.; Li, Z. Global and gene-specific translational regulation in escherichia coli across different conditions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1010641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izutsu, K.; Wada, A.; Wada, C. Expression of ribosome modulation factor (RMF) in escherichia coli requires ppgpp. Genes Cells 2001, 6, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usachev, K.S.; Yusupov, M.M.; Validov, S.Z. Hibernation as a stage of ribosome functioning. Biochem.-Mosc. 2020, 85, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikanov, Y.S.; Blaha, G.M.; Steitz, T.A. How hibernation factors RMF, HPF, and YfiA turn off protein synthesis. Science 2012, 336, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaova, E.A.; Kashevarova, N.M.; Tkachenko, A.G. Ribosome hibernation: Molecular strategy of bacterial survival (review). Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2022, 58, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasan, M.M.; Holsken, O.; Duerr, C.; Helfrich, S.; Branzk, N.; Philipp, A.; Leitz, D.; Duerr, J.; Almousa, Y.; Barrientos, G.; et al. Antibiotic use during pregnancy is linked to offspring gut microbial dysbiosis, barrier disruption, and altered immunity along the gut-lung axis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2350394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, T.S.; De Nys, R.; Netting, A.; Kumar, N.; Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M.; Kjelleberg, S. A novel and sensitive method for the quantification of n-3-oxoacyl homoserine lactones using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: Application to a model bacterial biofilm. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 2, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primers | Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| ftsZ-RT-F | CAGTCGTCGCTGAAGTGG |
| ftsZ-RT-R | TTTGTCGTTCGGGATAGTG |
| ftsY-RT-F | ACGAAACTGGACGGCAC |
| ftsY-RT-R | GACGCAAATCCTCAATACG |
| rmF-RT-F | CTGGAACGGGCACATCAAC |
| rmF-RT-R | TTACTACCCTGTCCGCCATG |
| sulA-RT-F | CTTCGTCGTTCTCAT CCG |
| sulA-RT-R | TGCTGACCGAGTTGCTGT |
| nrdA-RT-F | GATGGACACCTTTATCGA |
| nrdA-RT-R | GTACCAGATATTTGCCTTC |
| rpoS-RT-F | ACGATATGAAGCAGAGCATCGT |
| rpoS-RT-R | AGGCCAATTTCACGACCTACAT |
| 16S-RT-F | CGTGCTACAATGGACAATACAAA |
| 16S-RT-R | ATCTACGATTACTAGCGATTCCA |
| recA-RT-F | TGGCGGGTAACCTGAAGCA |
| recA-RT-R | CGAGACGAACAGAG GCGTAGAAT |
| 16s-BA-F | TCGCGTCCGGTGTGAAAG |
| 16s-BA-R | CCACATCCAGCATCCAC |
| 16s-Efm-F | CCCTTATTGTTAGTTGCCATCATT |
| 16s-Efm-R | ACTCGTTGTACTTCCCATTGT |
| 16s-BF-F | GAAAGCATTAAGTATTCCACCTG |
| 16s-BF-R | CGGTGATTGGTCACTGACA |
| 16s-E.coli-F | GTTAATACCTTTGCTCATTGA |
| 16s-E.coli-R | ACCAGGGTATCTAATCCTGTT |
| Intestinal Bacteria | 6 h | 12 h | 18 h | 24 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No AHL | AHL | No AHL | AHL | No AHL | AHL | No AHL | AHL | |
| E. coli | 4.29 | 4.39 | 4.42 | 4.63 | 4.52 | 4.66 | 4.68 | 4.86 |
| Enterococcus faecium | 3.74 | 3.41 | 3.77 | 3.45 | 3.92 | 3.58 | 3.93 | 3.78 |
| Bacteroides fragilis | 7.24 | 7.54 | 7.39 | 7.69 | 7.58 | 7.73 | 7.66 | 7.81 |
| Bifidobacterium | 5.94 | 6.28 | 6.09 | 6.35 | 6.14 | 6.45 | 6.30 | 6.59 |
| Taxonomy | NC | 3OC12-HSL | 3OC12-HSL+AiiA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus_murinus | 4.13% | 21.38% | 12.53% |
| Bacteroides_gallinaceum | 1.16% | 2.65% | 5.26% |
| Lactobacillus_reuteri | 0.46% | 1.57% | 1.34% |
| Clostridium_sp_Culture-27 | 1.45% | 0.91% | 0.11% |
| Helicobacter_typhlonius | 0.82% | 0.33% | 0.46% |
| Bacteroides_acidifaciens | 0.21% | 0.38% | 0.72% |
| Helicobacter_hepaticus | 0.67% | 0.24% | 0.31% |
| Romboutsia_ilealis | 0.11% | 0.21% | 0.52% |
| Escherichia_coli | 0.28% | 0.02% | 0.28% |
| Akkermansia_muciniphila | 0.00% | 0.18% | 0.27% |
| Others | 90.72% | 70.32% | 78.21% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Shao, J.; Han, Z.; Li, J.; Fang, Q.; Zhu, G. AiiA Lactonase Suppresses ETEC Pathogenicity Through 3OC12-HSL Quenching in a Murine Model. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080166
Yang Y, Shao J, Han Z, Li J, Fang Q, Zhu G. AiiA Lactonase Suppresses ETEC Pathogenicity Through 3OC12-HSL Quenching in a Murine Model. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(8):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080166
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Ji Shao, Zixin Han, Junpeng Li, Qiaoqiao Fang, and Guoqiang Zhu. 2025. "AiiA Lactonase Suppresses ETEC Pathogenicity Through 3OC12-HSL Quenching in a Murine Model" Microbiology Research 16, no. 8: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080166
APA StyleYang, Y., Shao, J., Han, Z., Li, J., Fang, Q., & Zhu, G. (2025). AiiA Lactonase Suppresses ETEC Pathogenicity Through 3OC12-HSL Quenching in a Murine Model. Microbiology Research, 16(8), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16080166






