In Utero Exposure to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin Impairs the Ability of Mice to Clear a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Adulthood
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Mouse Model of Toxicant Exposure
2.4. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Intraperitoneal (i.p.) Infection Model
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Cytokine Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethical Approval
3. Results
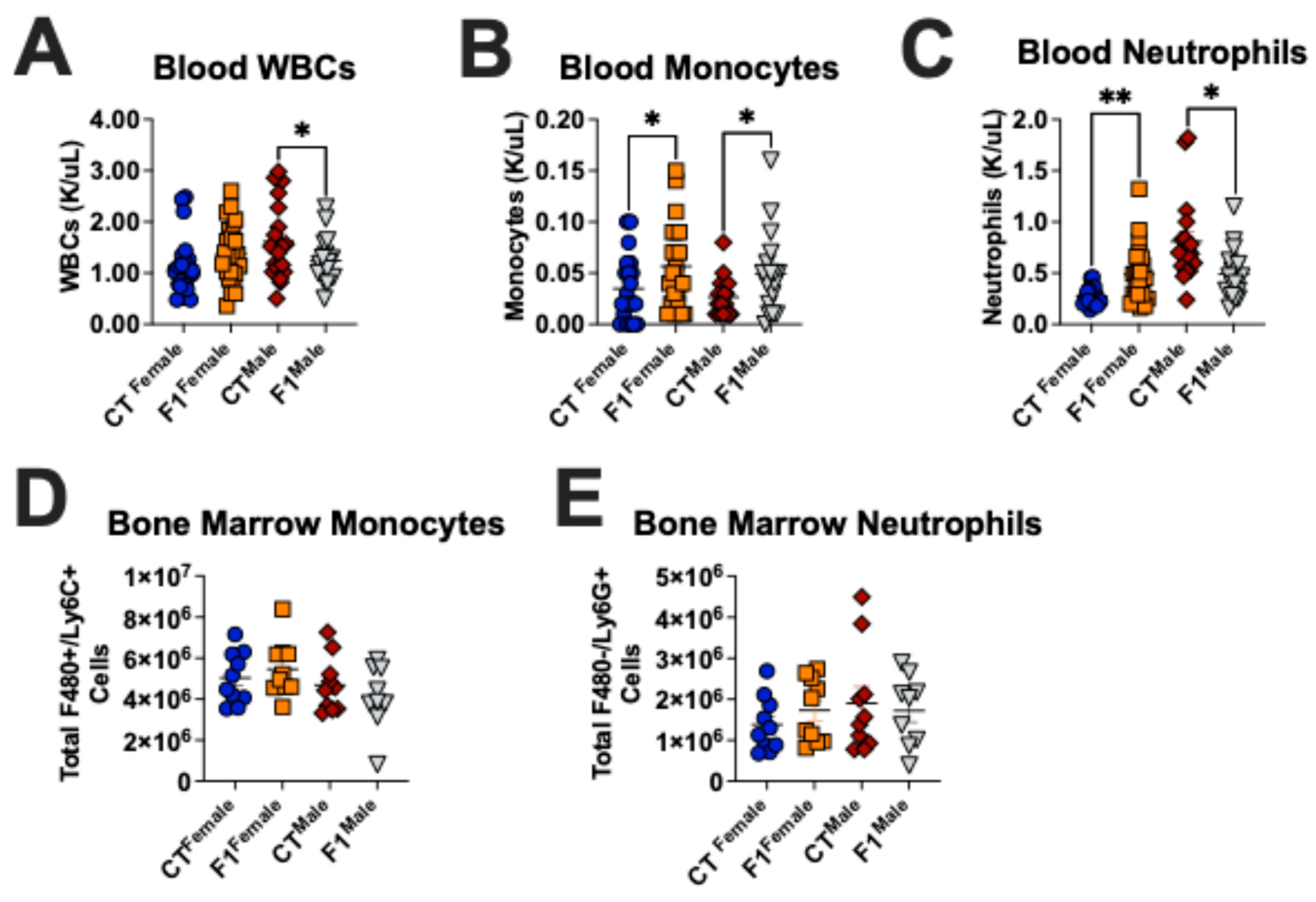
3.1. Prenatal TCDD Exposure Alters the Immune Cell Composition in Adult Mice
3.2. Prenatal TCDD Exposure Exacerbates Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Adult Mice
3.3. Prenatal TCDD Exposure Stunts Innate Immune Cell Recruitment During Infection in Adult Mice
3.4. Prenatal TCDD Exposure Alters Cytokine Production in Adult Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruner-Tran, K.L.; Osteen, K.G. Developmental exposure to TCDD reduces fertility and negatively affects pregnancy outcomes across multiple generations. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruner-Tran, K.L.; Duleba, A.J.; Taylor, H.S.; Osteen, K.G. Developmental Toxicant Exposure Is Associated with Transgenerational Adenomyosis in a Murine Model. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 95, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegoke, E.O.; Rahman, M.S.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.J.; Pang, M.-G. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Infectious Diseases: From Endocrine Disruption to Immunosuppression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajta, M.; Wójtowicz, A.K. Impact of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on neural development and the onset of neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalou, O.; Kandaraki, E.A.; Papadakis, G.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: An Occult Mediator of Metabolic Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, K.; Devaskar, S.U. Fetal origins of adult disease. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2011, 41, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J. The developmental origins of adult disease. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23 (Suppl. 6), 588s–595s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-León, P. Are the Effects of DES Over? A Tragic Lesson from the Past. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Ismail, Z.; Selamat, M.I.; Sheikh Abdul Kadir, S.H.; Shibraumalisi, N.A. A Review of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Pollution in the Air: Where and How Much Are We Exposed to? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Warren, S.H.; Kooter, I.; Williams, W.C.; George, I.J.; Vance, S.A.; Hays, M.D.; Higuchi, M.A.; Gavett, S.H.; DeMarini, D.M.; et al. Chemistry, lung toxicity and mutagenicity of burn pit smoke-related particulate matter. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurell, J.; Gullett, B.K.; Yamamoto, D. Emissions from open burning of simulated military waste from forward operating bases. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11004–11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokshagundam, S.; Ding, T.; Rumph, J.T.; Dallas, M.; Stephens, V.R.; Osteen, K.G.; Bruner-Tran, K.L. Developmental 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure of either parent enhances the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonatal mice. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayyar, T.; Bruner-Tran, K.L.; Piestrzeniewicz-Ulanska, D.; Osteen, K.G. Developmental exposure of mice to TCDD elicits a similar uterine phenotype in adult animals as observed in women with endometriosis. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 23, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumph, J.T.; Rayford, K.J.; Stephens, V.R.; Ameli, S.; Nde, P.N.; Osteen, K.G.; Bruner-Tran, K.L. A Preconception Paternal Fish Oil Diet Prevents Toxicant-Driven New Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Neonatal Mice. Toxics 2021, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumph, J.T.; Stephens, V.R.; Ameli, S.; Brown, L.K.; Rayford, K.J.; Nde, P.N.; Osteen, K.G.; Bruner-Tran, K.L. A Paternal Fish Oil Diet Preconception Reduces Lung Inflammation in a Toxicant-Driven Murine Model of New Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, C.M.; Myers, J.R.; Winans, B.; Lawrence, B.P. Postnatal administration of S-adenosylmethionine restores developmental AHR activation-induced deficits in CD8+ T cell function during influenza A virus infection. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 192, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.B.; Kerkvliet, N.I. Dioxin and immune regulation: Emerging role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the generation of regulatory T cells. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2010, 1183, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustowska, K.; Gregoraszczuk, E.E.; Grochowalski, A.; Milewicz, T.; Mika, M.; Krzysiek, J.; Chrzaszcz, R. Comparison of accumulation and altered steroid secretion by placental tissue treated with TCDD and natural mixture of PCDDs-PCDFs. Reproduction 2003, 126, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.D.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Diliberto, J.J. Rapid distribution of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) to embryonic tissues in C57BL/6N mice and correlation with palatal uptake in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 141, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingrich, J.; Ticiani, E.; Veiga-Lopez, A. Placenta Disrupted: Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Pregnancy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.X.; Chen, L.; Meng, X.Z.; Chen, B.H.; Chen, S.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.F.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Exposure levels of environmental endocrine disruptors in mother-newborn pairs in China and their placental transfer characteristics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Chang, C.C.; Shen, Y.J.; Hung, J.H.; Guo, B.R.; Chuang, H.Y.; Mao, I.F. Quantification of prenatal exposure and maternal-fetal transfer of nonylphenol. Chemosphere 2008, 73 (Suppl. 6), S239–S245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingrich, J.; Pu, Y.; Ehrhardt, R.; Karthikraj, R.; Kannan, K.; Veiga-Lopez, A. Toxicokinetics of bisphenol A, bisphenol S, and bisphenol F in a pregnancy sheep model. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabic, D.; Koenig, J.M. A perfect storm: Fetal inflammation and the developing immune system. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostol, A.C.; Jensen, K.D.C.; Beaudin, A.E. Training the Fetal Immune System Through Maternal Inflammation—A Layered Hygiene Hypothesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassado Ados, A.; D’Império Lima, M.R.; Bortoluci, K.R. Revisiting mouse peritoneal macrophages: Heterogeneity, development, and function. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardavín, C.; Alvarez-Ladrón, N.; Ferriz, M.; Gutiérrez-González, A.; Vega-Pérez, A. Mouse Tissue-Resident Peritoneal Macrophages in Homeostasis, Repair, Infection, and Tumor Metastasis. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 2023, 10, e2206617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, M.A.; Caja, K.R.; Patil, T.K.; Owen, A.M.; Luan, L.; Bohannon, J.K.; Hernandez, A.; Stothers, C.L.; Trenary, I.A.; Rahim, M.; et al. Immunoresponsive gene 1 facilitates TLR4 agonist-induced augmentation of innate antimicrobial immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2025, 117, qiae198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallaire, F.; Dewailly, E.; Vézina, C.; Muckle, G.; Weber, J.P.; Bruneau, S.; Ayotte, P. Effect of prenatal exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls on incidence of acute respiratory infections in preschool Inuit children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stølevik, S.B.; Nygaard, U.C.; Namork, E.; Haugen, M.; Kvalem, H.E.; Meltzer, H.M.; Alexander, J.; van Delft, J.H.; Loveren, H.; Løvik, M.; et al. Prenatal exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and dioxins is associated with increased risk of wheeze and infections in infants. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, V.R.; Moore, R.E.; Spicer, S.K.; Talbert, J.A.; Lu, J.; Chinni, R.; Chambers, S.A.; Townsend, S.D.; Manning, S.D.; Rogers, L.M.; et al. Environmental Toxicant Exposure Paralyzes Human Placental Macrophage Responses to Microbial Threat. ACS Infect. Dis. 2023, 9, 2401–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Acosta, O.; Vega, L.; Estrada-Muñiz, E.; Rodríguez, M.S.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Elizondo, G. Activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates the LPS/IFNγ-induced inflammatory response by inducing ubiquitin-proteosomal and lysosomal degradation of RelA/p65. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorito, F.; Santamaria, R.; Irace, C.; De Martino, L.; Iovane, G. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and the viral infection. Environ. Res. 2017, 153, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.L.; Martin, K.C.; Resseguie, E.; Lawrence, B.P. Differential consequences of two distinct AhR ligands on innate and adaptive immune responses to influenza A virus. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 137, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, C.E.; Funatake, C.J.; Kerkvliet, N.I. 2,3,7,8 Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin (TCDD) Directly Enhances the Maturation and Apoptosis of Dendritic Cells In Vitro. J. Immunotoxicol. 2005, 1, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorderstrasse, B.A.; Kerkvliet, N.I. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin affects the number and function of murine splenic dendritic cells and their expression of accessory molecules. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 171, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simones, T.; Shepherd, D.M. Consequences of AhR activation in steady-state dendritic cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 119, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stephens, V.R.; Bohannon, J.K.; Bruner-Tran, K.L.; Davis, X.D.; Oliver, M.A.; McBride, M.A.; Ameli, S.; Rumph, J.T.; Gaddy, J.A.; Sherwood, E.R.; et al. In Utero Exposure to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin Impairs the Ability of Mice to Clear a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Adulthood. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16050091
Stephens VR, Bohannon JK, Bruner-Tran KL, Davis XD, Oliver MA, McBride MA, Ameli S, Rumph JT, Gaddy JA, Sherwood ER, et al. In Utero Exposure to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin Impairs the Ability of Mice to Clear a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Adulthood. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(5):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16050091
Chicago/Turabian StyleStephens, Victoria R., Julia K. Bohannon, Kaylon L. Bruner-Tran, Xenia D. Davis, Mary A. Oliver, Margaret A. McBride, Sharareh Ameli, Jelonia T. Rumph, Jennifer A. Gaddy, Edward R. Sherwood, and et al. 2025. "In Utero Exposure to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin Impairs the Ability of Mice to Clear a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Adulthood" Microbiology Research 16, no. 5: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16050091
APA StyleStephens, V. R., Bohannon, J. K., Bruner-Tran, K. L., Davis, X. D., Oliver, M. A., McBride, M. A., Ameli, S., Rumph, J. T., Gaddy, J. A., Sherwood, E. R., & Osteen, K. G. (2025). In Utero Exposure to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin Impairs the Ability of Mice to Clear a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Adulthood. Microbiology Research, 16(5), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16050091







