Influence of Milking Process and Production System on Raw Goat Milk Bacteriome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin of Biological Material
2.2. Bacteriome Sequencing
2.3. Diversity Analysis
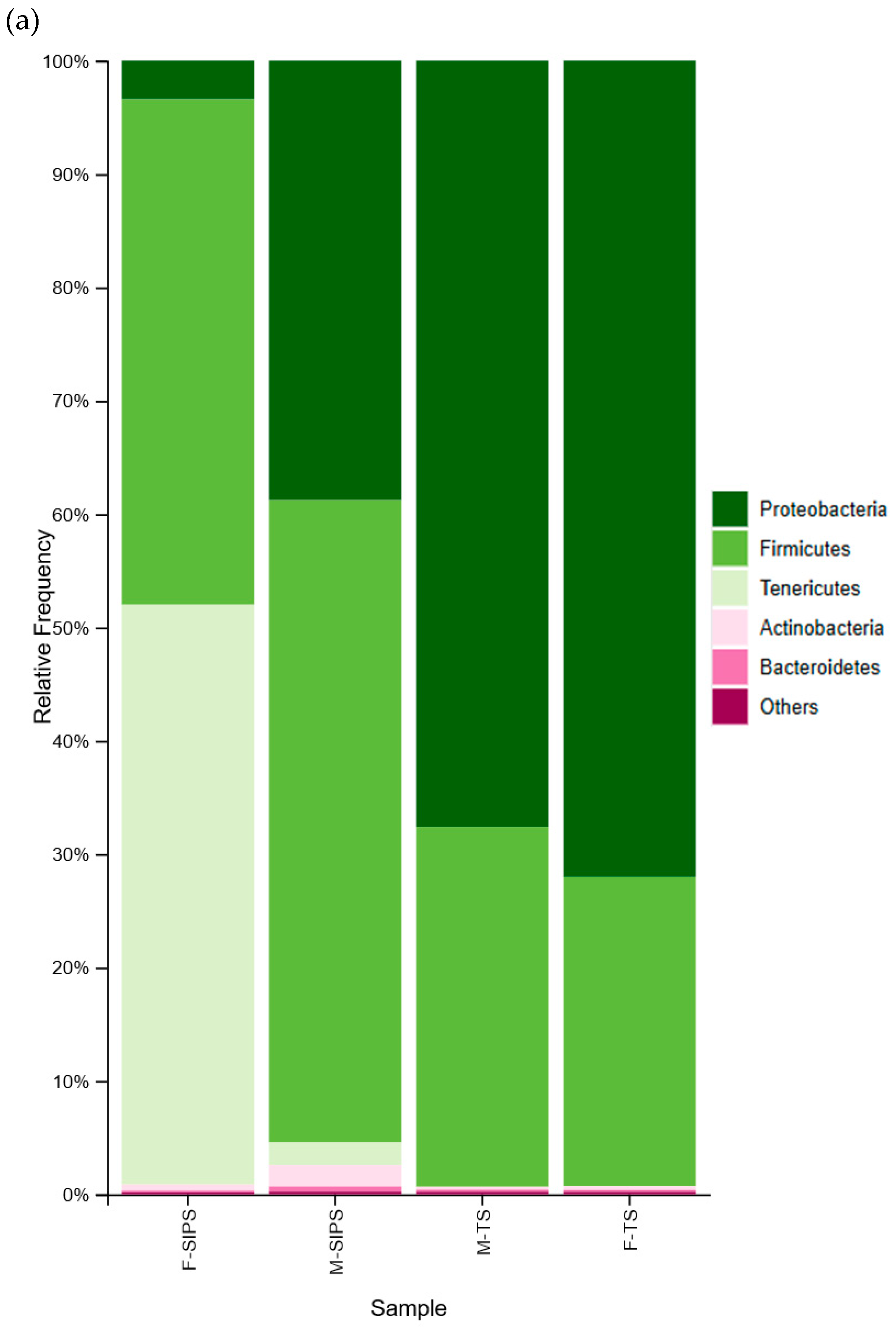
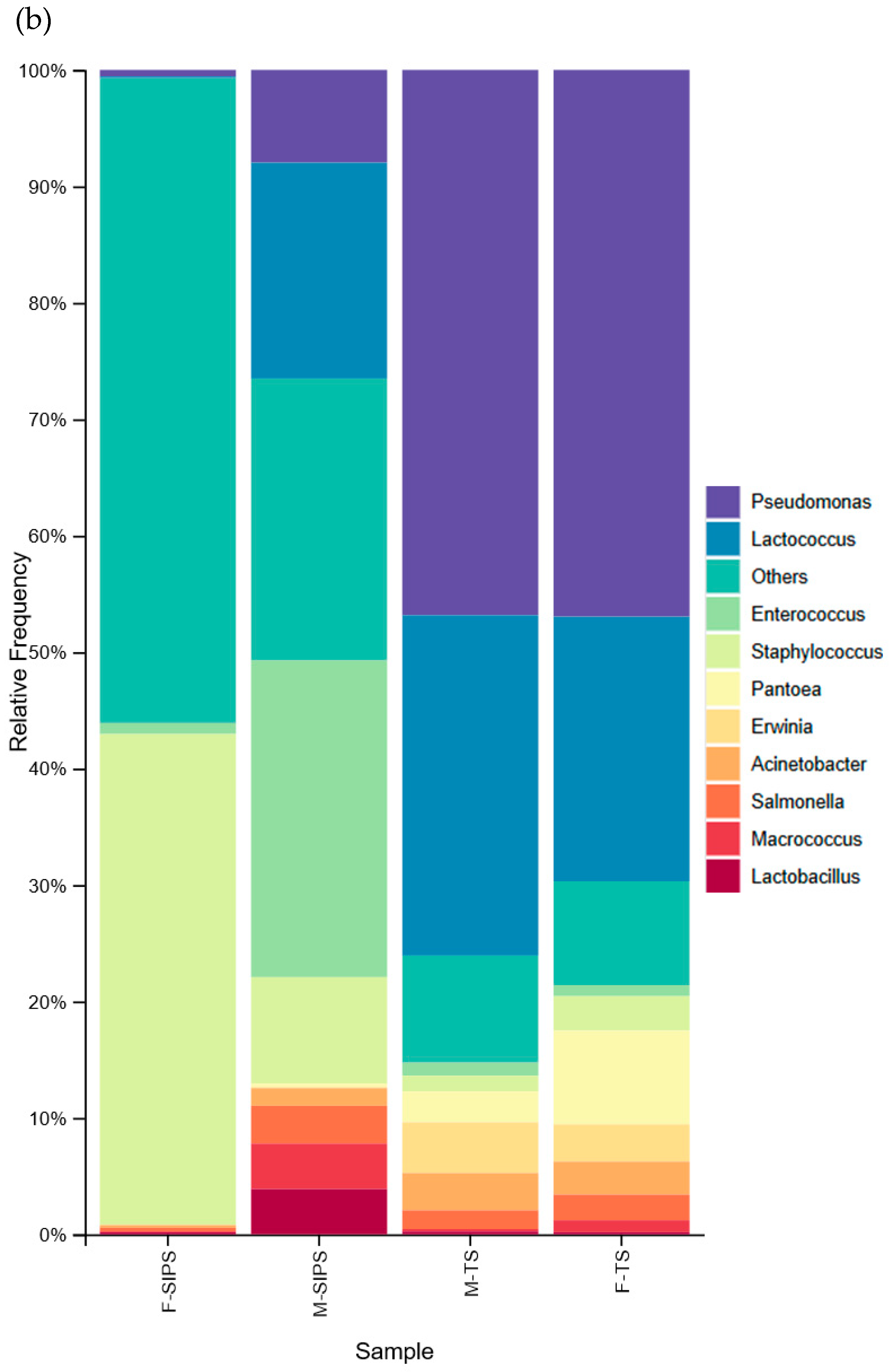
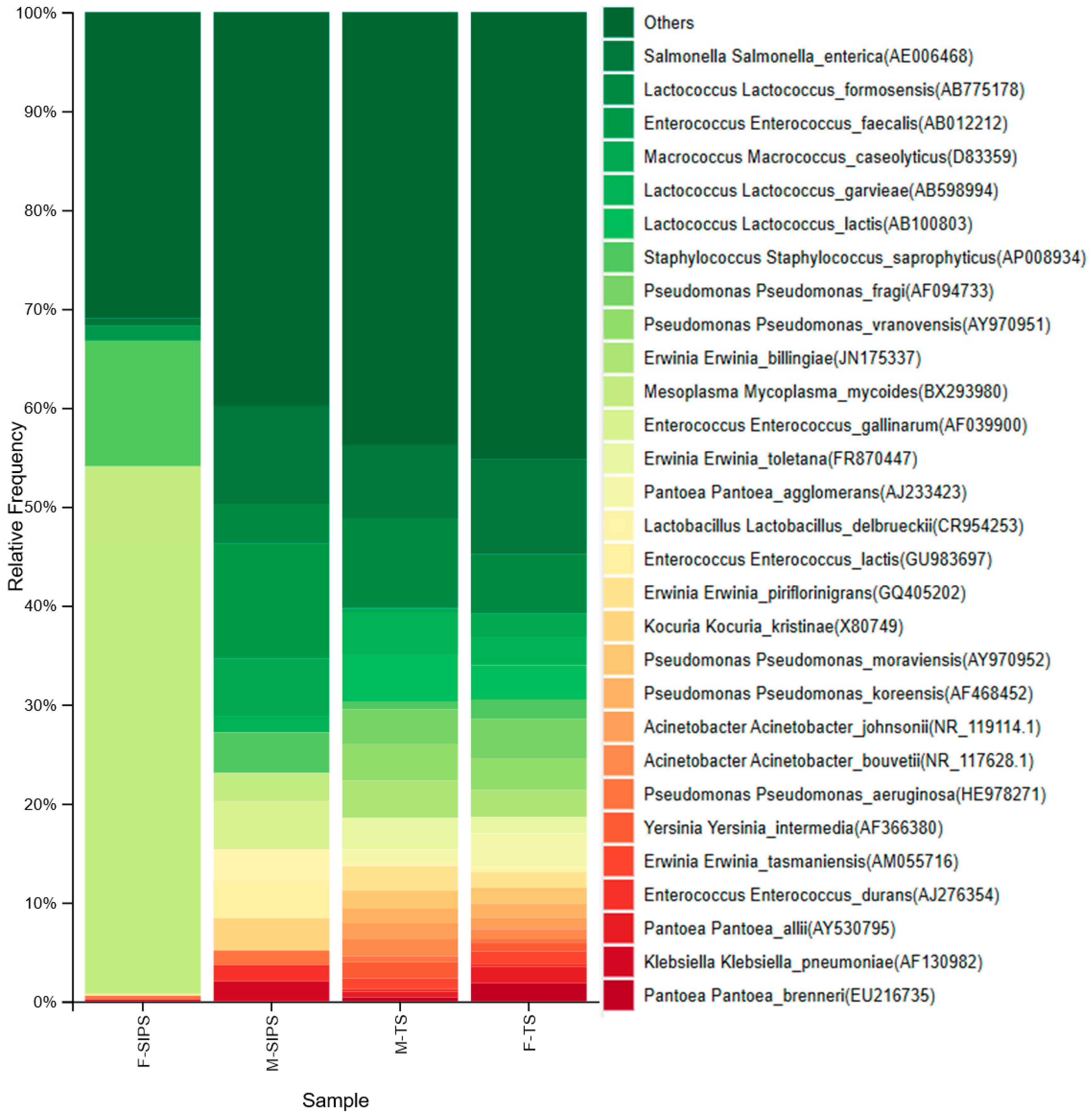
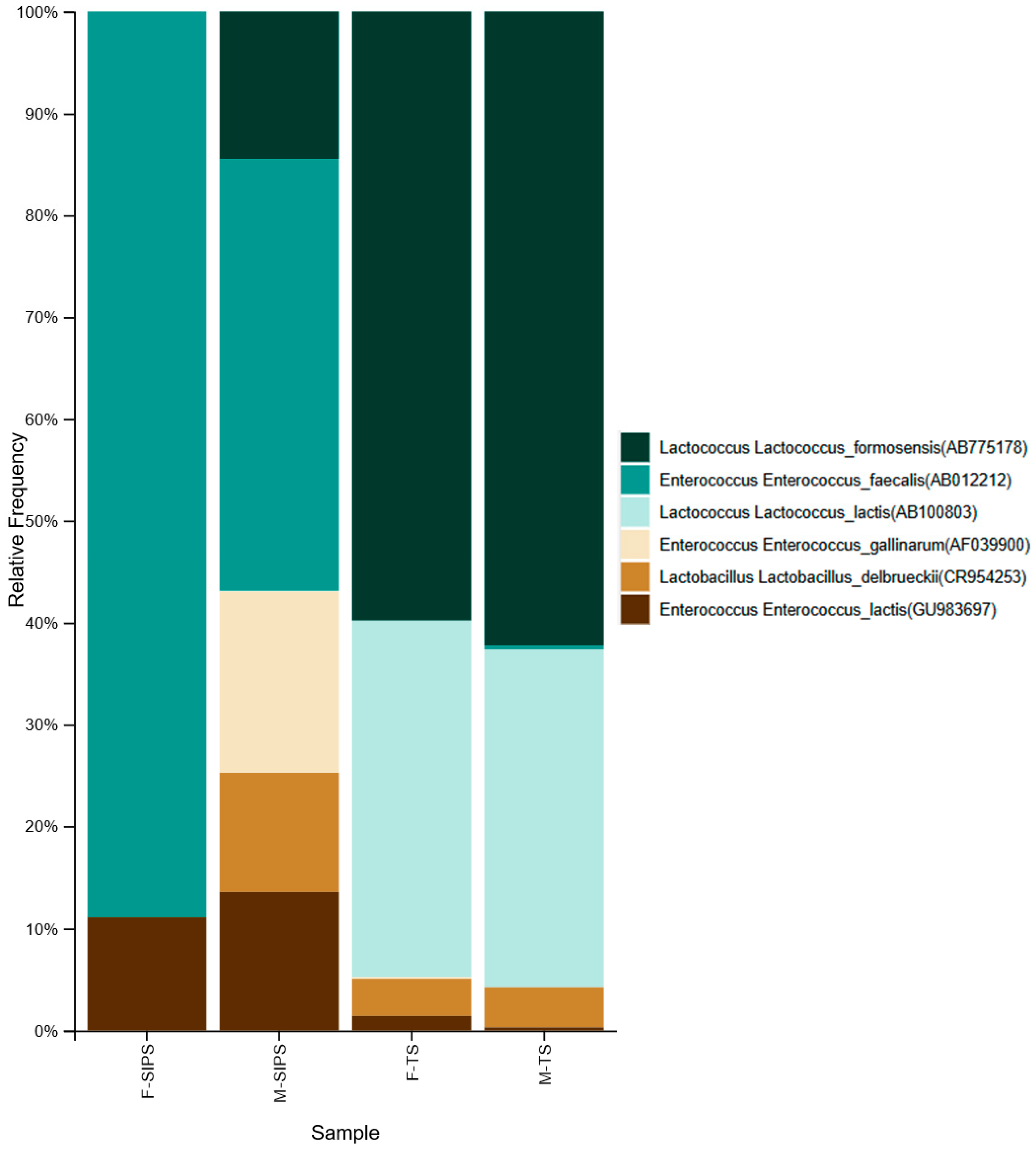
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, H.; Yadav, D.; Kumar, N.; Seth, R.; Goyal, A.K. Nutritional and nutraceutical properties of goat milk—A review. Indian J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 69, 513–518. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301693090 (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Nayik, G.A.; Jagdale, Y.D.; Gaikwad, S.A.; Devkatte, A.N.; Dar, A.H.; Dezmirean, D.S.; Bobis, O.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Ansari, M.J.; Hemeg, H.A.; et al. Recent insights into processing approaches and potential health benefits of goat milk and its products: A review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 789117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, C.G. Compositional and functional characteristics of goat milk and relevance as a base for infant formula. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayik, G.A.; Jagdale, Y.D.; Gaikwad, S.A.; Devkatte, A.N.; Dar, A.H.; Ansari, M.J. Nutritional profile, processing and potential products: A comparative review of goat milk. Dairy 2022, 3, 622–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioffredo, J.; Petryna, A. Caprinos: Generalidades, Nutrición, Reproducción e Instalaciones; Dpto. de Producción Animal, Facultad de Agronomía y Veterinaria, Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto: Río Cuarto, Argentina, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, Z.J.S. La caprinocultura en el marco de la ganadería poblana (México): Contribución de la especie caprina y sistemas de producción. Arch. Zootec. 2000, 49, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Meneses, R. Manual de Producción Caprina; Instituto de Desarrollo Agropecuario (INDAP) e Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias (INIA): Santiago, Chile, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, M.A.G.; Castelani, L.; Mitsunaga, T.M.; Soares, W.V.B.; Giglioti, R.; Júnior, L.C.R. Evaluation of fore-stripping milk and its effects on milk quality. Acta Vet. Bras. 2022, 16, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.M.; Ruegg, P.L. The effect of manual fore-stripping on milking performance of Holstein dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier-Metz, I.; Michel, V.; Delbes, C.; Montel, M.C. Do milking practices influence the bacterial diversity of raw milk? Food Microbiol. 2009, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnis, E.A.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Mills, D.A.; Maga, E.A. Analysis of raw goat milk microbiota: Impact of stage of lactation and lysozyme on microbial diversity. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayogo, F.A.; Budiharjo, A.; Kusumaningrum, H.P.; Wijanarka, W.; Suprihadi, A.; Nurhayati, N. Metagenomic applications in exploration and development of novel enzymes from nature: A review. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Yang, C.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Metagenomic features of traditional fermented milk products. LWT 2022, 155, 112945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karssa, T.H.; Kussaga, J.B.; Semedo-Lemsaddek, T.; Mugula, J.K. Perspectivas sobre la microbiología de los productos lácteos fermentados etíopes: Una revisión. Cienc. Aliment. Nutr. 2024, 12, 6990–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, A.J.; Ayers, T.; Grass, J.; Lynch, M.; Angulo, F.J.; Mahon, B.E. Nonpasteurized dairy products, disease outbreaks, and state laws—United States. 1993–2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, S.P.; Boor, K.J.; Murphy, S.C.; Murinda, S.E. Food safety hazards associated with consumption of raw milk. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G. Universal Bacterial Identification by PCR and DNA Sequencing of 16S rRNA Gene. In PCR for Clinical Microbiology; Schuller, M., Sloots, T., James, G., Halliday, C., Carter, I., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILLUMINA. Illumina DNA Prep (Reference Guide). Illumina. Available online: https://support-docs.illumina.com/LP/IlluminaDNAPrep/Content/LP/Illumina_DNA/DNA-Prep/Protocol_IDP.htm (accessed on 3 October 2025).
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Sun, J. Beta diversity metrics and ordination. In Bioinformatic and Statistical Analysis of Microbiome Data: From Raw Sequences to Advanced Modeling with QIIME 2 and R; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 335–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano Meraz, M.D.J.; Hernández, F.J.; Corral Rivas, S.; Nájera Luna, J.A. Diversidad arbórea a diferentes niveles de altitud en la región de El Salto, Durango. Rev. Mex. Cienc. For. 2017, 8, 57–68. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2007-11322017000200057&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Kim, B.R.; Shin, J.; Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Seol, K.H.; Isaacson, R.E. Deciphering diversity indices for a better understanding of microbial communities. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Lei, F.; Wang, B.; Jiang, S.; Peng, Q.; Shao, Y. Bacterial diversity in goat milk from the Guanzhong area of China. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7812–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormo, H.; Lekhal, D.A.H.; Roques, C. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from raw goat milk and effect of farming practices on the dominant species of lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 210, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilari, E.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Papademas, P.; Efthymiou, M.; Tretiak, S.; Tsaltas, D. Snapshot of Cyprus raw goat milk bacterial diversity via 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing; impact of cold storage conditions. Fermentation 2020, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callon, C.; Duthoit, F.; Delbès, C.; Ferrand, M.; Le Frileux, Y.; De Crémoux, R.; Montel, M.C. Stability of microbial communities in goat milk during a lactation year: Molecular approaches. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 30, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NNiyazbekova, Z.; Yao, X.-T.; Liu, M.-J.; Bold, N.; Tong, J.-Z.; Chang, J.-J.; Wen, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.-K.; et al. Compositional and functional comparisons of the microbiota in the colostrum and mature milk of dairy goats. Animals 2020, 10, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauková, A.; Micenková, L.; Grešáková, Ľ.; Maďarová, M.; Simonová, M.P.; Focková, V.; Ščerbová, J. Microbiome Associated with Slovak Raw Goat Milk, Trace Minerals, and Vitamin E ContentE. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 2022, 4595473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Pertiñez, M.; Alcalde, M.J.; Guzmán-Guerrero, J.L.; Castel, J.M.; Mena, Y.; Caravaca, F. Effect of hygiene-sanitary management on goat milk quality in semi-extensive systems in Spain. Small Rumin. Res. 2003, 47, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montel, M.C.; Buchin, S.; Mallet, A.; Delbes-Paus, C.; Vuitton, D.A.; Desmasures, N.; Berthier, F. Traditional cheeses: Rich and diverse microbiota with associated benefits. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 177, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshani, H.; Plaizier, J.C.; De Buck, J.; Barkema, H.W.; Khafipour, E. Composition of the teat canal and intramammary microbiota of dairy cows subjected to antimicrobial dry cow therapy and internal teat sealant. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 10191–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Hu, X.; Hou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L. Microbial community structure and diversity in different types of non-bovine milk. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 40, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, A.E.S.; Vasconcelos, P.C.; Saraiva, M.M.; Santos Filho, L.; Silva, N.M.; Givisiez, P.E.; Oliveira, C.J. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Staphylococcus spp. contaminating raw goat milk. Vet. World 2021, 14, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organji, S.R.; Abulreesh, H.H.; Elbanna, K.; Osman, G.E.; Almalki, M.H. Diversity and characterization of Staphylococcus spp. in food and dairy products: A foodstuff safety assessment. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2018, 7, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.U.; Barata, M.; Fraqueza, M.J.; Worning, P.; Bartels, M.D.; Goncalves, L.; Miragaia, M. Staphylococcus saprophyticus from clinical and environmental origins have distinct biofilm composition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 663768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, R.A.J. Improvements in the diagnosis and control of diseases of small ruminants caused by mycoplasmas. Small Rumin. Res. 2002, 45, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, J.; He, M.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y.; An, Q.; Wang, F. First Report and Comparative Genomic Analysis of a Mycoplasma mycoides Subspecies capri HN-A in Hainan Island. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorski, L.; Parker, C.T.; Liang, A.; Cooley, M.B.; Jay-Russell, M.T.; Gordus, A.G.; Mandrell, R.E. Prevalence, distribution, and diversity of Salmonella enterica in a major produce region of California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2734–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolini, D.; Casaburi, A.; Nasi, A.; Ferrocino, I.; Di Monaco, R.; Ferranti, P.; Villani, F. Different molecular types of Pseudomonas fragi have the same overall behaviour as meat spoilers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, L.; Raghu, H.V.; Ray, P.R. Milk and milk product safety and quality assurance for achieving better public health outcomes. In Agriculture, Livestock Production and Aquaculture: Advances for Smallholder Farming Systems Volume 1; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 217–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Lodh, J.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, D. Risk analysis, assessment, practices, and quality management in milk hygiene. In The Microbiology, Pathogenesis and Zoonosis of Milk Borne Diseases; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, C.; Kaur, S.; Crampton, B.; Maddock, D.; Arnold, D.; Denman, S. Transfer of Erwinia toletana and Erwinia iniecta to a novel genus Winslowiella gen. nov. as Winslowiella toletana comb. nov. and Winslowiella iniecta comb. nov. and description of Winslowiella arboricola sp. nov., isolated from bleeding cankers on broadleaf hosts. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1063107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonaurio, R.; Moretti, C.; da Silva, D.P.; Cortese, C.; Ramos, C.; Venturi, V. The olive knot disease as a model to study the role of interspecies bacterial communities in plant disease. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prod’homme, M.; Micol, L.A.; Weitsch, S.; Gassend, J.L.; Martinet, O.; Bellini, C. Cutaneous infection and bactaeremia caused by Erwinia billingiae: A case report. New Microbes New Infect. 2017, 19, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, J.; Knezevich, A.; Luzzati, R.; Di Bella, S. Clinical management of non-faecium non-faecalis vancomycin-resistant enterococci infection. Focus on Enterococcus gallinarum and Enterococcus casseliflavus/flavescens. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloso Daza, M.V.; Almeida-Santos, A.C.; Novais, C.; Read, A.; Alves, V.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Peixe, L. Distinction between Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus lactis by a gluP PCR-based assay for accurate identification and diagnostics. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e03268-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germond, J.E.; Lapierre, L.; Delley, M.; Mollet, B.; Felis, G.E.; Dellaglio, F. Evolution of the bacterial species Lactobacillus delbrueckii: A partial genomic study with reflections on prokaryotic species concept. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmotti, D.M.; Marcó, M.B.; Golowczyc, M.; Reinheimer, J.A.; Quiberoni, A.D.L. Probiotic potential of Lactobacillus delbrueckii strains and their phage resistant mutants. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoš, O.; Chmel, M.; Swierczková, I. The overlooked evolutionary dynamics of 16S rRNA revises its role as the “gold standard” for bacterial species identification. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montesinos Rivera, E.; Garza Brenner, E.; Ambriz Morales, P.; Arellano Vera, W.; Treviño-Rangel, R.d.J.; Sifuentes Rincón, A.M. Influence of Milking Process and Production System on Raw Goat Milk Bacteriome. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16100218
Montesinos Rivera E, Garza Brenner E, Ambriz Morales P, Arellano Vera W, Treviño-Rangel RdJ, Sifuentes Rincón AM. Influence of Milking Process and Production System on Raw Goat Milk Bacteriome. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(10):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16100218
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontesinos Rivera, Ezquibel, Estela Garza Brenner, Pascuala Ambriz Morales, Williams Arellano Vera, Rogelio de J. Treviño-Rangel, and Ana María Sifuentes Rincón. 2025. "Influence of Milking Process and Production System on Raw Goat Milk Bacteriome" Microbiology Research 16, no. 10: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16100218
APA StyleMontesinos Rivera, E., Garza Brenner, E., Ambriz Morales, P., Arellano Vera, W., Treviño-Rangel, R. d. J., & Sifuentes Rincón, A. M. (2025). Influence of Milking Process and Production System on Raw Goat Milk Bacteriome. Microbiology Research, 16(10), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16100218






