Influence of Mutations on Physicochemical Properties of Spike Proteins from Prototypical SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Detected in Amazonian Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrieval of Sequences
2.2. Multiple Sequence Alignment
2.3. Sequence Statistics Assessment
2.4. Prediction of Secondary Structures
2.5. Identification of Post-Translational Modification Sites
2.6. Determination of Antigenicity
2.7. Hypothesis Testing
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 VOCs Prototypically Detected in Amazonian Countries
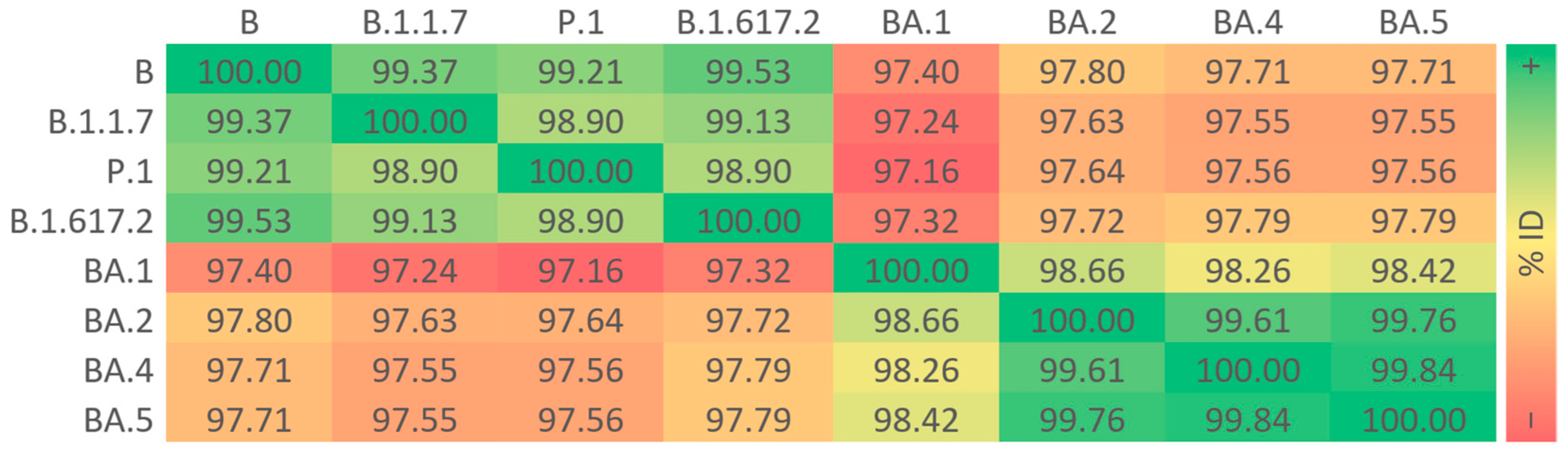
3.2. Sequence Identities of S Proteins
3.3. Lengths, Molecular Weights, and Isoelectric Points of S Proteins
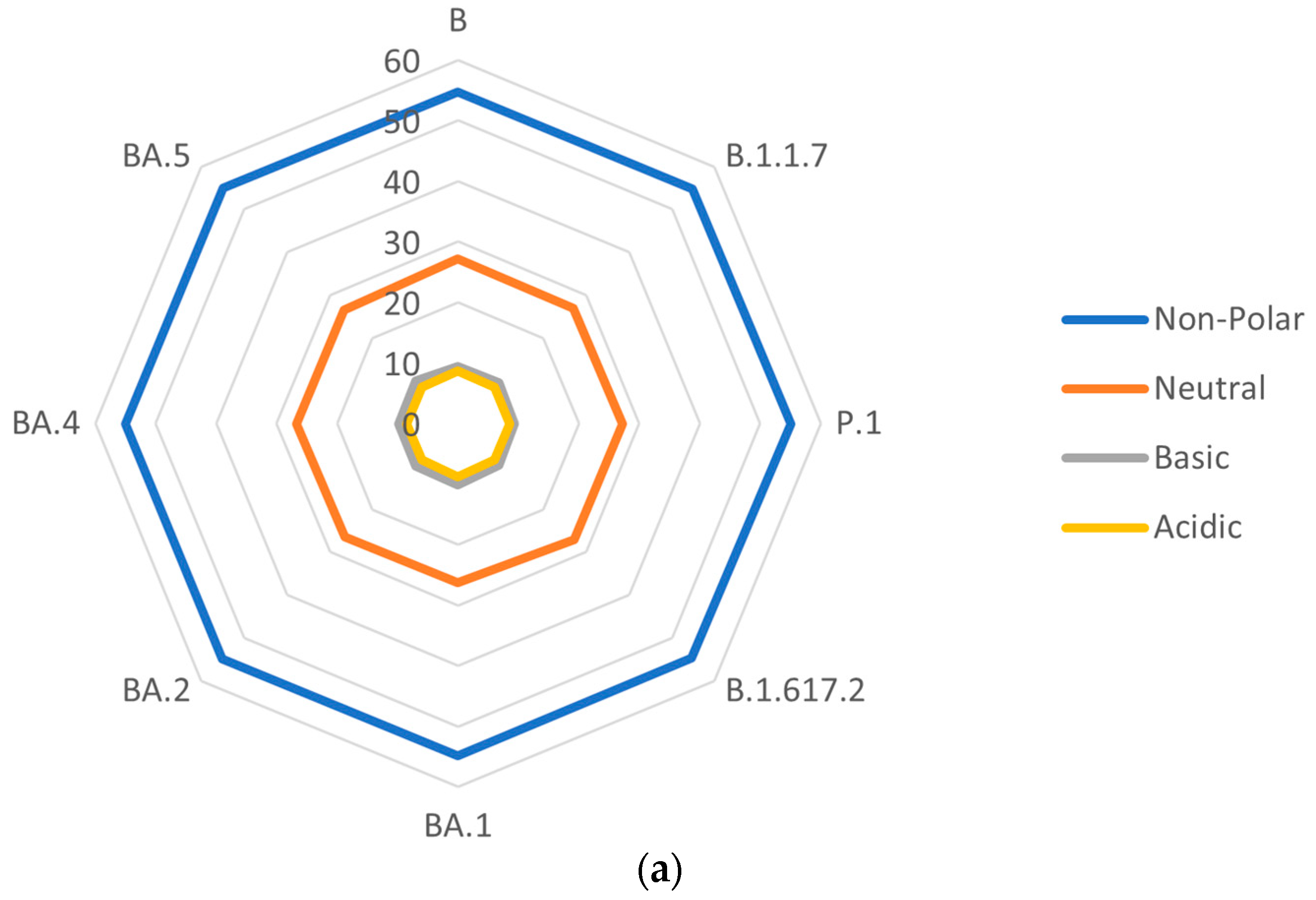
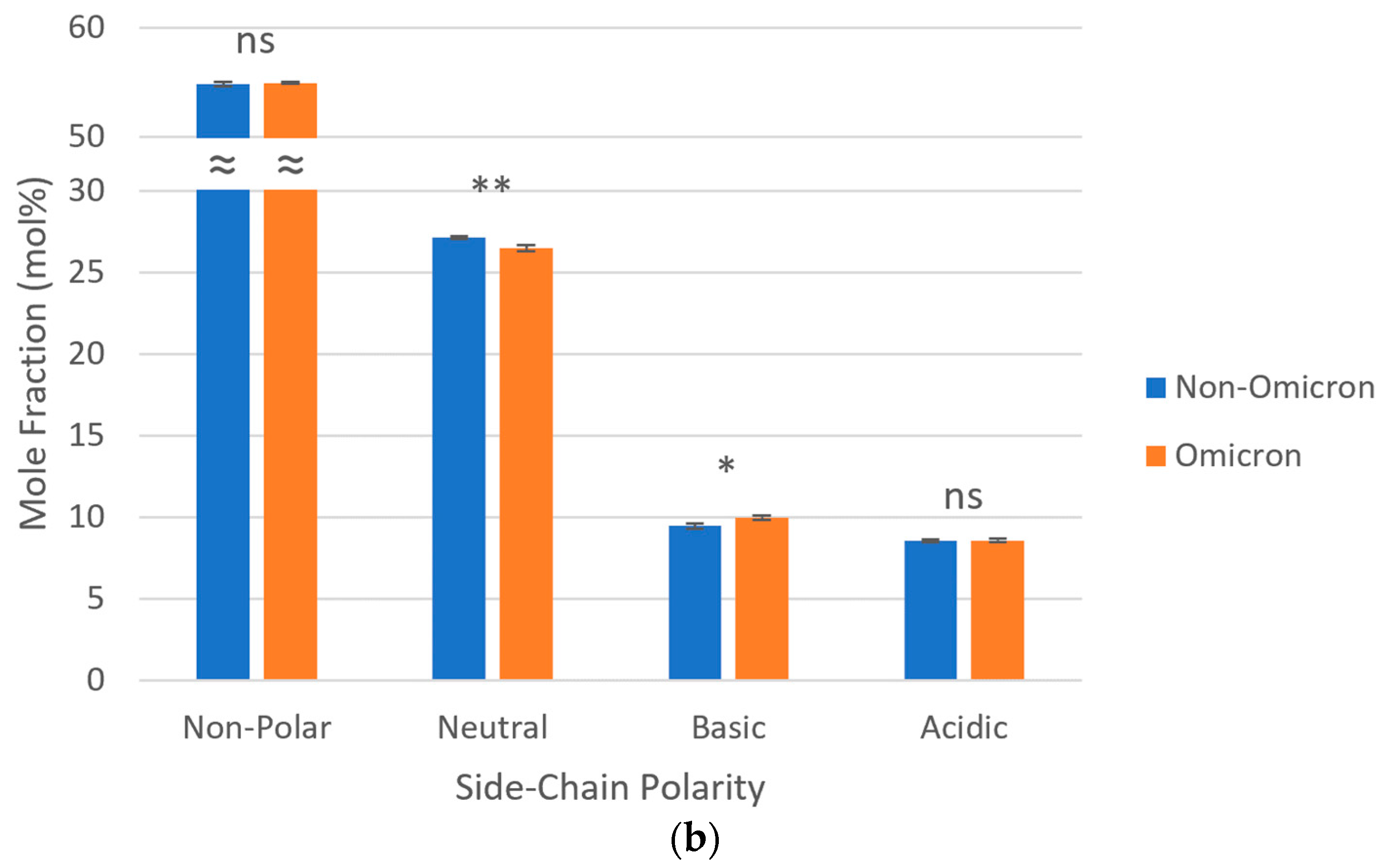
3.4. Side-Chain Polarities of S Proteins
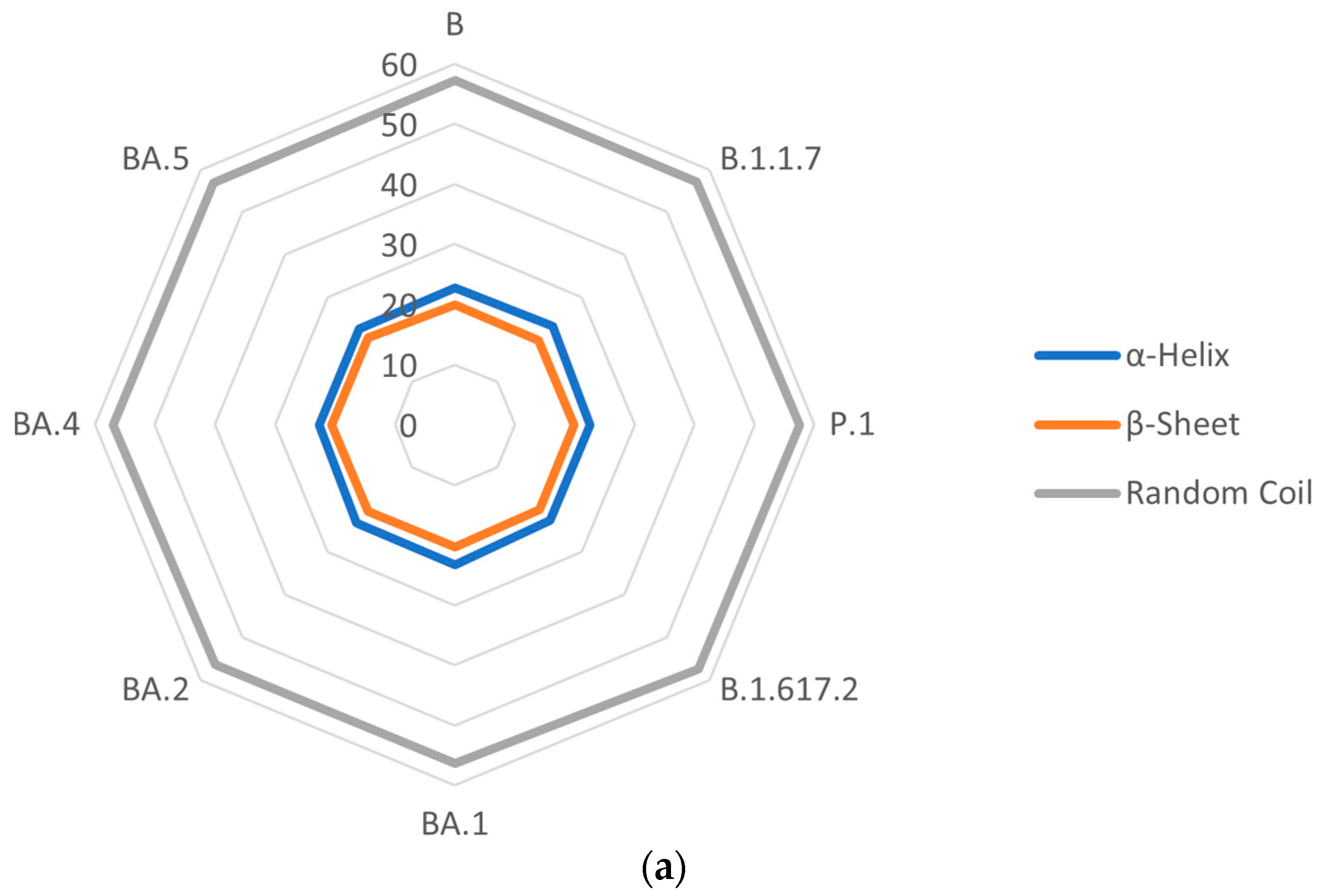
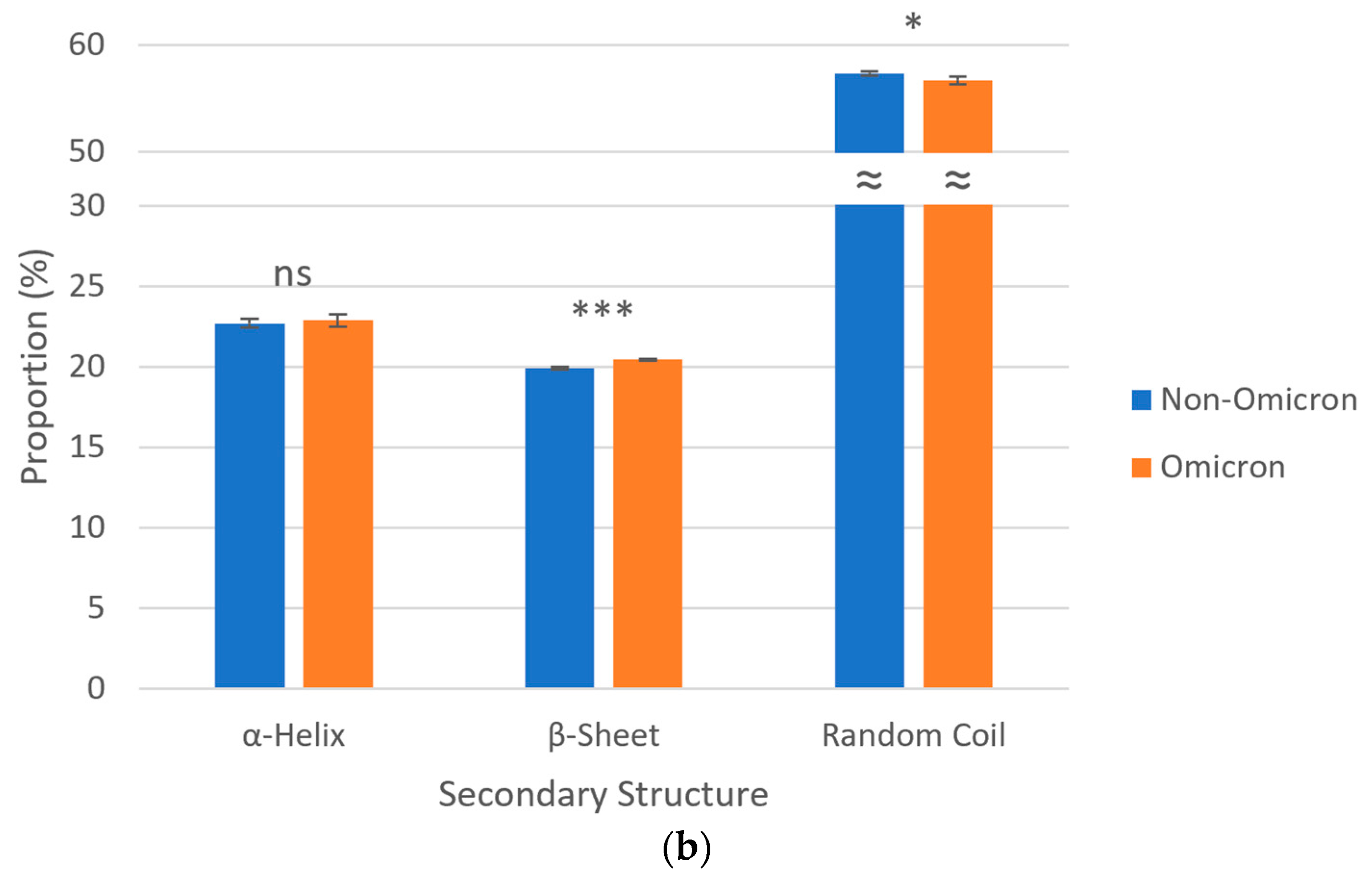
3.5. Secondary Structures of S Proteins
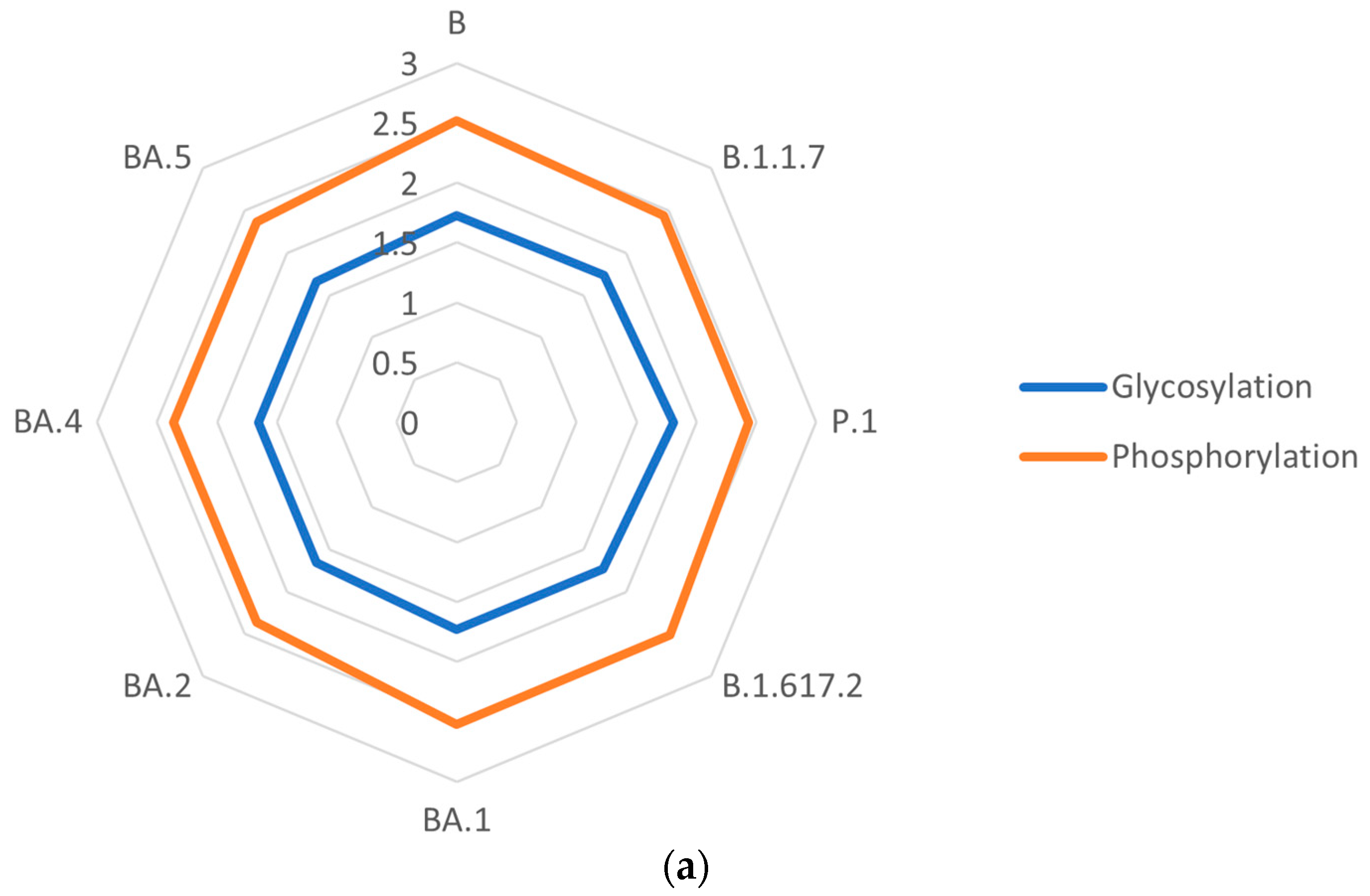
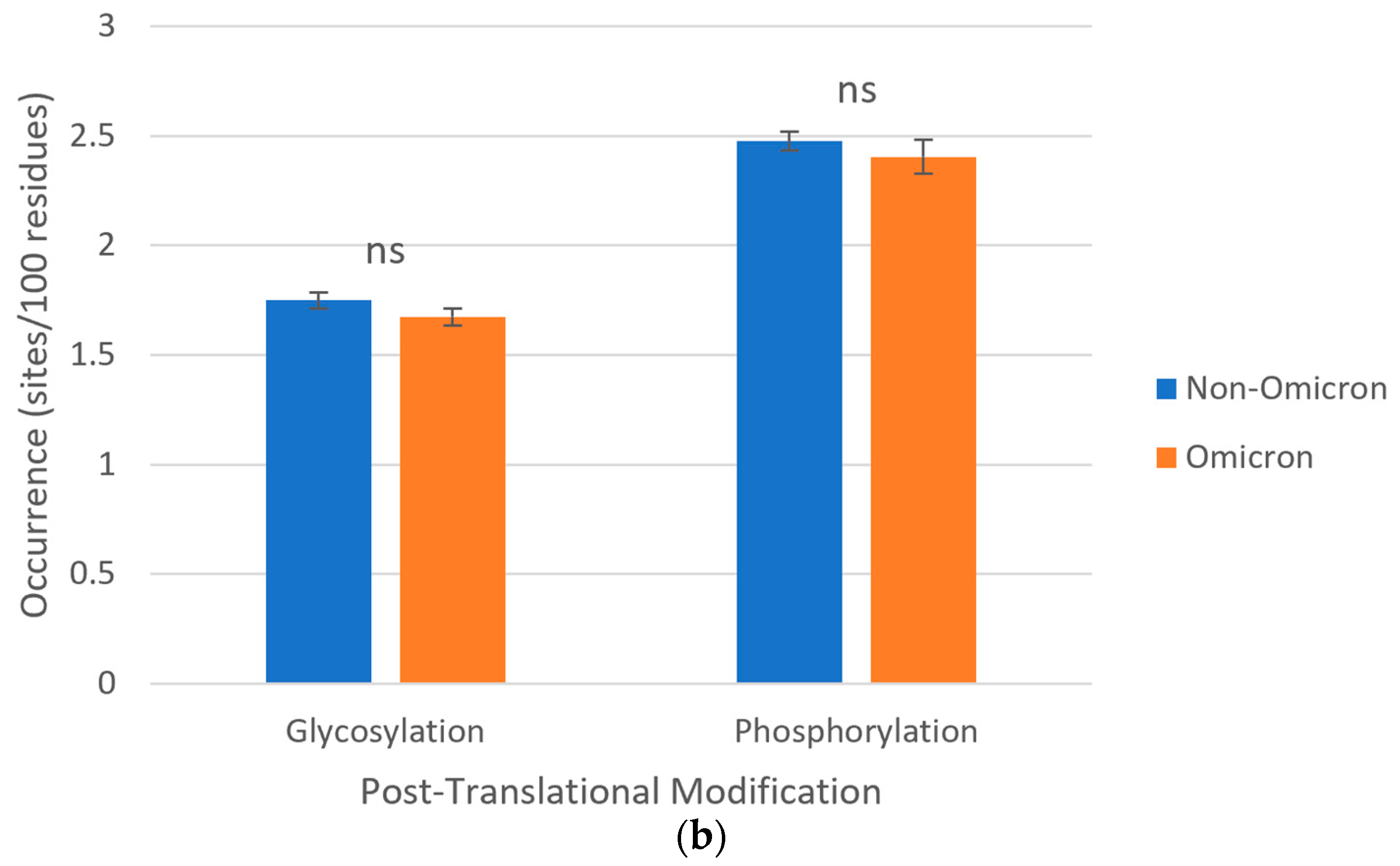
3.6. Post-Translational Modifications of S Proteins
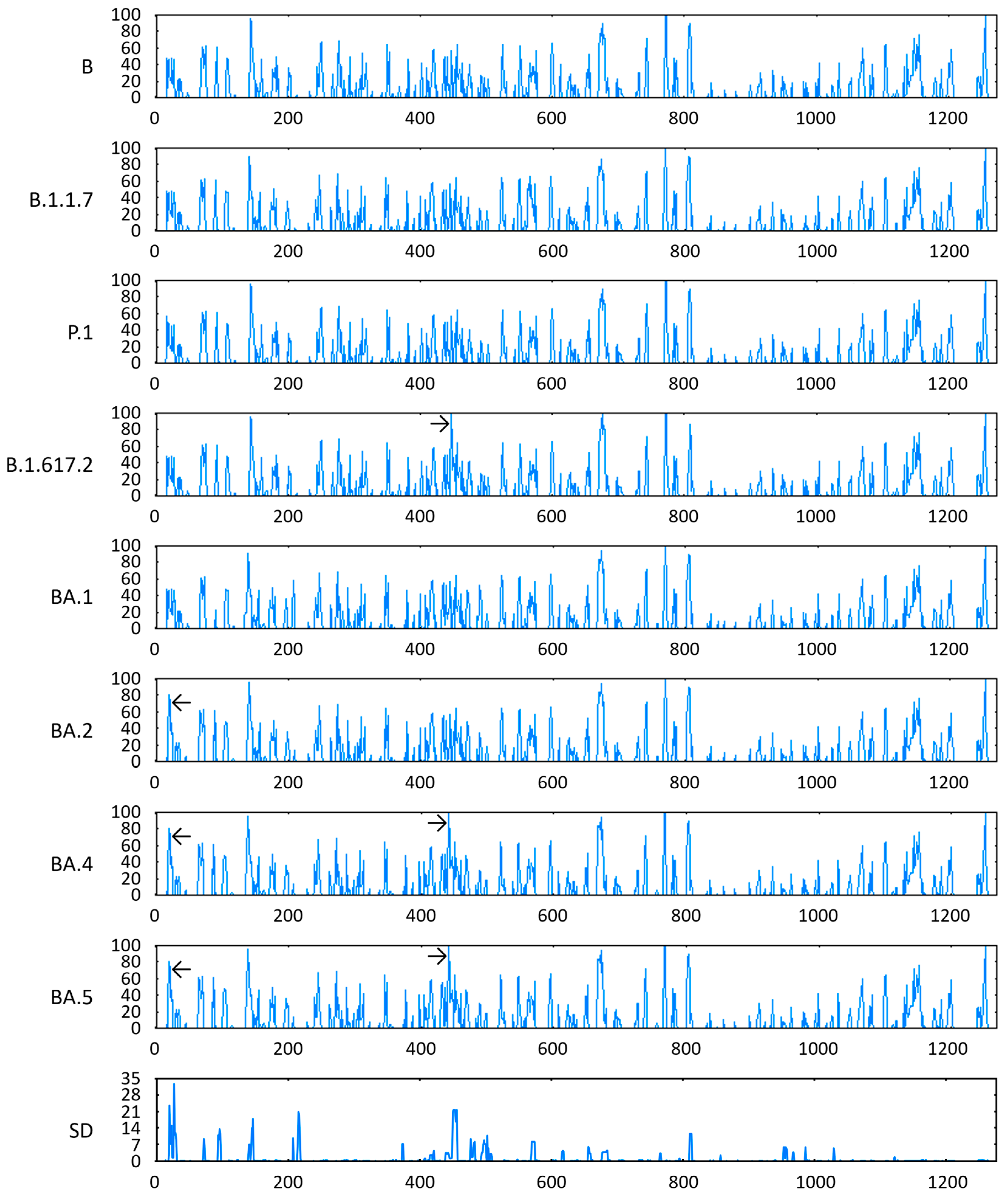
3.7. Antigenicity of S Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rabi, F.A.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Kasasbeh, G.A.; Salameh, D.M.; Al-Nasser, A.D. SARS-CoV-2 and coronavirus disease 2019: What we know so far. Pathogens 2020, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceraolo, C.; Giorgi, F.M. Genomic variance of the 2019-nCoV coronavirus. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Cai, Y.; Chen, B. Structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 50, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Vega, V.R.; Monroy-Molina, J.V.; Jiménez-Hernández, L.E.; Torres, A.G.; Santos-Preciado, J.I.; Rosales-Reyes, R. SARS-CoV-2: Evolution and emergence of new viral variants. Viruses 2022, 14, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, M.; Madabhavi, I. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: A review. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2023, 93, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, M.; Sharma, A.; Priyanka; Thakur, N.; Rajkhowa, T.K.; Choudhary, O.P. Delta variant (B.1.617.2) of SARS-CoV-2: Mutations, impact, challenges and possible solutions. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2068883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhama, K.; Nainu, F.; Frediansyah, A.; Yatoo, M.I.; Mohapatra, R.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Zhou, H.; Islam, M.R.; Mamada, S.S.; Kusuma, H.I.; et al. Global emerging Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: Impacts, challenges and strategies. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabelli, A.M.; Peacock, T.P.; Thorne, L.G.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium; Peacock, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; de Silva, T.I.; Towers, G.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRotta, J.; Escobar, O.; Ávila-Aguero, M.L.; Torres, J.P.; Sini de Almeida, R.; Morales, G.D.C.; Srivastava, A. COVID-19 in Latin America: A snapshot in time and the road ahead. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2023, 12, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frishman, D.; Argos, P. Incorporation of non-local interactions in protein secondary structure prediction from the amino acid sequence. Protein Eng. 1996, 9, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combet, C.; Blanchet, C.; Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. NPS@: Network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.M.; Guo, D.; Hodges, R.S. New hydrophilicity scale derived from high-performance liquid chromatography peptide retention data: Correlation of predicted surface residues with antigenicity and X-ray-derived accessible sites. Biochemistry 1986, 25, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, M.; Papakyriakou, A.; Chlichlia, K.; Markoulatos, P.; Oliver, S.G.; Amoutzias, G.D. Comparative analysis of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, including omicron, highlights their common and distinctive amino acid substitution patterns, especially at the spike ORF. Viruses 2022, 14, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, B.M.; Montoya, E.; Sakschewski, B.; Nascimento, N.; Staal, A.; Betts, R.A.; Levis, C.; Lapola, D.M.; Esquível-Muelbert, A.; Jakovac, C.; et al. Critical transitions in the Amazon forest system. Nature 2024, 626, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peisahovics, F.; Rohaim, M.A.; Munir, M. Structural topological analysis of spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern highlight distinctive amino acid substitution patterns. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 101, 151275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broni, E.; Miller, W.A., 3rd. Computational analysis predicts correlations among amino acids in SARS-CoV-2 proteomes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyášek, R.; Řehůřková, K.; Berta Marošiová, K.; Kovařík, A. Mutational asymmetries in the SARS-CoV-2 genome may lead to increased hydrophobicity of virus proteins. Genes 2021, 12, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cortés, G.I.; Palacios-Pérez, M.; Veledíaz, H.F.; Hernández-Aguilar, M.; López-Hernández, G.R.; Zamudio, G.S.; José, M.V. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is adapting because of selective pressures. Vaccines 2022, 10, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahim-Saraie, H.S.; Dehghani, B.; Mojtahedi, A.; Shenagari, M.; Hasannejad-Bibalan, M. Functional and structural characterization of SARS-Cov-2 spike protein: An in silico study. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2021, 31, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Gao, K.; Wang, R.; Wei, G.W. Prediction and mitigation of mutation threats to COVID-19 vaccines and antibody therapies. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 6929–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, U. Comparative structural analyses of selected spike protein-RBD mutations in SARS-CoV-2 lineages. Immunol. Res. 2022, 70, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, K.; Chen, T.; Tajkhorshid, E. Posttranslational modifications optimize the ability of SARS-CoV-2 spike for effective interaction with host cell receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119761119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.D.; Williamson, M.K.; Lewis, S.; Shoemark, D.; Carroll, M.W.; Heesom, K.J.; Zambon, M.; Ellis, J.; Lewis, P.A.; Hiscox, J.A.; et al. Characterisation of the transcriptome and proteome of SARS-CoV-2 reveals a cell passage induced in-frame deletion of the furin-like cleavage site from the spike glycoprotein. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venne, A.S.; Kollipara, L.; Zahedi, R.P. The next level of complexity: Crosstalk of posttranslational modifications. Proteomics 2014, 14, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majed, S.O.; Jalal, P.J.; Fatah, M.H.; Karim, K.K.; Karim, A.Y.; Miasko, M.; Hasannajad, S.; Mustafa, S.A. Genomic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 omicron sublineage BA.5.2.1 in Erbil/Iraq. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugathasan, R.; Sukhova, K.; Moshe, M.; Kellam, P.; Barclay, W. Deep mutagenesis scanning using whole trimeric SARS-CoV-2 spike highlights the importance of NTD-RBD interactions in determining spike phenotype. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Elbashir, S.M.; Wu, K.; Lee, D.; Renzi, I.; Ying, B.; Koch, M.; Sein, C.E.; Choi, A.; Whitener, B.; et al. Domain-based mRNA vaccines encoding spike protein N-terminal and receptor binding domains confer protection against SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadf4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pango Lineage | Accession Number * | Geographic Location | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | QIG55994.1 | Brazil | 28 February 2020 |
| B.1.1.7 | QQV29246.1 | Peru | 31 December 2020 |
| P.1 | UHM42580.1 | Brazil | 17 April 2020 |
| B.1.617.2 | UIJ16492.1 | Brazil | 1 July 2021 |
| BA.1 | URB54916.1 | Brazil | 6 December 2021 |
| BA.2 | UVJ69620.1 | Colombia | 5 March 2022 |
| BA.4 | UTZ03741.1 | Brazil | 8 June 2022 |
| BA.5 | UUC29660.1 | Brazil | 2 July 2022 |
| Pango Lineage | Length 1 | Molecular Weight 2 | Isoelectric Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 1273 | 141.18 | 6.61 |
| B.1.1.7 | 1270 | 140.89 | 6.73 |
| P.1 | 1273 | 141.31 | 6.67 |
| B.1.617.2 | 1273 | 141.25 | 6.97 |
| BA.1 | 1270 | 141.33 | 7.27 |
| BA.2 | 1270 | 141.19 | 7.28 |
| BA.4 | 1268 | 140.88 | 7.18 |
| BA.5 | 1268 | 140.92 | 7.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.C.B.; Carvalho, C.A.M. Influence of Mutations on Physicochemical Properties of Spike Proteins from Prototypical SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Detected in Amazonian Countries. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 1334-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030090
Silva ACB, Carvalho CAM. Influence of Mutations on Physicochemical Properties of Spike Proteins from Prototypical SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Detected in Amazonian Countries. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(3):1334-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030090
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Adriana Conceição B., and Carlos Alberto M. Carvalho. 2024. "Influence of Mutations on Physicochemical Properties of Spike Proteins from Prototypical SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Detected in Amazonian Countries" Microbiology Research 15, no. 3: 1334-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030090
APA StyleSilva, A. C. B., & Carvalho, C. A. M. (2024). Influence of Mutations on Physicochemical Properties of Spike Proteins from Prototypical SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Detected in Amazonian Countries. Microbiology Research, 15(3), 1334-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15030090







