The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
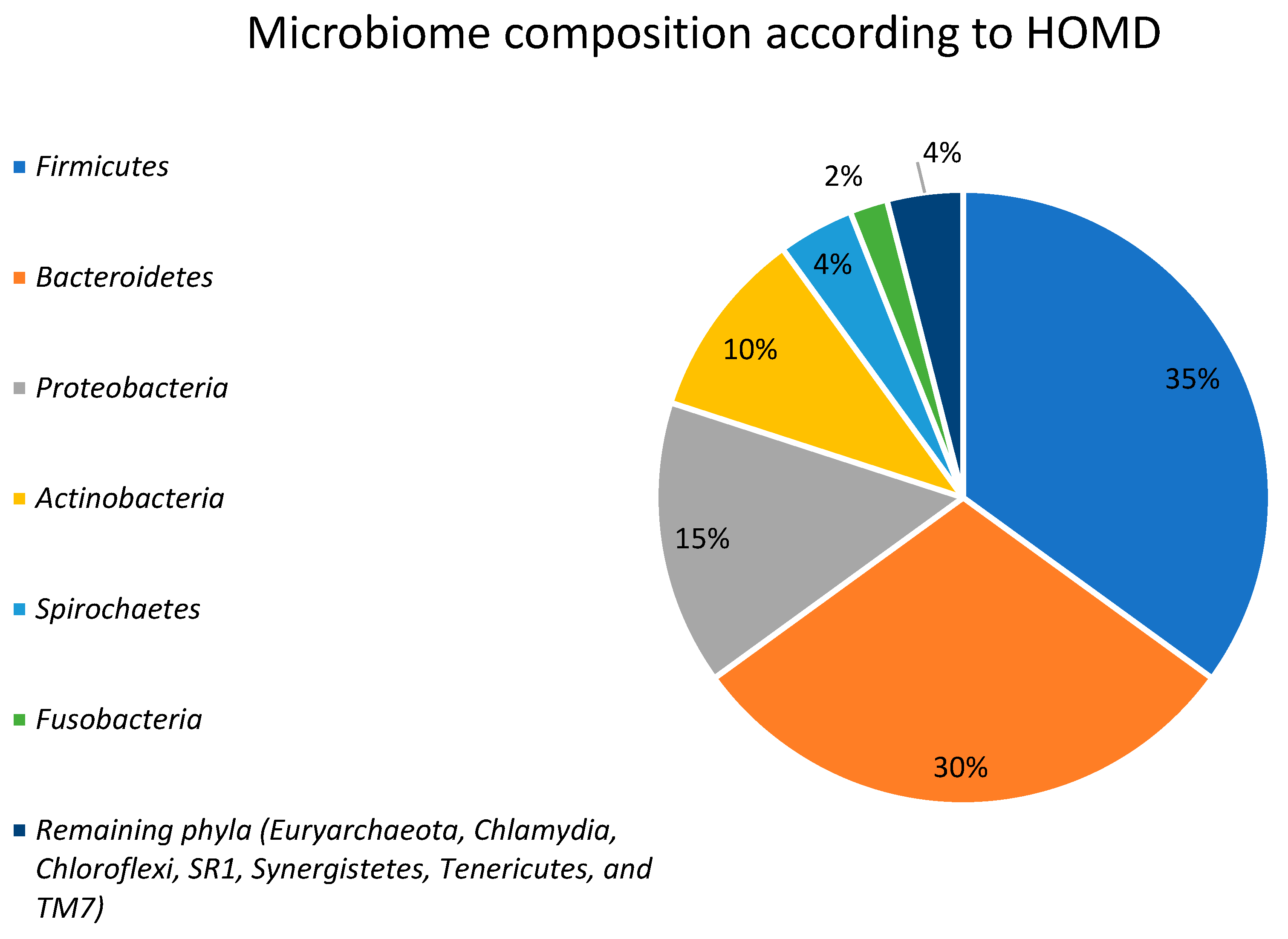
2. Gut Microbiota
3. Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Physiology
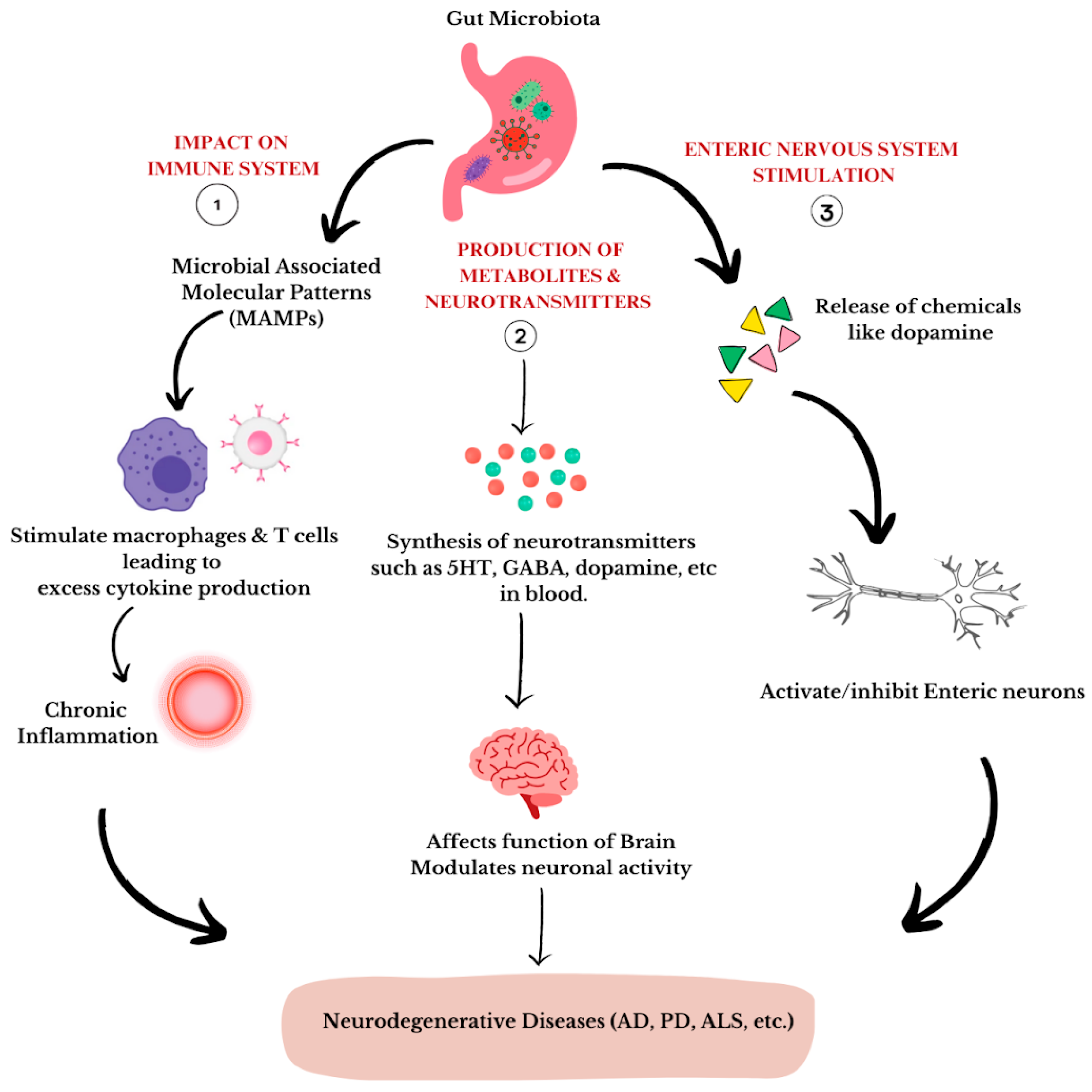
4. The Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis
5. Microbiota and Mental Health
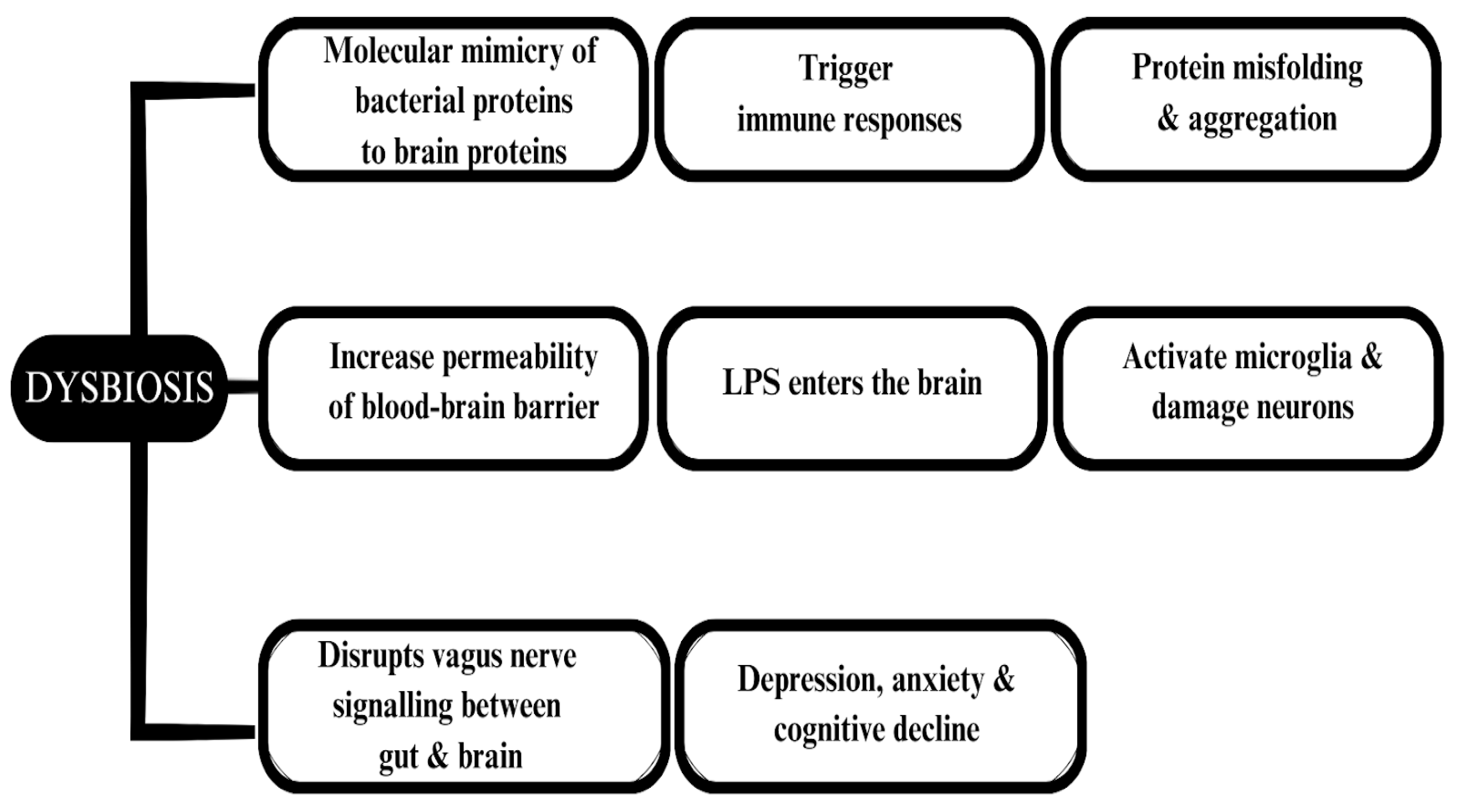
6. Neurodegenerative Diseases Associated with the Gut Microbiota
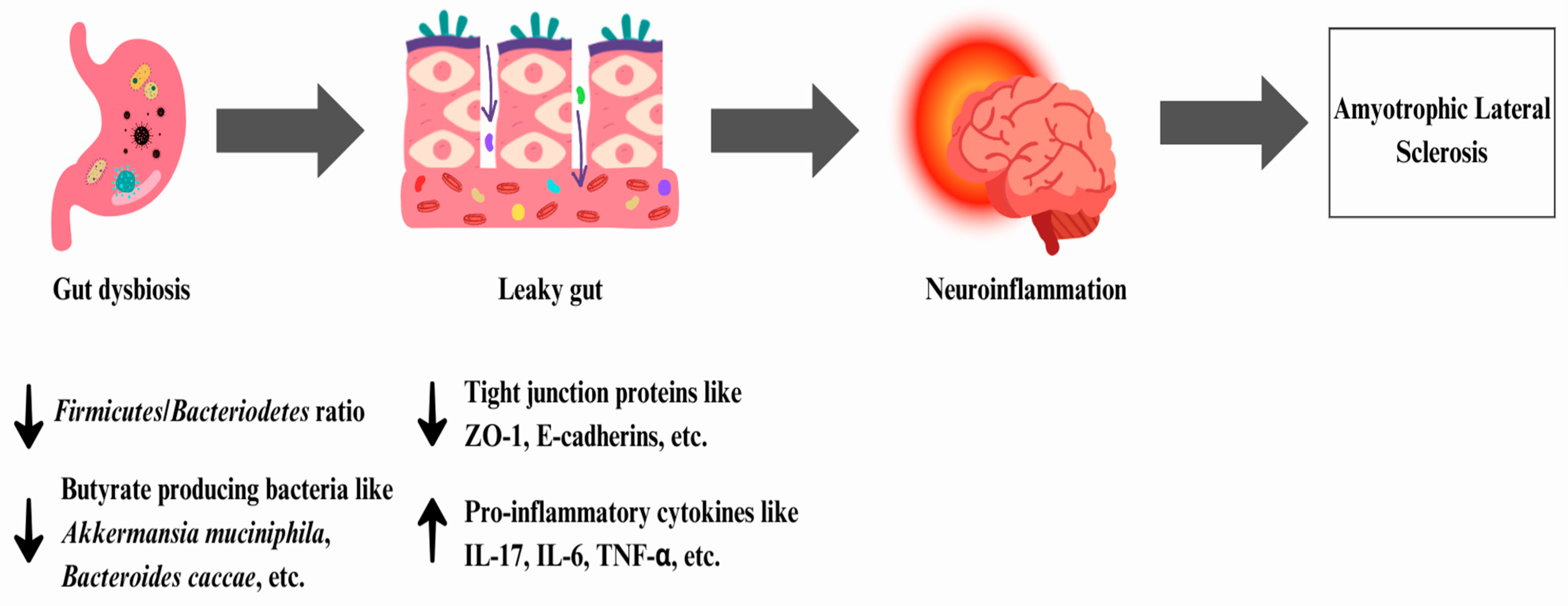
6.1. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
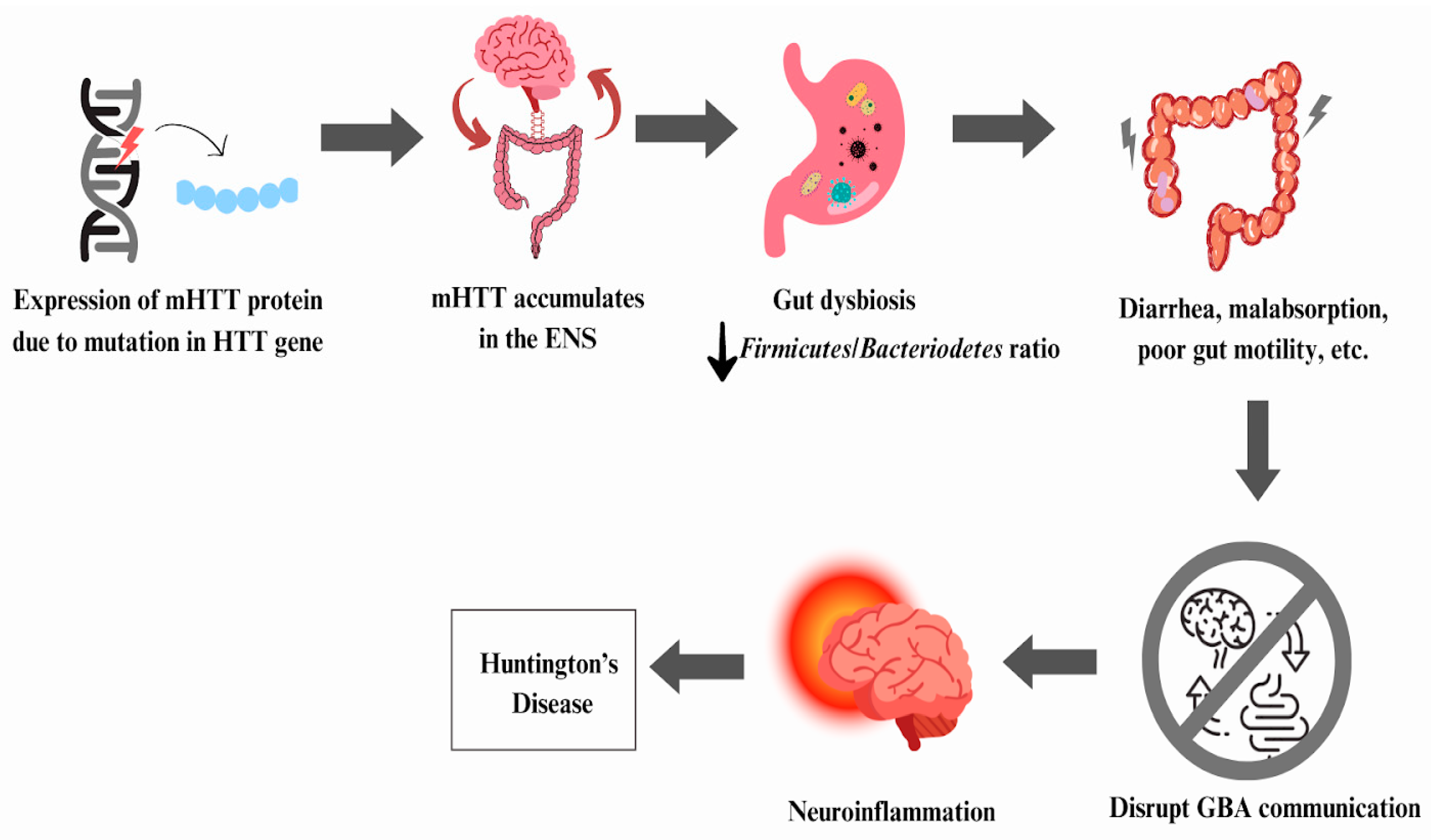
6.2. Huntington’s Disease
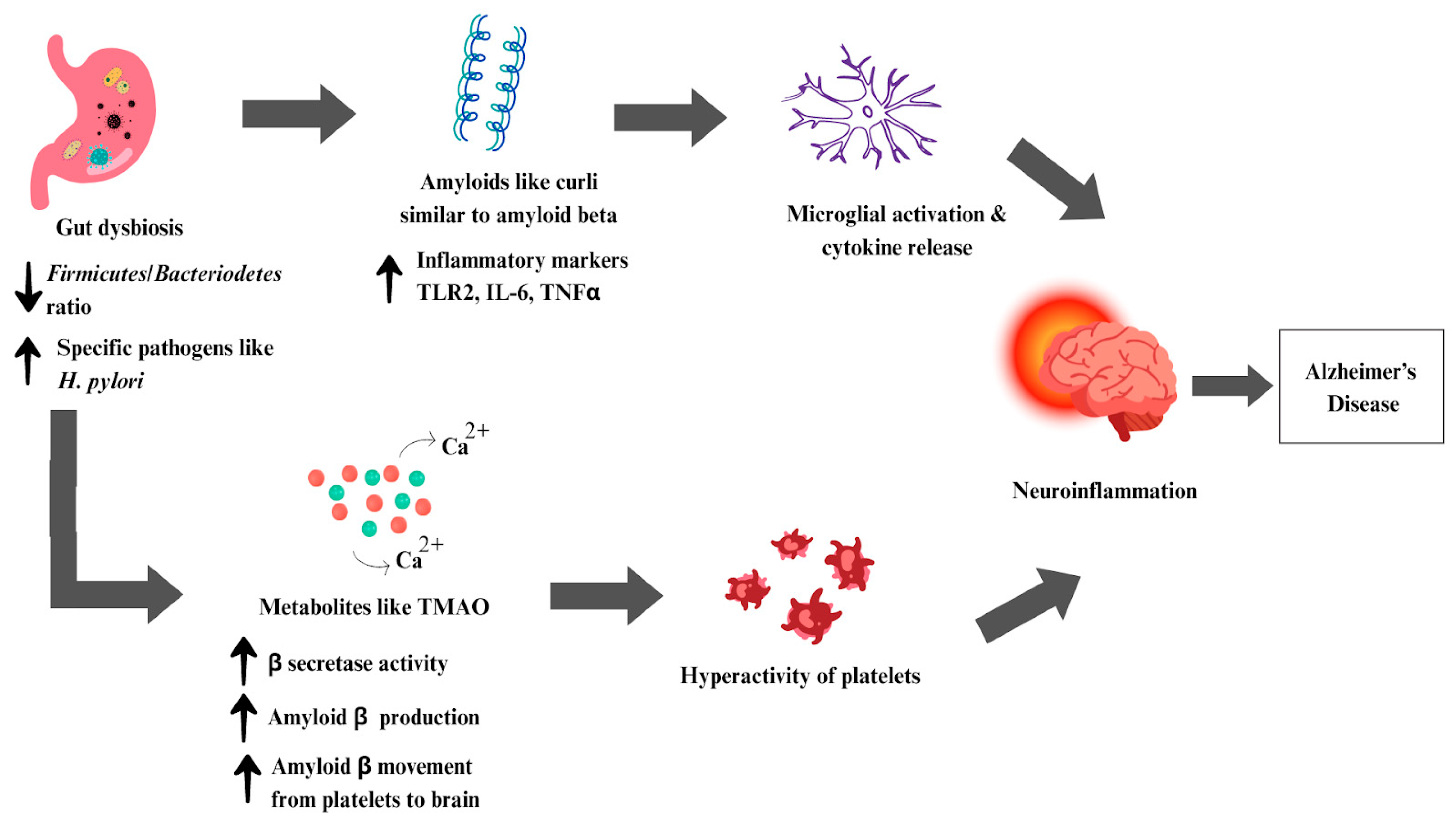
6.3. Alzheimer’s Disease
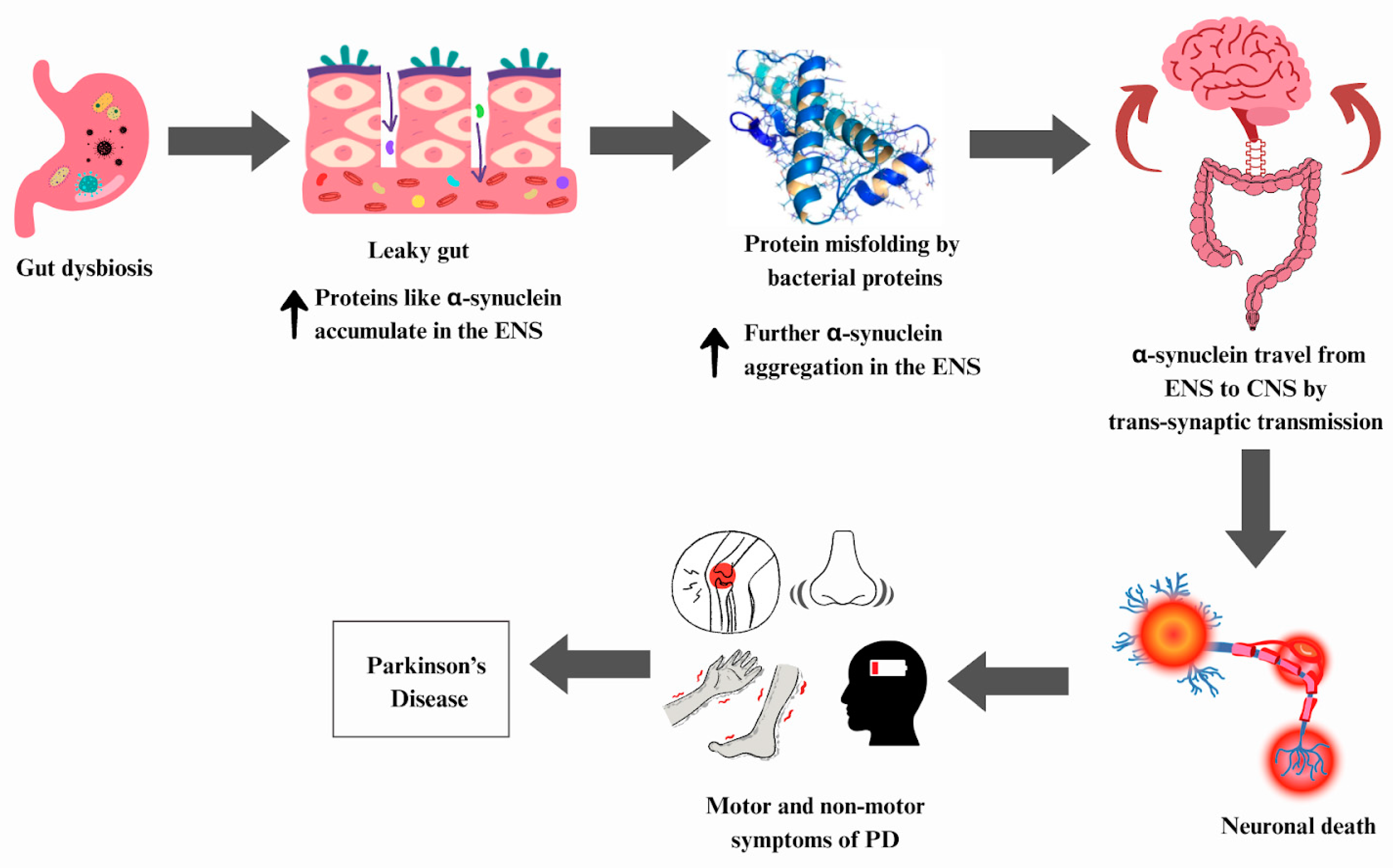
6.4. Parkinson’s Disease
7. The Gut Microbiota in Potential Treatment Strategies
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, C.W.Y.; Lam, Y.Y.; Holmes, A.J. Mechanistic links between gut microbial community dynamics, microbial functions and metabolic health. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16498–16517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manor, O.; Dai, C.L.; Kornilov, S.A.; Smith, B.; Price, N.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T. Health and disease markers correlate with gut microbiome composition across thousands of people. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illiano, P.; Brambilla, R.; Parolini, C. The mutual interplay of gut microbiota, diet and human disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 833–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Du, W.; Hu, X.; Yu, X.; Guo, C.; Jin, X.; Wang, W. Targeting the blood-brain barrier to delay aging-accompanied neurological diseases by modulating gut microbiota, circadian rhythms, and their interplays. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 4667–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, I.P. The Scientific Investigation of the Psychical Faculties or Processes in the Higher Animals. Science 1906, 24, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, G.; Liu, M.; Yuan, B.; Chai, H.; Wang, W.; Cheng, P. Implications of Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 785644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, D.; Ali, S.A.; Singh, R.K. Emerging role of gut microbiota in modulation of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration with emphasis on Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 106, 110112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Su, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, L.; Qin, C. Gut Microbiota Regulation and Their Implication in the Development of Neurodegenerative Disease. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.C.; Bhargava, R.; Bucher, M.; Brust, A.S.; Czy, D.M. Identification of proteotoxic and proteoprotective bacteria that non-specifically affect proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. bioRxiv 2023, 40, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Madkan, S.; Patil, P. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Insights and Therapeutic Implications. Cureus 2023, 15, 47861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubert, C.; Kong, G.; Renoir, T.; Hannan, A.J. Exercise, diet and stress as modulators of gut microbiota: Implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamjane, N.; Mechita, M.B.; Nourouti, N.G.; Barakat, A. Gut microbiota dysbiosis-associated obesity and its involvement in cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. A systematic review. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 151, 104601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, Y.D. Gut Microbiota: An Integral Moderator in Health and Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, M.; Higgins, P.D.; Middha, S.; Rioux, K.P. The human gut microbiome: Current knowledge, challenges, and future directions. Transl. Res. 2012, 160, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, W.K.; Chehadeh, F.; Husband, S. Recent Advances in Understanding the Structure and Function of the Human Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 825338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunrinola, G.A.; Oyewale, J.O.; Oshamika, O.O.; Olasehinde, G.I. The Human Microbiome and Its Impacts on Health. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 20, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ya, R.; Tang, X.; Cai, M. Role and interaction of bacterial sphingolipids in human health. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1289819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruigrok, R.A.A.A.; Weersma, R.K.; Vich Vila, A. The emerging role of the small intestinal microbiota in human health and disease. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2201155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.-X.; Goh, W.-R.; Wu, R.-N.; Yue, X.-Q.; Luo, X.; Khine, W.W.T.; Wu, J.-R.; Lee, Y.-K. Revisit gut microbiota and its impact on human health and disease. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: An integrative view. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-L.; Li, W.-X.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chen, X.-F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.-Q.; Wu, C.-Z.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Chen, Y.-L.; et al. Oxymatrine ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by rebalancing the homeostasis of gut microbiota and reducing blood-brain barrier disruption. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1095053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Bonfili, L.; Wei, T.; Eleuteri, A.M. Understanding the Gut–Brain Axis and Its Therapeutic Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve at the Interface of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangaleela, S.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Bharathi, M.; Chaiyasut, C. Role of the Gut-Brain Axis, Gut Microbial Composition, Diet, and Probiotic Intervention in Parkinson’s Disease. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cussotto, S.; Sandhu, K.V.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The Neuroendocrinology of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: A Behavioural Perspective. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 51, 80–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ruan, G.; Chen, L.; Ying, S.; Li, G.; Xu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Lv, L.; Ping, Y.; et al. Neurotransmitter and Intestinal Interactions: Focus on the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 817100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, R.; Wisniewski, P.J.; Alderman, B.L.; Campbell, S.C. Microbes and mental health: A review. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panduro, A.; Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Sepulveda-Villegas, M.; Roman, S. Genes, emotions and gut microbiota: The next frontier for the gastroenterologist. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3030–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvia, K.E.; Demas, G.E. A gut feeling: Microbiome-brain-immune interactions modulate social and affective behaviors. Horm. Behav. 2018, 99, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navidinia, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Seyfi, E. The clinical outcomes of gut-brain axis (GBA) microbiota influence on psychiatric disorders. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2023, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borre, Y.E.; Moloney, R.D.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The impact of microbiota on brain and behavior: Mechanisms & therapeutic potential. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 373–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burberry, A.; Wells, M.F.; Limone, F.; Couto, A.; Smith, K.S.; Keaney, J.; Gillet, G.; van Gastel, N.; Wang, J.-Y.; Pietilainen, O.; et al. C9orf72 suppresses systemic and neural inflammation induced by gut bacteria. Nature 2020, 582, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddy, S.L.; Giovannelli, I.; Sassani, M.; Cooper-Knock, J.; Snyder, M.P.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E.; Barker, L.A.; Shaw, P.J.; McDermott, C.J. The gut microbiome: A key player in the complexity of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). BMC Med. 2021, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, H.M.; Makpol, S. A review of the preclinical and clinical studies on the role of the gut microbiome in aging and neurodegenerative diseases and its modulation. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1007166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCombe, P.A.; Henderson, R.D.; Lee, A.; Lee, J.D.; Woodruff, T.M.; Restuadi, R.; McRae, A.; Wray, N.R.; Ngo, S.; Steyn, F.J. Gut microbiota in ALS: Possible role in pathogenesis? Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, S. Gut microbiota in neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 328, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, T.; Debelius, J.W.; Fang, F. Gut microbiome and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review of current evidence. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 758–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Dong, W.; Yang, Q.; Yu, X.; Ma, J.; Gu, W.; Huang, Y. Altered Gut Microbiota Related to Inflammatory Responses in Patients With Huntington’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 603594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wronka, D.; Karlik, A.; Misiorek, J.O.; Przybyl, L. What the Gut Tells the Brain-Is There a Link between Microbiota and Huntington’s Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotowska-Zimmer, A.; Przybyl, L.; Pewinska, M.; Suszynska-Zajczyk, J.; Wronka, D.; Figiel, M.; Olejniczak, M. A CAG repeat-targeting artificial miRNA lowers the mutant huntingtin level in the YAC128 model of Huntington’s disease. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 28, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, D.; Mestre, T.A. Therapeutic Update on Huntington’s Disease: Symptomatic Treatments and Emerging Disease-Modifying Therapies. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1645–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Lalonde, K.; Truesdell, A.; Gomes Welter, P.; Brocardo, P.S.; Rosenstock, T.R.; Gil-Mohapel, J. New Avenues for the Treatment of Huntington’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Zeng, M.X.; Cai, D.; Zhou, H.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, Z. Correlation between APOE4 gene and gut microbiota in Alzheimer’s disease. Benef. Microbes 2023, 14, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammann, D.; Lu, Y.; Cummings, M.J.; Zhang, M.L.; Cue, J.M.; Do, J.; Ebersole, J.; Chen, X.; Oh, E.C.; Cummings, J.L.; et al. Genetic correlations between Alzheimer’s disease and gut microbiome genera. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Mulak, A. Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harach, T.; Marungruang, N.; Duthilleul, N.; Cheatham, V.; Mc Coy, K.D.; Frisoni, G.; Neher, J.J.; Fåk, F.; Jucker, M.; Lasser, T.; et al. Erratum: Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Bella, R.; Alagona, G.; Ferri, R.; Carnemolla, A.; Pennisi, G. Helicobacter pylori and Alzheimer’s disease: A possible link. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 15, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.L. Gut Microbiota and Dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 5026–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodson, R. Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Publ. Group UK 2018, 559, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhoefer, L.; Reichmann, H. Pathogenesis of Parkinson disease—The gut–brain axis and environmental factors. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Q.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T. The role of the LRRK2 gene in Parkinsonism. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessi, D.R.; Sammler, E. LRRK2 kinase in Parkinson’s disease. Science 2018, 360, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, M.; Nishiwaki, H.; Hamaguchi, T.; Ohno, K. Gastrointestinal disorders in Parkinson’s disease and other Lewy body diseases. NPJ Park. Dis. 2023, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Yue, Y.; He, T.; Huang, C.; Qu, B.; Lv, W.; Lai, H.-Y. The Association Between the Gut Microbiota and Parkinson’s Disease, a Meta-Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 636545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, A.; Udayabanu, M. Gut microbiota: Implications in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulak, A.; Bonaz, B. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in Parkinson’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10609–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahl, M.V.C.; Andrade, B.d.S.; Perin, A.P.A.; Neves, G.A.; Duarte, L.d.S.; Uberti, A.F.; Hohl, K.S.; Follmer, C.; Carlini, C.R. Could the Urease of the Gut Bacterium Play a Role in the Altered Gut-Brain Talk Associated with Parkinson’s Disease? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardenhorst, S.K.; Cereda, E.; Severgnini, M.; Barichella, M.; Pezzoli, G.; Keshavarzian, A.; Desideri, A.; Pietrucci, D.; Aho, V.T.E.; Scheperjans, F.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in Parkinson disease: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 3581–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liao, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, F.; Fei, B.; Bao, C.; Cao, H.; Mao, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Effects of prebiotic supplement on gut microbiota, drug bioavailability, and adverse effects in patients with colorectal cancer at different primary tumor locations receiving chemotherapy: Study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. Trials 2023, 24, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Nicholson, J.K. Gut microbiota: A potential new territory for drug targeting. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Xu, H.; Luo, Q.; He, J.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Tang, W.; Nie, Y.; Zhou, Y. Fecal microbiota transplantation to treat Parkinson’s disease with constipation: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, 16163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, D.; Zimmer, V.C.; Kauffmann, J.; Spiegel, J.; Dillmann, U.; Schwiertz, A.; Faßbender, K.; Fousse, M.; Unger, M.M. Impact of oral COMT-inhibitors on gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 70, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casani-Cubel, J.; Benlloch, M.; Sanchis-Sanchis, C.E.; Marin, R.; Lajara-Romance, J.M.; de la Rubia Orti, J.E. The Impact of Microbiota on the Pathogenesis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and the Possible Benefits of Polyphenols. An Overview. Metabolites 2021, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schupack, D.A.; Mars, R.A.T.; Voelker, D.H.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Kashyap, P.C. The promise of the gut microbiome as part of individualized treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroszkiewicz, J.; Groblewska, M.; Mroczko, B. The Role of Gut Microbiota and Gut-Brain Interplay in Selected Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowska, M.; Laskus, T.; Radkowski, M. Gut Microbiota in Neurological Disorders. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2019, 67, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heravi, F.S.; Naseri, K.; Hu, H. Gut Microbiota Composition in Patients with Neurodegenerative Disorders (Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s) and Healthy Controls: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, X.; Chen, T.; Luo, S.; Zhang, X. The role of the probiotic Akkermansia muciniphila in brain functions: Insights underpinning therapeutic potential. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 49, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekanaviciute, E.; Yoo, B.B.; Runia, T.F.; Baranzini, S.E. Gut bacteria from multiple sclerosis patients modulate human T cells and exacerbate symptoms in mouse models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10713–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; Liu, X.; Alam, A.M.; Haran, J.P.; McCormick, B.A.; Shu, X.; Wang, X.; Ye, K. Bacteroides Fragilis in the gut microbiomes of Alzheimer’s disease activates microglia and triggers pathogenesis in neuronal C/EBPβ transgenic mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, K.; Bjornevik, K.; Abu-Ali, G.; Chan, J.; Cortese, M.; Dedi, B.; Jeon, M.; Xavier, R.; Huttenhower, C.; Ascherio, A.; et al. The human gut microbiota in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2021, 22, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bacterial Species | Impact on Physiology | References |
|---|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium longum | Anti-inflammatory Reduced amyloid aggregation | [69] |
| Clostridium perfringens type B | Produces toxins Damages tissues and nerves | [40] |
| Escherichia coli | Protein misfolding through molecular mimicry Pro-inflammatory | [70] |
| Lactobacilli acidophilus | Anti-inflammatory Strengthen gut barrier Produce beneficial SCFAs | [69,71] |
| Campylobacter concisus | Pro-inflammatory Produces endotoxins Protein misfolding through molecular mimicry Disrupts GBA communication | [72] |
| Akkermansia muciniphila | Anti-inflammatory Gut barrier fortification Promotes neurotransmitter levels | [73] |
| Dorea formicigenerans | Stimulates IFNγ Metabolizes sialic acid Degrades mucin | [70] |
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus | Stimulates pro-inflammatory cytokines Depresses regulatory CD4 T cells | [74] |
| Bacteroides fragilis | Pro-inflammatory Protein misfolding through molecular mimicry Leaky gut | [75] |
| Eubacterium rectale | Anti-inflammatory Produces beneficial SCFAs | [76] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Philip Mani, A.; Balasubramanian, B.; Mali, L.A.; Joseph, K.S.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Pappuswamy, M.; Joseph, B.V. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 489-507. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020033
Philip Mani A, Balasubramanian B, Mali LA, Joseph KS, Meyyazhagan A, Pappuswamy M, Joseph BV. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(2):489-507. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020033
Chicago/Turabian StylePhilip Mani, Arshilin, Balamuralikrishnan Balasubramanian, Linsha A. Mali, Kadanthottu Sebastian Joseph, Arun Meyyazhagan, Manikantan Pappuswamy, and Biljo V. Joseph. 2024. "The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases" Microbiology Research 15, no. 2: 489-507. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020033
APA StylePhilip Mani, A., Balasubramanian, B., Mali, L. A., Joseph, K. S., Meyyazhagan, A., Pappuswamy, M., & Joseph, B. V. (2024). The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Microbiology Research, 15(2), 489-507. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020033






