Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has become a critical global health challenge. Infections, particularly those caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens, rank among the top causes of human mortality worldwide. Pseudomonas aeruginosa occupies a prominent position among pathogens responsible for opportunistic infections in humans. P. aeruginosa stands as a primary cause of chronic respiratory infections, significantly contributing to the burden of these chronic diseases. In the medical domain, nanotechnologies offer significant potential, spanning various applications, including advanced imaging, diagnostic devices, drug delivery systems, implants, tissue-engineered structures, and pharmaceutical treatments. Given the challenges associated with AMR and the limited discovery of new drugs to combat MDR microbes, there is a critical need for alternative strategies to address the problem of AMR. In this study, we synthesized titanium–cerium nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs) using an eco-friendly green synthesis approach. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirmed the crystalline nature of the Ti–Ce–NCs and determined the particle size to be 17.07 nm. Electron microscopy revealed the size range of the particles to be 13 to 54 nm, where the majority of the particles were in the 20 to 25 nm range. Upon examining the composition, the Ti–Ce–NCs were determined to be composed of cerium, oxygen, and titanium, whose relative abundance were 36.86, 36.6, and 24.77% by weight, respectively. These nanocomposites were then evaluated for their effectiveness against various virulent traits and biofilms in P. aeruginosa. Out of six tested virulence factors, more than 50% inhibition of five virulence factors of P. aeruginosa was found. Roughly 60% inhibition of biofilm was also found in the presence of 400 µg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs. The nanocomposites also altered the biofilm architecture of the test bacterium. The success of this research opens doors for the potential use of such nanomaterials in the discovery of new antibacterial agents to combat drug-resistant bacteria.
1. Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) stands as one of the most pressing global health concerns today [1]. To put this in perspective, a daily toll of 2000 lives worldwide is claimed by infections stemming from resistant bacteria [2], totaling a grim count of 258,000 fatalities due to AMR within a similar timeframe. The mortality due to infections, mainly multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens, is a major contributor to human fatalities on a global scale [3]. The primary driver of AMR is the excessive and inappropriate use of antibiotics in both the medical and agricultural sectors. Simultaneously, the global proliferation of resistant bacteria and resistance genes is linked to deficiencies in infection control and prevention within healthcare facilities, as well as substandard hygiene and sanitation practices in communities [1]. These challenges are exacerbated by inadequate infrastructure and governance shortcomings [4]. In the United States, a striking 80% to 90% of human antibiotic consumption occurs in outpatient settings, with nearly half of this usage deemed unnecessary or inappropriate [1]. Unless swift and effective measures are implemented, it is anticipated that AMR rates against commonly employed antibiotics may surpass 40% to 60% in specific nations by 2030. Furthermore, by the year 2050, an alarming yearly toll of approximately 10 million lives could be attributed to resistance against antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents, with a significant portion (nearly 9 million) concentrated in the regions of Africa and Asia [2].
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a widely distributed microorganism, holds a prominent position among pathogens responsible for opportunistic infections in humans [5]. Thanks to its remarkable adaptability and metabolic flexibility, P. aeruginosa can thrive in various ecological niches, such as in aquatic environments, animals, plants, and soil [6]. In the realm of healthcare, P. aeruginosa ranks as a frequent and severe instigator of nosocomial infections, especially impacting immunocompromised individuals (particularly those with neutropenia) and patients in intensive care units. Ventilator-associated pneumonia and burn wound infections, both associated with mortality rates exceeding 30%, are predominantly caused by P. aeruginosa [7,8]. Additionally, P. aeruginosa is also responsible for the majority of respiratory infections in patients with cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, contributing significantly to the burden of these chronic diseases [9]. The escalating prevalence of nosocomial and chronic infections because of MDR or XDR P. aeruginosa strains presents a formidable challenge, making it increasingly difficult to select appropriate treatments and resulting in substantial morbidity and mortality [10,11].
Nanotechnology involves harnessing the unique properties exhibited by materials at the nano scale. When applied to the field of medicine and healthcare, it is known as nanomedicine, and it has proven effective in addressing prevalent diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular diseases [12]. Nanoscience, on the other hand, focuses on studying the distinct characteristics of materials within the 1–100 nanometer range, while nanotechnology translates this knowledge into the creation or modification of innovative objects [13,14]. Nanotechnology has left a significant mark on nearly every industry and facet of society by offering products that are superior in quality, safety, durability, and intelligence. Everyday items such as sunscreens, cosmetics, sporting goods, tires, and electronics have also incorporated nanomaterials to enhance their performance [15]. Nanomedicine specifically applies nanotechnologies to the realm of healthcare [16]. It employs nanoscale technologies and techniques to prevent, monitor, diagnose, and treat diseases [17]. In medicine, nanotechnologies hold immense promise, encompassing diagnostic tools, imaging methods, tissue-engineered constructs, drug delivery systems, implants, and pharmaceutical therapies [18]. The progress has significantly improved the treatment of various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular conditions, musculoskeletal disorders, neurodegenerative and psychiatric illnesses, viral and bacterial infections, and diabetes [19].
Considering the problems associated with AMR and the lack of discovery of new drugs to combat drug-resistant microbial pathogens, there is a concentrated need for the development of new antibiotics or alternative strategies to fight AMR. Nanomaterials are proving to be good antibacterial materials [20]. In this study, we synthesized titanium–cerium nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs) using green synthesis. The nanocomposites were tested against multiple virulent traits and a biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. If successful, such a nanomaterial could prove to be useful in the discovery of new antibacterial agents to fight against drug-resistant bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Ocimum tenuiflorum Leaf Extract and Synthesis of Ti–Ce–NCs
The process of obtaining extracts of Ocimum tenuiflorum leaves involved the addition of 200 g of finely powdered dried leaves to 1000 mL of methanol. The suspension was intermittently shaken for a few hours. Subsequently, the extract underwent filtration and then centrifugation to obtain clear extract. This plant extract served as a green reducing agent in the production of titanium–cerium nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs).
The synthesis process was initiated by combining 50 mM cerium nitrate hexahydrate with 50 mL of ethanol in a beaker with continuous stirring. Simultaneously, we introduced titanium (IV) dioxide into distilled water, maintaining the consistent stirring motion. When these two solutions were brought together, we added 15 mL of freshly prepared O. tenuiflorum leaf extract to the earlier mixture, maintaining continuous stirring. As a result, the mixture showed a dark brown color, and after 2 h, a yellow precipitate settled at the bottom. This yellow precipitate underwent three rounds of centrifugation at 15,000 rpm, followed by overnight drying in an 80 °C oven. The resulting material was further processed by grinding using a mortar and pestle. Lastly, it was subjected to a calcination process at 500 °C for a duration of 4 h, resulting in the production of a fine yellow powder of Ti–Ce–NCs. For all biofilm and quorum sensing assays, the fresh suspension of Ti–Ce–NCs was double-distilled by sonication for 30 min.
2.2. Characterization of Ti–Ce–NCs
The synthesized nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs) were characterized using numerous microscopic and spectroscopic tools, which are mentioned below.
2.2.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
For the X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, we employed a MiniFlexTM II XRD system from Rigaku Corporation in Tokyo, Japan. The CuKα radiation of wavelength 1.54060 Å with a nickel monochromator was used to capture the diffraction pattern, covering a 2θ range of 20° to 70°. The average crystal size of Ti–Ce–NCs was determined using Debye–Scherrer’s formula.
2.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
FTIR spectroscopy is a standard technique for nanoparticle characterization, offering insights into molecular vibrational and rotational modes. To prepare the Ti–Ce–NCs for analysis, the fine powder was mixed with KBr (1:100 ratio). He infrared spectrum was taken in diffuse reflectance mode, spanning from 4000 to 400 cm−1, with a resolution of 2 cm−1. We conducted FTIR spectroscopy using the Perkin Elmer FTIR spectrometer Spectrum II, USA.
2.2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
To facilitate TEM analysis, we suspended the fine Ti–Ce–NCs powder in double-distilled water and subjected it to 30 min of sonication to achieve a homogeneous suspension. Subsequently, we placed 10 µL of this aqueous Ti–Ce–NCs suspension onto a TEM grid, allowing it to dry at room temperature. The analysis was performed using a transmission electron microscope at the USIF in AMU, Aligarh, India. The distribution of particle size was determined by measuring the dimensions of individual nanoparticles.
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Elemental Composition Analysis
The finely powdered Ti–Ce–NCs were analyzed using a scanning electron microscope to visualize their surface morphology and determine their elemental composition. The instrument used was a JSM 6510LV from JEOL, Tokyo, Japan. The elemental composition of Ti–Ce–NCs was assessed using an INCAx-sight EDAX spectrometer (Oxford Instruments, Buckinghamshire, UK), which was integrated with the scanning electron microscope.
2.3. Bacterial Strain and Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
The MIC of Ti–Ce–NCs against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 was determined using TTC dye (2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride) [21]. P. aeruginosa PAO1 was cultured in 96-well polystyrene plates with varying Ti–Ce–NCs doses ranging from 25 to 1600 µg/mL for a duration of 24 h. A control group, without Ti–Ce–NCs, was included as the control set. Following overnight growth, 10 µL of 2 mg/mL TTC were added to each well. After a 20 min incubation, the presence of a pink color indicated metabolically active cells. The lowest dose of Ti–Ce–NCs at which no pink/red color was seen when TTC was added was considered as the MIC. The absence of bacterial growth in the wells of polystyrene plates was further confirmed by point-inoculating the bacterial culture on agar plates. All subsequent assays of quorum sensing and biofilm were performed at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). The viability of P. aeruginosa PAO1 in the presence of sub-MICs (200 and 400 µg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs and its absence was assayed and no significant difference in viability at the highest sub-MIC was found (Supplementary Figure S1). To further confirm that sub-MICs of Ti–Ce–NCs did not alter the growth of P. aeruginosa PAO1, growth curve assays were performed. The growth curve of P. aeruginosa PAO1 in the absence and presence of Ti–Ce–NCs is depicted in Supplementary Figure S2. It is evident from the data that there was a negligible effect on the growth of P. aeruginosa PAO1 in the presence of sub-MICs of Ti–Ce–NCs.
2.4. Assays for Inhibition of QS-Controlled Virulence Factors in P. aeruginosa PAO1
The effects of Ti–Ce–NCs on six virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 at sub-MICs were examined through the following detailed procedures.
2.4.1. Evaluation of Exoprotease Activity
The activity of exoproteases in P. aeruginosa PAO1 was assessed following the azocasein degradation protocol, a outlined previously [22]. The bacteria were grown without and with different doses (50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs for 18 h under constant shaking at physiological temperature (37 °C). After incubation, bacterial cultures were centrifuged to discard the bacterial cells and the cell-free supernatant (CFS) was taken. Briefly, 100 microliters of CFS from both the control and Ti–Ce–NCs-treated bacterial cultures was mixed with 1000 µL of 0.3% azocasein solution (containing 500 µM calcium chloride in 0.05 M Tris-HCl). This mixture was then incubated at 37 °C for 20 min. To stop the reaction, 0/5 mL of 10% TCA was added, and the reaction mixture was subsequently centrifuged for 12 min. The absorbance of the resulting supernatant was measured at 400 nm with a spectrophotometer.
2.4.2. Evaluation of Elastase Activity
The elastase activity in the culture supernatant of P. aeruginosa PAO1 was assessed with ECR (Elastin Congo Red) dye [23]. A volume of 100 µL of CFS from both the control and Ti–Ce–NCs-treated P. aeruginosa PAO1 was mixed with 900 µL ECR buffer (containing 1 mM CaCl2 and 5000 µg/mL ECR in 0.1 M Tris) and then incubated at 37 °C for 3 h with gentle mixing. To halt the reaction, 1 mL sodium phosphate buffer was added, followed by 30 min of cooling on ice. After centrifugation, the insoluble ECR was discarded, and absorbance was measured at 495 nm. The percentage inhibition in elastinolytic activity was computed by comparing with an untreated control.
2.4.3. Evaluation of Pyocyanin Pigment Production
The analysis of pyocyanin production was conducted in Pseudomonas broth (PB), consisting of 1.4 mg/mL MgCl2, 20 mg/mL peptone, and 10 mg/mL K2SO4, known to enhance pyocyanin production [24]. P. aeruginosa PAO1 was cultured in PB medium under various conditions: without Ti–Ce–NCs and with varying Ti–Ce–NCs doses (50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL) for a duration of 18 h. In total, 5 mL of the grown culture was extracted using 3 mL chloroform, with the aqueous phase removed. The top organic phase was then extracted with 1200 µL HCl (0.2 N). The absorbance of the resulting pink aqueous phase was measured at 520 nm. The concentration of pyocyanin was quantified in µg/mL by multiplying the absorbance by 17.072, as specified previously [25].
2.4.4. Evaluation of Pyoverdin Production
The assessment of pyoverdin production followed a previously described method [26]. In brief, an overnight-cultured sample of P. aeruginosa PAO1, cultured in the absence and presence of Ti–Ce–NCs as mentioned earlier, was collected. The culture was centrifuged to obtain a CFS. A volume of 100 microliters of the supernatant was added to 900 microliters of Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.4 and 50 mM). Using a spectrofluorometer, fluorescence signals of this solution were measured at 460 nm upon exciting at 400 nm. The percentage inhibition of pyoverdin was estimated with respect to the control.
2.4.5. Evaluation of Rhamnolipid Production
The rhamnolipid assay employed orcinol method with slight modifications based on a previous protocol [27]. A volume of 300 µL of CFS from both the control and Ti–Ce–NCs-treated cultures of P. aeruginosa PAO1 was extracted in 600 µL diethyl ether. After collecting the diethyl ether phase, it was dried at 37 °C and then re-dissolved in 0.1 mL deionized water. To each sample, 0.9 mL of a 0.19% orcinol solution was added. The samples were heated for half an hour at 80 °C, and then allowed to cool for 15 min at room temperature. Finally, the absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured at 421 nm.
2.4.6. Evaluation of Swarming Motility
For the assessment of swimming motility, 5 µL of an overnight-cultured sample of P. aeruginosa PAO1 was placed on 0.3% LB agar plates containing various doses (50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs and allowed to dry under a laminar flow [28]. Plates without Ti–Ce–NCs served as the control. After 18 h of incubation, the diameter of the swarm zone was measured, indicating the extent of swimming motility. The swarm zone was measured in millimeters, and the data are presented as %inhibition computed with respect to control.
2.5. Evaluation of Biofilm Formation
The inhibition of biofilm formation was conducted using a 96-well microtiter plate method with crystal violet staining [24]. Overnight cultures of P. aeruginosa PAO1 were added to the wells, each containing 150 µL of LB medium diluted at a 1:50 ratio. Treatment groups were supplemented with various doses of sub-MICs (50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs, while the control wells remained untreated. The microplate was then incubated overnight. After incubation, excess broth along with the planktonic cells were discarded by gently washing the wells with buffer (phosphate). Subsequently, the microplate wells were dried for 20 min. The biofilms in the wells were stained using a 0.2 mL crystal violet for 15 min. Following staining, the wells were rinsed with autoclaved buffer to remove any unbound dye. The crystal violet that had adhered to the biofilms was dissolved in 90% ethanol, and absorbance was measured at 620 nm. The MBIC50 and MBIC90 values (minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration) were calculated via Probit analysis.
2.6. Microscopic Examination of Biofilm
Cultures of P. aeruginosa PAO1 that had been grown overnight were introduced into 12-well polystyrene plates containing growth medium and sterilized glass coverslips were placed in the wells in a slanted position. P. aeruginosa PAO1 was cultured both in the absence and presence of the highest sub-MIC (400 µg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs. After overnight incubation, the coverslips were washed with phosphate buffer to eliminate loosely attached bacterial cells. Subsequently, they were stained with a crystal violet solution and allowed to air-dry. The crystal violet-stained glass coverslips were then observed with a light microscope. The images were taken at a magnification of 40×. For scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the same biofilm development process was followed as described above. Unattached bacterial cells were eliminated by washing with the phosphate buffer and biofilms were fixed with glutaraldehyde (2.5%). The dehydration of biofilms was achieved with a series of ethanol solutions (ranging from 20 to 100%) for 10 min each. Afterward, glass coverslips were air-dried and coated with a gold layer before being visualized.
2.7. Eradication of Biofilm
To test the effect of Ti–Ce–NCs on the established biofilms, we followed a standard method with some modifications [21]. We cultured the bacteria in 96-well plates for 24 h at 37 °C to form biofilms. Then, we gently removed the media and washed the wells with sterile buffer to get rid of unattached cells. We added fresh media (Luria Bertani broth) and Ti–Ce–NCs at different concentrations (400–1600 μg/mL) and incubated the plate for another 24 h without shaking. After that, we washed the wells again with sterile buffer and stained the biofilms with crystal violet for 20 min. We removed the stain and rinsed the wells. Finally, we dissolved the biofilms in ethanol and measured the absorbance using a microplate reader. The MBEC50 and MBEC90 values (minimum biofilm eradication concentration) were calculated with Probit analysis.
2.8. Statistical Analysis of Data
Each assay was conducted independently four times, and these experiments were replicated at least twice. The results presented in this research represent the mean values along with their respective standard deviations. The statistical significance of treatment groups was determined by comparing them to the untreated control to calculate p-values. Instances where * is indicated denote p-values of ≤0.05 compared to the control, and ** denotes p-values of ≤0.01 compared to the control.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Ti–Ce–NCs
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern was utilized to ascertain the lattice parameters of Ti–Ce–NCs. To compute the size of crystallites (D), the widely recognized Debye–Scherrer Formula (1) was employed.
where the symbol D represents crystallite size when the Scherrer constant (k) was set at 1.0 and the wavelength of X-ray radiation (k) was 1.5406 Å. Additionally, β stands for the full width at half maximum, while θ represents the Bragg’s angle associated with the specific diffraction peak. Figure 1A displays the XRD pattern of Ti–Ce–NCs. The peaks found at 2θ values of approximately 25.39, 37.53, 47.69, 54.59, and 62.42 correspond to the crystallographic planes (101), (110), (201), (202), and (113), respectively. By applying Scherrer’s equation, the particle size of Ti–Ce–NCs was determined to be 17.07 nm. These observed planes affirm that Ti–Ce–NCs have an FCC cubic fluorite structure [29]. The XRD pattern confirms the presence of single-phase Ti–Ce–NCs [30]. The further characterization of Ti–Ce–NCs was done using FTIR spectroscopy. The FTIR spectra of the O. tenuiflorum leaf extract, cerium nitrate hexahydrate, titanium (IV) dioxide, and Ti–Ce–NCs are shown in Figure 1B. The irregular bands at 1400–100 cm−1 (especially near 1383 and 1050 cm−1) in cerium nitrate hexahydrate reveal the presence of nitrate groups in cerium nitrate hexahydrate [31]. The band recorded around 1630 cm−1 in the titanium (IV) dioxide sample corresponds to the bending modes of the water Ti–OH. Moreover, a peak near 1410 to 1383 cm−1 is associated with Ti–O modes [32]. In the IR spectrum of the O. tenuiflorum leaf extract, the vibrational stretching identified near 2700–2800 cm−1 is an indicator of bioactive thiamine N=C=S stretching vibrations [33]. Moreover, the appearance of a peak at 1830 cm−1 is due to the COO- group present in various constituents of the O. tenuiflorum leaf extract [34]. A prominent peak at 3434 cm−1 is due to O–H groups within water molecules [35]. Additionally, a distinct band observed at 1384 cm−1 is associated with Ce–O–Ce vibrations [36]. A prominent peak at 520 cm−1 shows the presence of a perovskite structure [37]. Moreover, the noticeable peak starting at 400 cm−1 also suggests the formation of a Ce–O–Ti bond [38].
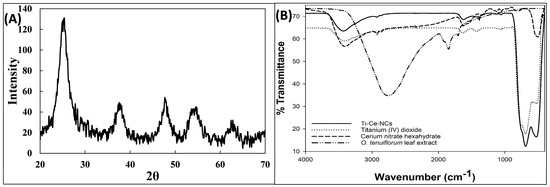
Figure 1.
(A) X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of titanium–cerium nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs) synthesized using Ocimum tenuiflorum leaf extract. (B) Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of Ocimum tenuiflorum leaf extract, cerium nitrate hexahydrate, titanium (IV) dioxide, and titanium–cerium nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs) synthesized using Ocimum tenuiflorum leaf extract.
A structural and morphological examination of Ti–Ce–NCs was conducted via electron microscopic examination. Figure 2A displays the transmission electron microscopic image of Ti–Ce–NCs. The micrograph reveals that the majority of the nanocomposites exhibited a spherical or spheroidal shape. These nanocomposites were polydispersed, with sizes ranging from 13 to 54 nm (Figure 2A). The average particle size of Ti–Ce–NCs was determined to be 26.96 ± 8.92 nm. Furthermore, the TEM image clearly demonstrates that the majority of nanocomposites were in the 20 to 25 nm range.
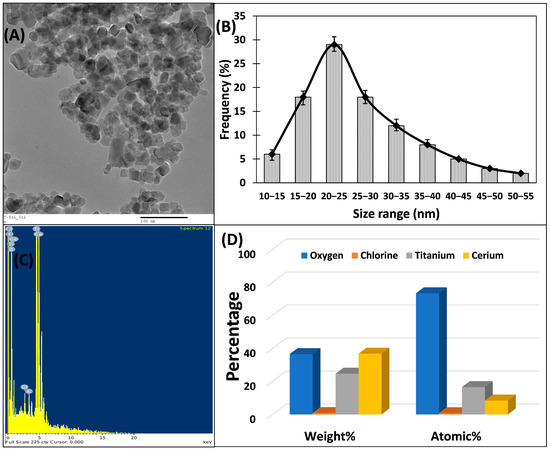
Figure 2.
(A) Transmission electron microscopic image of titanium–cerium nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs) synthesized using Ocimum tenuiflorum leaf extract. (B) Particle size distribution of Ti–Ce–NCs. (C) Atomic spectrum of Ti–Ce–NCs. (D) Elemental composition analysis of Ti–Ce–NCs.
The elemental composition of Ti–Ce–NCs was investigated through EDX analysis coupled with scanning electron microscopy. Figure 2C shows the atomic spectrum and elemental composition of Ti–Ce–NCs. The analysis shows that cerium, oxygen, and titanium were the predominant elements, constituting 36.86, 36.6, and 24.77% by weight (Figure 2D). Additionally, a trace amount of chlorine, less than 1%, was also detected in Ti–Ce–NCs, which may be attributed to its presence on the nanoparticle’s surface, potentially serving as a capping agent for these nanoparticles [39].
3.2. Ti–Ce–NCs Inhibits the Virulent Enzymes of P. aeruginosa PAO1
The effects of Ti–Ce–NCs on two enzymes of P. aeruginosa PAO1 were tested, and were shown to be virulent in nature. The proteases and elastases are essential factors contributing to the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa [40]. Figure 3 provides a detailed overview of the impact of Ti–Ce–NCs on exoprotease and elastase activity. Exoproteases, when secreted outside the bacterial cells, enhance the invasion of bacteria by breaking down proteins and evading the immune response [41]. While a lower concentration (50 µg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs demonstrated only a minimal reduction (less than 15%) in activity, higher concentrations led to significant inhibitions. The presence of 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs inhibited the activity of these azocasein-degrading enzymes by 30.98, 52.42, and 71.33%, respectively.
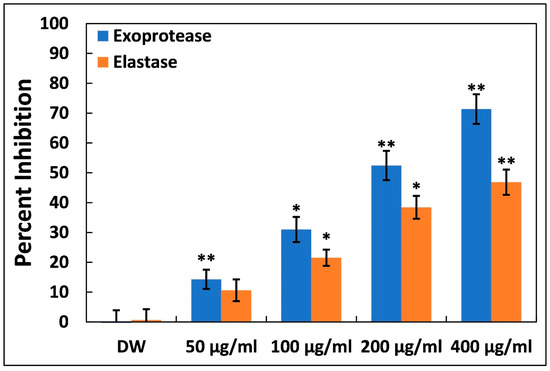
Figure 3.
Inhibition of exoprotease and elastase activity in P. aeruginosa PAO1 by Ti–Ce–NCs. Data are shown as average of four replicates with standard deviation. DW is distilled water, the negative control; * denotes p-values of ≤0.05 compared to the control; ** denotes p-values of ≤0.01 compared to the control.
Elastases, which belong to a group of hydrolytic enzymes, are known to degrade host tissues and interfere with the immune system [42]. The significance of virulent traits and biofilm formation in the pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa heavily relies on the expressions of las proteins, which are regulated by quorum sensing (QS). These enzymes also play a crucial role in virulence and biofilm development. At 50, 100, and 200 µg/mL of Ti–Ce–NCs, elastase activity was reduced by 10.60, 21.49, and 38.41%, respectively. At the highest sub-MIC, i.e., 400 µg/mL, a roughly 50% inhibition of elastinolytic enzyme was recorded. These findings strongly indicate that Ti–Ce–NCs interfere with P. aeruginosa’s lasI-lasR quorum sensing system, as is consistent with previous observations [28]. Other metal nanoparticles, like silver nanoparticles and tin oxide nanoparticles, have been reported to inhibit the virulent enzymes of P. aeruginosa by targeting quorum sensing [27,43].
3.3. Inhibition of Virulent Pigments of P. aeruginosa PAO1 by Ti–Ce–NCs
Pyocyanin, a distinctive blue-greenish pigment, is subjected to the direct regulation of quorum sensing in P. aeruginosa, contributing significantly to the bacterium’s virulence [44]. The synthesis of pyocyanin involves a series of steps, beginning with the generation of autoinducer molecules and the subsequent expression of specific genes (phzA-G). Pyocyanin is also known for its role in biofilm formation [45,46] and its influence on various cellular processes, primarily due to its redox properties, making it a pivotal component in P. aeruginosa’s pathogenicity [47]. Both phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (a pyocyanin precursor) and pyocyanin disrupt the normal rhythmic motion of respiratory cilia in humans and interfere with the expression of immune-modulating proteins in individuals with cystic fibrosis. Additionally, pyocyanin-induced oxidative stress exacerbates the severity of infection [48,49]. Treatment with Ti–Ce–NCs resulted in a reduction in pyocyanin production in P. aeruginosa PAO1, as illustrated in Figure 4A. At doses of 50 µg/mL, an insignificant (p > 0.05) degree of inhibition was found. Conversely, with higher doses (100, 200, and 400 µg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs, we saw 27.71, 51.90, and 67.80% inhibitions of pyocyanin pigment production. It is worth noting that tin oxide hollow nanoflowers have previously demonstrated the ability to inhibit pyocyanin levels in P. aeruginosa PA01 by roughly 60% [43].
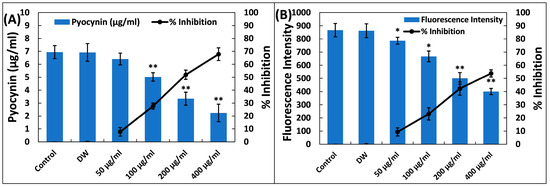
Figure 4.
(A) Inhibition of pyocyanin production in P. aeruginosa PAO1 by Ti–Ce–NCs. Percent inhibition is shown on the secondary y-axis. Data are shown as the average of four replicates with standard deviation. DW is distilled water, the negative control; * denotes p-values of ≤0.05 compared to the control; ** denotes p-values of ≤0.01 compared to the control. (B) Inhibition of pyoverdin in P. aeruginosa PAO1 by Ti–Ce–NCs. Percent inhibition is shown on the secondary y-axis. Data are shown as average of four replicates with standard deviation. DW is distilled water, the negative control; * denotes p-values of ≤0.05 compared to the control; ** denotes p-values of ≤0.01 compared to the control.
Another virulence factor, pyoverdin, known for its fluorescent properties, plays a critical role in P. aeruginosa’s virulence and subsequent infections [50]. Research has indicated that pyoverdin production is regulated by quorum sensing, as QS-deficient P. aeruginosa exhibited reduced pyoverdin levels [51]. This siderophore competes for iron within transferrin proteins, and so ensuring an ample supply of iron is crucial for P. aeruginosa’s survival in host systems [52]. Recent findings have also highlighted pyoverdin’s ability to evade recognition by the host’s defense protein, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, further contributing to P. aeruginosa infections inside the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis [50]. Ti–Ce–NCs treatment also resulted in decreased pyoverdin levels (Figure 4B). Reductions of 09.34, 23.05, 42.26, and 53.82% were observed compared to the control when treatments of 50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL of Ti–Ce–NCs were applied, respectively. This reduction in pigment synthesis underscores the effectiveness of Ti–Ce–NCs against quorum sensing-mediated virulence in P. aeruginosa.
3.4. Ti–Ce–NCs Inhibits Rhamnolipid Production and Motility in P. aeruginosa PAO1
Rhamnolipids, which are surfactant molecules, represent another significant virulence factor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These glycolipids are present in virulent strains and play a role in modulating human respiratory epithelium, facilitating cellular invasion [53,54]. Ti–Ce–NCs have demonstrated their effectiveness in suppressing rhamnolipid production in P. aeruginosa PAO1, as depicted in Figure 5A. The presence of 50, 100, and 200 µg/mL of Ti–Ce–NCs in culture media reduced rhamnolipid production by 18.14, 41.65, and 48.49%, respectively. There was a more than 60% inhibition of this surfactant in the presence of 400 µg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs (the highest sub-MIC). These surfactants not only initiate the formation of biofilms, but also exert an influence on bacterial motility [55].
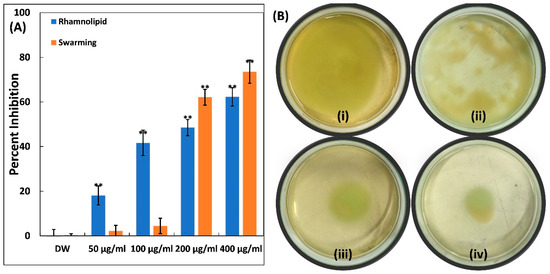
Figure 5.
(A) Quantitative data for inhibition of rhamnolipid production and swarming motility in P. aeruginosa PAO1 by Ti–Ce–NCs. Data are shown as the average of four replicates with standard deviation. DW is distilled water, the negative control; ** denotes p-values of ≤0.01 compared to the control. (B) Inhibition of swimming motility in P. aeruginosa PAO1, (i) control P. aeruginosa PAO1; (ii) P. aeruginosa PAO1 treated with 100 μg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs; (iii) P. aeruginosa PAO1 treated with 200 μg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs; (iv) P. aeruginosa PAO1 treated with 400 μg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs.
The impact of Ti–Ce–NCs was also assessed on the swarming motility of P. aeruginosa PAO1, and the results are presented in Figure 5A. The mobility of P. aeruginosa, including swarming, swimming, and twitching, plays a vital role in the dissemination of infections and the progression of biofilm [56]. As observed in control plates, P. aeruginosa PAO1 swarmed to the edge of the petri plate upon overnight incubation (Figure 5B). Moreover, there was also a characteristic light green color, which is due to the pigment production in P. aeruginosa PAO1. The presence of Ti–Ce–NCs in soft agar plates led to a progressive reduction in this bacterial motility. At lower doses (50 and 100 µg/mL), there was no effect on the motility of P. aeruginosa PAO1, yet some reduction in pigment production could be seen in soft agar plates. Nonetheless, reductions of 62.11 and 73.53% were found at 200 and 400 µg/mL of Ti–Ce–NCs, respectively, compared to the control. P. aeruginosa’s motility is a key factor in its ability to spread infections and establish biofilms [56]. There is evidence that silver nanoparticles, synthesized using an Murraya koenigii extract, significantly reduced the swarming motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by >85% [57]. In summary, Ti–Ce–NCs exhibit a multi-target action against P. aeruginosa, indicating their potential benefits in preventing and managing the infections.
3.5. Ti–Ce–NCs Inhibits the Biofilm of P. aeruginosa PAO1
Biofilms provide a distinct advantage for pathogenic bacteria, as they enhance survival under stressful conditions and facilitate successful establishment within hosts. The antibiofilm potential of Ti–Ce–NCs was investigated in P. aeruginosa PAO1 at sub-MICs, and the findings are presented in Figure 6. At the lowest tested sub-MIC (50 µg/mL), an insignificant (p > 0.05) change in the biofilm formation was found. However, the data indicate a reduction in the biofilm-forming ability of P. aeruginosa PAO1 by 23.30, 45.70, and 59.22% at 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs CANPs, respectively. The MBIC50 and MBIC90 of Ti–Ce–NCs against P. aeruginosa PAO1 were found to be 266.46 and 1482.28 µg/mL, respectively. The quantitative biofilm data were further validated with microscopic examinations. P. aeruginosa PAO1 formed dense cellular aggregates (Figure 7A). However, the treatment with 400 µg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs notably reduced cell aggregation and density (Figure 7B). This was further confirmed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) at a higher magnification. Untreated P. aeruginosa PAO1 cells appeared in thick clusters along with the exopolymeric substance encompassing the cells (Figure 7C), while Ti–Ce–NCs (400 µg/mL) treatment led to reduced aggregation. Moreover, a reduction in exopolymeric substance was also observed, as depicted in Figure 7D. These results provide compelling evidence of Ti–Ce–NCs’ ability to inhibit the biofilm of P. aeruginosa PAO1.
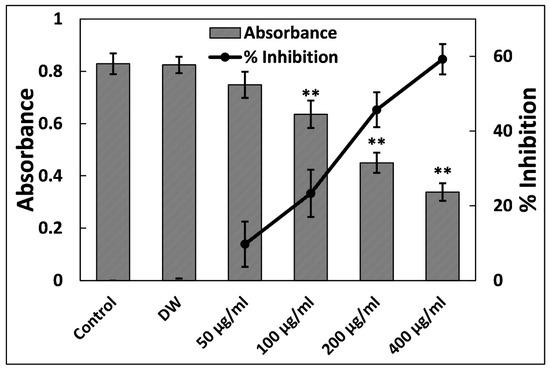
Figure 6.
Inhibition of biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa PAO1 by Ti–Ce–NCs. Percent inhibition is shown on the secondary y-axis. Data are shown as the average of four replicates with standard deviation. DW is distilled water, the negative control; ** denotes p-values of ≤ 0.01 compared to the control.
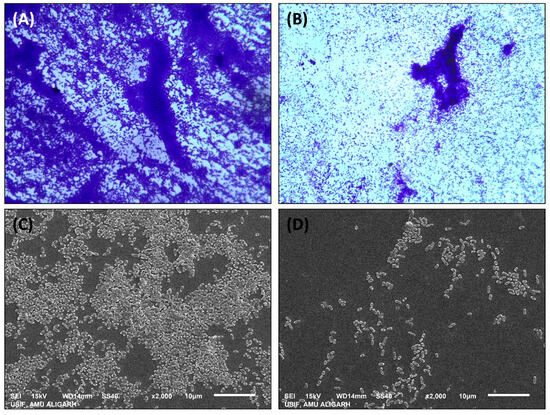
Figure 7.
(A) Light microscopic image of biofilm of untreated P. aeruginosa PAO1. (B) Light microscopic image of biofilm of P. aeruginosa PAO1 treated with 400 μg/ml Ti–Ce–NCs. (C) Scanning electron microscopic image of biofilm of untreated P. aeruginosa PAO1. (D) Scanning electron microscopic image of biofilm of P. aeruginosa PAO1 treated with 400 μg/ml Ti–Ce–NCs.
The protective barrier of biofilms significantly contributes to bacterial pathogenicity, making them more resilient against physical and chemical agents [58]. Biofilm formation follows a structured and sequential process that is positively correlated with quorum sensing (QS). It is well-documented that four out of five human infections are linked to microbes growing in biofilms [59]. The synthesized nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs) effectively inhibited biofilms in P. aeruginosa PAO1. Our findings align with the existing literature, wherein silver nanoparticles, zinc oxide nanoparticle, tin oxide nanoparticles, etc., reduced biofilm development in P. aeruginosa [27,43,60]. The role of Ti–Ce–NCs against biofilms is evident in our current investigation; however, further studies are required to explore the specific mode of action of Ti–Ce–NCs. Another study supports our findings, indicating that titanium-doped cerium oxide nanoparticles inhibited the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by approximately 75% [30].
3.6. Ti–Ce–NCs Eradicates the Biofilm of P. aeruginosa PAO1
Most antibacterial medications primarily target the planktonic form of bacterial growth, with only a few capable of impeding the formation of biofilms [61]. Eradicating established biofilms is generally more challenging than inhibiting their formation. In many infections, biofilms develop at the infection site. In this study, P. aeruginosa PAO1 was allowed to form biofilms in 96-well microtiter plates before treatment. The impact of Ti–Ce–NCs on pre-existing biofilms is illustrated in Figure 8. At lower tested doses (till 200 µg/mL), insignificant and less than 4% inhibition was recorded. In the presence of 400 µg/mL of Ti–Ce–NCs, a roughly 13% reduction in mature biofilms was observed; however, this is also statistically insignificant compared to control. The presence of Ti–Ce–NCs at concentrations of 800 and 1200 µg/mL Ti–Ce–NCs reduced the established P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilms by 35.17 and 61.66%, respectively. At a higher dose (1600 µg/mL), a more than 73% reduction in the preexisting biofilm was found. The MBEC50 and MBEC90 of Ti–Ce–NCs against P. aeruginosa PAO1 were found to be 995.01 and 2695.42 µg/mL, respectively. This result demonstrates the successful eradication of biofilms. Bacterial biofilms are clusters of bacterial cells surrounded by extracellular polymeric substances, primarily composed of polysaccharides, nucleic acids, polypeptides, and other biochemical components [62,63]. These substances create a barrier that hinders the entry of chemotherapeutic agents [64]. Our findings align with a previous report that established that biofilms of P. aeruginosa were disrupted by roughly 65%. Silver nanoparticles have been shown to penetrate the biofilm matrix, suggesting that Ti–Ce–NCs may similarly infiltrate established biofilms, leading to disruption. The results indicate that Ti–Ce–NCs are also effective in eradicating biofilms of P. aeruginosa PAO1.
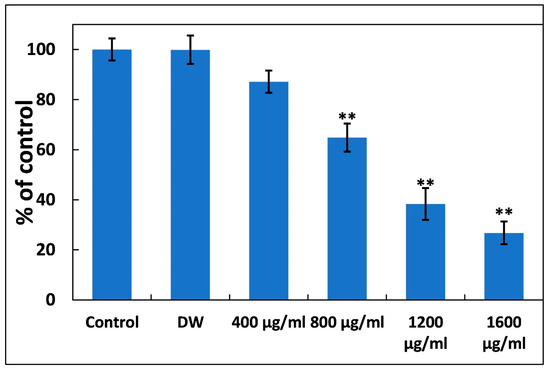
Figure 8.
Disruption of established P. aeruginosa PAO1 by Ti–Ce–NCs. Data are shown as the average of four replicates with standard deviation. DW is distilled water, the negative control; ** denotes p-values of ≤0.01 compared to the control.
4. Conclusions
AMR stands as a paramount global health crisis, mainly due to infections caused by MDR pathogens, ranking among the leading causes of worldwide human mortality. P. aeruginosa is a primary culprit behind chronic respiratory infections, significantly contributing to the burden of chronic diseases. Given the formidable challenges posed by AMR and the limited rate of discovery of new drugs to combat MDR microbes, there is a pressing requirement for alternative approaches to confront this crisis. Considering the excellent properties of nanomaterials, titanium–cerium nanocomposites (Ti–Ce–NCs) were prepared through the green synthesis method. Ti–Ce–NCs show a crystalline nature with average particle sizes of 17.07 nm. Cerium and titanium are among the top three constituents of Ti–Ce–NCs, with weight% values of 36.86% and 24.77%, respectively. Subsequently, Ti–Ce–NCs were subjected to rigorous evaluations for their effectiveness against various virulent traits and biofilms produced in P. aeruginosa. Remarkably, more than 50% inhibition was observed for five out of six tested virulence factors of P. aeruginosa, highlighting the potential of Ti–Ce–NCs as a countermeasure. Moreover, a substantial inhibition in biofilm (60%) was recorded in the presence of 400 µg/mL of Ti–Ce–NCs, along with notable alterations in the biofilm architecture of the test bacterium. The findings of this research pave the way for the possible application of such nanomaterials in the quest for novel antibacterial agents to combat drug-resistant bacteria.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microbiolres14040114/s1, Figure S1: The effect of sub-MICs (200 and 400 μg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs on the viability of P. aeruginosa PAO1. ns denotes a non-significant p-value more than 0.05; Figure S2: Growth curve of P. aeruginosa PAO1 in the absence and presence of sub-MICs (200 and 400 μg/mL) of Ti–Ce–NCs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.A.Q. and I.A.; methodology, M.A., N.P., F.A.Q. and K.M.A.; software, F.A.Q. and N.P.; data curation, M.A. and F.A.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A., N.P. and F.A.Q.; writing—review and editing, M.A. and F.A.Q.; supervision, M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2023R972), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2023R972), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for the support. F.A.Q. acknowledges CSIR, India {File no. 09/112(0626)2k19 EMR} for providing SRF.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| ECR | Elastin congo red |
| MDR | Multidrug resistance |
| QS | Quorum sensing |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| Ti–Ce–NCs | Titanium–cerium nanocomposites |
References
- Maillard, J.-Y.; Bloomfield, S.F.; Courvalin, P.; Essack, S.Y.; Gandra, S.; Gerba, C.P.; Rubino, J.R.; Scott, E.A. Reducing Antibiotic Prescribing and Addressing the Global Problem of Antibiotic Resistance by Targeted Hygiene in the Home and Everyday Life Settings: A Position Paper. Am. J. Infect. Control 2020, 48, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally. Available online: https://amr-review.org/Publications.html (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Serra-Burriel, M.; Keys, M.; Campillo-Artero, C.; Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M.; Gikas, A.; Palos, C.; López-Casasnovas, G. Impact of Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria on Economic and Clinical Outcomes of Healthcare-Associated Infections in Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, P.; Beggs, J.J.; Walsh, T.R.; Gandra, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Anthropological and Socioeconomic Factors Contributing to Global Antimicrobial Resistance: A Univariate and Multivariable Analysis. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e398–e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellatly, S.L.; Hancock, R.E.W. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: New Insights into Pathogenesis and Host Defenses. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silby, M.W.; Winstanley, C.; Godfrey, S.A.C.; Levy, S.B.; Jackson, R.W. Pseudomonas Genomes: Diverse and Adaptable. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 652–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.-L. Nosocomial Infections in Adult Intensive-Care Units. Lancet 2003, 361, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, A.; Mulet, X.; López-Causapé, C.; Juan, C. The Increasing Threat of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa High-Risk Clones. Drug Resist. Updates 2015, 21–22, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, A.; Mena, A.; Maciá, M.D. Evolution of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pathogenicity: From Acute to Chronic Infections. In Evolutionary Biology of Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 433–444. [Google Scholar]
- Livermore, D.M. Has the Era of Untreatable Infections Arrived? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, i29–i36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, C.; Suarez, C.; Gozalo, M.; Murillas, J.; Almirante, B.; Pomar, V.; Aguilar, M.; Granados, A.; Calbo, E.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; et al. Prospective Multicenter Study of the Impact of Carbapenem Resistance on Mortality in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Bloodstream Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.; Wong, N. Nanotechnology and Its Use in Imaging and Drug Delivery (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2021, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, K. Nanosystems: Molecular Machinery, Manufacturing, and Computation; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Belkin, A.; Hubler, A.; Bezryadin, A. Self-Assembled Wiggling Nano-Structures and the Principle of Maximum Entropy Production. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allhoff, F.; Lin, P.; Moore, D. What Is Nanotechnology and Why Does It Matter?: From Science to Ethics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P.; Rab, S.; Suman, R. Applications of Nanotechnology in Medical Field: A Brief Review. Glob. Health J. 2023, 7, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhzad, O.; Langer, R. Nanomedicine: Developing Smarter Therapeutic and Diagnostic Modalities. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1456–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Amiji, M.M. Application of Nanotechnology in Medical Diagnosis and Imaging. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 74, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A.; Caccamo, M.T. Smart Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Application: Development of Versatile Nanocarrier Platforms in Biotechnology and Nanomedicine. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 3702518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, U.; kumar Ponnala, A.; Jayabharathi, T.; Shanmugavel, M.; Sujatha, D.; Ezhilarasan, D. Antibacterial Properties of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles-An Overview. Appl. Microbiol. Theory Technol. 2023, 4, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Samreen; Ahmad, I. Broad-Spectrum Inhibitory Effect of Green Synthesised Silver Nanoparticles from Withania somnifera (L.) on Microbial Growth, Biofilm and Respiration: A Putative Mechanistic Approach. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, F.M.; Khan, R.A.; Hassan, I.; Shahzad, S.A.; AlHarbi, W. Coumarin Exhibits Broad-Spectrum Antibiofilm and Antiquorum Sensing Activity against Gram-Negative Bacteria: In Vitro and In Silico Investigation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 18823–18835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, F.M.; Arshad, M.; Khan, A.; Adil, M. Umbelliferone Modulates the Quorum Sensing and Biofilm of Gram−ve Bacteria: In Vitro and in Silico Investigations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I. Broad-Spectrum Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Inhibition by Green Tea against Gram-Negative Pathogenic Bacteria: Deciphering the Role of Phytocompounds through Molecular Modelling. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurachi, M. Studies on the Biosynthesis of Pyocyanine. II. Isolation and Determination of Pyocyanine. Bull. Inst. Chem. Res. Kyoto Univ. 1958, 36, 174–187. [Google Scholar]
- Qais, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, F.M.; Al-kheraif, A.A.; Arshad, M.; Alam, P. Plumbagin Inhibits Quorum Sensing-Regulated Virulence and Biofilms of Gram-Negative Bacteria: In Vitro and in Silico Investigations. Biofouling 2021, 37, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qais, F.A.; Shafiq, A.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, F.M.; Khan, R.A.; Hassan, I. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Carum Copticum: Assessment of Its Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Inhibitory Potential against Gram Negative Bacterial Pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 144, 104172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, F.M.; Alomar, S.Y.; Ahmad, N.; Albalawi, F.; Alam, P.; Albalawi, T. Interference of Quorum Sensing Regulated Bacterial Virulence Factors and Biofilms by Plumbago zeylanica Extract. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2021, 84, 3150–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, A.; Karthikeyan, C.; Haja Hameed, A.S.; Gopinath, K.; Gowri, S.; Karthika, V. Synthesis of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Using Gloriosa superba L. Leaf Extract and Their Structural, Optical and Antibacterial Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Iqbal, A.; Shafi, A.; Qais, F.A.; Ahamad, T.; Srivastava, S. Enhanced Removal of Crystal Violet Dye and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Ti Doped CeO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Phoenix Dactylifera Mediated Green Method. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 32, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathana, W.; Suetrong, N.; Kongsamai, P.; Chansaenpak, K.; Chuanopparat, N.; Hanlumyuang, Y.; Kanjanaboos, P.; Wannapaiboon, S. Crystallographic and Spectroscopic Investigations on Oxidative Coordination in the Heteroleptic Mononuclear Complex of Cerium and Benzoxazine Dimer. Molecules 2021, 26, 5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, A.; Reuquen, P.; Garín, C.; Segura, R.; Vargas, P.; Zapata, P.; Orihuela, P. FTIR and Raman Characterization of TiO2 Nanoparticles Coated with Polyethylene Glycol as Carrier for 2-Methoxyestradiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoepe, N.M.; Mbita, Z.; Mathipa, M.; Mketo, N.; Ntsendwana, B.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Biogenic Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Monsonia Burkeana for Use in Photocatalytic, Antibacterial and Anticancer Applications. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16999–17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapuram, B.R.; Alle, M.; Dadigala, R.; Dasari, A.; Maragoni, V.; Guttena, V. Catalytic Reduction of Methylene Blue and Congo Red Dyes Using Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles Capped by Salmalia Malabarica Gum. Int. Nano Lett. 2015, 5, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.-J.; Zhu, J.-M.; Liao, X.-H.; Xu, S.; Ding, T.; Chen, H.-Y. Preparation of Nanocrystalline Ceria Particles by Sonochemical and Microwave Assisted Heating Methods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 3794–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhu, H. Controlled Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles Using Novel Amphiphilic Cerium Complex Precursors. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 10, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Karthikeyan, A. Effect of Calcination Temperature on La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 Nanoparticles Synthesized with Modified Sol-Gel Route. Phys. Procedia 2014, 54, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoka, S.; Laokul, P.; Swatsitang, E.; Promarak, V.; Seraphin, S.; Maensiri, S. Synthesis, Structural and Optical Properties of CeO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Simple Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP) Solution Route. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, M.; Zeyad, M.T.; Hashmi, M.A.; Manoharadas, S.; Hussain, S.A.; Ali Abuhasil, M.S.; Almuzaini, M.A.M. Effective Inhibition and Eradication of Pathogenic Biofilms by Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Carum Copticum Extract. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 19248–19257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holder, I.A.; Haidaris, C.G. Experimental Studies of the Pathogenesis of Infections Due to Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: Extracellular Protease and Elastase as in Vivo Virulence Factors. Can. J. Microbiol. 1979, 25, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.S.; Iglewski, B.H.; Barbara, H.P. Aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Systems and Virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, M.B.K.; Zhu, H.; Sankaridurg, P.R.; Willcox, M.D.P. Salicylic Acid Reduces the Production of Several Potential Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Associated with Microbial Keratitis. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Ahmad, N.; Qais, F.A.; Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.S.; Khan, J.M.; Shahzad, S.A.; Ahmad, I. Facile Synthesis of Tin Oxide Hollow Nanoflowers Interfering with Quorum Sensing-Regulated Functions and Bacterial Biofilms. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, G.W.; Hassett, D.J.; Ran, H.; Kong, F. The Role of Pyocyanin in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrodi, D.V.; Bonsall, R.F.; Delaney, S.M.; Soule, M.J.; Phillips, G.; Thomashow, L.S. Functional Analysis of Genes for Biosynthesis of Pyocyanin and Phenazine-1-Carboxamide from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6454–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Kutty, S.K.; Tavallaie, R.; Ibugo, A.I.; Panchompoo, J.; Sehar, S.; Aldous, L.; Yeung, A.W.S.; Thomas, S.R.; Kumar, N.; et al. Phenazine Virulence Factor Binding to Extracellular DNA Is Important for Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm Formation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, H.; Hassett, D.J.; Lau, G.W. Human Targets of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pyocyanin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14315–14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fothergill, J.L.; Panagea, S.; Hart, C.A.; Walshaw, M.J.; Pitt, T.L.; Winstanley, C. Widespread Pyocyanin Over-Production among Isolates of a Cystic Fibrosis Epidemic Strain. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.C.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Lorenzi, M.M.; Grotzinger, H.; Martin, T.R.; Newman, D.K. Phenazine Content in the Cystic Fibrosis Respiratory Tract Negatively Correlates with Lung Function and Microbial Complexity. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, M.E.; Bhatnagar, A.; McCarty, N.A.; Zughaier, S.M. Pyoverdine, the Major Siderophore in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Evades NGAL Recognition. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2012, 2012, 843509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stintzi, A.; Evans, K.; Meyer, J.; Poole, K. Quorum-Sensing and Siderophore Biosynthesis in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: LasRllasI Mutants Exhibit Reduced Pyoverdine Biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 166, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.M.; Neely, A.; Stintzi, A.; Georges, C.; Holder, I.A. Pyoverdin Is Essential for Virulence of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Gupta, R.; Harjai, K. Multiple Virulence Factors Regulated by Quorum Sensing May Help in Establishment and Colonisation of Urinary Tract by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa during Experimental Urinary Tract Infection. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 31, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulianello, L.; Canard, C.; Kohler, T.; Caille, D.; Lacroix, J.-S.; Meda, P. Rhamnolipids Are Virulence Factors That Promote Early Infiltration of Primary Human Airway Epithelia by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3134–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’May, C.; Tufenkji, N. The Swarming Motility of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Is Blocked by Cranberry Proanthocyanidins and Other Tannin-Containing Materials. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.W.; Floyd, R.V.; Fothergill, J.L. The Contribution of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Virulence Factors and Host Factors in the Establishment of Urinary Tract Infections. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, I.; Altaf, M.; Manoharadas, S.; Al-Rayes, B.F.; Ali Abuhasil, M.S.; Almaroai, Y.A. Biofabricated Silver Nanoparticles Exhibit Broad-Spectrum Antibiofilm and Antiquorum Sensing Activity against Gram-Negative Bacteria. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13700–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompilio, A.; Crocetta, V.; De Nicola, S.; Verginelli, F.; Fiscarelli, E.; Di Bonaventura, G. Cooperative Pathogenicity in Cystic Fibrosis: Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia Modulates Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Virulence in Mixed Biofilm. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The Biofilm Matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Hassan, I.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Qais, F.A.; Oves, M.; Rahman, M.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, A.; et al. Biofabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle from Ochradenus Baccatus Leaves: Broad-Spectrum Antibiofilm Activity, Protein Binding Studies, and In Vivo Toxicity and Stress Studies. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 8612158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Tiwari, M.; Donelli, G.; Tiwari, V. Strategies for Combating Bacterial Biofilms: A Focus on Anti-Biofilm Agents and Their Mechanisms of Action. Virulence 2018, 9, 522–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, P.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y. Mechanisms and Control Measures of Mature Biofilm Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents in the Clinical Context. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22684–22690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karygianni, L.; Ren, Z.; Koo, H.; Thurnheer, T. Biofilm Matrixome: Extracellular Components in Structured Microbial Communities. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O.; Johansen, H.K.; Song, Z.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Bjarnsholt, T. The Clinical Impact of Bacterial Biofilms. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 3, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).