Abstract
Background: D-dimer, generated upon the degradation of fibrin, is extensively used to detect thrombosis in various diseases. It is also explored as a marker for thrombosis in cases with COVID-19 disease. Few studies have confirmed its utility as a marker for assessing disease severity. Objectives: The current research was undertaken to determine the role of D-dimer in patients with COVID-19 and to investigate any association with the progression and severity of the disease in the Saudi population. Methods: Clinical indices in confirmed COVID-19 patients were collected from tertiary care hospitals in Aljouf and Qassim regions. The plasma D-dimer levels were quantified directly in the samples collected from COVID-19 patients (n = 148) using an immunofluorescence assay, and the data were presented in Fibrinogen Equivalent Units (mg/L). The collected data of D-dimer were analyzed based on COVID-19 severity, age, and the gender of patients. Results: The findings show that the plasma D-dimer concentrations were significantly (p = 0.0027) elevated in COVID-19 cases (n = 148), compared to in the normal healthy uninfected controls (n = 309). Moreover, the D-dimer levels were analyzed according to the severity of the disease in the patients. The data revealed that D-dimer concentrations were significantly increased in patients with mild infection to moderate disease, and the levels were the highest in patients with severe COVID-19 disease (p < 0.05). Our analysis demonstrates that the D-dimer levels have no association with the age or gender of COVID-19 patients (p > 0.05) in the study population. Conclusions: D-dimer can serve as a biomarker not only for the detection of COVID-19 infection, but also for determining the severity of infection of COVID-19 disease.
1. Background
The identification of the first case of COVID-19 in 2019 was followed by its worldwide spread, and it was finally recognized as a pandemic by the World Health Organization in March 2020 [1]. It took a global toll with many deaths [2]. Although the pandemic wave is presently trailing, its global health, social, and economic impact has been immense and continues to pose a threat with its mutant forms. Most COVID-19 patients are asymptomatic, while others show varied symptoms, such fever, coughing, breathlessness, and mild pneumonia [3]. Some cases may develop severe pneumonia, followed by hypoxia and respiratory dysfunction [4]. An average of 5% of symptomatic patients also exhibit acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which can progress to multiple organ failure [4,5]. Severe illness and death primarily result from the development of acute ARDS, sepsis, and multiple organ failure, stemming from dysfunctional immunological, endothelial, and coagulation responses, triggered by viral infection. Among the abnormal laboratory findings, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, the development of a hypercoagulative state, and raised D-dimer concentrations, often require intensive care unit admissions [5,6].
Although the evaluation of biochemical and hematological indices, in order to understand the infectivity and severity of the disease, remains a promising approach for COVID-19 diagnosis, recently, the genetic make-up of the host has been envisioned as a critical determinant [7]. A striking relationship is observed between COVID-19 disease and distinct host gene polymorphisms, supported by the observed variability in the spread and severity of the disease across different ethnicities [8]. COVID-19 susceptibility, severity, and disease outcome reflect an association with gene expression patterns, mutations, deletions, and polymorphisms [8,9]. Some genetic polymorphisms in host ACE1, APOE, and IFITM3 genes demonstrate an increased infection risk, while polymorphisms in ACE2, AGTR1, TMPRSS2, VDR, and TNFA are associated with the severity of disease [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Studies have also indicated a high infectivity potential and increased severity of COVID-19 in the A blood group serotype, while the O blood group serotype is observed to be protective against infection [18]. Genetic polymorphism, SNPs, in-host immune response genes, including interferons, TNF, and interleukins, are attributed to inducing a high COVID-19 severity [19]. Additionally, besides the genetic and immune determinants, age and gender association has been widely observed in COVID-19 infectivity and severity [20,21]. Gender variation in COVID-19 remains multifactorial, and is mainly affected by lifestyle. However, it may also be attributed to the genetic differences in the key disease modifiers; for example, ACE2 regulation by estrogen explains its reduced infectivity and severity potential [21,22]. Existing morbid conditions are closely linked to a higher susceptibility and severity of COVID-19 [23,24,25].
Many studies have documented an elevation in D-dimer and plasma fibrinogen concentrations in the initial stages of COVID-19 infection [6,26]. Generally, D-dimer is one of the parameters used to detect thrombosis in several pathological conditions [27,28]. They are formed as a product when plasmin breaks down blood clots by cleaving fibrin. A three to four-fold increase in plasma D-dimer is related to a poor disease prognosis [28]. An elevation in D-dimer levels is also noted in COVID-19 cases, reflecting underlying conditions, such as cancer, diabetes, stroke, and pregnancy [29,30,31,32].
Monitoring the levels of D-dimer and other coagulation indices from the initial stages of the disease has shown promise in its management [33]. Worldwide, several studies have confirmed increased D-dimer in severe COVID-19 cases, reaching a high value in critically ill patients and a high death rate [33,34]. The COVID-19-related coagulopathy is presumed responsible for the elevation of D-dimer. Meta-analysis studies have also demonstrated the association of venous thromboembolism with COVID-19 severity [5]. A correlation between the D-dimer and COVID-19 disease, and age and gender-related disease severity, has been recognized [35,36]. Sporadic reports have also shown an association between elevated D-dimer levels, and the delta and omicron variants [37].
Incidences of infection by COVID-19 variants continue to trickle through, even when the global COVID-19 wave has subsided. Urgency is still present if the infection is detected in a patient with underlying conditions, such as cardiovascular disease or diabetes mellitus. Management of such cases can be improved by monitoring the D-dimer, which can predict outcomes [29,30].
Present research on the diagnostic importance of D-dimer in assessing COVID-19 severity is encouraging, yet it is still in the potential phase and mandates confirmation [38,39,40]. Nonetheless, D-dimer holds promise as a prognostic biomarker, alongside procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and ferritin, for assessing COVID-19 severity. Hence, the difference in the plasma levels of D-dimer can be used to detect underlying comorbidities and co-infections in patients with COVID-19 [15,41,42]. This will help to facilitate clinical management that is both more personalized and more efficient, allowing speedier recovery and significantly reducing the mortality rate.
2. Objectives
In our study, we aimed to measure the D-dimer plasma concentration of COVID-19 patients, in order to ascertain any correlation with disease severity, age, and gender.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design and Clinical Setting
This study included 148 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 infection between January and November 2021, attending hospitals in Aljouf and Qassim Regions in Saudi Arabia. Patient enrollment was limited to hospital encounters, including inpatient and emergency, to ascertain the availability of demographic data and clinical results of all confirmed cases. The demographic and biochemical parameters were collected and analyzed (Table 1). The D-dimer concentration was compared between patients with severe and non-severe infection, and between age and gender.

Table 1.
Summary of COVID-19 patients.
Patients with any secondary infection, including bacterial, viral, and fungal, or with insufficient pretreatment clinical results, were excluded. A criterion was followed to confirm COVID-19 positivity, comprising at least two (+ve) findings of the RT-PCR (Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction) assay. Patients who showed negative COVID-19 test results were also excluded. Healthy infected subjects, who had never had COVID-19 disease and were confirmed negative by a COVID-19 test before sampling, were included as a control. The severity of the disease was assessed by SpO2 <94%, biochemical tests, and chest X-rays.
3.2. Laboratory Testing
The clinical parameters of the confirmed positive cases of COVID-19 were obtained from the hospitals, and blood samples from the same patients collected into blue-top sodium citrate tubes were used to assess biochemical parameters. The D-dimer was quantified directly in the plasma of positive COVID-19 (n = 148) samples using an automated, standardized immunofluorescence assay, and the data were presented in Fibrinogen Equivalent Units (FE mg/L). The immunofluorescence assay for D-dimer testing is well established, a highly standardized procedure in our lab routinely used for testing D-dimer in many pathological conditions. The data for D-dimer were analyzed based on the severity of COVID-19, age, and gender of the patients. The normal level for the D-dimer assay used was 0.23 mg/L FEU, equivalent to 230 ng/mL, set as an upper limit.
3.3. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism-9 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) to determine the prevalence, mean, and 95% CI. A comparison analysis was carried out using one-way or two-way ANOVA. A p-value of < 0.05 and lower was considered statistically significant.
4. Results
4.1. D-Dimer Can Differentiate between Positive and Negative COVID-19 Cases
We observed that the concentration of D-dimer in COVID-19 patients (n = 148) was significantly high (1.37 ± 1.71 mg/L FEU), compared to non-infected healthy (n = 309) controls (0.37 ± 1.62 mg/L FEU), with a p-value of 0.0027. Figure 1 indicates that the difference in D-dimer values between non-infected healthy subjects (NHS) and COVID-19 patients is very significant.
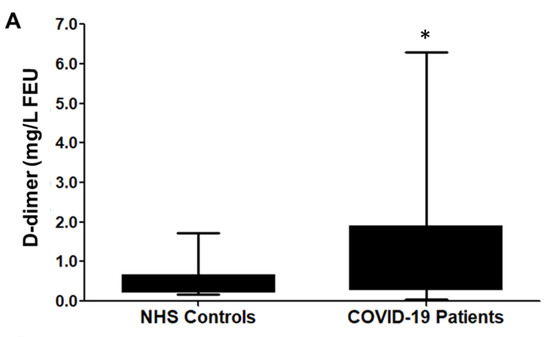
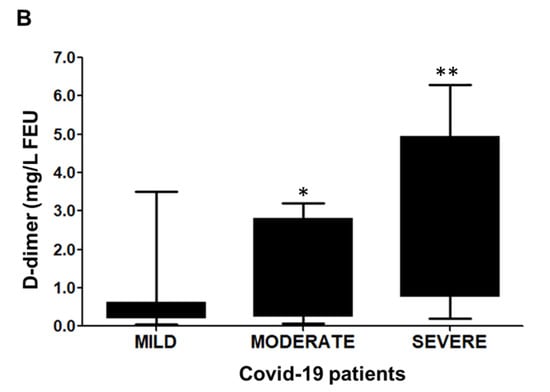
Figure 1.
D-dimer in COVID-19 patients. The graphs represent the D-dimer concentration in mg/L FEU± SD. (A) D-dimer levels in the blood samples of COVID-19 patients (n = 148) and in never-infected human subjects (NHS, n = 309 A * p = 0.0027 were obtained in COVID-19 vs. NHS. A comparison analysis was carried out using the Mann–Whitney test. (B) D-dimer levels in COVID-19 patients with mild (n = 66), moderate (n = 48), and severe (n = 34) infection were highly significant with a, * p < 0.05 (95% CI −2.285 to −0.04205) vs. mild infection; ** p < 0.05 (95% CI −2.591 to −0.1751) vs. moderate infection; and ** p < 0.001 (95% CI −3.243 to −1.850) vs. severe infection. Box and Whisker show the Min to Max values with median ±SD. Comparison analysis was performed via the one-way ANOVA method, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
4.2. D-Dimer Can Be Used for COVID-19 Disease Stratification
The D-dimer levels were also analyzed regarding the hospitalization status of the COVID-19 patients. The results show that the D-dimer levels were significantly increased between the patient groups with mild infection to moderate infection, and were highest in patients with severe COVID-19 disease (p < 0.05).
4.3. Variations in D-Dimer Concentration Do Not Corroborate with the Age or Gender of COVID-19 Infected Patients
Analysis of the data to ascertain gender variations (male and female) and age ranges did not show any significant differences in our study sample (p > 0.05).
5. Discussion
With moderate heterogeneity, the diagnostic potential of D-dimer has shown promise in assessing the COVID-19 disease progression. Similar to other studies, we also observed a significant (p-value of ≤ 0.001) increase in the plasma D-dimer concentrations in COVID-19 patients (1.37 ± 1.71 mg/L FEU), compared to healthy controls never infected with COVID-19 (0.37 ± 1.62 mg/L FEU) (Figure 1A). Furthermore, we also observed a significant association between D-dimer levels and the severity of the disease, indicating a sequential elevation in the D-dimer concentration with an increase in the severity of the disease (Figure 1B). The comparison of the plasma D-dimer values, among mild (0.54 ± 1.77 mg/L FEU, moderate (1.88 ± 0.74 mg/L FEU) and severe (3.23 ± 1.2 mg/L FEU) COVID-19 disease, point to a very significant (p ≤ 0.05) difference in plasma D-dimer concentrations; this reflects its use as a diagnostic index. The D-dimer concentrations for mild, moderate, and severe cases corroborated with the clinically-confirmed disease severity, evaluated through low SpO2 values, biochemical tests, and radiographs for COVID-19 patients.
COVID-19 disease management depends on the stratification of the disease pathogenesis and fostering treatment for the patients accordingly [43,44]. In this regard, a diagnostic value in evaluating the severity of the disease may facilitate better disease management. Increased levels of D-dimer among COVID-19 cases also reflect inflammatory responses to other infections, plus endothelial cell dysfunction leading to thrombin production and hypoxic conditions [45,46]. D-dimer is observed to be persistently higher than normal in about 15% of patients who have experienced severe COVID-19 disease, indicating an underlying pathology as an effect of COVID-19 [47]. Thus, a distinctive value of D-dimer, associated with different pathological conditions in COVID-19 disease, may help to evaluate and stratify COVID-19 cases according to the severity of the disease.
There exists a differential risk for thrombosis in males and females, and quite a few studies have indicated a relationship between gender and age with the D-dimer values in COVID-19 patients [48,49]. This difference in the risk of the thrombotic pattern may be attributed to the difference in genetic make-up and gene expression patterns in males vs. females. The role of host-genetic variation is currently being tested as an underlying cause of COVID-19 susceptibility and severity [50]. Recently, cohort studies and meta-analyses have observed a difference in the elevation of D-dimer among males and females. They propose a corroboration to be mandated through further studies to achieve a distinct conclusion [51]. Although there is a gender bias in the outcome of COVID-19 infection in Saudi Arabia, our results do not show any marked difference (p > 0.05) in the D-dimer values between males and females (Figure 2). The effect of gender on D-dimer values may be more clearly discernible if the sample size is increased. We also assessed age-dependent variation in the D-dimer levels by categorizing the COVID-19 patients into above 50 years and below 50 years groups, but no significant (p > 0.05) association was observed (Figure 3). The D-dimer correlation with age and COVID-19 disease has been variable in the literature. Some studies indicate a severe disease pattern in males, with no correlation to age [52]. On the other hand, some studies observe a correlation between D-dimer and disease severity with age [53,54]. In our study, we do not observe D-dimer differences in relation to the age and gender of the patient (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Hence, based on the results of our study, D-dimer does not appear to be a confounding factor in assessing COVID-19 severity according to age.
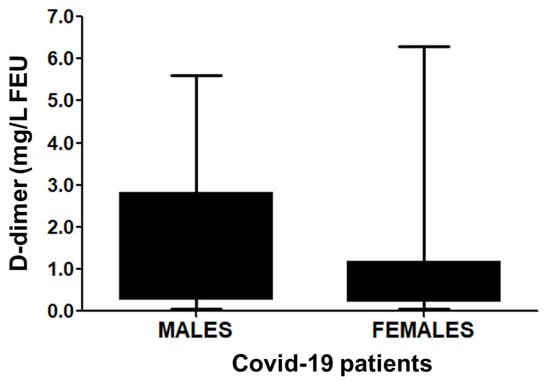
Figure 2.
D-dimer levels in male and female COVID-19 patients. Of the COVID-19 patients, levels of D-dimer in the blood samples of males (n = 97) and females (n = 51) were measured. Male COVID-19 patients vs. female COVID-19 patients, p = 0.4488 (95% CI -0.4277 to 0.9575). Box and Whisker show the Min to Max values with median ± SD.
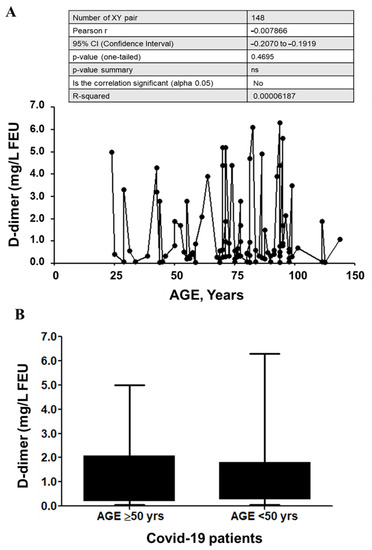
Figure 3.
Age-wise distribution of D-dimer levels in COVID-19 patients. (A) D-dimer correlation with the age of COVID-19 patients. Pearson r = -0.007866; p = 0.4695 (95% CI -0.2070 to 0.1919). (B) D-dimer levels in COVID-19 cases with age ≥50 years (Age ≥ 50 years; n = 41) and age < 50 years (Age < 50 years; n = 107), p = 0.6869. Box and Whisker show the Min to Max values with median ± SD. Comparison analysis was carried out using a two-way ANOVA method and the Bonferroni post hoc test.
6. Conclusions
Our study aims to investigate the role played by D-dimer in COVID-19 patients, evaluating any association with the progress and severity of the disease. Our findings indicate that high D-dimer levels are specifically related to COVID-19 progression. In patients with symptoms that progress to pulmonary complications, the utility of D-dimer as a potential biomarker, used to monitor COVID-19 severity, is relevant to stratify the cases and recommend a specific treatment regime. Furthermore, a high or increasing D-dimer level can provide prognostic information, useful for assessing COVID-19 patients at risk of developing severe disease. This study concludes that the concentration of D-dimers can serve as a valuable biomarker to stratify COVID-19 disease patients according to severity, and to diagnose the presence of a pro-thrombotic state.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.A. (Abdullah Alsrhani), Z.R. and A.F.; Methodology: Z.R. and A.F.; Investigation, Z.R. and A.A. (Ahmad Alshomar); Writing original draft: A.F. and A.A. (Abdullah Alsrhani); Analysis: A.F. and Z.R.; Review and editing, A.A. (Abdullah Alsrhani) and A.Y.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors thank the Deanship of Scientific Research, Jouf University, for funding this research, through grant number 40/297.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the research ethics committee of Qurayyat Health Affairs (protocol code 109 and 30 December 2021 of approval).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated during the study is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thankfully acknowledge the hospital staff in King Abdul Aziz Specialty Hospital, Aljouf region, Saudi Arabia for the assistance and support during this research project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Harapan, H.; Itoh, N.; Yufika, A.; Winardi, W.; Keam, S.; Te, H.; Megawati, D.; Hayati, Z.; Wagner, A.L.; Mudatsir, M. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A literature review. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, L.; Viboud, C. Mortality: A comprehensive look at the COVID-19 pandemic death toll. Elife 2021, 10, e71974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Q. Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Luo, T.; Liu, Q. Clinical determinants of the severity of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malviya, A.; Jandial, A.; Gupta, A.; Agastam, S.; Kumar, D. Coagulation abnormalities & thromboprophylaxis in COVID-19. Indian J. Med. Res. 2021, 153, 606. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo Marin, B.; Aghagholi, G.; Lavine, K.; Yang, L.; Siffy, E.J.; Chiang, S.S.; Salazar-Mather, T.P.; Dumenco, L.; Savaria, M.C.; Salazar-Mather, T.P.; et al. Predictors of COVID-19 severity: A literature review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Kaur, G.; Pathak, T.; Banerjee, I. Systematic review and meta-analysis of human genetic variants contributing to COVID-19 susceptibility and severity. Gene 2022, 844, 146790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.; Mehendale, M.; AlRawashdeh, M.M.; Sestacovschi, C.; Sharath, M.; Pandav, K.; Marzban, S. The association of COVID-19 severity and susceptibility and genetic risk factors: A systematic review of the literature. Gene 2022, 836, 146674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Minnier, J.; Wan, E.S.; Huffman, J.E.; Gao, L.; Joseph, J.; Ho, Y.-L.; Wu, W.-C.; Cho, K.; Gorman, B.R.; et al. A MUC5B Gene Polymorphism, rs35705950-T, Confers Protective Effects against COVID-19 Hospitalization but Not Severe Disease or Mortality. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsiwaritt, W.; Jittikoon, J.; Chaikledkaew, U.; Udomsinprasert, W. Genetic polymorphisms of ACE1, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 associated with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, A.; Cao, H.; Zhang, F. Unraveling risk genes of COVID-19 by multi-omics integrative analyses. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsen, T.H. Understanding COVID-19 through genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 368–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibord, F.; Chan, M.V.; Chen, M.-H.; Johnson, A.D. A year of COVID-19 GWAS results from the GRASP portal reveals potential genetic risk factors. Hum. Genet. Genom. Adv. 2022, 3, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Choudhari, R.; Nema, V.; Khan, A.A. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms in various diseases with special reference to its impact on COVID-19 disease. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planquette, B.; Khider, L.; Le Berre, A.; Soudet, S.; Pernod, G.; Le Mao, R.; Besutti, M.; Gendron, N.; Yannoutsos, A.; Smadja, D.M.; et al. Adjusting D-dimer to lung disease extent to exclude Pulmonary Embolism in COVID-19 patients (Co-LEAD). Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 1888–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Oliveira, A.A.; da Silva, A.M.P.; da Silva Queiroz, J.A.; de Souza, P.R.F.; Salcedo, J.M.V.; Vieira, D.S. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms and the development of COVID-19: A review of the literature. Int. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 6, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Latini, A.; Agolini, E.; Novelli, A.; Borgiani, P.; Giannini, R.; Gravina, P.; Smarrazzo, A.; Dauri, M.; Andreoni, M.; Rogliani, P.; et al. COVID-19 and genetic variants of protein involved in the SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host cells. Genes 2020, 11, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibeeb, S.; Khan, A. ABO blood group association and COVID-19. COVID-19 susceptibility and severity: A review. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2022, 44, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakil, M.K.; Mansoori, Y.; Al-Awsi, G.R.L.; Hosseinipour, A.; Ahsant, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Ekrahi, M.; Montaseri, Z.; Pezeshki, Z.; Mohaghegh, P. Individual genetic variability mainly of Proinflammatory cytokines, cytokine receptors, and toll-like receptors dictates pathophysiology of COVID-19 disease. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 4088–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, P. Immune determinants of COVID-19 disease presentation and severity. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groban, L.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Ahmad, S.; Ferrario, C.M. Is sex a determinant of COVID-19 infection? Truth or myth? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenham, C.; Smith, J.; Morgan, R. COVID-19: The gendered impacts of the outbreak. Lancet 2020, 395, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejaz, H.; Alsrhani, A.; Zafar, A.; Javed, H.; Junaid, K.; Abdalla, A.E.; Abosalif, K.O.; Ahmed, Z.; Younas, S. COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyaolu, A.; Okorie, C.; Marinkovic, A.; Patidar, R.; Younis, K.; Desai, P.; Hosein, Z.; Padda, I.; Mangat, J.; Altaf, M. Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adab, P.; Haroon, S.; O’Hara, M.E.; Jordan, R.E. Comorbidities and covid-19. Br. Med. J. Publ. Group 2022, 377, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, M.; Yilmaz, A.; Cakmak, V.; Beyoglu, R.; Oskay, A.; Seyit, M.; Senol, H. D-Dimer as a potential biomarker for disease severity in COVID-19. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 40, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkins, L.A.; Takach Lapner, S. Review of D-dimer testing: Good, Bad, and Ugly. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2017, 39, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruchter, O.; Yigla, M.; Kramer, M.R. D-dimer as a prognostic biomarker for mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 349, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Y.; Pathak, B.K.; Mohakuda, S.S.; Tilak, T.; Sen, S.; Harikrishnan, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.R. Relation of D-dimer levels of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1927–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Fan, Y.; Liu, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, W.; Wu, X. D-dimer as a predictor of cardiovascular outcomes in patients with diabetes mellitus. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Kawano, H.; Yamashiro, K.; Tanaka, R.; Kameda, T.; Kurita, N.; Hira, K.; Miyamoto, N.; Ueno, Y.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Post-Treatment Plasma D-Dimer Levels Are Associated with Short-Term Outcomes in Patients with Cancer-Associated Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 868137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djusad, S.; Irwinda, R.; Harzif, A.K.; Surya, R.; Wibowo, N.; Saroyo, Y.B.; Adjie, J.S. Determining laboratory parameters in pregnant women with severe COVID-19. SAGE Open Med. 2022, 10, 20503121221132168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Lateef, A.E.; Alghamdi, S.; Ebid, G.; Khalil, K.; Kabrah, S.; Abdel Ghafar, M.T. Coagulation Profile in COVID-19 Patients and its Relation to Disease Severity and Overall Survival: A Single-Center Study. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 79, 10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasif, W.A.; Ali, A.S.E.-M.; Mukhtar, M.H.; Alhuzali, A.M.H.; Alnashri, Y.A.Y.; Gadah, Z.I.A.; Edrees, E.A.A.; Albarakati, H.A.M.; Aloufi, H.S.M. Elucidating the Correlation of D-Dimer Levels with COVID-19 Severity: A Scoping Review. Anemia 2022, 2022, 9104209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barek, M.A.; Aziz, M.A.; Islam, M.S. Impact of age, sex, comorbidities and clinical symptoms on the severity of COVID-19 cases: A meta-analysis with 55 studies and 10014 cases. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.G.; Klepac, P.; Liu, Y.; Prem, K.; Jit, M.; Eggo, R.M.; CMMID COVID-19 Working Group. Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, D.; Visseaux, B.; Kassasseya, C.; Daoud, A.; Fémy, F.; Hermand, C.; Truchot, J.; Beaune, S.; Javaud, N.; Peyrony, O.; et al. Comparison of patients infected with Delta versus Omicron COVID-19 variants presenting to Paris emergency departments: A retrospective cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varikasuvu, S.R.; Varshney, S.; Dutt, N.; Munikumar, M.; Asfahan, S.; Kulkarni, P.P.; Gupta, P. D-dimer, disease severity, and deaths (3D-study) in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 100 studies. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; Montazerin, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Independent and incremental prognostic value of D-dimer in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Future Med. 2021, 16, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cidade, J.P.; Coelho, L.; Costa, V.; Morais, R.; Moniz, P.; Morais, L.; Fidalgo, P.; Tralhão, A.; Paulino, C.; Nora, D.; et al. Predictive value of D-dimer in the clinical outcome of severe COVID19 patients: Are we giving it too much credit? Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. 2022, 28, 10760296221079612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Ouyang, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Tang, L.; Luo, Q.; Xu, M.; Yang, L.; et al. Evaluation of variation in D-dimer levels among COVID-19 and bacterial pneumonia: A retrospective analysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 50, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, I.; Pranata, R.; Lim, M.A.; Oehadian, A.; Alisjahbana, B. C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, D-dimer, and ferritin in severe coronavirus disease-2019: A meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620937175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ŞENER, G. The effectiveness of coagulation parameters in classifying patients and predicting mortality in COVID-19. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2022, 39, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Ghosh, K. D-Dimer: An analyte with increasing application in COVID-19 infection. Expert Rev. 2022, 15, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timurkaan, M.; Altuntas, G.; Kalayci, M.; Timurkaan, E.; Ayyildiz, H. Early warning triad for pulmonary microemboli in COVID-19 pneumonia: Pulmonary artery diameter, D-dimer and NT-proBNP. Medicine 2022, 11, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Long, H.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, K.; Tong, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, Q.; et al. New laboratory evidence for the association between endothelial dysfunction and COVID-19 disease progression. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3112–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.; Prosch, H.; Zehetmayer, S.; Gysan, M.R.; Bernitzky, D.; Vonbank, K.; Idzko, M.; Gompelmann, D. Impact of persistent D-dimer elevation following recovery from COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Why Does the Severity of COVID-19 Differ with Age?: Understanding the Mechanisms Underlying the Age Gradient in Outcome Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2022, 41, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Yachi, S.; Takeyama, M.; Nishimoto, Y.; Tsujino, I.; Nakamura, J.; Yamamoto, N.; Nakata, H.; Ikeda, S.; Umetsu, M.; et al. Influence of sex on development of thrombosis in patients with COVID-19: From the CLOT-COVID study. Thromb. Res. 2022, 213, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Rostam, H.S.; Fatah, M.H.; Noori, C.M.; Ali, K.M.; Tawfeeq, H.M. HMSerum troponin, D-dimer, and CRP level in severe coronavirus (COVID-19) patients. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2022, 10, e582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Talmor, N.; Xia, Y.; Berger, J.S.; Iturrate, E.; Adhikari, S.; Pulgarin, C.; Quinones-Camacho, A.; Yuriditsky, E.; Horowitz, J.; et al. Sex differences in the prognostic value of troponin and D-dimer in COVID-19 illness. Heart Lung 2023, 58, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E.; DePerrior, S.E.; Ahmad, Q.; Dodani, S. Gender-based disparities in COVID-19 patient outcomes. J. Investig. Med. 2021, 69, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.E.; Al-Aklobi, O.S.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Al-Ghamdi, M.A. Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory findings for patients of different age groups with confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a hospital in Saudi Arabia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsagaby, S.A.; Aljouie, A.; Alshammari, T.H.; Mir, S.A.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Alshaalan, H.; Alomaish, H.; Daghistani, R.; Alsehawi, A.; et al. Haematological and radiological-based prognostic markers of COVID-19. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).