Virucidal Efficacy of Household Dishwashers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Viral Stocks
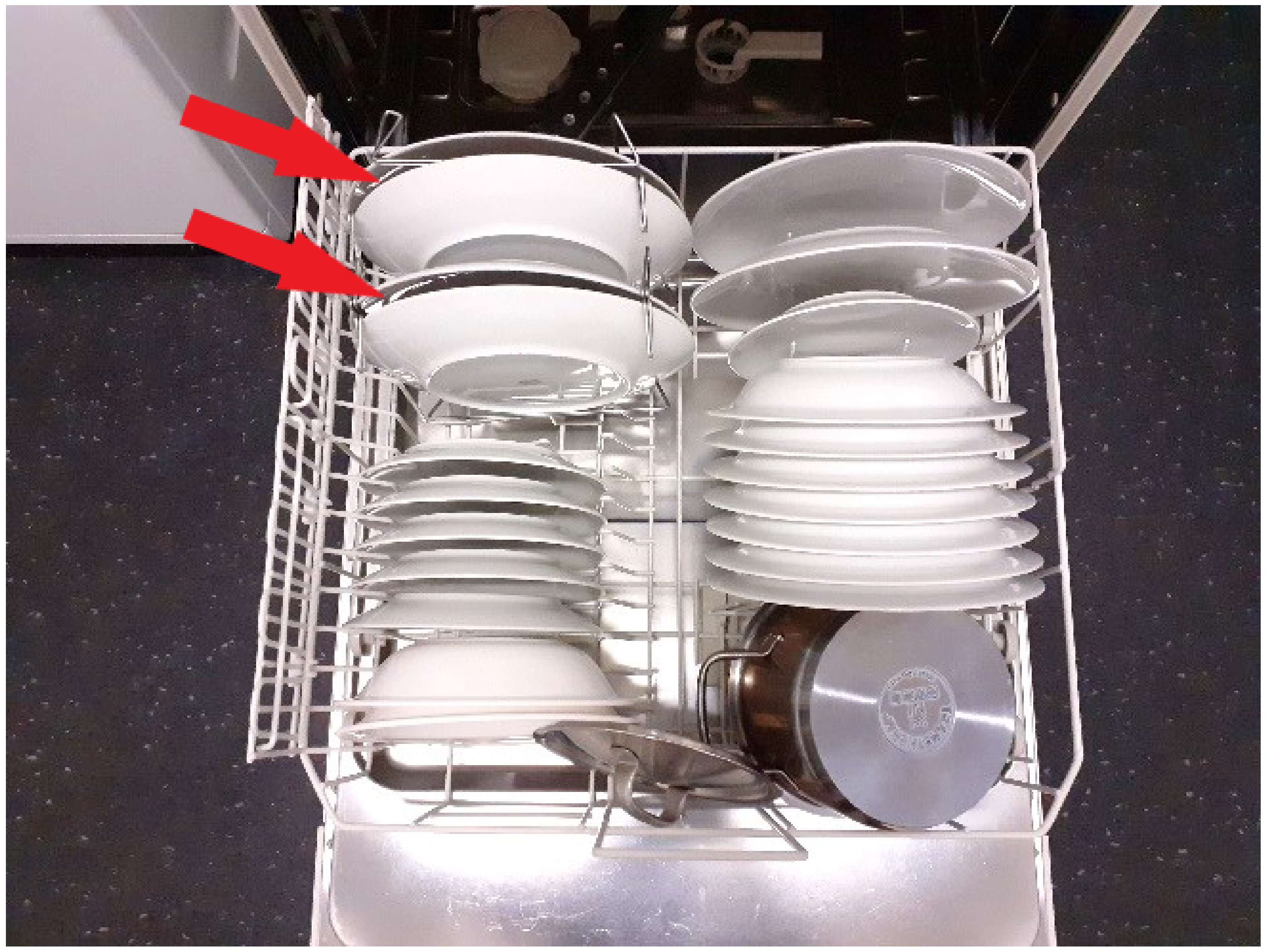
2.2. Preparation of Soil Matrix and Bio Carriers
2.3. Dishwasher Process
2.4. Extraction of Viral RNA/DNA after Treatment with Propidium Monoazide
2.5. RT qPCR/qPCR
2.6. Primer Pairs for RT qPCR and qPCR
2.7. Calculations of Log Reduction
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Temperature Profiles of Dishwasher Programs
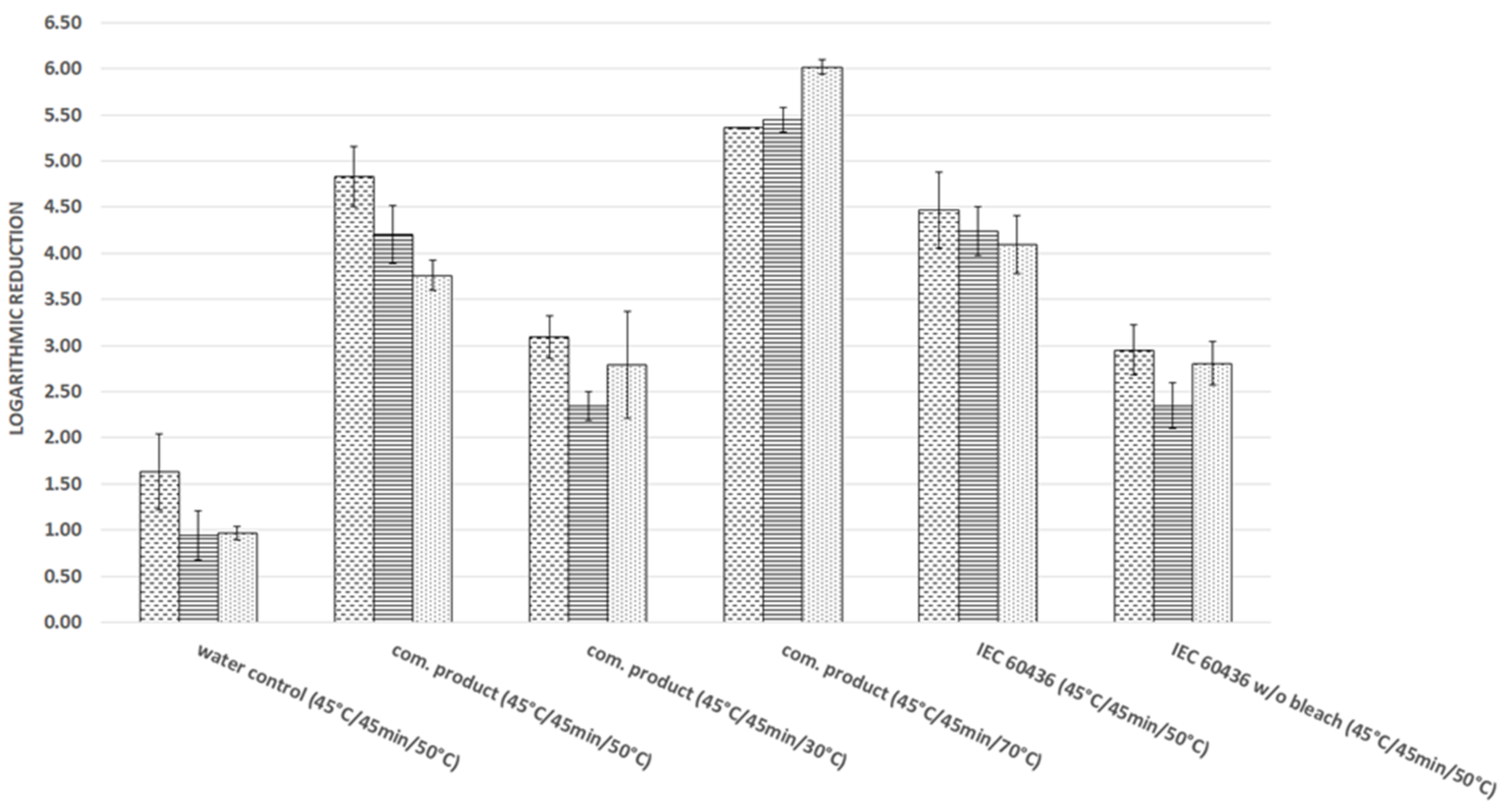
3.2. Logarithmic Reduction of Viruses under Specific Conditions
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Turkey’s Multiple Comparison Test | Mean. Diff. | 95% Cl of Diff. | Significant? | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| water control (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. com. Product (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | −3.087 | −3.737 to −2.436 | Yes | **** |
| water control (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. (45 °C/45 min/30 °C) | −1.56 | −2.211 to −0.9093 | Yes | **** |
| water control (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. (45 °C/45 min/70 °C) | −4.427 | −5.077 to −3.776 | Yes | **** |
| water control (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. IEC 60436 (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | −3.087 | −3.737 to −2.436 | Yes | **** |
| water control (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. IEC 60436 w/o bleach (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | −1.518 | −2.169 to −0.8677 | Yes | **** |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. com. Product (45 °C/45 min/30 °C) | 1.527 | 0.8760 to 2.177 | Yes | **** |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. com. Product (45 °C/45 min/70 °C) | −1.34 | −1.991 to −0.6893 | Yes | **** |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. IEC 60436 (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | 3.974E−08 | −0.6507 to 0.6507 | No | ns |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. IEC 60436 w/o bleach (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | 1.568 | 0.9177 to 2.219 | Yes | **** |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/30 °C) vs. com. Product (45 °C/45 min/70 °C) | −2.867 | −3.517 to −2.216 | Yes | **** |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/30 °C) vs. IEC 60436 (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | −1.527 | −2.177 to −0.8760 | Yes | **** |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/30 °C) vs. IEC 60436 w/o bleach (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | 0.04167 | −0.6090 to 0.6923 | No | ns |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/70 °C) vs. IEC 60436 (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | 1.34 | 0.6893 to 1.991 | Yes | **** |
| com. Product (45 °C/45 min/70 °C) vs. IEC 60436 w/o bleach (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | 2.908 | 2.258 to 3.559 | Yes | **** |
| IEC 60436 (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) vs. IEC 60436 w/o bleach (45 °C/45 min/50 °C) | 1.568 | 0.9177 to 2.219 | Yes | **** |
References
- Kutter, J.S.; Spronken, M.I.; Fraaij, P.L.; Fouchier, R.A.; Herfst, S. Transmission routes of respiratory viruses among humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 28, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaythorpe, K.A.M.; Trotter, C.L.; Lopman, B.; Steele, M.; Conlan, A.J.K. Norovirus transmission dynamics: A modelling review. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, D.H.; Sair, A.; Williams, K.; Papafragkou, E.; Jean, J.; Moore, C.; Jaykus, L. Persistence of caliciviruses on environmental surfaces and their transfer to food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 108, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Deng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Han, J.; Bei, Z.; et al. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 on environmental surfaces and in human excreta. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 107, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonta, W.; Mauroy, A.; Farnir, F.; Thiry, E. Comparative Virucidal Efficacy of Seven Disinfectants Against Murine Norovirus and Feline Calicivirus, Surrogates of Human Norovirus. Food Environ. Virol. 2016, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzel, M.; Kyas, A.; Weide, M.; Breves, R.; Bockmühl, D.P. Evaluation of the virucidal performance of domestic laundry procedures. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2010, 213, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebner, W.; Eitel, A.; Scherrer, M.; Daschner, F. Can household dishwashers be used to disinfect medical equipment? J. Hosp. Infect. 2000, 45, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutala, W.M.; Weber, D.J. Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities. CDC Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/disinfection (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Gastañaduy, P.A.; Vicuña, Y.; Salazar, F.; Broncano, N.; Gregoricus, N.; Vinjé, J.; Chico, M.; Parashar, U.D.; Cooper, P.J.; Lopman, B. Transmission of Norovirus Within Households in Quininde, Ecuador. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmithausen, R.M.; Sib, E.; Exner, M.; Hack, S.; Rösing, C.; Ciorba, P.; Bierbaum, G.; Savin, M.; Bloomfield, S.F.; Kaase, M.; et al. The Washing Machine as a Reservoir for Transmission of Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase (CTX-M-15)-ProducingKlebsiella oxytocaST201 to Newborns. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01435-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V. Chemical Disinfectants and Antiseptics—Quantitative Suspension Test for the Evaluation of Virucidal Activity in the Medical Area—Test Method and Requirements (Phase 2/Step 1); DIN EN 14476; Beuth: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwebke, I.; Eggers, M.; Gebel, J.; Geisel, B.; Glebe, D.; Rapp, I.; Steinmann, J.; Rabenau, F. Prüfung und Deklaration der Wirksamkeit von Desinfektionsmitteln gegen Viren zur Anwendung im human-medizinischen Bereich. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundh. Gesundh. 2017, 60, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Alhatlani, B.; Arias, A.; Caddy, S.L.; Christodoulou, C.; Cunha, J.B.; Emmott, E.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.; Kolawole, A.; Lu, J.; et al. Murine Norovirus: Propagation, Quantification, and Genetic Manipulation. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2014, 33, 15K.2.1–15K.2.61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogue, B.G.; King, B.; Brian, D.A. Antigenic Relationships Among Proteins of Bovine Coronavirus, Human Respiratory Coronavirus OC43, and Mouse Hepatitis Coronavirus A59. J. Virol. 1984, 51, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornemann, S.; Harlin, O.; Staib, C.; Kisling, S.; Erfle, V.; Kaspers, B.; Häcker, G.; Sutter, G. Replication of Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara in Primary Chicken Embryo Fibroblasts Requires Expression of the Interferon Resistance Gene E3L. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8394–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brands, B.; Struchtrup, S.S.; Stamminger, R.; Bockmühl, D. A method to evaluate factors influencing the microbial reduction in domestic dishwashers. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinn, M.-K.; Klapper, D.; von Esmarch-Rummler, B.; Bockmühl, D. Development of a Test Method for Analyzing the Hygienic Performance of Commercial Dishwashers Operating on the Fresh Water Principle. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2018, 55, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V. Elektrische Geschirrspuler für den Hausgebrauch-Messverfahren für Gebrauchseigenschaften (IEC 60436:2004, Modifiziert + A1:2009, Modifiziert + A2:2012, Modifiziert); DIN EN 50242/DIN € EN 60436:2018–06; VDE 0705–436:2018–06; Deutsche Fassung EN 50242:2016; Beuth: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Quijada, N.M.; Fongaro, G.; Barardi, C.R.M.; Hernández, M.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D. Propidium Monoazide Integrated with qPCR Enables the Detection and Enumeration of Infectious Enteric RNA and DNA Viruses in Clam and Fermented Sausages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Amer, H.M.; Almajhdi, F.N. Development of a SYBR Green I based real-time RT-PCR assay for detection and quantification of bovine coronavirus. Mol. Cell. Probes 2011, 25, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaki, K.I.; Ike, F.; Kajita, A.; Yasuno, W.; Yanagiba, M.; Goto, M.; Sakai, K.; Ami, Y.; Kyuwa, S. A Broadly Reactive One-Step SYBR Green I Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Rapid Detection of Murine Norovirus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.L.; Ward, B.M. Development and comparison of a quantitative TaqMan-MGB real-time PCR assay to three other methods of quantifying vaccinia virions. Virol. Methods 2014, 196, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parshionikar, S.; Laseke, I.; Fout, G.S. Use of Propidium Monoazide in Reverse Transcriptase PCR To Distinguish between Infectious and Noninfectious Enteric Viruses in Water Samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4318–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Virus | Acronym | Strain | Structure | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murine Norovirus | MNV | S99 | non-enveloped ss-RNA | EVAg | [11,12] |
| Bovine Coronavirus | BCV | S378 Riems | enveloped ss-RNA | EVAg | [11,12] |
| Modified Vaccinia Virus | MVA | Ankara | enveloped ds-DNA | Dr. Brill + Partner | [11,12] |
| Cleaning Temp. (°C) | Cleaning Time (min) | Rinsing Temp. (°C) | Cleansing Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 45 | 50 | water control |
| 45 | 45 | 50 | commercial product |
| 45 | 45 | 50 | reference w/o bleach |
| 45 | 45 | 50 | reference with bleach |
| 45 | 45 | 30 | commercial product |
| 45 | 45 | 70 | commercial product |
| Virus | Primer | Sequence 5′–3′ | Reference | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCV | forward | TGG ATC AAG ATT AGA GTT GGC | [20] | Eurofins Genomics |
| BCV | reverse | CCT TGT CCA TTC TTC TGA CC | [20] | Eurofins Genomics |
| MNV | forward | ATG GTR GTC CCA CGC CAC | [21] | Eurofins Genomics |
| MNV | reverse | TGC GCC ATC ACT CAT CC | [21] | Eurofins Genomics |
| MVA | forward | CGG CTA AGA GTT GCA CAT CCA | [22] | Eurofins Genomics |
| MVA | reverse | CTC TGC TCC ATT TAG TAC CGA TTC T | [22] | Eurofins Genomics |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucassen, R.; Weide, M.; Bockmühl, D. Virucidal Efficacy of Household Dishwashers. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 395-402. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12020027
Lucassen R, Weide M, Bockmühl D. Virucidal Efficacy of Household Dishwashers. Microbiology Research. 2021; 12(2):395-402. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucassen, Ralf, Mirko Weide, and Dirk Bockmühl. 2021. "Virucidal Efficacy of Household Dishwashers" Microbiology Research 12, no. 2: 395-402. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12020027
APA StyleLucassen, R., Weide, M., & Bockmühl, D. (2021). Virucidal Efficacy of Household Dishwashers. Microbiology Research, 12(2), 395-402. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12020027






