Vasculonecrotic Reaction Caused by Mycobacterium Lepromatosis Infection—A Case Report of an HIV/Leprosy-Coinfected Patient
Abstract
1. Introduction
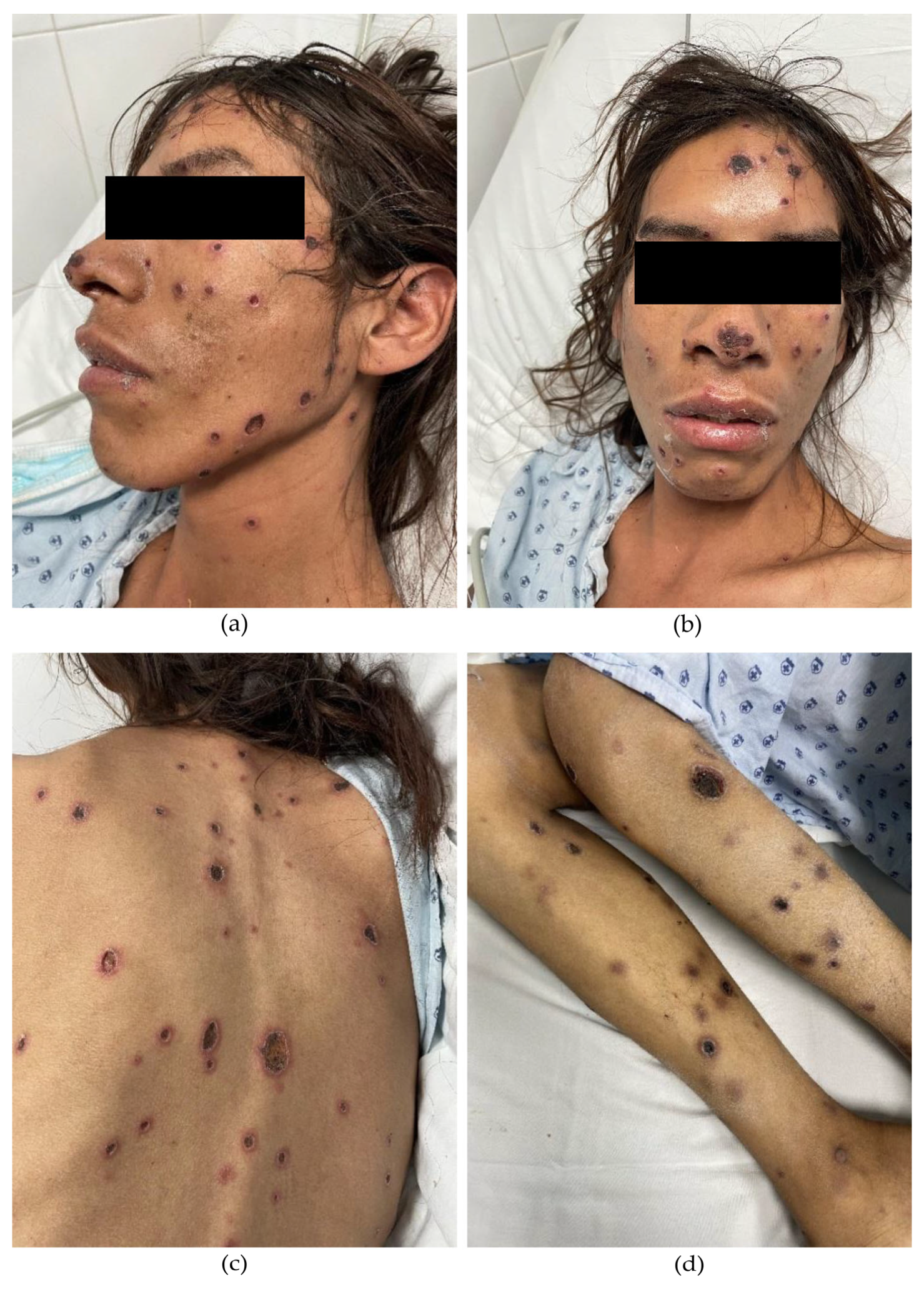
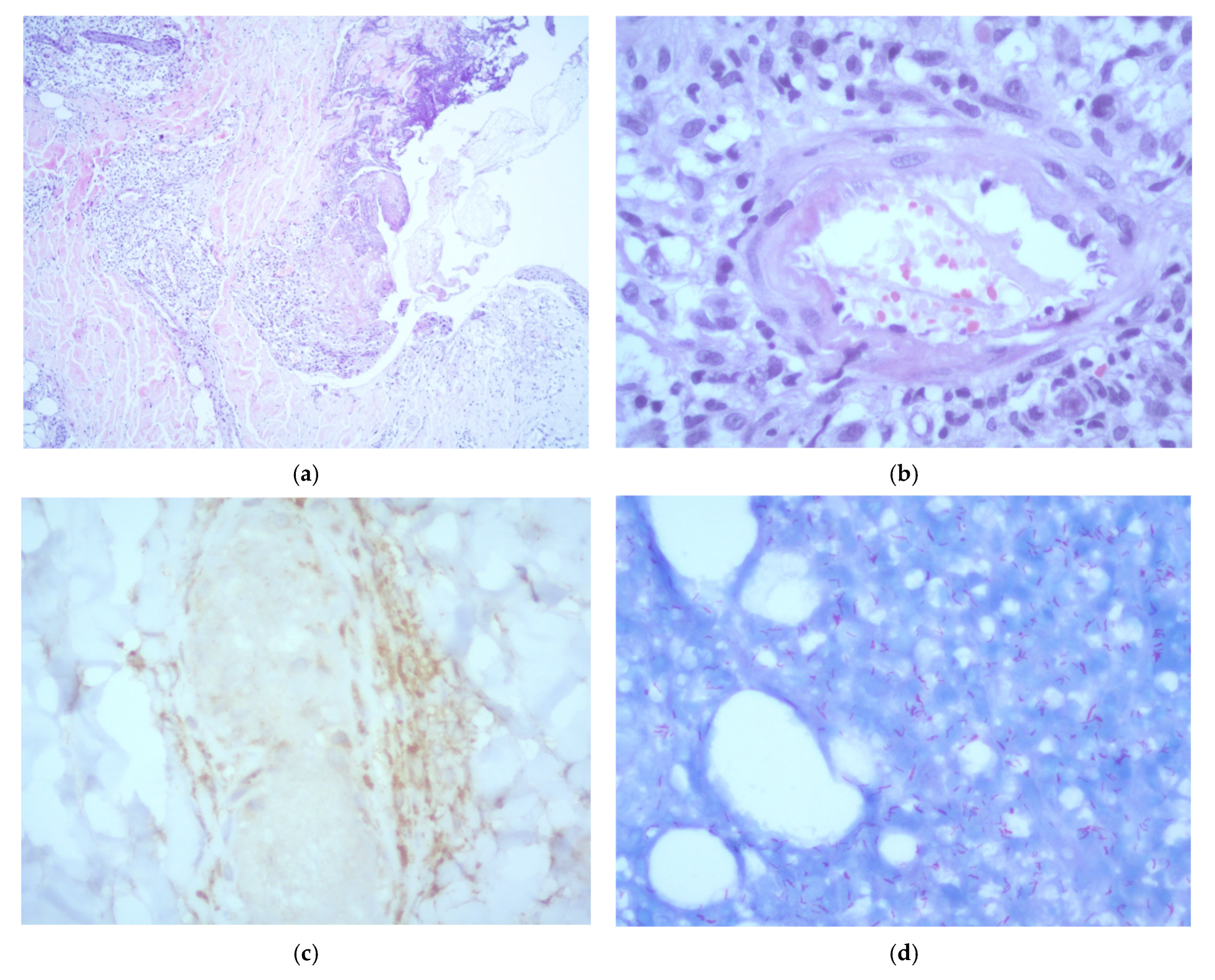
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, X.Y.; Mistry, N.A.; Thompson, E.J.; Tang, H.L.; Khanna, K.; Zhang, L. Draft Genome Sequence of New Leprosy Agent Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00513-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Benjak, A.; Schuenemann, V.J.; Herbig, A.; Avanzi, C.; Busso, P.; Nieselt, K.; Krause, J.; Vera-Cabrera, L.; Cole, S.T. Insight into the evolution and origin of leprosy bacilli from the genome sequence of Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4459–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, D.E.; Santos, D.F.; Lima, M.I.S.; Caixeta, L.P.; Correa, M.B.C.; Moraes, E.C.d.S.; Conceição, N.C.A.; Goulart, L.R.; Goulart, I.M.B. Clinical, epidemiological, and laboratory prognostic factors in patients with leprosy reactions: A 10-year retrospective cohort study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 841030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Kiriya, M.; Tanigawa, K.; Kawashima, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishii, N.; Suzuki, K. Host-Related Laboratory Parameters for Leprosy Reactions. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 694376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góes, L.D.M.; Morais PMde Rebello, P.F.B.; Schettini, A.P.M. Necrotic erythema nodosum reaction associated with histological alterations of Lucio’s phenomenon. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2022, 97, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourlaki, A.; Marzano, A.V.; Gianotti, R.; Fiallo, P.; Nunzi, E.; Alessi, E. Necrotic Erythema Nodosum Leprosum as the First Manifestation of Borderline Lepromatous Leprosy. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 818–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Singh, N.; Chatterjee, D.; Saikia, U.N.; Narang, T.; Dogra, S. Lucio phenomenon or necrotic erythema nodosum leprosum: Walking the thin line. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, L.; Kumari, R.; Thappa, D.; Badhe, B.; Ranugha, P. Is it lucio phenomenon or necrotic erythema nodosum leprosum? Indian J. Dermatol. 2013, 58, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogagnolo, L.; Souza EMde Cintra, M.L.; Velho, P.E.N.F. Vasculonecrotic reactions in leprosy. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, G.; Sakai-Valente, N.Y.; Bianconcini Trindade, M.A. Concomitant Lucio Phenomenon and Erythema Nodosum in a Leprosy Patient: Clues for Their Distinct Pathogeneses. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2009, 31, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto Spandonari, C.; Villagra, D.J.; Flor, L.; Agüero Zaputovich, F.; Di Martino, B.; Aldama, A. Lucio’s phenomenon. About a case. An. Fac. Cienc. Méd. 2022, 55, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade, M.A.C.; Coltro, P.S.; Filho, F.B.; Horácio, G.S.; Neto, A.A.; da Silva, V.Z.; Westin, A.T.; Guimarães, F.R.; Innocentini, L.M.; Motta, A.C.; et al. Lucio’s phenomenon: A systematic literature review of definition, clinical features, histopathogenesis and management. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2021, 88, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velarde-Félix, J.S.; Alvarado-Villa, G.; Vera-Cabrera, L. “Lucio’s Phenomenon” Associated with Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ang, P.; Tay, Y.K.; Ng, S.K.; Seow, C.S. Fatal Lucio’s phenomenon in 2 patients with previously undiagnosed leprosy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldama, A.; Wattiez, V.; Mendoza, G. Fenómeno de Lucio. Comunicación de 14 casos. Piel 2018, 33, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curi, P.F.; Villaroel, J.S.; Migliore, N.; Albertengo, A.; Aquino, M.L.; Ceccato, F.; Paira, S. Lucio’s phenomenon: Report of five cases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M.; Liu, S.W.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, Y.C. Lucio’s phenomenon. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2023, 56, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilipbhai Bodar, P.; Kailashbhai Patel, J.; Subramonia Pillai, D.; Vipul Vora, R. Lucio phenomenon; A case report. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2025, 91, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Seo, Y.H.; Sizer, K.C.; Schoberle, T.; May, G.S.; Spencer, J.S.; Li, W.; Nair, R.G. A New Mycobacterium Species Causing Diffuse Lepromatous Leprosy. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 130, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Quintanilla, M. Diffuse Lepromatous Leprosy Due to Mycobacterium lepromatosis in Quintana Roo, Mexico. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3695–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Sharma, V.D. Mycobacterium lepromatosis Lepromatous Leprosy in US Citizen Who Traveled to Disease-Endemic Areas. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, S.M.; Lima, A.; Heringer, S.; Sanders, V.; Pessotti, H.A.; Deps, P. Systematic Review of Hansen Disease Attributed to Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucio, R.; Alvarado, I.; Francis, A. Opúsculo Sobre el mal de San Làzaro, ó, Elefanciasis de los Griegos; Imprenta de M. Murguía y Compañia: Mexico City, Mexico, 1852. [Google Scholar]
- Latapi, F.; Chevez-Zamora, A. The “spotted” leprosy of Lucio: An introduction to its clinical and histological study. Int. J. Lepr. 1948, 16, 421–423. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Y.; Sizer, K.C.; Velarde-Félix, J.S.; Frias-Castro, L.O.; Vargas-Ocampo, F. The leprosy agents Mycobacterium lepromatosis and Mycobacterium leprae in Mexico. Int. J. Dermatol. 2012, 51, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Aung, F.M.; Choon, S.E.; Werner, B. Analysis of the Leprosy Agents Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatosis in Four Countries. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 142, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Singh, P.; McCoy, R.C.; Lenz, S.M.; Donovan, K.; Ochoa, M.T.; Estrada-Garcia, I.; Silva-Miranda, M.; Jurado-Santa Cruz, F.; Balagon, M.F.; et al. Isolation of Mycobacterium lepromatosis and Development of Molecular Diagnostic Assays to Distinguish Mycobacterium leprae and M. lepromatosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, e262–e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trave, I.; Barabino, G.; Cavalchini, A.; Parodi, A. Long-term ulcerations caused by Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2020, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Jessurun, J. Severe Leprosy Reactions Due to Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 345, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Cabrera, L.; Escalante-Fuentes, W.G.; Gomez-Flores, M.; Ocampo-Candiani, J.; Busso, P.; Singh, P.; Cole, S.T. Case of Diffuse Lepromatous Leprosy Associated with “Mycobacterium lepromatosis”. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4366–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massone, C.; Talhari, C.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, R.; Sindeaux, R.H.M.; Mira, M.T.; Talhari, S.; Naafs, B. Leprosy and HIV coinfection: A critical approach. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustianowski, A.P.; Lawn, S.D.; Lockwood, D.N. Interactions between HIV infection and leprosy: A paradox. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deps, P.; Lucas, S.; Porro, A.M.; Maeda, S.M.; Tomimori, J.; Guidella, C.; Reuter, T.; Oliveira, N.S.; Madureira, B.P.R.; Souza, V.A.; et al. Clinical and histological features of leprosy and human immunodeficiency virus co-infection in Brazil. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 38, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, C.A.A.; de Miranda, M.F.R.; Bittencourt Mde, J.S.; de Brito, A.C.; Xavier, M.B. Comparison between histopathologic features of leprosy in reaction lesions in HIV coinfected and non-coinfected patients. Bras. Dermatol. 2015, 90, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, E.P.; Caneshi, J.R.; Nery, J.A.; Duppre, N.C.; Pereira, G.M.; Vieira, L.M.; Moreira, A.L.; Kaplan, G.; Sarno, E.N. Cellular immune response to Mycobacterium leprae infection in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couppié, P.; Domergue, V.; Clyti, E.; El Guedj, M.; Vaz, T.; Sainte-Marie, D.; Marty, C.; Nacher, M. Increased incidence of leprosy following HAART initiation: A manifestation of the immune reconstitution disease. AIDS 2009, 23, 1599–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Vidyadharan, S. Hansen’s disease in association with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussone, G.; Charlier, C.; Bille, E.; Caux, F.; Lévy, A.; Viard, J.P.; Lecuit, M.; Lortholary, O. Unmasking Leprosy: An Unusual Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in a Patient Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchard, A.; Blaizot, R.; Graille, J.; Couppié, P.; Bertin, C. Leprosy as immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in patients living with HIV: Description of French Guiana’s cases over 20 years and systematic review of the literature. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, D.N.J.; Lambert, S.M. Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Leprosy: An Update. Dermatol. Clin. 2011, 29, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M.D.; Porro, A.M.; Maeda, S.M.; Gomes, E.E.; Yoshioka, M.C.N.; Enokihara, M.M.; Tomimori, J. Leprosy Reversal Reaction as Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Patients with AIDS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, e56–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, C.A.A.; Jucá Neto, F.O.M.; de Albuquerque, N.C.; Macedo, G.M.M.; Batista, K.d.N.M.; Xavier, M.B. Leprosy Reactions in Patients Coinfected with HIV: Clinical Aspects and Outcomes in Two Comparative Cohorts in the Amazon Region, Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, V.M.; Nery, J.A.C.; Sales, A.M.; Miranda, A.; Galhardo, M.C.G.; Bastos, F.I.; Sarno, E.N.; Hacker, M.A. Epidemiological and clinical patterns of 92 patients co-infected with HIV and Mycobacterium leprae from Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 108, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arakkal, G.; Damarla, S.; Chanda, G. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome unmasking erythema nodosum leprosum: A rare case report. Indian J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Coll, H.A.; Beltrán-Alzate, J.C.; Buitrago, S.M.; Cardona-Castro, N. Lepromatous leprosy and human immunodeficiency virus co-infection associated with phenomenon of Lucio versus immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Infectio 2016, 20, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusini, A.; Gunthard, H.F.; Weber, R.; Huber, M.; Kamarashev, J.; Bertisch, B.; Peter, S.; Beck, B. Lepromatous leprosy with erythema nodosum leprosum as immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in an HIV-1 infected patient after initiation of antiretroviral therapy. Case Rep. 2009, 2009, bcr0520091904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes Filho, F.; Pess, D.; Akabane, A.L.; Foss, N.T.; Frade, M.A.C. Lucio’s phenomenon: A life-threatening medical emergency. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 69, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Thappa, D.M.; Basu, D. A fatal case of Lucio phenomenon from India. Dermatol. Online J. 2008, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amador-Lara, F.; Mayorga-Garibaldi, J.L.; Bustos-Rodríguez, F.J.; González-Hernández, L.A.; Martínez-Ayala, P.; Andrade-Villanueva, J.F. Vasculonecrotic Reaction Caused by Mycobacterium Lepromatosis Infection—A Case Report of an HIV/Leprosy-Coinfected Patient. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030058
Amador-Lara F, Mayorga-Garibaldi JL, Bustos-Rodríguez FJ, González-Hernández LA, Martínez-Ayala P, Andrade-Villanueva JF. Vasculonecrotic Reaction Caused by Mycobacterium Lepromatosis Infection—A Case Report of an HIV/Leprosy-Coinfected Patient. Infectious Disease Reports. 2025; 17(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmador-Lara, Fernando, Jorge L. Mayorga-Garibaldi, Felipe J. Bustos-Rodríguez, Luz A. González-Hernández, Pedro Martínez-Ayala, and Jaime F. Andrade-Villanueva. 2025. "Vasculonecrotic Reaction Caused by Mycobacterium Lepromatosis Infection—A Case Report of an HIV/Leprosy-Coinfected Patient" Infectious Disease Reports 17, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030058
APA StyleAmador-Lara, F., Mayorga-Garibaldi, J. L., Bustos-Rodríguez, F. J., González-Hernández, L. A., Martínez-Ayala, P., & Andrade-Villanueva, J. F. (2025). Vasculonecrotic Reaction Caused by Mycobacterium Lepromatosis Infection—A Case Report of an HIV/Leprosy-Coinfected Patient. Infectious Disease Reports, 17(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030058





