The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker of Fournier’s Gangrene Severity: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
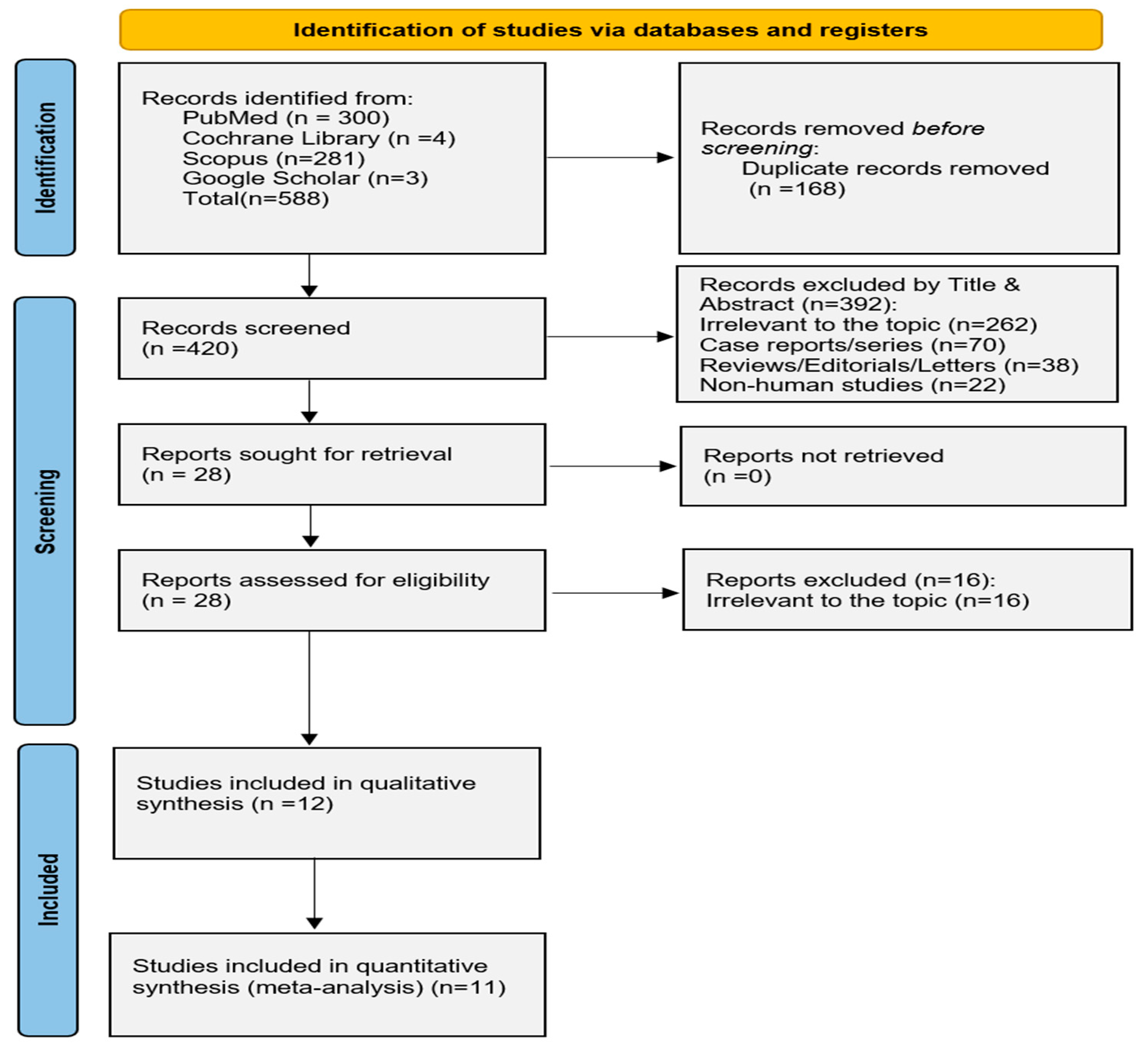
2.2. Eligibility of Relevant Studies and Study Selection
2.3. Data Collection and Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Study Characteristics
3.2. Patient Characteristics and Baseline Clinical Profile
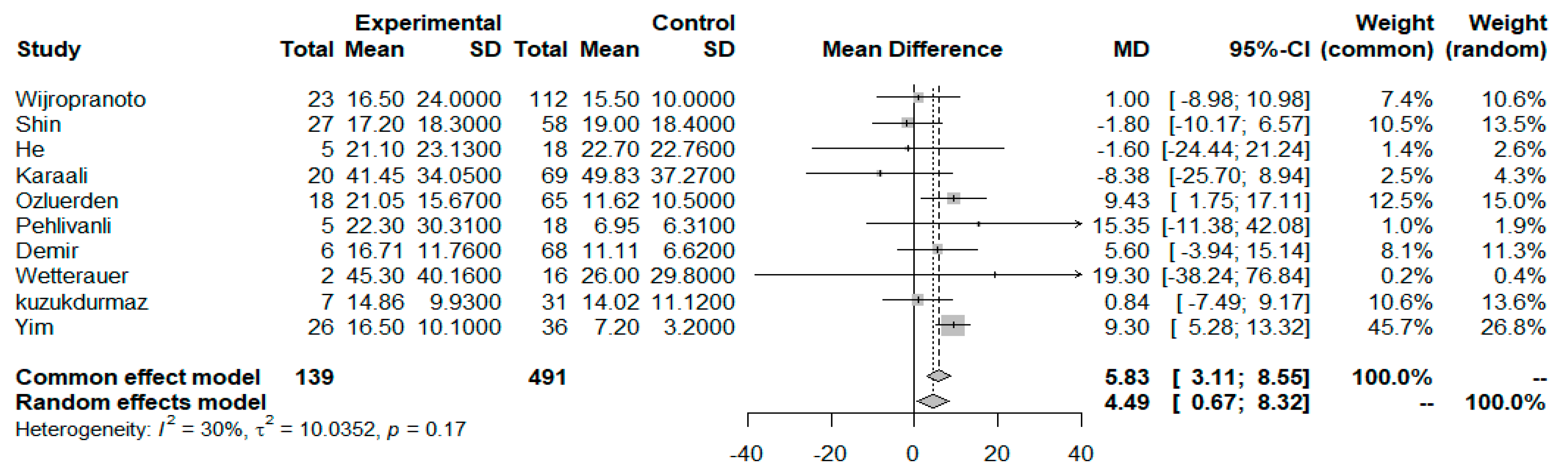
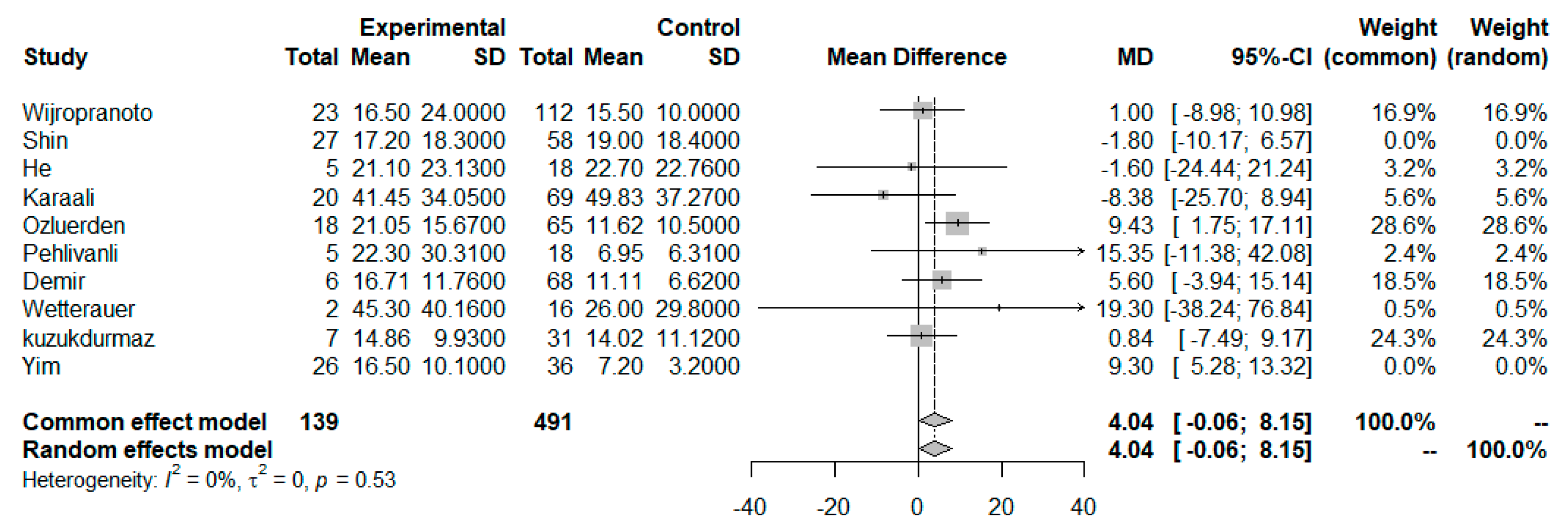
3.3. NLR as a Prognosticator Index
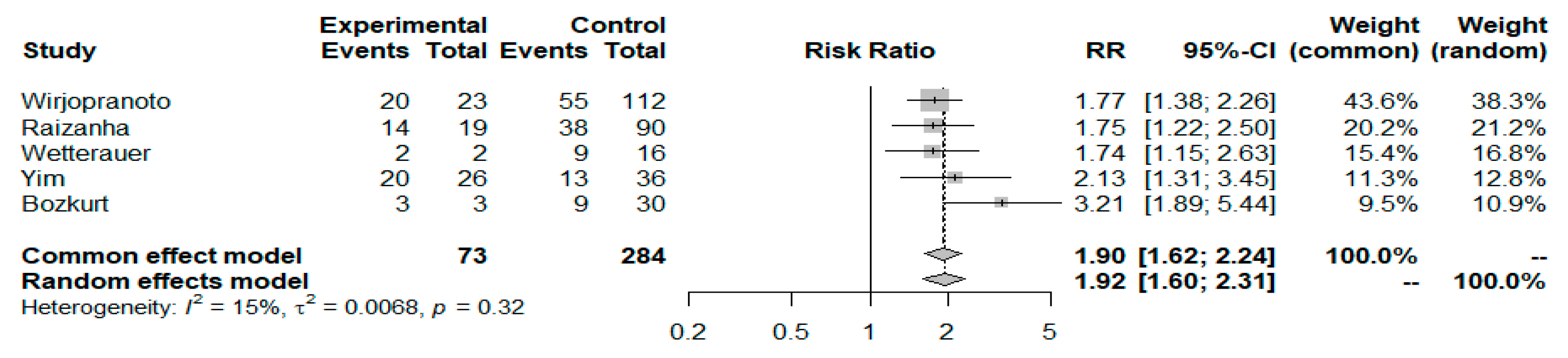
3.4. NLR Cutoff Values and FG Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FG | Fournier Gangrene |
| FGSI | Fournier Gangrene Severity Index |
| SFGSI | Simplified Fournier Gangrene Severity Index |
| LRINEC | Laboratory Risk Indicator For Necrotizing Fasciitis |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
Appendix A
Pubmed Search String
References
- Desai, R.; Batura, D. A contemporaneous narrative review of Fournier’s gangrene. Urologia 2023, 90, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagedorn, J.C.; Wessells, H. A contemporary update on Fournier’s gangrene. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, N. Fournier’s gangrene: A review of 1726 cases. Br. J. Surg. 2000, 87, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjelloun, E.B.; Souiki, T.; Yakla, N.; Ousadden, A.; Mazaz, K.; Louchi, A.; Kanjaa, N.; Taleb, K.A. Fournier’s gangrene: Our experience with 50 patients and analysis of factors affecting mortality. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2013, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.; Juliebø-Jones, P.; Somani, B.K. Global outcomes and lessons learned in the management of Fournier’s gangrene from highvolume centers: Findings from a literature review over the last two decades. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.; Hughes, T.; Juliebø-Jones, P.; Somani, B. Fournier’s gangrene: A review of predictive scoring systems and practical guide for patient management. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, 20499361241238521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufano, A.; Dipinto, P.; Passaro, F.; Anceschi, U.; Franco, G.; Flammia, R.S.; Proietti, F.; Antonelli, L.; Di Pierro, G.B.; Prata, F.; et al. The Value of Fournier’s Gangrene Scoring Systems on Admission to Predict Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laor, E.; Palmer, L.S.; Tolia, B.M.; Reid, R.E.; Winter, H.I. Outcome prediction in patients with Fournier’s gangrene. J. Urol. 1995, 154, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Ou, C.; Tzai, T.; Tong, Y.; Chang, C.; Cheng, H.; Yang, W.; Lin, Y. Validation and simplification of Fournier’s gangrene severity index. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmazlar, T.; Ozturk, E.; Ozguc, H.; Ercan, I.; Vuruskan, H.; Oktay, B. Fournier’s gangrene: An analysis of 80 patients and a novel scoring system. Tech. Coloproctol. 2010, 14, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.H.; Khin, L.W.; Heng, K.S.; Tan, K.C.; Low, C.O. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: A tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretis, K.; Sfaelos, K.; Boptsi, E.; Gaitanis, G.; Bassukas, I.D. The Neutrophil-to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Biomarker in Cutaneous Oncology: A Systematic Review of Evidence beyond Malignant Melanoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio: An emerging marker of the relationships between the immune system and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, past, present and future perspectives. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2021, 122, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmelé, T.; Payen, D.; Cantaluppi, V.; Marshall, J.; Gomez, H.; Gomez, A.; Murray, P.; Kellum, J.A. Immune Cell Phenotype and Function in Sepsis. Shock 2016, 45, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, P.; Khalifa, C.; Defour, J.P.; Latinne, D.; Van Pel, M.C.; De Kock, M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts—Rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Chilvers, E.R.; Summers, C.; Koenderman, L. The Neutrophil Life Cycle. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warny, M.; Helby, J.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Birgens, H.; Bojesen, S.E. Incidental lymphopenia mortality: Aprospective cohort study. CMAJ 2020, 192, E25–E33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidar, D.A.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Liu, Y.; Krieger, N.I.; Perzynski, A.T.; Osnard, M.; Nmai, C.; Anthony, D.D.; Lederman, M.M.; Freeman, M.L.; et al. Association of lymphopenia with risk of mortality among adults in the US general population. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019, 2, e1916526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, C.; Sabarimurugan, S.; Madurantakam, R.M.; Lakhotiya, K.; Samiappan, S.; Baxi, S.; Nachimuthu, R.; Gothandam, K.M.; Jayaraj, R. Prognostic significance of blood inflammatory biomarkers NLR, PLR, and LMR in cancer-A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e14834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komura, N.; Mabuchi, S.; Yokoi, E.; Kozasa, K.; Kuroda, H.; Sasano, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kimura, T. Comparison of clinical utility between neutrophil count and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in patients with ovarian cancer: A single institutional experience and a literature review. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 23, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoyama, Y.; Umegaki, O.; Inoue, S.; Agui, T.; Kadono, N.; Minami, T. The Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Is Superior to Other Inflammation-Based Prognostic Scores in Predicting the Mortality of Patients with Pneumonia. Acta Med. Okayama 2018, 72, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Kalemaki, D.; Tzagkarakis, E.; Lydakis, C. Pitfalls in studies of eosinopenia and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte count ratio. Infect. Dis. 2018, 50, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fest, J.; Ruiter, T.R.; Koerkamp, B.G.; Rizopoulos, D.; Ikram, M.A.; van Eijck, C.H.J.; Stricker, B.H. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with mortality in the general population: The Rotterdam Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 34, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Graubard, B.I.; Rabkin, C.S.; Engels, E.A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mortality in the United States general population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahramanca, S.; Kaya, O.; Ozgehan, G.; Irem, B.; Dural, I.; Kucukpinar, T.; Kargici, H. Are neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio as effective as Fournier’s gangrene severity index for predicting the number of debridements in Fourner’s gangrene? Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2014, 20, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpston, M.; Chandler, J. Chapter IV: Updating a Review. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022); Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomized studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Wirjopranoto, S. Comparison between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as predictors of mortality on Fournier’s gangrene cases. Indian J. Urol. 2023, 39, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, I.S.; Gong, S.C.; An, S.; Kim, K. Delta neutrophil index as a prognostic factor for mortality in patients with Fournier’s gangrene. Int. J. Urol. 2022, 29, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xiang, X.; Zou, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, L.; Bi, Y.; Kan, D. Distinctions between Fournier’s gangrene and lower extremity necrotising fasciitis: Microbiology and factors affecting mortality. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 122, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizandha, M.A.; Hidayatullah, F.; Kloping, Y.P.; Rizaldi, F. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and fournier gangrene severity index are not prognostic factors of mortality in fournier gangrene patients. Universa Med. 2022, 41, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaali, C.; Salimoglu, S.; Emiroglu, M.; Budak, G.G.; Calik, B.; Aydin, C. Is it possible to estimate the mortality rate of Fournier Gangrene with new parameters? Kuwait Med. J 2019, 52, 286–290. [Google Scholar]
- Özlülerden, Y.; Baser, A.; Celen, S.; Alkis, O. Can we predict poor prognosis in Fournier gangrene? J. Surg. Med. 2020, 4, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivanlı, F.; Aydin, O. Factors Affecting Mortality in Fournier Gangrene: A Single Center Experience. Surg. Infect. 2019, 20, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, C.Y.; Yuzkat, N.; Ozsular, Y.; Kocak, O.F.; Soyalp, C.; Demirkiran, H. Fournier Gangrene: Association of Mortality with the Complete Blood Count Parameters. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 68e–75e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetterauer, C.; Ebbing, J.; Halla, A.; Kuehl, R.; Erb, S.; Egli, A.; Schaefer, D.J.; Seifert, H.H. A contemporary case series of Fournier’s gangrene at a Swiss tertiary care center-can scoring systems accurately predict mortality and morbidity? World J. Emerg. Surg. 2018, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükdurmaz, F.; Sahinkanat, T.; Temizer, M.; Resim, S. Fournier gangreninde mortaliteyi etkileyen faktörlerin değerlendirilmesi: 38 hastalık deneyimimiz. [Fournier’s gangrene: Our experience with 38 patients and analysis of factors affecting mortality]. Yeni Urol. Derg.—New J. Urol. 2017, 12, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, S.U.; Kim, S.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Chung, H.; Hwang, E.C.; Yu, H.S.; Oh, K.J.; Jung, S.I.; Kang, T.W.; et al. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratios Are More Effective than the Fournier’s Gangrene Severity Index for Predicting Poor Prognosis in Fournier’s Gangrene. Surg. Infect. 2016, 17, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, O.; Sen, V.; Demir, O.; Esen, A. Evaluation of the utility of different scoring systems (FGSI, LRINEC and NLR) in the management of Fournier’s gangrene. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 47, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guemes-Quinto, A.; Godinez-Vidal, A.R.; Villanueva-Herrero, J.A.; Jiménez-Bobadilla, B.; Pérez-Escobedo, S.U.; Bandeh-Moghaddam, H.; Gracida-Mancilla, N.I. Usefulness of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as predictors of severity on Fournier fasciitis of the Hospital General de México “Dr. Eduardo Liceaga”. Rev. Med. Hosp. Gen. Mex. 2019, 82, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenório, C.E.L.; Lima, S.V.C.; Albuquerque, A.V.; Cavalcanti, M.P.; Teles, F. Risk factors for mortality in Fournier’s gangrene in a general hospital: Use of simplified Fournier gangrene severe index score (SFGSI). Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Qushayri, A.E.; Khalaf, K.M.; Dahy, A.; Mahmoud, A.R.; Benmelouka, A.Y.; Ghozy, S.; Mahmoud, M.U.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Alkahtani, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Fournier’s gangrene mortality: A 17-year systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.; Devakumar, S.; Huespe, I.; Kashyap, R.; Chisti, I. A Comprehensive Literature Review of Fournier’s Gangrene in Females. Cureus 2023, 15, e38953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, M.D.; Krieger, J.N. Fournier’s gangrene: Epidemiology and outcomes in the general US population. Urol. Int. 2016, 97, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czymek, R.; Frank, P.; Limmer, S.; Schmidt, A.; Jungbluth, T.; Roblick, U.; Bürk, C.; Bruch, H.-P.; Kujath, P. Fournier’s gangrene: Is the female gender a risk factor? Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2009, 394, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinchón-Romer, I.; Ramos-Belinchón, A.; Lobato-Martínez, E.; Sánchez-García, V.; Ramos-Rincón, J.-M. National Study of Fournier Gangrene in Spain (2016–2021): Gender/Sex Differences in Mortality and Risks. Medicina 2024, 60, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.; Hacker, E.; Ghaffar, U.; Hakam, N.; Li, K.D.; Alazzawi, S.; Fernandez, A.; Patel, H.V.; Breyer, B.N. Higher morbidity and mortality in females with Fournier’s gangrene compared to males: Insights from National Inpatient Sample data. J. Urol. 2025, 213, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Luo, X.; Hong, J.; Pan, K.; Lin, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio positively correlates to age in healthy population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2015, 29, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Country | Groups | N | Sex | Age (y) | DM (n) | Hypertension (n) | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wijropranoto, 2023 [32] | Indonesia | Survivors | 112 | M: 103 | F: 9 | 50.4 ± 15 | 63 | 9 | NLR (MD) NLR (Cutoff) |
| Non-Survivors | 23 | M: 20 | F: 3 | 53.2 ± 14.7 | 11 | 3 | |||
| Shin, 2022 [33] | South Korea | Survivors | 58 | M: 53 | F: 5 | 58 ± 14 | 23 | 23 | NLR (MD) |
| Non-Survivors | 27 | M: 20 | F: 7 | 65.3 ± 15 | 8 | 9 | |||
| He, 2022 [34] | China | Survivors | 13 | M: 9 | F: 4 | 48.6 ± 13.6 | 4 | NR | NLR (MD) |
| Non-Survivors | 5 | M: 3 | F: 2 | 60.6 ± 10.4 | 3 | NR | |||
| Raizandha, 2022 [35] | Indonesia | Survivors | 90 | NR | 49 ± 14.9 | 40/109 | NR | NLR (Cutoff) |
| Non-Survivors | 19 | NR | 54 ± 13.8 | NR | ||||
| Karaali, 2020 [36] | Turkey | Survivors | 69 | M: 58 | F: 31 | 53.9 ± 13.57 | 31 | 19 | NLR (MD) |
| Non-Survivors | 20 | 67.6 ± 11.52 | 13 | 7 | ||||
| Ozluerden, 2020 [37] | Turkey | Survivors | 65 | M: 60 | F: 5 | 50.02 ± 16.4 | 30 | NR | NLR (MD) |
| Non-Survivors | 18 | M: 13 | F: 5 | 68.28 ± 14.58 | 13 | NR | |||
| Pehlivanli, 2019 [38] | Turkey | Survivors | 18 | M: 15 | F: 3 | 63 ± 16.33 | 9 | NR | NLR (MD) |
| Non-Survivors | 5 | M: 4 | F: 1 | 78 ± 10.83 | 2 | NR | |||
| Demir, 2018 [39] | Turkey | Survivors | 68 | M: 46 | F:22 | 58.3 ± 14.55 | 31 | NR | NLR (MD) |
| Non-Survivors | 6 | M: 3 | F: 3 | 49.66 ± 22.73 | 6 | NR | |||
| Wetterauer, 2018 [40] | Switzerland | Survivors | 16 | M: 16 | F: 0 | 57.71 ± 15.89 | NR | NR | NLR (MD) NLR (Cutoff) |
| Non-Survivors | 2 | M: 2 | F: 0 | 83 ± 14.93 | NR | NR | |||
| Kuzukdurmaz, 2017 [41] | Turkey | Survivors | 31 | NR | 53.25 ± 16.07 | 15 | NR | NLR (MD) |
| Non-Survivors | 7 | NR | 71.14 ± 12.5 | 2 | NR | |||
| Yim, 2016 [42] | South Korea | Survivors | 36 | M: 35 | F: 1 | 57.1 ± 14.4 | 10 | NR | NLR (MD) NLR (Cutoff) |
| Non-Survivors | 26 | M: 26| F: 0 | 56.2 ± 13 | 11 | NR | |||
| Bozkurt, 2015 [43] | Turkey | Survivors | 30 | NR | 56 ± 12.8 | 22/33 | 10/33 | NLR (Cutoff) |
| Non-Survivors | 3 | NR | 72.9 ± 7.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seretis, K.; Bounas, N.; Sfaelos, K.; Gaitanis, G.; Bassukas, I. The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker of Fournier’s Gangrene Severity: A Meta-Analysis. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030055
Seretis K, Bounas N, Sfaelos K, Gaitanis G, Bassukas I. The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker of Fournier’s Gangrene Severity: A Meta-Analysis. Infectious Disease Reports. 2025; 17(3):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeretis, Konstantinos, Nikolaos Bounas, Konstantinos Sfaelos, Georgios Gaitanis, and Ioannis Bassukas. 2025. "The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker of Fournier’s Gangrene Severity: A Meta-Analysis" Infectious Disease Reports 17, no. 3: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030055
APA StyleSeretis, K., Bounas, N., Sfaelos, K., Gaitanis, G., & Bassukas, I. (2025). The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Biomarker of Fournier’s Gangrene Severity: A Meta-Analysis. Infectious Disease Reports, 17(3), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030055







