Emerging and Re-Emerging Parasitic Infections of the Central Nervous System (CNS) in Europe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Parasitic Infections of the CNS
2.1. Protozoal Infections of CNS
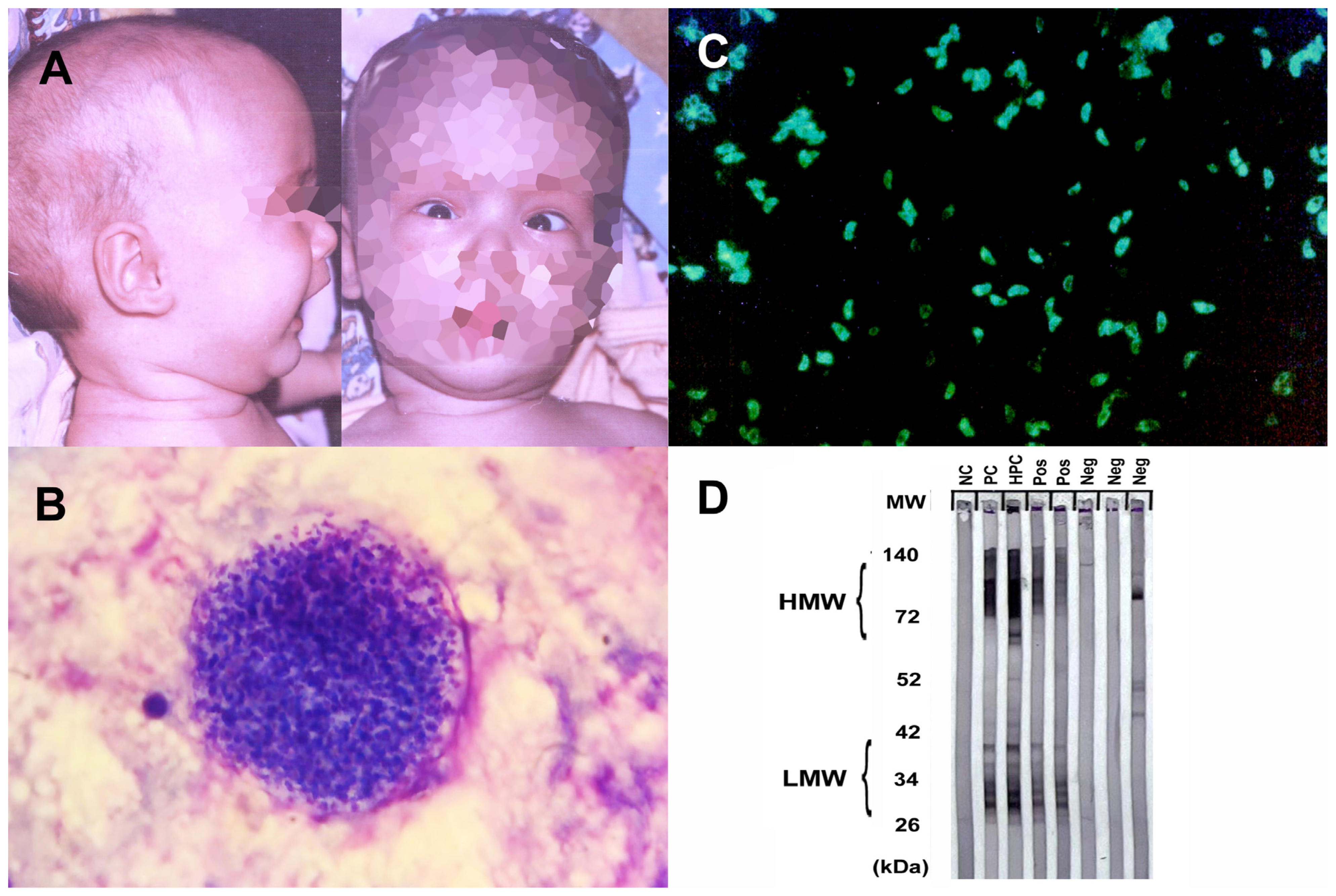
2.1.1. Amebiasis (Entamoeba histolytica)
2.1.2. Free-Living Amebiasis
2.1.3. Cerebral Malaria
2.1.4. Toxoplasmosis
2.1.5. Trypanosomiasis
| Parasites and Diseases | Countries with Reported Cases (Europe) | Mode of Transmission | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entamoeba histolytica Amebiasis | Turkey, Spain [13,14] | Ingestion of cysts | Radiology, serology, molecular | Metronidazole, surgical drainage |
| Free living amoeba Naegleria fowleri Acanthamoeba spp. Balamuthia mandrillaris Sappinia | Belgium, Czech Republic, Italy, the Netherlands, United Kingdom [20,22,23,24] | Trophozoites through nasal passage, olfactory nerve Cysts or trophozoites through eye, nasal passage, lung, or skin | Microscopy, molecular | Symptomatic |
| Plasmodium falciparum Cerebral malaria | United Kingdom, Switzerland [33,34], Italy, Germany, France, Denmark, Belgium [32] | Mosquito bite | Microscopy, molecular | Quinine and artemisinin |
| Toxoplasma gondii Toxoplasmosis | France, Spain, Czech Republic, United Kingdom, Germany, Denmark, Serbia [39] | Ingestion of oocysts or tissue cysts | Radiology, serology | Pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine |
| Trypanosoma brucei African trypanosomiasis (HAT) | France, Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, Poland [56] | Tsetse fly bite | Microscopy, molecular | Pentamidine, eflornithine, nifurtimox, melarsoprol, suramin |
| Trypanosoma cruzi South American trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease (CD)) | Spain, Portugal, Italy, France, the United Kingdom, Switzerland [54] | Metacyclic trypomastigotes through mucous membranes or skin abrasions | Microscopy, molecular | Nifurtimox, benznidazole |
2.2. Helminth Infections of CNS
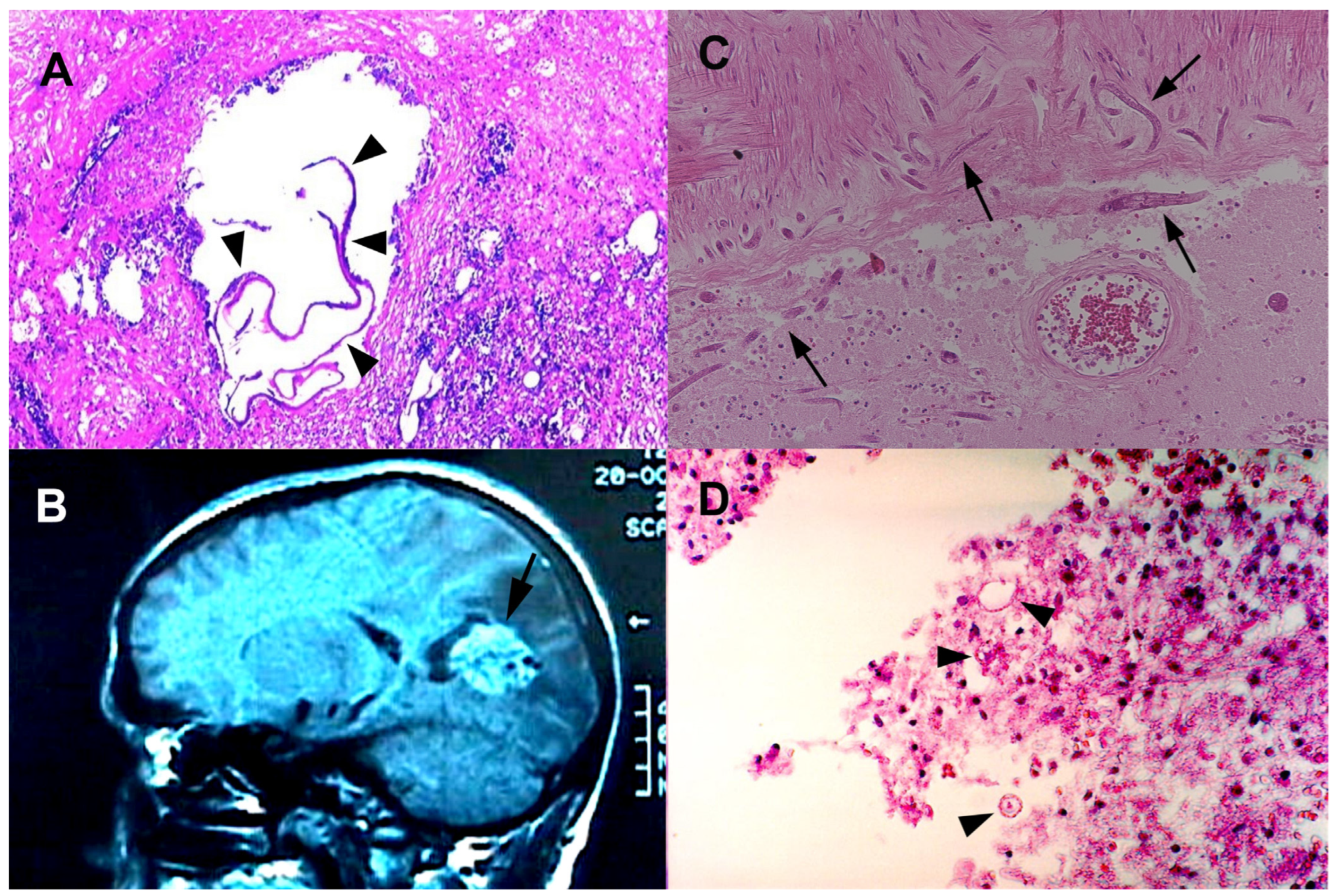
2.2.1. Angiostrongyliasis
2.2.2. Echinococcosis
2.2.3. Schistosomiasis
2.2.4. Strongyloidiasis
2.2.5. Taeniasis (Neurocysticercosis)
2.2.6. Toxocariasis
2.2.7. Trichinellosis (Neurotrichinellosis)
| Parasites and Diseases | Countries with Reported Cases (Europe) | Mode of Transmission | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angiostrongylus cantonensis Angiostrongyliasis | France, Germany, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, Croatia, Italy, Spain, United Kingdom [59,62] | Ingestion of raw or undercooked molluscs, crabs, or freshwater shrimp | Radiology | Symptomatic |
| Echinococcus granulosus Cystic echinococcosis Echinococcus multilocularis Alveolar echinococcosis | Greece, Italy, Turkey, Romania, Bulgaria [67] Belgium, Netherlands, Italy, Austria, Hungary, and Slovenia [68] | Ingestion of eggs | Radiology, serology | Surgery, PAIR, albendazole |
| Schistosoma spp. | France, United Kingdom, Spain, Portugal [79,80,81,82,83] | Skin penetration | Demonstration of eggs in stool or urine, serology | Praziquantel |
| Strongyloides stercoralis Strongyloidiasis | France, Belgium, Portugal [88,89,90] | Skin penetration | Demonstration larvae, serology | Ivermectin |
| Taenia solium Cycticercosis | Prevalent in both eastern and western Europe [97,98,99] | Ingestion of eggs | Radiology, serology | Surgery, albendazole, and praziquantel |
| Toxocara spp. Visceral larva migrans Ocular larva migrans Neurotoxocariasis | Spain, France, Denmark, Sweden [102,104,105] | Ingestion of eggs | Serology | Albendazole |
| Trichinella spp. Trichinellosis | France, Romania, Germany, Turkey, Serbia [110,114,115,116,117] | Ingestion of raw or undercooked pork | Demonstration larvae, serology | Symptomatic, albendazole |
2.2.8. Other Helminthiases of CNS
Filariidae (Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Brugia timori, Onchocerca volvulus)
Paragonimus spp.
Soil-Transmitted Helminths (STHs)
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deksne, G.; Davidson, R.K.; Buchmann, K.; Kärssin, A.; Kirjušina, M.; Gavarāne, I.; Miller, A.L.; Pálsdóttir, G.R.; Robertson, L.J.; Mørk, T.; et al. Parasites in the changing world—Ten timely examples from the Nordic-Baltic region. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2020, 10, e00150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deigendesch, N.; Schlüter, D.; Siebert, E.; Stenzel, W. Infections of the central nervous system by protozoa, helminths and fungi. Nervenarzt 2019, 90, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, A.; Romo, M.L.; Parkhouse, R.M.E.; Short, B.; Dua, T. Parasitic diseases of the central nervous system: Lessons for clinicians and policy makers. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Giessen, J.; Deksne, G.; Gómez-Morales, M.A.; Troell, K.; Gomes, J.; Sotiraki, S.; Rozycki, M.; Kucsera, I.; Djurković-Djaković, O.; Robertson, L.J. Surveillance of foodborne parasitic diseases in Europe in a One Health approach. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2021, 13, e00205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, T.E.; Mahanty, S.; Loeb, J.A.; Theodore, W.H.; Friedman, A.; Sander, J.W.; Singh, G.; Cavalheiro, E.; Del Brutto, O.H.; Takayanagui, O.M.; et al. Neurocysticercosis: A natural human model of epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, F.C.; Lepard, J.R.; Mekary, R.A.; Davis, M.C.; Yunusa, I.; Gormley, W.B.; Baticulon, R.E.; Mahmud, M.R.; Misra, B.K.; Rattani, A.; et al. Epidemiology of central nervous system infectious diseases: A meta-analysis and systematic review with implications for neurosurgeons worldwide. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 1107–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, C.; Torgerson, P.R.; Robertson, L.J. Foodborne Parasites in Europe: Present Status and Future Trends. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, J.C.; Paz, S. Climate change and infectious disease in Europe: Impact, projection and adaptation. Lancet Reg. Health—Eur. 2021, 9, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenfak, A.; Eperon, G.; Schibler, M.; Lamoth, F.; Vargas, M.; Stahl, J. Diagnostic approach to encephalitis and meningoencephalitis in adult returning travellers. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Review of zoonotic amebiasis: Epidemiology, clinical signs, diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 136, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, A.; Torresi, J.; Schlagenhauf, P.; Thursky, K.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Connor, B.A.; Schwartz, E.; Vonsonnenberg, F.; Keystone, J.; O’Brien, D.P. A global study of pathogens and host risk factors associated with infectious gastrointestinal disease in returned international travellers. J. Infect. 2009, 59, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirley, D.-A.T.; Farr, L.; Watanabe, K.; Moonah, S. A Review of the Global Burden, New Diagnostics, and Current Therapeutics for Amebiasis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, P.S.; Gallotti, A.C.; Ramos, R.; López, J.L.; González, Y.; Mejía, R.A.; Vinasco, A.C.O.; Fuentes, I.; Merino, F.J. An Unexpected Case of Disseminated Amebiasis with Cerebral Involvement and Successful Recovery in a Non-Endemic Context. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e934188-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, G.S.; Öncel, S.; Gökbulut, S.; Arisoy, E.S. A rare case of multilocus brain abscess due to Entamoeba histolytica infection in a child. Saudi Med. J. 2015, 36, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Huston, C.D.; Hughes, M.; Houpt, E.; Petri, W.A. Amebiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, P.; Serrano-Vázquez, A.; Rojas-Velázquez, L.; González, E.; Pérez-Juárez, H.; Hernández, E.G.; Padilla, M.d.L.A.; Zaragoza, M.E.; Portillo-Bobadilla, T.; Ramiro, M.; et al. Amoebiasis: Advances in Diagnosis, Treatment, Immunology Features and the Interaction with the Intestinal Ecosystem. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkerke, H.P.; Petri, W.A.; Marie, C.S. The Dynamic Interdependence of Amebiasis, Innate Immunity, and Undernutrition. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofman, A.; Guarner, J. Infections Caused by Free-Living Amoebae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, JCM0022821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharpure, R.; Bliton, J.; Goodman, A.; Ali, I.K.M.; Yoder, J.; Cope, J.R. Epidemiology and Clinical Characteristics of Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Naegleria fowleri: A Global Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e19–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciver, S.K.; Piñero, J.E.; Lorenzo-Morales, J. Is Naegleria fowleri an Emerging Parasite? Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wei, Z.; Cao, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Q. The global epidemiology and clinical diagnosis of Acanthamoeba keratitis. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogo, P.E.; Scagli, M.; Gatti, S.; Rossetti, F.; Alaggio, R.; Laverda, A.M.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, L.; Visvesvara, G.S. Fatal Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1835–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Beek, N.A.; van Tienen, C.; de Haan, J.E.; Roelfsema, J.; Wismans, P.J.; van Genderen, P.J.; Tanghe, H.L.; Verdijk, R.M.; Titulaer, M.J.; van Hellemond, J.J. Fatal Balamuthia mandrillaris Meningoencephalitis in the Netherlands after Travel to The Gambia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, S.; Miracco, C.; Cusi, M.G.; Tordini, G.; Muzii, V.F.; Iacoangeli, F.; Nocentini, C.; Ali, I.K.M.; Roy, S.; Cerase, A.; et al. Non-granulomatous cerebellar infection by Acanthamoeba spp. in an immunocompetent host. Infection 2018, 46, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capewell, L.G.; Harris, A.M.; Yoder, J.S.; Cope, J.R.; Eddy, B.A.; Roy, S.L.; Visvesvara, G.S.; Fox, L.M.; Beach, M.J. Diagnosis, Clinical Course, and Treatment of Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis in the United States, 1937–2013. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2015, 4, e68–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiess, N.; Villabona-Rueda, A.; Cottier, K.E.; Huether, K.; Chipeta, J.; Stins, M.F. Pathophysiology and neurologic sequelae of cerebral malaria. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Lavstsen, T.; Berger, S.S.; Wang, C.W.; Petersen, J.E.V.; Avril, M.; Brazier, A.J.; Freeth, J.; Jespersen, J.S.; Nielsen, M.A.; et al. Severe malaria is associated with parasite binding to endothelial protein C receptor. Nature 2013, 498, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.H.; Grau, G.E. Cytokines: Accelerators and brakes in the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondorp, A.M.; Ince, C.; Charunwatthana, P.; Hanson, J.; van Kuijen, A.; Faiz, M.A.; Rahman, M.R.; Hasan, M.; Bin Yunus, E.; Ghose, A.; et al. Direct In Vivo Assessment of Microcirculatory Dysfunction in Severe Falciparum Malaria. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossner, C.M.; Hallmaier-Wacker, L.; Briet, O.; Haussig, J.M.; de Valk, H.; Wijermans, A.; Bakonyi, T.; Madubuko, T.; Frank, C.; Noel, H.; et al. Arthropod-borne diseases among travellers arriving in Europe from Africa, 2015 to 2019. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahittikorn, A.; Mala, W.; Wilairatana, P.; Siri, S.; Masangkay, F.R.; Kotepui, K.U.; Kotepui, M. Prevalence, anti-malarial chemoprophylaxis and causes of deaths for severe imported malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 49, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurth, F.; Develoux, M.; Mechain, M.; Malvy, D.; Clerinx, J.; Antinori, S.; Gjørup, I.E.; Gascon, J.; Mørch, K.; Nicastri, E.; et al. Severe malaria in Europe: An 8-year multi-centre observational study. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Marks, M.; Armstrong, M.; Suvari, M.M.; Batson, S.; Whitty, C.J.M.; Chiodini, P.L.; Bellinghan, G.; Doherty, J.F. Severe imported falciparum malaria among adults requiring intensive care: A retrospective study at the hospital for tropical diseases, London. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannone, B.; Hedrich, N.; Schlagenhauf, P. Imported malaria in Switzerland, (1990–2019): A retrospective analysis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 45, 102251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.T.H.; Day, N.P.; Van Chuong, L.; Waller, D.; Phu, N.H.; Bethell, D.B.; Hien, T.T.; White, N.J. Post-malaria neurological syndrome. Lancet 1996, 348, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, A.; Ali, H.B.; Savini, H.; Kaphan, E.; Parola, P. Post-malaria neurological syndrome: Imported case series and literature review to unscramble the auto-immune hypothesis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 29, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamzali, Y.; Demeret, S.; Haddad, E.; Guillot, H.; Caumes, E.; Jauréguiberry, S. Post-malaria neurological syndrome: Four cases, review of the literature and clarification of the nosological framework. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, S.K.; Rinkenberger, N.; Dunay, I.R.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma gondii infection and its implications within the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-D.; Wang, S.-C.; Liu, H.-H.; Ma, H.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Wei, F.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Liu, Q. Prevalence and burden of Toxoplasma gondii infection in HIV-infected people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet HIV 2017, 4, e177–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleyer, U.; Groß, U.; Schlüter, D.; Wilking, H.; Seeber, F. Toxoplasmosis in Germany: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Risk factors, and Treatment. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2019, 116, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, N.; Meintjes, G.; Calmy, A.; Bygrave, H.; Migone, C.; Vitoria, M.; Penazzato, M.; Vojnov, L.; Doherty, M.; Asero, P.; et al. Managing Advanced HIV Disease in a Public Health Approach. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, S106–SS110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrey, E.F.; Bartko, J.J.; Yolken, R.H. Toxoplasma gondii and Other Risk Factors for Schizophrenia: An Update. Schizophr. Bull. 2012, 38, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutterland, A.L.; Fond, G.; Kuin, A.; Koeter, M.W.J.; Lutter, R.; van Gool, T.; Yolken, R.; Szoke, A.; Leboyer, M.; de Haan, L. Beyond the association. Toxoplasma gondii in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and addiction: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2015, 132, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.-D.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhu, X.-Q. Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis and typing of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of Toxoplasmosis: Historical Perspective, Animal Models, and Current Clinical Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagni, R.; Novara, R.; Minardi, M.L.; Frallonardo, L.; Panico, G.G.; Pallara, E.; Cotugno, S.; Bartoli, T.A.; Guido, G.; De Vita, E.; et al. Human African Trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness): Current knowledge and future challenges. Front. Trop. Dis. 2023, 4, 1087003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J. Trypanosomiasis and the brain. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, M.D.; Salimi, H.; Diamond, M.S.; Klein, R.S. Mechanisms of Pathogen Invasion into the Central Nervous System. Neuron 2019, 103, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büscher, P.; Cecchi, G.; Jamonneau, V.; Priotto, G. Human African trypanosomiasis. Lancet 2017, 390, 2397–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidani, K.C.F.; Andrade, F.A.; Bavia, L.; Damasceno, F.S.; Beltrame, M.H.; Messias-Reason, I.J.; Sandri, T.L. Chagas Disease: From Discovery to a Worldwide Health Problem. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2019, 49, 458711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Govic, Y.; Demey, B.; Cassereau, J.; Bahn, Y.-S.; Papon, N. Pathogens infecting the central nervous system. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, L.H.; Singh, G.D.; Amsterdam, E.A. The Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Management of Chagas Heart Disease. Clin. Cardiol. 2015, 38, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Ochoa, S.A.; Rojas, L.Z.; Echeverría, L.E.; Muka, T.; Franco, O.H. Global, Regional, and National Trends of Chagas Disease from 1990 to 2019: Comprehensive Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. Glob. Heart 2022, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antinori, S.; Galimberti, L.; Bianco, R.; Grande, R.; Galli, M.; Corbellino, M. Chagas disease in Europe: A review for the internist in the globalized world. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 43, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinazo, M.-J.; Espinosa, G.; Cortes-Lletget, C.; Posada, E.d.J.; Aldasoro, E.; Oliveira, I.; Muñoz, J.; Gállego, M.; Gascon, J. Immunosuppression and Chagas Disease: A Management Challenge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautret, P.; Clerinx, J.; Caumes, E.; Simon, F.; Jensenius, M.; Loutan, L.; Schlagenhauf, P.; Castelli, F.; Freedman, D.; Miller, A.; et al. Imported human African trypanosomiasis in Europe, 2005–2009. Eurosurveillance 2009, 14, 19327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Chan, D.; Sandaradura, I.; Malik, R.; Spielman, D.; Lee, R.; Marriott, D.; Harkness, J.; Ellis, J.; Stark, D. Angiostrongylus cantonensis: A review of its distribution, molecular biology and clinical significance as a human pathogen. Parasitology 2016, 143, 1087–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Esquivel, C.; Sola, J.; Delgado-Serra, S.; Riera, M.P.; Negre, N.; Miranda, M.Á.; Jurado-Rivera, J.A. Angiostrongylus cantonensis in North African hedgehogs as vertebrate hosts, Mallorca, Spain, October 2018. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1900489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federspiel, F.; Skovmand, S.; Skarphedinsson, S. Eosinophilic meningitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Europe. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Carrillo, N.; Feliu, C.; Abreu-Acosta, N.; Izquierdo-Rodriguez, E.; Dorta-Guerra, R.; Miquel, J.; Abreu-Yanes, E.; Martin-Alonso, A.; García-Livia, K.; Quispe-Ricalde, M.A.; et al. A Peculiar Distribution of the Emerging Nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis in the Canary Islands (Spain): Recent Introduction or Isolation Effect? Animals 2021, 11, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Serra, S.; Sola, J.; Negre, N.; Paredes-Esquivel, C. Angiostrongylus cantonensis Nematode Invasion Pathway, Mallorca, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Gómez-Samblás, M.; Osuna, A.; Sáez-Durán, S.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Fuentes, M.V. Update on the First Finding of the Rat Lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, in Rattus spp. in Continental Europe, Valencia, Spain, 2022. Pathogens 2023, 12, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, Y.C.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Kazacos, K.R. Central nervous system manifestations of Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Acta Trop. 2015, 141, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.R.; Modry, D.; Paredes-Esquivel, C.; Foronda, P.; Traversa, D. Angiostrongylosis in Animals and Humans in Europe. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melot, B.; Delvallez, G.; Gourinat, A.C.; Molko, N.; Goarant, C.; Ducrot, Y.M.; Huguon, E.; Cazorla, C.; Chauvet, M.; Biron, A.; et al. Eosinophilic meningitis in New Caledonia: The role of Angiostrongylus cantonensis? PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Y.; Rossi, B.; Argy, N.; Baker, C.; Nickel, B.; Marti, H.; Zarrouk, V.; Houzé, S.; Fantin, B.; Lefort, A. Autochthonous Case of Eosinophilic Meningitis Caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis, France, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1045–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echinococcosis—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/echinococcosis-annual-epidemiological-report-2020 (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Zancanaro, G. Annual assessment of Echinococcus multilocularis surveillance reports submitted in 2020 in the context of Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2018/772. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquier, M.; Piroth, L. Vertebral Hydatidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperato, A.; Consales, A.; Ravegnani, M.; Castagnola, E.; Bandettini, R.; Rossi, A. Primary Hydatid Cyst of the Brain in a Child: A Case Report. Pol. J. Radiol. 2016, 81, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantzanou, M.; Karalexi, M.A.; Vassalos, C.M.; Kostare, G.; Vrioni, G.; Tsakris, A. Central nervous system cystic echinococcosis: A systematic review. Germs 2022, 12, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algros, M.-P.; Majo, F.; Bresson-Hadni, S.; Koch, S.; Godard, J.; Cattin, F.; Delbosc, B.; Kantelip, B. Intracerebral Alveolar Echinococcosis. Infection 2003, 31, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenni, L.; Simoncini, A.; Massetti, L.; Rizzoli, A.; Hauffe, H.C.; Massolo, A. Current and future distribution of a parasite with complex life cycle under global change scenarios: Echinococcus multilocularis in Europe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023, 29, 2436–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carod Artal, F.J. Cerebral and spinal schistosomiasis. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2012, 12, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, C.C.; Carabin, H.; Montano, S.M.; Bangirana, P.; Zunt, J.R.; Peterson, P.K. Global research priorities for infections that affect the nervous system. Nature 2015, 527, S178–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.G.; McManus, D.P.; Farrar, J.; Hunstman, R.J.; Gray, D.J.; Li, Y.S. Neuroschistosomiasis. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, S.; Alomar, S.Y.; Yahya, G. Blocking prostanoid receptors switches on multiple immune responses and cascades of inflammatory signaling against larval stages in snail fever. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43546–43555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, M.J.; Wilkinson, P.A.; Doherty, J.F.; Jarman, P.R. Neuroschistosomiasis presenting as brainstem encephalitis. Neurology 2008, 70, 2262–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wilton, A.; Aggarwal, D.; Jäger, H.R.; Manji, H.; Chiodini, P.L. Delayed diagnosis of spinal cord schistosomiasis in a non-endemic country: A tertiary referral centre experience. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuset, G.; Wolff, V.; Marescaux, C.; Abou-Bacar, A.; Candolfi, E.; Lefebvre, N.; Christmann, D.; Hansmann, Y. Cerebral vasculitis associated with Schistosoma mansoni infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauréguiberry, S.; Caumes, E.; Perez, L.; Bricaire, F.; Danis, M.; Ansart, S. Acute neuroschistosomiasis: Two cases associated with cerebral vasculitis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 964–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte Armindo, R.; Costa, S.; Almeida, V.; Barroso, C. Cerebral schistosomiasis in a patient travelling from São Tomé and Príncipe. BJR Case Rep. 2020, 6, 20190055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarabini-Castellani, P.; González-Chinchón, G.; Aldamiz-Echebarría, M.; Portu-Zapirain, J.; Apraiz-Garmendia, L.; De Arcaya, A.A. Neuroschistosomiasis: A challenging diagnosis. Rev. Neurol. 2007, 44, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keiser, P.B.; Nutman, T.B. Strongyloides stercoralis in the Immunocompromised Population. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslahi, A.V.; Badri, M.; Nahavandi, K.H.; Houshmand, E.; Dalvand, S.; Riahi, S.M.; Johkool, M.G.; Asadi, N.; Ahangari, S.A.H.; Taghipour, A.; et al. Prevalence of strongyloidiasis in the general population of the world: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pathog. Glob. Health 2021, 115, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, J.; Schwartz, K.L.; Keystone, J.; Dimitrakoudis, D.; Downing, M.; Krajden, S. Case Report: Central Nervous System Strongyloidiasis: Two Cases Diagnosed Antemortem. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.A.; Hartmeyer, G.N.; Stensvold, C.R.; Martin-Iguacel, R. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome with cerebral involvement. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 15, e247032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geri, G.; Rabbat, A.; Mayaux, J.; Zafrani, L.; Chalumeau-Lemoine, L.; Guidet, B.; Azoulay, E.; Pène, F. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome: A case series and a review of the literature. Infection 2015, 43, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pypen, Y.; Oris, E.; Meeuwissen, J.; Laenen, M.V.; Van Gompel, F.; Coppens, G. Late onset of Strongyloides stercoralis meningitis in a retired Belgian miner. Acta Clin. Belg. 2015, 70, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado Maury, I.; Neves, D.; Pereira, A. Recurrent meningitis associated to Strongyloides hyperinfection. Enferm. Infecciosas Microbiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brutto, O.H. Human cysticercosis (Taenia solium). Trop. Parasitol. 2013, 3, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, H.H.; Nash, T.E.; Del Brutto, O.H. Clinical symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of neurocysticercosis. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodjinotho, U.F.; Lema, J.; Lacorcia, M.; Schmidt, V.; Vejzagic, N.; Sikasunge, C.; Ngowi, B.; Winkler, A.S.; da Costa, C.P. Host immune responses during Taenia solium Neurocysticercosis infection and treatment. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, H.H.; Gonzalez, A.E.; Gilman, R.H. Taenia solium Cysticercosis and Its Impact in Neurological Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00085-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butala, C.; Brook, T.M.; Majekodunmi, A.O.; Welburn, S.C. Neurocysticercosis: Current Perspectives on Diagnosis and Management. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammarchi, L.; Bonati, M.; Strohmeyer, M.; Albonico, M.; Requena-Méndez, A.; Bisoffi, Z.; Nicoletti, A.; García, H.H.; Bartoloni, A.; The COHEMI Project Study Group. Screening, diagnosis and management of human cysticercosis and Taenia solium taeniasis: Technical recommendations by the COHEMI project study group. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2017, 22, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laranjo-González, M.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Trevisan, C.; Allepuz, A.; Sotiraki, S.; Abraham, A.; Afonso, M.B.; Blocher, J.; Cardoso, L.; da Costa, J.M.C.; et al. Epidemiology of taeniosis/cysticercosis in Europe, a systematic review: Western Europe. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, C.; Sotiraki, S.; Laranjo-González, M.; Dermauw, V.; Wang, Z.; Kärssin, A.; Cvetkovikj, A.; Winkler, A.S.; Abraham, A.; Bobić, B.; et al. Epidemiology of taeniosis/cysticercosis in Europe, a systematic review: Eastern Europe. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrador, Z.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Benito, A.; Lopez-Velez, R. Clinical Cysticercosis epidemiology in Spain based on the hospital discharge database: What’s new? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Morales, M.A.; Gárate, T.; Blocher, J.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Smit, G.S.A.; Schmidt, V.; Perteguer, M.J.; Ludovisi, A.; Pozio, E.; Dorny, P.; et al. Present status of laboratory diagnosis of human taeniosis/cysticercosis in Europe. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshayes, S.; Bonhomme, J.; de La Blanchardière, A. Neurotoxocariasis: A systematic literature review. Infection 2016, 44, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Holland, C.V.; Wang, T.; Hofmann, A.; Fan, C.K.; Maizels, R.M.; Hotez, P.J.; Gasser, R.B. Human toxocariasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e14–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, J.; Cicero, C.E.; Rateau, G.; Quattrocchi, G.; Marin, B.; Bruno, E.; Dalmay, F.; Druet-Cabanac, M.; Nicoletti, A.; Preux, P.-M. Updated evidence of the association between toxocariasis and epilepsy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strube, C.; Raulf, M.-K.; Springer, A.; Waindok, P.; Auer, H. Seroprevalence of human toxocarosis in Europe: A review and meta-analysis. Adv. Parasitol. 2020, 109, 375–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgoin, G.; Callait-Cardinal, M.-P.; Bouhsira, E.; Polack, B.; Bourdeau, P.; Ariza, C.R.; Carassou, L.; Lienard, E.; Drake, J. Prevalence of major digestive and respiratory helminths in dogs and cats in France: Results of a multicenter study. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neghina, R.; Neghina, A.M.; Marincu, I.; Iacobiciu, I. Trichinellosis, another helminthiasis affecting the central nervous system. Parasitol. Int. 2011, 60, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, E.C.; Tudor, R.; Cornea, A.; Simu, M. Central Nervous System Involvement in Trichinellosis: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, F.; Brunetti, E.; Pozio, E. Neurotrichinellosis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 114, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neghina, R.; Neghina, A.M.; Marincu, I.; Iacobiciu, I. Reviews on Trichinellosis (II): Neurological Involvement. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezević, K.; Turkulov, V.; Canak, G.; Lalosević, V.; Tomić, S. Neurotrichinosis: A cerebrovascular disease associated with myocardial injury and hypereosinophilia. Brain 1993, 116 Pt 3, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzikowiec, M.; Góralska, K.; Błaszkowska, J. Neuroinvasions caused by parasites. Ann. Parasitol. 2017, 63, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalcin, D.; Zarlenga, D.S.; Larter, N.C.; Hoberg, E.; Boucher, D.A.; Merrifield, S.; Lau, R.; Ralevski, F.; Cheema, K.; Schwartz, K.L.; et al. Trichinella Nativa Outbreak with Rare Thrombotic Complications Associated with Meat from a Black Bear Hunted in Northern Ontario. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feydy, A.; Touze, E.; Miaux, Y.; Bolgert, F.; Martin-Duverneuil, N.; Laplane, D.; Chiras, J. MRI in a case of neurotrichinosis. Neuroradiology 1996, 38 (Suppl. 1), S80–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosca, E.C.; Simu, M. Border zone brain lesions due to neurotrichinosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, S.; Kirsch, M.; Khaw, A.V.; Stein, T.; Vogelgesang, S.; Hosten, N. Diffusion-weighted imaging proves watershed infarction in neurotrichinosis. Eur. J. Radiol. Extra 2007, 64, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelal, F.; Kumral, E.; Vidinli, B.D.; Erdogan, D.; Yucel, K.; Erdogan, N. Diffusion-weighted and conventional MR imaging in neurotrichinosis. Acta Radiol. 2005, 46, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrovic, N.; Milosevic, B.; Urosevic, A.; Nikolic, N.; Dakic, Z.; Nikolic, I.; Korac, M. Severe trichinellosis with neurological involvement-neurotrichinellosis: A case report. Vet. Glas. 2019, 73, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.D.; Zunt, J.R. Neuroparasitic Infections: Cestodes, Trematodes, and Protozoans. Semin. Neurol. 2005, 25, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Cromwell, E.; A Schmidt, C.; Kwong, K.T.; Pigott, D.M.; Mupfasoni, D.; Biswas, G.; Shirude, S.; Hill, E.; Donkers, K.M.; Abdoli, A.; et al. The global distribution of lymphatic filariasis, 2000–2018: A geospatial analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e1186–e1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyagang, S.M.; Cumber, S.N.; Cho, J.F.; Keka, E.I.; Nkfusai, C.N.; Wepngong, E.; Tsoka-Gwegweni, J.M.; Fokam, E.B. Prevalence of onchocerciasis, attitudes and practices and the treatment coverage after 15 years of mass drug administration with ivermectin in the Tombel Health District, Cameroon. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 35, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, D.; Dumas, M.; Preux, P.-M. Neurological manifestations of filarial infections. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 114, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadermann, A.; Amaral, L.-J.; Van Cutsem, G.; Fodjo, J.N.S.; Colebunders, R. Onchocerciasis-associated epilepsy: An update and future perspectives. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Angwafor, S.A.; Njamnshi, A.K.; Fraimow, H.; Sander, J.W. Zoonotic and vector-borne parasites and epilepsy in low-income and middle-income countries. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndts, K.; Kegele, J.; Massarani, A.S.; Ritter, M.; Wagner, T.; Pfarr, K.; Lämmer, C.; Dörmann, P.; Peisker, H.; Menche, D.; et al. Epilepsy and nodding syndrome in association with an Onchocerca volvulus infection drive distinct immune profile patterns. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterer, J.; Auer, H. Parasitoses of the human central nervous system. J. Helminthol. 2013, 87, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.Y. Paragonimiasis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 114, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabone, M.; Wiethase, J.; Clark, P.F.; Rollinson, D.; Cumberlidge, N.; Emery, A.M. Endemicity of Paragonimus and paragonimiasis in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and mapping reveals stability of transmission in endemic foci for a multi-host parasite system. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, D. Paragonimiasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1154, 105–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.-Y.; Jung, B.-K. General overview of the current status of human foodborne trematodiasis. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1262–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildner, T.E.; Cepon-Robins, T.J.; Urlacher, S.S. Cumulative host energetic costs of soil-transmitted helminth infection. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurscheid, J.; Laksono, B.; Park, M.J.; Clements, A.C.A.; Sadler, R.; McCarthy, J.S.; Nery, S.V.; Soares-Magalhaes, R.; Halton, K.; Hadisaputro, S.; et al. Epidemiology of soil-transmitted helminth infections in Semarang, Central Java, Indonesia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Gurwith, M. Europe’s neglected infections of poverty. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e611–e619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momčilović, S.; Cantacessi, C.; Arsić-Arsenijević, V.; Otranto, D.; Tasić-Otašević, S. Rapid diagnosis of parasitic diseases: Current scenario and future needs. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, E.E.; Caminade, C.; Thomas, B.N. Climate Change Contribution to the Emergence or Re-Emergence of Parasitic Diseases. Infect. Dis. Res. Treat. 2017, 10, 117863361773229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romig, T. Echinococcus multilocularis in Europe—State of the art. Vet. Res. Commun. 2009, 33 (Suppl. 1), 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Moreno, F.; Hernández, S.; López-Cobos, E.; Becerra, C.; Acosta, I.; Martínez-Moreno, A. Estimation of canine intestinal parasites in Córdoba (Spain) and their risk to public health. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 143, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tunali, V.; Korkmaz, M. Emerging and Re-Emerging Parasitic Infections of the Central Nervous System (CNS) in Europe. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2023, 15, 679-699. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr15060062
Tunali V, Korkmaz M. Emerging and Re-Emerging Parasitic Infections of the Central Nervous System (CNS) in Europe. Infectious Disease Reports. 2023; 15(6):679-699. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr15060062
Chicago/Turabian StyleTunali, Varol, and Metin Korkmaz. 2023. "Emerging and Re-Emerging Parasitic Infections of the Central Nervous System (CNS) in Europe" Infectious Disease Reports 15, no. 6: 679-699. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr15060062
APA StyleTunali, V., & Korkmaz, M. (2023). Emerging and Re-Emerging Parasitic Infections of the Central Nervous System (CNS) in Europe. Infectious Disease Reports, 15(6), 679-699. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr15060062






