A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
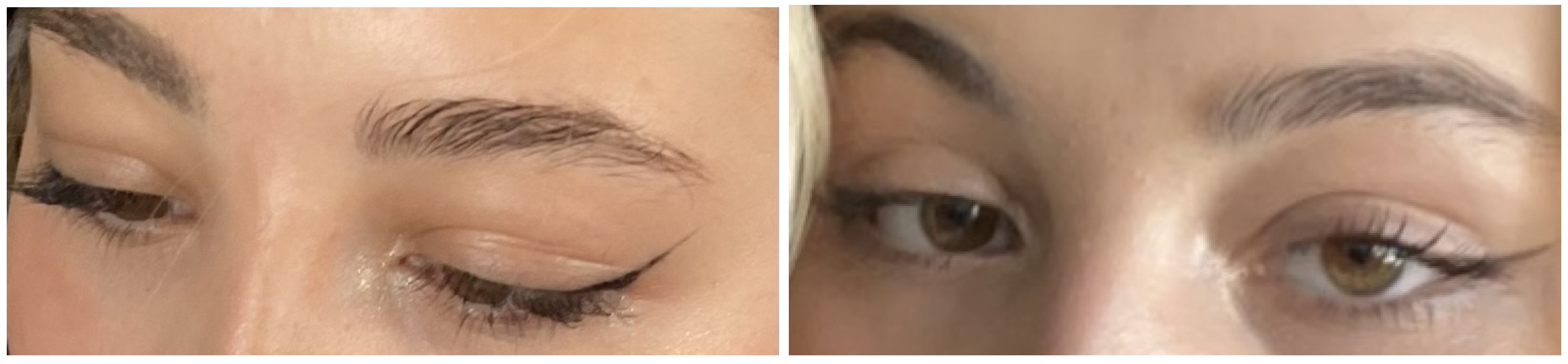
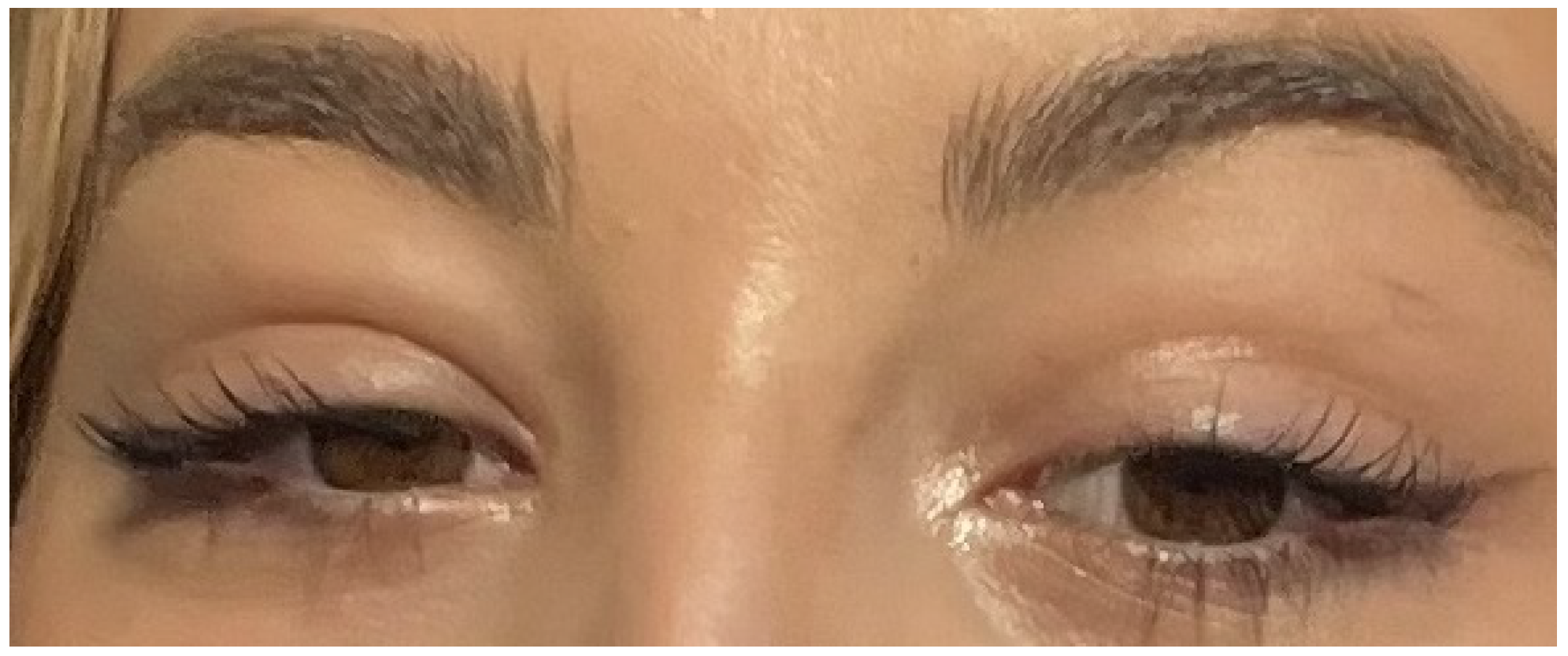
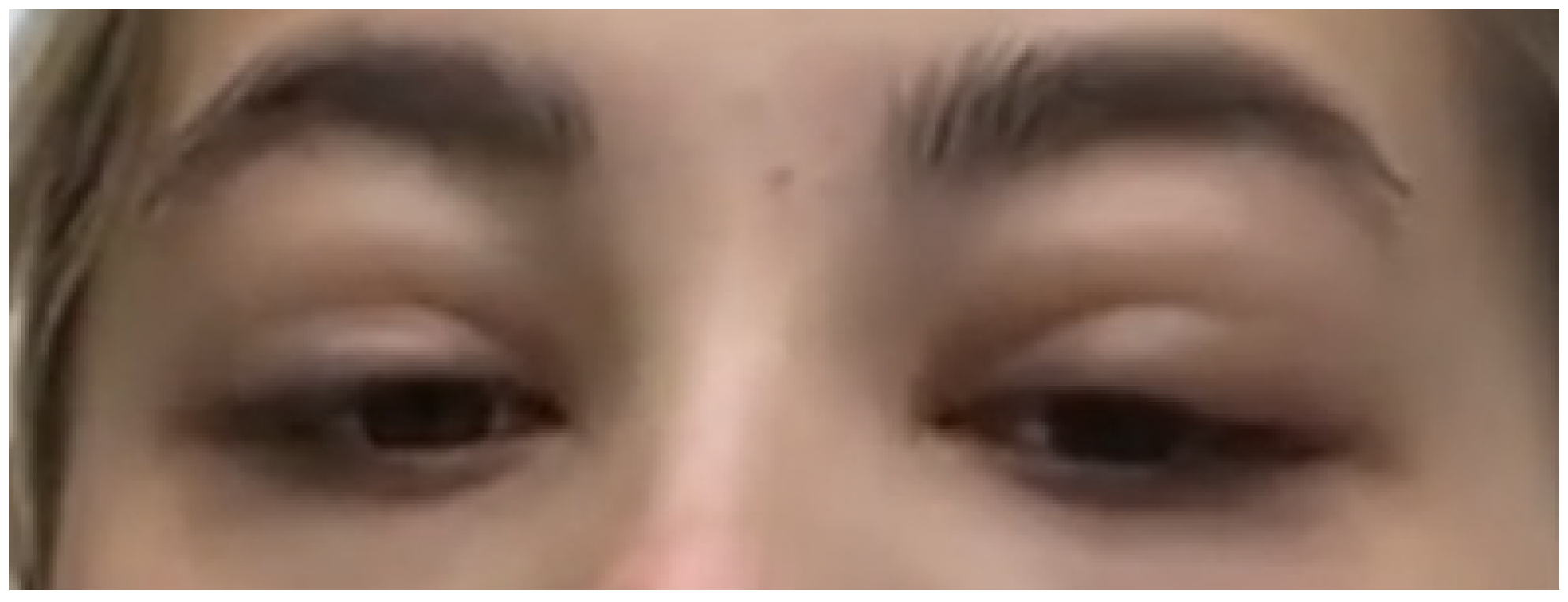
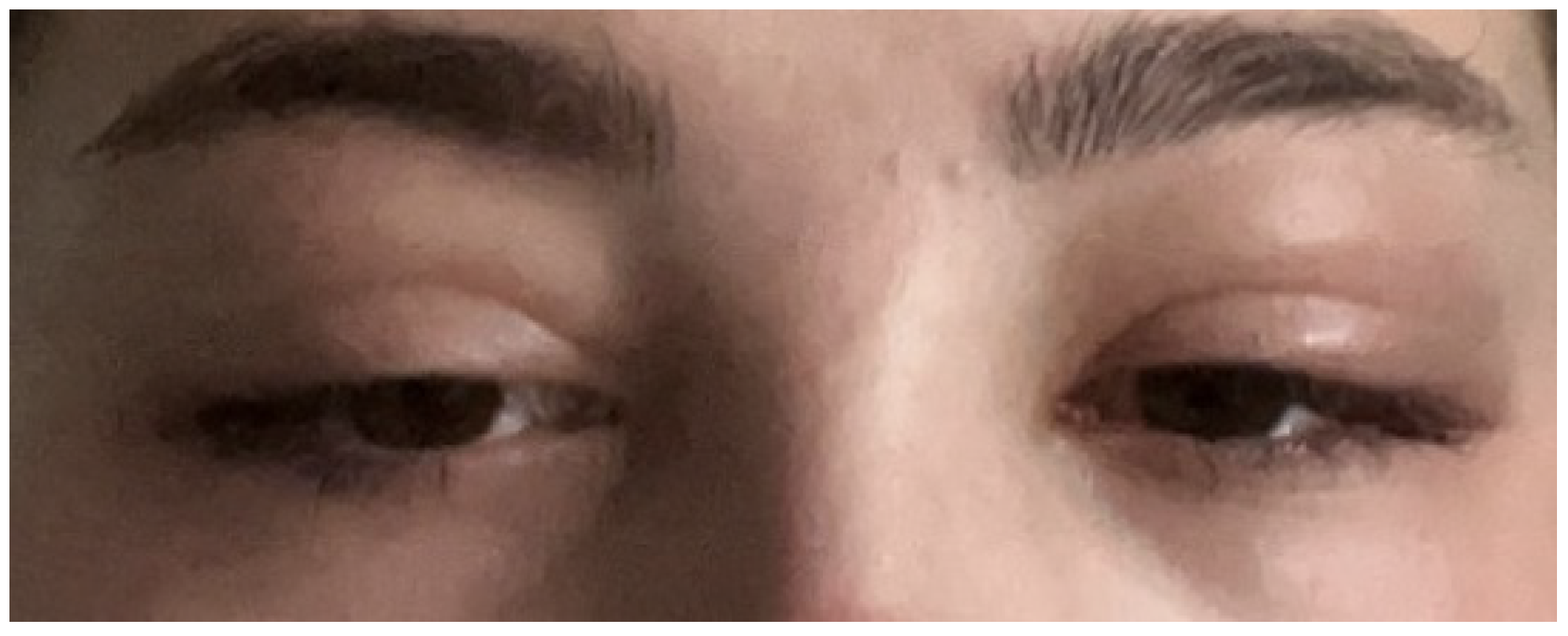
2. Case
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naughton, P.; Healy, M.; Enright, F.; Lucey, B. Infectious Mononucleosis: Diagnosis and clinical interpretation. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 78, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronz, G.; Zanetti, B.; Bianchetti, M. Bilateral upper eyelid swelling (Hoagland sign) in Epstein-Barr infectious mononucleosis: Prospective experience. Infection 2022, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louppides, S.; Kakoullis, L.; Parpas, G.; Panos, G. Upper eyelid oedema in a patient with pharyngitis/exudative tonsillitis and malaise: Hoagland sign in infectious mononucleosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e233719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, Y.; Kishida, M. Hoagland sign: Bilateral upper eyelid oedema. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e250857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Miyata, Y.; Maekawa, M. Infectious Mononucleosis with Eyelid Edema and Palatal Petechiae. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 36, 1027–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunmire, S.; Hogquist, K.; Balfour, H. Infectious Mononucleosis. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 390, 211–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland, R. Infectious mononucleosis. Am. J. Med. 1952, 13, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, M. Periorbital edema as the initial sign of infectious mononucleosis. J. Pediatr. 1954, 45, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süer, K.; Kaptanoglu, A. Association of Periorbital Edema and Fever in Acute Infectious Mononucleosis: A Case Report. Kafkas J. Med. Sci. 2013, 3, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Thurau, S.; Haritoglou, C. Beidseitige Oberlidschwellung bei Mononucleosis Infectiosa (Hoagland-Zeichen). Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 2005, 222, 1014–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburn, N.; Sullivan, T. Infectious Mononucleosis Presenting with Dacryoadenitis. Ophthalmology 1996, 103, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, S. Hoagland Sign: An early manifestation of acute infectious mononucleosis—A case report. Curr. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 21, 400–401. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hasselt, W.; Schreuder, R.; Houwerzijl, E. Periorbital oedema. Neth. J. Med. 2009, 67, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demonchy, E.; Pulcini, C. Three cases of primary EBV infection in young adults manifested by periorbital and eye-lid oedema. Infection 2008, 41, 1029–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.; Doerr, T.; Hengerer, A. Infectious Mononucleosis and Corticosteroids. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 131, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rafailidis, P.; Falagas, M. Fever and Periorbital Edema: A Review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2007, 52, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depetri, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Cugno, M. Angioedema and emergency medicine: From pathophysiology to diagnosis and treatment. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 59, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medović, R.; Igrutinović, Z.; Radojević-Marjanović, R.; Marković, S.; Rasković, Z.; Simović, A.; Tanasković-Nestorović, J.; Radovanović, M.; VuIetić, B. Clinical and laboratory differences between Epstein-Barr and cytomegalovirus infectious mononucleosis in children. Srpski Arhiv Celokupno Lekarstvo 2016, 144, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, R. Clinical presentation & management of glomerular diseases: Hematuria, nephritic & nephrotic syndrome. Mo Med. 2011, 108, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiala, M.; Heiner, D.; Turner, J.; Rosenbloom, B.; Guze, L. Infectious mononucleosis and mononucleosis syndromes. West J. Med. 1977, 126, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricardo, D. A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 942-945. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14060092
Ricardo D. A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus. Infectious Disease Reports. 2022; 14(6):942-945. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14060092
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicardo, Daryl. 2022. "A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus" Infectious Disease Reports 14, no. 6: 942-945. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14060092
APA StyleRicardo, D. (2022). A Protracted Course of Periorbital Oedema in Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Epstein–Barr Virus. Infectious Disease Reports, 14(6), 942-945. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr14060092





