Abstract
Transient CD4 lymphocytopenia is defined as the transitory presence of CD4+ T lymphocyte fewer than 300 cells/mm3 or less than 20% of T cells without HIV infection. It can occur due to multiple causes; however, it is rare for it to occur due to opportunistic infections. Few cases have been described in the literature where antimicrobial treatment normalizes the CD4 count, being more frequent in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. To date, this phenomenon has not been described in Cryptococcus neoformans infections. This would be the first reported case according to our knowledge, of a patient who normalizes CD4 count after antifungal treatment, later developing alveolar proteinosis due to M. Tuberculosis.
1. Introduction
The way the immune system responds to infections is still under continuous investigation since there are many features not yet understood. The current conception that opportunistic infections are the consequence of an immunosuppressive condition might not always be true, and occasionally infectious stimuli lead to transient immunosuppressive states, such as CD4 lymphocytopenia [1,2]. Transient CD4 lymphocytopenia was defined as the transitory presence of CD4+ T lymphocyte fewer than 300 cells/mm3 or less than 20% of T cells without HIV, this extrapolated from the 1992 CDC definition, without having a stipulated recovery time [1]. Transient CD4 lymphocytopenia associated with infectious conditions has been described previously, but so far not reported with Cryptococcus neoformans infections [2].
Alveolar proteinosis is a lung disease characterized by the accumulation of lipoproteinaceous material and dysregulation of macrophages in the alveoli. Any trigger that alters macrophage function can cause this condition, including genetic, autoimmune, toxic, infectious, and neoplastic causes. Macrophage dysfunction may also lead to a state of immunosuppression and a special susceptibility to pathogens whose elimination requires a strong innate immune response, such as M. tuberculosis [3]. Differentiating between the cause and the consequences of alveolar proteinosis could be challenging in the clinical scenario, and response to antimicrobial treatment could help to distinguish the initial trigger. The present would be among the first 15 cases to our knowledge describing the association between M. tuberculosis and alveolar proteinosis [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15].
2. Case Report
A 32-year-old man, farmer with exposure to pigeon’s droppings and barn hay, was admitted in November-2020 for progressive dyspnea and dry cough of 2 months of evolution, exacerbated a week before admission. He did not present fever, myalgias, anosmia, dysgeusia, headache, or another symptomatology. He had a medical history of meningeal cryptococcosis and CD4 lymphocytopenia (264 cells/mm3) diagnosed in 2019, managed with induction scheme (amphotericin b + flucytosine) and currently on maintenance scheme with fluconazole.
On physical examination he was, tachycardic, tachypneic, febrile, hypoxemic, with decreased intensity of lung sounds on both sides and requiring use of accessory breathing muscles. As the only additional finding, primary gaze was deconjugated with bilateral exophoria and limitation for adduction of both eyes, findings related to the sequelae of previous meningeal cryptococcosis. Laboratories on admission presented normal cell lines, severe hypoxemia, CD4 lymphocyte count of 349 cells/mm3, and no other organic compromise. Tomographic findings are shown in Figure 1.
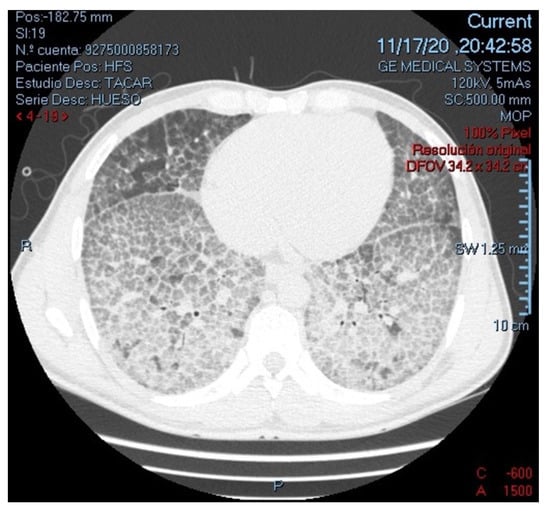
Figure 1.
High-resolution computed tomography of the chest (parenchymal view), showing multiple ground-glass opacities with thickening of interlobular septae, configuring an extensive characteristic “Crazy-paving” pattern in both lungs.
Based on clinical and radiological pattern, the initial diagnostic impression was pneumonia by common microorganisms, SARS-CoV-2 or Pneumocystis jirovecii; and treatment was started with Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole, Dexamethasone, and Cefepime. The patient presented a torpid evolution, respiratory deterioration progressing to acute respiratory distress syndrome, and required invasive mechanical ventilation.
Initial microbiologic studies are shown in Table 1. All of them were negative except for a positive latex cryptococcal antigen agglutination test in peripheral blood. It has been documented that this antigenic test could present cross-reactivity false-positives in other infections by microorganisms, such as non-neoformans Cryptococcus, Trichosporon spp., and Capnocytophaga canimorsus; and in non-infectious conditions, such as rheumatoid factor positivity [15,16]. Nonetheless, the previous meningeal infection was well-documented with cerebrospinal fluid culture confirmation, basal ganglia hyperintense lesions, and high cerebrospinal fluid opening pressure; so the probability of a true-positive is highly likely. The HIV status of the patient was also confirmed negative in three separate occasions, using two 4-generation tests (ELISA) and a viral load.

Table 1.
Microbiologic studies.
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy was performed, with an only positive finding of abundant hyaline secretion without endobronchial lesions. Bronchoalveolar lavage revealed a positive molecular test for M. tuberculosis (MBT) and abundant mesothelial cells of reactive appearance, histiocytes, and lymphocytes. Biopsy of the right lower lobe was performed which revealed changes suggestive of alveolar proteinosis; however, due to an insufficient sample, the patient underwent wedge lung biopsy confirming the diagnosis (Figure 2).
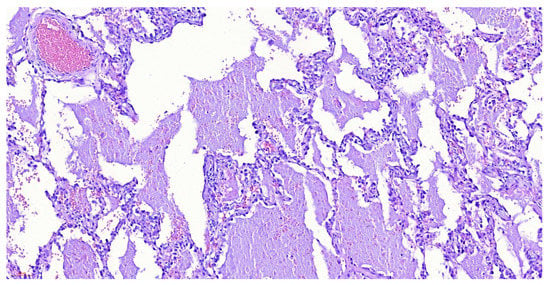
Figure 2.
Wedge lung biopsy with hematoxylin-eosin stain, demonstrating pulmonary parenchyma with emphysematous and reactive epithelial changes, pneumocyte hyperplasia, and dilated alveoli occupied by eosinophilic material, with a low-grade hemorrhage and occasional histiocytes and anthracosis. Negative for malignancy, changes related to alveolar proteinosis.
After ruling out viral disease, common bacteria, and other opportunistic microorganisms, antibiotic treatment was suspended and Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol, and Pyrazinamide (HRZE) were started. Regarding the alveolar proteinosis, he was taken to whole lung lavage twice, with a progressive resolution of respiratory symptoms. Hematologic and autoimmune causes were ruled out due to reports of normal bone marrow studies, absence of connective tissue disease manifestations and a negative immune profile, respectively. Unfortunately, we did not measure anti-granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factor antibodies (anti-GM-CSF) to diagnose idiopathic pulmonary proteinosis, so considering the adequate response to management with HRZE, successful extubation, and resolution of respiratory distress in two weeks, we considered MBT as the trigger for alveolar proteinosis. The patient reported a progressive decrease on shortness of breath, and a significant improvement on quality of life. He continues using supplementary oxygen to date.
3. Discussion
Some opportunistic infections cause transient CD4+ lymphocytopenia, and their treatment has been related to immune recovery. This transient phenomenon has been described in infections associated with an immune-response mainly mediated by T lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytic cells, especially with the CD4+ subset of lymphocytes [17,18]. However, this immune response also requires a cytokine release network activation. In acute infection, levels of Interleukin-1β (IL-1B), soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-a) increase [1]. It is hypothesized that this activation conversely reduces the CD4+ count, and increases the CD8+ count, reducing the CD4+/CD8+ ratio. Proper treatment directly modulates the cytokine network activation, restoring the CD4+/CD8+ population ratio and normalizing the CD4+ count. The role of cytokine response as a regulator of T-cell differentiation under these circumstances is not yet fully understood, but these events may have clinical implications as transient immunosuppressive periods [3].
Kony et al. [17] report that up to 14% of patients with tuberculosis, HIV-negative, and no other immunosuppressive conditions have CD4 counts below 300 cells/mm3. Luo et al. [18], demonstrated that treatment directed at this population was associated with an increase in CD4+ lymphocyte count, as well as a decrease in levels of IL-1B, sIL-2R, IL-6 and TNF-a. Similarly, cryptococcal infection has been consistently correlated with CD4+ lymphocytopenia; however, to date, treatment of cryptococcosis has not been reported to improve lymphocyte counts.
Another relevant aspect is the finding of alveolar proteinosis, which cannot be confirmed as idiopathic or secondary due to absence of anti-GM-CSF measurement tests. In most cases, infection by MBT is favored by the structural and immunological changes observed in alveolar proteinosis (mainly macrophage dysfunction) [19]. However, it has also been proposed that alveolar proteinosis is the consequence of infections by microorganisms, including MBT infection, which pathophysiologically can be explained by the stimulation of type II pneumocytes by the mycobacteria, increasing the secretion of pulmonary surfactant and favoring the development of proteinosis [19]. Similarly, it has been described that a decrease in GM-CSF correlates with a higher risk of developing tuberculosis. Alveolar proteinosis could be associated with other infectious conditions, such as cryptococcal post-infectious inflammatory response syndrome (PIIRS) [20], or infections due to Nocardia spp., Pneumocystis spp., Acinetobacter spp., Aspergillus spp., and Cladosporium spp. [8]. However, PIIRS usually presents at the induction or consolidation phases of cryptococcal management and requires corticosteroid treatment for improvement [20]. Other microbiological studies were negative with no evidence of microorganisms other than MBT, and, after antituberculous treatment, the patient presented rapid clinical improvement with progressive resolution of alveolar proteinosis. Other non-infectious conditions that could present with a similar radiological pattern include sarcoidosis, non-specific interstitial pneumonia and diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome has been described to cause interstitial infiltrates along with other features such as bilateral nodules or pleural effusion [21]. All of these non-infectious differential diagnoses were ruled out after laboratory results and histopathologic studies.
The present case would be among the few cases reported since 1979 to date [13], in which alveolar proteinosis is described because of MBT infection. Literature describes two patterns: The first in which MBT infection is documented before the diagnosis of alveolar proteinosis with a negative report of anti-GM-CSF; and the second in which the measurement of anti-GM-CSF is not available, but antituberculous treatment leads to a decrease in proteinosis and favorable clinical outcomes [3,4,5,6,7,9,10,11,13,14]. Our case belongs to the second pattern of presentation; however, to our knowledge it would be the first case reporting alveolar proteinosis secondary to M. tuberculosis in a patient with transient CD4 lymphocytopenia and cryptococcosis.
4. Conclusions
This case is relevant to the literature, demonstrating how cryptococcosis treatment is related to an increase in lymphocyte count. Likewise, this immune reconstitution and a concomitant infection by M. tuberculosis could aid the development of alveolar proteinosis, with a favorable resolution after antituberculous treatment.
Author Contributions
D.A.M.A. and D.A.C.-D. contributed to study design, data collection, data analysis and writing; M.A.P.-H. and N.M.-A. contributed to study design and writing; M.Z.P., M.B.T. and C.M.C.V. contributed to data collection and data analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital Universitario de la Samaritana. Code 170220.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant information has been presented in the case report. Any additional data may be made available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| Anti-GM-CSF | Anti Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor antibodies |
| DRESS | Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| HRZE | Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| MBT | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PIIRS | Cryptococcal post infectious inflammatory response syndrome |
| RT PCR | Reverse Transcription - Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SARS-CoV2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
References
- Sattler, S. The Role of the Immune System Beyond the Fight Against Infection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1003, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.K.; Neal, J.J.; Holmberg, S.D. Unexplained opportunistic infections and CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia without HIV infection. An investigation of cases in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control Idiopathic CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia Task Force. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemskerk, D.; Caws, M. Pathogenesis-Tuberculosis in Adults and Children-NCBI Bookshelf 2015. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK344406/ (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- de Athayde, R.A.B.; Arimura, F.E.; Kairalla, R.A.; Carvalho, C.R.R.; Baldi, B.G. Characterization and outcomes of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in Brazil: A case series. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2018, 44, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekgül, S.; Bilaceroglu, S.; Ozkaya, S.; Coskun, A.; Komurcuoglu, B.; Cirak, A.K. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis and superinfection with pulmonary tuberculosis in a case. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2012, 5, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruben, F.L.; Talamo, T.S. Secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis occurring in two patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am. J. Med. 1986, 80, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Silva, J.L.; Marinho, M.M.; Veloso, T.V.; Coelho, J.C. Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis and tuberculosis in a diabetic patient: A rare or a seldom diagnosed association. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 6, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Tian, X.; Feng, R.; Guo, X.; Wang, P.; Situ, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, K.-F. Secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: A single-center retrospective study (a case series and literature review). BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, H.; Tazawa, R.; Kaneko, C.; Saraya, T.; Inoue, Y.; Hamano, E.; Kogure, Y.; Tomii, K.; Terada, M.; Takada, T.; et al. Clinical features of secondary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: Pre-mortem cases in Japan. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, A.; Parsa, T.; Naghan, P.A.; Dutau, H.; Razavi, F.; Farzanegan, B.; Tootkaboni, M.P.; Abedini, A. An eleven-year retrospective cross-sectional study on pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Adv. Respir. Med. 2018, 86, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baro, A.; Shah, I.; Chandane, P.; Khosla, I. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in a 10-year-old girl masquerading as tuberculosis. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2015, 2015, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Witty, L.A.; Tapson, V.F.; Piantadosi, C.A. Isolation of mycobacteria in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Medicine 1994, 73, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, J.M.; Putong, P.B. Association of pulmonary alveolar lipoproteinosis with mycobacterial infection. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1980, 74, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lathan, S.R.; Williams, J.D.; McLean, R.L.; Ramirez, J. Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: Treatment of a Case Complicated by Tuberculosis. Chest 1971, 59, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mayoralas Alises, S.; Gómez Carrera, L.; Díaz Lobato, S. Proteinosis alveolar o la importancia de identificar infecciones sobreañadidas. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2003, 39, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Umeda, Y.; Makimura, K. Cross-reactivity in Cryptococcus antigen latex agglutination test in two commercial kits. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kony, S.J.; Hane, A.A.; Larouzé, B.; Samb, A.; Cissoko, S.; Sow, P.S.; Sané, M.; Maynart, M.; Diouf, G.; Murray, J.; et al. Tuberculosis-associated severe CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia in HIV-seronegative patients from Dakar. SIDAK Research Group. J. Infect. 2000, 41, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Wu, F.; Ma, J.; Xiao, H.; Cui, H. Immunological recovery in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis after intensive phase treatment. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 3539–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Abdelmalak, B.; Inoue, Y.; Culver, D.A. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in adults: Pathophysiology and clinical approach. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, P.R.; Jarvis, J.N.; Panackal, A.A.; Fisher, M.C.; Molloy, S.F.; Loyse, A.; Harrison, T. Cryptococcal meningitis: Epidemiology, immunology, diagnosis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taweesedt, P.T.; Nordstrom, C.W.; Stoeckel, J.; Dumic, I. Pulmonary manifestations of drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome: A systematic review. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7863815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).