Exploring Perianal Fistulas: Insights into Biochemical, Genetic, and Epigenetic Influences—A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
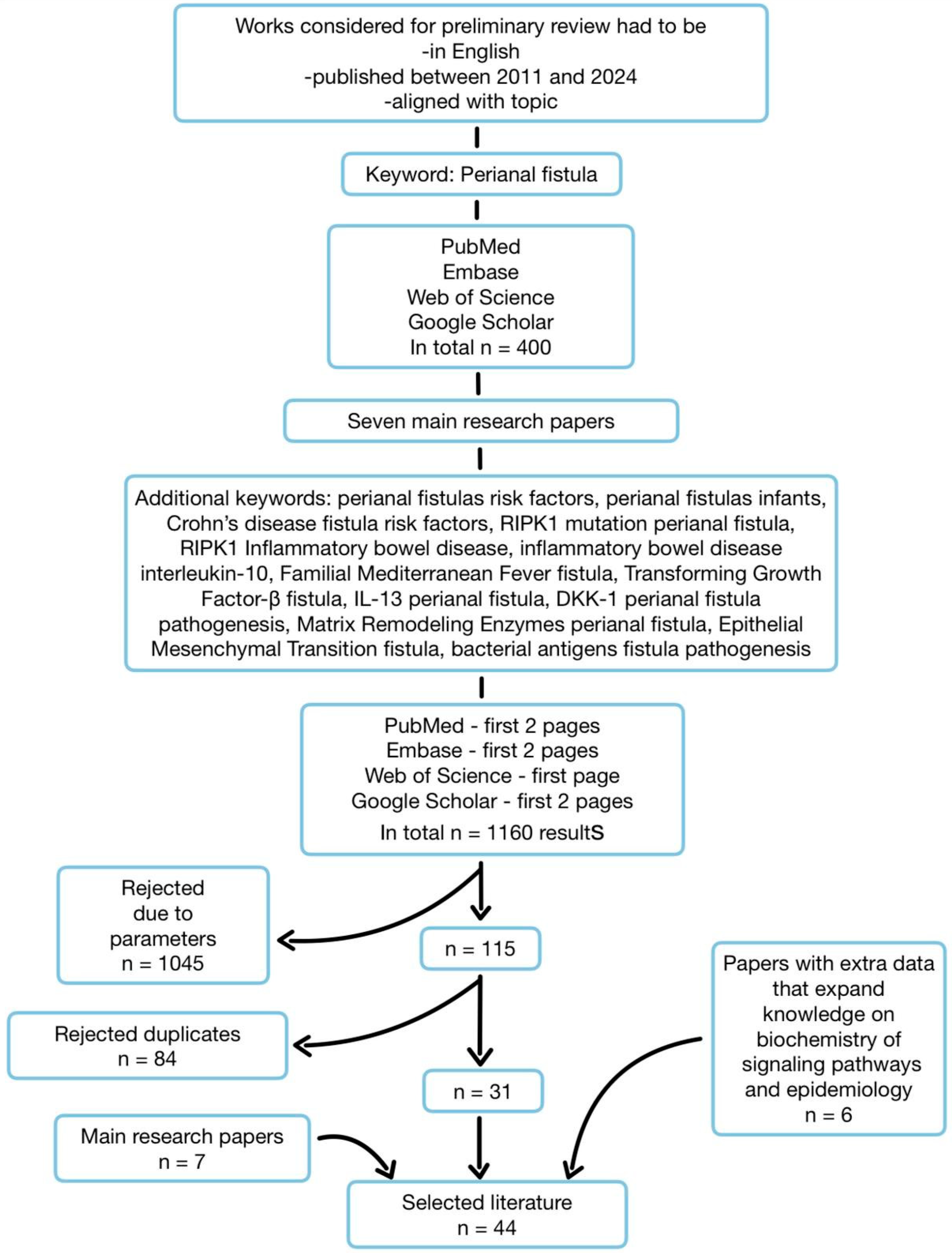
2. Methodology
3. Results
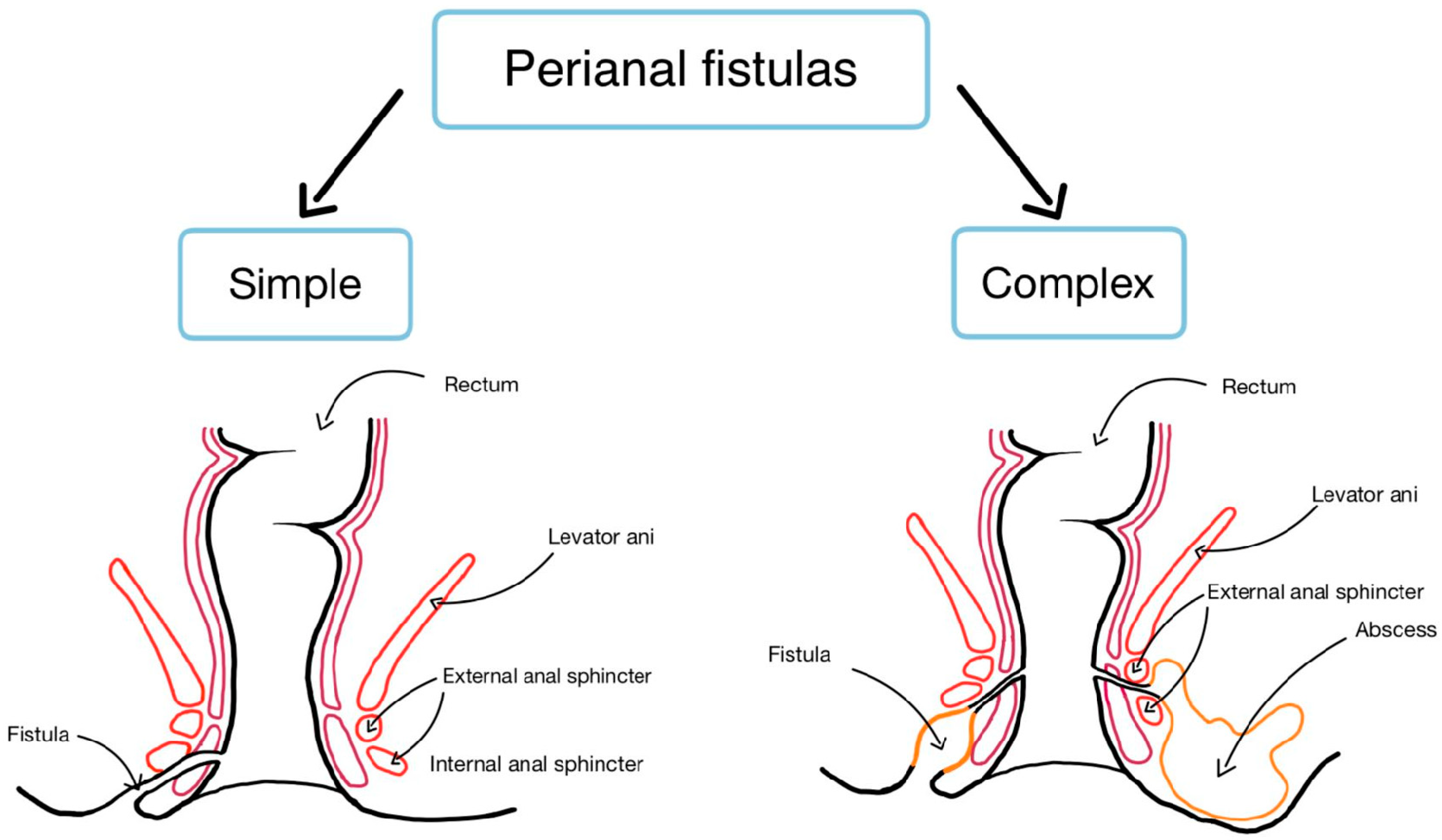
3.1. Risk Factors
3.2. Pathogenesis
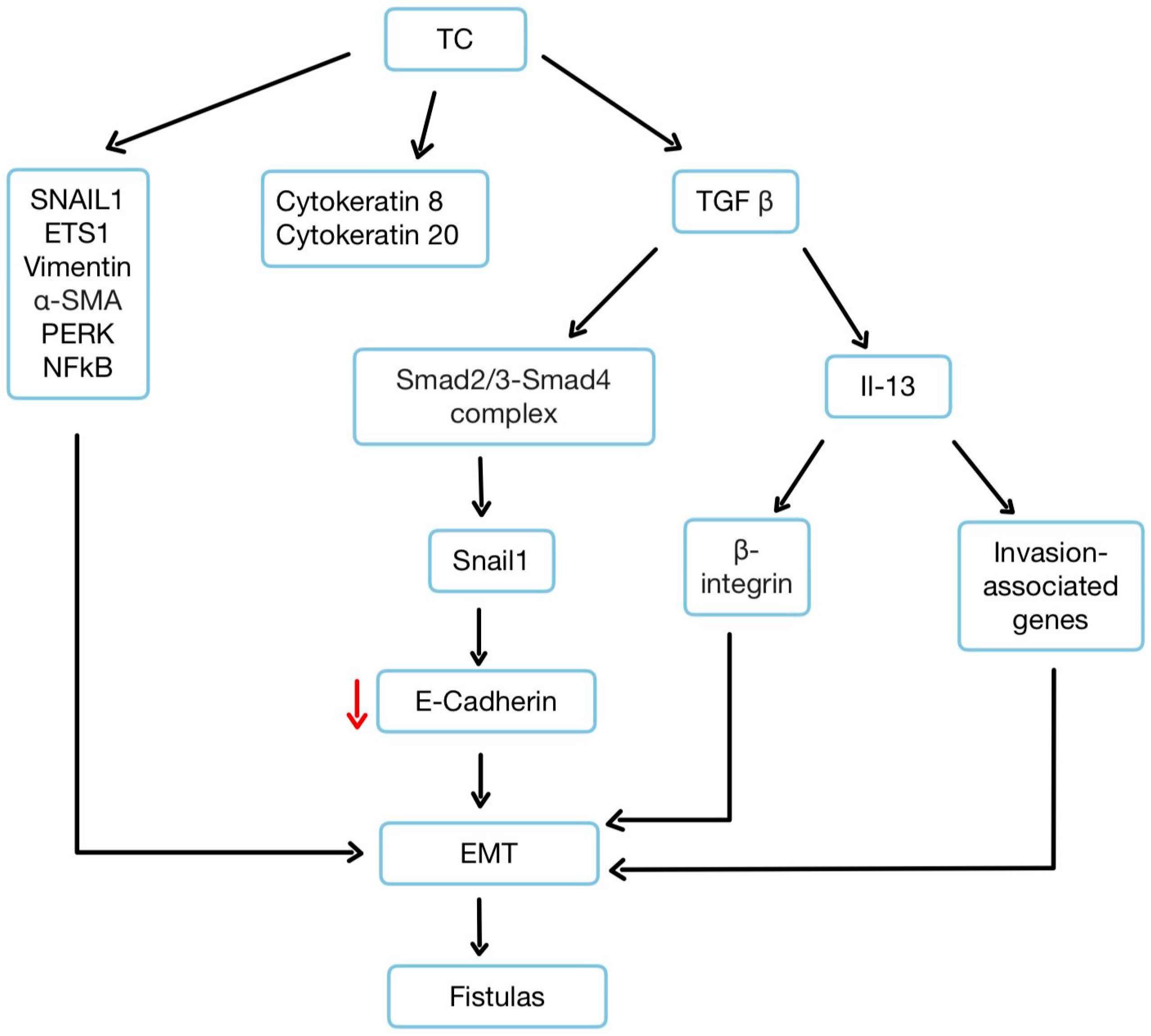
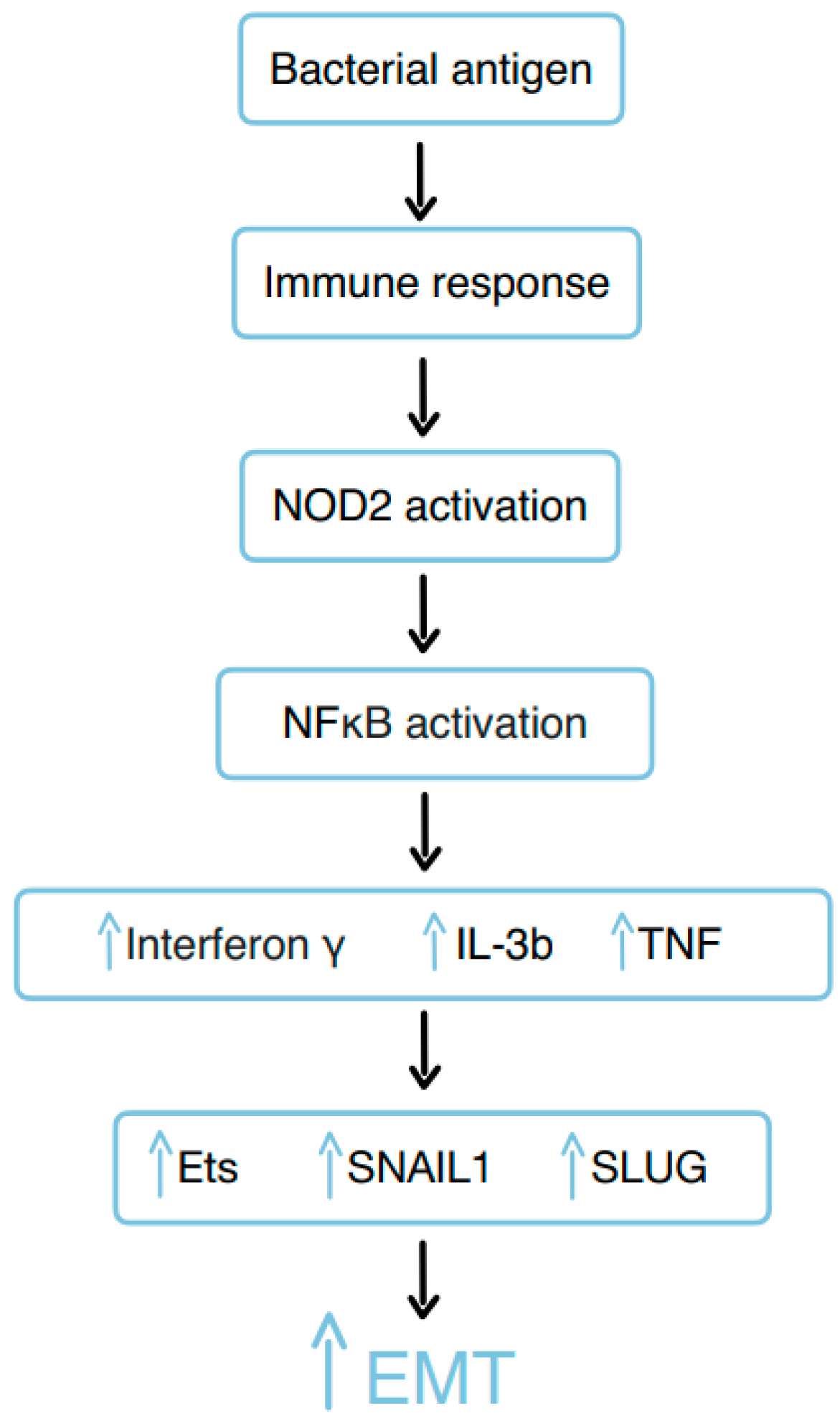
3.3. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition
3.4. The Role of RIPK1
3.5. The Significance of IL-10R
3.6. Mediterranean Fever Gene (MEFV)
| Reference and Number of Patients | Mutated Protein | Affected Mechanism | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sultan et al., 2022 [25]—14 people with the mutation, 12 of them with PAs or fistulas | RIPK1 | Inflammasome activation—increased secretion of IL-1β and IL-18, decreased production of IL-6 | Development of fistulas through severe intestinal inflammation and tissue damage in perianal region |
| Glocker et al., 2009 [32]—4 Hung et al., 2021 [31]—1 Kotlarz et al., 2012b [33]—10 Pigneur et al., 2013b [34]—16 n = 31 | IL-10R | Suppression of IL-6 secretion in response to LPS/IL-10, increased levels of TNF-α and other pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and IL-1 | Excessive inflammation of intestinal tract |
| Asakura et al., 2018 [35]—1 Baran et al., 2018 [36]—1 Fidder et al., 2005 [39]—18 n = 20 | MEFV | Reduced amounts of pyrin produced or production of malformed pyrin protein | Inappropriate or prolonged inflammatory response |
3.7. The Role of TGF-β, TNF-α, and IL-13
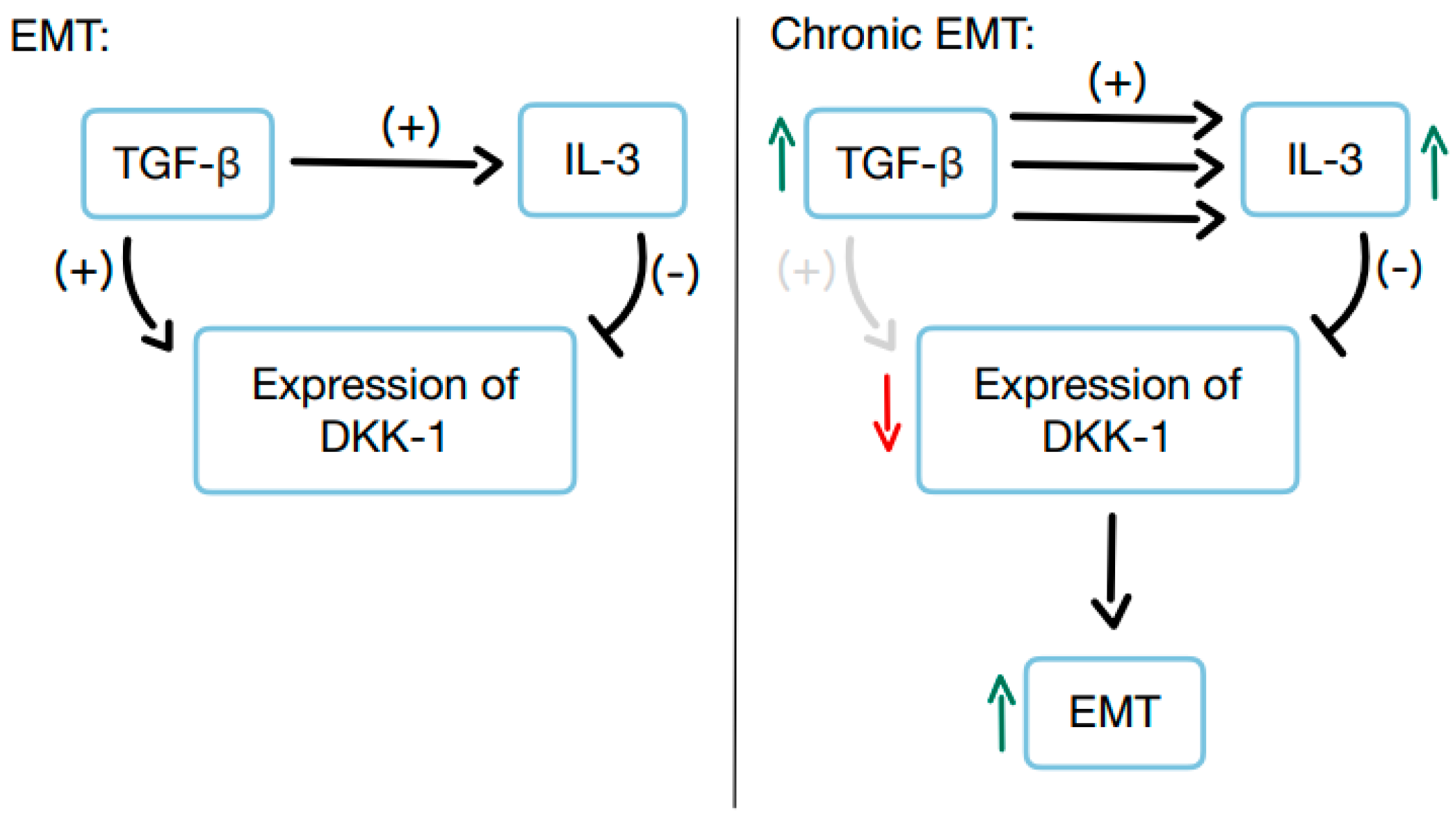
3.8. The Significance of DKK-1
3.9. Matrix Remodeling Enzymes
3.10. Bacterial Remnants
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gold, S.L.; Cohen-Mekelburg, S.; Schneider, Y.; Steinlauf, A. Perianal Fistulas in Patients with Crohn’s Disease, Part 1: Current Medical Management. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 14, 470. [Google Scholar]
- Scharl, M.; Weber, A.; Fürst, A.; Farkas, S.; Jehle, E.; Pesch, T.; Kellermeier, S.; Fried, M.; Rogler, G. Potential role for SNAIL family transcription factors in the etiology of Crohn’s disease-associated fistulae. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, A.; Yanai, H.; Girardi, P.; Milicevic, S.; Carvello, M.; Maroli, A.; Avedano, L. The Impact of Crohn’s Perianal Fistula on Quality of Life: Results of an International Patient Survey. Crohns Colitis 2023, 5, otad036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Włodarczyk, M.; Włodarczyk, J.; Sobolewska-Włodarczyk, A.; Trzciński, R.; Dziki, Ł.; Fichna, J. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of cryptoglandular perianal fistula. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 300060520986669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottingham, J.M.; Rentea, R.M. Anal Fistulotomy; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- American Gastroenterological Association Clinical Practice Committee. American gastroenterological association medical position statement: Perianal Crohn′s disease. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Panés, J.; Rimola, J. Perianal fistulizing Crohn’s disease: Pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ouboter, L.F.; Peeters, K.C.M.J.; Hawinkels, L.J.A.C.; Holman, F.; Pascutti, M.F.; Barnhoorn, M.C.; Jong, A.E.v.d.M.-D. Crohn’s Disease-Associated and Cryptoglandular Fistulas: Differences and Similarities. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, G.C.; Lee, M.J.; Hind, D.; Brown, S.R. Prognostic factors affecting outcomes in fistulating perianal Crohn’s disease: A systematic review. Tech. Coloproctol. 2017, 21, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Jin, T.; Wu, G.; Shan, B.; Christofferson, D.E.; Qi, C.; Yu, Q.; et al. Death-domain dimerization-mediated activation of RIPK1 controls necroptosis and RIPK1-dependent apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2001–E2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Budi, E.H. Specificity, versatility, and control of TGF-β family signaling. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaav5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notani, D.; Gottimukkala, K.P.; Jayani, R.S.; Limaye, A.S.; Damle, M.V.; Mehta, S.; Purbey, P.K.; Joseph, J.; Galande, S. Global regulator SATB1 recruits β-catenin and regulates TH2 differentiation in Wnt-dependent manner. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, R.C.; Bellovin, D.I.; Brown, C.; Maynard, E.; Wu, B.; Kawakatsu, H.; Sheppard, D.; Oettgen, P.; Mercurio, A.M. Transcriptional activation of integrin β6 during the epithelial-mesenchymal transition defines a novel prognostic indicator of aggressive colon carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.R.; Keller, D.S. Perianal Fistulas. Dis. Colon Rectum 2020, 63, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Epidemiology and risk factors for IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsamis, N.; Kosmidis, C.; Chatzimavroudis, G.; Sapalidis, K.; Efthymiadis, C.; Kiouti, F.A.; Ioannidis, A.; Arnaoutoglou, C.; Zarogoulidis, P.; Kesisoglou, I. Perianal fistulas: A review with emphasis on preoperative imaging. Adv. Med. Sci. 2022, 67, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festen, C.; Van Hat-Ten, H. Perianal Abscess and Fistula-in-An0 in Infants. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1998, 33, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosemann, J.H.; Lacher, M. Perianal Abscesses and Fistulas in Infants and Children. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 30, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, C.; Festa, V.; Fagnani, C.; Stazi, A.; Antonelli, G.; Moretti, A.; Koch, M.; Capurso, L. Evolution of clinical behaviour in Crohn’s disease: Predictive factors of penetrating complications. Dig. Liver Dis. 2005, 37, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditrich, F.; Blümel, S.; Biedermann, L.; Fournier, N.; Rossel, J.-B.; Ellinghaus, D.; Franke, A.; Stange, E.F.; Rogler, G.; Scharl, M.; et al. Genetic risk factors predict disease progression in Crohn’s disease patients of the Swiss inflammatory bowel disease cohort. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820959252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, S.M.; Pesch, T.; Lang, S.; Weber, A.; Jehle, E.; Vavricka, S.R.; Fried, M.; Rogler, G.; Scharl, M. A Role for Tumor Necrosis Factor and Bacterial Antigens in the Pathogenesis of Crohn’s Disease–Associated Fistulae. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, S.M.; Hemsley, C.; Pesch, T.; Lang, S.; Weber, A.; Jehle, E.; Rühl, A.; Fried, M.; Rogler, G.; Scharl, M. The Role for Dickkopf-Homolog-1 in the Pathogenesis of Crohn’s Disease-Associated Fistulae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharl, M.; Frei, S.; Pesch, T.; Kellermeier, S.; Arikkat, J.; Frei, P.; Fried, M.; Weber, A.; Jehle, E.; Rühl, A.; et al. Interleukin-13 and transforming growth factor β synergise in the pathogenesis of human intestinal fistulae. Gut 2013, 62, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, M.; Adawi, M.; Kol, N.; McCourt, B.; Adawi, I.; Baram, L.; Tal, N.; Werner, L.; Lev, A.; Snapper, S.B.; et al. RIPK1 mutations causing infantile-onset IBD with inflammatory and fistulizing features. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1041315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Führer, M.; Bahrami, E.; Socha, P.; Klaudel-Dreszler, M.; Bouzidi, A.; Liu, Y.; Lehle, A.S.; Magg, T.; Hollizeck, S.; et al. Human RIPK1 deficiency causes combined immunodeficiency and inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Ying, W.; Wang, W.; Sun, B.; Sun, J.; Wang, X. Clinical phenotype of a Chinese patient with RIPK1 deficiency due to novel mutation. Genes Dis. 2020, 7, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuchet-Lourenço, D.; Eletto, D.; Wu, C.; Plagnol, V.; Papapietro, O.; Curtis, J.; Nejentsev, S. Biallelic RIPK1 mutations in humans cause severe immunodeficiency, arthritis, and intestinal inflammation. Science 2018, 361, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, Y.; A Kim, C.; Pastorino, A.C.; Ceroni, J.; Lima, P.P.; Dorna, M.d.B.; Honjo, R.S.; Bertola, D.; Hamanaka, K.; Fujita, A.; et al. Primary immunodeficiency with chronic enteropathy and developmental delay in a boy arising from a novel homozygous RIPK1 variant. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.H.; Lee, H.C.; Yeung, C.Y.; Wang, N.L.; Tang, T.Y.; Winter, H.S.; Jiang, C.B. Importance of early detection of infantile inflammatory bowel disease with defective IL-10 pathway: A case report. Medicine 2021, 100, E25868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glocker, E.-O.; Kotlarz, D.; Boztug, K.; Gertz, E.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Noyan, F.; Perro, M.; Diestelhorst, J.; Allroth, A.; Murugan, D.; et al. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Mutations Affecting the Interleukin-10 Receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlarz, D.; Beier, R.; Murugan, D.; Diestelhorst, J.; Jensen, O.; Boztug, K.; Pfeifer, D.; Kreipe, H.; Pfister, E.; Baumann, U.; et al. Loss of interleukin-10 signaling and infantile inflammatory bowel disease: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigneur, B.; Escher, J.; Elawad, M.; Lima, R.; Buderus, S.; Kierkus, J.; Guariso, G.; Canioni, D.; Lambot, K.; Talbotec, C.; et al. Phenotypic characterization of very early-onset IBD due to mutations in the IL10, IL10 receptor alpha or beta gene: A survey of the GENIUS working group. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 2820–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakura, K.; Yanai, S.; Nakamura, S.; Kawaski, K.; Eizuka, M.; Ishida, K.; Endo, M.; Sugai, T.; Migita, K.; Matsumoto, T. Familial Mediterranean fever mimicking Crohn disease. Medicine 2018, 97, e9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.; Çağan Appak, Y.; Garipcin, P.; Demirçelik, Y.; Pala, E.E.; Özyilmaz, B.; Karakoyun, M.; Ergün, O. The role of familial mediterranean fever gene mutation in treatment of infantile colitis with resistant perianal fistula. Arch. Rheumatol. 2018, 33, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, A.; Akyüz, F.; Göktürk, S.; Evirgen, S.; Akyüz, U.; Örmeci, A.; Soyer, Ö.; Karaca, C.; Demir, K.; Gundogdu, G.; et al. Small bowel mucosal damage in familial Mediterranean fever: Results of capsule endoscopy screening. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beser, O.F.; Cokugras, F.C.; Kutlu, T.; Erginoz, E.; Gulcu, D.; Kasapcopur, O.; Erkan, T. Association of familial mediterranean fever in Turkish children with inflammatory bowel disease. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2014, 49, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidder, H.; Chowers, Y.; Ackerman, Z.; Pollak, R.D.; Crusius, J.B.A.; Livneh, A.; Bar-Meir, S.; Avidan, B.; Shinhar, Y. The familial Mediterranean fever (MEVF) gene as a modifier of Crohn’s disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-M.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, E.-H. The Molecular Mechanism of Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling for Intestinal Fibrosis: A Mini-Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Rubbino, F.; Elangovan, S.; Sammarco, G.; Lovisa, S.; Restelli, S.; Chavez, S.E.P.; Massimino, L.; Lamparelli, L.; Paulis, M.; et al. Dysfunctional Extracellular Matrix Remodeling Supports Perianal Fistulizing Crohn′s Disease by a Mechanoregulated Activation of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 741–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharl, M.; Rogler, G. Pathophysiology of fistula formation in Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2014, 5, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taxonera, C.; Schwartz, D.A.; García-Olmo, D. Emerging treatments for complex perianal fistula in Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 4263–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groof, E.J.; Sahami, S.; Lucas, C.; Ponsioen, C.Y.; Bemelman, W.A.; Buskens, C.J. Treatment of perianal fistula in Crohn’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing seton drainage and anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment. Color. Dis. 2016, 18, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Mutation | Effect |
|---|---|
| ZMIZ1 (Zinc Finger MIZ-Type Containing 1) | ZMIZ1 is associated with transcription regulation and interaction with other transcription factors. SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) in this gene may affect its function, which could have implications for inflammatory and immune processes related to CD. |
| LOC105373831 | LOC105373831 is a gene with a less well-known function, that is considered a region susceptible to genetic changes associated with IBD. SNPs in this locus may influence the expression of nearby genes or the functioning of signaling pathways. |
| KSR1 (Kinase Suppressor of Ras 1) | KSR1 is involved in the Ras/MAPK signaling pathways, which regulate cell growth and inflammatory responses. SNPs in KSR1 may alter its function, potentially affecting inflammatory mechanisms related to CD. |
| TNFSF15 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily Member 15) | TNFSF15, also known as TL1A, is an inflammatory factor that plays a role in regulating immune and inflammatory responses. SNPs in this gene can affect its level or function, potentially leading to increased inflammation and progression of CD. |
| CEBPB-PTPN1 (CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein Beta–Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Non-Receptor Type 1) | CEBPB is a transcription factor that regulates inflammatory response, and PTPN1 is a phosphatase protein that can modulate inflammatory signaling. SNPs in this region may affect the expression or function of these genes, which could impact the development and progression of CD. |
| Reference | Protein | Role of Protein in Fistula Formation | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| M. Scharl et al., 2013 [24] | TGF-β | Reduces level of E-Cadherin, induces IL-13 expression | Promotes EMT |
| S.M. Frei et al., 2013 [22] | TNF-α | Stimulates production of TGF-β | Promotes EMT |
| M. Scharl et al., 2013 [24] | IL-13 | Increases expression of β6-integrin and transcription factor SLUG | Triggers expression of genes involved in cell invasion, leading to formation of fistulas |
| S.M. Frei et al., 2013 [22] | DKK-1 | Antagonist of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, mediator of inflammation | Inhibits TGF-β/Wnt signaling, but also helps to activate IL-13, which promotes cell invasion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawecki, M.P.; Kruk, A.M.; Drążyk, M.; Domagała, Z.; Woźniak, S. Exploring Perianal Fistulas: Insights into Biochemical, Genetic, and Epigenetic Influences—A Comprehensive Review. Gastroenterol. Insights 2025, 16, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent16010010
Kawecki MP, Kruk AM, Drążyk M, Domagała Z, Woźniak S. Exploring Perianal Fistulas: Insights into Biochemical, Genetic, and Epigenetic Influences—A Comprehensive Review. Gastroenterology Insights. 2025; 16(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent16010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawecki, Maciej Przemysław, Agnieszka Marianna Kruk, Mateusz Drążyk, Zygmunt Domagała, and Sławomir Woźniak. 2025. "Exploring Perianal Fistulas: Insights into Biochemical, Genetic, and Epigenetic Influences—A Comprehensive Review" Gastroenterology Insights 16, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent16010010
APA StyleKawecki, M. P., Kruk, A. M., Drążyk, M., Domagała, Z., & Woźniak, S. (2025). Exploring Perianal Fistulas: Insights into Biochemical, Genetic, and Epigenetic Influences—A Comprehensive Review. Gastroenterology Insights, 16(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent16010010







