First Therapeutic Approval for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Definition and Symptoms
1.2. Pathogenesis
1.3. Prevalence
1.4. Complications
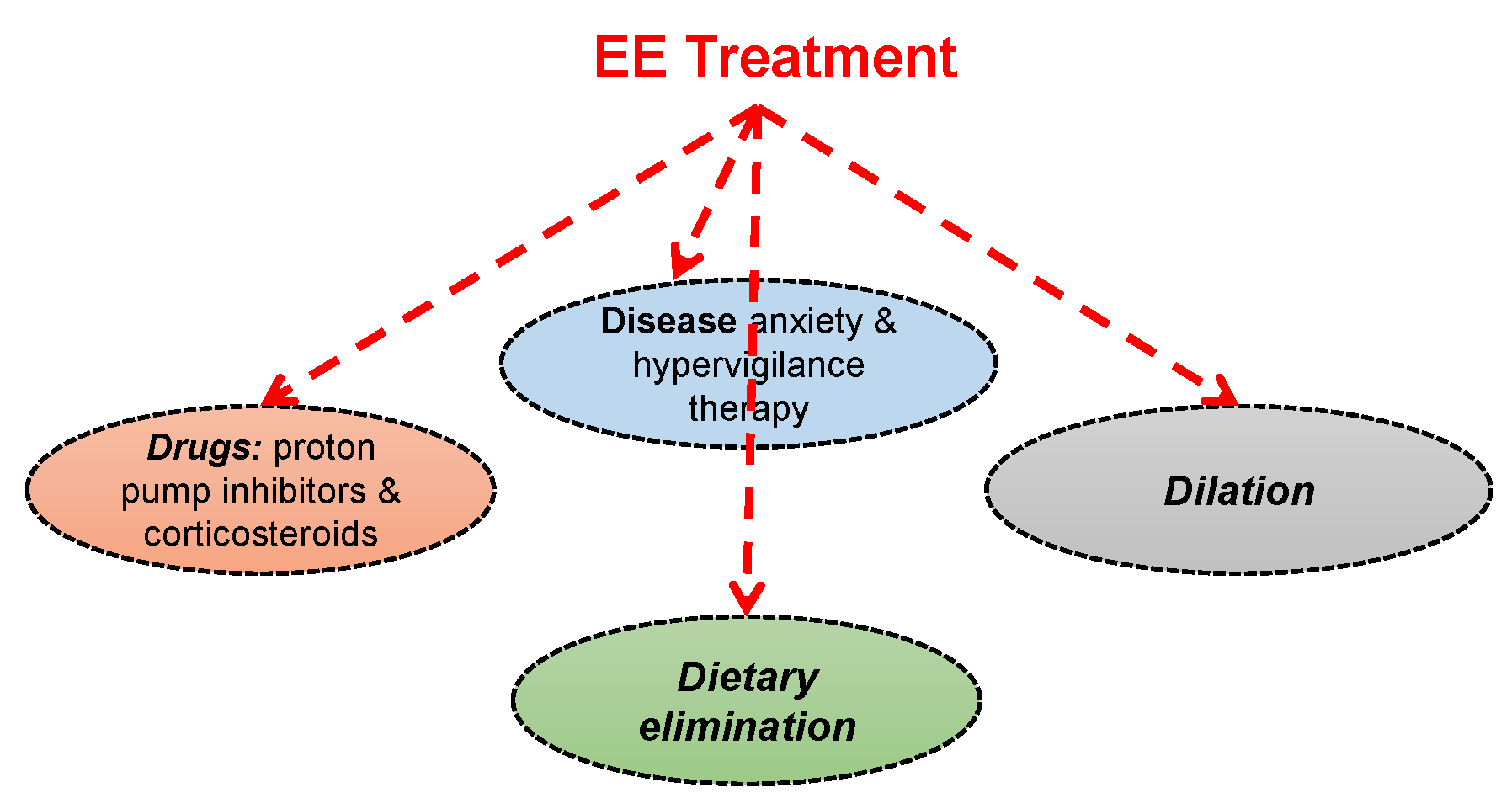
1.5. Current Treatment Strategies
2. Dupilumab (Dupixent®, Regeneron)
3. Discussion of the Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liacouras, C.A.; Furuta, G.T.; Hirano, I.; Atkins, D.; Attwood, S.E.; Bonis, P.A.; Burks, A.W.; Chehade, M.; Collins, M.H.; Dellon, E.S.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 3–20.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dellon, E.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I.; Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Katzka, D.A. ACG Clinical Guideline: Evidenced Based Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, G.T.; Katzka, D.A. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, E.T.; Hoffman, K.; Shaheen, N.J.; Genta, R.M.; Dellon, E.S. Esophageal Eosinophilia is Increased in Rural Areas With Low Population Density: Results From a National Pathology Database. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, E.T.; Kappelman, M.D.; Kim, H.P.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Dellon, E.S. Early Life Exposures as Risk Factors for Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Nimwegen, F.A.; Penders, J.; Stobberingh, E.E.; Postma, D.S.; Koppelman, G.H.; Kerkhof, M.; Reijmerink, N.E.; Dompeling, E.; van den Brandt, P.A.; Ferreira, I.; et al. Mode and place of delivery, gastrointestinal microbiota, and their influence on asthma and atopy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 948.e3–955.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapel, R.C.; Miller, J.K.; Torres, C.; Aksoy, S.; Lash, R.; Katzka, D.A. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Prevalent Disease in the United States That Affects All Age Groups. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, E.S.; Martin, L.J.; Collins, M.H.; Kottyan, L.C.; Sucharew, H.; He, H.; Mukkada, V.A.; Succop, P.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Foote, H.; et al. Twin and family studies reveal strong environmental and weaker genetic cues explaining heritability of eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1084–1092.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Gao, P.-S.; Stucke, E.M.; Blanchard, C.; Collins, M.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Franciosi, J.P.; Kushner, J.P.; Abonia, J.P.; Assa’Ad, A.H.; et al. Variants of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and its receptor associate with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 160–165.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchard, C.; Wang, N.; Stringer, K.F.; Mishra, A.; Fulkerson, P.C.; Abonia, J.; Jameson, S.C.; Kirby, C.; Konikoff, M.R.; Collins, M.H.; et al. Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kottyan, L.C.; Davis, B.P.; Sherrill, J.D.; Liu, K.; Rochman, M.; Kaufman, K.; Weirauch, M.T.; Vaughn, S.; Lazaro, S.; Rupert, A.M.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of eosinophilic esophagitis provides insight into the tissue specificity of this allergic disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sleiman, P.M.A.; Wang, M.-L.; Cianferoni, A.; Aceves, S.; Gonsalves, N.; Nadeau, K.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Hakonarson, H. GWAS identifies four novel eosinophilic esophagitis loci. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katzka, D.A.; Tadi, R.; Smyrk, T.C.; Katarya, E.; Sharma, A.; Geno, D.M.; Camilleri, M.; Iyer, P.G.; Alexander, J.A.; Buttar, N.S. Effects of Topical Steroids on Tight Junction Proteins and Spongiosis in Esophageal Epithelia of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1824–1829.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzka, D.A.; Ravi, K.; Geno, D.M.; Smyrk, T.C.; Iyer, P.G.; Alexander, J.A.; Mabary, J.E.; Camilleri, M.; Vaezi, M.F. Endoscopic Mucosal Impedance Measurements Correlate With Eosinophilia and Dilation of Intercellular Spaces in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1242–1248.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rhijn, B.D.; Weijenborg, P.W.; Verheij, J.; van den Bergh Weerman, M.A.; Verseijden, C.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; de Jonge, W.J.; Smout, A.J.; Bredenoord, A.J. Proton pump inhibitors partially restore mucosal integrity in patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia but not eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1815.e2–1823.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, C.; Stucke, E.M.; Burwinkel, K.; Caldwell, J.M.; Collins, M.H.; Ahrens, A.; Buckmeier, B.K.; Jameson, S.C.; Greenberg, A.; Kaul, A.; et al. Coordinate Interaction between IL-13 and Epithelial Differentiation Cluster Genes in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4033–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Kc, K.; Wu, D.; Djukic, Z.; Caldwell, J.M.; Stucke, E.M.; Kemme, K.A.; Costello, M.; Mingler, M.K.; Blanchard, C.R.; et al. Desmoglein-1 regulates esophageal epithelial barrier function and immune responses in eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 7, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kc, K.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Sherrill, J.D. In vitro model for studying esophageal epithelial differentiation and allergic inflammatory responses identifies keratin involvement in eosinophilic esophagitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, D.J.; Mak, N.; Hurlbut, D.J.; Justinich, C.J. Atopic and non-atopic eosinophilic oesophagitis are distinguished by immunoglobulin E-bearing intraepithelial mast cells. Histopathology 2012, 61, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Bauer, M.; Fischer, B.; Blaser, K.; Simon, H.U. Idiopathic eosinophilic esophagitis is associated with a T(H)2-type allergic inflammatory response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noti, M.; Wojno, E.T.; Kim, B.S.; Siracusa, M.C.; Giacomin, P.; Nair, M.; Benitez, A.J.; Ruymann, K.R.; Muir, A.B.; Hill, D.; et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin–elicited basophil responses promote eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lexmond, W.S.; Neves, J.F.; Nurko, S.; Olszak, T.; Exley, M.A.; Blumberg, R.S.; Fiebiger, E. Involvement of the iNKT Cell Pathway Is Associated With Early-Onset Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Response to Allergen Avoidance Therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clayton, F.; Fang, J.C.; Gleich, G.J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Olalla, J.M.; Vinson, L.A.; Lowichik, A.; Chen, X.; Emerson, L.; Cox, K.; et al. Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Adults Is Associated With IgG4 and Not Mediated by IgE. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dellon, E.S.; Jensen, E.T.; Martin, C.F.; Shaheen, N.J.; Kappelman, M.D. Prevalence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 589–596.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aceves, S.S. Food Allergy Testing in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: What the Gastroenterologist Needs to Know. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desai, T.K.; Stecevic, V.; Chang, C.-H.; Goldstein, N.S.; Badizadegan, K.; Furuta, G.T. Association of eosinophilic inflammation with esophageal food impaction in adults. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 61, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruz, P.; Straumann, A.; Bussmann, C.; Heer, P.; Simon, H.-U.; Zwahlen, M.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Swiss EoE Study Group. Escalating incidence of eosinophilic esophagitis: A 20-year prospective, population-based study in Olten County, Switzerland. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1349–1350.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, J.; Talley, N.J.; Aro, P.; Storskrubb, T.; Johansson, S.-E.; Lind, T.; Bolling-Sternevald, E.; Vieth, M.; Stolte, M.; Walker, M.M.; et al. Prevalence of oesophageal eosinophils and eosinophilic oesophagitis in adults: The population-based Kalixanda study. Gut 2007, 56, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansoor, E.; Cooper, G.S. The 2010–2015 Prevalence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the USA: A Population-Based Study. Dig Dis Sci. 2016, 61, 2928–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishimura, N.; Shimura, S.; Jiao, D.; Mikami, H.; Okimoto, E.; Uno, G.; Aimi, M.; Oshima, N.; Ishihara, S.; Kinoshita, Y. Clinical features of eosinophilic esophagitis: Differences between Asian and Western populations. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonia, J.P.; Wen, T.; Stucke, E.M.; Grotjan, T.; Griffith, M.S.; Kemme, K.A.; Collins, M.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Franciosi, J.P.; von Tiehl, K.F.; et al. High prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients with inherited connective tissue disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulder, D.J.; Hookey, L.C.; Hurlbut, D.J.; Justinich, C.J. Impact of Crohn disease on eosinophilic esophagitis: Evidence for an altered T(H)1-T(H)2 immune response. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.; Lebwohl, B.; Genta, R.; Dellon, E. Increased Risk of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Patients With Active Celiac Disease on Biopsy: Results From a National Pathology Database. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Zhang, X.; Huo, X.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.H.; Spechler, S.J.; Souza, R.F. Omeprazole blocks eotaxin-3 expression by oesophageal squamous cells from patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis and GORD. Gut 2013, 62, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thakkar, K.P.; Fowler, M.; Keene, S.; Iuga, A.; Dellon, E.S. Long-term efficacy of proton pump inhibitors as a treatment modality for eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Dellon, E.S.; Moawad, F.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Aceves, S.S.; Rothenberg, M.E. Transcriptome analysis of proton pump inhibitor–responsive esophageal eosinophilia reveals proton pump inhibitor–reversible allergic inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 135, 187–197.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Votto, M.; De Filippo, M.; Lenti, M.V.; Rossi, C.M.; Di Sabatino, A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Diet Therapy in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Focus on a Personalized Approach. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 9, 820192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, Á.; González-Cervera, J.; Tenias, J.M.; Lucendo, A.J. Efficacy of Dietary Interventions for Inducing Histologic Remission in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Główczewski, A.; Krogulska, A. Formulations of Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—Current Treatment and Emerging Possibilities. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Lucendo, A.J.; Schlag, C.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Falk, G.W.; Eagle, G.; Nezamis, J.; Comer, G.M.; Knoop, K.; Hirano, I. Fluticasone Propionate Orally Disintegrating Tablet (APT-1011) for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.; Falk, G.W. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirley, M. Dupilumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves New Eczema Drug Dupixent. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-eczema-drug-dupixent (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Highlights of Prescribing Informat. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/761055s014lbl.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Li, Z.; Radin, A.; Li, M.; Hamilton, J.D.; Kajiwara, M.; Davis, J.D.; Takahashi, Y.; Hasegawa, S.; Ming, J.E.; DiCioccio, A.T.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Safety, and Tolerability of Dupilumab in Healthy Adult Subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020, 9, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, C.; Davis, J.D.; Kanamaluru, V.; Lu, Q. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of dupilumab in adult and adolescent patients with asthma. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2021, 10, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves First Treatment for Eosinophilic Esophagitis, a Chronic Immune Disorder. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-treatment-eosinophilic-esophagitis-chronic-immune-disorder (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Highlights of Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/761055s042lbl.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Hirano, I.; Dellon, E.S.; Hamilton, J.D.; Collins, M.H.; Peterson, K.; Chehade, M.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Safroneeva, E.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Falk, G.W.; et al. Efficacy of Dupilumab in a Phase 2 Randomized Trial of Adults With Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 111–122.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Press Release: FDA Approves Dupixent® (dupilumab) as First Treatment for Adults and Children Aged 12 and Older with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Available online: https://www.sanofi.com/en/media-room/press-releases/2022/2022-05-20-21-15-00-2447906 (accessed on 21 May 2022).
| Part A | Part B | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dupilumab 300 mg QW c n = 42 | Placebo c n = 39 | Difference vs. Placebo (95% CI) c | Dupilumab 300 mg QW c n = 80 | Placebo c n = 79 | Difference vs. Placebo (95% CI) c | |
| Primary Endpoints | ||||||
| Proportion of subjects achieving histological remission (peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil count ≤6 eos/hpf a), n (%) | 25 (59.5) | 2 (5.1) | 57.0 (40.9, 73.1) | 47 (58.8) | 5 (6.3) | 53.5 (41.2, 65.8) |
| Absolute change from baseline in DSQ score (0–84 b), LS mean (SE) | −21.9 (2.5) | −9.6 (2.8) | −12.3 (−19.1, −5.5) | −23.8 (1.9) | −13.9 (1.9) | −9.9 (−14.8, −5.0) |
| Parts A and B | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | Dupilumab 300 mg QW n = 122 n (%) | Placebo n = 117 n (%) |
| Injection site reaction a | 46 (38%) | 39 (33%) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection b | 22 (18%) | 12 (10%) |
| Arthralgia | 3 (2%) | 1 (1%) |
| Herpes viral infections c | 3 (2%) | 1 (1%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Horani, R.A.; Chiles, R. First Therapeutic Approval for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 13, 238-244. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13030024
Al-Horani RA, Chiles R. First Therapeutic Approval for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology Insights. 2022; 13(3):238-244. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Horani, Rami A., and Raquel Chiles. 2022. "First Therapeutic Approval for Eosinophilic Esophagitis" Gastroenterology Insights 13, no. 3: 238-244. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13030024
APA StyleAl-Horani, R. A., & Chiles, R. (2022). First Therapeutic Approval for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology Insights, 13(3), 238-244. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13030024







