Predictive Energy Management Strategy for Heavy-Duty Series Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Drive Power Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Platform
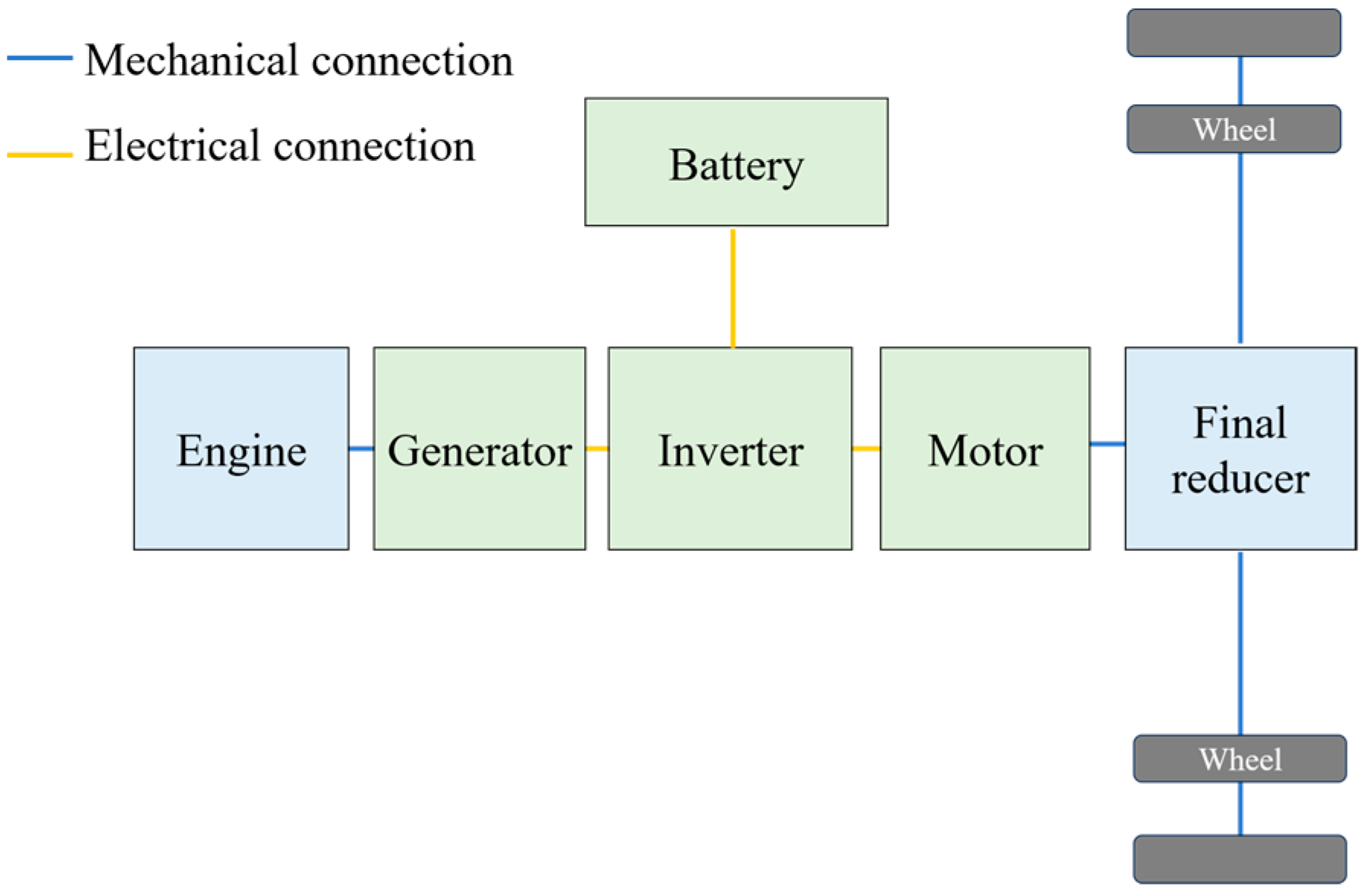
2.1. Heavy-Duty Series Hybrid Electric Vehicle Modelling
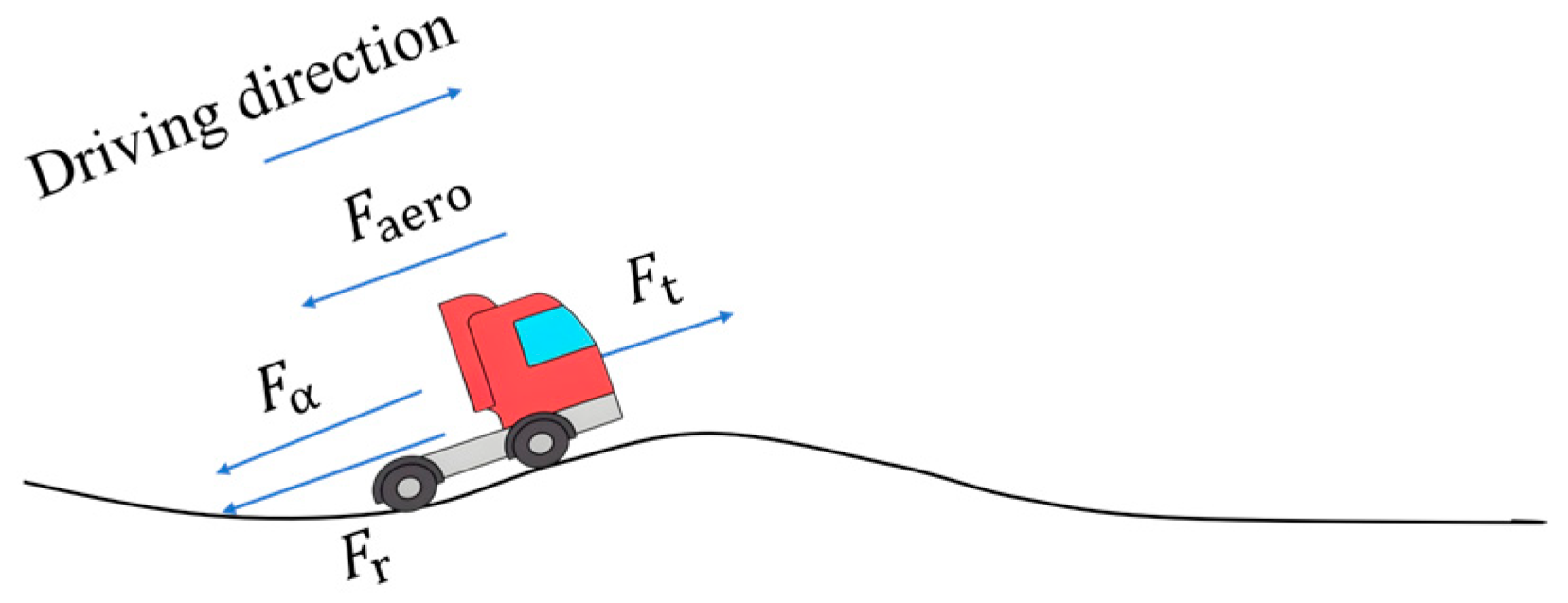
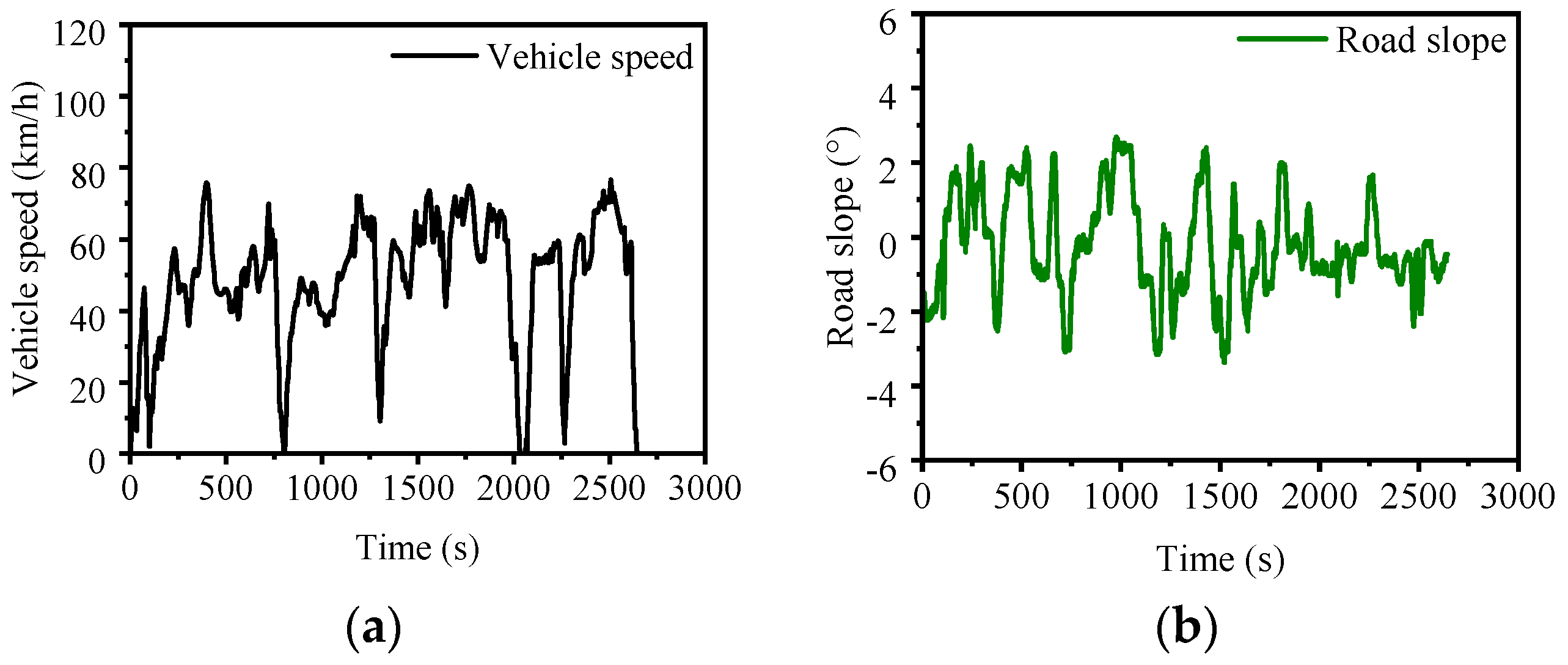
2.2. Test Route
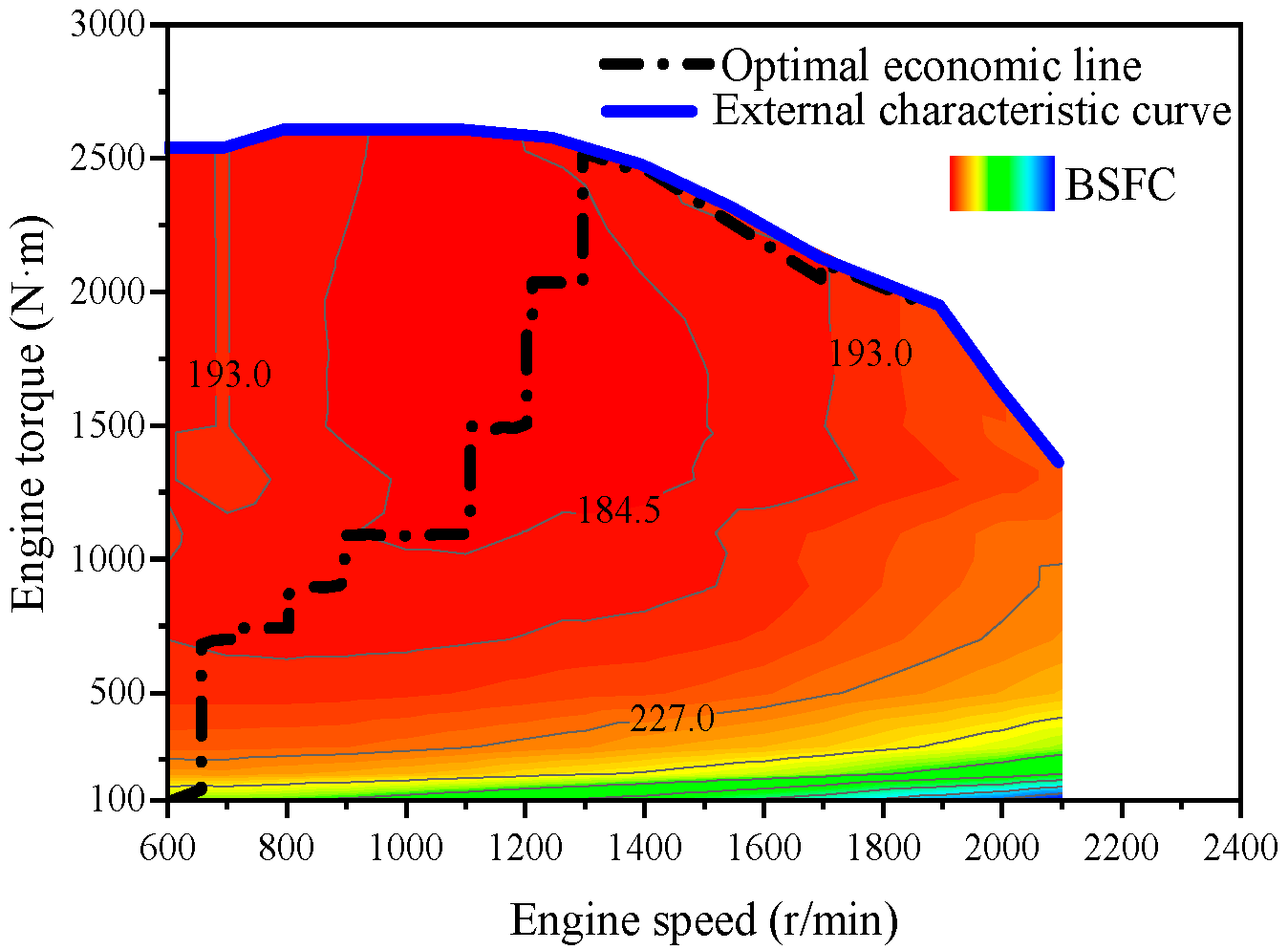
2.3. Vehicle Simulation Model Drive Power Validation
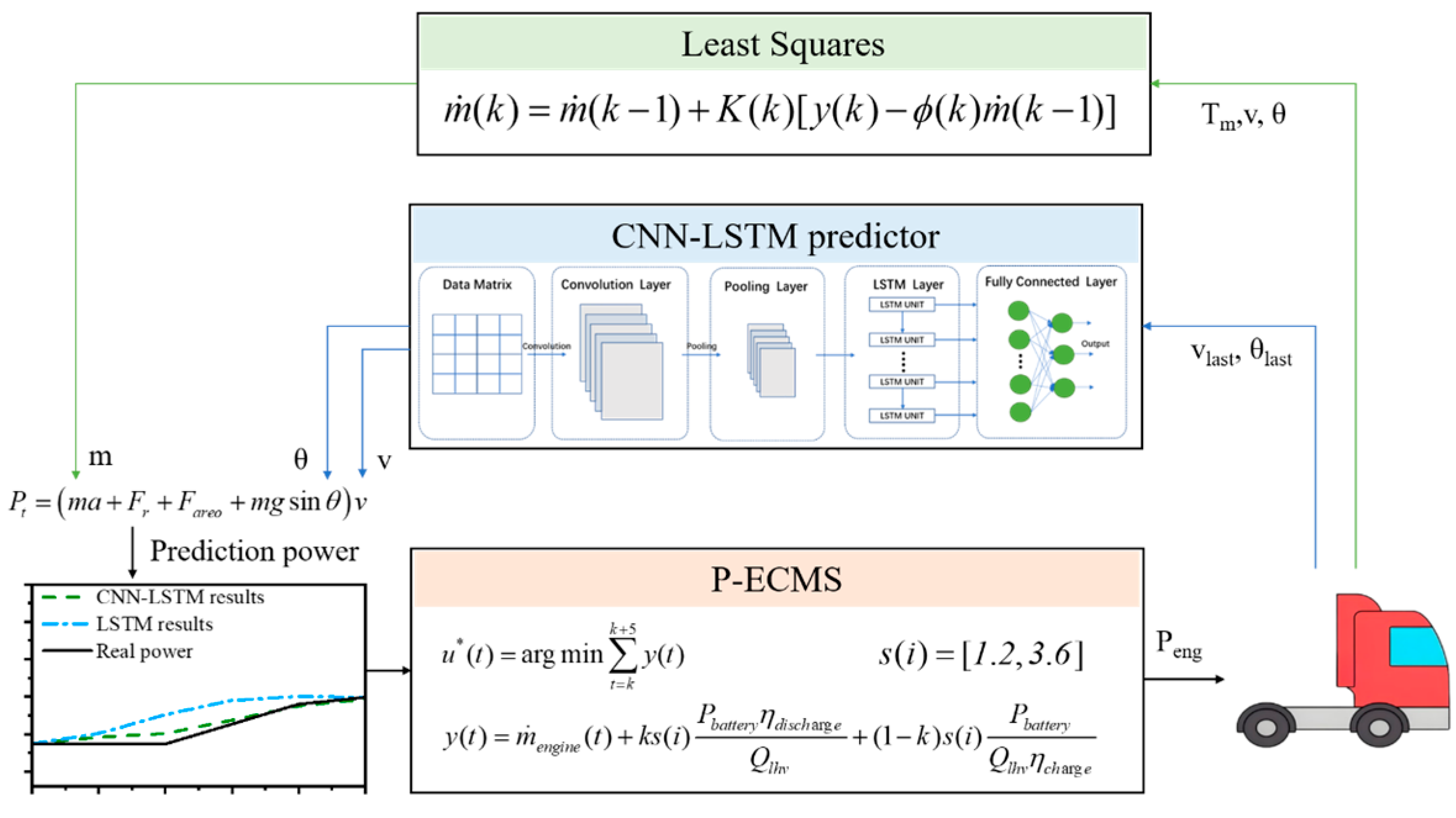
3. Predictive Energy Management Methodology
3.1. Mass Estimation
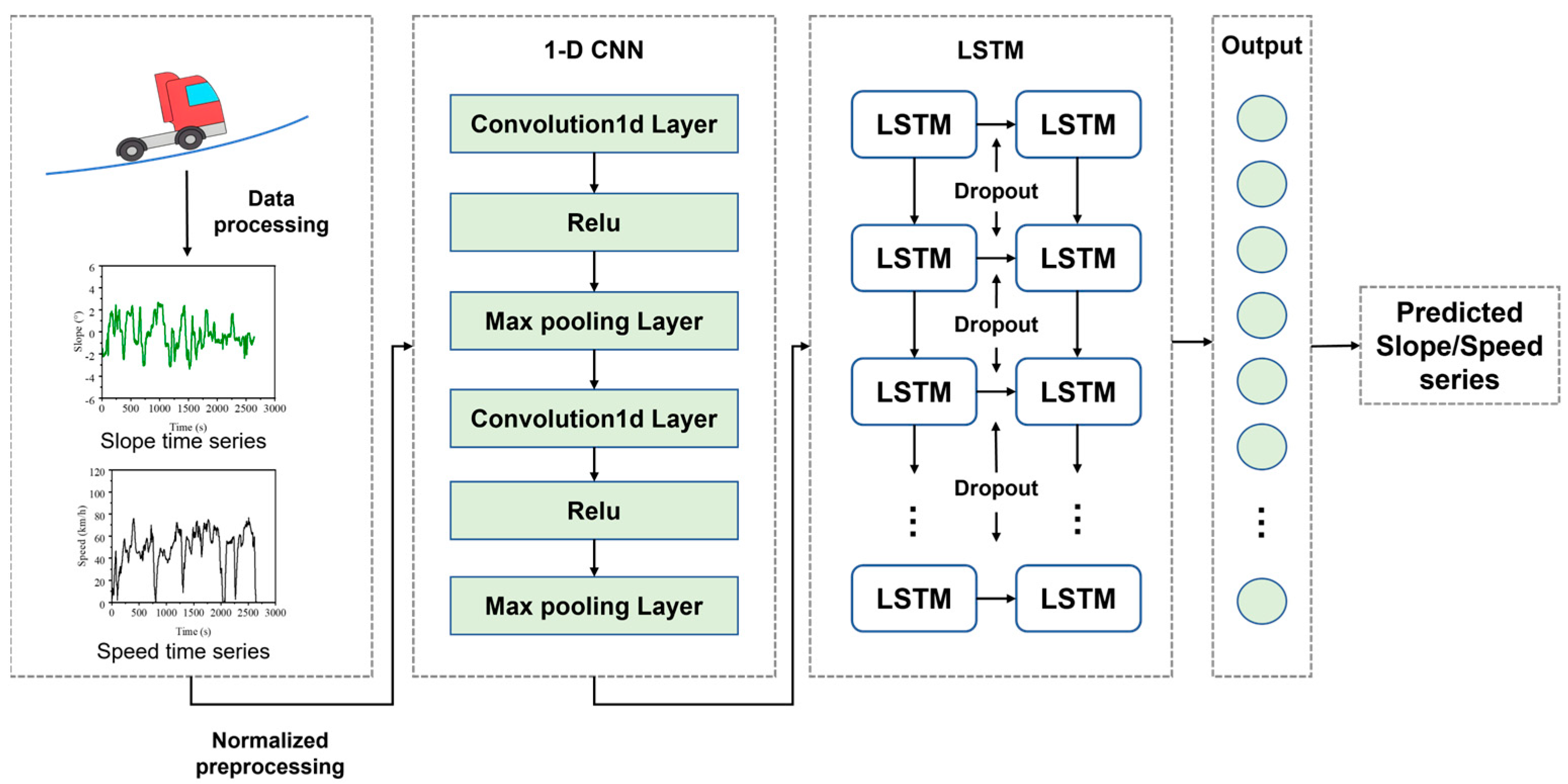
3.2. Speed and Slope Prediction
3.3. Future Drive Power Calculation
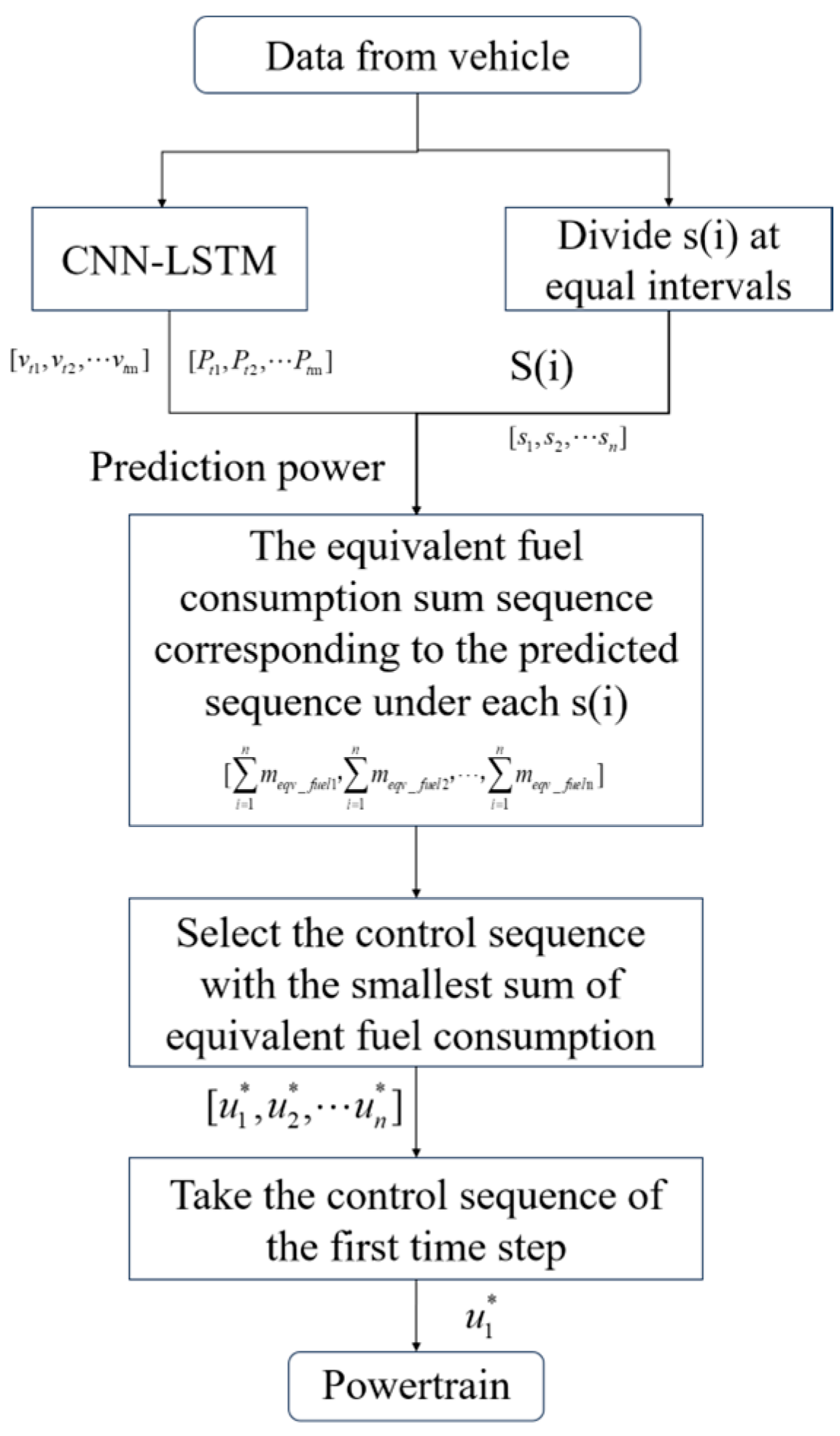
3.4. Predictive ECMS
4. Results and Discussion
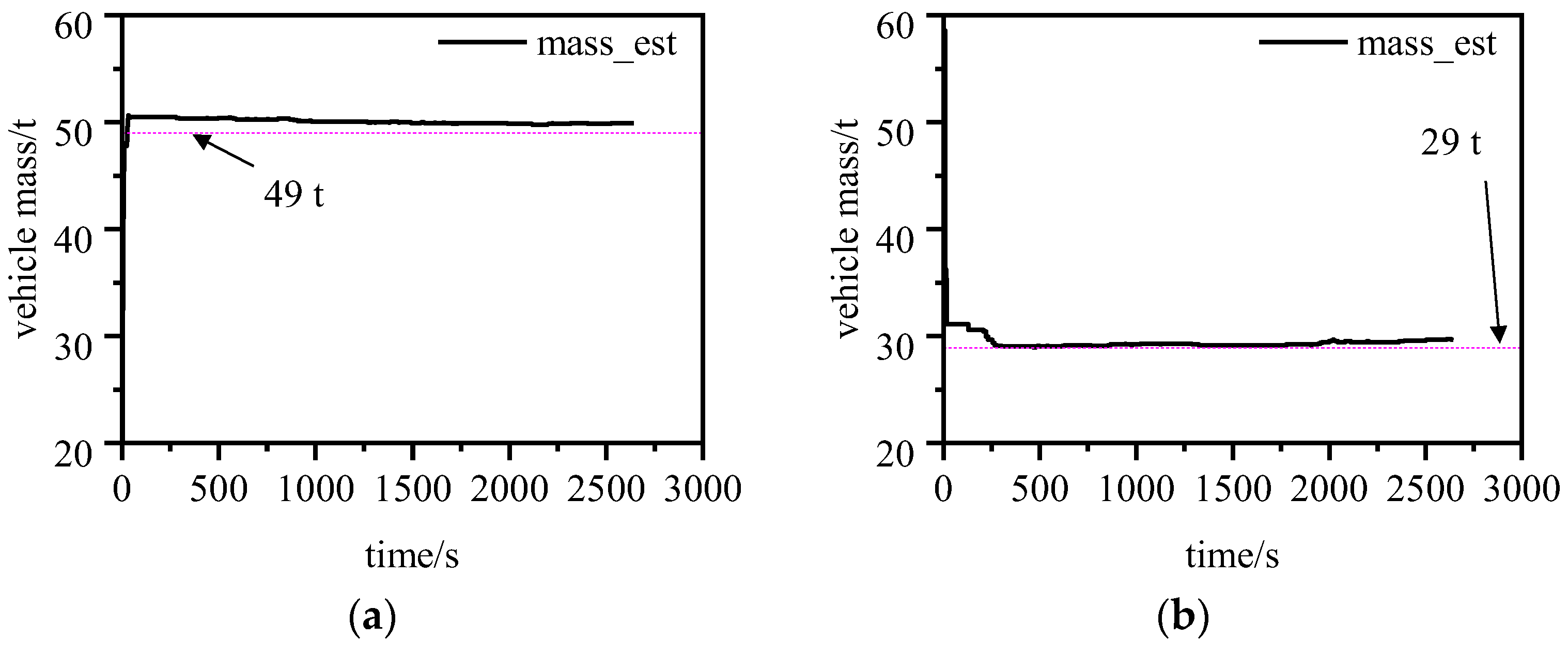
4.1. Mass Estimation Results
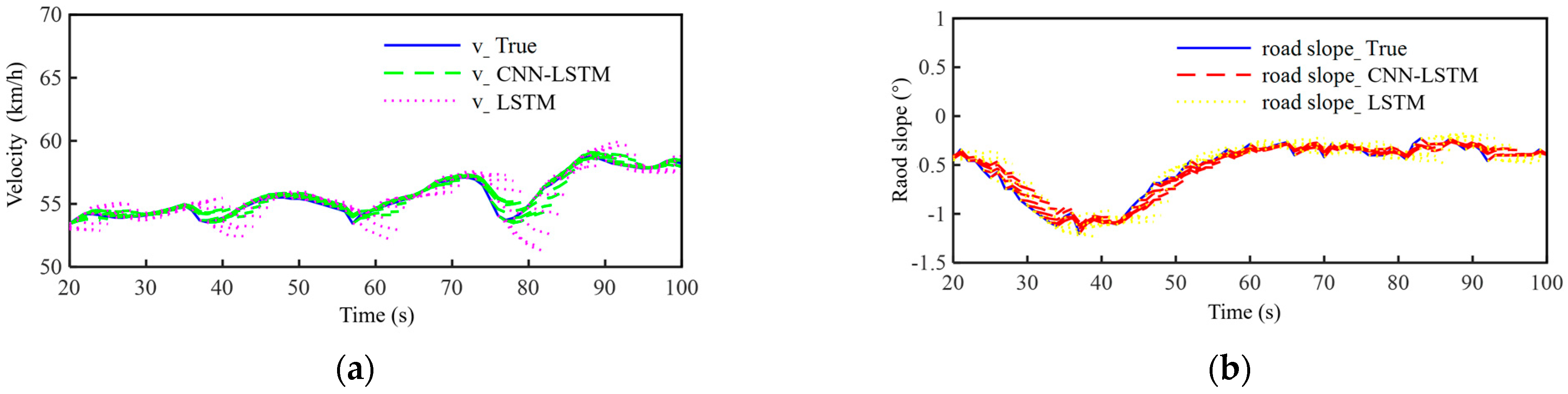
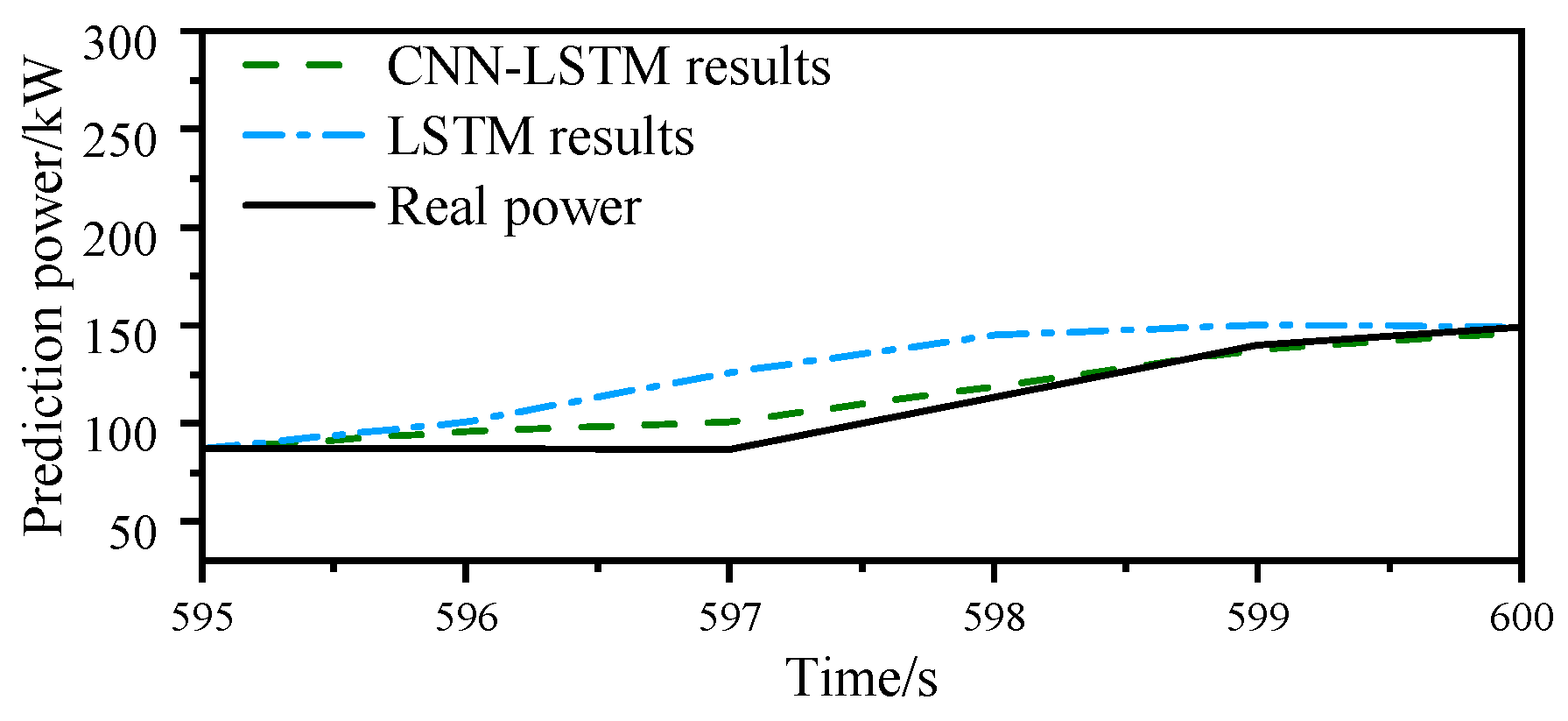
4.2. Drive Power Prediction
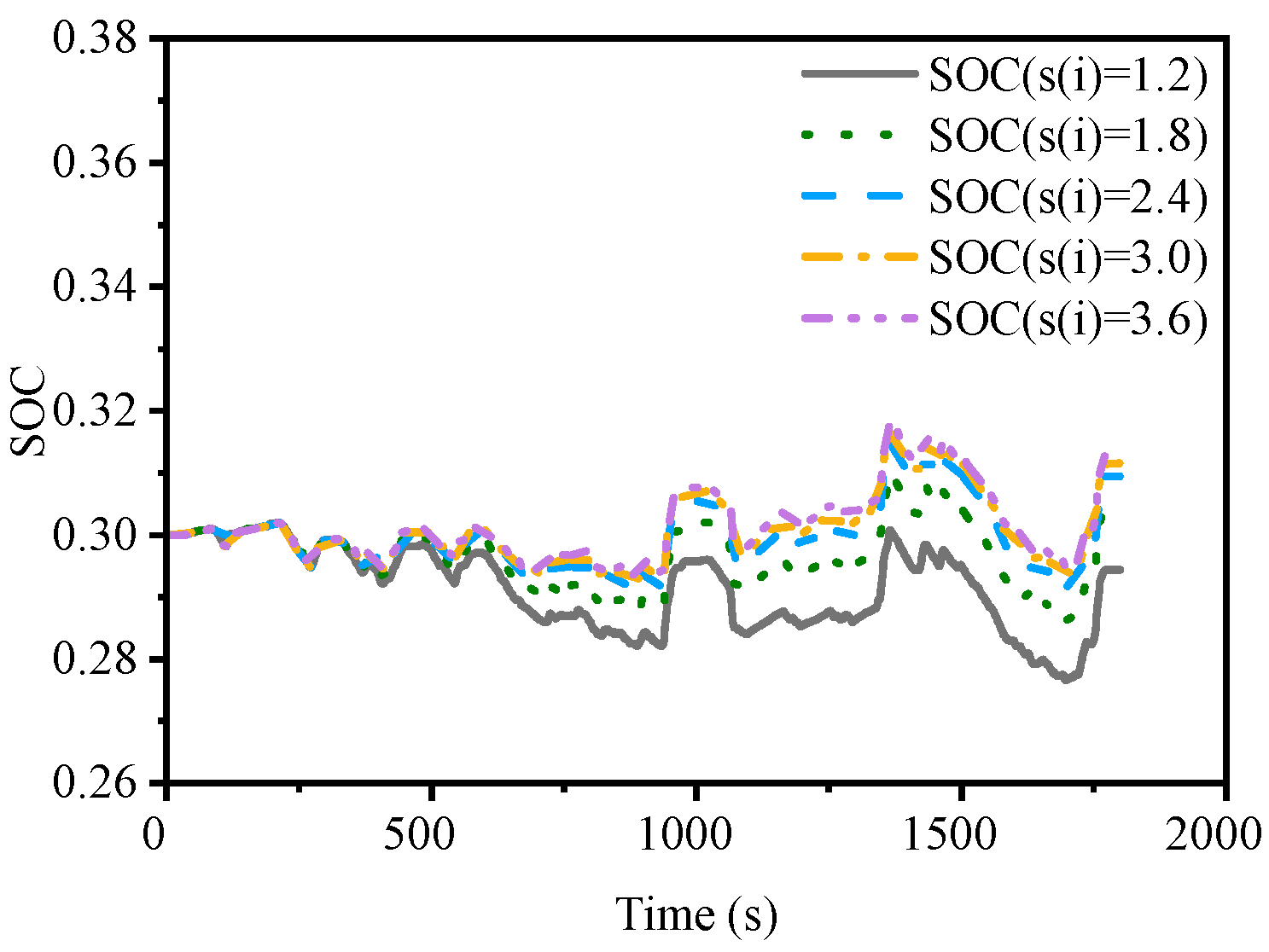
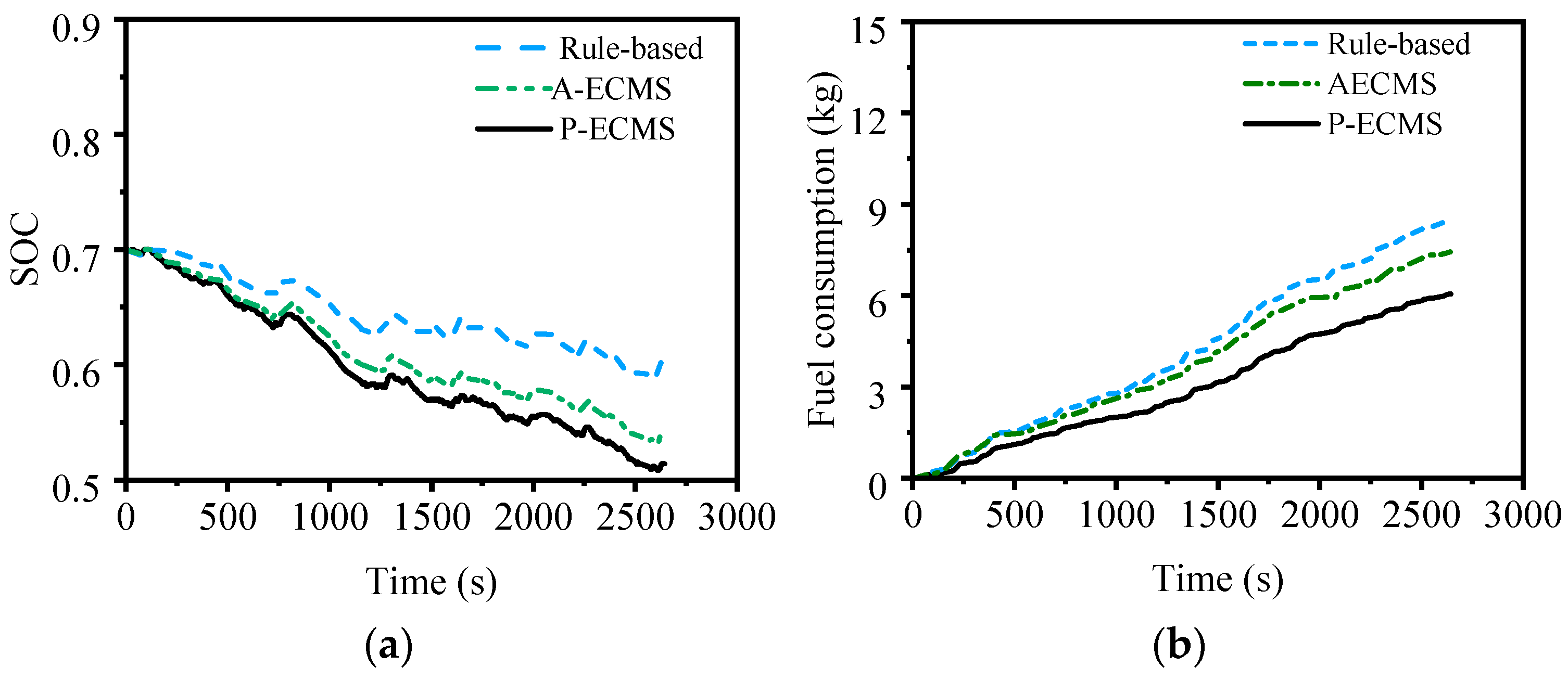
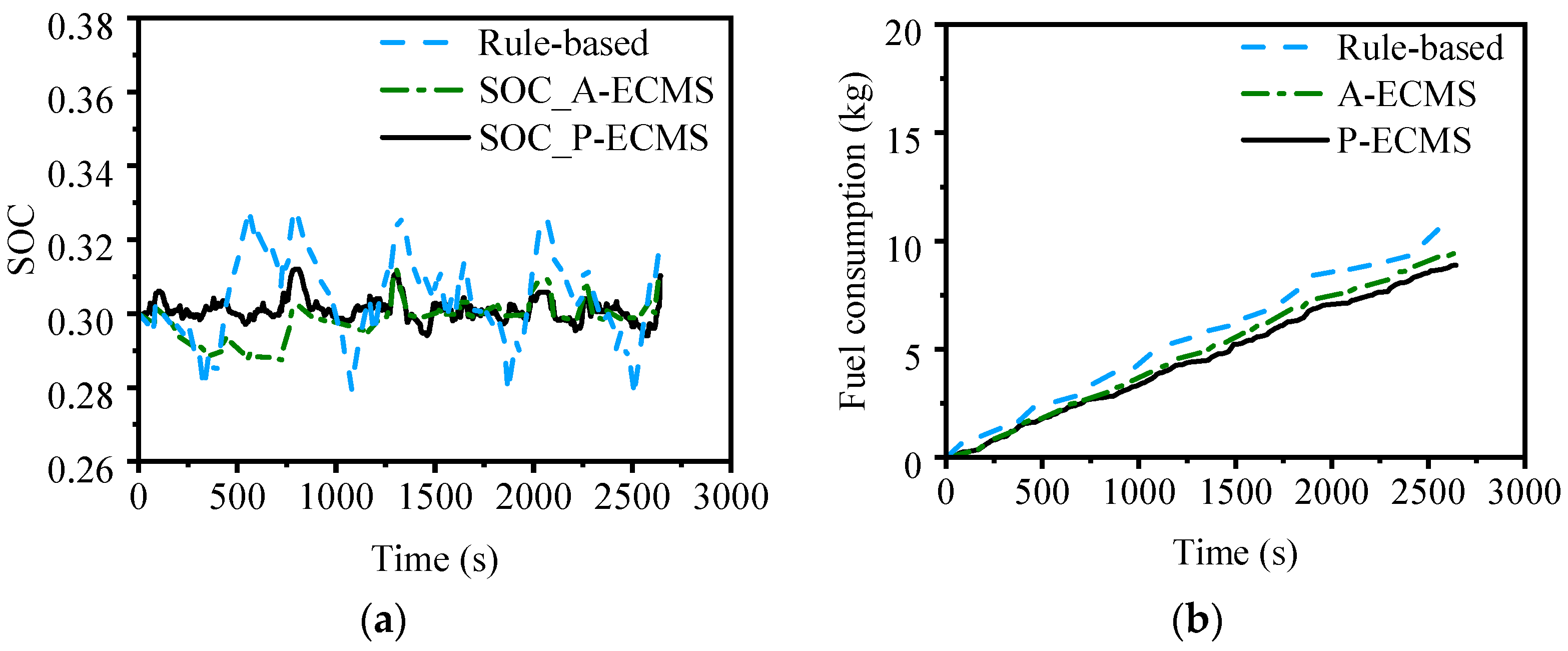
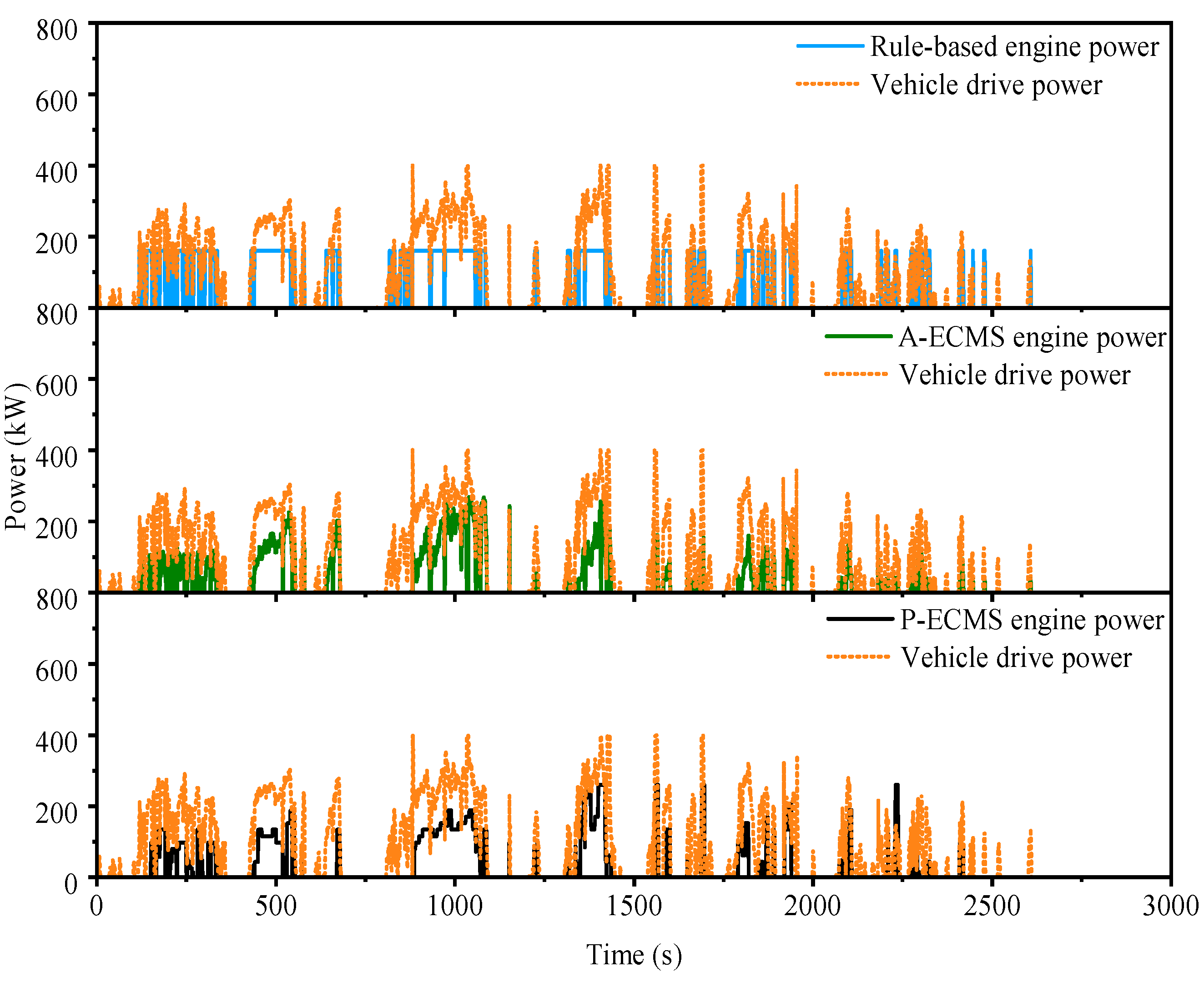
4.3. Energy Consumption of EMSs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, X.; Bhatt, N.P.; Khajepour, A.; Hashemi, E. Integrated Inertial-LiDAR-Based Map Matching Localization for Varying Environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 4307–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Li, S.; He, X.H.; Xie, C.; He, S.; Xu, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X. Hybrid Electric Vehicles: A Review of Energy Management Strategies Based on Model Predictive Control. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İşbitirici, A.; Giarré, L.; Xu, W.; Falcone, P. LSTM-Based Virtual Load Sensor for Heavy-Duty Vehicles. Sensors 2024, 24, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Cai, L.; Pi, D.; Wang, E. Truck Mass Estimation Method Based on the On-Board Sensor. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2020, 234, 2429–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyuddin, M.N.; Na, J.; Herrmann, G.; Ren, X.; Barber, P. Adaptive Observer-Based Parameter Estimation with Application to Road Gradient and Vehicle Mass Estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2851–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, T.; Peng, P.; Pi, D.; Wang, E. Two-Layer Structure Algorithm for Estimation of Commercial Vehicle Mass. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2020, 234, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L. Intelligent Two-Step Estimation Approach for Vehicle Mass and Road Grade. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 218853–218862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, W.; Tulpule, P.; Midlam-Mohler, S.; Rizzoni, G. Data-Driven Adaptive Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy for Hybrid Electric and Connected Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, R.; Ge, H. Short-Term Vehicle Speed Prediction Based on BiLSTM-GRU Model Considering Driver Heterogeneity. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 610, 128410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, T.; Mo, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. Research on Highway Slope Monitoring Data Prediction Based on Long Short-Term Memory Network. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 571, 012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liao, Z.; Ma, X. Nonlinear Model Predictive Control for Heavy-Duty Hybrid Electric Vehicles Using Random Power Prediction Method. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 202819–202835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, C.; Besselink, I.; Nijmeijer, H. Combined Rolling Resistance and Road Grade Estimation Based on EV Powertrain Data. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 3201–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qin, T.; Chen, D.; Wang, G.; Chen, T. Driving Power Prediction of Heavy Commercial Vehicles Based on Multi-Task Learning. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Yamamoto, T. Improving Electricity Consumption Estimation for Electric Vehicles Based on Sparse GPS Observations. Energies 2017, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H. MPC-ECMS Energy Management of Extended-Range Vehicles Based on LSTM Multi-Signal Speed Prediction. Electronics 2023, 12, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Tian, G. Adaptive Fuzzy Logic Energy Management Strategy Based on Reasonable SOC Reference Curve for Online Control of Plug-in Hybrid Electric City Bus. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Son, H.; Kim, H.; Hwang, S. Development of an Advanced Rule-Based Control Strategy for a PHEV Using Machine Learning. Energies 2018, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Li, L.; Liang, H. A Novel Braking Control Strategy for Hybrid Electric Buses Based on Vehicle Mass and Road Slope Estimation. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 35, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Yao, Z.; Fan, H.; Xia, R.; Chen, T. Vehicle Road Grade Prediction Based on CNN-LSTM. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023, 56, 3066–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 37340-2019; Conversion Methods for Energy Consumption of Electric Vehicles. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Yao, D.; Lu, X.; Chao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, F. Adaptive Equivalent Fuel Consumption Minimization Based Energy Management Strategy for Extended-Range Electric Vehicle. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Full load mass (t) | 49 |
| Tractor mass (t) | 9 |
| Engine displacement (L) | 12.5 |
| Engine max power (kW) | 320 |
| Generator max power (kW) | 350 |
| Motor max power (kW) | 380 |
| Battery capacity (kW·h) | 100 |
| Mode | Switch Conditions | Engine Power Demand | Motor Power Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | SOC ≤ e1 || (SOC > e1 and Preq > p1) | Pa | Preq |
| CD | SOC > e1 and Preq ≤ p1 | 0 | Preq |
| Mechanical braking | Pdemand < 0 and (v ≤ 10 km/h || SOC ≥ e2) | 0/Pidle | 0 |
| Motor braking energy recovery | Pdemand < 0 and v > 10 km/h and SOC < e2 | 0/Pidle | Preq |
| Model | RMSE of Speed Prediction (km/h) | RMSE of Slope Prediction (°) | RMSE of Power Prediction (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 1.5 | 0.162 | 17.2 |
| CNN-LSTM | 1.4 (−6.7%) | 0.141 (−13.0%) | 14.8 (−14.0%) |
| Operation Mode | EMS | Fuel Consumption (L/100 km) | Final SOC | Equivalent Energy Consumption (L/100 km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | Rule | 24.32 | 0.603 | 27.10 |
| A-ECMS | 21.14 | 0.531 | 26.00 | |
| P-ECMS | 20.08 | 0.514 | 25.43 | |
| CS | Rule | 34.88 | 0.321 | 34.28 |
| A-ECMS | 29.99 | 0.309 | 29.73 | |
| P-ECMS | 29.42 | 0.310 | 29.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Liang, C.; Cheng, S.; Yin, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Sun, C.; Chen, T. Predictive Energy Management Strategy for Heavy-Duty Series Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Drive Power Prediction. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16030186
Cao Y, Liang C, Cheng S, Yin X, Chen D, Liu Z, Sun C, Chen T. Predictive Energy Management Strategy for Heavy-Duty Series Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Drive Power Prediction. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(3):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16030186
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yuan, Changshui Liang, Shi Cheng, Xinxian Yin, Daxin Chen, Zhixi Liu, Chaoyang Sun, and Tao Chen. 2025. "Predictive Energy Management Strategy for Heavy-Duty Series Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Drive Power Prediction" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 3: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16030186
APA StyleCao, Y., Liang, C., Cheng, S., Yin, X., Chen, D., Liu, Z., Sun, C., & Chen, T. (2025). Predictive Energy Management Strategy for Heavy-Duty Series Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Drive Power Prediction. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(3), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16030186





