Abstract
The link failure due to the secondary users exiting the licensed channels when primary users reoccupy the licensed channels is very important in cognitive wireless mesh networks (CWMNs). A multipath routing and spectrum allocation algorithm based on channel interference and reusability with Quality of Service (QoS) constraints in CWMNs (MRIR) was proposed. Maximizing the throughput and the acceptance ratio of the wireless service is the objective of the MRIR. First, a primary path of resource conservation with QoS constraints was constructed, then, a resource conservation backup path based on channel interference and reusability with QoS constraints was constructed. The MRIR algorithm contains the primary path routing and spectrum allocation algorithm, and the backup path routing and spectrum allocation algorithm. The simulation results showed that the MRIR algorithm could achieve the expected goals and could achieve a higher throughput and acceptance ratio.
1. Introduction
A Cognitive Wireless Mesh Network (CWMN) is a kind of Wireless Mesh Network (WMN) that uses Cognitive Radio (CR) [1]. CWMN uses CR technology to sense the spectrum and to share spectrum resources [2]. A CR-Mesh node (such as a CR-Mesh gateway, a CR-Mesh router, or a CR-Mesh client) integrates CR technology, can sense the spectrum that Primary Users (PUs) are not using and access the vacancy spectrum resources, and improve the spectrum utilization and end-to-end network performance, and are called Secondary Users (SUs). The PU has a higher usage priority for the authorized (licensed) spectrum (channel). Once the PU needs to re-occupy the authorized channel, then the SU must unconditionally quit the occupied channel, which causes the link to be interrupted. Multipath routing is an effective technique used to solve the link failure problem.
The research results on the routing problem in the WMNs cannot be directly applied to CWMNs [3,4]. Some research results on the routing problem in the CWMNs were obtained from References [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18].
A problem-solving framework based on economics with the goal of network profit maximization was proposed by Amini et al. [6]. Aiming to minimize the end-to-end delay for the joint optimization of routing and resource allocation problem, the problem was formulated as a nonlinear integer programming problem. The Lagrange dual method was proposed based on a distributed solution in CWMN by El-Sherif et al. [7], and a novel opportunistic spectrum aware routing in the CWMNs was proposed by Ramli [8], which allowed for the CR users to effectively occupy the spectrum band depending on the spectrum availability, and to also perform dynamic channel switching for performance optimization. The throughput maximization problem in the CWMNs in combination with power control, channel allocation, and routing under the Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) model was studied by Jia [9]. Furthermore, a decision theory framework was used to model the problem of routing under the uncertainties involved in a cognitive radio network by Soltani [10]. A utility function was designed to capture the effect of spectrum measurement, fluctuation of bandwidth availability, and path quality, and the authors investigated how to jointly optimize the route setup and channel assignment. An integrated data transmission cost to quantitatively measure the communication quality of links was proposed by Tang [11]. Spectrum-mobility-incurred route-switching problems in both the spatial and frequency domains for CRNs was investigated by Liang [12], where spatial switching determined which relays and links should be reselected, and the frequency switching decided which channels ought to be reassigned to the spatial routes. A geographic routing protocol for cognitive radio mobile ad hoc networks (TIGHT) was proposed by Jin [13]. TIGHT offered three routing modes and allowed for secondary users to fully explore the transmission opportunities over a primary channel without affecting the primary users (PUs). A spectrum aggregation-based cooperative routing protocol, termed as SACRP, was proposed by Ping [14] to provide higher energy efficiency, improve throughput, and reduce network delay. A routing metric, including link security, link conflict, link reliability, and link available bandwidth was proposed by Kuang [15]. The SIEB (link Security, link conflIct, link rEliability, and link available Bandwidth) included the two aspects of link security and link performance. To resist various hole attacks, the link trust value based on two hop neighbor feedback was computed in the link security weight computing of SIEB. The problem of routing in Cognitive Radio Ad Hoc Networks (CRAHNs) is that it targets the creation and maintenance of the wireless multi-hop paths among the cognitive nodes by deciding both the spectrum to be used and the relay nodes of the path. A cognitive cross-layer multipath probabilistic routing was therefore proposed by Deepti [16].
A spectrum aware on-demand routing protocol, which focused on reliable routing and considered opportunistic spectrum, link disruption, as well as node failure, was proposed by Song [17]. A route selection metric for multipath routing in cognitive networks was also proposed by Beltagy [18]. Route closeness, the proposed metric, favors routes that are not close to each other, therefore, selecting non-close routes makes them less vulnerable to the activities of the PUs as it would be less possible for an active mobile PU to interrupt all of the routes at the same time.
When the PU node needs to access the channel, the SU node must quit the occupied authorized channel, which will cause link failure and the throughput to decrease. Multipath routing can effectively solve the link failure in CWMNs and improve network throughput. In contrast, this paper differs from the existing research as it not only uses multipath to improve network throughput, but it also saves the network resources that are based on channel interference and a reusability strategy in the construction of multipath, which can further improve network throughput.
In this paper, the motivations based on the channel interference and reusability strategy is as follows:
- (1)
- The primary and backup paths that are configured for the wireless request are not transmitted at the same time, therefore, a link with the higher primary path interference degree is included when constructing a backup path. The higher the degree of interference, then the higher the priority to be selected as the backup path.
- (2)
- The probability that the primary path of two wireless requests with the same backup path (or backup link) emerges as a link failure at the same time is relatively low. Therefore, a wireless link with the interference of multiple wireless requests is included for constructing the backup path. The link with the highest reuse degree, which is selected as the backup path, has a higher priority.
This paper offers the following innovations when compared to the existing research. (1) The problem of multi-path routing and spectrum allocation based on channel interference and reusability with the Quality of Service (QoS) constraints is investigated, with the goal of improving the network throughput and the acceptance ratio of wireless requests. For each new arriving wireless request, a primary path and a backup path are constructed simultaneously. The differences between the available channels are considered, which means that different channels have different bandwidths; (2) Based on the characteristics of the primary and the backup path that are not transmitted simultaneously, when the backup path is constructed, the link with a higher interference to the primary path and with a higher reuse degree has a higher priority selected for constructing the backup path. This can save the use of network resources, and improve the acceptance ratio of wireless requests and network throughput; (3) A multi-path routing and spectrum allocation algorithm (MRIR) with QoS constraints is proposed based on channel interference and reusability, which contains the primary path construction and spectrum allocation algorithm, as well as the backup path configuration and spectrum allocation algorithm.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. We discuss the network model and problem description in Section 2. The proposed multipath routing and spectrum allocation algorithm MRIR is presented in Section 3. Section 4 and Section 5 present the primary path construction and spectrum allocation algorithm and the backup path configuration and spectrum allocation algorithm, respectively. Simulations comparing the performance of the proposed algorithms are presented in Section 6. Section 7 concludes the paper and outlines our future work.
2. Network Model and Problem Description
2.1. Network Model
The SU obtains the unused spectrum of the PU by the spectrum sensing algorithm in CWMNs. This paper did not address the specific spectrum sensing algorithm, but focused on how to construct a routing path to satisfy the QoS constraints, and to allocate the unused spectrum resources after the available spectrum is sensed.
It was assumed that there is a common control channel (CCC) for transmitting the available spectrum information and control information between the SUs [19]. The communication distance of each node is TR, and the interference distance is IR, and IR = 2 × TR.
We adopted a simple undirected graph G = (V,E) model of a CWMN, where V represents the set of the CR-Mesh node, and E represents the set of wireless links. The physical distance between node vi and node vj is represented by d(vi,vj). As each node is in a different location and the PU uses a spectrum with a different pattern, the sensed available spectrum of each node was not the same. Each node vi ∈ V had an available channel set Ki, which had been sensed.
Two CR-Mesh nodes that can communicate with each other must satisfy the following conditions: (1) there are common available channels, Ki ∩ Kj ≠ ; and, (2) the nodes must satisfy the restriction of distance, d(vi,vj) < TR.
The set of available channels K was {1,2,3,4,5} in the current network, and the bandwidth of the channel k was Mbps. Different channels had different bandwidths, i.e., different channels i and j, leads to Bi ≠ Bj. x(u,v) = k represents the wireless link (u,v) allocated to channel k. x(u,v) = 0 represents the wireless link (u,v) not allocated to any channel. Every wireless link was either allocated only one channel, or was not allocated a channel.
2.2. Problem Description
The problem of multi-path routing and spectrum allocation based on channel interference and reusability with the QoS constraints was investigated. For each new arriving wireless request, a primary path and a backup path were constructed simultaneously.
In the backup path construction, a strategy based on channel interference and reusability was proposed to meet the following objectives: (1) when link failure occurs on the primary path, the backup path continues to transmit data to reduce the impact on the accepted wireless request, and improve the network throughput; and, (2) in the construction of the backup path, it is desirable to include a link with the interference to the primary path, and with interference, to a plurality of wireless request primary paths to save resources and to improve the acceptance rate of wireless requests and network throughput.
Let Δ = {γi = (si,di,bi)} be the set of wireless requests, where si and di represent the source and destination node of the wireless request γi; and bi represents the bandwidth constraint of the wireless request γi.
The primary path and backup path from the source node si to the destination node di constructed for the wireless request γi is denoted as and , respectively.
Definition 1.
Primary link, which means that for any one of the links (u,v), if (u,v) ∈ , then (u,v) is called the primary link.
Definition 2.
Backup link, which means that for any one of the links (u,v), if (u,v) ∈
, then (u,v) is called the backup link.
Definition 3.
Idle link, which means that for any one of the links (u,v), if (u,v) , then (u,v) is called the idle link.
Any link (u,v) ∈ E can only be either the primary link, backup link, or idle link. Wireless links (,) and (,) that meet the following conditions will interfere with each other. (1) , or , or , or ; (2) The two links are allocated the same channel, i.e., .
The allocated channel set of links (u,v) is denoted as K(u,v), which is given by
K(u,v) = Ku ∩ Kv
I(u,v) represents the set of all the links that interfere with the link (u,v). If the link (u,v) is allocated a different channel, the I(u,v) is different. Ik(u,v) denotes the link set that interferes with the link (u,v) allocated the channel k, which is given by
Definition 4.
Interference degree, which means the number of links in the Ik(u,v).
denotes the primary link set that interferes with the link (u,v) allocated the channel k, which is given by
Definition 5.
Primary link interference degree, which is the number of links in the set .
denotes the backup link set that interferes with the link (u,v) allocated the channel k, which is given by
Definition 6.
Backup link interference degree, which is the number of links in the set .
denotes the idle link set that interferes with the link (u,v) allocated the channel k, which is given by
Definition 7.
Idle link interference degree, which is the number of links in the set .
The set of link loads is denoted as , and the load of the link (u,v) on channel k is denoted as Mbps. The available bandwidth of the link (u,v) on channel k is denoted as , which is given by
where is the proportion of the bandwidth of the link (,) used to transmit load .
3. Multipath Routing and Spectrum Allocation Algorithm
This section first describes the basic ideas of multipath routing and the spectrum allocation algorithm, and then provides the pseudo-code algorithm. The primary path routing and spectrum allocation algorithm and the backup path routing and spectrum allocation algorithm are introduced in Section 4 and Section 5.
3.1. Fundamental
The multipath routing and spectrum allocation algorithm (MRIR) is proposed in this section. The fundamental idea is as follows: first, for each link (u,v), the set of available channels of the link and the remaining bandwidth of each channel is calculated. If the link (u,v) is allocated a channel, then the remaining bandwidth of the allocated channel is less than the wireless request bandwidth constraint, or, the link (u,v) is not allocated a channel, but the maximum bandwidth of all the available channels is less than the wireless request bandwidth constraint, then the link (u,v) is hidden. This means that the link (u,v) is not included in the path construction (Lines 1 to 13 in Algorithm 1). Second, the primary path routing construction and spectrum allocation is completed. If the primary path satisfying the QoS constraint is constructed, then the backup path that satisfies the QoS constraint is constructed. If the primary or backup path satisfying the QoS constraint cannot be constructed, then the wireless request is rejected (Lines 14 to 28 in Algorithm 1). Third, the hidden edges of G are shown (Line 29 in Algorithm 1).
The primary path routing construction algorithm (PPC) and primary path spectrum allocation algorithm (PPSR) in Lines 14 and 16 of Algorithm 1 are presented in Section 4.1 and Section 4.2, respectively. The backup path routing construction algorithm (BPC) and backup path spectrum allocation algorithm (BPSR) in Lines 19 and 20 of Algorithm 1 are presented in Section 5.1 and Section 5.2, respectively.
3.2. MRIR Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. The multi-path routing and spectrum allocation algorithm MRIR. | |
| Input: G = (V,E), γi = (si,di,bi) | |
| Output: ,, x(v,u) | |
| (1) | while (){ |
| (2) | calculate K(u,v) according to Equation (1); |
| (3) | while (){ |
| (4) | calculate according to Equation (6); |
| (5) | }//end while |
| (6) | if (x(u,v) ≠ 0&&) { |
| (7) | Hide (u,v); |
| (8) | }//end if |
| (9) | if(x(u,v) = 0){ |
| (10) | C Max{} ; |
| (11) | if(C < bi) hide (u,v); |
| (12) | }//end if |
| (13) | }//end while |
| (14) | PPC(γi); |
| (15) | if( found) { |
| (16) | if(PPSR() = 0){ |
| (17) | reject γi; |
| (18) | }else{ |
| (19) | BPC(γi); |
| (20) | if ( found && BPSR() = 1){ |
| (21) | accept γi; |
| (22) | }else{ |
| (23) | reject γi; |
| (24) | }//end if |
| (25) | }//end if |
| (26) | }else{ |
| (27) | reject γi; |
| (28) | }//end if |
| (29) | Show all hidden edges of G |
4. Primary Path Routing Construction and Spectrum Allocation Algorithm
The primary path routing construction algorithm (PPC) and the primary path spectrum allocation algorithm (PPSR) are presented in this section. The goal of the proposed algorithm was to improve the network throughput and wireless request acceptance ratio. Multipath routing is an effective method to improve network throughput. Meanwhile, improving the wireless request acceptance ratio can further improve the network throughput.
To improve the wireless request acceptance ratio, the proposed algorithm saves the use of network resources to accept more wireless requests. The use of a channel interference and reusability strategy to save network resources is presented. For the primary path construction, a primary path construction algorithm based on the interference degree is proposed. As the primary path and the backup path are not transmitted at the same time, the wireless link with a high degree of link interference will have a low value. However, we wanted to generate less interference between the primary paths of different wireless requests. Therefore, the link with a lower degree of primary link interference will have a lower weight, and the link with a higher degree of idle link interference has a lower weight.
The weight of the link (u,v) allocated channel is denoted as , which is given by
where , and are the primary link interference degree, backup link interference degree, and idle link interference degree, respectively.
If the link (u,v) is allocated channel , then . If the link (u,v) is not allocated a channel, then is the minimum of the on all of the available channels, which is given by
The allocated channel of link (u,v) is denoted as when the minimum of the is obtained, which is given by
4.1. Primary Path Construction Algorithm
The primary path construction algorithm (PPC) contains the following steps: First, if the link (u,v) belongs to the backup path of some wireless request, then the link (u,v) is hidden. The purpose is not to include the backup link in the process of constructing the primary path. If the link (u,v) does not belong to the backup path of some wireless request, then the link weight of all the available channels is calculated according to Equation (8). Second, the primary path is constructed using the Dijkstra algorithm. If a primary path is constructed, then the is returned, otherwise, the null path is returned.
| Algorithm 2. PPC | |
| Input: G = (V,E),γi = (si,di,bi) | |
| Output: | |
| (1) | while (){ |
| (2) | if((u,v) is Backup link for the accepted request){ |
| (3) | Hide (u,v); |
| (4) | }else{ |
| (5) | while (){ |
| (6) | Calculate according to Equation (8); |
| (7) | }//end while |
| (8) | }//end if |
| (9) | }//end while |
| (10) | Dijkstra(); |
| (11) | if( is found){ |
| (12) | return ; |
| (13) | }else{ |
| (14) | return null; |
| (15) | }//end if |
4.2. Primary Path Spectrum Allocation Algorithm
When the primary path is constructed, a channel on each link of the path is allocated. The primary path spectrum allocation algorithm (PPSR) is proposed in this section. The PPSR algorithm is seen in Line 16 of Algorithm 1.
For each link (u,v) in the primary path , if the link (u,v) is allocated a channel, then its previously allocated channel is used continually. If the link (u,v) is not allocated a channel, then the channel on the link is allocated through Equation (10). However, when the primary path is allocated a channel, the situation that is shown in Figure 1 may occur. The following example illustrates the situation, and the solution is also presented.
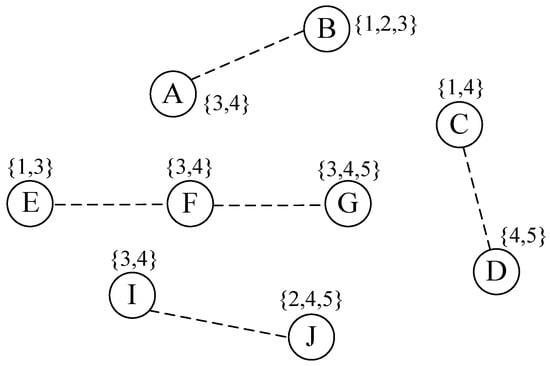
Figure 1.
The situation of bandwidth constraints cannot be met.
We assume that γ1 = (A,B,8), γ2 = (C,D,10), and γ3 = (I,J,12) is the accepted wireless request. The primary path of γ1, γ2, and γ3 are , , and , respectively. The new arriving wireless request is γ4 = (E,G,6). Table 1 shows the results of the wireless link weight when the link (E,F) and (F,G) are allocated different channels.

Table 1.
The link weight of (E,F) and (F,G).
The calculating formula of is given by
For the convenience of depiction, the backup path of the accepted wireless request is not shown in Figure 1. Hence, and .
We can see from Table 1 that the primary path of γ4 is constructed by the PPC algorithm. Interflow interference is not considered by the PPC algorithm, which means that the available bandwidth of the wireless link (E,F) and (F,G) is shown in Equations (11) and (12) before the link (E,F) allocated on channel 3.
We can see that the available bandwidth of (E,F) and (F,G) can meet the needs of the bandwidth constraints of γ4. However, after the available bandwidth of links (E,F) and (E,F) is allocated to channel 3, then the available bandwidth of link (F,G) is given by
We can see that the available bandwidth of link (F,G) could not meet the need of the bandwidth constraints of γ4. To solve the problem shown in Figure 1, the allocated channel of the link was adjusted. The basic idea was to sort the link (u,v) on each channel according to the non-descending order of the value of . If the link (u,v) on channel k with the residual bandwidth was larger than the bandwidth constraint bi, and less was found, then the channel k was allocated to link (u,v).
The fundamental idea of the PPSR algorithm is as follows: for all of the links (u,v) of , if the link (u,v) is allocated a channel, then the link keeps the same allocated channel. If the link (u,v) is not allocated a channel, then the following strategy is used to allocate the channel. Channel k is selected according to Equation (10), and the residual bandwidth is calculated according to Equation (6). If is larger than bi, then the channel k is allocated to link (u,v). If there is a link that cannot meet the QoS constraint, then the tag variable flag is set to 0, which means that the request cannot be accepted.
| Algorithm 3. PPSR | |
| Input: G = (V,E), γi = (si,di,bi), | |
| Output: x(u,v) | |
| (1) | Flag ← 1; |
| (2) | while (){ |
| (3) | if( x(u,v) = 0){ |
| (4) | Calculate according to Equation (9); |
| (5) | k; |
| (6) | Calculate according to Equation (6); |
| (7) | if(bi > ){ |
| (8) | Sort ascending; |
| (9) | while(){ |
| (10) | if(bi < ){ |
| (11) | x(u,v); |
| (12) | break; |
| (13) | }//end if |
| (14) | }//end while |
| (15) | }else{ |
| (16) | x(u,v); |
| (17) | }//end if |
| (18) | }//end if |
| (19) | if(x(u,v) = 0){ |
| (20) | flag ← 0; |
| (21) | break; |
| (22) | }//end if |
| (23) | }//end while |
| (24) | return flag |
5. Backup Path Routing and Spectrum Allocation Algorithm
The backup path routing construction algorithm (BPC), which is based on channel interference and reusability, and the backup path spectrum allocation algorithm (BPSR) are presented in this section.
The link weight function based on channel interference and reusability was proposed. The weight function of link (u,v) on channel k is given by
where and are the primary link interference degree and interference link reuse degree (u,v) on channel k, respectively. Then, is given by
where A{•} is the condition function to judge whether it is true. denotes whether the backup link (u,v) and the primary link (a,b) that is a link in the primary path for the accepted request interfere each other.
We can see that a higher primary link interference degree and the interference link reuse degree leads to a lower link weight.
If the link (u,v) is allocated to channel before, then . If the link (u,v) is not allocated to any channel, then is set to the minimum of on all of the channels, which is given by
The allocated channel of link (u,v) when obtains the minimum is , which is given by
5.1. Backup Path Construction Algorithm
The backup path construction algorithm (BPC) contains the following steps: first, if the link (u,v) belongs to the primary path of some wireless request, then the link (u,v) is hidden. The purpose is not to include the primary link in the process of constructing the backup path. If the link (u,v) does not belong to the primary path of some wireless request, thent the link weight of all the available channels is calculated according to Equation (14). Second, the backup path is constructed using the Dijkstra algorithm. If a backup path is constructed, then is returned, otherwise, the null path is returned.
| Algorithm 4. BPC | |
| Input: G = (V,E), γi = (si,di,bi) | |
| Output: | |
| (1) | while (){ |
| (2) | if((u,v) is Primary link for the accepted request){ |
| (3) | Hide (u,v); |
| (4) | }else{ |
| (5) | while ()){ |
| (6) | Calculate according to Equation (14); |
| (7) | }//end while |
| (8) | }//end if |
| (9) | }//end while |
| (10) | Dijkstra(); |
| (11) | if( is found){ |
| (12) | While ((∀ u,v) ∈ ){ |
| (13) | Calculate according to Equation (15); |
| (14) | } |
| (15) | return ; |
| (16) | }else{ |
| (17) | return null; |
| (18) | }//end if |
5.2. Backup Path Spectrum Allocation Algorithm
When the backup path is constructed, the channel on each link of the path is allocated. The backup path spectrum allocation algorithm (BPSR) is proposed in this section. The BPSR algorithm is seen in Line 20 of Algorithm 1.
The fundamental idea of the BPSR algorithm is as follows: for all link (u,v) of , if the link (u,v) is allocated a channel, then the link keeps the same allocated channel. If the link (u,v) is not allocated a channel, then the following strategy is used to allocate the channel. The channel is selected according to Equation (18).
If the link (u,v) and the link (a,b) (which is a primary link of the primary path for γi,) are allocated the same channel, the two links interfere with each other, so then the channel is allocated to (u,v), and the load on channel is set to 0, . If not, then the channel is allocated to (u,v), and the load on channel is set to , .
It is also possible that the bandwidth constraints cannot be satisfied as per Figure 1 in the BPSR algorithm. The same channel adjustment strategy can be used to solve the problem. If there is a link that cannot meet the QoS constraint, then the tag variable flag is set to 0, which means that the request could not be accepted.
| Algorithm 5. BPSR | |
| Input: G = (V,E), γi = (si,di,bi), , | |
| Output: x(u,v) | |
| (1) | flag ← 1; |
| (2) | while (){ |
| (3) | Calculate according to Equation (17); |
| (4) | if(x(u,v) = 0){ |
| (5) | while(){ |
| (6) | if( = x(a,b)){ |
| (7) | x(u,v); |
| (8) | k ← x(u,v); |
| (9) | ; |
| (10) | break; |
| (11) | }//end if |
| (12) | }//end while |
| (13) | }//end if |
| (14) | if(x(u,v) = 0){ |
| (15) | k ; |
| (16) | Calculate according to Equation (6); |
| (17) | if(bi > ){ |
| (18) | sort ascending; |
| (19) | while(){ |
| (20) | if(bi < ){ |
| (21) | x(u,v) ← k; |
| (22) | ; |
| (23) | break; |
| (24) | }//end if |
| (25) | }//end while |
| (26) | if(x(u,v) = 0){ |
| (27) | flag 0; |
| (28) | break; |
| (29) | }//end if |
| (30) | }else{ |
| (31) | x(u,v) ; |
| (32) | k ; |
| (33) | ; |
| (34) | }//end if |
| (35) | }//end if |
| (36) | }//end while |
| (37) | return flag |
6. Simulation and Results
In this section, we present a comprehensive evaluation on the performance of MRIR, Route-Stability [17], and the Route-Closeness [18] algorithm using Matlab R2010a (7.10, MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA, 2010.9). The network topology region size was 2000 m × 2000 m, and TR = 50 m, IR = 100 m. |V| = 60 represents the number of Secondary Users (SUs). Ten primary users (PUs) were randomly distributed in the area. The PUs randomly occupied and accessed the authorized channel. If the PUs needed to access the authorization channel again, then the SUs needed to quit the use of the authorized channel, which led to the failure of the wireless link to the SUs. In this simulation, the time and duration of the access channel of each PU node were randomly generated. The available channel number was |K| = 12, and the bandwidth of each channel was randomly generated in the range of 0–50 Mbps. The wireless request demand bandwidth bp was also randomly generated in the range of 0–20 Mbps. The wireless requests randomly arrived and departed. In a duration time of 1800 s, the arrival wireless request was |∆| = 20. The following simulation results were the mean of 200 independent simulation results. The simulation was mainly based on the number of wireless requests, the number of available channels as parameters, the analysis and comparison of the average throughput, and the wireless request acceptance rate.
6.1. Comparison Average Throughput
The average throughputs with different numbers of requests are shown in Figure 2. From Figure 2, we can see that the average throughput decreased with the increments of the number of requests for the three algorithms. In the case that network resources were unchanged, this was because the number of wireless requests increased, therefore increasing the probability of link failure. The average throughput of the MRIR was higher than the Route-Stability and Route-Closeness. This was because the MRIR can save network resources based on channel interference and reusability for accepting more wireless requests, which can improve the average throughput for the MRIR. When the wireless request was |∆| = 40, the average throughput of MRIR was 33% and 35% higher than that of the Route-Stability and Route-Closeness.
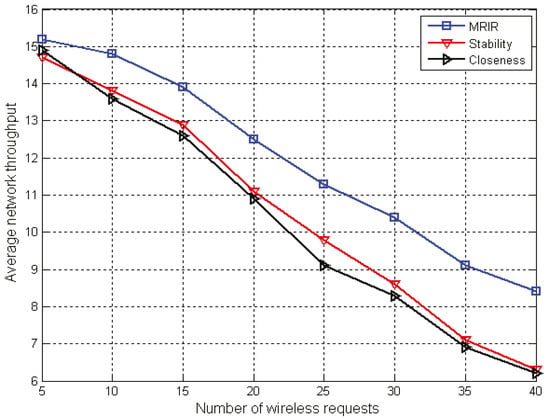
Figure 2.
Average throughput with different numbers of requests.
From Figure 3, we can also see that the average throughput increased with the increment of the number of available channels for the three algorithms. This was because the probability of link failure was reduced when the available channel increased. When the number of available channels was |K| = 6, the average throughput of the MRIR was 46% and 51% higher than that of the Route-Stability and Route-Closeness.
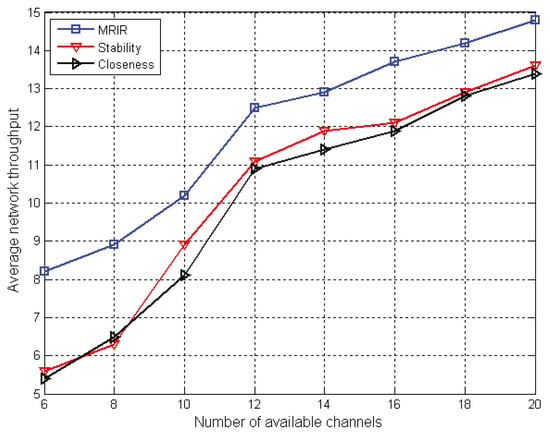
Figure 3.
Average throughput with different numbers of available channels.
6.2. Comparison Wireless Acceptance Ratio
The wireless acceptance ratios with a different number of requests are shown in Figure 4. From Figure 4, we can see that when the number of wireless request was |∆| = 5, the wireless acceptance ratio of the three algorithms was one. This meant that the five wireless requests could be accepted. When the number of wireless requests was larger than five, then the wireless acceptance ration was higher than the other two algorithms because MRIR uses the strategy of interference link reuse, which can effectively save the network resources. With the increase of wireless requests, MRIR’s advantage was more obvious. When the wireless request was |∆| = 40, the wireless acceptance ratios of MRIR were 32% and 37% higher than that of the Route-Stability and Route-Closeness.
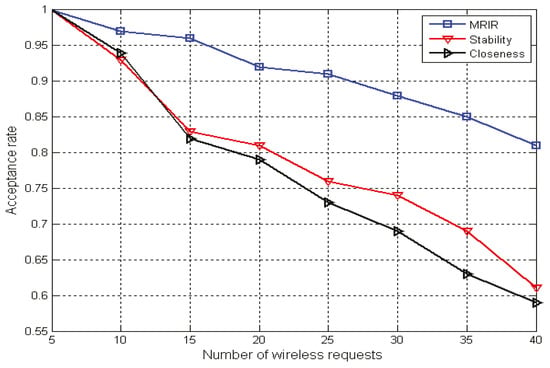
Figure 4.
Acceptance ratio with different numbers of requests.
From Figure 5, we can see that the wireless acceptance ratio increased with the increment of the number of available channels for the three algorithms. This was because more wireless requests could be accepted when the number of available channels increased. When the number of available channels was |K| = 6, the wireless acceptance ratios of MRIR were 77% and 81% higher than that of the Route-Stability and Route-Closeness.
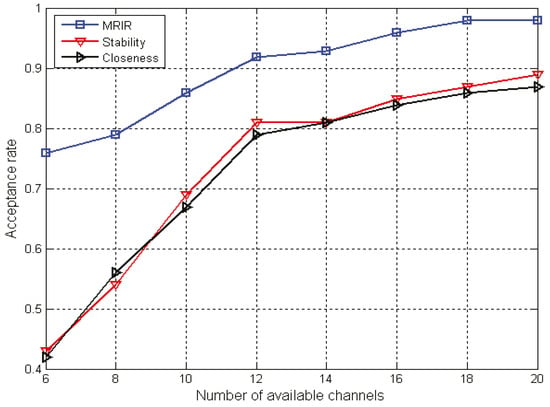
Figure 5.
Acceptance rate with different numbers of available channels.
7. Conclusions
Aiming at the problem of link failure in CWMNs, this paper studied the problem of multipath routing and spectrum allocation, which aims to improve the network throughput and the wireless request acceptance ratio, and satisfy the QoS constraint. A multipath routing and spectrum allocation algorithm based on channel interference and reusability was proposed, which included the primary path construction and spectrum allocation algorithm, as well as the backup path construction and spectrum allocation algorithm. In the primary path construction and backup path construction, different link weight functions were proposed. For each new wireless request arrival, a primary path and a backup path were constructed. The simulation results showed that the MRIR could achieve the goal of improving the network throughput and wireless request acceptance ratio. The throughput and acceptance ratio of the MRIR algorithm was higher than that of the Route-Stability and Route-Closeness algorithms. The multipath routing and spectrum allocation algorithm based on power control to meet the QoS constraints is an interesting topic to explore in the future.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61309027, 61772553, 61702562, and 61702561; the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department under No. 13B148; the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under No. 2013M542136; and the Key Research and Development Project of Hunan Science and Technology Plan Project under No. 2016SK2028.
Author Contributions
Zhufang Kuang and Gongqiang Li reviewed the multipath routing algorithm in cognitive wireless mesh network in recent years; Junshan Tan and Zhigang Chen classified the various algorithms, and analyzed the data; Gongqiang Li collected the data; Zhufang Kuang drafted the manuscript; Zhufang Kuang and Junshan Tan revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chowdhury, K.R.; Akyildiz, I.F. Cognitive wireless mesh networks with dynamic spectrum access. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2008, 26, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitola, J., III. Cognitive radio: Making software radio more personal. IEEE Pers. Commun. 1999, 6, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, E.; Mukerjee, B. A Survey on routing algorithms for wireless Ad-Hoc and mesh networks. Comput. Netw. 2012, 56, 940–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, Y.; Salim, F.; Rehmani, M.H. Routing and channel selection from cognitive radio network’s perspective: A survey. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2015, 42, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abdelatif, M.; Chen, L.; Vasilakos, A.V. Routing Metrics of Cognitive Radio Networks: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, R.M.; Dziong, Z. An Economic Framework for Routing and Channel Allocation in Cognitive Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2014, 11, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherif, A.A.; Mohamed, A. Joint Routing and Resource Allocation for Delay Minimization in Cognitive Radio Based Mesh Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, N.; Kean, C.W.; Mohamad, H.; Alias, M.Y. A novel opportunistic spectrum aware routing for cognitive radio wireless mesh network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, Shanghai, China, 13–15 October 2014; pp. 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. A genetic approach on cross-layer optimization for cognitive radio wireless mesh network under SINR model. Ad Hoc Netw. 2015, 27, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Mutka, M.W. A decision tree cognitive routing scheme for cognitive radio mesh networks. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2015, 15, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.L.; Guo, M.Y.; Guo, S.; Xu, C.-Z. Mobility Prediction Based Joint Stable Routing and Channel Assignment for Mobile Ad Hoc Cognitive Networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2016, 27, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.K.; Wang, X.B.; Tian, X.H.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Q. Two-Dimensional Route Switching in Cognitive Radio Networks: A Game-Theoretical Framework. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2015, 23, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.C.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J.C.; Zhang, Y.C. TIGHT: A Geographic Routing Protocol for Cognitive Radio Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 4670–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, S.Y.; Aijaz, A.; Holland, O.; Aghvami, A.H. SACRP: A Spectrum Aggregation-Based Cooperative Routing Protocol for Cognitive Radio Ad-Hoc Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 2015–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.-F.; Chen, Z.-G.; Wang, G.-J.; Liu, H. A Secure and High Throughput Routing Protocol with QoS Constraints in Cognitive Wireless Mesh Networks. J. Commun. 2014, 35, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Deepti, S.; Murthy, G.R. Cognitive cross-layer multipath probabilistic routing for cognitive networks. Wirel. Netw. 2015, 21, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Lian, X. Spectrum Aware Highly Reliable Routing in Multihop Cognitive Radio Networks. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing, (WCSP 2009), Nanjing, China, 13–15 November 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Beltagy, I.; Youssef, M.; El-Derini, M. A new routing metric and protocol for multipath routing in cognitive networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on wireless communication and networking conference (WCNC2011), Cancun, Mexico, 28–31 March 2011; pp. 974–979. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Juboori, S.; Hussain, S.J.; Fernando, X. Cognitive Spectrum Sensing with Multiple Primary Users in Rayleigh Fading Channels. Electronics 2014, 3, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).