A Low Energy Consumption DOA Estimation Approach for Conformal Array in Ultra-Wideband
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Application of LDPA
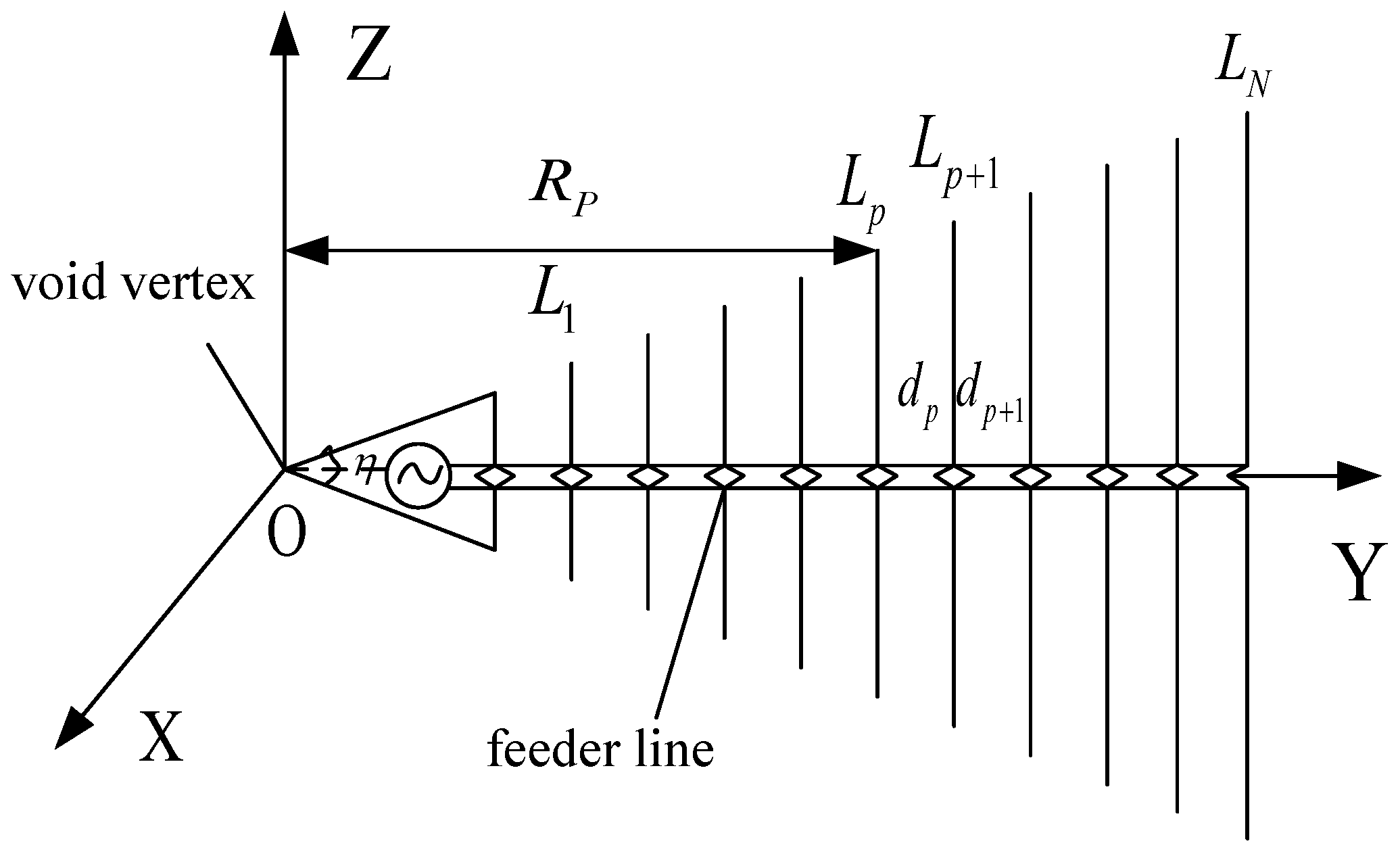
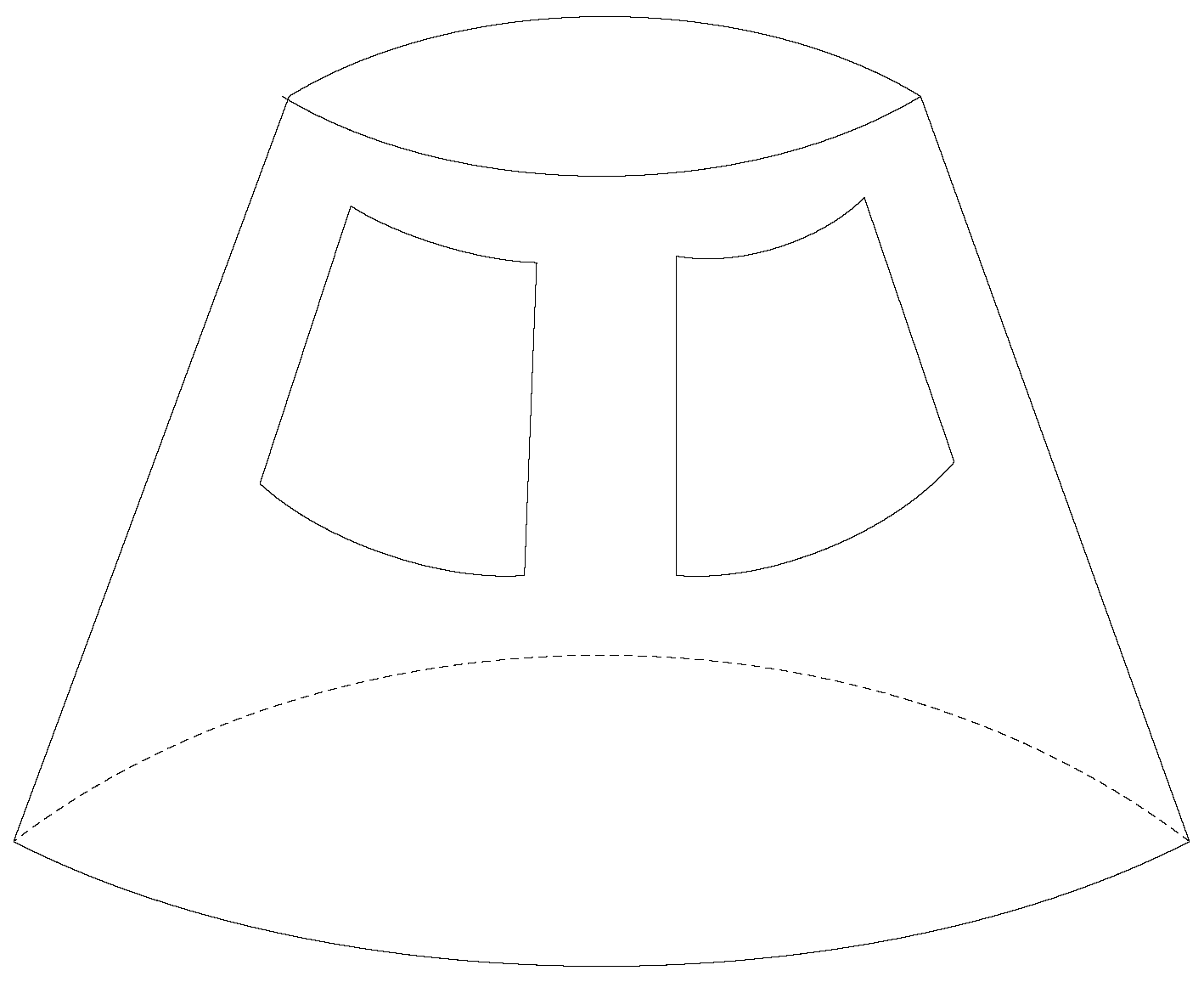
3. The Principle of Arbitrary Baseline Algorithm
3.1. The Model of the Incident Signal
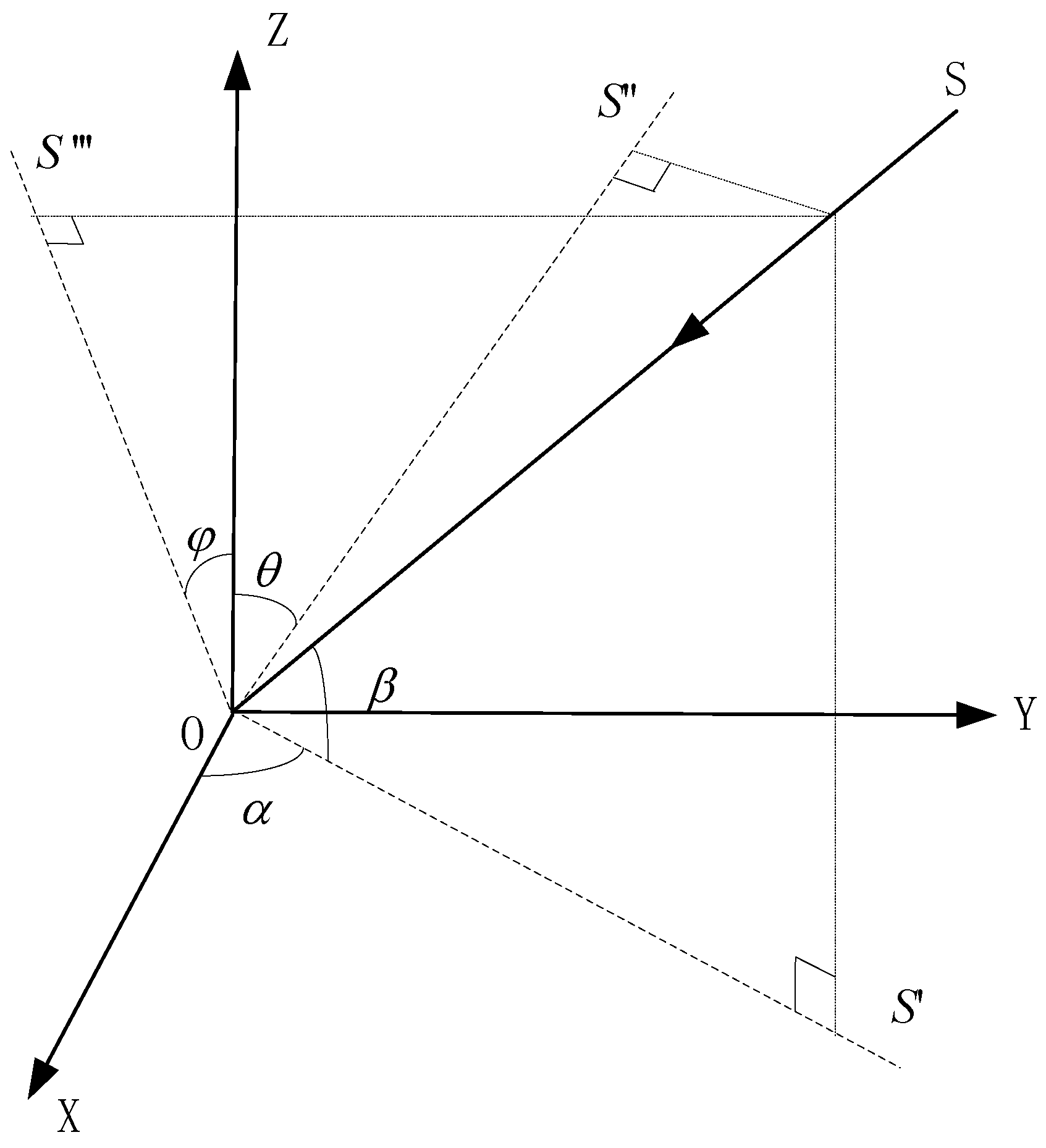
3.2. The 2D Arbitrary Baseline Algorithm
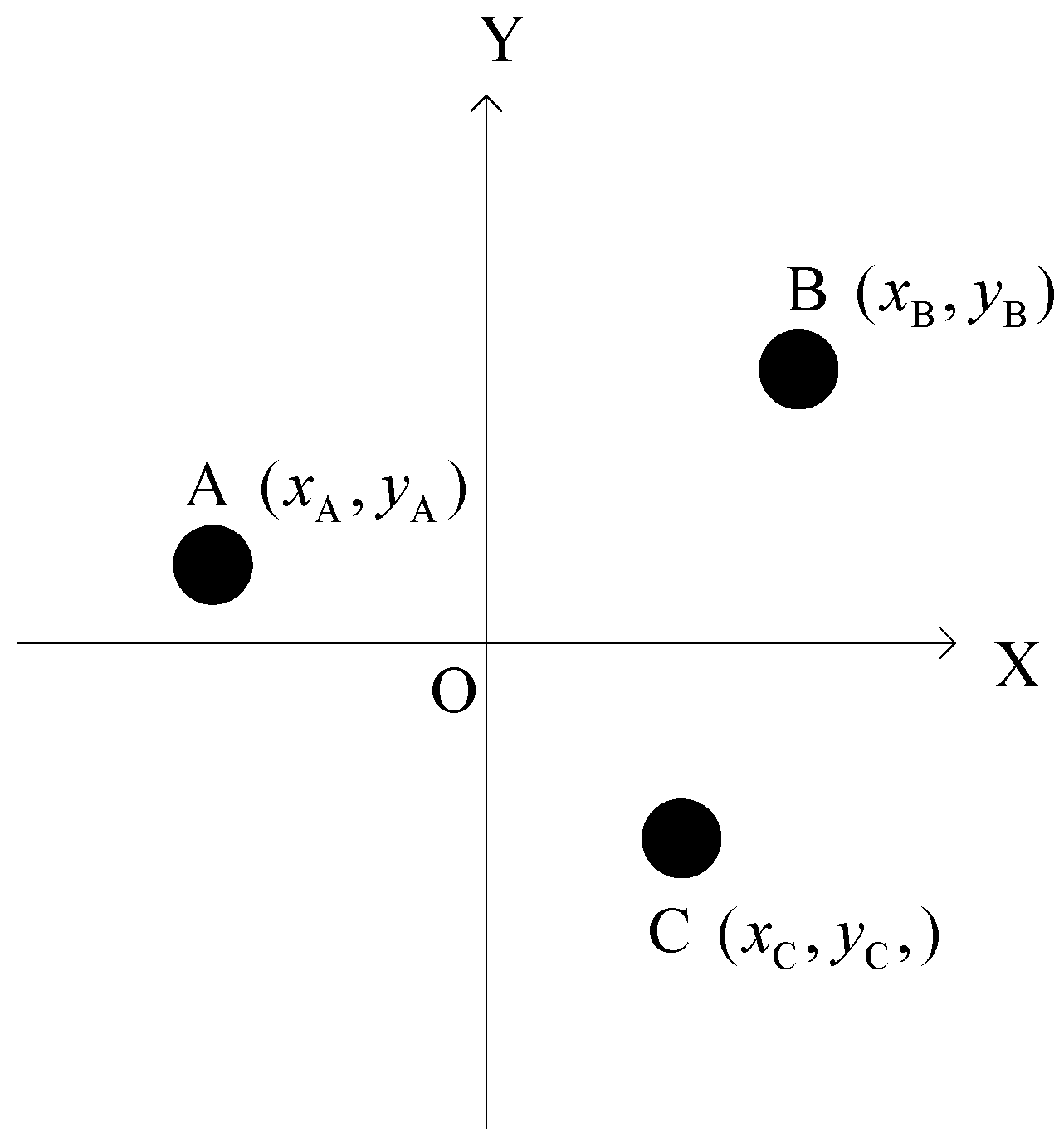
4. The 3D Arbitrary Baseline Algorithm
4.1. The Principle of 3D Arbitrary Baseline Algorithm
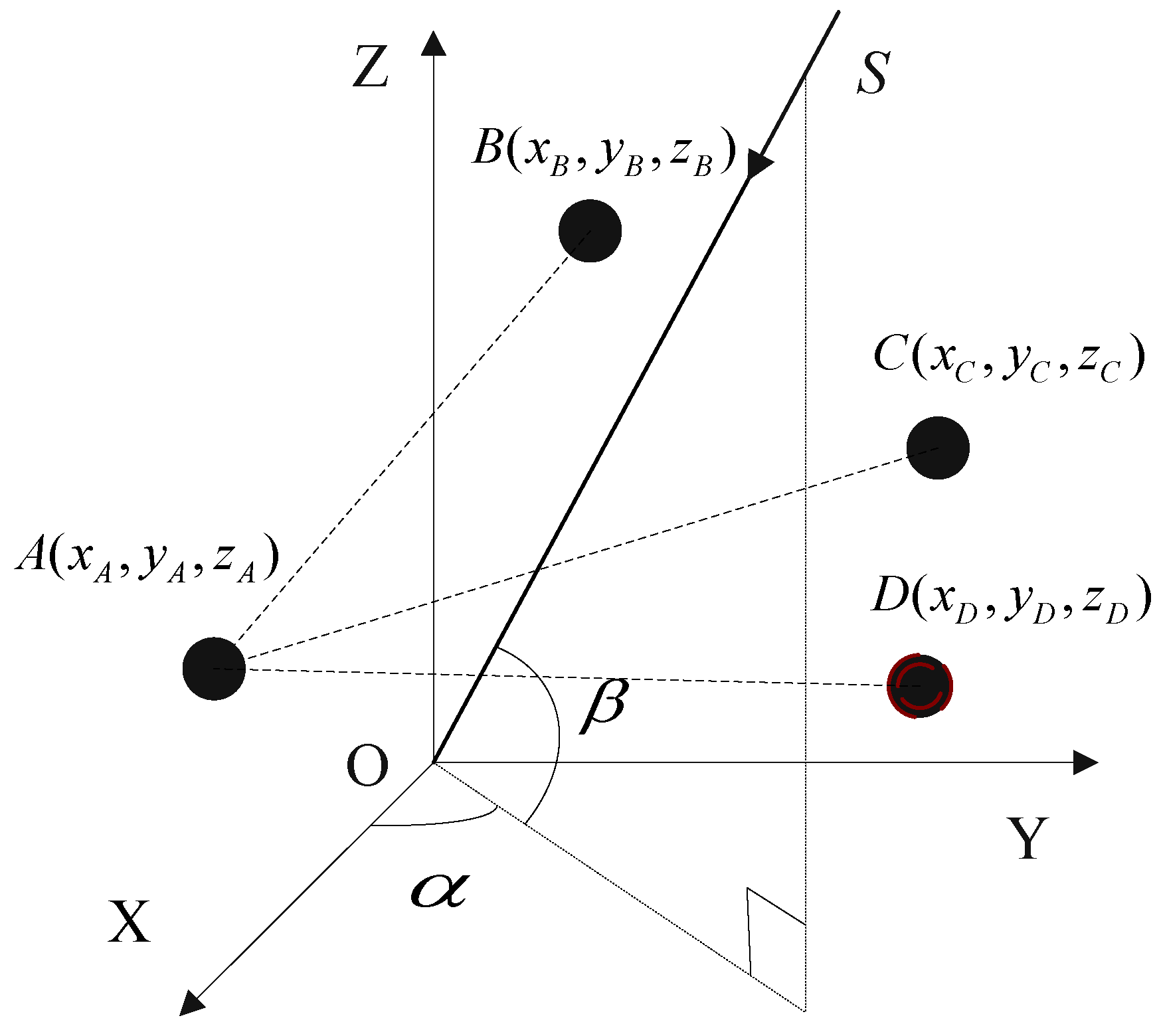
4.2. The Virtual Elements Based on Virtual Baseline
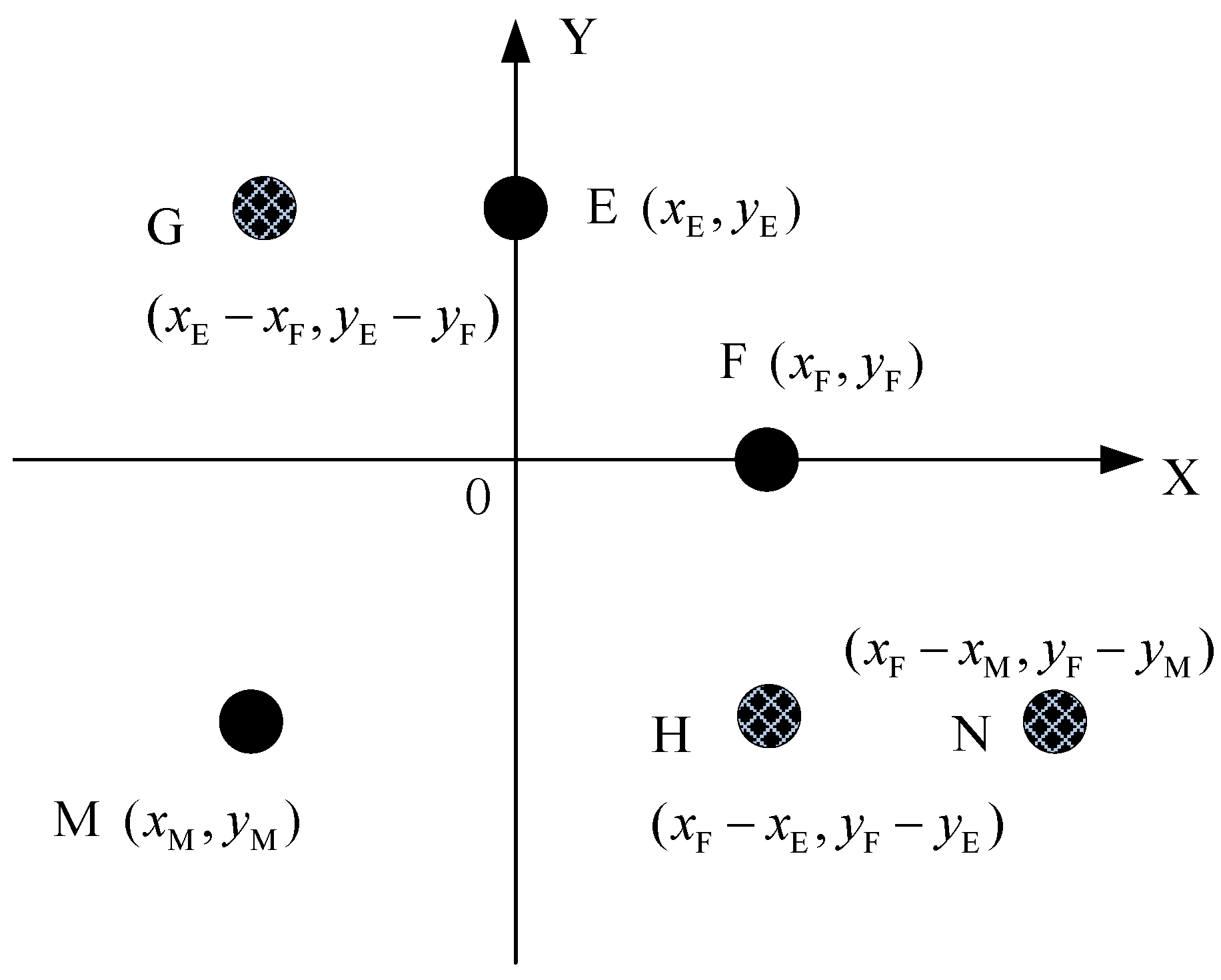
4.3. The Solving Ambiguous Method Based on Rotation Comparison
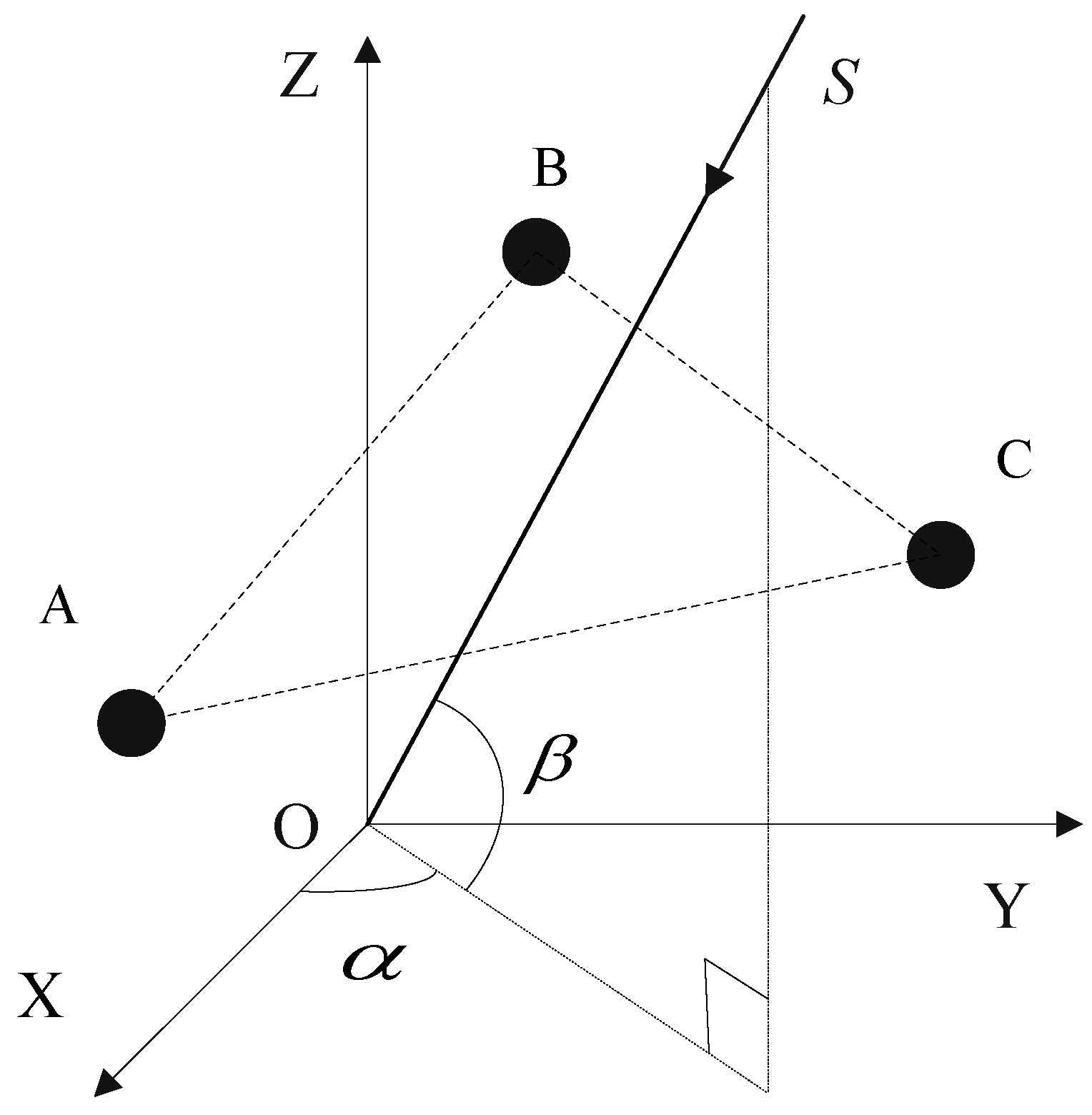
5. The Algorithm Based on Conformal Antenna
5.1. The Pre-Processing of Sub-Array Divided Technique
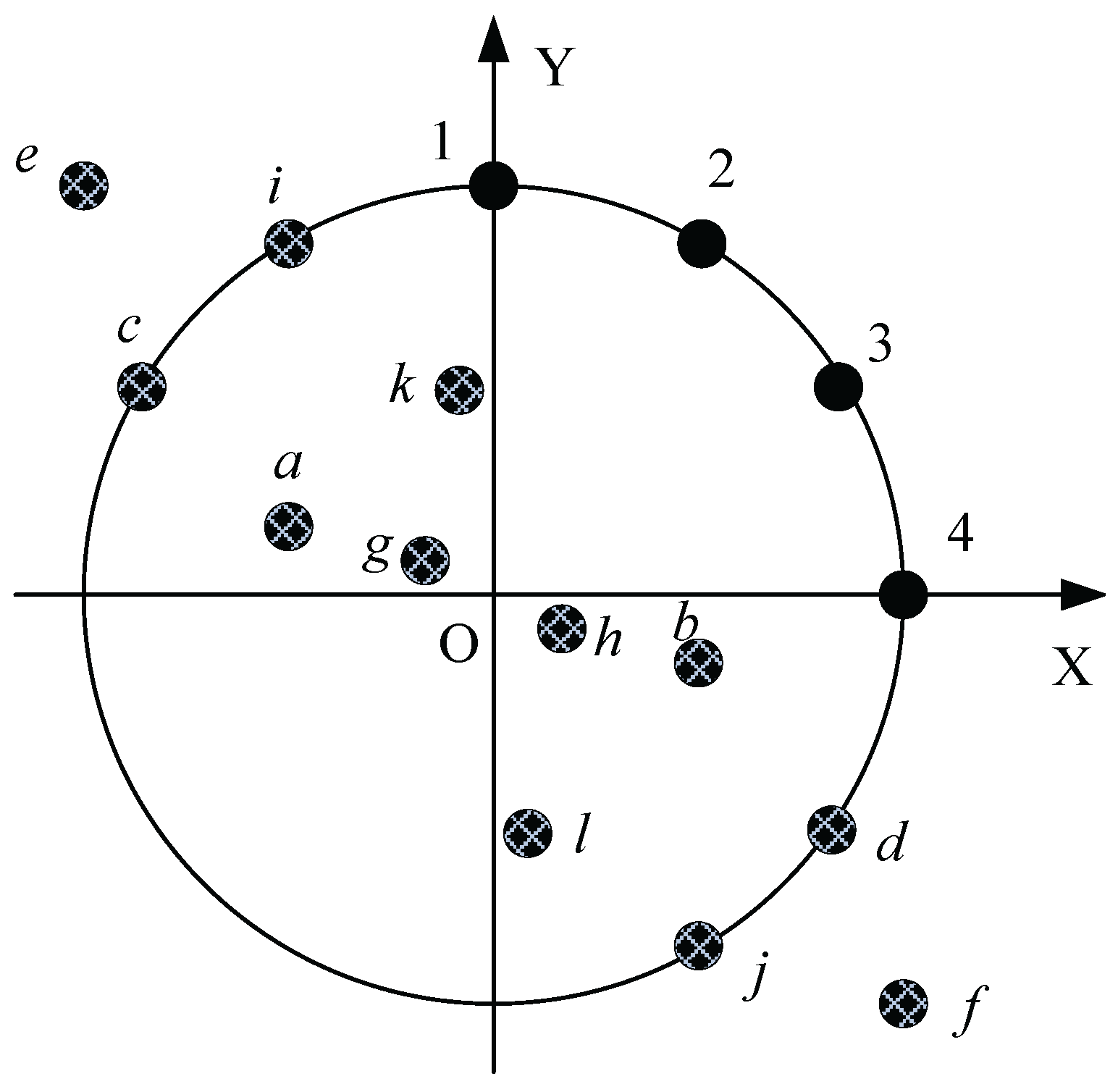
5.2. The Algorithm Step
- The array antennas mounted on aircraft are arranged reasonably. Two combinations are selected in each sub-array for direction finding, the four antenna elements (including the virtual elements) constitute a combination;
- The azimuth α and the elevation β can be obtained by solving Equations (16) or (17) of one combination. By checking whether and are positive or negative, the mirrored ambiguous problem can be solved. All values including ambiguous values are obtained, which will be recorded as the first solution;
- Apply the same procedure for another combination as step 2;
- According to Equation (20), the 2D-DOA of the incident signal can be obtained;
- Comparing the 2D-DOA of each sub-array (There is a greater difference between the error angle and the real angle due to the “shadow effect”), the closest value of each sub-array’s 2D-DOA is regarded as the real value, and the average value is calculated. Using transformation Equations (2) and (3), the course angle θ and pitching angle can be obtained finally.
6. The Analysis of Direction Finding Error
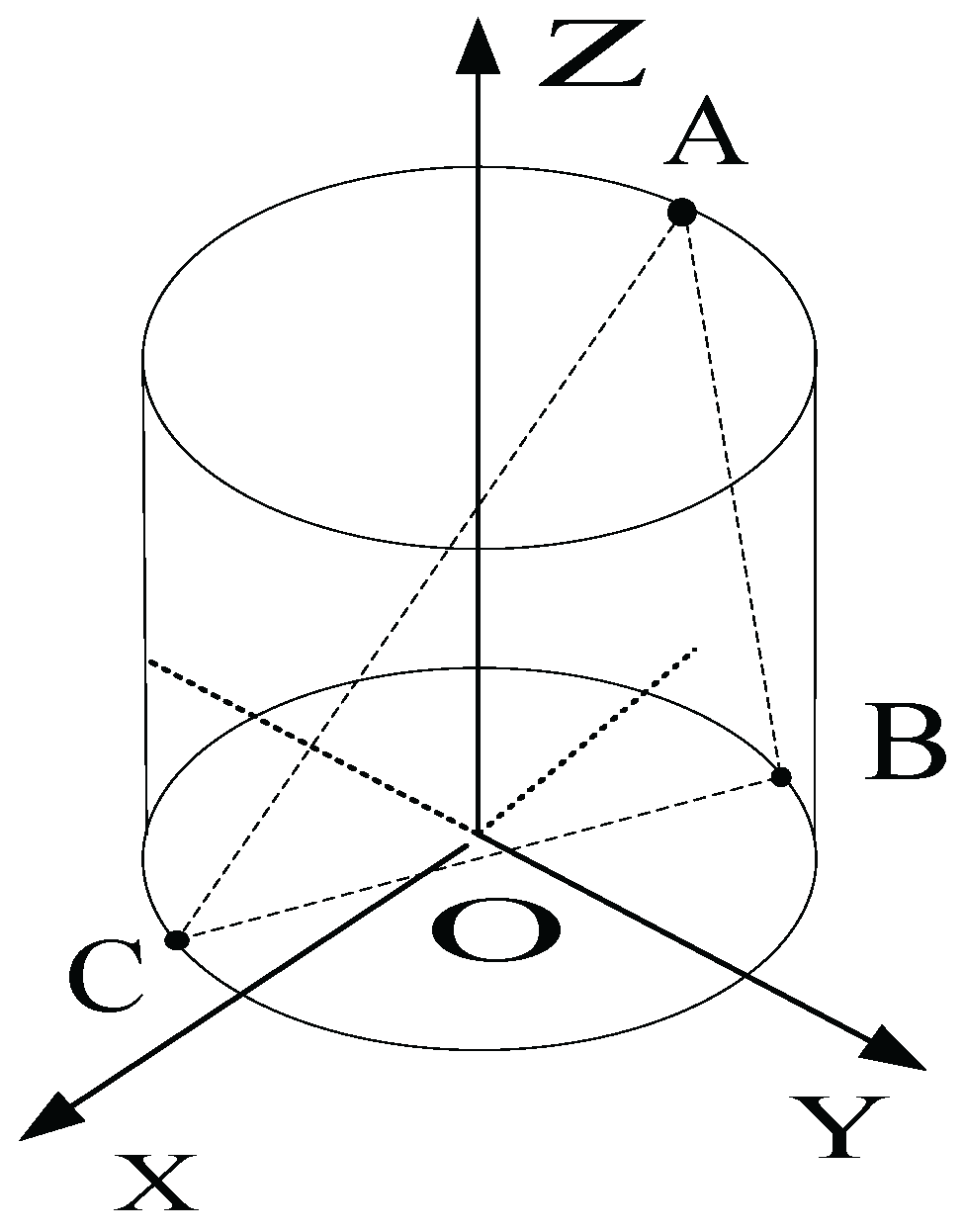
7. Simulation Results
7.1. The Antenna Model

7.2. Simulation Results
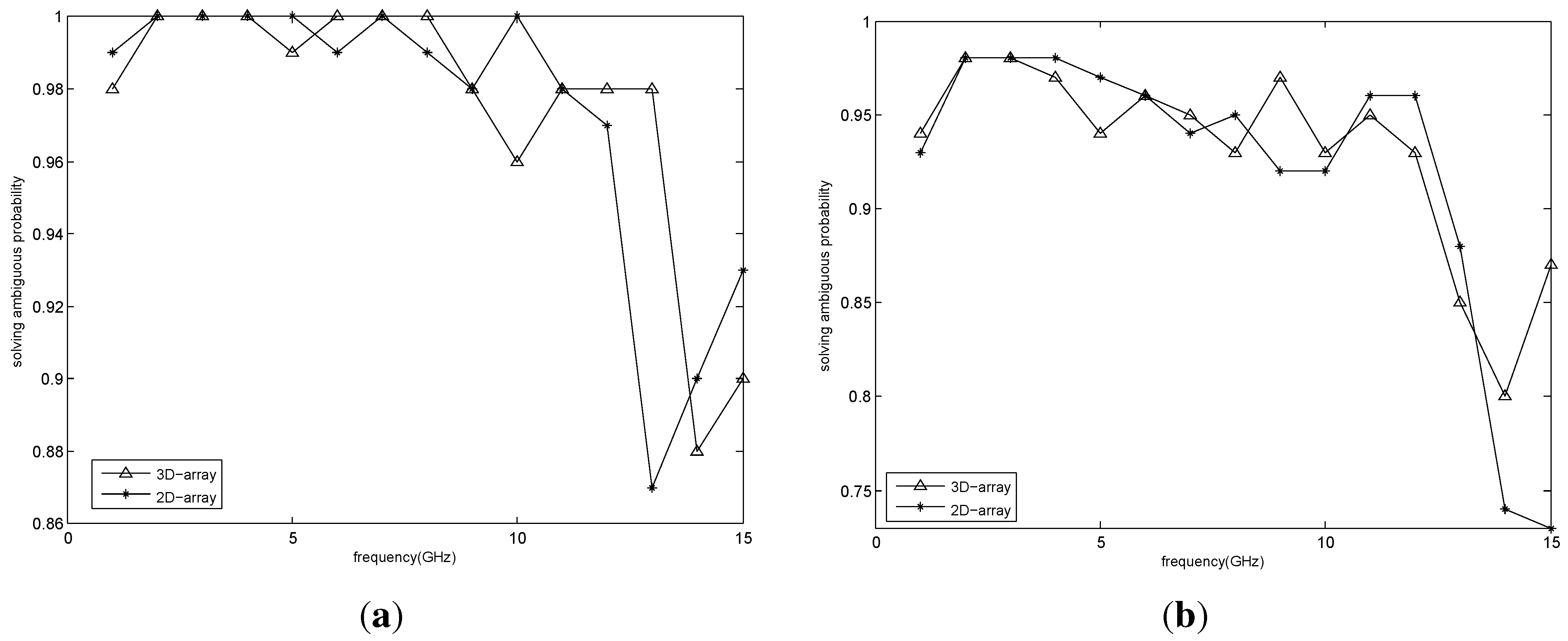
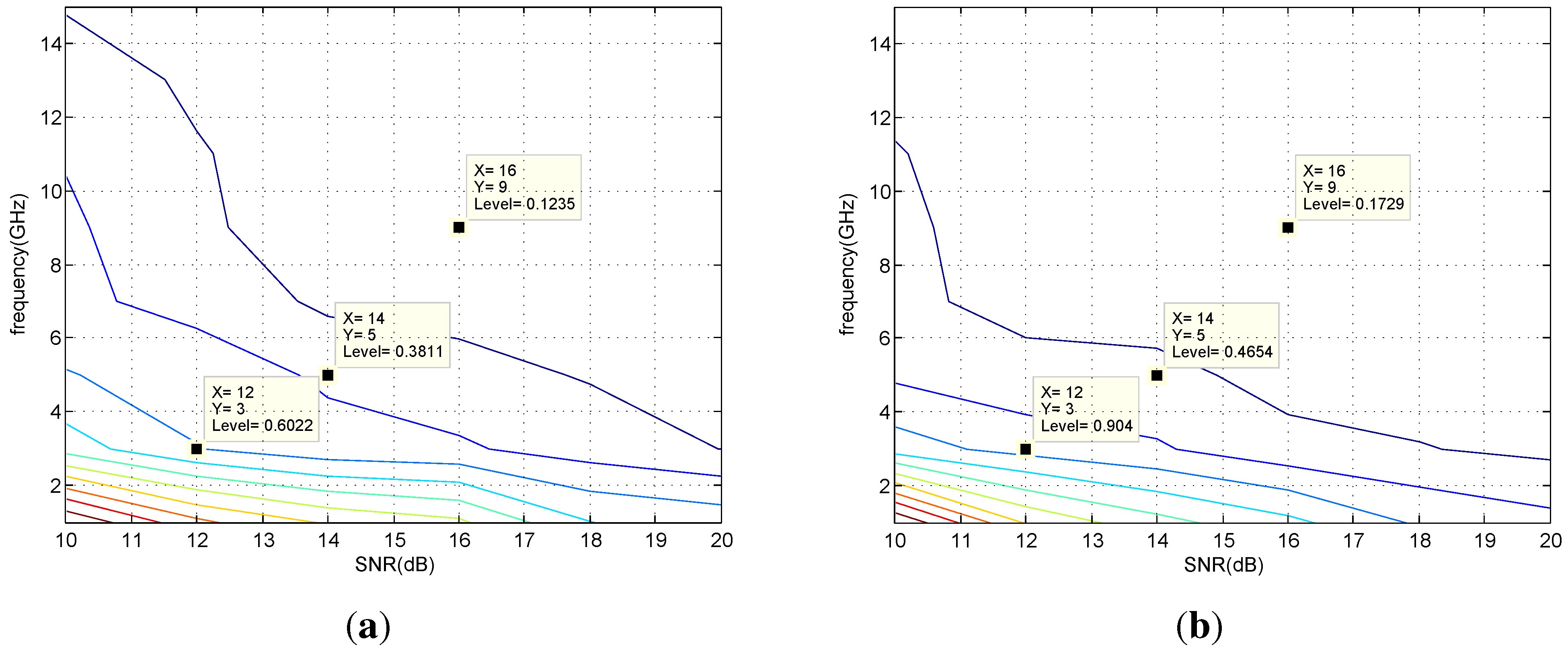
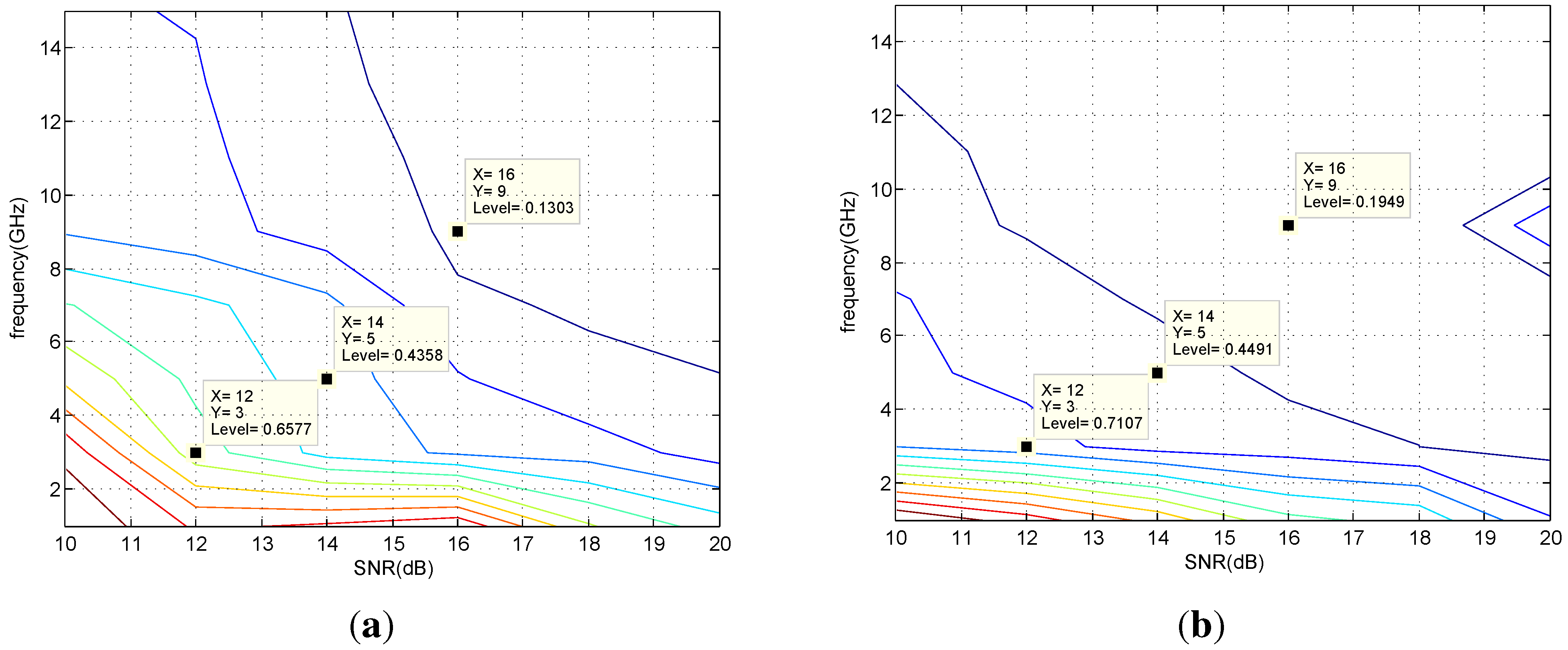
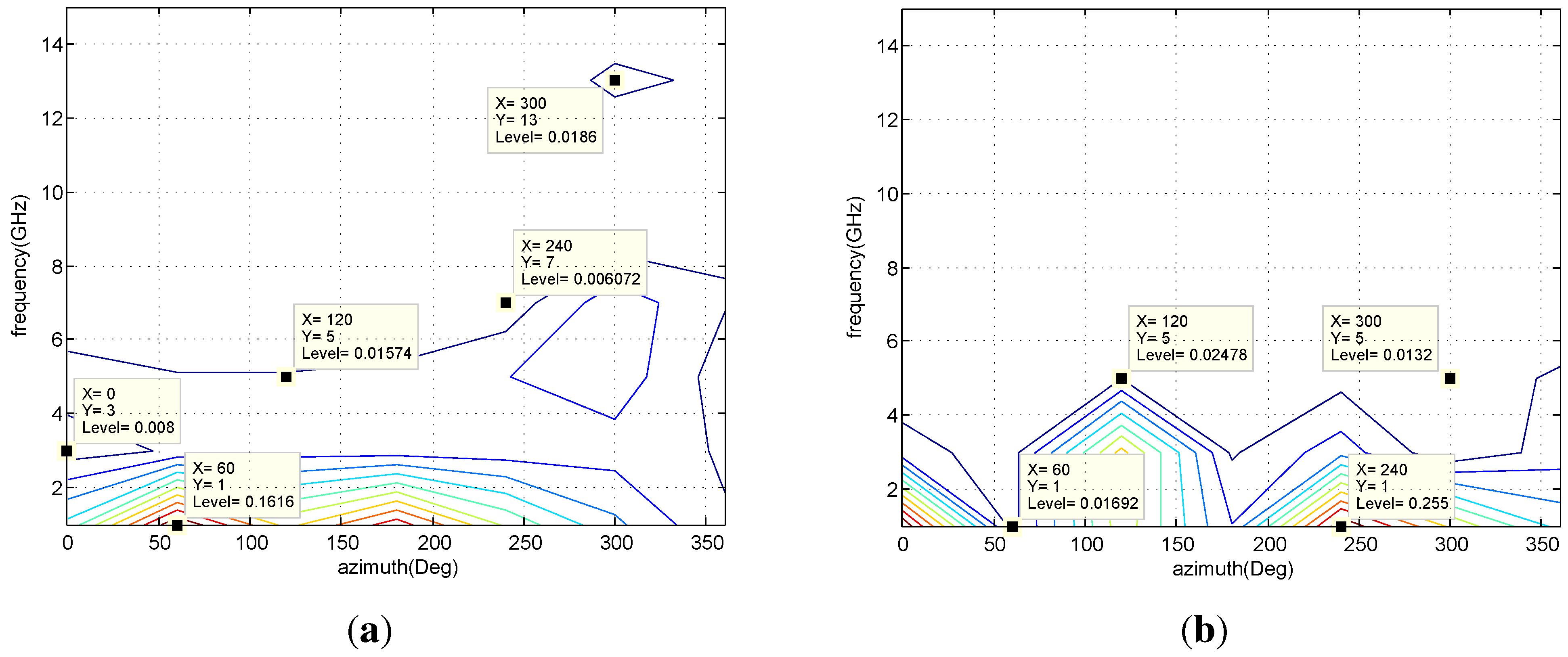

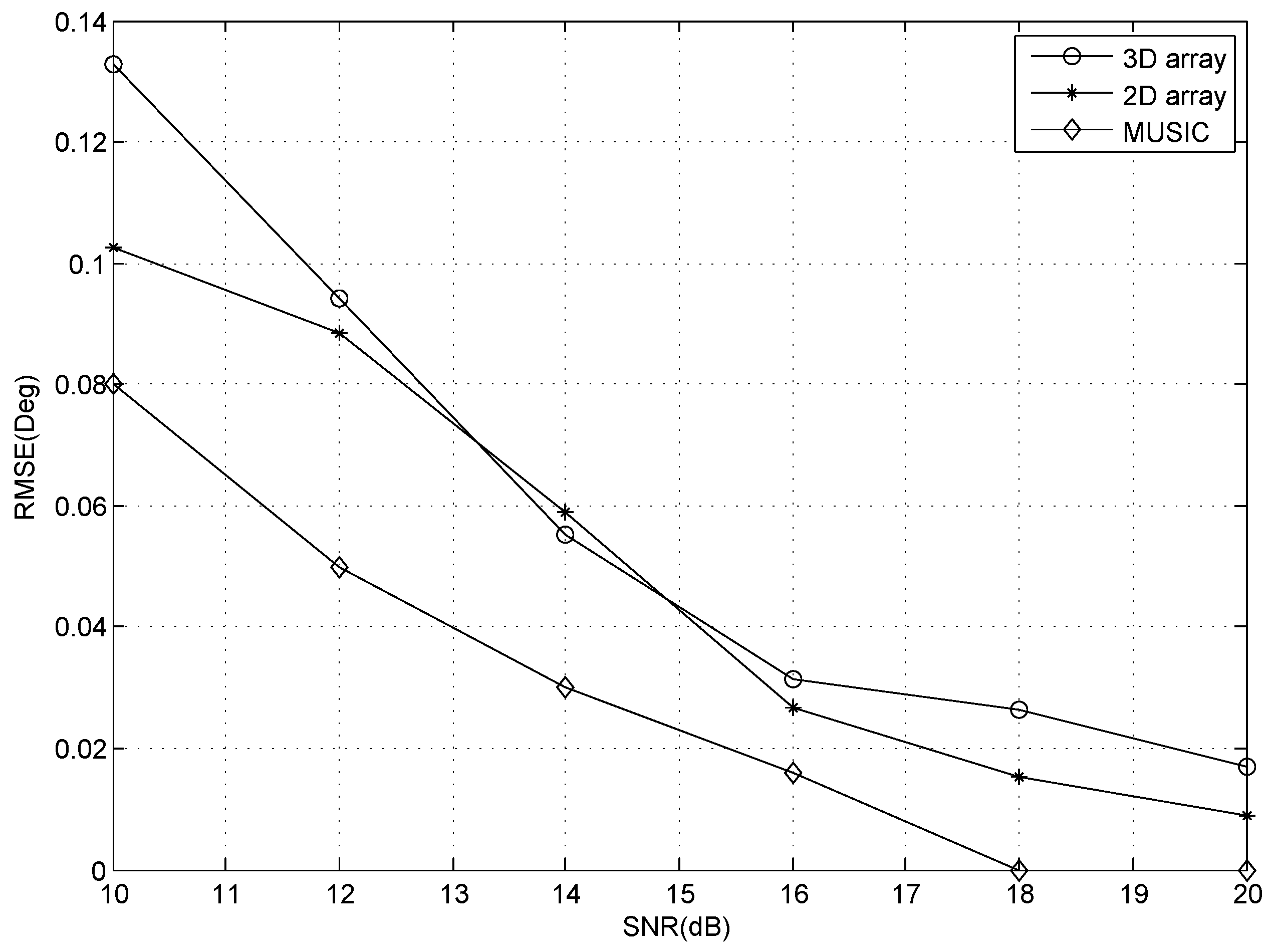
| Algorithm | 100 | 200 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2D array | 0.54 s | 0.94 s | 2.22 s |
| 3D array | 4.53 s | 9.05 s | 22.29 s |
| MUSIC | 20.06 s | 41.79 s | 108.10 s |
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsui, K.M.; Chan, S.C. Pattern synthesis of narrowband conformal arrays using iterative second-order cone programming. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, Q.; Huang, A.M. Localization of narrow band sources in the presence of mutual coupling via sparse solution finding. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2008, 86, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.J. Practicability analysis and application of PBG structures on cylindrical conformal microstrip antenna and array. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2011, 115, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Chua, K.M.; Lu, A.C.W. Circuit model of microstrip patch antenna on ceramic land grid array package for antenna-chip codesign of highly integrated RF transceivers. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 3877–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakis, N.P.; Karanasiou, I.S.; Uzunoglu, N.K. Non-invasive microwave radiometric system for intracranial applications: A study using the conformal L-notch microstrip patch antenna. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2011, 117, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisso, M.; Vescovo, R. Fast co-polar and cross-polar 3D pattern synthesis with dynamic range ratio reduction for conformal antenna arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, T. More applications of euler rotation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Mag. 1999, 41, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Lin, Y.Z. Frequency-invariant pattern synthesis of conformal array antenna with low cross-polarisation. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2008, 2, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Lasenby, J.; He, Z.S. Beamformer for cylindrical conformal array of non-isotropic antennas. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2011, 1, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Lasenby, J.; He, Z.S. Beamforming with distortionless co-polarisation for conformal arrays based on geometric algebra. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeringer, D.W.; Werner, D.H.; Machuga, D.W. A simultaneous parameter adaptation scheme for genetic algorithms with application to phased array synthesis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T.; Hei, Y.Q.; Shi, X.W. Pattern synthesis of conformal arrays by a modified particle swarm optimization. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2011, 117, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.Z. Pattern synthesis of conformal antenna array by the hybrid genetic algorithm. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2008, 79, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, W.Y. A Novel dielectric conformal FDTD method for computing SAR distribution of the human body in a metallic cabin illuminated by an intentional electromagnetic pulse (Iemp). Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 126, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaskelainen, L.I. Constrained least-squares optimization in conformal array antenna synthesis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solimene, R.; Dell’Aversano, A.; Leone, G. Interferometric time reversal MUSIC for small scatterer localization. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 131, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, Y.S.; Cho, S.W.; Yeo, W.Y.; Pister, K.S.J. Application of the Newton method to improve the accuracy of to a estimation with the beamforming algorithm and the MUSIC Algorithm. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2011, 116, 475–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yang, F.; Nie, Z.P. DOA estimation using MUSIC algorithm on a cylindrical conformal antenna array. IEEE Antennas Propag. Symp. 2007, 5299–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yang, F.; Nie, Z.P. DOA estimation with sub-array divided technique and interporlated esprit algorithm on a cylindrical conformal antenna array. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2010, 103, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, B.H. Blind direction-of-arrival estimation algorithm for conformal array antenna with respect to polarization diversity. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2011, 5, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Lasenby, J.; He, Z. Direction and polarization estimation using polarized cylindrical conformal arrays. IET Signal Process. 2012, 6, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.J.; Wan, L.T.; Liu, L.T.; Tian, Z.X. Fast estimation of frequency and 2-D DOAs for cylindrical conformal array antenna using state-space and propagator method. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 137, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, D. Two L-shaped array-based 2-d DOAs estimation in the presence of mutual coupling. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2011, 112, 273–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henault, S.; Podilchak, S.K.; Mikki, S.M.; Antar, Y.M.M. A methodology for mutual coupling estimation and compensation in antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, X. Hydrostatic pressure sensor based on a gold-coated fiber Modal interferometer using lateral offset splicing of single mode fiber. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 124, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.Y.; Chang, T.H. Experimental and theoretical studies of a broadband superluminality in fabry-perot interferometer. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 122, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengarajan, S.R. Reflectarrays of rectangular microstrip patches for dual-polarization dual-beam radar interferometers. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 133, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, L.; Mellon, D.; Saquib, M. Interference cancellation and signal direction finding with low complexity. IEEE AES Syst. 2010, 46, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawase, S. Radio interferometer for geosynchronous-satellite direction finding. IEEE AES Syst. 2007, 43, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, K.R.; Mallik, R.K.; Murthy, U.M.S. Modulo conversion method for estimating the direction of arrival. IEEE AES Syst. 2000, 36, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, P.E.; Wickershan, D.; Jenn, D.C. High-resolution phase sampled interferometry using symmetrical number systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2001, 49, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, M.A.; Doron, E. Wavefield modeling and array processing. I. Spatial sampling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, R.; Bogaert, I.; Rogier, H. Phase-mode processing for spherical antenna arrays with a finite number of antenna elements and including mutual coupling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 3783–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, M.A.; Doron, E. Wavefield modeling and array processing. II. Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 2560–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, R.; Rogier, H.; Werbrouck, S. UCA Root-MUSIC with sparse uniform circular arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 4095–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, L.; Liu, L.; Han, G.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. A Low Energy Consumption DOA Estimation Approach for Conformal Array in Ultra-Wideband. Future Internet 2013, 5, 611-630. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi5040611
Wan L, Liu L, Han G, Rodrigues JJPC. A Low Energy Consumption DOA Estimation Approach for Conformal Array in Ultra-Wideband. Future Internet. 2013; 5(4):611-630. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi5040611
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Liangtian, Lutao Liu, Guangjie Han, and Joel J. P. C. Rodrigues. 2013. "A Low Energy Consumption DOA Estimation Approach for Conformal Array in Ultra-Wideband" Future Internet 5, no. 4: 611-630. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi5040611
APA StyleWan, L., Liu, L., Han, G., & Rodrigues, J. J. P. C. (2013). A Low Energy Consumption DOA Estimation Approach for Conformal Array in Ultra-Wideband. Future Internet, 5(4), 611-630. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi5040611







