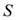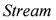Plausible Description Logic Programs for Stream Reasoning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Integrating Plausible Rules with Ontologies
3.1. Plausible Logic
 is the disjunction of positive or negative atoms
is the disjunction of positive or negative atoms  . If both an atom and its negation appear, the clause is a tautology. A contingent clause is a clause which is neither empty nor a tautology [20].
. If both an atom and its negation appear, the clause is a tautology. A contingent clause is a clause which is neither empty nor a tautology [20]. , where
, where  is a set of contingent clauses, called axioms, characterising the aspects of the situation that are certain,
is a set of contingent clauses, called axioms, characterising the aspects of the situation that are certain,  is a set of plausible rules,
is a set of plausible rules,  is a set of defeater rules, and
is a set of defeater rules, and  is a priority relation on
is a priority relation on  .
.  of strict rules from the definite facts
of strict rules from the definite facts  . Thus, a plausible knowledge base consists of strict rules (
. Thus, a plausible knowledge base consists of strict rules (  ), plausible rules (
), plausible rules (  ), defeater (warning) rules (
), defeater (warning) rules (  ), and a priority relation on the rules (
), and a priority relation on the rules (  ). Strict rules are rules in the classical sense (that is, whenever the premises are indisputable), then so is the conclusion. An atomic fact is represented by a strict rule with an empty antecedent. The plausible rule
). Strict rules are rules in the classical sense (that is, whenever the premises are indisputable), then so is the conclusion. An atomic fact is represented by a strict rule with an empty antecedent. The plausible rule  means that if all the antecedents
means that if all the antecedents  are proved and all the evidence against the consequent
are proved and all the evidence against the consequent  has been defeated, then
has been defeated, then  can be deduced. The plausible conclusion
can be deduced. The plausible conclusion  can be defeated by contrary evidence.
can be defeated by contrary evidence. allows the representation of preferences among non-strict rules.
allows the representation of preferences among non-strict rules. that, given a proof algorithm
that, given a proof algorithm  and a formula
and a formula  in conjunctive normal form, returns
in conjunctive normal form, returns  if
if  was proved,
was proved,  if there is no proof for
if there is no proof for  , or 0 when
, or 0 when  is undecidable due to looping. Plausible Logic has five proof algorithms
is undecidable due to looping. Plausible Logic has five proof algorithms  , in which one is monotonic and four are non-monotonic:
, in which one is monotonic and four are non-monotonic:  monotonic, strict, like classical logic;
monotonic, strict, like classical logic;  ;
;  plausible, propagating-ambiguity;
plausible, propagating-ambiguity;  plausible, blocking-ambiguity; and
plausible, blocking-ambiguity; and  .
. in a refrigerator room.
in a refrigerator room. is a strict one: whenever the temperature
is a strict one: whenever the temperature  measured by the sensor
measured by the sensor  is above 4
is above 4  C the alarm starts automatically. The rule
C the alarm starts automatically. The rule  is a plausible one: if the measured temperature is above 0
is a plausible one: if the measured temperature is above 0  C, there is a reason to support the decision to trigger the alarm. The algorithm analyses if there are other reasons supporting the opposite conclusion or trying to defeat it. Rule
C, there is a reason to support the decision to trigger the alarm. The algorithm analyses if there are other reasons supporting the opposite conclusion or trying to defeat it. Rule 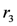 is such a rule. If both rules can be fired, we have an ambiguity. In case of the propagating-ambiguity strategy, both consequences are derived by the system. In case of the blocking-ambiguity strategy, no conclusion would be valid. Note that the rule
is such a rule. If both rules can be fired, we have an ambiguity. In case of the propagating-ambiguity strategy, both consequences are derived by the system. In case of the blocking-ambiguity strategy, no conclusion would be valid. Note that the rule 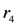 is a defeater that, in case of activation, blocks the derivation of the conclusion
is a defeater that, in case of activation, blocks the derivation of the conclusion  . If active,
. If active, 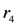 being stronger than
being stronger than 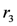 is able to block the corresponding decision. At this moment the consequence of the rule
is able to block the corresponding decision. At this moment the consequence of the rule  is no longer attacked by any valid rule. This mechanism corresponds to the argumentative semantics characterising the family of the defeasible logics [22].
is no longer attacked by any valid rule. This mechanism corresponds to the argumentative semantics characterising the family of the defeasible logics [22].3.2. Description Logic
 , concepts are built using the set of constructors formed by negation, conjunction, disjunction, value restriction, and existential restriction, as Table 1 bears out [23]. Here,
, concepts are built using the set of constructors formed by negation, conjunction, disjunction, value restriction, and existential restriction, as Table 1 bears out [23]. Here,  and
and  represent concept descriptions, whilst
represent concept descriptions, whilst  and
and  role names. In this study we used the extension of
role names. In this study we used the extension of  with transitivity (
with transitivity (  ) on roles and role hierarchy (
) on roles and role hierarchy (  ), known as
), known as  or
or  . The syntax of
. The syntax of  is defined by the following grammar:
is defined by the following grammar:

 represents an atomic concept and
represents an atomic concept and  the top level concept.
the top level concept. , where the domain
, where the domain  of
of  contains a non-empty set of individuals, whilst the interpretation function
contains a non-empty set of individuals, whilst the interpretation function  maps each concept name
maps each concept name  to a set of individuals
to a set of individuals  and each role
and each role  to a binary relation
to a binary relation  . The second column of Table 1 illustrates the extension of
. The second column of Table 1 illustrates the extension of  to arbitrary concepts.
to arbitrary concepts.| Syntax | Semantics |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 is satisfiable if there exists an interpretation
is satisfiable if there exists an interpretation  such that
such that  . The concept
. The concept  subsumes the concept
subsumes the concept  (
(  ) if
) if  for all interpretations
for all interpretations  .
.  is a finite set of concept assertions
is a finite set of concept assertions  or role assertions
or role assertions  , where
, where  represents a concept,
represents a concept,  a role, and
a role, and  and
and  are two instances. Usually, the unique name assumption holds within the same
are two instances. Usually, the unique name assumption holds within the same  . A
. A  is a finite set of terminological axioms of the form
is a finite set of terminological axioms of the form  or
or  .
.  . Let the terminology:
. Let the terminology: 

 as a wireless sensor with the measurement accuracy of 0.1
as a wireless sensor with the measurement accuracy of 0.1  C, where the value is interpreted as an instance of the class MeasureUnit. Based on the second axiom in the TBox, the subsumption reasoning service of the DL derives
C, where the value is interpreted as an instance of the class MeasureUnit. Based on the second axiom in the TBox, the subsumption reasoning service of the DL derives  as an instance of the Sensor concept.
as an instance of the Sensor concept.3.3. Translating from DL to Plausible Logic Programs
 classes), whilst conjunction, disjunction and existential restriction appearing in the left-hand side are translated into rule bodies (
classes), whilst conjunction, disjunction and existential restriction appearing in the left-hand side are translated into rule bodies (  classes). Figure 1 presents the mapping function
classes). Figure 1 presents the mapping function 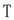 from DL to strict rules in a plausible knowledge base, where
from DL to strict rules in a plausible knowledge base, where  ,
,  and
and  are concepts such that
are concepts such that  ,
,  ,
,  is an atomic concept,
is an atomic concept,  ,
, 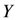 and
and  are variables, and
are variables, and  and
and  are roles.
are roles.
 is subsumed by
is subsumed by  , then each individual
, then each individual  in
in  is also an instance of the class
is also an instance of the class  . The axiom
. The axiom  says that, with certainty, all the roles
says that, with certainty, all the roles  point towards individuals of type
point towards individuals of type  . It is translated in second line of Figure 1 as: if there is a relation
. It is translated in second line of Figure 1 as: if there is a relation  between
between  and
and 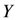 , the element
, the element 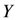 should be of type
should be of type  . Similar semantics is applied for the inverse role
. Similar semantics is applied for the inverse role  , where the domain and range are interchanged. If
, where the domain and range are interchanged. If  is interpreted as a
is interpreted as a  concept, then
concept, then  is of type
is of type  . The role assertion
. The role assertion  is interpreted as the two individuals
is interpreted as the two individuals  and
and  being in relation
being in relation  . The mapping of role subsumption
. The mapping of role subsumption  outputs that given two elements
outputs that given two elements  and
and 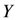 in relation
in relation  , they are linked by the more general relation
, they are linked by the more general relation  . The transitivity property of roles
. The transitivity property of roles  says that if the instance
says that if the instance  is related to
is related to 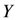 by the role
by the role  and if
and if 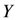 is related to
is related to  by the same role, then it is necessary that
by the same role, then it is necessary that  is related to
is related to  by the same role
by the same role  .
.4. Data Stream Management System in Haskell

4.1. The Haskell Platform

 annotated with their time stamps
annotated with their time stamps  .
. 

 wants to sell a specific item for 30$, the offer being made at the time step 14.32. The stream is implemented with the infinite list data structure in Haskell.
wants to sell a specific item for 30$, the offer being made at the time step 14.32. The stream is implemented with the infinite list data structure in Haskell.4.2. Streams Module
| Type | Function | Signature |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | constructor |  ::a - ::a -  S
a - S
a -  Sa Sa |
| extract the first element | head:: S a -  a a | |
| extracts the sequence following the stream’s head | tail:: S a -  S a S a | |
| takes a stream and returns all its finite prefixes | inits :: S a -  S ([a]) S ([a]) | |
| takes a stream and returns all its suffixes | tails :: S a -  S (S a) S (S a) | |
| Transformation | applies a function over all elements | map :: (a -  b) - b) -  S a - S a -  S b S b |
| interleaves 2 streams | inter :: Stream a -  Stream a
- Stream a
-  S a S a | |
| yields a stream of successive reduced values | scan :: (a -  b - b -  a) - a) -  a - a -  S b - S b -  S a S a | |
| computes the transposition of a stream of streams | transp :: S (S a) -  S (S a) S (S a) | |
| Building streams | repeated applications of a function | iterate :: (a -  a) - a) -  a - a -  S a S a |
| constant streams | repeat :: a -  S a S a | |
| returns the infinite repetition of a set of values | cycle :: [a] -  S a S a | |
| Extracting sublists | takes the first elements | take :: Int -  S a - S a -  [a] [a] |
| drops the first elements | drop :: Int -  S a - S a -  S a S a | |
| returns the longest prefix for which p holds | takeWhile :: (a -  Bool) - Bool) -  S a - S a -  [a] [a] | |
| returns the suffix remaining after takeWhile | dropWhile :: (a -  Bool) - Bool) -  S a - S a -  S a S a | |
| removes elements that do not satisfy p | filter :: a -  Bool) - Bool) -  S a - S a -  S a S a | |
| Index | returns the element of the stream at index n | !!:: S a -  Int - Int -  a a |
returns the index of the first element
equal with  | elemIndex :: Eq a =  a - a -  S a - S a -  Int Int | |
| returns the index of the first element satisfying p | findIndex :: (a -  Bool) - Bool) -  S a - S a -  Int Int | |
| Aggregation | returns a list of corresponding pairs from 2 streams | zip :: S a -  S b - S b -  S (a,b) S (a,b) |
| combines two streams based on a given function | ZipWith :: (a -  b - b -  c) - c) -  S a - S a -  S b - S b -  S c S c |

 , where the current value sums all the previously ones.
, where the current value sums all the previously ones. and
and  , expressed by two different currencies:
, expressed by two different currencies:

 .
.
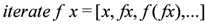 . An incoming stream can be dynamically split into two streams, based on a predicate p.
. An incoming stream can be dynamically split into two streams, based on a predicate p.4.3. The Mapping Module
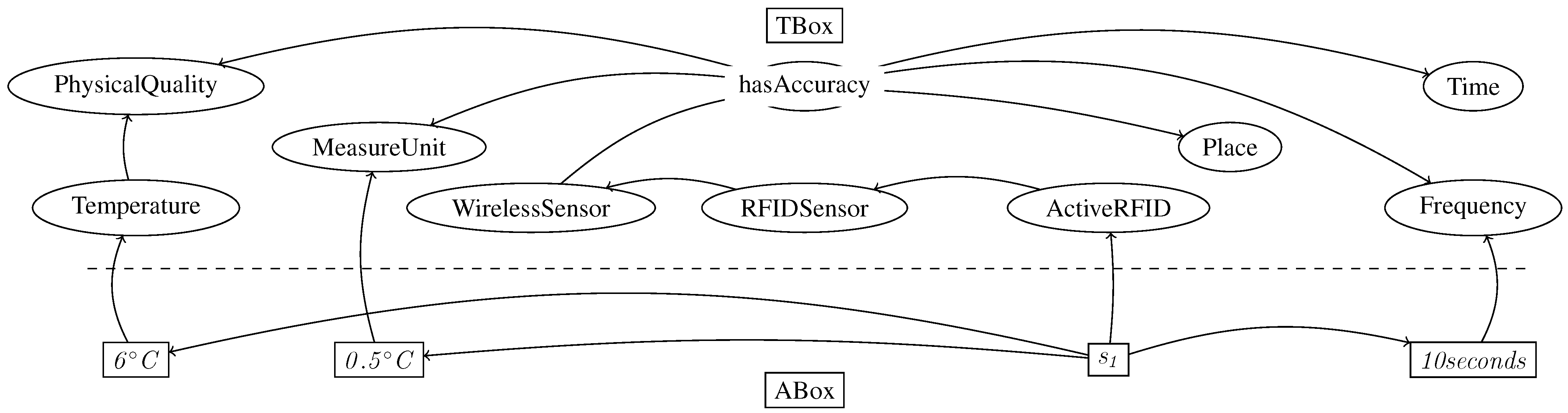
 is an instance of the class ActiveRDF and it measures temperature with an accuracy of 0.5
is an instance of the class ActiveRDF and it measures temperature with an accuracy of 0.5  C. The current temperature is 6
C. The current temperature is 6  C, and the measurement frequency is six observations per minute (Figure 4). Noting that Temperature is a PhysicalQuality (axiom 9 in Figure 3), there is a role measure between the sensor
C, and the measurement frequency is six observations per minute (Figure 4). Noting that Temperature is a PhysicalQuality (axiom 9 in Figure 3), there is a role measure between the sensor  and the temperature value
and the temperature value 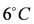 , as axiom 1 defines. The corresponding RDF stream for the sensor
, as axiom 1 defines. The corresponding RDF stream for the sensor  looks like:
looks like:

 C to 6
C to 6  C.
C. on the transformation function
on the transformation function 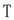 , each axiom in the description logic is converted to strict rules as soon as it appears:
, each axiom in the description logic is converted to strict rules as soon as it appears:




4.4. Efficiency Remarks
- The implementation of a family of defeasible logic is polynomial [7]. Plausible logic, being a particular case of defeasible reasoning, belongs to this efficiency class. The extensive experiments in [7] have proved that the family of defeasible reasoning tools that we integrated in our framework can deal with knowledge bases up to hundreds of thousands of rules, with a theoretical complexity of O(N log N). The cpu time for proving a conclusion was 0.4 seconds in case of 4200 contradictory rules, 3.83 seconds for 42,000 rules, and 21.15 seconds for 210,000 rules. This cpu time includes the time consumed by the garbage collector in Haskell [7].
- Under the assumption that the domain is static, the translation from description logic axioms into strict rules can be performed offline, before taking real-time decisions. The resulted Description Logic Programs are sub-fragments of Horn logics and their complexity is polynomial, as reported in [8].
- Only few general ontologies and few medical ontologies have this size. Most of the domain ontologies do no reach the comparable size of 4200 axioms. Depending on the time constraints for the given problem, a smaller ontology can be imported instead of a refined one.
- The plausible rules and preferences added by the human expert also do not go up to thousands of rules. Given the experience from the expert systems domain, few of the existing commercial expert systems do contain thousands of rules [28].
- The possibility to select the current inference algorithm among
can also be exploited to adjust the reasoning task to the complexity of the current real-time decision.
5. Running Scenario
 of whole milk, and two types of low fat milk
of whole milk, and two types of low fat milk  and
and 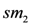 . Some peak periods are associated to each commercialised item.
. Some peak periods are associated to each commercialised item.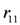 . The plausible rule
. The plausible rule 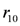 says that if the milk stock
says that if the milk stock 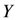 is below the alert threshold
is below the alert threshold 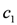 , the NormalSupply action should be executed. NormalSupply assures a stock value of
, the NormalSupply action should be executed. NormalSupply assures a stock value of 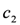 . Instead, the PeakSupply action is derived by the rule
. Instead, the PeakSupply action is derived by the rule 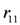 .
.

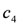 , this implies not to supply the higher quantity
, this implies not to supply the higher quantity 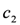 (the rule
(the rule 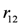 ). Whether the action is executed or not depends on the priority relation between the rules
). Whether the action is executed or not depends on the priority relation between the rules 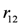 and
and 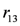 ,
,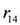 ). A broken sensor defeats the stock information asserted in the knowledge base related to the measured item (the defeater
). A broken sensor defeats the stock information asserted in the knowledge base related to the measured item (the defeater 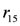 ).
).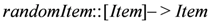 based on the list of available items returns a random item. The infinite output stream for the payment point
based on the list of available items returns a random item. The infinite output stream for the payment point 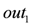 would be:
would be:

 of sold items (item sold price) and the associated time of measurement, where the predicate sold and the price value are removed for clarity reasons:
of sold items (item sold price) and the associated time of measurement, where the predicate sold and the price value are removed for clarity reasons:


 stream. Based on the fact
stream. Based on the fact  and the rule
and the rule 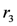 , one can conclude that
, one can conclude that 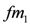 is a milk item. Similarly, based on the facts
is a milk item. Similarly, based on the facts 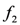 and
and 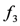 , the rule
, the rule 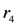 categorises the instances
categorises the instances 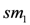 and
and 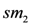 as milk items. The filter function is used to monitor each milk item, either low fat or not:
as milk items. The filter function is used to monitor each milk item, either low fat or not:

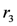 or
or 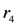 . The map function is used to select only the element item from the tuples
. The map function is used to select only the element item from the tuples  from the stream
from the stream  : the composition
: the composition 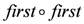 is used to extract the first element in the first tuple.
is used to extract the first element in the first tuple. , the milkItems is:
, the milkItems is: 
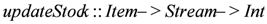 function is activated to compute the available stock for a specific category of products. Consider the current stock for milk is 102 and the threshold
function is activated to compute the available stock for a specific category of products. Consider the current stock for milk is 102 and the threshold 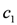 for triggering the alarm is 100. Assume the function updateStock is called with the first input parameter milk and the second parameter milkItems. At time 1,
for triggering the alarm is 100. Assume the function updateStock is called with the first input parameter milk and the second parameter milkItems. At time 1, 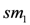 being low fat milk, identified as a subtype of milk, the stock is updated at the value 101. At instance 3,
being low fat milk, identified as a subtype of milk, the stock is updated at the value 101. At instance 3, 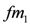 being fat milk, identified also as a subtype of milk, the stock is updated at the value 100. At time step 6,
being fat milk, identified also as a subtype of milk, the stock is updated at the value 100. At time step 6, 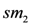 , the stock value reaches
, the stock value reaches 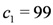 . At this moment, the predicate
. At this moment, the predicate 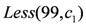 becomes valid.
becomes valid.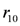 in Figure 7 is plausibly activated. The algorithm checks whether any defeater or stronger rule can block the derivation of the conclusion of the rule
in Figure 7 is plausibly activated. The algorithm checks whether any defeater or stronger rule can block the derivation of the conclusion of the rule 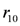 . If no one blocks it, the action normalSupply for milk of value
. If no one blocks it, the action normalSupply for milk of value 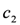 is executed. If, for instance in case of a peak period, the defeater
is executed. If, for instance in case of a peak period, the defeater 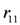 is active, since
is active, since 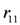 is stronger than the rule
is stronger than the rule 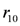 , it successfully blocks the derivation of the action normalSupply. Instead, the consequent of the rule
, it successfully blocks the derivation of the action normalSupply. Instead, the consequent of the rule 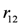 will be executed.
will be executed.6. Conclusions
- to translate the domain specific ontologies into strict rules, which is automatically performed by the mapping module;
- to design plausible rules and priorities by a domain expert;
- to import the most adequate sensor ontology for the current problem (for instance SWEET or W3S SSN Ontology).
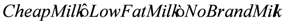 . Also, subclases of a complex class expression which is existential quantified cannot be translated, such as
. Also, subclases of a complex class expression which is existential quantified cannot be translated, such as 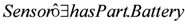 . Our solution allows this limitation of expressivity in order to perform reasoning in real time within the efficient plausible logic framework.
. Our solution allows this limitation of expressivity in order to perform reasoning in real time within the efficient plausible logic framework.Acknowledgments
References
- Christin, D.; Mogre, P.S.; Hollick, M. Survey on wireless sensor network technologies for industrial automation: The security and quality of service perspectives. Future Internet 2010, 2, 96–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Phuoc, D.; Parreira, J.X.; Hausenblas, M.; Hauswirth, M. Unifying Stream Data and Linked Open Data; Technical Report for Digital Enterprise Research Institute (DERI): Galway, Ireland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Valle, E.D.; Ceri, S.; van Harmelen, F.; Fensel, D. It’s a streaming world! Reasoning upon rapidly changing information. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granitzer, M.; Sabol, V.; Onn, K.W.; Lukose, D.; Tochtermann, K. Ontology alignment—A survey with focus on visually supported semi-automatic techniques. Future Internet 2010, 2, 238–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, D.; Braga, D.; Ceri, S.; Valle, E.D.; Grossniklaus, M. Incremental reasoning on streams and rich background knowledge. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2010, 6088, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, N. Twitter as medium and message. Commun. ACM 2011, 54, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, M.J.; Rock, A.; Antoniou, G.; Billington, D.; Miller, T. Efficient defeasible reasoning systems. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 2001, 10, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krötzsch, M.; Rudolph, S.; Hitzler, P. Complexity boundaries for horn descriptionl logics. In Proceedings of the 22nd national conference on Artificial intelligence, Toronto, Canada, 22–26 July 2012; AAAI Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 452–457. [Google Scholar]
- Letia, I.A.; Groza, A. Description Plausible Logic Programs for Stream Reasoning; Filipe, J., Fred, A.L.N., Eds.; SciTePress: Setubal, Portugal, 2012; pp. 560–566. [Google Scholar]
- Calbimonte, J.P.; Corcho, Ó.; Gray, A.J.G. Enabling ontology-based access to streaming data sources. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2010, 6496, 96–111. [Google Scholar]
- Palopoli, L.; Terracina, G.; Ursino, D. A plausibility description logic for handling information sources with heterogeneous data representation formats. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 2003, 39, 385–430. [Google Scholar]
- Heintz, F.; Kvarnström, J.; Doherty, P. Stream reasoning in DyKnow: A knowledge processing middleware system. In Presented at 1st International Workshop on Stream Reasoning,, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 31 May 2009.
- Bolles, A.; Grawunder, M.; Jacobi, J. Streaming SPARQL extending SPARQL to process data streams. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2008, 5021, 448–462. [Google Scholar]
- Anicic, D.; Fodor, P.; Rudolph, S.; Stühmer, R.; Stojanovic, N.; Studer, R. A rule-based language for complex event processing and reasoning. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2010, 6333, 42–57. [Google Scholar]
- Anicic, D.; Rudolph, S.; Fodor, P.; Stojanovic, N. Retractable complex event processing and stream reasoning. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2011, 6826, 122–137. [Google Scholar]
- Corcho, Ó.; Garcia-Castro, R. Five challenges for the Semantic Sensor Web. Semant. Web 2010, 1, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- ASPIRE Project (Advanced Sensors and lightweight Programmable middleware for Innovative Rfid Enterprise applications). Available online: http://www.fp7-aspire.eu/ (accessed on 15 October 2012).
- Sensei Project. Available online: http://www.ict-sensei.org/Sensei090422/ (accessed on 15 October 2012).
- Ruta, M.; Colucci, S.; Scioscia, F.; Sciascio, E.D.; Donini, F.M. Finding commonalities in RFID semantic streams. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 5, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, A. Implementation of Decisive Plausible Logic; Technical Report for School of Information and Communication Technology, Griffith University: South Brisbane, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Billington, D.; Rock, A. Propositional plausible logic: Introduction and implementation. Stud. Log. 2001, 67, 243–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governatori, G.; Maher, M.J.; Antoniou, G.; Billington, D. Argumentation semantics for defeasible logic. J. Log. Comput. 2004, 14, 675–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baader, F.; Calvanese, D.; McGuinness, D.; Nardi, D.; Patel-Schneider, P. The Description Logic Handbook: Theory, Implementation and Applications; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, S.A.; Chesnevar, C.I.; Simari, G.R. A defeasible logic programming approach to the integration of rules and ontologies. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2010, 10, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Grosof, B.N.; Horrocks, I.; Volz, R.; Decker, S. Description logic programs: Combining logic programs with description logic. In Proceedings of the 12th international conference on World Wide Web, Budapest, Hungary, 20–24 May 2003; pp. 48–57.
- Stuckenschmidt, H.; Ceri, S.; Valle, E.D.; van Harmelen, F. Towards expressive stream reasoning. In Semantic Challenges in Sensor Networks; Aberer, K., Gal, A., Hauswirth, M., Sattler, K.U., Sheth, A.P., Eds.; Schloss Dagstuhl—Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik: Dagstuhl, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Decisive Plausible Logic Tool. Available online: http://www.ict.griffith.edu.au/arock/DPL/ (accessed on 15 October 2012).
- De Hoog, R. Expert Systems—Past, Present, and Future; Technical Report for Metis, University of Amsterdam: Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Groza, A.; Letia, I.A. Plausible Description Logic Programs for Stream Reasoning. Future Internet 2012, 4, 865-881. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi4040865
Groza A, Letia IA. Plausible Description Logic Programs for Stream Reasoning. Future Internet. 2012; 4(4):865-881. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi4040865
Chicago/Turabian StyleGroza, Adrian, and Ioan Alfred Letia. 2012. "Plausible Description Logic Programs for Stream Reasoning" Future Internet 4, no. 4: 865-881. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi4040865
APA StyleGroza, A., & Letia, I. A. (2012). Plausible Description Logic Programs for Stream Reasoning. Future Internet, 4(4), 865-881. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi4040865