Abstract
The mapping of different aspects of urban phenomena and their relation to the physical cityscape has been greatly extended by the use of geomatics. The tradition to base reasoning on ‘understanding the world’ dates from the time of Aristotle. The extension plan for Barcelona (Eixample), developed by Cerdà, which opened the era of modern urban planning, was preceded by analyses of rich data, describing both detailed demographic issues and physical structures. The contemporary, postmodernist city planning continues this tradition, although a shift towards analyses of more human-related issues can be observed, covering, inter alia, citizens’ perception, cultural differences and patterns of human activities with regard to distinct social groups. The change towards a more human-related perspective and the inclusion of urban morphology analyses are direct consequences of this trend. The required data may be gathered within a crowd-sourcing participation process. According to communicative planning theory, communication with the wider public is indispensable in order to achieve the best results, and can be realized with the use of sophisticated IT tools. Evidence-based reasoning may be supported by images of significant aesthetic values, which inspire immediate reactions.
1. Introduction
Human geomatics, analogous to humanistic geography—with origins relating to the works of Yi Fu Tuan [1]—introduces a qualitative description of human activities, including perception and emotions, into the general concept of geomatics, which developed as a qualitative method of describing the phenomena of the physical world. Urban design, from its perceptual, visual, social and functional perspective [2], has a substantial interest in capturing human responses and activities. The tradition of basing decisions on reasoning dates back to the time of Aristotle [3,4]. Between 1847 and 1857, during the design process of Barcelona's Eixample, Ildefons Cerdà, considered to be the founder of contemporary urbanism, gathered a set of statistical data covering demography, education and life standards, but also such factors as carriage transport and parameters describing the physical structure, including: construction intensity, impermeability and city facilities, such as infrastructure, lighting systems and paving [5]. Considerable research, covering the use of geomatics in describing human activities and perception, has been conducted by a number of analysts and teams, with the most important studies developed by: (1) the Space Syntax group, e.g., the Cityware project UK [6] and several projects using methodology provided by Space Syntax [7,8] all over the world [9]; (2) MIT SENSEable City Lab [10], among others the Real-time city data project [11,12,13]; (3) Urban Informatics Research Lab, QUT [14]; and (4) Architectural League of NY, i.e.,: Sentient City [15]. These projects concentrate mostly on the modeling of human activities, although the issues of perception and human reactions to the environment also constitute an attractive subject for studies, e.g. [16,17].
In this context, the mapping of non-material phenomena is nothing new. Maps of social group distribution, such as the location of poverty or ethnic groups in the city, are a common tool for urban analyses, introduced by the Chicago sociological school [18]. However, the possibility of overlaying them with other data, describing different phenomena, as well as the ease with which such juxtapositions may be converted into manageable information, provide a useful tool for contemporary urban planners in influencing a powerful discourse, focusing on a successful and legitimate vision of the future in diverse social environments. The recent IT potential, enabling mapping of numeric data, including tweeting or SMS intensity, provides additional opportunities for visualizing human activities [10,11,12,13], formerly restricted to traffic simulation and statistics. As the contemporary city is partly extended into virtuality [19,20,21], research should also include this perspective, and perceive the city, both as a platform of mutual communication and a set of phenomena, which require description.
Contemporary urban planning makes extensive use of evidence-based methodology [22]. The philosophical basis for communicative planning theory derives from the concept of communicative action by Jürgen Habermas [23]. According to this theory, the validity of a norm may be justified in a dialectic process between proponents of different approaches. ‘Normative rightness’ results from mutual understanding achieved in the argument process [24]. “The power of dominant discourses,” as Healey [23], argues that presenting the assumptions of the institutionalist theory of spatial planning may be challenged in dialogue, “through the power of knowledgeable, reflective discourse, through good arguments (...)”, in order to achieve consensus by taking into account the arguments and at the same time respecting differences. Human geomatics—the mapping of the invisible aspects of the city—adds an important perspective to the debate on the form and functioning of the urban settings.
2. Methodology
As Lynch [25] admits: “In the development of an image, education will be quite as important as the reshaping of what is seen. Indeed, they together form a circular, or hopefully a spiral, process: visual education impelling the citizen to act upon his visual world, and this action causing him to see even more accurately. A highly-developed art of urban design is linked to the creation of a critical and attentive audience. If art and audience grow together, then our cities will be a source of daily enjoyment to millions of their inhabitants”. “Words, words, words, I’m sick of words!” states Lisa Doolittle in My Fair Lady, after Tollitt P. [26]. “A picture is worth a thousand words,” says an ancient Chinese proverb. We may find similar conclusions in the work of Mintzberg, Westley [27] regarding the decision-making process. Thus, the ability to successfully observe, analyze and then convert gathered data into a comprehensible presentation is one of key skills to be gained by architecture and urbanism students.
The paper includes two case studies developed by students of Architecture for the Society of Knowledge, a Master of Sciences degree program in Architecture and Urban Planning at the Faculty of Architecture, Warsaw University of Technology, and realized as a research work within the course entitled: ‘GIS basics-parametric description of urban space’. Each study describes different immaterial phenomena, which occur in the city, and looks for their relation with the physical city structure. The methodology for each study was different. One of them—the City Tagging project—adopted crowd-sourcing as a data gathering tool. The study describing the ethnic structure of central Brussels provides analyses based on the GIS municipal data. Also, the detailed methodology adopted both for the research and for the presentation was different in each case.
The “abstract forces (urban phenomena) shaping urban life” may be rendered “artistically, spatially and informatively in the form of alternative ‘maps’ which represent urban dynamics (...)” [28]. The research for inspiration included both current mash-ups web-sites [29,30,31,32], as well as theoretical background: the work of Batty et al. [33,34], and other papers from CASA, papers by eCAADe, and many others, e.g.,: [35,36,37]. The course concentrated on the mapping of phenomena other than the physical structure, although the structure as such served as a frame of reference and the relations between the invisible and the physical remained the objective of the final studies, which concentrated on the research for the most appropriate “language of form”, able to capture “in a geometric web, such varied and dynamic human and natural elements” and allowing the retention of the “surcharge of information that can be intuited or ‘read’ by people whose history and emotional and intellectual background make such information accessible to them”. [37].
3. Brussels Ethnic Division
Brussels is a shrinking city with strong social polarization. The borders between the neighborhoods occupied by different ethnic groups are clearly defined in the urban structure along the edge of the Charleroi Canal. The divisions date from the 1940s, following the terminology by Kesteloot [38]: they were formed in the Fordist and strengthened in Post-Fordist period. The disjuncture between both parts of the city prompts the question of the role of the architect in the social stimulation process. The research was supposed to provide a set of data for architectural design assessment.
3.1. Methodology
The research focused on mapping of the few factors that block integration processes in the city, starting from two different approaches: examination of the physical development and of the social structure on both sides of the canal [39]. Regarding the physical development, the presence of all objects/spaces that might influence the canal’s accessibility was taken into account, including distribution of services and factories, public buildings, residential areas, green spaces, open spaces and sprawling areas (Figure 1). Referring to the social structure, the objective was to map different ethnic groups living in the immediate neighborhood of the canal and the transitions between them, including the reasons for movement between neighborhoods and the trip destinations.
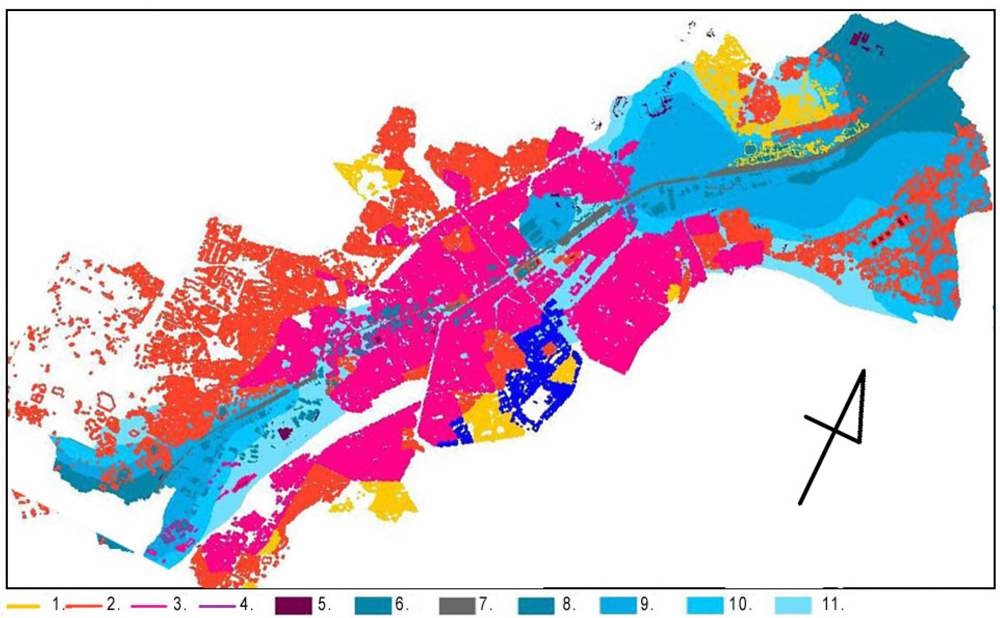
Figure 1.
Overlapping of all factors influencing the current problems associated with the city integration processes: 1.–4. Social divisions: 1. Advantaged groups; 2. Average neighborhood; 3. Disadvantaged groups; 4. Government properties; 5. Public edifices; 6. Industrial buildings; 7. Canal; 8.–11. Distances to the nearest shop: 8. 1500 m; 9. 1000 m; 10. 500 m; 11. 250 m.
3.2. Results
The areas along the entire canal are dominated by industry and by occupied or vacant warehouses. The proportions and relations between residential and industrial areas show the dominance of the latter (Figure 2I.). The homogeneous industrial zone does not provide attractive settings for the public; its presence obstructs access to the waterfront and circulation of people, hence reducing the space’s safety. The impact of factories (noise, pollution) influences the quality of the environment, which prevents high-income groups from choosing the location. The life quality assessment includes an evaluation of the accessibility of open, green spaces, which is hampered in the central area, where the population density is the highest (Figure 2II.). The open spaces map shows a number of small, unused, green places, spread around the canal, which may be converted into successful, small-scale social spaces.
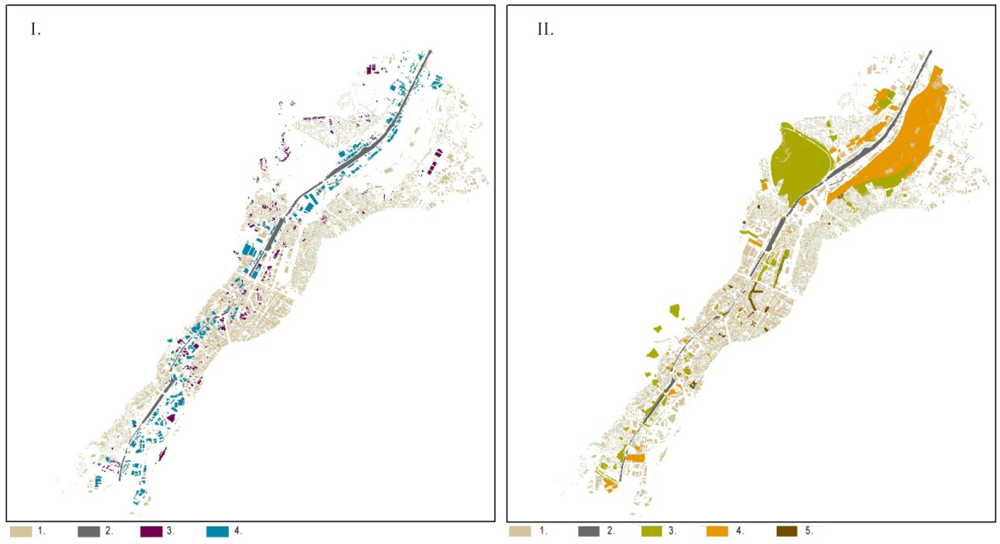
Figure 2.
I. Distribution of residential buildings (1), public buildings (3), industrial buildings (4) and their relation to the canal (2); II. Distribution of green areas (3), open spaces (4) and impermeable surfaces (5) and their relation to the housing density (1) and canal (2).
The direct neighborhood of the former industrial district is inhabited by excluded groups, mostly unskilled migrant workers, arrived in the 1960s from Mediterranean countries, mainly: Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. The population density is three times higher than in other central districts. Unemployment, social and educational deprivation result in neighborhood detriment and the lack of proper maintenance of housing estates. The social divisions result from the presence of clear cut borders between advantaged groups, average neighborhoods and disadvantaged groups, with no transition zones in between.
3.3. Conclusions
The overlay maps of physical and social aspects provide an explanation for neighborhood deprivation. Both groups of factors, physical and social, strongly influence each other. The spatial organization underlies the division between the two banks and disables city-like development in the central areas. Low quality of life, lack of education and cultural differences lead to a 'ghettoisation' of the whole neighborhood, which is perceived by the citizens as dangerous. Lack of a transition zone between neighborhoods, growing prejudice and social differences inflame these relations. Urban re-planning, including zoning laws to re-mix land-use, improving canal accessibility and quality of environment is strongly recommended. It should result in relocation of industry and in improved management, as well as taking into account the cultural differences between native Belgians and immigrants. Minor architectural and urban redesign may also introduce new values to the neighborhood along the canal. This change, eliminating perception of the canal as a visual border between polarized parts of the city, may also become a city-development catalyst .
4. City Tagging
Sensor network deployments in cities are assumed to increase dramatically within the coming decade, according to SENSEable City Lab [11]. This forecast, based mainly on the drastic price reduction of the sensor network components, fosters hope of creating a global centralized pervasive sensing network, which might be able to monitor urban environment in real time. Such a network might enable understanding and a re-design of the urban environment [40].
The growing interest in environmental and ecological issues within cities requires real time monitoring capable of visualizing the impact of municipal decisions on the community. SENSEable City Lab goes even further with their concept of WikiCity, which interprets the city as a “control system”, where the physical environment remains connected with digital space [41]. Ubiquitous sensor networks creating a digital representation of the real world can establish this connection between the physical and the digital. Moreover, these sensors introduce the possibility of a feedback loop, as they can not only view and analyze the city as a functional entity, but can also influence urban processes in real time by coupling them with decision support mechanisms, location-based services (LBS) or other spatial-temporal technologies.
Therefore, there is a huge potential in creating pervasive urban sensing networks, based not on the top-down approach of the global network of urban sensors, but on a volunteered network of personal devices. Currently, mobile smart phones are already used as ubiquitous personal information devices to co-ordinate and adjust our plans on-the-fly and at a distance by receiving up-to-date information on our environment. Moreover, people are producing geo-localized information by using various social services, such as Facebook or Twitter. Such information could be used not only to monitor the city environment in real time, but also to create a feedback loop between the city management and citizens. Urban Informatics Lab developed an iPhone application FixVegas, which allows the sending offix-o-gram requests directly to Brisbane City Council [42]. Thanks to this application, citizens can take a photo of the problem and submit it directly to the Council along with the coordinates of the reported issue. Residents can save time and get more involved in their city development without having to phone the Council or write to them.
The City Tagging project is a research of exploratory character, which focuses on possibilities of using a similar approach for collecting sensory data about city space. The research was made with the use of commonly accessible tools, allowing quantitative measurement of urban environment stimuli, correlated with human response [43,44].
4.1. Methodology
In order to perform the measurements, a specific itinerary was set up in the centre of Warsaw. The path led from the Faculty of Architecture to the Warsaw Central Railway Station (Figure 3). Along the itinerary, 11 measurement points were established. Each point was located in different settings, e.g., at a loud crossing, on a wide square and in an entrance to a shopping centre. Two factors were selected to quantify the external data concerning city space: luminosity and noise. Luminosity was chosen to represent data captured by sight, and the data for noise captured by hearing.
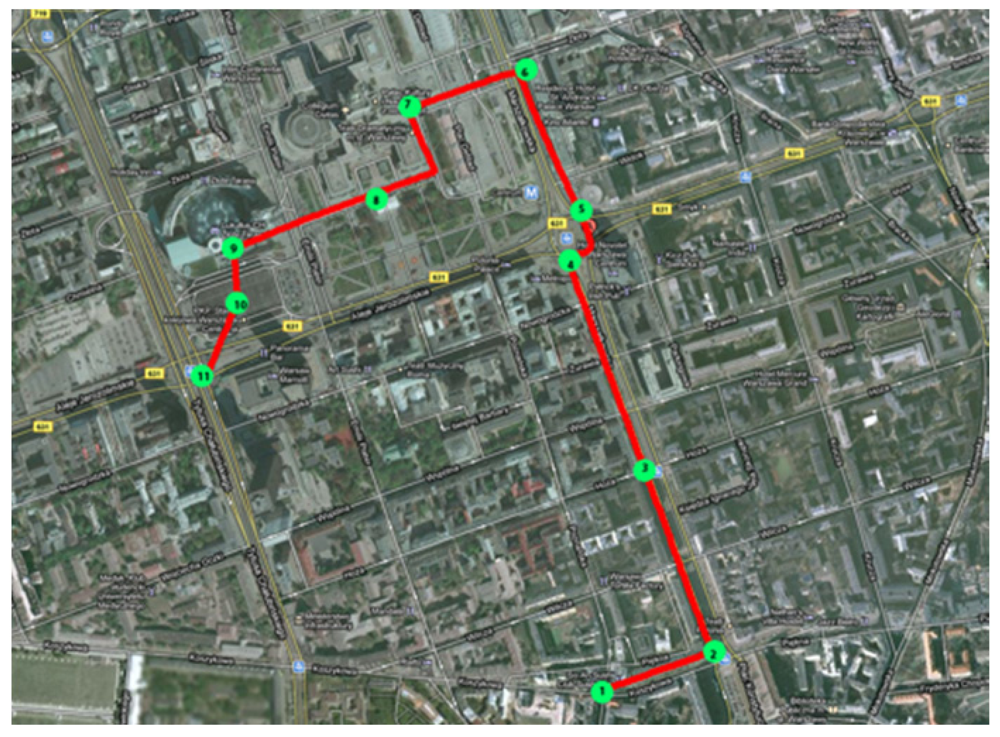
Figure 3.
City tagging itinerary.
To measure luminosity, a camera with fixed settings was used. Pictures were made from the same height (eye-level) with the axis of the lens parallel to the ground (Figure 4). It allowed comparable information from the key points of the itinerary to be obtained. The pictures where then processed using Adobe Photoshop to get the numeric data of brightness. As a representation of the luminosity (brightness of the picture), the mean grey value of the picture was selected. For measuring noise level, an iPhone using a Decibel application was used [45]. The application displayed three different values of sound in dB: average level, peak level, maximum level (Figure 5). The average sound level was chosen as a main result.
Pulse and blood pressure values were selected to acquire the data on the biometric response of the human body. The parameters of three students were checked with the use of a wrist blood pressure monitor. All methods of collecting data were chosen, based on their common availability.

Figure 4.
City tagging luminosity measurement method.

Figure 5.
City tagging noise measurement method.
4.2. Results
The research concerning noise and luminosity provided values shown in Figure 6. The highest value of luminosity and noise were registered in point no. 2, located on Konstytucji Square. The lowest level of sound was registered in point no. 9, located near the Złote Tarasy shopping centre. The lowest value of light was measured in point no. 10, located at the Warsaw Central Railway Station (Table 1).
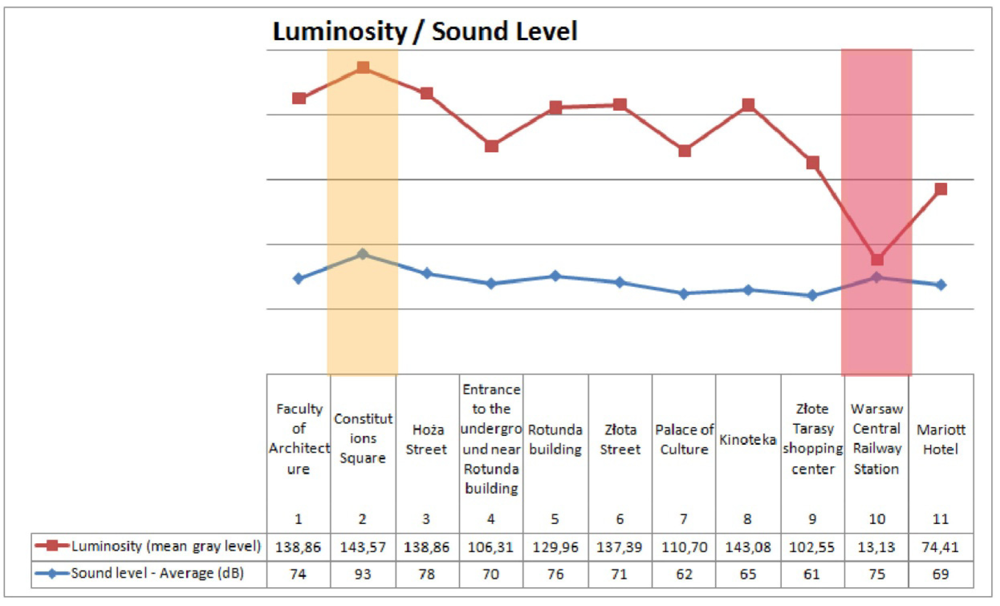
Figure 6.
Noise and Luminosity measurements results chart.

Table 1.
Noise and brightness measurement results.
| Minimum/maximum values | Nr | Location | Average sound level |
|---|---|---|---|
| loudest point | #2 | Konstytucji Square | 93 dB |
| quietest point | #9 | Złote Tarasy shopping center | 61 dB |
| darkest point | #10 | Warsaw Central Railway Station | |
| brightest point: | #2 | Konstytucji Square |
The juxtaposition of the results shows that the point located at the Warsaw Central Railway Station provides the lowest comfort for users as far as light and sound conditions are concerned (Figure 5). The results of human body response were similar for all three examination participants [44]. The graphs illustrating the data present analogous profiles. Regardless of individual health conditions, the assumption can be made that similar factors provoke similar reactions, e.g., all participants were more stressed in loud and crowded streets and more relaxed near the green areas (Figures 7, 8). There are also many external factors which have impact on the results, such as the individual characteristics of pulse/blood pressure, walking speed, gender, age, physique, diet, etc. Therefore, to acquire values that are more reliable, there is a need to perform measurements on a larger sample.
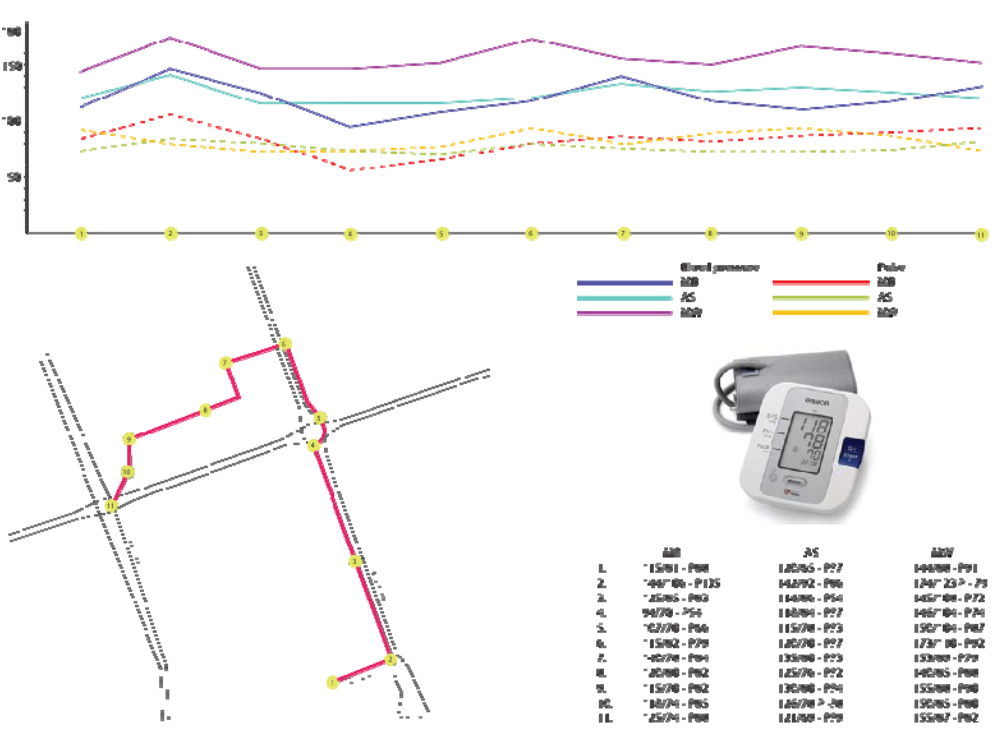
Figure 7.
Research results: pulse and blood pressure.
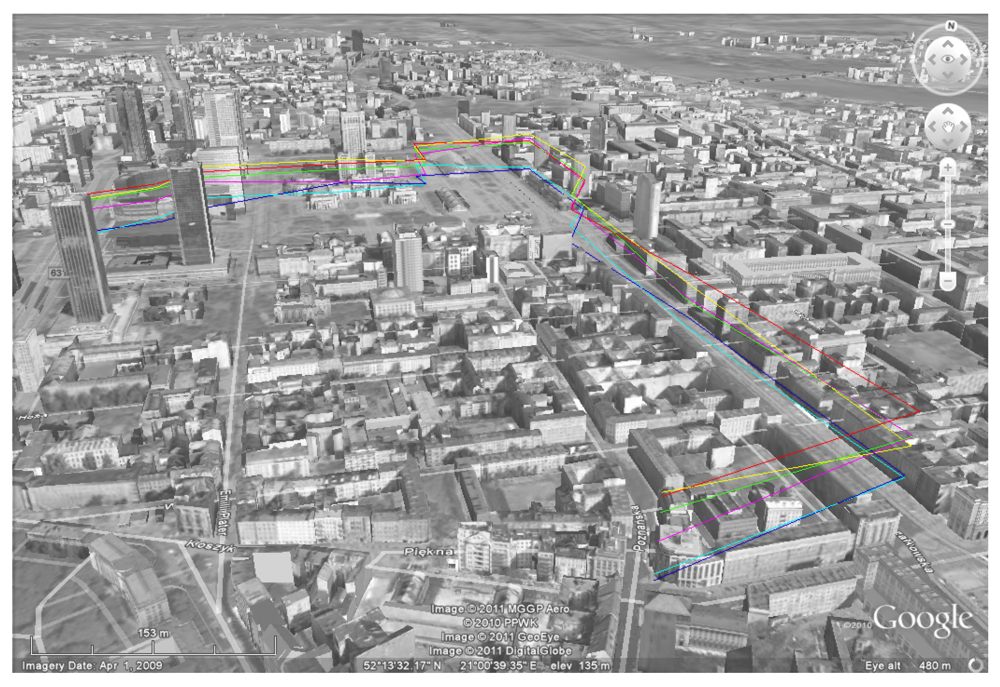
Figure 8.
Research results shown in a 3D-Google mash-up.
4.3. Conclusions
The result of the City Tagging project is insufficient to draw definitive conclusions. The number of measurements was small. The acquisition of information on specific factors influencing the perception of space by the senses needs further development. The monitoring of the city through distributed sensors gives only very general results. We still do not know how people perceive the space, how they feel in it, how the space affects them, and how the body reacts to the planned urban space. Therefore, the most accurate acquisition of information seems to be based on senses.
Subjective information from the users of the city and from personal device technology is essential for this process. In order to coordinate information on the way space is experienced, a methodology which adopts the evaluation of algorithms is required (quantitative, confirming the reliability of measurements, eliminating environmental disturbances, etc.).
The results of these analyses may affect the modern way of communicating between officials and inhabitants, and may bring rapid and effective responses to the needs of residents, delivered directly through their mobile devices. This will create a new quality to monitor urban environment in real time. Standardized and complete definition techniques allow the acquisition of data. Integrating them with additional services, such as location-based services, will have a significant impact on the development of the project and on better use of collected data, resulting in new possibilities to enhance city design.
5. Results Summary
The two case studies assumed overlapping analyses of different urban phenomena, including the description of the physical structure of the city, social factors and the parameters describing city functioning. The methodology allows for understanding the reasons of processes which take place in the city, and thus enhances the ability to find appropriate solutions. The results may support potential urban interventions at the municipal scale, with the aim of improving the image of the city, and to advance the quality of urban space and thus urban life, enhancing management and planning efficiency, dynamism, and the precision of interventions.
The Brussels case shows the importance of an edge, following the Lynch’s terminology [25], in the city structure, both in physical and in social terms. Recent research [46] proves that concentration of ethnically distinguished groups favors social exclusion. As Wirth stated “the larger, the more densely populated, and the more heterogeneous a community, the more accentuated the characteristics associated with urbanism will be”. [47]. The lack of an intermediate, socially mixed zone fosters separation, thus belonging to the ‘folk society’, following Redfield's terms [48], rather than introducing an urban, more heterogeneous culture. Social exclusion is usually followed by increased crime rates. Use of GIS for examination of social phenomena, such as crime patterns analyses, has been extensively developed with regard to the aggregation methodology [49]. The detailed analyses of crime patterns point at the relation of these phenomena with both qualities of the physical landscape and distribution of social patterns [50,51]. The latest research on distinguished social group allocation in cities [52,53] confirms Wirth’s and Redfield’s theses [47,48] concerning the presence of heterogeneous, urban specific transition zones between ethnic groups, instead of distinct borders proper for urban communities.
The City Tagging measurements of exploratory character proved the need for a more detailed research study, focusing on the relations between environmental conditions occurring in the city space, which might be highly influential on people’s behavior. The research methodology requires development and the number of measurements must be increased in order to get a linear or surface map with parameters applicable to architectural design. The further development of the crowd-sourcing approach would be of great use in this case. One of the development directions could be the creation of an application for a mobile device, e.g., the iPhone, which would allow many users to gather different types of data at the same time. A freeware application could be used by people as they walk through the city, allowing them to gather many sets of comparable data and create a real network of relations between different factors.
6. Conclusions
“(...) cities need to be seen as an entity inseparable from its people and their actions. (...) They together produce a city”. [35]. Many different approaches are present in the perception of cities. The shift towards considering the physical form of the urban structures [54,55] and in-depth analyses of city morphology [56,57], instead of restricting structure description to modernist land-use only, as well as the inclusion of sequential analyses of cityscapes [58,59], is parallel to postmodernist philosophy. The search for Aristotle’s city, which should constitute a good place for living, compels urban planners to look for answers in the area of humanist sciences: sociology, human geography, psychology and anthropology, which leads towards the unity of urban sciences [60]. Professionals should be able to include different perspectives in their advocacy of urban planning, in order to understand different approaches and to look for a common platform of communication. Public engagement, achieved through the extended use of crowd-sourcing methodology, provides additional potential in examining human reactions to different environments, and allows the enrichment of scope, both of social analyses or—as could be done in the Brussels case—allows, e.g., for extension of the inventory of unused spaces. Apart of the obvious differences in the research subjects developed under the common umbrella of human-related aspects of urban analysis and design, the two case studies differ in the data used and in the overall accuracy of results. The Brussels case presents the top-down approach and the City Tagging project remains bottom-up.
Every modeling process, as Guhathakurta argues [61], serves to tell a story, and provides evidence in the public reasoning process [22]. Urban modeling allows the presentation of different invisible aspects of the city which influences citizens’ behavior and thus the shape of the city’s physical form. In fulfilling this task, the ability first to observe, and then to transform the observations into analyses, and finally into information presented in a comprehensible, visual form, is enhanced by sophisticated IT tools (mash-ups, crowd-sourcing, different kinds of graphics, volume simulations, videos, etc.). The spectrum of problems which may be tackled is unlimited - as Kempf [35] states: “Ultimately, dealing with the city we need to embrace its emergent nature, its unfolding events and ceaseless encounters that are informed and imagined by many people at a time”.
Acknowledgments
The paper presents the works of the students of the course entitled: ‘GIS basics—parametric description of urban space’, taught at the Architecture for the Society of Knowledge, Master of Sciences degree program in the area of Architecture and Urban Planning, at the Faculty of Architecture, Warsaw University of Technology. The tutor was M. Hanzl. The case studies were also presented in [62]. The review was conducted throughout by appointed researchers, including Prof. M. Batty and B. Murgante, allowing the improvement of the final quality of the paper. The authors would hereby like to express their gratitude.
References and Notes
- Tuan, Y.F. Space and Place the Perspective of Experience; University of Minnesota Press: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona, M.; Heath, T.; Oc, T.; Tiesdell, S. Public Places Urban Spaces The Dimensions of Urban Design; Architectural Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Perseus Digital Library. Available online: http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/ (accessed on 19 March 2011).
- Broadie, S. Interpreting Aristotle’s Directions. In Method in Ancient Philosophy; Gentzler, J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 291–306. [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski, M. Część Ogólna—Problemy oraz Podstawy Merytoryczne. In Study on the Preconditions and Directions for The Physical Development of Lodz; UMŁ: Lodz, Poland, 1997–2002; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Cityware: urban design and pervasive systems. Available online: http://gow.epsrc.ac.uk/ ViewGrant.aspx?GrantRef=EP/C547691/1 (accessed on 19 March 2012).
- Hillier, B.; Hanson, J. The Social Logic of Space; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, B. Space Is the Machine. Available online: http://www.spacesyntx.com (accessed on 12 December 2011).
- e.g. Space Syntax conferences: 8th International Space Syntax Symposium, Santiago de Chile; 3–6 01 2012.
- MIT Senseable City Lab. Available online: http://senseable.mit.edu/ (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Rensch, B.; Britter, R.; Ratti, C. Live Urbanism—Towards SENSEable Cities and Beyond. In Sustainable Environmental Design in Architecture: Impact on Health; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 56, pp. 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, F.; Ratti, C. Nolli 2.0 or How to Rebuild Rome Without Even Asking Permission from the Historic Preservation Authority! In Uneternal City Urbanism beyond Rome; Betsky, A., Ed.; Marsilio: Rome, Italy, 2008; pp. 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, F.C.; Vaccari, A.; Giardin, F.; Chiu, C.; Ratti, C. Crowdsensing in the Web: Analyzing the Citizen Experience in the Urban Space. In From Social Butterfly to Engaged Citizen: Urban Informatics, Social Media, Ubiquitous Computing, and Mobile Technology to Support Citizen Engagement; Foth, M., Forlano, L., Satchell, C., Gibbs, M., Eds.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 353–373. [Google Scholar]
- Urban Informatics Research Lab at Queensland University of Technology. Available online: http://www.urbaninformatics.net (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Towards the Sentient City Project. Available online: http://www.sentientcity.net (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Nold, C., Ed. Emotional Cartography, Technologies of the Self. 2009. Available online: http://emotionalcartography.net/ (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Gartner, G. EmoMap Project. Available online: http://www2.ffg.at/verkehr/projekte.php?id=754&lang=en&browse=programm (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Hannerz, U. Exploring the City, Inquiries towards an Urban Anthropology; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, W.J. City of Bits; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, W.J. E-topia; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, W.J. Me++; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Faludi, A.; Waterhout, B. Introducing Evidence-Based Planning. disP Plan. Rev. 2006, 165, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Healey, P. Collaborative Planning: Shaping Places in Fragmented Societies; University of British Columbia Press: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Habermas, J. The Theory of Communicative Action: Reason and the Rationalization of Society; Beacon Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, K. The Image of the City; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Tollitt, P. The Illusion of Illustration—Urban Design London Online Training Cataloque. Available online: http://www.urbannous.org.uk/urbandesignlondon/Penelope%20Tollitt.htm (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Mintzberg, H.; Westley, F. Decision making: It’s not what you think. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2001, 42, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Amoroso, N. The Exposed City, Mapping the Urban Invisibles; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, M. VisualComplexity. blog. Available online: http://www.visualcomplexity.com (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Rankin, B. Radical Cartography. blog. Available online: http://www.radicalcartography.net/ (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- OWjL summer course. Available online: http://mappingweirdstuff.wordpress.com/ (accessed on 20 November 2011).
- Hudson-Smith, A. Digital Urban. blog. Available online: http://www.digitalurban.org/ (accessed on 20 November 2011).
- Brail, R.; Klosterman, R. Visualizing the City, Communicating Urban Design to Planners and Decision Makers. In Planning Support Systems: Integrating Geographic Information Systems, Models and Visualization Tools; Brail, R.K., Klosterman, R.E., Eds.; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 405–443. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M.; Crooks, A.; Hudson-Smith, A.; Milton, R.; Anand, S.; Jackson, M.; Morley, J. Data mash-ups and the future of mapping. Available online: http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1312085/ (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Kempf, P. You are the City, Observation, Organization and Transformation of Urban Settings; Lars Müller Publishers: Baden, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Manau, J.L.E.; Ortoneda, J.M., Solano. Squatting Geometries-Guerilla Barcelona. In Sensing the 21st-Century City Close-Up and Remote; McGrath, B., Shane, G., Eds.; Academy Press: London, UK, 2005; Volume 75, pp. 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Passoneau, J.R.; Wurman, R.S. Urban Atlas: 20 American Cities: A Communication Study Notating Selected Urban Data at a Scale of 1:48 000; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1966; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kesteloot, C. Brussels: Post-Fordist Polarization in a Fordist Spatial Canvas. In Globalizing Cities: A New Spatial Order, Studies in Urban and Social Change; Marcuse, P., van Kempen, R., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stankiewicz, E.; Wierzbicka, A.Ł. Charleroi Canal in Brussels. Available online: http://system.asknow.eu/groups/canalinbrussels/ (accessed on 20 November 2011).
- Sense of the City: An Alternate Approach to Urbanism; Zardini, M.; Schivelbusch, W. (Eds.) Lars Müller Publishers: Baden, Switzerland, 2006.
- Calabrese, F.; Kloeckl, K.; Ratti, C. WikiCity: Real-time Urban Environments. Pervasive Comput. Mobile Ubiquitous Syst. 2007, 6, 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- FixVegas iPhone Application. Available online: http://www.urbaninformatics.net/projects/fixvegas/ (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Dzik, K.; Kowalczyk, P.; Kwieciński, K. City Tagging 1: Noise and Luminosity. Available online: http://system.asknow.eu/groups/citytagging/blog/?tag=ct1 (accessed on 20 November 2011).
- Burdalski, M.; Śliwka, A.; Wójcicki, M. City Tagging 2: Pulse and Blood Pressure. Available online: http://system.asknow.eu/groups/citytagging/blog/?tag=ct2 (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Decibel application, iTunes. Available online: http://itunes.apple.com/app/decibel/id290788852?mt=8 (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Ladányi, J. The Hungarian Neoliberal State, Ethnic Classification, and the Creation of a Roma Underclass. In Poverty, Ethnicity, and Gender in Eastern Europe During the Market Transition; Emigh, R.J., Szelényi, I., Eds.; Praeger: London, UK, 2001; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, L. Urbanism as a way of life. Am. J. Sociol. 1938, 44, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Redfield, R. The folk society. Am. J. Sociol. 1947, 52, 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschfield, A.; Yarwood, D.; Bowers, K. Crime Pattern Analysis, Spatial Targeting and GIS: The development of new approaches for use in evaluating Community Safety initiatives. In Crime and health data analysis using GIS; Evans-Mudie, N, Ed.; SCGISA: Sheffield, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Buhmann, E.; Pietsch, M. Maltese Criminological Landscapes: A Spatio-Temporal Case Where Physical and Social Worlds Meet. In Peer Reviewed. In Proceedings of Digital Landscape Architecture; Anhalt University of Applied Sciences, Wichmann Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bottoms, A.E.; Wiles, P.W. Explanations of Crime and Space. In Crime, Policing and Place: Essays in Environmental Criminology; Evans, D.J., Fyfe, N.R., Herbert, D.T., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rankin, W. Cartography and the Reality of Boundaries. Perspecta 2010, 42, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rankin, W. Radical Cartography: Chicago Boundaries. Available online: http://www.radicalcartography.net/index.html?chicagodots (accessed on 12 November 2011).
- Rossi, A. The Architecture of the City; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Krier, R. L’espace de la ville, Theorie et Pratique; Archives d’Architecture Modern: Brussels, Belgium, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Panerai, P.; Depaule, J.C.; Demorgon, M. Analyse Urbaine; Édition Parenthèses: Marseille, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bandini, M. Some Architectural Approaches to Urban Form. In Urban Landscapes International Perspectives; Whitehand, J.W.R., Larkham, P.J., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, G. The Concise Townscape; Elsevier Architectural Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dresmé, F. Mapping Rotterdams city center. Available online: http://www.21bis.nl/project/22 (accessed on 14 March 2012).
- Lefebvre, H. The Urban Revolution; University of Minnesota Press: Minnesota, MN, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guhathakurta, S. Urban modeling as storytelling: Using simulation models as a narrative. Environ. Plan. B 2002, 29, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzl, M.; Stankiewicz, E.; Wierzbicka, A.; Kujawski, T.; Dzik, K.; Kowalczyk, P.; Kwiecinski, K.; Burdalski, M.; Śliwka, A.; Wójcicki, M. Mapping Invisibles—Acquiring GIS for Urban Planner Workshop. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2011, 6783, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).