Energy Efficiency and Load Optimization in Heterogeneous Networks through Dynamic Sleep Strategies: A Constraint-Based Optimization Approach
Abstract
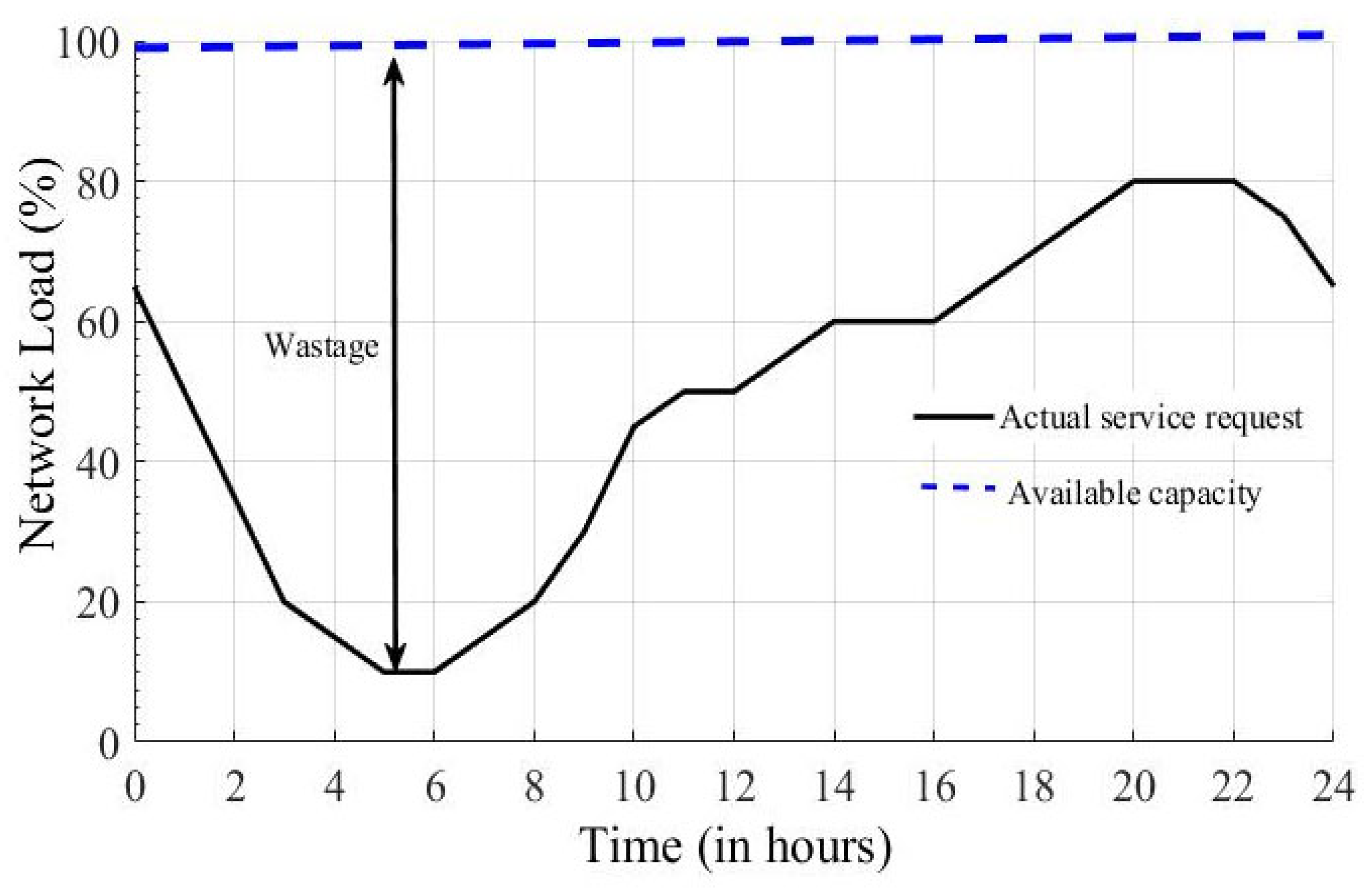
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
State-of-the-Art Sleep Mode Strategies
3. Proposed Dynamical DOSS Model
4. Problem Formulation
5. Results and Analysis
5.1. Simulation Assumptions
5.2. Voronoi Tessellation Plot
5.3. Probability of Coverage
5.4. Energy Utilization Efficiency (EUE)
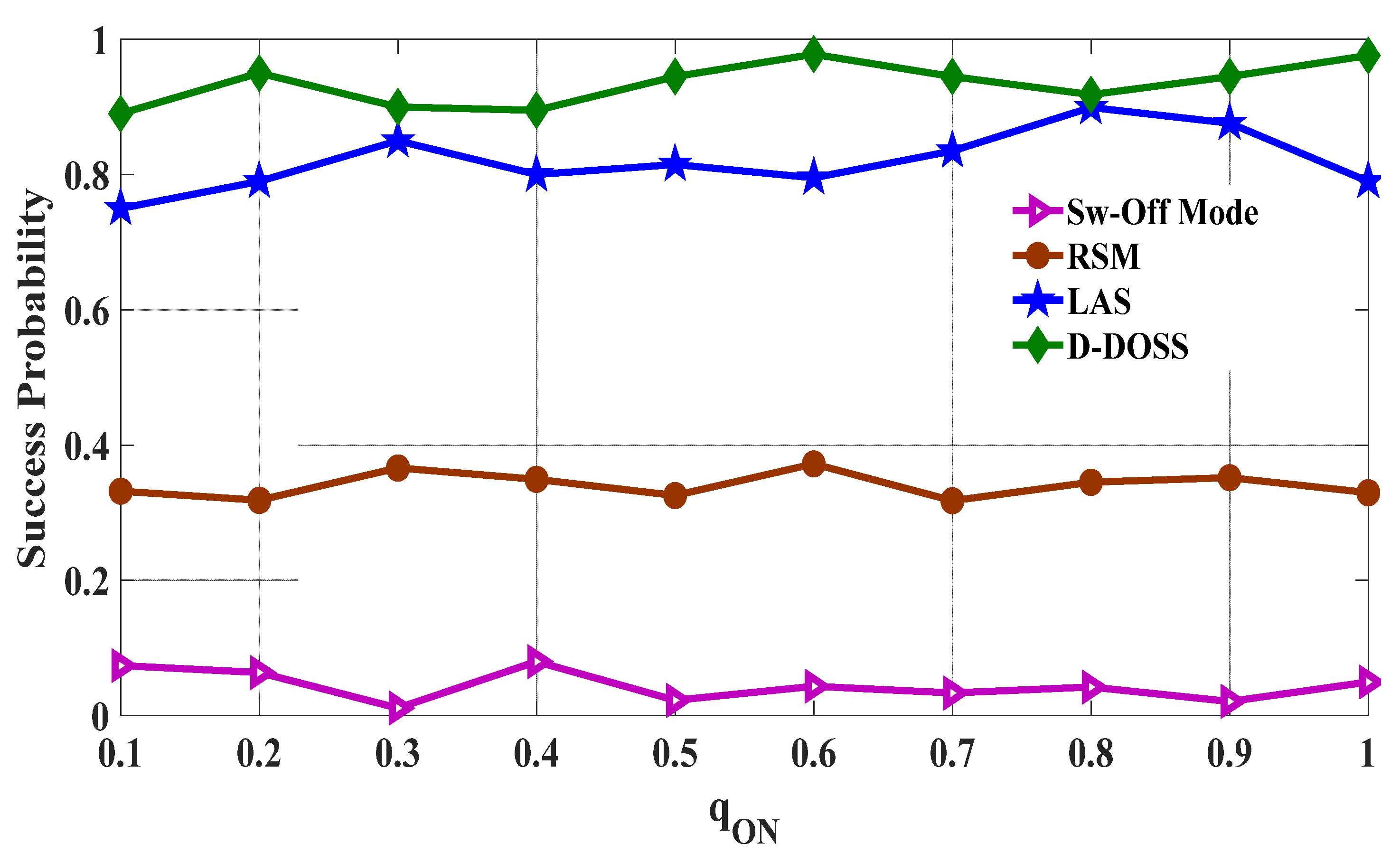
5.5. Success Probability
5.6. Data Throughput
6. Conclusions
7. Limitation and Future Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ericsson. Ericsson, 2023, Mobile Data Traffic Outlook: Ericsson Mobility Report. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report/dataforecasts/mobile-traffic-forecast (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Elkashlan, M.; Wong, K.-K.; Schober, R.; Hanzo, L. User association in 5G networks: A survey and an outlook. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1018–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.G.; Buzzi, S.; Choi, W.; Hanly, S.V.; Lozano, A.; Soong, A.C.; Zhang, J.C. What will 5G be? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, A.; Ali, Z.; Mateen, A.; Tahir, M.; Hannan, A.; Garcia, N.M.; Pires, I.M. A Comprehensive review on 5G-based Smart Healthcare Network Security: Taxonomy, Issues, Solutions and Future research directions. Array 2023, 18, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorincz, J.; Klarin, Z.; Begusic, D. Advances in Improving Energy Efficiency of Fiber–Wireless Access Networks: A Comprehensive Overview. Sensors 2023, 23, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, J.M.; Bensaou, B. A reinforcement learning approach to energy efficiency and QoS in 5G wireless networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2019, 37, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Jia, W. Improved clustering and resource allocation for ultra-dense networks. China Commun. 2020, 17, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Munir, M.E.; Marey, M.; Mostafa, H.; Zakaria, Z.; Al-Gburi, A.J.A.; Bhatti, F.A. A compact MIMO multiband antenna for 5G/WLAN/WIFI-6 devices. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Wadhwa, S.; Rani, S.; Khan, Z.; Boulila, W. EEDC: An Energy Efficient Data Communication Scheme Based on New Routing Approach in Wireless Sensor Networks for Future IoT Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madi, N.K.; Nasralla, M.M.; Hanapi, Z.M. Delay-based resource allocation with fairness guarantee and minimal loss for eMBB in 5G heterogeneous networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 75619–75636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountouris, M.; Pappas, N. HetNets and massive MIMO: Modeling, potential gains, and performance analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE-APS Topical Conference on Antennas and Propagation in Wireless Communications (APWC), Turin, Italy, 9–13 September 2013; pp. 1319–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, J.; Baruah, S.; Das, S.; Biswas, D. Analysis of Massive MIMO and Small Cells based 5G Cellular Networks: Simulative Approach. Radioelectron. Commun. Syst. 2022, 65, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.H.; Fan, Z.; Haines, R. Emerging technologies and research challenges for 5G wireless networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2014, 21, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.H.; Nordin, R. Evolution towards fifth generation (5G) wireless networks: Current trends and challenges in the deployment of millimetre wave, massive MIMO, and small cells. Telecommun. Syst. 2017, 64, 617–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kryszkiewicz, P.; Kliks, A. Increasing energy efficiency of massive-MIMO network via base stations switching using reinforcement learning and radio environment maps. Comput. Commun. 2021, 169, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Nirmalraj, S.; Murugan, S.; Manikandan, R.; Al-Turjman, F. Optimization of energy and security in mobile sensor network using classification based signal processing in heterogeneous network. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2023, 95, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrivelan, P.; Rishabavarthani, P.; Swetha, V. A Systematic Investigation of Uplink Massive MIMO and Interference Management in Heterogeneous Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Technologies for Sustainable Electric and Communications Systems (iTech SECOM), Coimbatore, India, 18–19 December 2023; pp. 513–517. [Google Scholar]
- Papazafeiropoulos, A.; Björnson, E.; Kourtessis, P.; Chatzinotas, S.; Senior, J.M. Scalable cell-free massive MIMO systems: Impact of hardware impairments. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 9701–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israr, A.; Yang, Q.; Li, W.; Zomaya, A.Y. Renewable energy powered sustainable 5G network infrastructure: Opportunities, challenges and perspectives. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 175, 102910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugume, E.; So, D.K. Deployment optimization of small cell networks with sleep mode. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 10174–10186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagari, N.M.; Idris, M.Y.I.; Salleh, R.B.; Ahmedy, I.; Murtaza, G.; Shehadeh, H.A. Heterogeneous energy and traffic aware sleep-awake cluster-based routing protocol for wireless sensor network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 12232–12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahdine, F.; Opadere, J.; Liu, Q.; Han, T.; Zhang, N.; Wu, S. A survey on sleep mode techniques for ultra-dense networks in 5G and beyond. Comput. Netw. 2021, 201, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.; Samaee, M.; Massicotte, D. A Review on Automated Sleep Study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 52, 1463–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, D.; De Domenico, A.; Piovesan, N.; Xinli, G.; Bao, H.; Qitao, S.; Debbah, M. A survey on 5G radio access network energy efficiency: Massive MIMO, lean carrier design, sleep modes, and machine learning. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 653–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amine, A.; Chaiban, J.-P.; Hassan, H.A.H.; Dini, P.; Nuaymi, L.; Achkar, R. Energy optimization with multi-sleeping control in 5G heterogeneous networks using reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2022, 19, 4310–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugume, E.; So, D.K. User association in energy-aware dense heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Mao, Y.; Leng, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Pan, L.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Energy-efficient offloading for mobile edge computing in 5G heterogeneous networks. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 5896–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Naeem, M.; Ejaz, W.; Iqbal, M.; Anpalagan, A.; Haneef, M. Energy cooperation with sleep mechanism in renewable energy assisted cellular hetnets. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 116, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, A.; Rizvi, S.; Alam, M.M.; Shirazi, F.; Su’ud, M.M. Optimizing energy efficiency in heterogeneous networks: An integrated stochastic geometry approach with novel sleep mode strategies and QoS framework. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqasir, A.M.; Kamal, A.E. Cooperative small cell HetNets with dynamic sleeping and energy harvesting. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2020, 4, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arani, A.H.; Omidi, M.J.; Mehbodniya, A.; Adachi, F. A distributed satisfactory sleep mode scheme for self-organizing heterogeneous networks. In Proceedings of the Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Iranian Conference on, Mashhad, Iran, 8–10 May 2018; pp. 476–481. [Google Scholar]
- Mugume, E. Green Heterogeneous Cellular Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Björnson, E.; Sanguinetti, L.; Kountouris, M. Deploying dense networks for maximal energy efficiency: Small cells meet massive MIMO. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 832–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesodiakaki, A.; Adelantado, F.; Alonso, L.; Verikoukis, C. Energy-efficient context-aware user association for outdoor small cell heterogeneous networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 10–14 June 2014; pp. 1614–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Natarajan, B.; Xia, H. Small cell base station sleep strategies for energy efficiency. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muirhead, D.; Imran, M.A.; Arshad, K. A survey of the challenges, opportunities and use of multiple antennas in current and future 5G small cell base stations. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2952–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, H.S.; Ganti, R.K.; Baccelli, F.; Andrews, J.G. Modeling and analysis of K-tier downlink heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2012, 30, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, H.S.; Ganti, R.K.; Andrews, J.G. Load-aware modeling and analysis of heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 1666–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Andrews, J.G. Joint resource partitioning and offloading in heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadr, S.; Adve, R.S. Tier association probability and spectrum partitioning for maximum rate coverage in multi-tier heterogeneous networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2014, 18, 1791–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Bao, W.; Yu, W.; Liang, B. Optimizing user association and spectrum allocation in HetNets: A utility perspective. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, M.S.; Rao, K.R.; Reddy, B.N.K. Developing an adaptive active sleep energy efficient method in heterogeneous wireless sensor network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 13689–13706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, E.; Hasan, C.; Hanawal, M.K.; Shitz, S.S.; Gorce, J.-M.; El-Azouzi, R.; Roullet, L. Stochastic geometric models for green networking. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, Y.S.; Quek, T.Q.; Kountouris, M. Dynamic sleep mode strategies in energy efficient cellular networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Budapest, Hungary, 9–13 June 2013; pp. 3131–3136. [Google Scholar]
- Aprem, A.; Murthy, C.R.; Mehta, N.B. Transmit power control policies for energy harvesting sensors with retransmissions. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2013, 7, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Yates, R.; Greenstein, L. A generic model for optimizing single-hop transmission policy of replenishable sensors. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, A.; Hsu, J.; Zahedi, S.; Srivastava, M.B. Power management in energy harvesting sensor networks. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. (TECS) 2007, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabuchandran, K.; Meena, S.K.; Bhatnagar, S. Q-learning based energy management policies for a single sensor node with finite buffer. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2013, 2, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoying, G.; Luyang, W.; Xinxin, F.; Jing, L.; Hui, Y.; Zhizhong, Z.; Haitao, L. Energy efficient switch policy for small cells. China Commun. 2015, 12, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Jin, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, G. Dynamic switching off algorithms for pico base stations in heterogeneous cellular networks. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2015, 2015, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhang, J. Cluster-based resource allocation scheme with QoS guarantee in ultra-dense networks. IET Commun. 2018, 12, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradshteyn, I.S. (Ed.) Gradshteyn and Ryzhik’s Table of Integrals, Series, and Products; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bouras, C.; Diles, G. “E”. In Wireless Days; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 143–145. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, J.G.; Baccelli, F.; Ganti, R.K. A tractable approach to coverage and rate in cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2011, 59, 3122–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bao, Y.; Miao, G.; Zhou, S.; Niu, Z. Base-station sleeping control and power matching for energy–delay tradeoffs with bursty traffic. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 3657–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J. Survey of Strategies for Switching Off Base Stations in Heterogeneous Networks for Greener 5G Systems. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 4959–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Kong, Q.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.T. On efficient utilization of green energy in heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 11, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






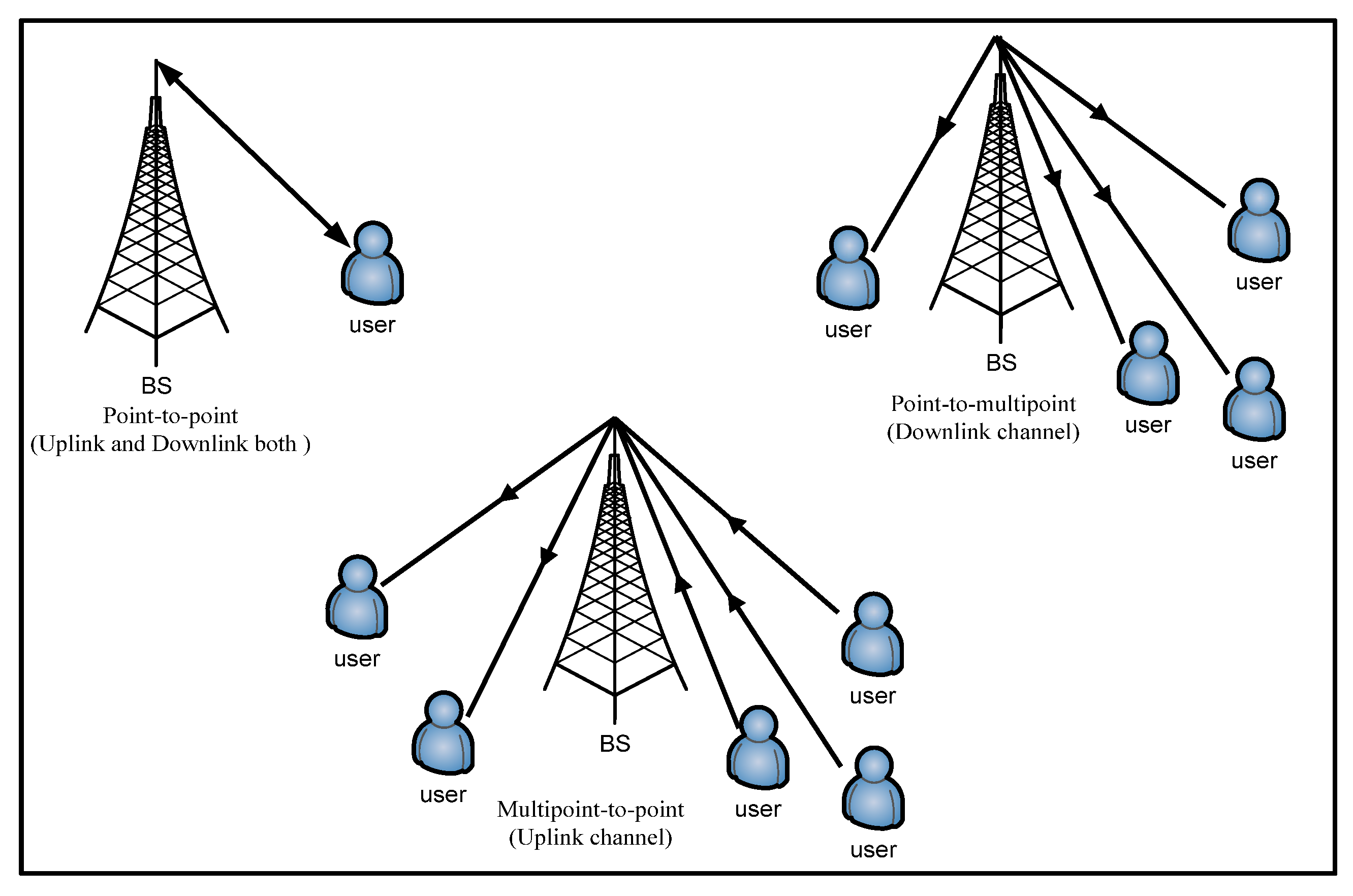
 Macro,
Macro,  Pico and
Pico and  MU).
MU).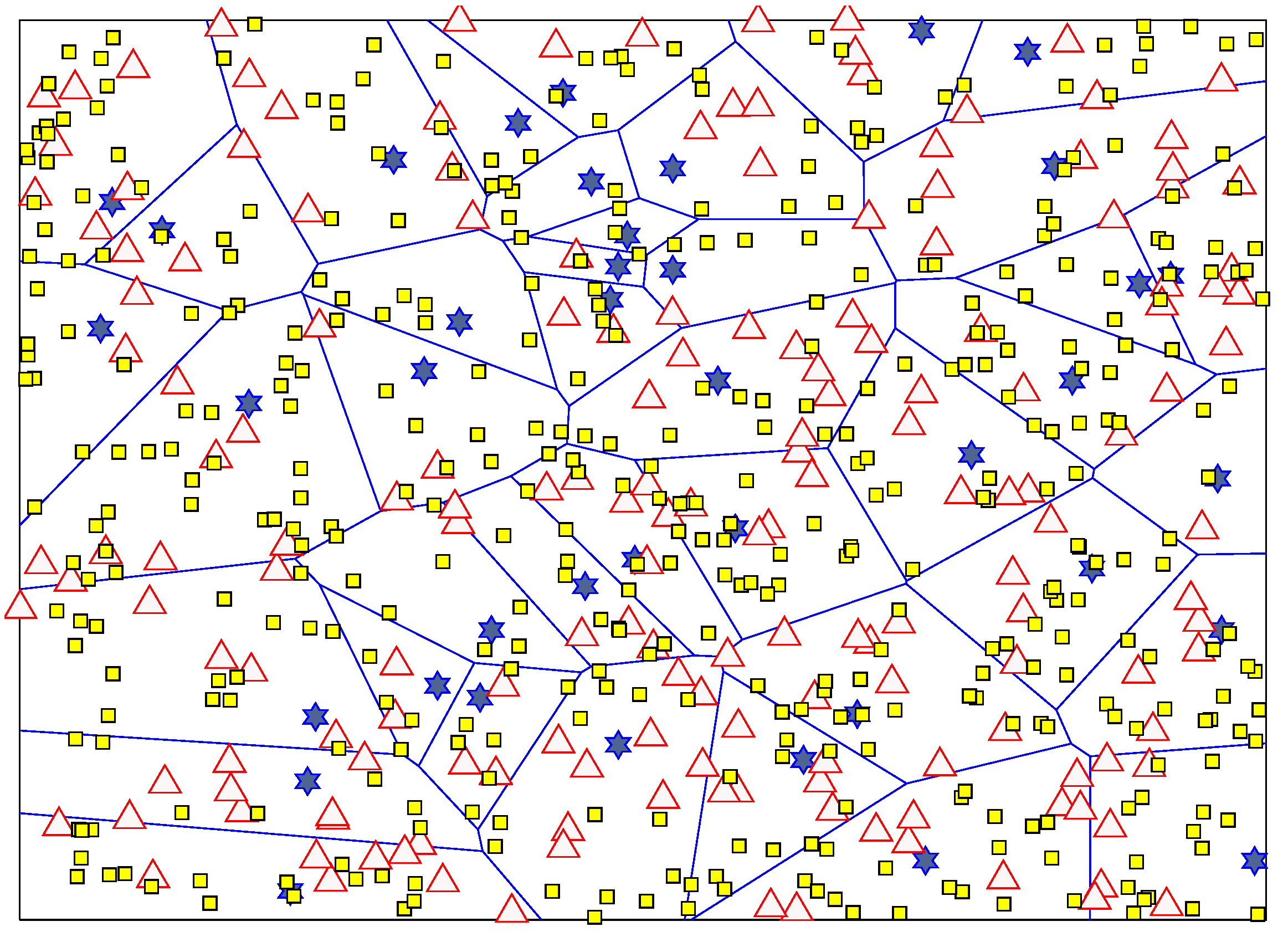



| Technology | Enabling Solutions | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Data Rate | High Capacity | Low Energy Consumption | High Coverage | High Implementation Cost | ||
| HetNets | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | [13,14,15,16,17] |
| m-MIMO | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | ✓ | |
| BS Sleeping Techniques | Approach | Key Points/Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile User Association (MUA) | Mobile users transfer themselves from sleeping BS to the nearest BS | Maximum energy efficiency is dependent on the channel state information and access conditions of the nearest BS |
| Self-Organizing Network (SON) | BSs shared their traffic conditions with other BSs and then automatically configured themselves for sleep/active modes | While preserving QoS requirements, this technique aims to minimize the active BSs through collaboration among multiple small cells. |
| Cell Breathing/Cell Zooming | BSs continuously monitor the traffic conditions and adaptively change their coverage regions concerning traffic requirements | EE can be optimized by taking computationally complex zooming algorithms for BS cooperation |
| Small Cells Deployment or HetNets | Macrocells should remain in active mode while small BSs can go asleep | Optimal density deployment of both macro and small-cell BS is desired |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Total number of users in the network | |
| can take | |
| users | |
| User density or arrival rate | |
| Base station density or arrival rate | |
| = 3.575 | |
| Gamma function for factorial generalization | |
| Cumulative probability of having fewer users | |
| Number of tiers in the network | |
| The probability of having exactly one user | |
| The probability of having no users | |
| The probability of a BS being active | |
| Probability of a BS transitioning to sleep mode | |
| Power consumption in the ON state | |
| Power consumption in the standby state | |
| Power consumption in the sleep state | |
| Power consumption in the switch-off state | |
| Transmit power of the Femto-tier base station | |
| Total power consumption | |
| Transmit power of the i-th tier base station | |
| α | Exponent of path loss |
| A function involving SINR and path loss exponent | |
| SINR threshold for the i-th tier | |
| Minimum threshold of SINR | |
| SINR threshold for the Femto-tier | |
| Probability of coverage when the BSs are in the ON state | |
| SINR threshold for QoS maintenance | |
| Delay constraint | |
| Probability to go into sleep mode | |
| Small Base Station density or arrival rate of small BS | |
| Probability density function of X | |
| EE | Energy efficiency Function |
| SINR threshold for the small-cell tier | |
| SINR threshold for the macro BS tier |
| BS Distribution | PPP |
|---|---|
| Number of simulations | 500 |
| Tier-1 (macro BSs) density | 1/500 m2 |
| Tier-2 (femto BSs) density | 4/500 m2 |
| The power consumption of macro BSs | 400 W |
| The power consumption of femto BSs | 40 W |
| 1.1 | |
| 1.3 | |
| Path loss exponent | 2 |
| System bandwidth | 10 MHz |
| Path loss model for macro | L = 128.1 + 37.6log10(R) (R in km) |
| Path loss Model for small cell | L = 140.7 + 36.7log10(R) (R in km) |
| MU rate requirement for macro BS | 400 kbps |
| MU rate requirement for small-cell BS | 400 kbps |
| The minimum distance between macro BS and MU | 35 m |
| The minimum distance between macro BS and small-cell BS | 75 m |
| The minimum distance between macro BS and MU | 35 m |
| The minimum distance between small-cell BS and MU | 10 m |
| The minimum distance between two small-cell BSs | 40 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shabbir, A.; Shirazi, M.F.; Rizvi, S.; Ahmad, S.; Ateya, A.A. Energy Efficiency and Load Optimization in Heterogeneous Networks through Dynamic Sleep Strategies: A Constraint-Based Optimization Approach. Future Internet 2024, 16, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16080262
Shabbir A, Shirazi MF, Rizvi S, Ahmad S, Ateya AA. Energy Efficiency and Load Optimization in Heterogeneous Networks through Dynamic Sleep Strategies: A Constraint-Based Optimization Approach. Future Internet. 2024; 16(8):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16080262
Chicago/Turabian StyleShabbir, Amna, Muhammad Faizan Shirazi, Safdar Rizvi, Sadique Ahmad, and Abdelhamied A. Ateya. 2024. "Energy Efficiency and Load Optimization in Heterogeneous Networks through Dynamic Sleep Strategies: A Constraint-Based Optimization Approach" Future Internet 16, no. 8: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16080262
APA StyleShabbir, A., Shirazi, M. F., Rizvi, S., Ahmad, S., & Ateya, A. A. (2024). Energy Efficiency and Load Optimization in Heterogeneous Networks through Dynamic Sleep Strategies: A Constraint-Based Optimization Approach. Future Internet, 16(8), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16080262







