Intrusion Detection in IoT Using Deep Residual Networks with Attention Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Considering the spatiotemporal characteristics of IoT traffic data, we proposed an improved residual network structure that avoids the performance impact of extracting only a single feature.
- We introduced an attention mechanism in the model to compute weights representing the importance of different features to help the model focus on the most important features.
- Higher detection accuracy. The performance of the algorithm proposed in this paper, in terms of detection accuracy, is superior to some current state-of-the-art methods.
- Stronger generalization ability. With a certain amount of data, this paper improves the model’s expressiveness by increasing the network width and optimizing the loss function to reach the global optimum.
2. Related Work
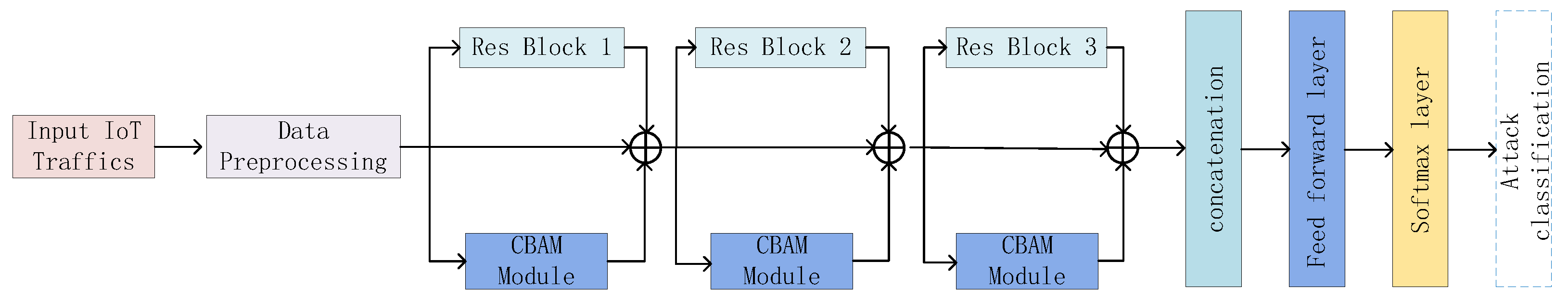
3. Proposed Model
Model Overview
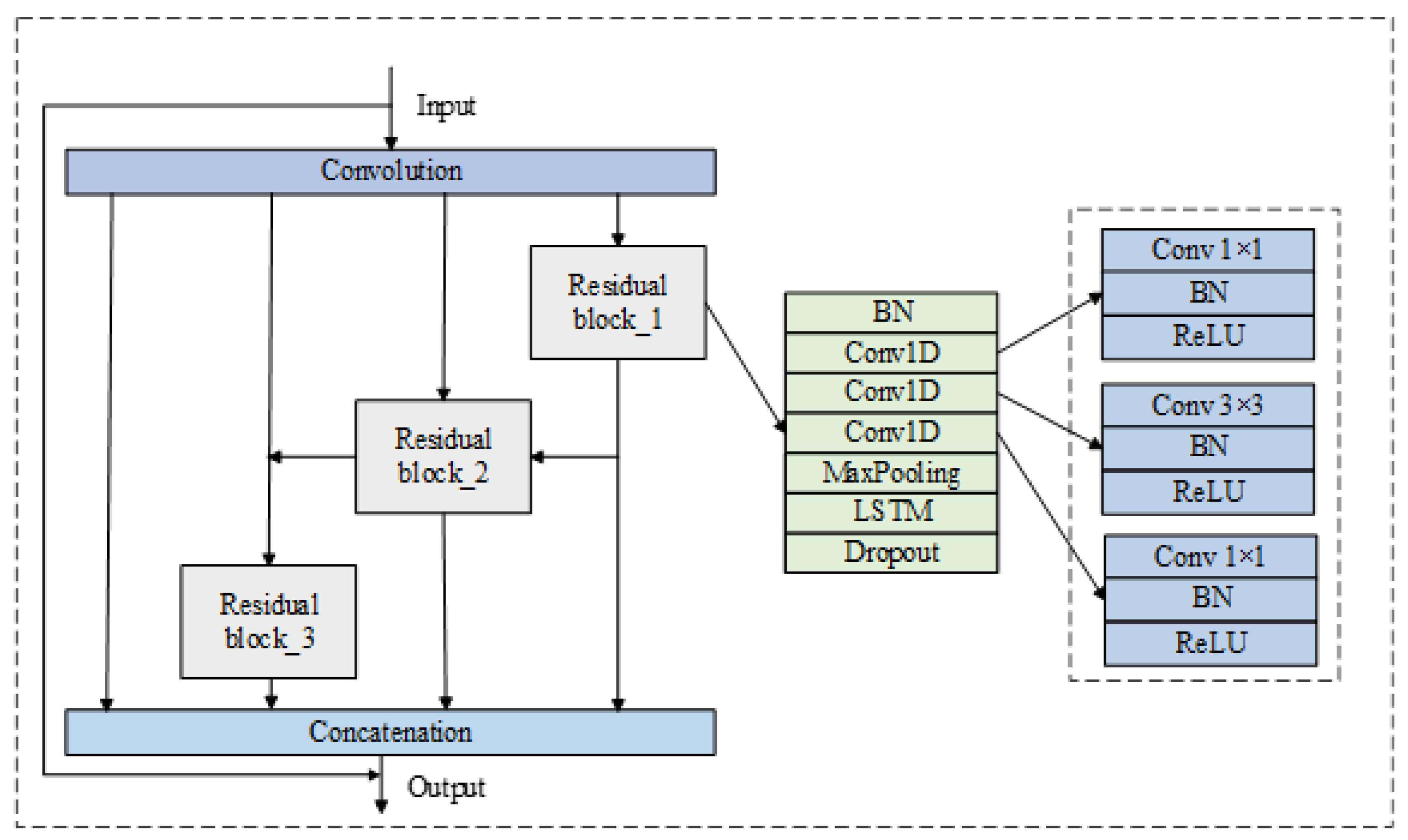
4. Residual Network Architecture
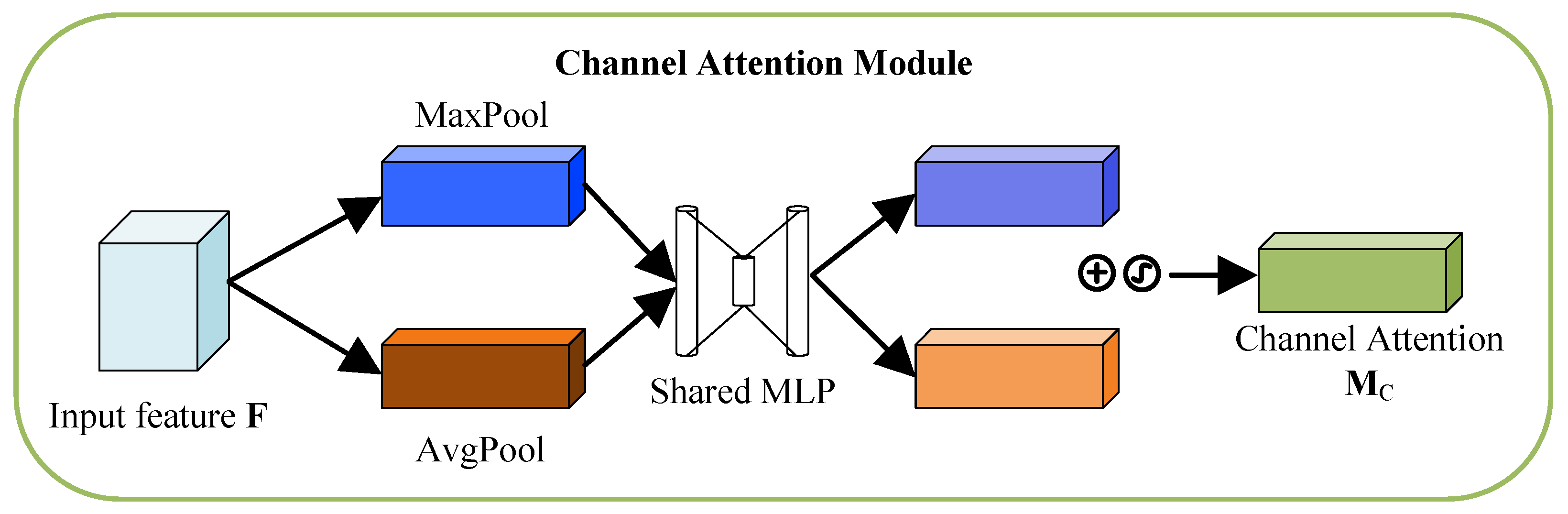
5. Convolutional Block Attention Mechanism
6. Model Evaluation and Discussions
6.1. Dataset Description
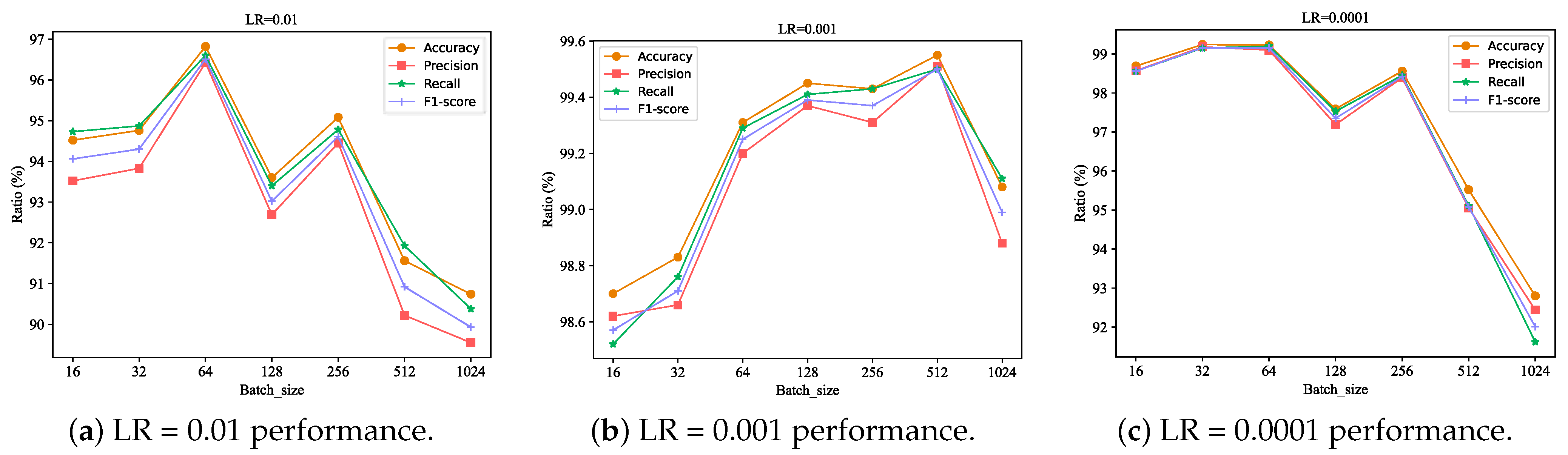
6.2. Hyperparameter Settings
- Learning rate (LR): A critical hyperparameter in deep learning that regulates the network model’s learning progress. In this paper, we set three learning rate values to obtain the best performance.
- Batch size: This parameter indicates the number of samples selected for one training. The batch size affects the memory usage, as well as the optimization and speed of the model. The batch size cannot be set too large or too small, so we set the range of batch size to 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024.
- Epoch: The epoch represents the process of training all the training samples once. Too many epochs can lead to overfitting, while too few epochs may result in suboptimal training parameters. In this study, the number of epochs is set to 100.
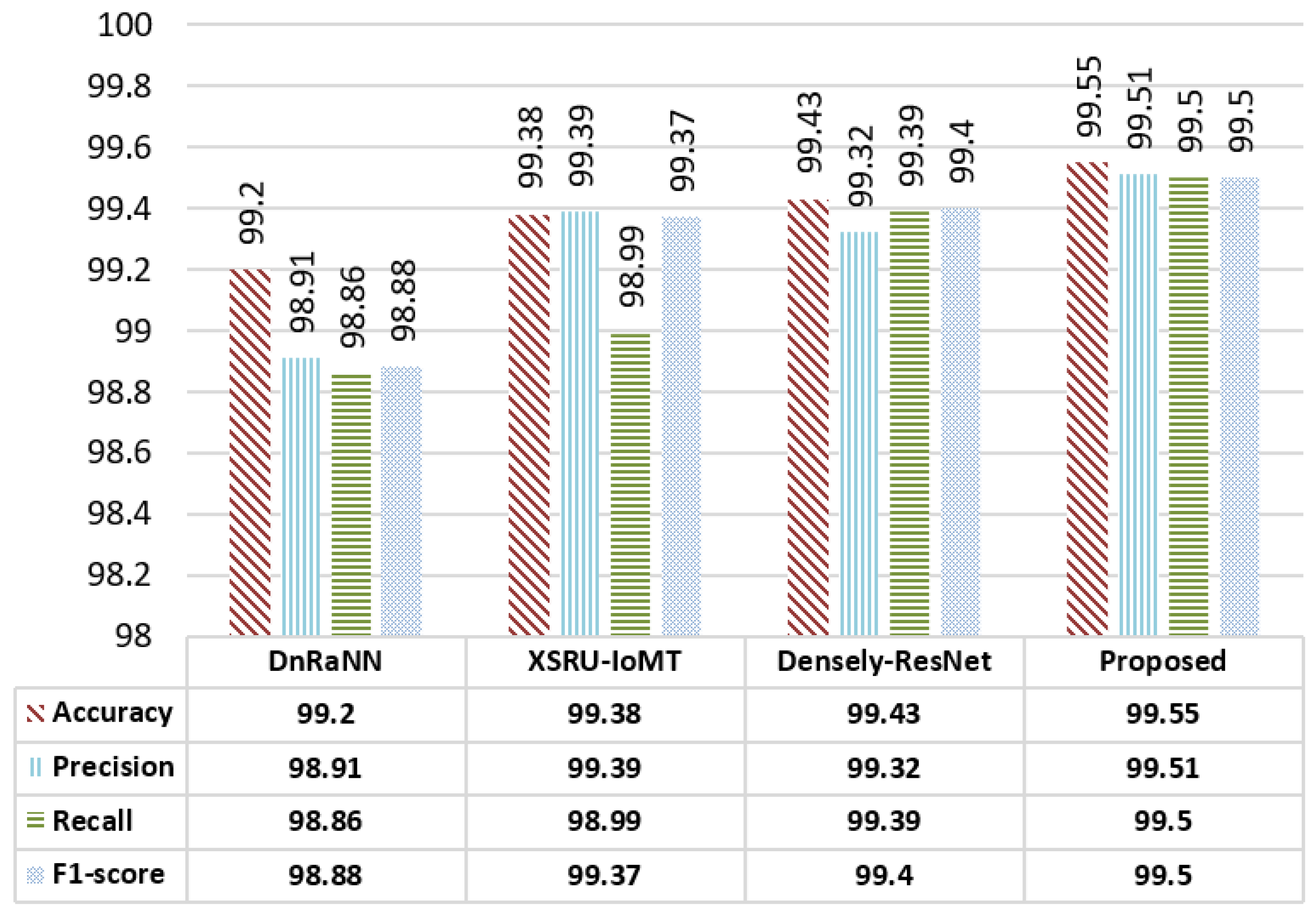
6.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bertino, E.; Islam, N. Botnets and internet of things security. Computer 2017, 50, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolias, C.; Kambourakis, G.; Stavrou, A.; Voas, J. DDoS in the IoT: Mirai and other Botnets. Computer 2017, 50, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abomhara, M.; Koien, G.M. Cyber security and the internet of things: Vulnerabilities, threats, intruders and attacks. J. Cyber Secur. Mobil. 2015, 4, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, A.; Lohiya, R. A review on machine learning and deep learning perspectives of IDS for IoT: Recent updates, security issues, and challenges. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 3211–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Garadi, M.A.; Mohamed, A.; Al-Ali, A.K.; Du, X.; Ali, I.; Guizani, M. A survey of machine and deep learning methods for internet of things (IoT) security. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2020, 22, 1646–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.R.; Veena, K.N. A survey on attack detection methods for IoT using machine learning and deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICPSC), Coimbatore, India, 13–14 May 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 625–630. [Google Scholar]
- Denning, D.E. An intrusion-detection model. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 1987, SE-13, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabouni, N.; Mosbah, M.; Zemmari, A.; Sauvignac, C.; Faruki, P. Network intrusion detection for IoT security based on learning techniques. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2671–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsoufi, M.A.; Razak, S.; Siraj, M.M.; Nafea, I.; Ghaleb, F.A.; Saeed, F.; Nasser, M. Anomaly-based intrusion detection systems in IoT using deep learning: A systematic literature review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvapandian, D.; Santhosh, R. Deep learning approach for intrusion detection in IoT-multi cloud environment. Autom. Softw. Eng. 2021, 28, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, T.V.; Saputra, Y.M.; Hoang, D.T.; Trung, N.L.; Nguyen, D.; Ha, N.V.; Dutkiewicz, E. Collaborative learning model for cyberattack detection systems in IoT industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 25–28 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Adnan Khan, M.; Rehman, A.; Rahman, M.; Kim, S.H. A real-time sequential deep extreme learning machine cybersecurity intrusion detection system. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 1785–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booij, T.M.; Chiscop, I.; Meeuwissen, E.; Moustafa, N.; Den Hartog, F.T. ToN_IoT: The role of heterogeneity and the need for standardization of features and attack types in IoT network intrusion data sets. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimenidis, S.; Lagkas, T.; Rantos, K. Deep learning in IoT intrusion detection. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 2022, 30, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Moustafa, N.; Yang, S.; Guo, H. Densely connected residual network for attack recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 19th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), Guangzhou, China, 29 December 2020–1 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.; Islam, M.M.; Zarif, M.I.I.; Hashem, M.M.A. Attack and anomaly detection in IoT sensors in IoT sites using machine learning approaches. Internet Things 2019, 7, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, N.; Shalinie, S.M. Learning-driven detection and mitigation of DDoS attack in IoT via SDN-cloud architecture. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 3559–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhao, X. Network intrusion detection method based on PCA and Bayes algorithm. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 1914980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Chang, V.; Hawash, H.; Chakrabortty, R.K.; Ryan, M. Deep-IFS: Intrusion detection approach for industrial internet of things traffic in fog environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 7704–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Garg, S.; Nie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Kang, J.; Hossain, M.S. Deep anomaly detection for time-series data in industrial IoT: A communication-efficient on-device federated learning approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 6348–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yan, J.; Wang, H.; Jin, Y. Anomaly detection of time series with smoothness-inducing sequential variational auto-encoder. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Gan, L.; Buschendorf, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Li, P.; Dong, X.; Lu, T. Omni SCADA intrusion detection using deep learning algorithms. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, G.D.L.T.; Rad, P.; Choo, K.K.R.; Beebe, N. Detecting internet of things attacks using distributed deep learning. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 163, 102662. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.A.; Moustafa, N.; Razzak, I.; Tanveer, M.; Pi, D.; Pan, Y.; Ali, B.S. XSRU-IoMT: Explainable simple recurrent units for threat detection in internet of medical things networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 127, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Guo, H. LuNET: A deep neural network for network intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Xiamen, China, 6–9 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 617–624. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, S.; e Huma, Z.; Jamal, S.S.; Ahmed, F.; Ahmad, J.; Zahid, A.; Dashtipour, K.; Aftab, M.U.; Ahmad, M.; Abbasi, Q.H. Intrusion detection framework for the internet of things using a dense random neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 6435–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Maglaras, L.; Moschoyiannis, S.; Janicke, H. Deep learning for cyber security intrusion detection: Approaches, datasets, and comparative study. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2020, 50, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.H.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, Z.N.; Jiang, P.T.; Mu, T.J.; Zhang, S.H.; Martin, R.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Attention mechanisms in computer vision: A survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa, N.; Slay, J. UNSW-NB15: A comprehensive data set for network intrusion detection systems (UNSW-NB15 network data set). In Proceedings of the 2015 Military Communications and Information Systems Conference (MilCIS), Canberra, Australia, 10–12 November 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]


| Record Type | Number of Records |
|---|---|
| Backdoor | 35,000 |
| DDoS | 25,000 |
| DoS | 20,000 |
| Injection | 35,000 |
| MITM | 1043 |
| Password | 35,000 |
| Ransomware | 16,030 |
| Scanning | 3973 |
| XSS | 6116 |
| Normal | 245,000 |
| Record Type | Number of Records |
|---|---|
| Analysis | 2000 |
| Backdoor | 1746 |
| DoS | 12,264 |
| Exploits | 33,393 |
| Fuzzers | 18,184 |
| Generic | 40,000 |
| Reconnaissance | 10,491 |
| Shellcode | 1133 |
| Worms | 130 |
| Normal | 56,000 |
| Performance Parameters | Batch Size | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 1024 | ||
| LR = 0.01 | Accuracy | 0.9452 | 0.9476 | 0.9682 | 0.9360 | 0.9508 | 0.9156 | 0.9074 |
| Precision | 0.9352 | 0.9383 | 0.9642 | 0.9269 | 0.9445 | 0.9022 | 0.8955 | |
| Recall | 0.9473 | 0.9487 | 0.9660 | 0.9340 | 0.9478 | 0.9193 | 0.9038 | |
| F1-score | 0.9406 | 0.9430 | 0.9651 | 0.9302 | 0.9461 | 0.9092 | 0.8993 | |
| LR = 0.001 | Accuracy | 0.9870 | 0.9883 | 0.9931 | 0.9945 | 0.9943 | 0.9955 | 0.9908 |
| Precision | 0.9862 | 0.9866 | 0.9920 | 0.9937 | 0.9931 | 0.9951 | 0.9888 | |
| Recall | 0.9852 | 0.9876 | 0.9929 | 0.9941 | 0.9943 | 0.9950 | 0.9911 | |
| F1-score | 0.9857 | 0.9871 | 0.9925 | 0.9939 | 0.9937 | 0.9950 | 0.9899 | |
| LR = 0.0001 | Accuracy | 0.9869 | 0.9924 | 0.9923 | 0.9759 | 0.9856 | 0.9552 | 0.9280 |
| Precision | 0.9857 | 0.9918 | 0.9910 | 0.9719 | 0.9839 | 0.9505 | 0.9244 | |
| Recall | 0.9856 | 0.9915 | 0.9920 | 0.9753 | 0.9845 | 0.9511 | 0.9162 | |
| F1-score | 0.9856 | 0.9916 | 0.9915 | 0.9735 | 0.9842 | 0.9508 | 0.9201 | |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.7015 | 0.7754 | 0.7724 | 0.8628 |
| LuNet | 0.7267 | 0.7850 | 0.8290 | 0.8750 |
| Densely-ResNet | 0.7393 | 0.8094 | 0.8668 | 0.8811 |
| CNN | 0.8163 | 0.8094 | 0.8578 | 0.8121 |
| LSTM-ResNet | 0.8923 | 0.8883 | 0.8777 | 0.8825 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, B.; Chai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, K. Intrusion Detection in IoT Using Deep Residual Networks with Attention Mechanisms. Future Internet 2024, 16, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16070255
Cui B, Chai Y, Yang Z, Li K. Intrusion Detection in IoT Using Deep Residual Networks with Attention Mechanisms. Future Internet. 2024; 16(7):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16070255
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Bo, Yachao Chai, Zhen Yang, and Keqin Li. 2024. "Intrusion Detection in IoT Using Deep Residual Networks with Attention Mechanisms" Future Internet 16, no. 7: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16070255
APA StyleCui, B., Chai, Y., Yang, Z., & Li, K. (2024). Intrusion Detection in IoT Using Deep Residual Networks with Attention Mechanisms. Future Internet, 16(7), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16070255








